Deep Learning for the Differential Diagnosis between Transient Osteoporosis and Avascular Necrosis of the Hip
Abstract
:1. Introduction
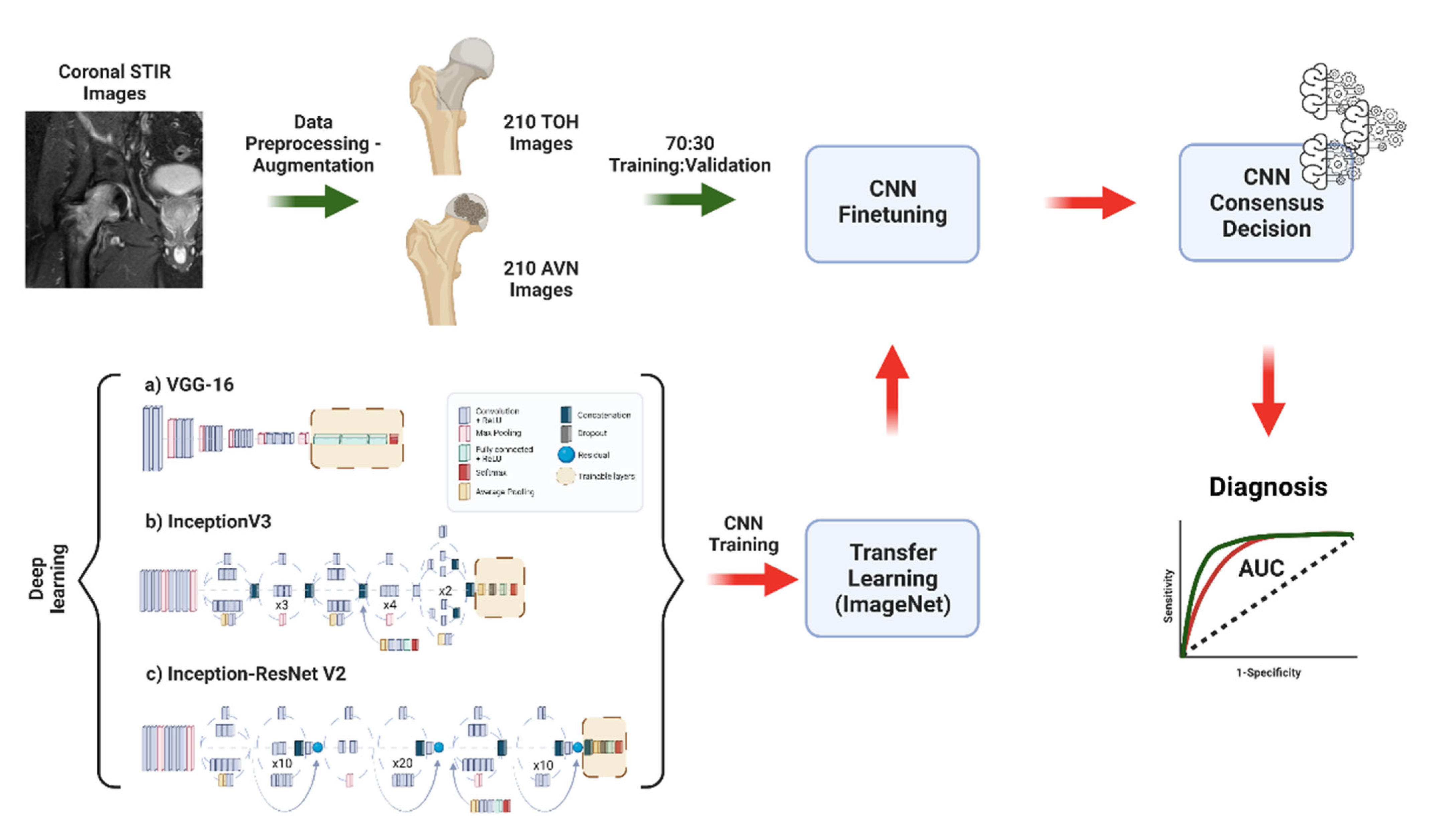
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. MR Imaging
2.3. Data Preparation, Deep Learning, and Comparison to Experts
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
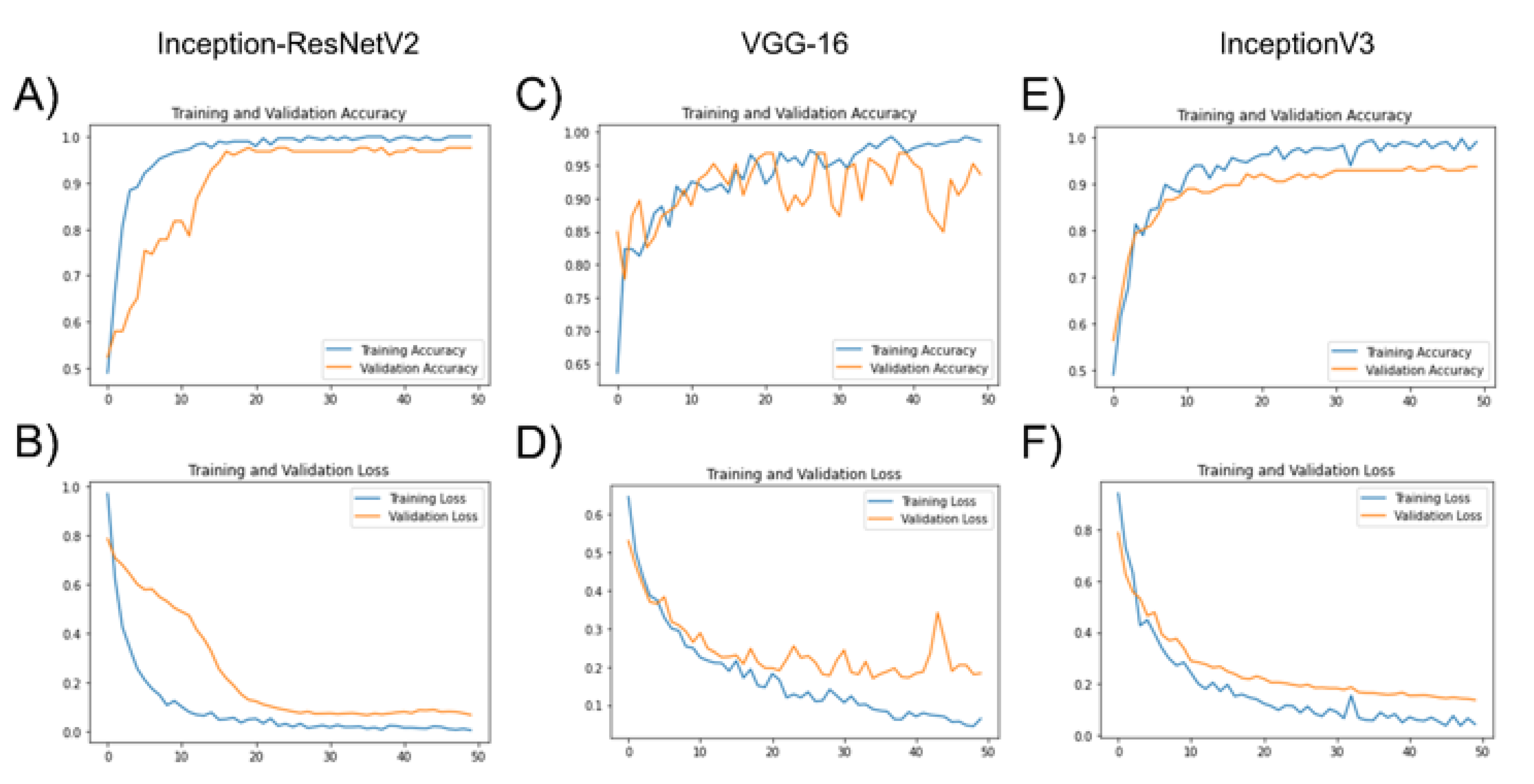
3.1. Deep Learning Model Training with Transfer Learning
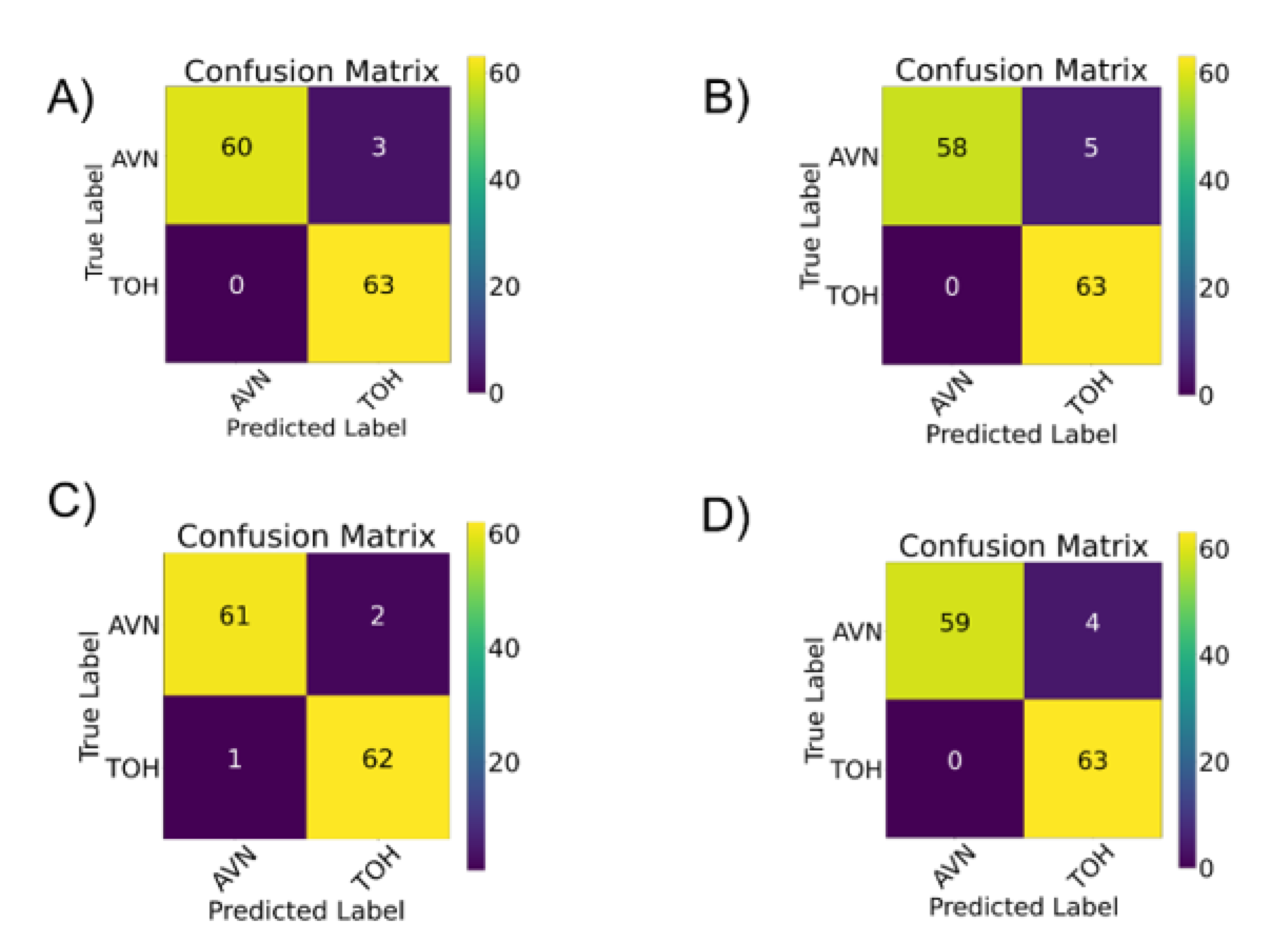
3.2. Comparison of Deep Learning to Expert Readers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karantanas, A.H.; Drakonaki, E.E. The role of MR imaging in avascular necrosis of the femoral head. Semin. Musculoskelet. Radiol. 2011, 15, 281–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klontzas, M.E.; Vassalou, E.E.; Zibis, A.H.; Bintoudi, A.S.; Karantanas, A.H. MR imaging of transient osteoporosis of the hip: An update on 155 hip joints. Eur. J. Radiol. 2015, 84, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klontzas, M.E.; Zibis, A.H.; Vassalou, E.E.; Karantanas, A.H. MRI of the hip: Current concepts on bone marrow oedema. Hip. Int. 2017, 27, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, E.J. Osteonecrosis and transient osteoporosis of the hip: Diagnostic and treatment dilemmas. J. Can. Chir. 2003, 46, 168–169. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, T.; Kubo, T.; Hirasawa, Y.; Noguchi, Y.; Iwamoto, Y.; Sueishi, K. A clinicopathologic study of transient osteoporosis of the hip. Skelet. Radiol. 1999, 28, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geith, T.; Stellwag, A.C.; Müller, P.E.; Reiser, M.; Baur-Melnyk, A. Is bone marrow edema syndrome a precursor of hip or knee osteonecrosis? Results of 49 patients and review of the literature. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2020, 26, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klontzas, M.E.; Manikis, G.C.; Nikiforaki, K.; Vassalou, E.E.; Spanakis, K.; Stathis, I.; Kakkos, G.A.; Matthaiou, N.; Zibis, A.H.; Marias, K.; et al. Radiomics and Machine Learning Can Differentiate Transient Osteoporosis from Avascular Necrosis of the Hip. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Väänänen, M.; Tervonen, O.; Nevalainen, M.T. Magnetic resonance imaging of avascular necrosis of the femoral head: Predictive findings of total hip arthroplasty. Acta Radiol. Open 2021, 10, 20584601211008379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koçak, B.; Durmaz, E.Ş.; Ateş, E.; Kılıçkesmez, Ö. Radiomics with artificial intelligence: A practical guide for beginners. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2019, 25, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neri, E.; de Souza, N.; Brady, A. What the radiologist should know about artificial intelligence—An ESR white paper. Insights Imaging 2019, 10, 44. [Google Scholar]
- Van Griethuysen, J.J.; Fedorov, A.; Parmar, C.; Hosny, A.; Aucoin, N.; Narayan, V.; Beets-Tan, R.G.; Fillion-Robin, J.C.; Pieper, S.; Aerts, H.J. Computational radiomics system to decode the radiographic phenotype. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, e104–e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Papanikolaou, N.; Matos, C.; Koh, D.M. How to develop a meaningful radiomic signature for clinical use in oncologic patients. Cancer Imaging 2020, 20, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillies, R.J.; Kinahan, P.E.; Hricak, H. Radiomics: Images are more than pictures, they are data. Radiology 2016, 278, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karantanas, A.H. Accuracy and limitations of diagnostic methods for avascular necrosis of the hip. Expert Opin. Med. Diagn. 2013, 7, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malizos, K.N.; Karantanas, A.H.; Varitimidis, S.E.; Dailiana, Z.H.; Bargiotas, K.; Maris, T. Osteonecrosis of the femoral head: Etiology, imaging and treatment. Eur. J. Radiol. 2007, 63, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zibis, A.H.; Karantanas, A.H.; Roidis, N.T.; Hantes, M.E.; Argiri, P.; Moraitis, T.; Malizos, K.N. The role of MR imaging in staging femoral head osteonecrosis. Eur. J. Radiol. 