Platelet, Fibrinolytic and Other Coagulation Abnormalities in Newly-Diagnosed Patients with Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Sample Collection Method
2.3. Coagulation Assays
2.3.1. PFA-100
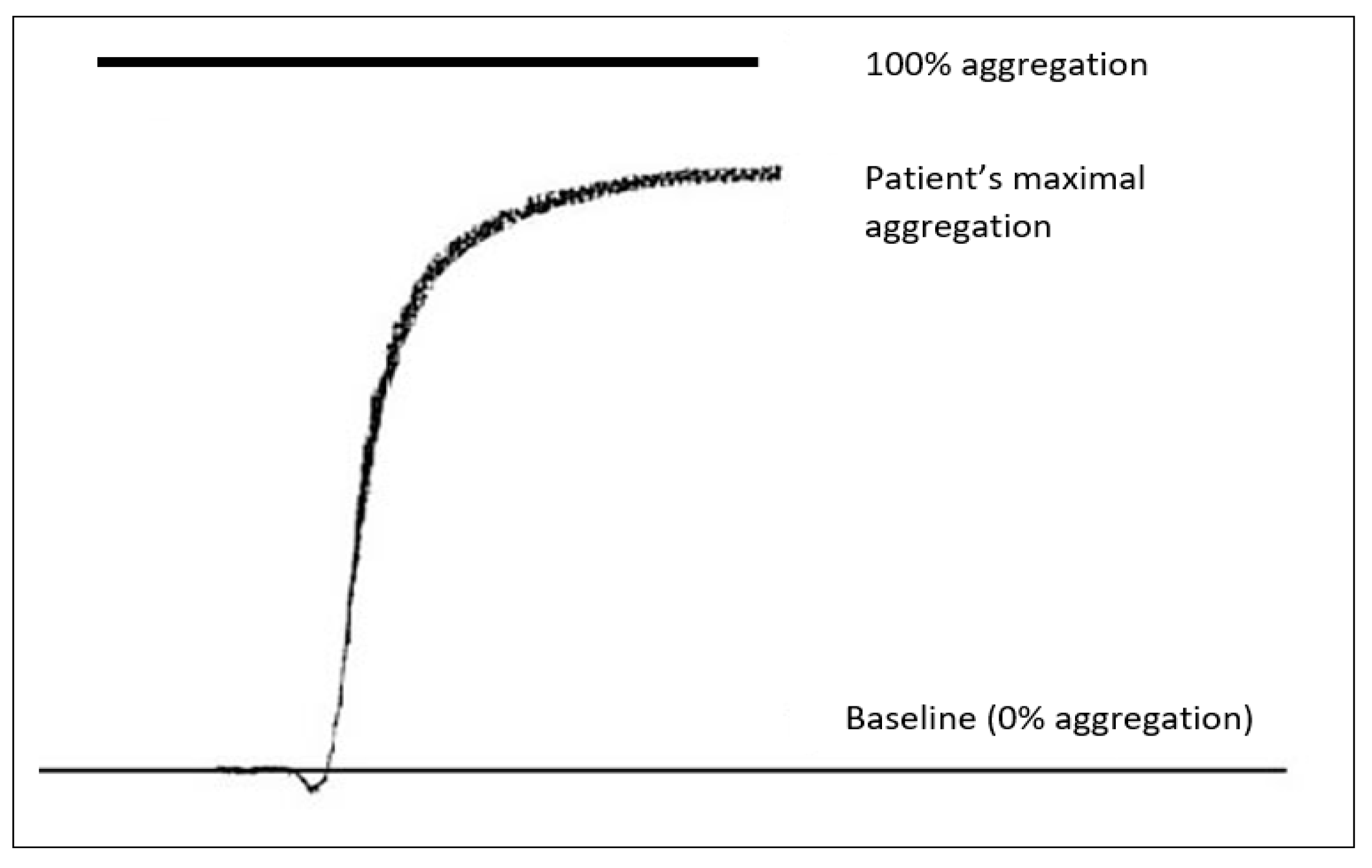
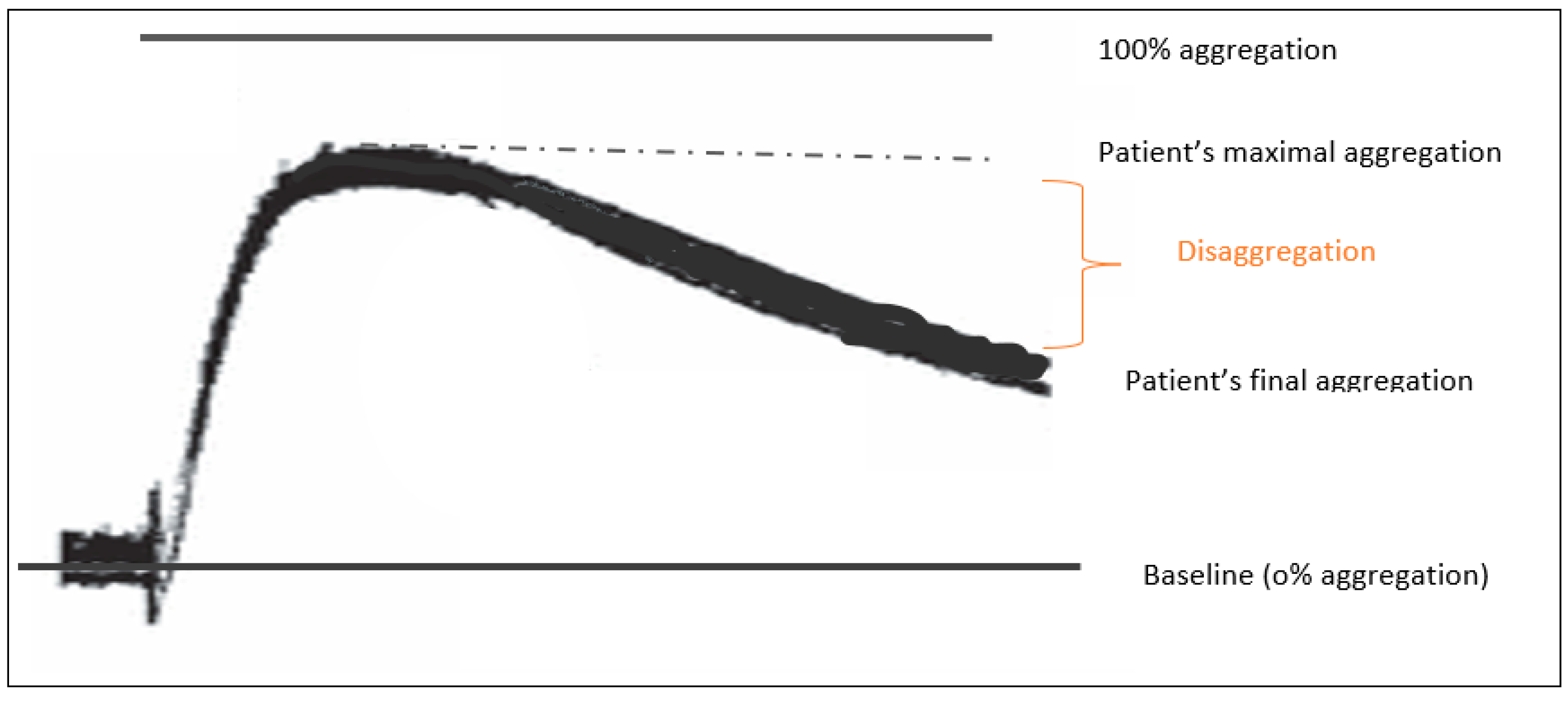
2.3.2. LTA
2.3.3. Rotem
2.3.4. ETP
- The time needed until the start of thrombin generation (lag time/tlag),
- The total amount of thrombin generated (area under the curve/AUC),
- The maximum thrombin concentration (Cmax), and
- The time needed to reach maximum thrombin generation (tmax).
