Development of Artificial Neural Network-Based Prediction Model for Evaluation of Maxillary Arch Growth in Children with Complete Unilateral Cleft Lip and Palate
Abstract
1. Introduction
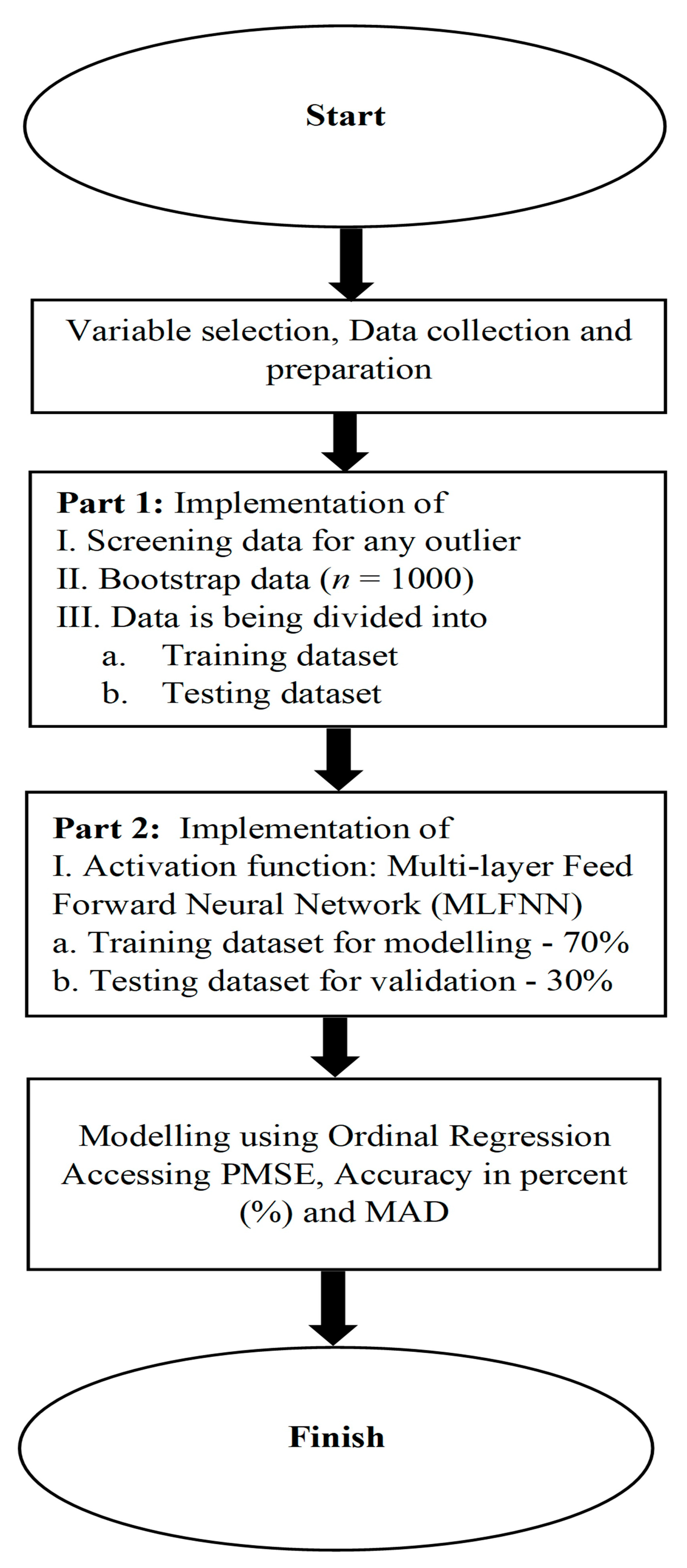
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ordinal Logistic Regression
2.2. Model Equation
β2 × 2 + β3 × 3 + β4 × 4 +,…,+ βk Xk
2.3. Model Summary
The Bootstrap Method
2.4. Methodology Building Using R Syntax
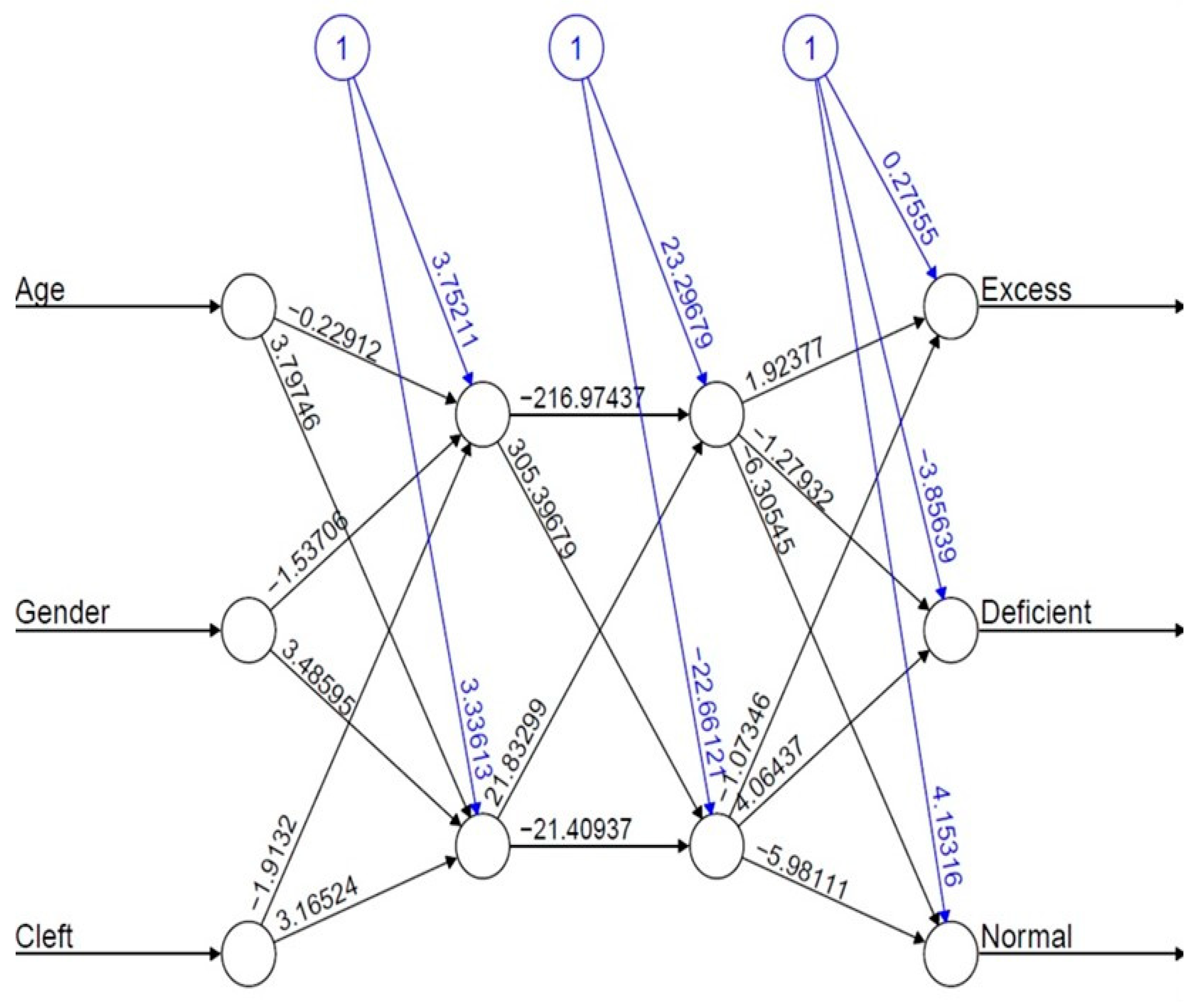
3. Results
Bootstrap
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ali, S.Y.; Abdul, Z.A.; Mirani, S.A.; Shaikh, M.I.; Khattak, M.N.; Sahito, M.A. Demographic data on the characterization of oral clefts in malaysia. Pak. Oral Dent. J. 2015, 35, 108–110. [Google Scholar]
- Leslie, E.J.; Marazita, M.L. Genetics of cleft lip and cleft palate. Am. J. Med. Genet. C Semin. Med. Genet. 2013, 163 Pt C, 246–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strong, E.B.; Buckmiller, L.M. Management of the cleftpalate. Facial. Plast. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2001, 9, 15–25. [Google Scholar]
- Stanier, P.; Moore, G.E. Genetics of cleft lip and palate:syndromic genes contribute to the incidence of non-syndromicclefts. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2004, 1, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.Y.; Mirani, S.A.; Sahito, M.A. Evaluating occurrence of variable cleft lip and palate types among Ethnic Groups of Malaysia. JPDA 2018, 27, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Lau, K.L.; Ong, S.C.; Sulaiman, W.S. Comparison between parents’ and patients’ satisfaction level towards cleft management using Cleft Evaluation Profile. IIUM J. Orofac. Health Sci. 2021, 28, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, J.C. Gene/environment causes of cleft lip and/or palate. Clin. Genet. 2002, 61, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschner, R.E.; Rossa, D.L. Cleft lip and palate. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2000, 36, 1191–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mossey, P.A.; Little, J.; Munger, R.G.; Dixon, M.J.; Shaw, W.C. Cleft lip and palate. Lancet 2009, 374, 1773–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPDTOC Working Group. Prevalence at birth of cleft lip with or without cleft palate: Data from the International Perinatal Database of Typical Oral Clefts (IPDTOC). Cleft Palate-Craniofacial J. 2011, 48, 66–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, M.; Han, J.; Wang, H.; Li, S. Three-dimensional evaluation of maxillary sinus and maxilla for adolescent patients with unilateral cleft lip and palate using cone-beam computed tomography. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2020, 135, 110085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Filho, O.G.; Normando, A.D.; Capelozza Filho, L. Mandibular growth in patients with cleft lip and/or cleft palate--the influence of cleft type. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 1993, 104, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberton, D.K.; Verma, P.; Almpani, K.; Fung, P.W.; Mishra, R.; Oberoi, S.; Şenel, F.Ç.; Mah, J.K.; Huang, J.; Padwa, B.L.; et al. Craniofacial Analysis May Indicate Co-Occurrence of Skeletal Malocclusions and Associated Risks in Development of Cleft Lip and Palate. J. Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, P.; K, M.; Mathai, P. Cleft Maxillary Hypoplasia. In Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery for the Clinician; Bonanthaya, K., Panneerselvam, E., Manuel, S., Kumar, V.V., Rai, A., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2021; pp. 1675–1702. [Google Scholar]
