Recent Advances of Artificial Intelligence Applications in Interstitial Lung Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Artificial Intelligence in ILDs
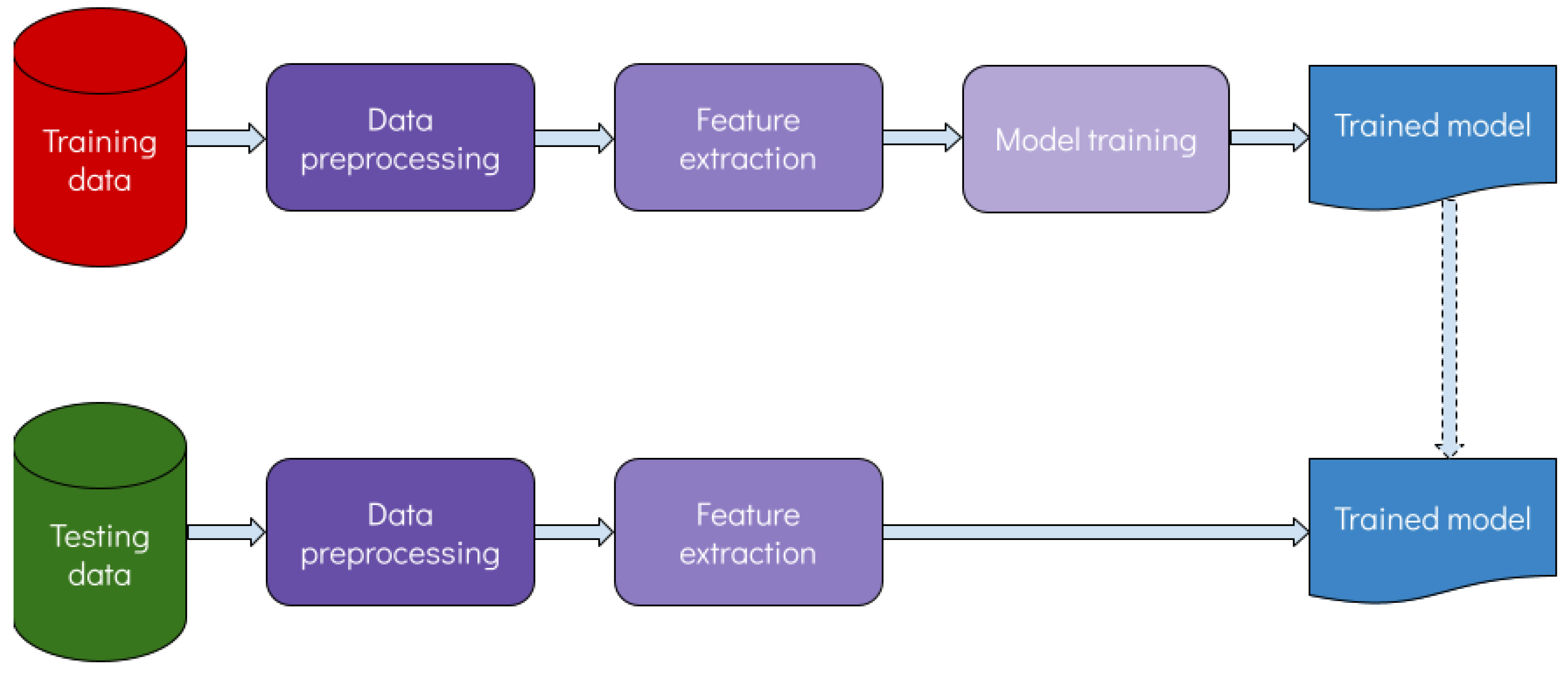
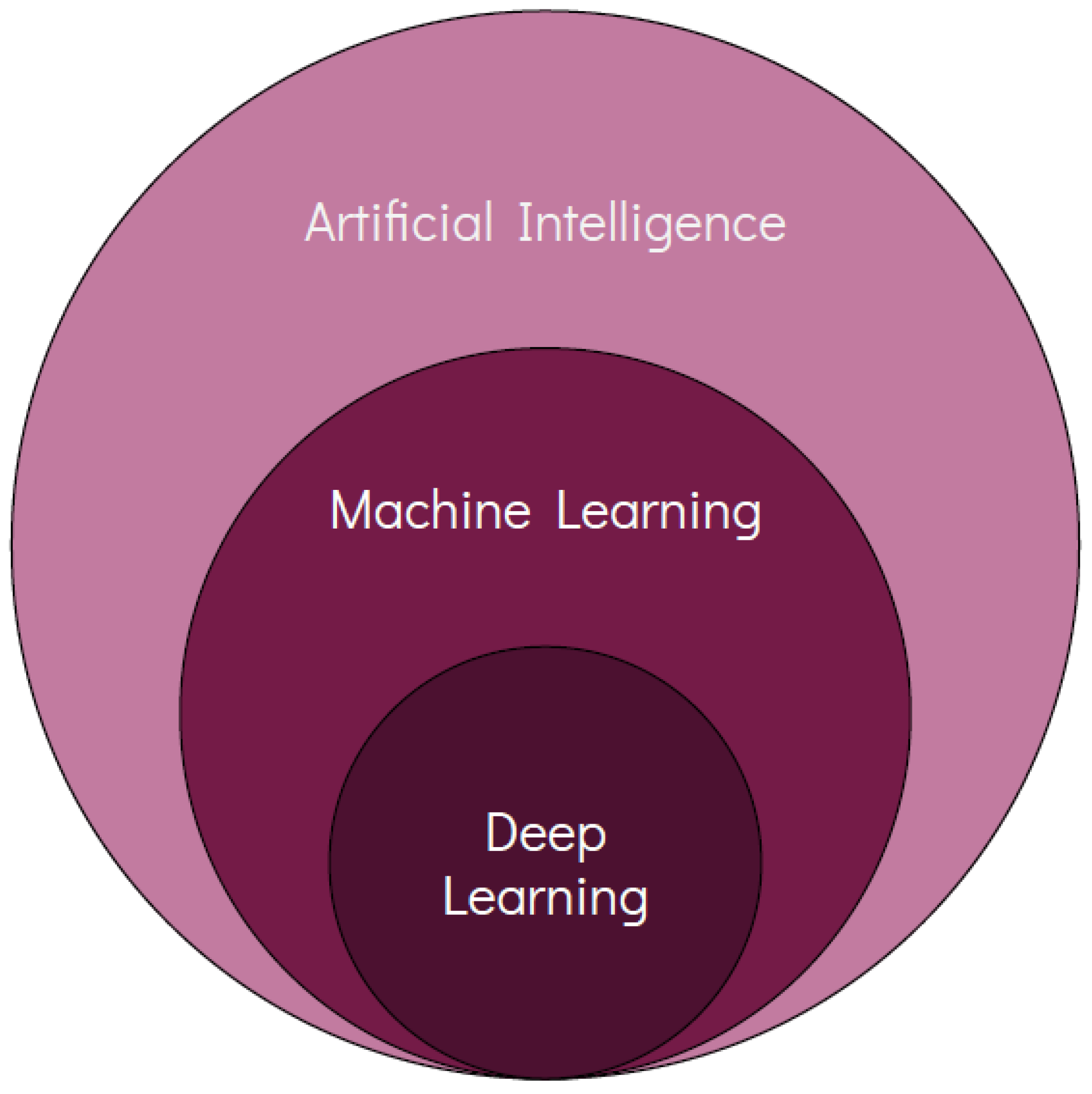
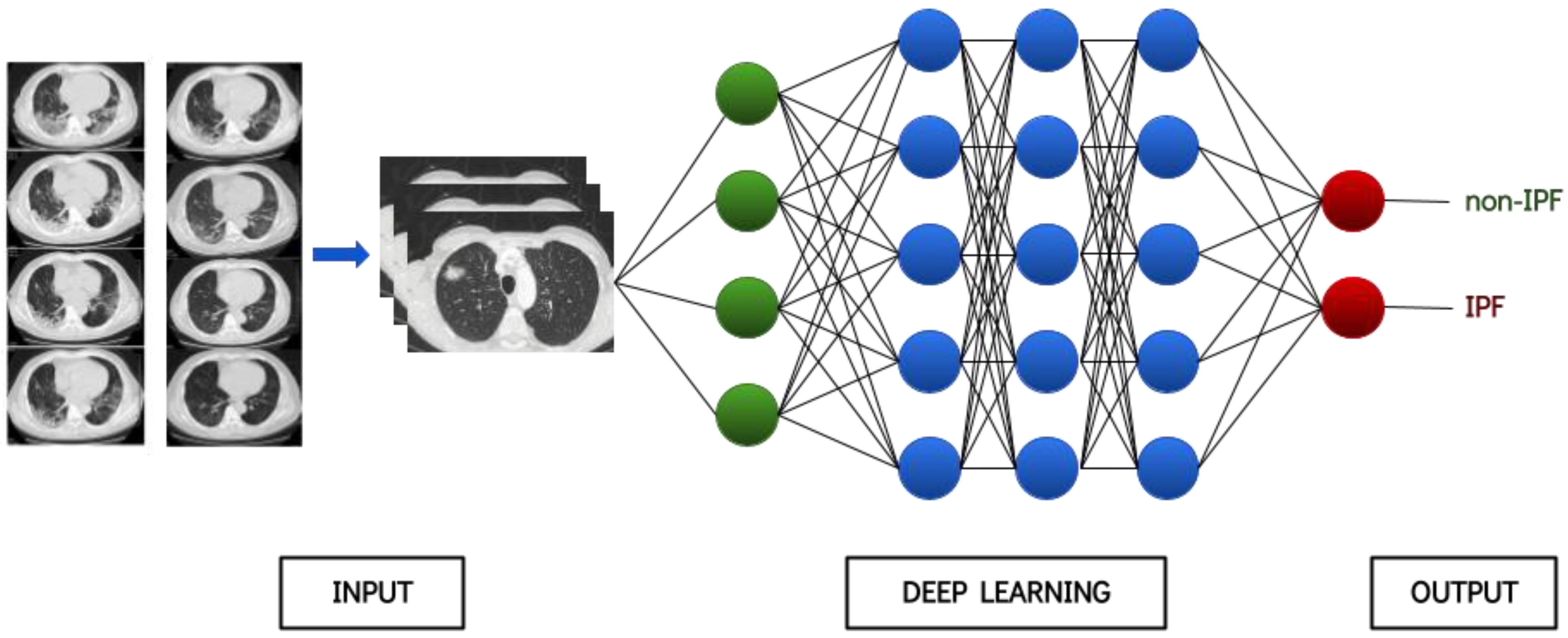
2.1. Overview and Rationale
2.2. Data Repositories
- OSIC data repository: launched by the Open Source Imaging Consortium, the OSIC repository contains approximately 1500 anonymized high-resolution CT scans alongside with clinical data for a wide range of interstitial lung diseases, primarily IPF [7]. The repository contains treatment information, as well as follow-up data and mortality. It was built by a collaboration of experts in the fields of pulmonology, radiology and AI, aiming primarily to facilitate the role of the latter in patient care and precision medicine. A subset of the OSIC data repository containing information regarding pulmonary fibrosis progression has become available from Kaggle, for researchers to develop tools and algorithms aiming to predict lung function decline. The subset repository contains 200 cases with approximately 1–2 years of follow-up.
- ILD Database from medGIFT [8]: a publicly available multimedia collection of ILD cases built from the University Hospitals of Geneva. The database contains high-resolution CT scans with annotated regions of pathological lung areas coupled with clinical parameters from patients with pathologically proven diagnoses of ILDs. Overall, the library contains data from 128 patients affected with 1 of the 13 ILD diseases.