2007, 63, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongan, J.; Moy, L.; Kahn, C.E. Checklist for Artificial Intelligence and Medical Imaging (CLAIM): A guide for authors and reviewers. Radiol. Artif. Intell. 2020, 2, e200029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, S.H.; Han, K. Methodologic guide for evaluating clinical performance and effect of artificial intelligence technology for medical diagnosis and prediction. Radiology 2018, 286, 800–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varoquaux, G.; Cheplygina, V. Machine learning for medical imaging: Methodological failures and recommendations for the future. NPJ Digit. Med. 2022, 5, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klontzas, M.E.; Vassalou, E.E.; Kakkos, G.A.; Spanakis, K.; Zibis, A.; Marias, K.; Karantanas, A.H. Differentiation between subchondral insufficiency fractures and advanced osteoarthritis of the knee using transfer learning and an ensemble of convolutional neural networks. Injury 2022, 53, 2035–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsiknakis, N.; Savvidaki, E.; Manikis, G.C.; Gotsiou, P.; Remoundou, I.; Marias, K.; Alissandrakis, E.; Vidakis, N. Pollen Grain classification based on Ensemble Transfer Learning on the Cretan Pollen Dataset. Plants 2022, 11, 919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.E.; Cosa-Linan, A.; Santhanam, N.; Jannesari, M.; Maros, M.E.; Ganslandt, T. Transfer learning for medical image classification: A literature review. BMC Med. Imaging 2022, 22, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candemir, S.; Nguyen, X.V.; Folio, L.R.; Prevedello, L.M. Training strategies for radiology deep learning models in data-limited scenarios. Radiol. Artif. Intell. 2021, 3, e210014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeLong, E.R.; DeLong, D.M.; Clarke-Pearson, D.L. Comparing the areas under two or more correlated receiver operating characteristic curves: A nonparametric approach. Biometrics 1988, 44, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragab, Y.; Emad, Y.; Abou-Zeid, A. Bone marrow edema syndromes of the hip: MRI features in different hip disorders. Clin. Rheumatol. 