- Haque, S.; Khamis, M.F.; Alam, M.K.; Ahmad, W.M.A.W. Effects of multiple factors on treatment outcome in the three-dimensional maxillary arch morphometry of children with unilateral cleft lip and palate. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2020, 31, e534–e538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adetayo, A.M.; Adetayo, M.O.; Adeyemo, W.L.; James, O.O.; Adeyemi, M.O. Unilateral cleft lip: Evaluation and comparison of treatment outcome with two surgical techniques based on qualitative (subject/guardian and professional) assessment. J. Korean Assoc. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 45, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schilling, G.R.; Cardoso, M.C.A.F.; Maahs, M.A.P. Effect of palatoplasty on speech, dental occlusion issues and upper dental arch in children and adolescents with cleft palate: An integrative literature review. Rev. CEFAC 2019, 21, e12418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.K.; Kajii, T.S.; Sato, Y.; Iida, J. Clinical investigation of congenital factor affecting craniofacial morphology of unilateral cleft lip and palate in Japanese patients. Pesqui. Bra. Odontopediatria Clín Integr. 2019, 19, 4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, S.; Alam, M.K.; Khamis, M.F. The effect of various factors on the dental arch relationship in non-syndromic unilateral cleft lip and palate children assessed by new approach: A retrospective study. BMC Pediatr. 2017, 17, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, A.I.; Alam, M.K.; Khamis, M.F. Assessment of complete unilateral cleft lip and palate patients: Assessment of complete unilateral cleft lip and palate patients: Determination of factors effecting dental arch relationships. Int. J. Ped. Otorhinolaryngol. 2017, 92, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.K.; Alfawzan, A.A.; Haque, S.; Mok, P.L.; Marya, A.; Venugopal, A.; Jamayet, N.B.; Siddiqui, A.A. Sagittal Jaw Relationship of Different Types of Cleft and Non-cleft Individuals. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 651951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deolia, S.G.; Chhabra, C.; Chhabra, K.G.; Kalghatgi, S.; Khandelwal, N. Dental anomalies of the deciduous dentition among Indian children: A survey from Jodhpur, Rajasthan, India. J. Indian Soc. Pedod. Prev. Dent. 2015, 33, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, A.; Marla, V.; Shrestha, S. Developmental anomalies affecting the morphology of teeth—A review. RSBO 2015, 12, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Iccha, K.; MaharjanIbrahim, H.A.; Abuaffan, A.H. Prevalence of malocclusion and orthodontic treatment needs among Down syndrome Sudanese individuals. Braz. Dent. Sci. 2015, 18, 95–101. [Google Scholar]