2.3.5. Markers of Platelet Activation and Endothelial Dysfunction
2.3.6. Conventional Coagulation Tests
2.3.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| aPTT | activated partial thromboplastin time |
| AST | aspartate aminotransferase |
| ALT | alanine transaminase |
| CI | cardiac index |
| Hb | hemoglobin |
| INR | international normalized ratio |
| mPAP | mean pulmonary arterial pressure |
| NT-proBNP | N-terminal pro brain natriuretic peptide |
| PVR | pulmonary vascular resistance |
| PLT | platelets |
| WBC | white blood cell |
| 6MWT | 6 min walk test |
References
- Galiè, N.; Humbert, M.; Vachiery, J.L.; Gibbs, S.; Lang, I.; Torbicki, A.; Simonneau, G.; Peacock, A.; VonkNoordegraaf, A.; Beghetti, M.; et al. 2015 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: The Joint Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS): Endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC), International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT). Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 67–119. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mahmud, E.; Madani, M.M.; Kim, N.H.; Poch, D.; Ang, L.; Behnamfar, O.; Patel, M.P.; Auger, W.R. Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension: Evolving Therapeutic Approaches for Operable and Inoperable Disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 2468–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Luo, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Jin, Q.; Yu, X.; Zhang, Y. Research progress on the pathogenesis of CTEPH. Heart Fail. Rev. 2019, 24, 1031–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gall, H.; Hoeper, M.M.; Richter, M.; Cacheris, W.; Hinzmann, B.; Mayer, M. An epidemiological analysis of the burden of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension in the USA, Europe and Japan. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2017, 26, 160121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepke-Zaba, J.; Delcroix, M.; Lang, I.; Mayer, E.; Jansa, P.; Ambroz, D.; Treacy, C.; D’Armini, A.M.; Morsolini, M.; Snijder, R.; et al. Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH): Results from an international prospective registry. Circulation 2011, 124, 1973–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.H.; Delcroix, M.; Jenkins, D.P.; Channick, R.; Dartevelle, P.; Jansa, P.; Lang, I.; Madani, M.M.; Ogino, H.; Pengo, V.; et al. Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. J. Am. Coll Cardiol. 2013, 62, D92–D99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klok, F.A.; Couturaud, F.; Delcroix, M.; Humbert, M. Diagnosis of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension after acute pulmonary embolism. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 2000189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruaro, B.; Baratella, E.; Caforio, G.; Confalonieri, P.; Wade, B.; Marrocchio, C.; Geri, P.; Pozzan, R.; Andrisano, A.G.; Cova, M.A.; et al. Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension: An Update. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, T.A.; Marsh, J.J.; Chiles, P.G.; Auger, W.R.; Fedullo, P.F.; Woods, V.L. Fibrin Derived from Patients with Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension Is Resistant to Lysis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 173, 1270–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonneau, G.; Dorfmüller, P.; Guignabert, C.; Mercier, O.; Humbert, M. Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: The magic of pathophysiology. Ann. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2022, 11, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabini, D.; Heinemann, A.; Foris, V.; Nagaraj, C.; Nierlich, P.; Bálint, Z.; Kwapiszewska, G.; Lang, I.M.; Klepetko, W.; Olschewski, H.; et al. Comprehensive analysis of inflammatory markers in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension patients. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 44, 951–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vrigkou, E.; Tsangaris, I.; Bonovas, S.; Kopterides, P.; Kyriakou, E.; Konstantonis, D.; Pappas, A.; Anthi, A.; Gialeraki, A.; Orfanos, S.E.; et al. Platelet and coagulation disorders in newly diagnosed patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Platelets 2019, 30, 646–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favaloro, E.J.; Bonar, R. An update on quality control for the PFA-100/PFA-200. Platelets 2018, 29, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Blanc, J.; Mullier, F.; Vayne, C.; Lordkipanidzé, M. Advances in Platelet Function Testing-Light Transmission Aggregometry and Beyond. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadowski, P.P.; Eichelberger, B.; Kopp, C.W.; Pultar, J.; Seidinger, D.; Koppensteiner, R.; Lang, I.M.; Panzer, S.; Gremmel, T. Disaggregation Following Agonist-Induced Platelet Activation in Patients on Dual Antiplatelet Therapy. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2017, 10, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Whiting, D.; DiNardo, J.A. TEG and ROTEM: Technology and clinical applications. Am. J. Hematol. 2014, 89, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Görlinger, K.; Pérez-Ferrer, A.; Dirkmann, D.; Saner, F.; Maegele, M.; Calatayud, Á.; Kim, T.Y. The role of evidence-based algorithms for rotational thromboelastometry-guided bleeding management. Korean J. Anesthesiol. 2019, 72, 297–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöchl, H.; Maegele, M.; Solomon, C.; Görlinger, K.; Voelckel, W. Early and individualized goal-directed therapy for trauma-induced coagulopathy. Scand. J. Trauma Resusc. Emerg. Med. 2012, 20, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkens, M. Anwendungen des endogenen Thrombinpotenzials [Endogenous thrombin potential in practical use]. Hamostaseologie 2011, 31, 88–93. [Google Scholar]
- Pettersen, A.Å.; Arnesen, H.; Opstad, T.B.; Bratseth, V.; Seljeflot, I. Markers of endothelial and platelet activation are associated with high on-aspirin platelet reactivity in patients with stable coronary artery disease. Thromb. Res. 2012, 130, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, M.W.; Han, S.T.; Gunderson, K.A.; Busse, W.W.; Jarjour, N.N.; Mosher, D.F. Platelet activation, P-selectin, and eosinophil β1-integrin activation in asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 185, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neculaes, B.; Frelinger, A.L.; Gerrits, A.J.; Gremmel, T.; Forde, E.E.; Klopman, S.; Carmichael, S.L.; Michelson, A.D. Activation of platelet-rich plasma by pulse electric fields: Voltage, pulse width and calcium concentration can be used to control and tune the release of growth factors, serotonin and hemoglobin. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0249209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horvath, B.; Hegedus, D.; Szapary, L.; Marton, Z.; Alexy, T.; Koltai, K.; Czopf, L.; Wittmann, I.; Juricskay, I.; Toth, K.; et al. Measurement of von Willebrand factor as the marker of endothelial dysfunction in vascular diseases. Exp. Clin. Cardiol. 2004, 9, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Remková, A.; Šimková, I.; Valkovičová, T. Platelet abnormalities in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 9700. [Google Scholar]