- ILDgenDB [9]: an integrated genetic knowledge resource for interstitial lung diseases, which, as the name implies, contains genetic data about several ILDs. This resource contains literature-curated disease candidate genes enriched with regulatory elements, as well as single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) that have been associated with specific ILDs. For this propose, ILDgenDB is enriched with information from multiple popular genetic resources such as GAD (Genetic Association Database), OMIM (Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man) and GeneCards. The objective of this resource is to pinpoint potential genetic targets related to the pathogenesis, diagnosis, monitoring and treatment of ILDs.
- ILDGDB [10]: a similarly oriented repository as ILDgenDB, utilizing genomic, transcriptomic, proteomic and drug information for interstitial lung diseases. ILDGDB incorporates 2018 entries for 20 ILDs and over 600 genes; its purpose is to decipher gene mechanisms that take place in ILDs.
3. AI Applications in ILD Research
3.1. Screening
3.2. Diagnosis and Classification
3.3. Prognosis
4. Discussion
Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wijsenbeek, M.; Suzuki, A.; Maher, T.M. Interstitial Lung Diseases. Lancet 2022, 400, 769–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosgrove, G.P.; Bianchi, P.; Danese, S.; Lederer, D.J. Barriers to Timely Diagnosis of Interstitial Lung Disease in the Real World: The INTENSITY Survey. BMC Pulm. Med. 2018, 18, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouda, W.; Sama, N.U.; Al-Waakid, G.; Humayun, M.; Jhanjhi, N.Z. Detection of Skin Cancer Based on Skin Lesion Images Using Deep Learning. Healthcare 2022, 10, 1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Yang, R. Diagnosis of Ulcerative Colitis from Endoscopic Images Based on Deep Learning. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2022, 73, 103443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamai, G.; Livne, A.; Polónia, A.; Sabo, E.; Cretu, A.; Bar-Sela, G.; Kimmel, R. Deep Learning-Based Image Analysis Predicts PD-L1 Status from H&E-Stained Histopathology Images in Breast Cancer. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6753. [Google Scholar]
- Maher, T.M.; Nambiar, A.M.; Wells, A.U. The Role of Precision Medicine in Interstitial Lung Disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2022, 60, 2102146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Balas, V.E.; Shaw, R.N.; Ghosh, A. Prediction Analysis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Progression from OSIC Dataset. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Computing, Power and Communication Technologies (GUCON), Greater Noida, India, 2–4 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Depeursinge, A.; Vargas, A.; Platon, A.; Geissbuhler, A.; Poletti, P.-A.; Müller, H. Building a Reference Multimedia Database for Interstitial Lung Diseases. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2012, 36, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Shah, M.I.; Sarkar, M.; Asati, N.; Rout, C. ILDgenDB: Integrated Genetic Knowledge Resource for Interstitial Lung Diseases (ILDs). Database 2018, 2018, bay053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wu, G.; Shang, Y.; Qi, Y.; Wang, X.; Ning, S.; Chen, H. ILDGDB: A Manually Curated Database of Genomics, Transcriptomics, Proteomics and Drug Information for Interstitial Lung Diseases. BMC Pulm. Med. 2020, 20, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bermejo-Peláez, D.; Ash, S.Y.; Washko, G.R.; San José Estépar, R.; Ledesma-Carbayo, M.J. Classification of Interstitial Lung Abnormality Patterns with an Ensemble of Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwala, S.; Kale, M.; Kumar, D.; Swaroop, R.; Kumar, A.; Kumar Dhara, A.; Basu Thakur, S.; Sadhu, A.; Nandi, D. Deep Learning for Screening of Interstitial Lung Disease Patterns in High-Resolution CT Images. Clin. Radiol. 