- Honda, Y.; Suzuki, A.; Ohishi, M.; Tashiro, H. Longitudinal study on the changes of maxillary arch dimensions in japanese children with cleft lip and/or palate: Infancy to 4 years of age. Cleft Palate Craniofac. J. 1995, 32, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botticelli, S.; Kuseler, A.; Marcusson, A.; Mølsted, K.; Nørholt, S.E.; Cattaneo, P.M.; Pedersen, T.K. Do infant cleft dimensions have an influence on occlusal relations? A subgroup analysis within an RCT of primary surgery in patients with unilateral cleft lip and palate. Cleft Palate Craniofac. J. 2020, 57, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sajovic, J.; Setnikar Lesjak, A.; Plut, A.; Eberlinc, A.; Primožič, J.; Drevenšek, E.; Drevenšek, M. Maxillary arch dimensions, occlusion assessment and space conditions in patients with cleft palate in the period of deciduous dentition—A retrospective study. J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2023, 124, 101356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banker, A.M.; Pillai, J.P.; Patel, K.D. Determination of normal maxillary transverse dimension by using intercanine width and interpalatal first molar width. Indian J. Dent. Res. 2016, 27, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhazmi, A.; Alhazmi, Y.; Makrami, A.; Masmali, A.; Salawi, N.; Masmali, K.; Patil, S. Application of artificial intelligence and machine learning for prediction of oral cancer risk. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2021, 50, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanagar, S.B.; Al-Ehaideb, A.; Maganur, P.C.; Vishwanathaiah, S.; Patil, S.; Baeshen, H.A.; Sarode, S.C.; Bhandi, S. Developments, application, and performance of artificial intelligence in dentistry–A systematic review. J. Dent. Sci. 2020, 16, 508–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyide Tugce, G.; Arda, B.; Mehmet Eray, K. Artificial Intelligence in Dentistry. In Human Teeth—From Function to Esthetics; Lavinia Cosmina, A., Laura-Cristina, R., Eds.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2023; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Efron, B.; Tibshirani, R.J. An Introduction to the Bootstrap; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Efron, B. The Jackknife, the Bootstrap and Other Resampling Plans; Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Shafi, N.; Bukhari, F.; Iqbal, W.; Almustafa, K.M.; Asif, M.; Nawaz, Z. Cleft prediction before birth using deep neural network. J. Health Inform. 2020, 26, 2568–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z. A gentle introduction to artificial neural networks. Ann. Transl. Med. 2016, 4, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, I.-A.; Ngnamsie Njimbouom, S.; Lee, K.-O.; Kim, J.-D. DCP: Prediction of Dental Caries Using Machine Learning in Personalized Medicine. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, S.; Tang, M.; Yin, H.; Huang, H.; He, L. Hypernasality net: Deep recurrent neural network for automatic hypernasality detection. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2019, 129, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, R.A.; de Oliveira Silva, C.; Martelli-Junior, H.; das Neves, L.T.; Coletta, R.D. Machine learning in prediction of genetic risk of non-syndromic oral clefts in the Brazilian population. Clin. Oral. Investig. 