Evaluation of the Reliability and the Performance of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Radiomics in the Presence of Randomly Generated Irrelevant Features for Prostate Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Datasets
Training Dataset and Testing Dataset
2.2. The Addition of Randomly Generated Irrelevant Features
2.3. Radiomics Feature Selection Methods
2.4. Machine Learning Classifiers
2.5. Data Training, Validation, and Testing
2.6. Features Importance
2.7. Statistics
- A = Dataset A
- B = Dataset B
- Di = Dataset i (with i representing the number of repetitions)
3. Results
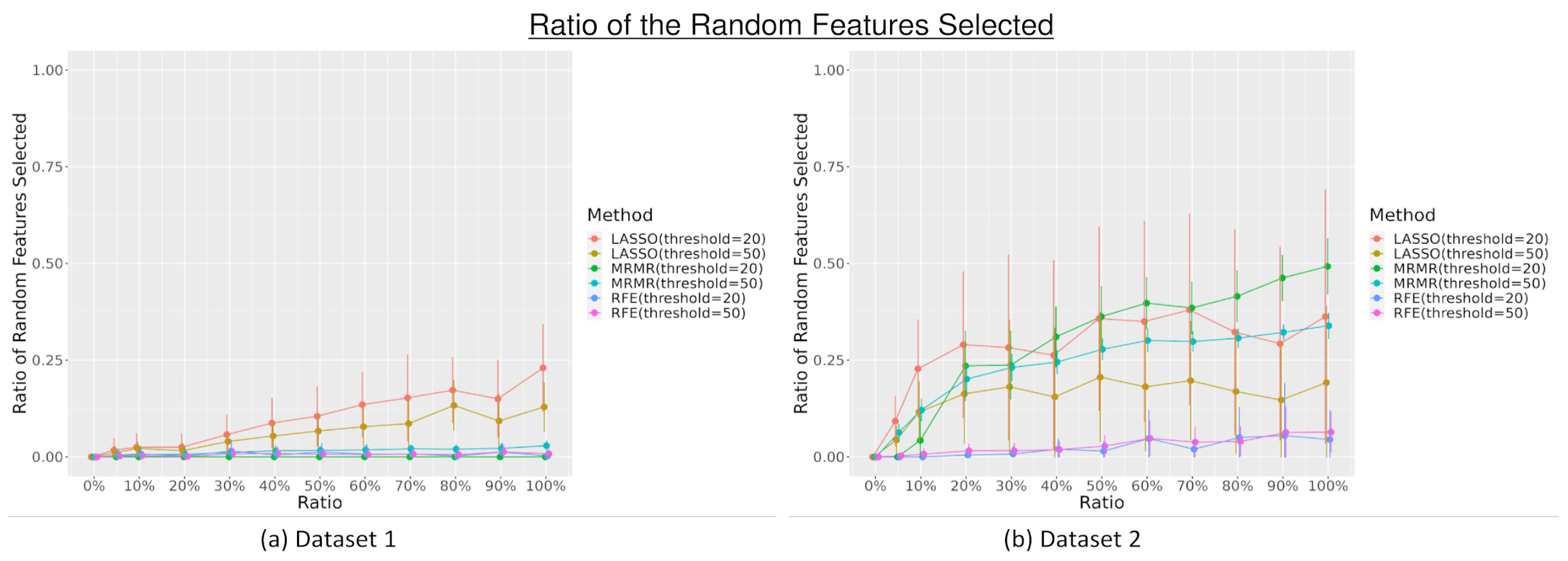
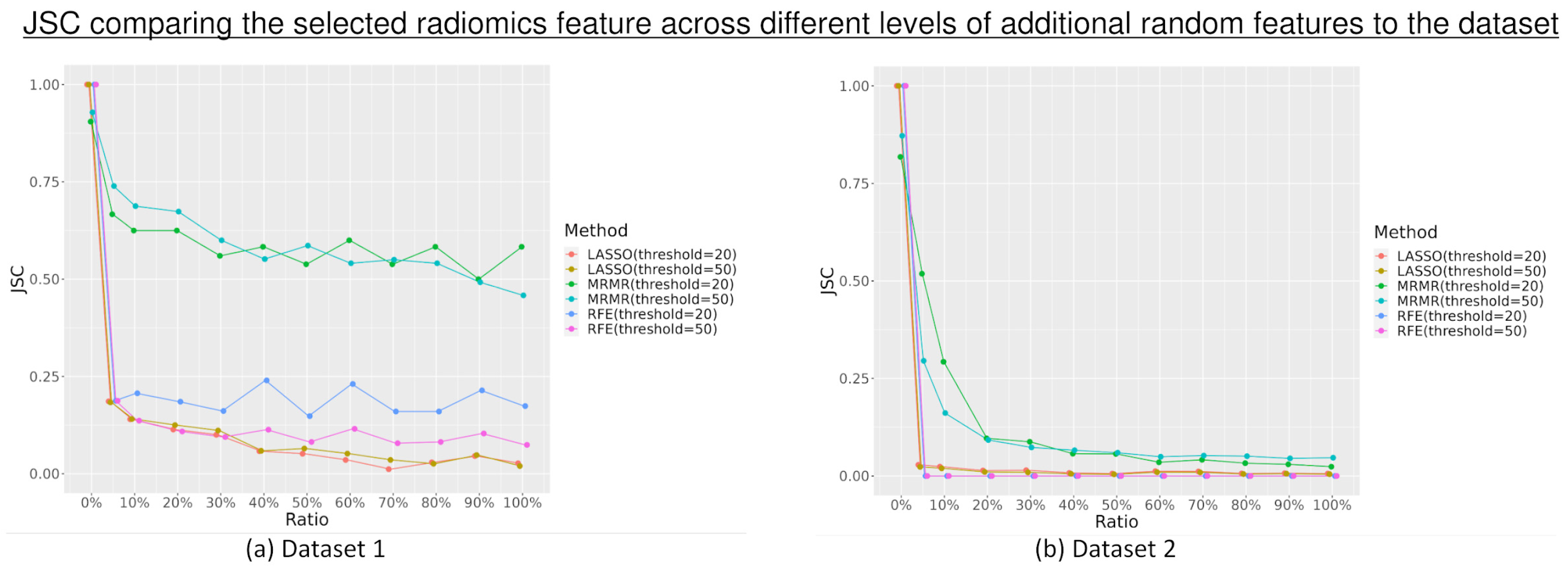
3.1. Feature Selection
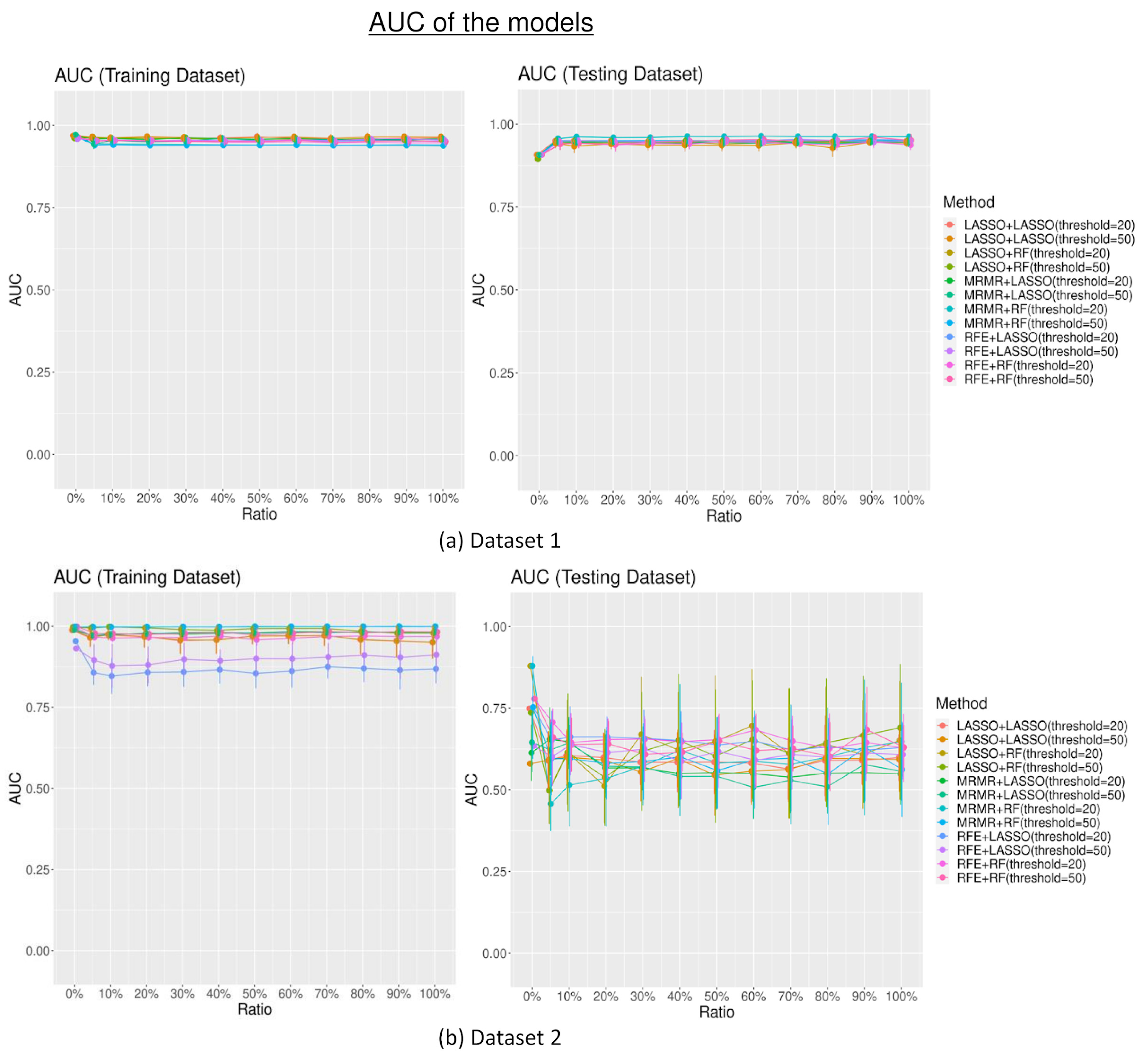
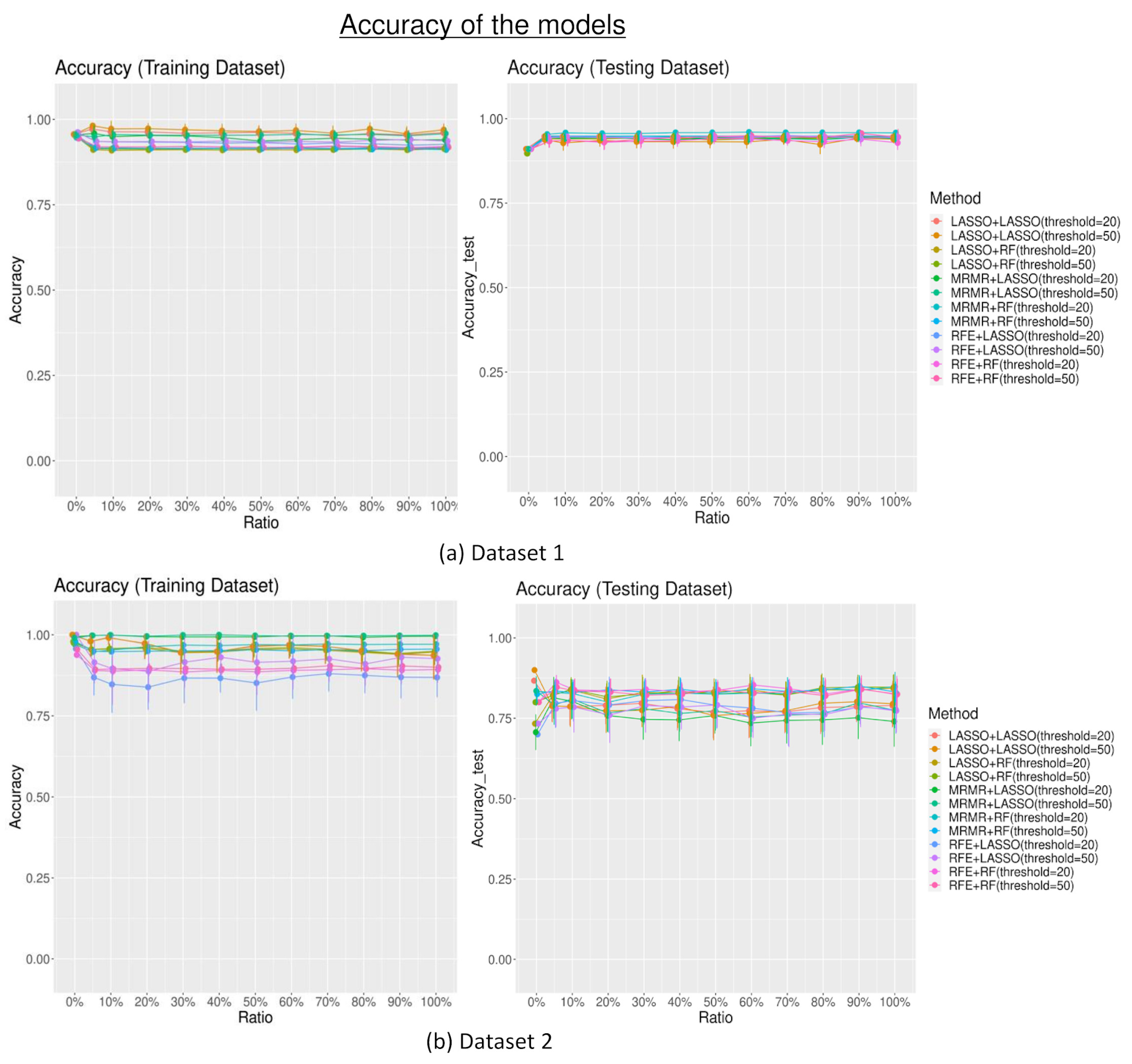
3.2. Model Performances
3.2.1. Area under the Curve (AUC)
3.2.2. Model Accuracy
3.2.3. Feature Importance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lambin, P.; Rios-Velazquez, E.; Leijenaar, R.; Carvalho, S.; van Stiphout, R.G.; Granton, P.; Zegers, C.M.; Gillies, R.; Boellard, R.; Dekker, A.; et al. Radiomics: Extracting more information from medical images using advanced feature analysis. Eur. J. Cancer 2012, 48, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillies, R.J.; Kinahan, P.E.; Hricak, H. Radiomics: Images Are More than Pictures, They Are Data. Radiology 2016, 278, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawla, P. Epidemiology of Prostate Cancer. World J. Oncol. 2019, 10, 63–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lorenzo, G.; Buonerba, L.; Ingenito, C.; Crocetto, F.; Buonerba, C.; Libroia, A.; Sciarra, A.; Ragone, G.; Sanseverino, R.; Iaccarino, S.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of Metastatic Prostate Cancer Patients Infected with COVID-19 in South Italy. Oncology 2020, 98, 743–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delahunt, B.; Miller, R.J.; Srigley, J.R.; Evans, A.J.; Samaratunga, H. Gleason grading: Past, present and future. Histopathology 2012, 60, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zawaideh, J.P.; Sala, E.; Pantelidou, M.; Shaida, N.; Koo, B.; Caglic, I.; Warren, A.Y.; Carmisciano, L.; Saeb-Parsy, K.; Gnanapragasam, V.J.; et al. Comparison of Likert and PI-RADS version 2 MRI scoring systems for the detection of clinically significant prostate cancer. Br. J. Radiol. 2020, 93, 20200298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nketiah, G.A.; Elschot, M.; Scheenen, T.W.; Maas, M.C.; Bathen, T.F.; Selnæs, K.M.; Attenberger, U.I.; Baltzer, P.A.T.; Fütterer, J.J.; Haider, M.A.; et al. Utility of T2-weighted MRI texture analysis in assessment of peripheral zone prostate cancer aggressiveness: A single-arm, multicenter study. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, C.-J.; Bao, M.-L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.-N.; Zhang, Y.-D. Machine learning-based analysis of MR radiomics can help to improve the diagnostic performance of PI-RADS v2 in clinically relevant prostate cancer. Eur. Radiol. 2017, 27, 4082–4090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yuan, J.; Xue, C.; Poon, D.M.C.; Yang, B.; Yu, S.K.; Cheung, K.Y. A pilot study of MRI radiomics for high-risk prostate cancer stratification in 1.5 T MR-guided radiotherapy. Magn. Reson. Med. 2023, 89, 2088–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Yuan, J.; Lo, G.G.; Chang, A.T.Y.; Poon, D.M.C.; Wong, O.L.; Zhou, Y.; Chu, W.C.W. Radiomics feature reliability assessed by intraclass correlation coefficient: A systematic review. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2021, 11, 4431–4460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reuzé, S.; Schernberg, A.; Orlhac, F.; Sun, R.; Chargari, C.; Dercle, L.; Deutsch, E.; Buvat, I.; Robert, C. Radiomics in Nuclear Medicine Applied to Radiation Therapy: Methods, Pitfalls, and Challenges. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2018, 102, 1117–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, C.; Yuan, J.; Poon, D.M.