18F-FDG and 18F-NaF PET/CT Global Assessment of Large Joint Inflammation and Bone Turnover in Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
:1. Background
2. Methods
2.1. Patient Population
2.2. Clinical Variables
2.3. Imaging
2.4. Image Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Imagama, T.; Tokushige, A.; Seki, K.; Taguchi, T. Weight Bearing Joints Destruction in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Curr. Rheumatol. Rev. 2017, 13, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, V.; Schmidt, W.; Backhaus, M.; Hartung, W. Arthritis of the Knee Joint in Rheumatoid Arthritis-Evaluation of Treatment Response by Ultrasound in Daily Clinical Practice. Open Rheumatol. J. 2016, 10, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Al-Zaghal, A.; Yellanki, D.P.; Ayubcha, C.; Werner, T.J.; Høilund-Carlsen, P.F.; Alavi, A. CT-based tissue segmentation to assess knee joint inflammation and reactive bone formation assessed by 18F-FDG and 18F-NaF PET/CT: Effects of age and BMI. Hell. J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 21, 102–107. [Google Scholar]
- Lachiewicz, P.F. Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Hip. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 1997, 5, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayubcha, C.; Raynor, W.; Acosta-Montenegro, O.; Werner, T.; Vilstrup, M.; Hoilund-Carlsen, P.F.; Alavi, A. Measuring the effects of aging using 18F-sodium fluoride uptake in the spine. J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58 (Suppl. S1), 1227. [Google Scholar]
- Hayer, S.; Zeilinger, M.; Weiss, V.; Dumanic, M.; Seibt, M.; Niederreiter, B.; Shvets, T.; Pichler, F.; Wadsak, W.; Podesser, B.K.; et al. Multimodal [18F]FDG PET/CT Is a Direct Readout for Inflammatory Bone Repair: A Longitudinal Study in TNFalpha Transgenic Mice. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2019, 34, 1632–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khaw, T.H.; Raynor, W.Y.; Borja, A.J.; Al-Zaghal, A.; Jonnakuti, V.S.; Cheng, N.; Houshmand, S.; Werner, T.J.; Alavi, A. Assessing the effects of body weight on subchondral bone formation with quantitative 18F-sodium fluoride PET. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2020, 34, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.S.; Shejul, Y.; Asopa, R.; Basu, S. Quantitative metabolic volumetric product on 18Fluorine-2fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose-positron emission tomography/computed tomography in assessing treatment response to disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs in rheumatoid arthritis: Multiparametric analysis integrating American college of Rheumatology/European League against Rheumatism criteria. World J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 16, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamura, K.; Yonemoto, Y.; Arisaka, Y.; Takeuchi, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Oriuchi, N.; Tsushima, Y.; Takagishi, K. The assessment of biologic treatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis using FDG-PET/CT. Rheumatology 2012, 51, 1484–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, Y.-J.; Wang, W.-H.; Huang, T.-Y.; Weng, W.-H.; Fang, C.-K.; Chen, Y.-C.; Hwang, J.