2021, 25, 1273–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orozco-Arroyave, J.R.; Vargas-Bonilla, J.F.; Vásquez-Correa, J.C.; Castellanos-Dominguez, C.G.; Nöth, E. Automatic detection of hypernasal speech of children with cleft lip and palate from Spanish vowels and words using classical measures and nonlinear analysis. Rev. Fac. Ing. Univ. Antioq. 2016, 80, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golabbakhsh, M.; Abnavi, F.; Kadkhodaei Elyaderani, M.; Derakhshandeh, F.; Khanlar, F.; Rong, P.; Kuehn, D.P. Automatic identification of hypernasality in normal and cleft lip and palate patients with acoustic analysis of speech. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2017, 141, 929–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athanasiou, A.E.; Mazaheri, M.; Zarrinnia, K. Dental arch dimensions in patients with unilateral cleft lip and palate. Cleft Palate J. 1988, 25, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gopinath, V.K.; Samsudin, A.R.; Mohd Noor, S.N.F.; Mohamed Sharab, H.Y. Facial profile and maxillary arch dimensions in unilateral cleft lip and palate children in the mixed dentition stage. Eur. J. Dent. 2017, 11, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rando, G.M.; Ambrosio, E.C.P.; Jorge, P.K.; Prado, D.Z.A.; Falzoni, M.M.M.; Carrara, C.F.C.; Soares, S.; Machado, M.; Oliveira, T.M. Anthropometric Analysis of the Dental Arches of Five-Year-Old Children with Cleft Lip and Palate. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2018, 29, 1657–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shetye, P.R. Facial growth of adults with unoperated clefts. Clin Plast Surg. 2004, 2, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chigurupati, R. Orthognathic surgery for secondary cleft and craniofacial deformities. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2005, 4, 503–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posnick, J.C.; Ricalde, P. Cleft-orthognathic surgery. Clin. Plast. Surg. 2004, 2, 315–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, J.H.; Nish, I.; Daskalogiannakis, J. Orthognathic surgery in cleft patients. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2012, 129, 535e–548e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Generali, C.; Primozic, J.; Richmond, S.; Bizzarro, M.; Flores-Mir, C.; Ovsenik, M.; Perillo, L. Three-dimensional evaluation of the maxillary arch and palate in unilateral cleft lip and palate subjects using digital dental casts. Eur. J. Orthod. 2017, 39, 641–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, M.; Karki, S.; Ylikontiola, L.; Lithovius, R.; Sándor, G.K.; Harila, V. Maxillary Arch Dimensions in 6-Year-Old Cleft Children in Northern Finland: A Cross-Sectional Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 18147432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corthouts, P.; Boels, F.; Van de Casteele, E.; Nadjmi, N. Effects of various surgical protocols on maxillofacial growth in patients with unilateral cleft lip and palate: A systematic review. Plast Aesthet. Res. 2020, 7, 46. [Google Scholar]