2020, 75, 481.e1–481.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.S.; Choe, J.; Hwang, H.J.; Lee, S.M.; Yun, J.; Kim, N.; Ko, M.-S.; Yi, J.; Yu, D.; Seo, J.B. Interstitial Lung Abnormalities (ILA) on Routine Chest CT: Comparison of Radiologists’ Visual Evaluation and Automated Quantification. Eur. J. Radiol. 2022, 157, 110564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikiori, H.; Kuronuma, K.; Hirota, K.; Yama, N.; Suzuki, T.; Onodera, M.; Onodera, K.; Ikeda, K.; Mori, Y.; Asai, Y.; et al. Deep-Learning Algorithm to Detect Fibrosing Interstitial Lung Disease on Chest Radiographs. Eur. Respir. J. 2023, 61, 2102269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onishchenko, D.; Marlowe, R.J.; Ngufor, C.G.; Faust, L.J.; Limper, A.H.; Hunninghake, G.M.; Martinez, F.J.; Chattopadhyay, I. Screening for Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Using Comorbidity Signatures in Electronic Health Records. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 2107–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axelsson, G.T.; Gudmundsson, G.; Pratte, K.A.; Aspelund, T.; Putman, R.K.; Sanders, J.L.; Gudmundsson, E.F.; Hatabu, H.; Gudmundsdottir, V.; Gudjonsson, A.; et al. The Proteomic Profile of Interstitial Lung Abnormalities. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 206, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, S.P.; Talbar, S.N. Two-Stage Hybrid Approach of Deep Learning Networks for Interstitial Lung Disease Classification. BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 7340902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Lee, F.; Miao, R.; Si, Q.; Lu, C.; Chen, Q. A Deep Convolutional Neural Network Architecture for Interstitial Lung Disease Pattern Classification. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2020, 58, 725–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choe, J.; Hwang, H.J.; Seo, J.B.; Lee, S.M.; Yun, J.; Kim, M.-J.; Jeong, J.; Lee, Y.; Jin, K.; Park, R.; et al. Content-Based Image Retrieval by Using Deep Learning for Interstitial Lung Disease Diagnosis with Chest CT. Radiology 2022, 302, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, C.W.; Williams, J.M.; Liu, G.; Panda, A.; Patel, P.P.; Frota Lima, L.M.M.; Karwoski, R.A.; Moua, T.; Larson, N.B.; Bratt, A. Quantitative CT and Machine Learning Classification of Fibrotic Interstitial Lung Diseases. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 8152–8161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, T.; Oyama, S.; Yokota, H.; Kondoh, Y.; Kataoka, K.; Johkoh, T.; Fukuoka, J.; Hashimoto, N.; Sakamoto, K.; Shiratori, Y.; et al. A Comprehensible Machine Learning Tool to Differentially Diagnose Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis from Other Chronic Interstitial Lung Diseases. Respirology 2022, 27, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christe, A.; Peters, A.A.; Drakopoulos, D.; Heverhagen, J.T.; Geiser, T.; Stathopoulou, T.; Christodoulidis, S.; Anthimopoulos, M.; Mougiakakou, S.G.; Ebner, L. Computer-Aided Diagnosis of Pulmonary Fibrosis Using Deep Learning and CT Images. Investig. Radiol. 2019, 54, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratt, A.; Williams, J.M.; Liu, G.; Panda, A.; Patel, P.P.; Walkoff, L.; Sykes, A.-M.G.; Tandon, Y.K.; Francois, C.J.; Blezek, D.J.; et al. Predicting Usual Interstitial Pneumonia Histopathology from Chest CT Imaging With Deep Learning. Chest 2022, 162, 815–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Tang, Z.