2008, 27, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malizos, K.N.; Zibis, A.H.; Dailiana, Z.; Hantes, M.; Karahalios, T.; Karantanas, A.H. MR imaging findings in transient osteoporosis of the hip. Eur. J. Radiol. 2004, 50, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karantanas, A.H.; Nikolakopoulos, I.; Korompilias, A.V.; Apostolaki, E.; Skoulikaris, N.; Eracleous, E. Regional migratory osteoporosis in the knee: MRI findings in 22 patients and review of the literature. Eur. J. Radiol. 2008, 67, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geith, T.; Niethammer, T.; Milz, S.; Dietrich, O.; Reiser, M.; Baur-Melnyk, A. Transient bone marrow edema syndrome versus osteonecrosis: Perfusion patterns at dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging with high temporal resolution can allow differentiation. Radiology 2017, 283, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Timmeren, J.E.; Cester, D.; Tanadini-Lang, S.; Alkadhi, H.; Baessler, B. Radiomics in medical imaging—“how-to” guide and critical reflection. Insights Imaging 2020, 11, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasci, E.; Uluturk, C.; Ugur, A. A voting-based ensemble deep learning method focusing on image augmentation and preprocessing variations for tuberculosis detection. Neural. Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 15541–15555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier, R.; Kraus, T.M.; Schaeffeler, C.; Torka, S.; Schlitter, A.M.; Specht, K.; Haller, B.; Waldt, S.; Rechl, H.; Rummeny, E.J.; et al. Bone marrow oedema on MR imaging indicates ARCO stage 3 disease in patients with AVN of the femoral head. Eur. Radiol. 2014, 24, 2271–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lekadir, K.; Osuala, R.; Gallin, C.; Lazrak, N.; Kushibar, K.; Tsakou, G.; Aussó, S.; Alberich, L.C.; Marias, K.; Tsiknakis, M.; et al. FUTURE-AI: Guiding principles and consensus recommendations for trustworthy artificial intelligence in medical imaging. arXiv 2021, arXiv:210909658v3. [Google Scholar]