- Nicoleau, S.; Wojciak-Stothard, B. Beyond Thrombosis: The Role of Platelets in Pulmonary Hypertension. Sci. Med. J. 2020, 2, 242–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaoita, N.; Shirakawa, R.; Fukumoto, Y.; Sugimura, K.; Miyata, S.; Miura, Y.; Nochioka, K.; Miura, M.; Tatebe, S.; Aoki, T.; et al. Platelets Are Highly Activated in Patients of Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 2486–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslan, J.E.; Tormoen, G.W.; Loren, C.P.; Pang, J.; McCarty, O.J. S6K1 and mTOR regulate Rac1-driven platelet activation and aggregation. Blood 2011, 118, 3129–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rucker, D.; Dhamoon, A.S. Physiology, Thromboxane A2. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539817/ (accessed on 10 March 2022).
- Ulrich, S.; Huber, L.C.; Fischler, M.; Treder, U.; Maggiorini, M.; Eberli, F.R.; Speich, R. Platelet Serotonin Content and Transpulmonary Platelet Serotonin Gradient in Patients with Pulmonary Hypertension. Respiration 2011, 81, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolberg, A.S.; Campbell, R.A. Thrombin generation, fibrin clot formation and hemostasis. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2008, 38, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonneau, G.; Torbicki, A.; Dorfmüller, P.; Kim, N. The pathophysiology of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2017, 26, 160112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennigs, J.K.; Baumann, H.J.; Lüneburg, N.; Quast, G.; Harbaum, L.; Heyckendorf, J.; Sydow, K.; Schulte-Hubbert, B.; Halank, M.; Klose, H. Fibrinogen plasma concentration is an independent marker of haemodynamic impairment in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arunthari, V.; Burger, C.D. Utility of d-dimer in the diagnosis of patients with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Open Respir. Med. J. 2009, 3, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zanjani, K.S. Platelets in pulmonary hypertension: A causative role or a simple association? Iran. J. Pediatr. 2012, 22, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