-R.; Chen, J.; Tang, M.; Wang, S.; Qi, W.; Yao, C.; Yu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Yu, Z. Pneumoconiosis Computer Aided Diagnosis System Based on X-Rays and Deep Learning. BMC Med. Imaging 2021, 21, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horimasu, Y.; Ohshimo, S.; Yamaguchi, K.; Sakamoto, S.; Masuda, T.; Nakashima, T.; Miyamoto, S.; Iwamoto, H.; Fujitaka, K.; Hamada, H.; et al. A Machine-Learning Based Approach to Quantify Fine Crackles in the Diagnosis of Interstitial Pneumonia: A Proof-of-Concept Study. Medicine 2021, 100, e24738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plantier, L.; Smolinska, A.; Fijten, R.; Flamant, M.; Dallinga, J.; Mercadier, J.J.; Pachen, D.; d’Ortho, M.P.; van Schooten, F.J.; Crestani, B.; et al. The Use of Exhaled Air Analysis in Discriminating Interstitial Lung Diseases: A Pilot Study. Respir. Res. 2022, 23, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, S.; Huang, T. Identification of Chronic Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Biomarkers with Machine Learning and Differential Co-Expression Analysis. Curr. Gene Ther. 2021, 21, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhao, H.; Yan, P.; Yuan, H.; Zhao, M.; Wan, R.; Yu, G.; Wang, L. Artificial Neural Network Identified the Significant Genes to Distinguish Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.H.J.; Weigt, S.S.; Belperio, J.A.; Brown, M.S.; Shi, Y.; Lai, J.H.; Goldin, J.G. Prediction of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Progression Using Early Quantitative Changes on CT Imaging for a Short Term of Clinical 18-24-Month Follow-Ups. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handa, T.; Tanizawa, K.; Oguma, T.; Uozumi, R.; Watanabe, K.; Tanabe, N.; Niwamoto, T.; Shima, H.; Mori, R.; Nobashi, T.W.; et al. Novel Artificial Intelligence-Based Technology for Chest Computed Tomography Analysis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2022, 19, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budzikowski, J.D.; Foy, J.J.; Rashid, A.A.; Chung, J.H.; Noth, I.; Armato, S.G. 3rd Radiomics-Based Assessment of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Is Associated with Genetic Mutations and Patient Survival. J. Med. Imaging Bellingham 2021, 8, 031903. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, C.-H.; Liu, Y.-C.; Wan, Y.-L.; Yun, C.-H.; Wu, W.-J.; López-González, R.; Huang, W.-M. Quantification of Cancer-Developing Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Using Whole-Lung Texture Analysis of HRCT Images. Cancers 2021, 13, 5600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, R.; Iwasawa, T.; Saka, T.; Yamashiro, T.; Utsunomiya, D.; Misumi, T.; Baba, T.; Ogura, T. Effects of Automatic Deep-Learning-Based Lung Analysis on Quantification of Interstitial Lung Disease: Correlation with Pulmonary Function Test Results and Prognosis. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, W.S.; Newton, C.A.; Linderholm, A.L.; Neely, M.L.; Pugashetti, J.V.; Kaul, B.; Vo, V.; Echt, G.A.; Leon, W.; Shah, R.J.; et al. Proteomic Biomarkers of Progressive Fibrosing Interstitial Lung Disease: A Multicentre Cohort Analysis. Lancet Respir. Med. 2022, 10, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayr, C.H.; Simon, L.M.; Leuschner, G.; Ansari, M.; Schniering, J.; Geyer, P.E.; Angelidis, I.; Strunz, M.; Singh, P.; Kneidinger, N.; et al. Integrative Analysis of Cell State Changes in Lung Fibrosis with Peripheral Protein Biomarkers. EMBO Mol. Med. 2021, 13, e12871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mali, S.A.; Ibrahim, A.; Woodruff, H.C.; Andrearczyk, V.; Müller, H.; Primakov, S.; Salahuddin, Z.; Chatterjee, A.; Lambin, P. Making Radiomics More Reproducible across Scanner and Imaging Protocol Variations: A Review of Harmonization Methods. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinton, G. Deep Learning—A Technology with the Potential to Transform Health Care. JAMA 2018, 320, 1101–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniou, K.M.; Tsitoura, E.; Vasarmidi, E.; Symvoulakis, E.K.; Aidinis, V.; Tzilas, V.; Tzouvelekis, A.; Bouros, D. Precision Medicine in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Therapy: From Translational Research to Patient-Centered Care. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2021, 57, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, K.-K.; Balijepalli, M.K.; Pichika, M.R. Success Stories of AI in Drug Discovery—Where Do Things Stand? Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2022, 17, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Author(s) | Scope | Dataset | Type of Data | Performance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bermejo-Peláez et al. [11] | Screening | 208 CT scans | Imaging | Sensitivity: 91.41% |
| Agarwala et al. [12] | Screening | 168 CT scans | Imaging | Success rate: 85.3% |
| Kim et al. [13] | Screening | 336 participants | Imaging | Accuracy: 90.5% |
| Nishikiori et al. [14] | Screening | 1159 chest X-rays | Imaging | AUC = 0.979 |
| Onishchenko et al. [15] | Screening | 2,983,215 participants | Electronic Health Records | AUC > 0.840 |
| Axelsson et al. [16] | Screening | >10,000 patients | Proteins | - |
| Pawar and Talbar [17] | Diagnosis & classification | 108 CT scans | Imaging | Accuracy: 89.39% |
| Huang et al. [18] | Diagnosis & classification | 108 CT scans | Imaging | F1-score > 0.96 |
| Chloe et al. [19] | Diagnosis & classification | 300 patients | Imaging | Accuracy: 60.9% |
| Koo et al. [20] | Diagnosis & classification | 1085 patients | Imaging | AUC > 0.900 |
| Furukawa et al. [21] | Diagnosis & classification | 1068 patients | Imaging | Accuracy: 83.6% |
| Christe et al. [22] | Diagnosis & classification | 105 patients | Imaging | Accuracy: 81% |
| Bratt et al. [23] | Diagnosis & classification | 1239 patients | Imaging | AUC = 0.870 |
| Yang et al. [24] | Diagnosis & classification | 1760 chest X-rays | Imaging | Accuracy: 92.46% |
| Horimasu et al. [25] | Diagnosis & classification | 60 patients | Auscultation | Accuracy: 75% |
| Plantier et al. [26] | Diagnosis & classification | 150 patients | Volatile Organic Compounds | Accuracy: 77.5% |
| Zhang et al. [27] | Diagnosis & classification | 300 patients | Gene Expression | - |
| Li et al. [28] | Diagnosis & classification | 600 patients | Gene Expression | AUC = 0.856 |
| Kim et al. [29] | Prognosis | 192 patients | Imaging | - |
| Handa et al. [30] | Prognosis | 465 patients | Imaging | - |
| Budzikowski et al. [31] | Prognosis | 169 patients | Imaging and Genomic | - |
| Liang et al. [32] | Prognosis | 116 patients | Imaging | AUC = 0.870 |
| Aoki et al. [33] | Prognosis | 104 patients | Imaging | - |
| Bowman et al. [34] | Prognosis | 589 patients | Proteomic | Sensitivity: 90% |
| Mayr et al. [35] | Prognosis | 124 patients | Proteomic | Accuracy: 83% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Exarchos, K.P.; Gkrepi, G.; Kostikas, K.; Gogali, A. Recent Advances of Artificial Intelligence Applications in Interstitial Lung Diseases. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2303. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13132303
Exarchos KP, Gkrepi G, Kostikas K, Gogali A. Recent Advances of Artificial Intelligence Applications in Interstitial Lung Diseases. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(13):2303. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13132303
Chicago/Turabian StyleExarchos, Konstantinos P., Georgia Gkrepi, Konstantinos Kostikas, and Athena Gogali. 2023. "Recent Advances of Artificial Intelligence Applications in Interstitial Lung Diseases" Diagnostics 13, no. 13: 2303. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13132303
APA StyleExarchos, K. P., Gkrepi, G., Kostikas, K., & Gogali, A. (2023). Recent Advances of Artificial Intelligence Applications in Interstitial Lung Diseases. Diagnostics, 13(13), 2303. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13132303