-J. Quetiapine ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis in mice via the suppression of the AKT and ERK signaling pathways. Inflamm. Res. 2018, 67, 847–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravikanth, R.; Singh, J. Semi-quantitative analysis of 18F fluorodeoxyglucose uptake in the assessment of disease activity and therapeutic response in rheumatoid arthritis: An institutional experience. World J. Nucl. Med. 2020, 19, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raychaudhuri, S.; Abria, C.; Harmany, Z.T.; Smith, C.M.; Kundu-Raychaudhuri, S.; Raychaudhuri, S.P.; Chaudhari, A.J. Quantitative tracking of inflammatory activity at the peak and trough plasma levels of tofacitinib, a Janus kinase inhibitor, via in vivo 18F-FDG PET. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 22, 2165–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raynor, W.Y.; Jonnakuti, V.S.; Zadeh, M.Z.; Werner, T.J.; Cheng, G.; Zhuang, H.; Høilund-Carlsen, P.F.; Alavi, A.; Baker, J.F. Comparison of methods of quantifying global synovial metabolic activity with FDG-PET/CT in rheumatoid arthritis. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 22, 2191–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suto, T.; Okamura, K.; Yonemoto, Y.; Okura, C.; Tsushima, Y.; Takagishi, K. Prediction of Large Joint Destruction in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis Using 18F-FDG PET/CT and Disease Activity Score. Medicine 2016, 95, e2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takata, T.; Taniguchi, Y.; Ohnishi, T.; Kohsaki, S.; Nogami, M.; Nakajima, H.; Kumon, Y.; Terada, Y.; Ogawa, Y.; Tarutani, M.; et al. 18FDG PET/CT is a powerful tool for detecting subclinical arthritis in patients with psoriatic arthritis and/or psoriasis vulgaris. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2011, 64, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayant, V. Potential of 18F-FDG-PET as a valuable adjunct to clinical and response assessment in rheumatoid arthritis and seronegative spondyloarthropathies. World J. Radiol. 2012, 4, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.; Caplan, L.; Yazdany, J.; Robbins, M.L.; Neogi, T.; Michaud, K.; Saag, K.G.; O’Dell, J.R.; Kazi, S. Rheumatoid arthritis disease activity measures: American College of Rheumatology recommendations for use in clinical practice. Arthritis Care Res. 2012, 64, 640–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alecu, M.; Geleriu, L.; Coman, G.; Gălăţescu, L. The interleukin-1, interleukin-2, interleukin-6 and tumour necrosis factor alpha serological levels in localised and systemic sclerosis. Rom. J. Intern. Med. 2000, 36, 251–259. [Google Scholar]
- Jonnakuti, V.S.; Raynor, W.Y.; Taratuta, E.; Werner, T.J.; Alavi, A.; Baker, J.F. A novel method to assess subchondral bone formation using [18F]NaF-PET in the evaluation of knee degeneration. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2018, 39, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neame, R.; Zhang, W.; Deighton, C.; Doherty, M.; Doherty, S.; Lanyon, P.; Wright, G. Distribution of radiographic osteoarthritis between the right and left hands, hips, and knees. Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 50, 1487–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaku, A.; Hashimoto, M.; Furu, M.; Ito, H.; Yamakawa, N.; Yamamoto, W.; Fujii, T.; Matsuda, F.; Mimori, T.; Terao, C. Relationship between handedness and joint involvement in rheumatoid arthritis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattarai, A.; Nakajima, T.; Sapkota, S.; Arisaka, Y.; Tokue, A.; Yonemoto, Y.; Tsushima, Y. Diagnostic value of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose uptake parameters to differentiate rheumatoid arthritis from other types of arthritis. Medicine 2017, 96, e7130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tibrewala, R.; Bahroos, E.; Mehrabian, H.; Foreman, S.C.; Link, T.M.; Pedoia, V.; Majumdar, S. [18F]-Sodium Fluoride PET/MR Imaging for Bone-Cartilage Interactions in Hip Osteoarthritis: A Feasibility Study. J. Orthop. Res. 2019, 37, 2671–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watkins, L.; MacKay, J.; Haddock, B.; Mazzoli, V.; Uhlrich, S.; Gold, G.; Kogan, F. Assessment of quantitative [18F]Sodium fluoride PET measures of knee subchondral bone perfusion and mineralization in osteoarthritic and healthy subjects. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2021, 29, 849–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, B. Rheumatoid Arthritis: Early diagnosis and treatment outcomes. Casp. J. Intern. Med. 2011, 2, 161–170. [Google Scholar]
- Yellanki, D.P.; Kothekar, E.; Al-Zaghal, A.; Cheng, N.; Werner, T.J.; Høilund-Carlsen, P.F.; Alavi, A. Efficacy of 18F-FDG and 18F-NaF PET/CT imaging: A novel semi-quantitative assessment of the effects of age and obesity on hip joint inflammation and bone degeneration. Hell. J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 21, 181–185. [Google Scholar]
- Helliwell, P.S.; Hetthen, J.; Sokoll, K.; Green, M.; Marchesoni, A.; Lubrano, E.; Veale, D.; Emery, P. Joint symmetry in early and late rheumatoid and psoriatic arthritis: Comparison with a mathematical model. Arthritis Rheum. 2000, 43, 865–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangger, P.; Keystone, E.C.; Bogoch, E.R. Asymmetry of small joint involvement in rheumatoid arthritis: Prevalence and tendency towards symmetry over time. Jt. Bone Spine 2005, 72, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chihara, K.; Hattori, N.; Ichikawa, N.; Matsuda, T.; Saito, T. Re-evaluation of serum leptin and adiponectin concentrations normalized by body fat mass in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messier, S.P.; Gutekunst, D.J.; Davis, C.; DeVita, P. Weight loss reduces knee-joint loads in overweight and obese older adults with knee osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52, 2026–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.; Lee, Y.H. Causal association between body mass index and risk of rheumatoid arthritis: A Mendelian randomization study. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 49, e13076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azevedo, S.; Santos-Faria, D.; Silva, J.L.; Rodrigues, J.R.; Neves, J.S.; Peixoto, D.; Tavares-Costa, J.; Alcino, S.; Afonso, C.; Teixeira, F. Obesity, metabolic syndrome and other comorbidities in rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis: Influence on disease activity and quality of life. Acta Reumatol. Port. 2020, 44, 322–324. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, H.; Bea, E.-K.; Lee, J.; Koh, E.-M.; Cha, H.-S. Body mass index and estrogen predict radiographic progression in the spine in ankylosing spondylitis. Jt. Bone Spine 2015, 82, 473–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoja, S.S.; Patterson, C.G.; Goodpaster, B.H.; Delitto, A.; Piva, S.R. Skeletal muscle fat in individuals with rheumatoid arthritis compared to healthy adults. Exp. Gerontol. 