- Abd Rahman, N.; Abdullah, N.; Samsudin, A.R.; Naing Mohd Ayub Sadiq, L. Dental anomalies and facial profile abnormality of the non-syndromic cleft lip and palate children in kelantan. Malays. J. Med. Sci. 2004, 11, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Asquith, J.A.; McIntyre, G.T. Dental arch relationships on three-dimensional digital study models and conventional plaster study models for patients with unilateral cleft lip and palate. Cleft Palate Craniofac. J. 2012, 49, 530–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thurzo, A.; Urbanová, W.; Neuschlová, I.; Paouris, D.; Čverha, M. Use of optical scanning and 3D printing to fabricate customized appliances for patients with craniofacial disorders. Semin. Orthod. 2022, 28, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | UCLP | Non-UCLP | Frequency (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | UCLP | Non-UCLP | |
| Age | 14.56 (1.24) | 12.94 (2.30) | - | - |
| Sex | ||||
| Male | - | - | 29 (58) | 14 (28) |
| Female | - | - | 21 (42) | 36 (72) |
| Ehnic group | ||||
| Malay | - | - | 39 (78) | 33 (66) |
| Chinese | - | - | 11 (22) | 17 (34) |
| Variable | Estimate | Std. Error | t Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | −0.2346258 | 0.0324986 | −7.2195676 | 5.215314 × 10−13 * |
| Gender | 0.1198695 | 0.1287074 | 0.9313337 | 3.516810 × 10−1 * |
| Cleft | −1.2477741 | 0.1464901 | −8.5178031 | 1.626084 × 10−17 * |
| Deficient|Excess | −3.7506324 | 0.4316391 | −8.6892792 | 3.647463 × 10−18 * |
| Excess|Normal | −1.5794811 | 0.4104307 | −3.8483501 | 1.189160 × 10−4 * |
| Actual | Predicted |
|---|---|
| 1 | 0.996924 |
| 0 | 0.446150 |
| 1 | 0.999999 |
| 1 | 0.998960 |
| 0 | 0.587971 |
| 0 | 0.599176 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huqh, M.Z.U.; Abdullah, J.Y.; AL-Rawas, M.; Husein, A.; Ahmad, W.M.A.W.; Jamayet, N.B.; Genisa, M.; Yahya, M.R.B. Development of Artificial Neural Network-Based Prediction Model for Evaluation of Maxillary Arch Growth in Children with Complete Unilateral Cleft Lip and Palate. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3025. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13193025
Huqh MZU, Abdullah JY, AL-Rawas M, Husein A, Ahmad WMAW, Jamayet NB, Genisa M, Yahya MRB. Development of Artificial Neural Network-Based Prediction Model for Evaluation of Maxillary Arch Growth in Children with Complete Unilateral Cleft Lip and Palate. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(19):3025. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13193025
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuqh, Mohamed Zahoor Ul, Johari Yap Abdullah, Matheel AL-Rawas, Adam Husein, Wan Muhamad Amir W Ahmad, Nafij Bin Jamayet, Maya Genisa, and Mohd Rosli Bin Yahya. 2023. "Development of Artificial Neural Network-Based Prediction Model for Evaluation of Maxillary Arch Growth in Children with Complete Unilateral Cleft Lip and Palate" Diagnostics 13, no. 19: 3025. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13193025
APA StyleHuqh, M. Z. U., Abdullah, J. Y., AL-Rawas, M., Husein, A., Ahmad, W. M. A. W., Jamayet, N. B., Genisa, M., & Yahya, M. R. B. (2023). Development of Artificial Neural Network-Based Prediction Model for Evaluation of Maxillary Arch Growth in Children with Complete Unilateral Cleft Lip and Palate. Diagnostics, 13(19), 3025. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13193025