- Bento, M.; Fantini, I.; Park, J.; Rittner, L.; Frayne, R. Deep learning in large and multi-site structural brain MR Imaging datasets. Front. Neuroinform. 2022, 15, 805669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| AUC | Group | Precision | Recall | f1-Score | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model ensemble | 97.62% | ||||
| AVN | 1 | 0.95 | 0.98 | ||
| TOH | 0.95 | 1 | 0.98 | ||
| VGG-16 | 96.03% | ||||
| AVN | 1 | 0.92 | 0.96 | ||
| TOH | 0.93 | 1 | 0.96 | ||
| InceptionV3 | 96.82% | ||||
| AVN | 1 | 0.94 | 0.97 | ||
| TOH | 0.94 | 1 | 0.97 | ||
| Inception-ResNet-V2 | 97.62% | ||||
| AVN | 0.98 | 0.97 | 0.98 | ||
| TOH | 0.97 | 0.98 | 0.98 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Klontzas, M.E.; Stathis, I.; Spanakis, K.; Zibis, A.H.; Marias, K.; Karantanas, A.H. Deep Learning for the Differential Diagnosis between Transient Osteoporosis and Avascular Necrosis of the Hip. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1870. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12081870
Klontzas ME, Stathis I, Spanakis K, Zibis AH, Marias K, Karantanas AH. Deep Learning for the Differential Diagnosis between Transient Osteoporosis and Avascular Necrosis of the Hip. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(8):1870. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12081870
Chicago/Turabian StyleKlontzas, Michail E., Ioannis Stathis, Konstantinos Spanakis, Aristeidis H. Zibis, Kostas Marias, and Apostolos H. Karantanas. 2022. "Deep Learning for the Differential Diagnosis between Transient Osteoporosis and Avascular Necrosis of the Hip" Diagnostics 12, no. 8: 1870. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12081870
APA StyleKlontzas, M. E., Stathis, I., Spanakis, K., Zibis, A. H., Marias, K., & Karantanas, A. H. (2022). Deep Learning for the Differential Diagnosis between Transient Osteoporosis and Avascular Necrosis of the Hip. Diagnostics, 12(8), 1870. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12081870