2020, 129, 110768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, R.; Kull, M.; Lember, M.; Põlluste, K.; Valner, A.; Kallikorm, R. Insulin Resistance in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis Is Associated with Low Appendicular Lean Mass. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 9584720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Takase-Minegishi, K.; Ihata, A.; Kunishita, Y.; Kishimoto, D.; Kamiyama, R.; Hama, M.; Yoshimi, R.; Kirino, Y.; Asami, Y.; et al. 18F-FDG and 18F-NaF PET/CT demonstrate coupling of inflammation and accelerated bone turnover in rheumatoid arthritis. Mod. Rheumatol. 2016, 26, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhawan, R.; Lokitz, K.; Lokitz, S.; Caldito, G.; Takalkar, A.M. FDG PET Imaging of Extremities in Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. State Med Soc. Off. Organ La. State Med. Soc. 2016, 168, 156–161. [Google Scholar]
- Yonemoto, Y.; Okamura, K.; Kaneko, T.; Okura, C.; Kobayashi, T.; Suto, T.; Tsushima, Y.; Takagishi, K. Effect of total knee arthroplasty on other joints in patients with rheumatoid arthritis evaluated by 18-FDG-PET. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 20, 702–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruijnen, S.T.; van der Weijden, M.A.; Klein, J.P.; Hoekstra, O.S.; Boellaard, R.; van Denderen, J.C.; Dijkmans, B.A.; E Voskuyl, A.; E van der Horst-Bruinsma, I.; van der Laken, C.J. Bone formation rather than inflammation reflects Ankylosing Spondylitis activity on PET-CT: A pilot study. Thromb. Haemost. 2012, 14, R71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Cai, L.; Xu, T.; Tang, D.; Liu, L.; Chen, Y. Comparative Evaluation of 68Ga-Citrate PET/CT and 18F-FDG PET/CT in the Diagnosis of Type II Collagen-Induced Arthritis in Rats. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2019, 2019, 2353658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chung, S.-J.; Yoon, H.-J.; Youn, H.; Kim, M.J.; Lee, Y.-S.; Jeong, J.M.; Chung, J.-K.; Kang, K.W.; Xie, L.; Zhang, M.-R.; et al. 18F-FEDAC as a Targeting Agent for Activated Macrophages in DBA/1 Mice with Collagen-Induced Arthritis: Comparison with 18F-FDG. J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 59, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]





| Characteristic | n (%) |
|---|---|
| Total | 18 |
| Male | 13 (72.2) |
| Female | 5 (27.8) |
| Left-handed | 4 (22.2) |
| Right-handed | 13 (72.2) |
| Ambidextrous | 1 (5.6) |
| Age (years) | |
| Median (IQR) | 60.5 (14.3) |
| Range | 25–69 |
| Weight (kg) | |
| Median (IQR) | 77.7 (14.5) |
| Range | 47.0–130.3 |
| Height (cm) | |
| Median (IQR) | 170.8 (18.8) |
| Range | 153.1–188.7 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | |
| Median (IQR) | 28.5 (7.2) |
| Range | 18.7–44.1 |
| RA duration (years) | |
| Median (IQR) | 8.4 (14.8) |
| Range | 0.1–35.8 |
| ESR (mm/h) | |
| Median (IQR) | 21 (32) |
| Range | 3–66 |
| CRP (mg/dL) | |
| Median (IQR) | 1.2 (1.0) |
| Range | 0.5–3.1 |
| IL-1 (pg/mL) (normal, 0–5 pg/mL) [18] | |
| Median (IQR) | 0.3 (0.1) |
| Range | 0.2–0.9 |
| IL-6 pg/mL (normal, 5–15 pg/mL) [18] | |
| Median (IQR) | 2.3 (2.3) |
| Range | 0.5–8.7 |
| DAS28-CRP | |
| Median (IQR) | 4.1 (2.4) |
| Range | 1.6–5.4 |
| VAS-PtGlobal | |
| Median (IQR) | 46.5 (26.0) |
| Range | 4–75 |