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, B.; Yu, S.K.; Cheung, Y.K. Reliability of MRI radiomics features in MR-guided radiotherapy for prostate cancer: Repeatability, reproducibility, and within-subject agreement. Med. Phys. 2021, 48, 6976–6986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, C.; Yuan, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wong, O.L.; Cheung, K.Y.; Yu, S.K. Acquisition repeatability of MRI radiomics features in the head and neck: A dual-3D-sequence multi-scan study. Vis. Comput. Ind. Biomed. Art 2022, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiset, S.; Welch, M.L.; Weiss, J.; Pintilie, M.; Conway, J.L.; Milosevic, M.; Fyles, A.; Traverso, A.; Jaffray, D.; Metser, U.; et al. Repeatability and reproducibility of MRI-based radiomic features in cervical cancer. Radiother. Oncol. 2019, 135, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Xue, C.; Lo, G.; Wong, O.L.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, S.K.; Cheung, K.Y. Quantitative assessment of acquisition imaging parameters on MRI radiomics features: A prospective anthropomorphic phantom study using a 3D-T2W-TSE sequence for MR-guided-radiotherapy. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2021, 11, 1870–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demircioğlu, A. The effect of preprocessing filters on predictive performance in radiomics. Eur. Radiol. Exp. 2022, 6, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyon, I.; Hur, A.B.; Gunn, S.; Dror, G. Result analysis of the NIPS 2003 feature selection challenge. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 17; Saul, L., Weiss, Y., Buttou, L., Eds.; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2004; pp. 545–552. [Google Scholar]
- Naseri, H.; Skamene, S.; Tolba, M.; Faye, M.D.; Ramia, P.; Khriguian, J.; Patrick, H.; Andrade Hernandez, A.X.; David, M.; Kildea, J. Radiomics-based machine learning models to distinguish between metastatic and healthy bone using lesion-center-based geometric regions of interest. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, C.; Grossmann, P.; Bussink, J.; Lambin, P.; Aerts, H.J.W.L. Machine Learning methods for Quantitative Radiomic Biomarkers. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.-D.; Hou, Y.; Yan, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, M.; Yao, Y.-F.; Yang, G. FeAture Explorer (FAE): A tool for developing and comparing radiomics models. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toivonen, J.; Montoya Perez, I.; Movahedi, P.; Merisaari, H.; Pesola, M.; Taimen, P.; Boström, P.J.; Pohjankukka, J.; Kiviniemi, A.; Pahikkala, T.; et al. Radiomics and machine learning of multisequence multiparametric prostate MRI: Towards improved non-invasive prostate cancer characterization. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demircioğlu, A. Evaluation of the dependence of radiomic features on the machine learning model. Insights Imaging 2022, 13, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaccard, P. The distribution of the flora in the alpine zone. New Phytol. 1912, 11, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajian-Tilaki, K. Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) Curve Analysis for Medical Diagnostic Test Evaluation. Casp. J. Intern. Med. 2013, 4, 627–635. [Google Scholar]
- Grandvalet, Y.; Canu, S.; Boucheron, S. Noise Injection: Theoretical Prospects. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1093–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berisha, V.; Krantsevich, C.; Hahn, P.R.; Hahn, S.; Dasarathy, G.; Turaga, P.; Liss, J. Digital medicine and the curse of dimensionality. NPJ Digit. Med. 2021, 4, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, F.; La Civita, E.; Della Ventura, B.; Ferro, M.; Cennamo, M.; Bruzzese, D.; Crocetto, F.; Velotta, R.; Terracciano, D. A Combinatorial Neural Network Analysis Reveals a Synergistic Behaviour of Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance and Prostate Health Index in the Identification of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2022, 20, e406–e410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Dataset | Sample Size | No. of Features | Outcome | Outcome Balance (%) | Modality | DOI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Song (dataset 1) [21] | 260 lesions | 265 | clinically significant vs. non-clinically significant PC | 49 | Multiparametric MRI (T2W, DWI, and ADC maps) | https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0237587 (accessed on 12 April 2023) |