| Knee Joint | FDG SUVmean | NaF SUVmean | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R-Value | p-Value | R-Value | p-Value | |
| Age | 0.362 | 0.153 | −0.039 | 0.877 |
| Weight | 0.506 | 0.038 | 0.457 | 0.056 |
| Height | −0.193 | 0.458 | 0.017 | 0.947 |
| BMI | 0.619 | 0.008 | 0.501 | 0.034 |
| Leptin | 0.500 | 0.008 | 0.509 | 0.031 |
| Sclerostin | −0.545 | 0.444 | −0.489 | 0.040 |
| Total Fat | 0.520 | 0.001 | 0.541 | 0.031 |
| CRP | 0.304 | 0.133 | 0.261 | 0.296 |
| ESR | −0.124 | 0.961 | 0.246 | 0.341 |
| IL-1 | 0.356 | 0.161 | 0.182 | 0.470 |
| IL-6 | 0.307 | 0.231 | 0.138 | 0.585 |
| DAS28-CRP | −0.034 | 0.850 | −0.008 | 0.976 |
| VAS-PtGlobal | −0.152 | 0.773 | −0.231 | 0.357 |
| Hip Joint | FDG SUVmean | NaF SUVmean | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R-Value | p-Value | R-Value | p-Value | |
| Age | 0.066 | 0.796 | −0.381 | 0.131 |
| Weight | −0.051 | 0.840 | 0.412 | 0.101 |
| Height | −0.001 | 0.998 | −0.256 | 0.322 |
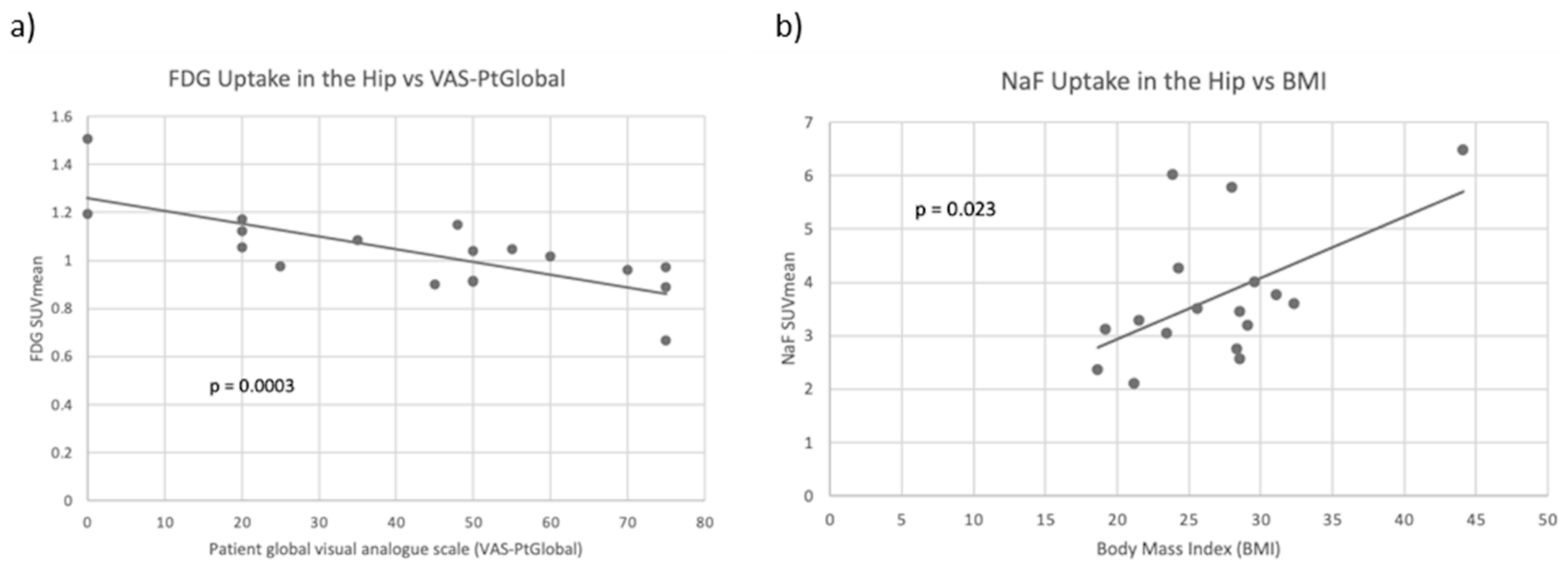
| BMI | −0.096 | 0.703 | 0.548 | 0.023 |
| Leptin | −0.038 | 0.122 | 0.61 | 0.009 |
| Sclerostin | 0.077 | 0.762 | −0.583 | 0.014 |
| Total Fat | −0.120 | 0.635 | 0.504 | 0.039 |
| CRP | 0.318 | 0.198 | 0.368 | 0.147 |
| ESR | 0.340 | 0.181 | 0.091 | 0.739 |
| IL-1 | 0.337 | 0.172 | −0.026 | 0.922 |
| IL-6 | 0.299 | 0.229 | −0.094 | 0.721 |
| DAS28-CRP | −0.529 | 0.024 | 0.083 | 0.752 |
| VAS-PtGlobal | −0.755 | <0.001 | −0.096 | 0.713 |
| SI Joint | FDG SUVmean | NaF SUVmean | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R-Value | p-Value | R-Value | p-Value | |
| Age | −0.055 | 0.827 | −0.423 | 0.091 |
| Weight | 0.087 | 0.732 | 0.379 | 0.134 |
| Height | 0.302 | 0.224 | −0.295 | 0.250 |
| BMI | −0.111 | 0.661 | 0.536 | 0.027 |
| Leptin | −0.442 | 0.066 | 0.592 | 0.012 |
| Sclerostin | −0.038 | 0.882 | −0.506 | 0.038 |
| Total Fat | −0.125 | 0.623 | 0.462 | 0.062 |
| CRP | 0.325 | 0.189 | 0.231 | 0.372 |
| ESR | 0.215 | 0.407 | 0.113 | 0.677 |
| IL-1 | 0.248 | 0.321 | −0.170 | 0.515 |
| IL-6 | 0.335 | 0.175 | −0.190 | 0.465 |
| DAS28-CRP | −0.459 | 0.055 | 0.249 | 0.336 |
| VAS-PtGlobal | −0.650 | 0.003 | 0.113 | 0.666 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reddy, N.; Raynor, W.Y.; Werner, T.J.; Baker, J.F.; Alavi, A.; Revheim, M.-E. 18F-FDG and 18F-NaF PET/CT Global Assessment of Large Joint Inflammation and Bone Turnover in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2149. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13132149
Reddy N, Raynor WY, Werner TJ, Baker JF, Alavi A, Revheim M-E. 18F-FDG and 18F-NaF PET/CT Global Assessment of Large Joint Inflammation and Bone Turnover in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(13):2149. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13132149
Chicago/Turabian StyleReddy, Natasha, William Y. Raynor, Thomas J. Werner, Joshua F. Baker, Abass Alavi, and Mona-Elisabeth Revheim. 2023. "18F-FDG and 18F-NaF PET/CT Global Assessment of Large Joint Inflammation and Bone Turnover in Rheumatoid Arthritis" Diagnostics 13, no. 13: 2149. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13132149
APA StyleReddy, N., Raynor, W. Y., Werner, T. J., Baker, J. F., Alavi, A., & Revheim, M.-E. (2023). 18F-FDG and 18F-NaF PET/CT Global Assessment of Large Joint Inflammation and Bone Turnover in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Diagnostics, 13(13), 2149. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13132149