| Toivonen (dataset 2) [22] | 100 lesions | 7106 | clinically significant vs. non-clinically significant PC | 80 | T2-TSE, DWI, and T2 mapping | https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0217702 (accessed on 12 April 2023) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xue, C.; Yuan, J.; Lo, G.G.; Poon, D.M.C.; Chu, W.C.W. Evaluation of the Reliability and the Performance of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Radiomics in the Presence of Randomly Generated Irrelevant Features for Prostate Cancer. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3580. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13233580
Xue C, Yuan J, Lo GG, Poon DMC, Chu WCW. Evaluation of the Reliability and the Performance of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Radiomics in the Presence of Randomly Generated Irrelevant Features for Prostate Cancer. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(23):3580. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13233580
Chicago/Turabian StyleXue, Cindy, Jing Yuan, Gladys G. Lo, Darren M. C. Poon, and Winnie C. W. Chu. 2023. "Evaluation of the Reliability and the Performance of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Radiomics in the Presence of Randomly Generated Irrelevant Features for Prostate Cancer" Diagnostics 13, no. 23: 3580. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13233580
APA StyleXue, C., Yuan, J., Lo, G. G., Poon, D. M. C., & Chu, W. C. W. (2023). Evaluation of the Reliability and the Performance of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Radiomics in the Presence of Randomly Generated Irrelevant Features for Prostate Cancer. Diagnostics, 13(23), 3580. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13233580