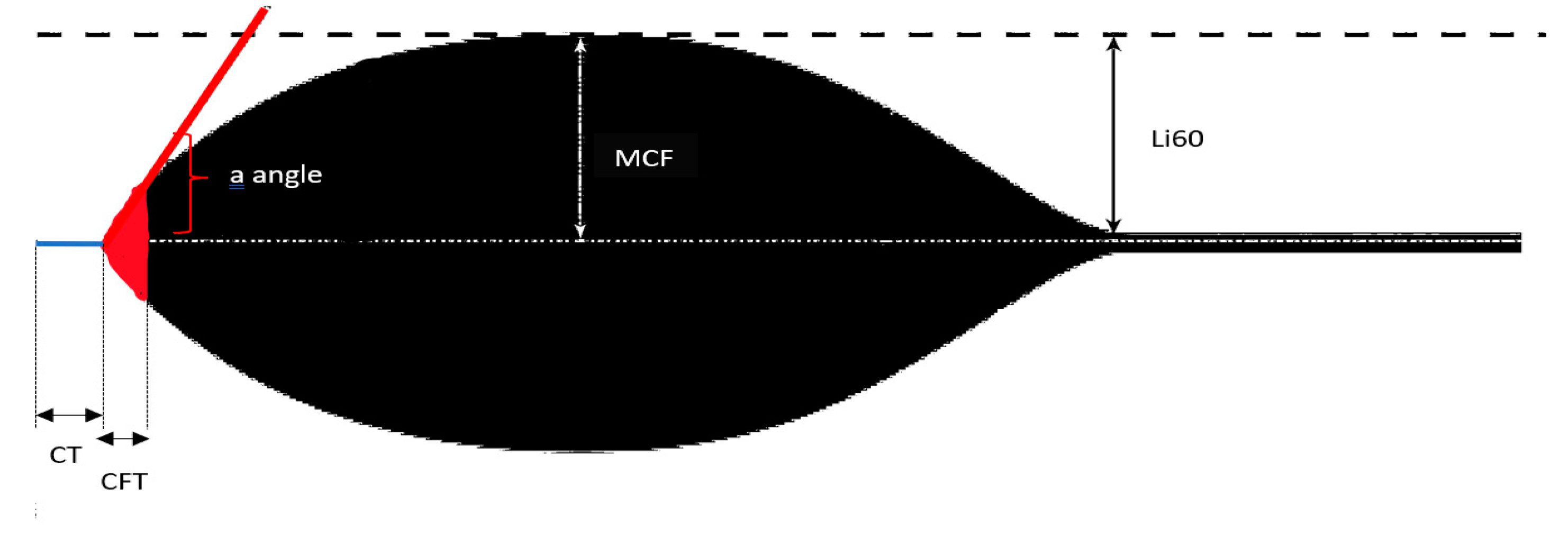
| Rotem Parameters | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| Clotting time (CT) | Time needed for clotting to start; it assesses thrombin formation and the initition of clot polymerization |
| Clot formation time (CFT) | Time needed to reach a specific clot strength (20 mm); It assesses fibrin polymerization and clot stability by platelets and factor XIII |
| a angle | Estimates the speed of thrombus formation (clotting kinetics) |
| Maximum clot firmness (MCF) | Represents the ultimate strength of the thrombus; It assesses final clot stability by the polymerized fibrin, platelets and factor XIII |
| Lysis index at 60 min (Li60) | Represents the stability of the thrombus (compared to MCF) 60 min after CT; It assesses the rate of fibrinolysis |
| Healthy Controls (n = 35) | CTEPH Patients (n = 40) | |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 59.9 ± 11.9 | 60.1 ± 15.9 |
| Female (%) | 21/35 (60%) | 26/40 (65%) |
| Caucasian Race (%) | 35/35 (100%) | 40/40 (100%) |
| PLTs (103/μL) | 250 ± 46 | 268 ± 54 |
| WBC (/μL) | 6750 ± 1010 | 6268 ± 1640 |
| Hb (g/dL) | 14.3 ± 1.4 | 13.2 ± 2.0 |
| INR | 1 ± 0.08 | 1.1 ± 0.2 |
| aPTT (sec) | 30.4 ± 3.5 | 32 ± 3.9 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 1 ± 0.2 |
| AST (U/L) | 21.2 ± 13.4 | 17 ± 6.7 |
| ALT (U/L) | 20.7 ± 11.5 | 18 ± 8.0 |
| mPAP (mm Hg) | - | 40.7 ± 16.5 |
| PVR (Wood units) | - | 9.4 ± 4.7 |
| CI (L/min/m2) | - | 2.2 ± 0.5 |
| NT-proBNP (pg/mL) | - | 1148 ± 1734 |
| 6MWT (m) | - | 378 ± 102 |
| Healthy Controls | CTEPH Patients | Significance | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CEPI CT (sec) | 131.6 ± 17.9 | 142.6 ± 58.7 | p = 0.43 |
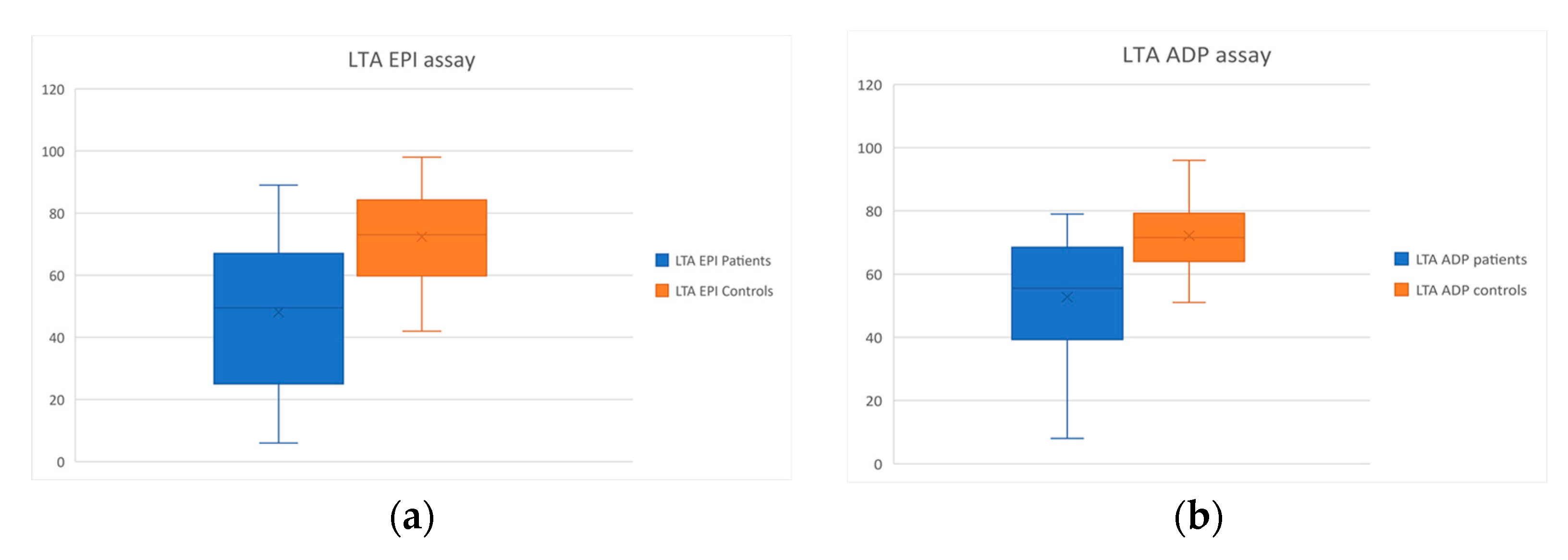
| LTA Epi (%) | 72.4 ± 15.1 | 48.1 ± 22.6 | p < 0.001 |
| LTA ADP (%) | 72.1 ± 10 | 52.7 ± 18.3 | p < 0.001 |
| Patients (%) with disaggregation | 0/35 (0%) | 24/40 (60%) | p < 0.001 |
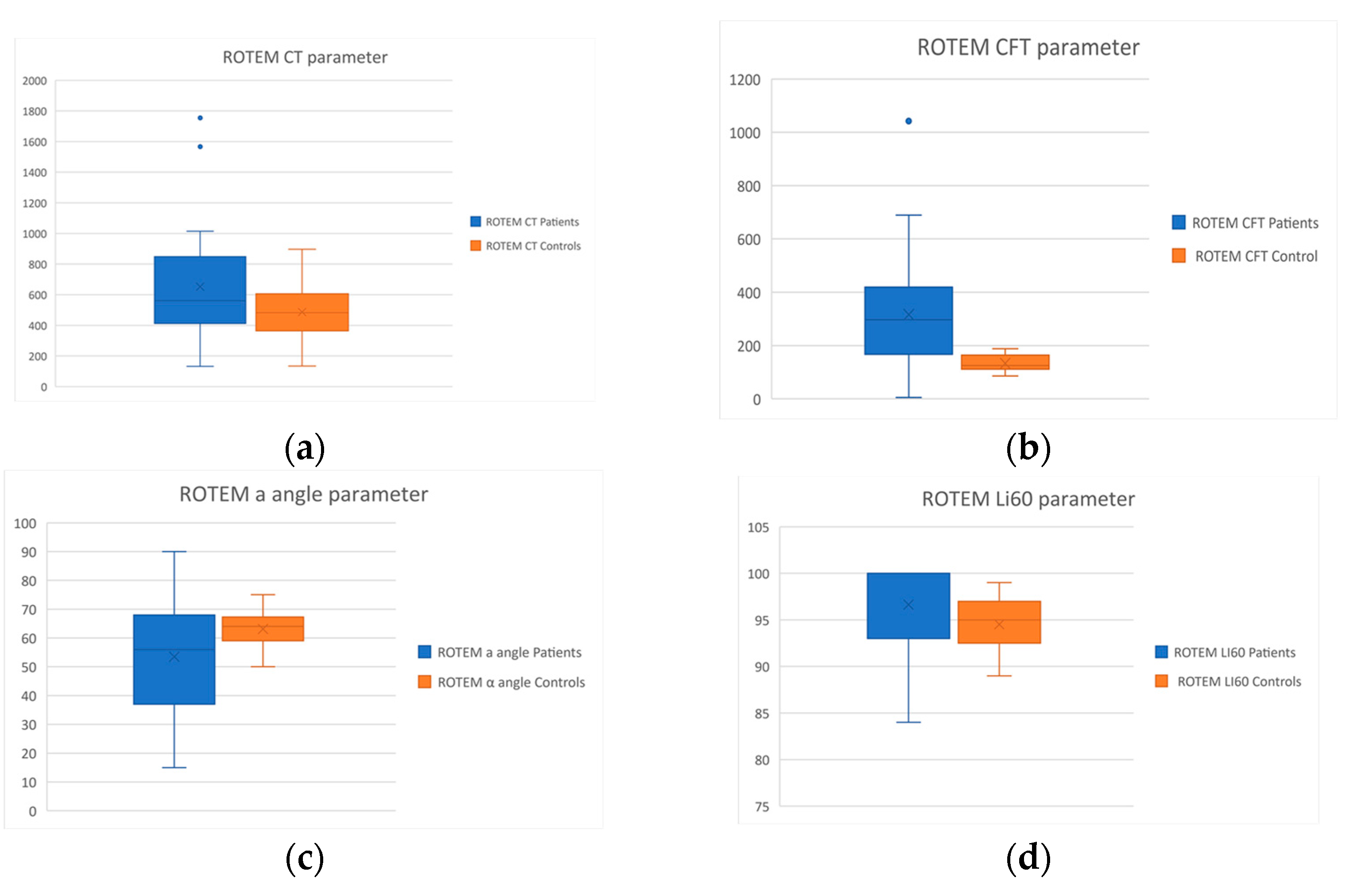
| CT (sec) | 486.7 ± 168.9 | 651.9 ± 366.9 | p = 0.02 |
| CFT (sec) | 133.5 ± 29.8 | 316.4 ± 203.1 | p < 0.001 |
| a (o) | 63.1 ± 6.3 | 53.5 ± 20.1 | p = 0.01 |
| MCF (mm) | 58.1 ± 5.7 | 56.4 ± 16.6 | p = 0.57 |
| Li60 (%) | 94.5 ± 2.7 | 96.6 ± 5.1 | p = 0.04 |
| Lag time (sec) | 30 ± 5.2 | 30.1 ± 5.4 | p = 0.97 |
| Tmax (sec) | 83.7 ± 16 | 82 ± 18.7 | p = 0.90 |
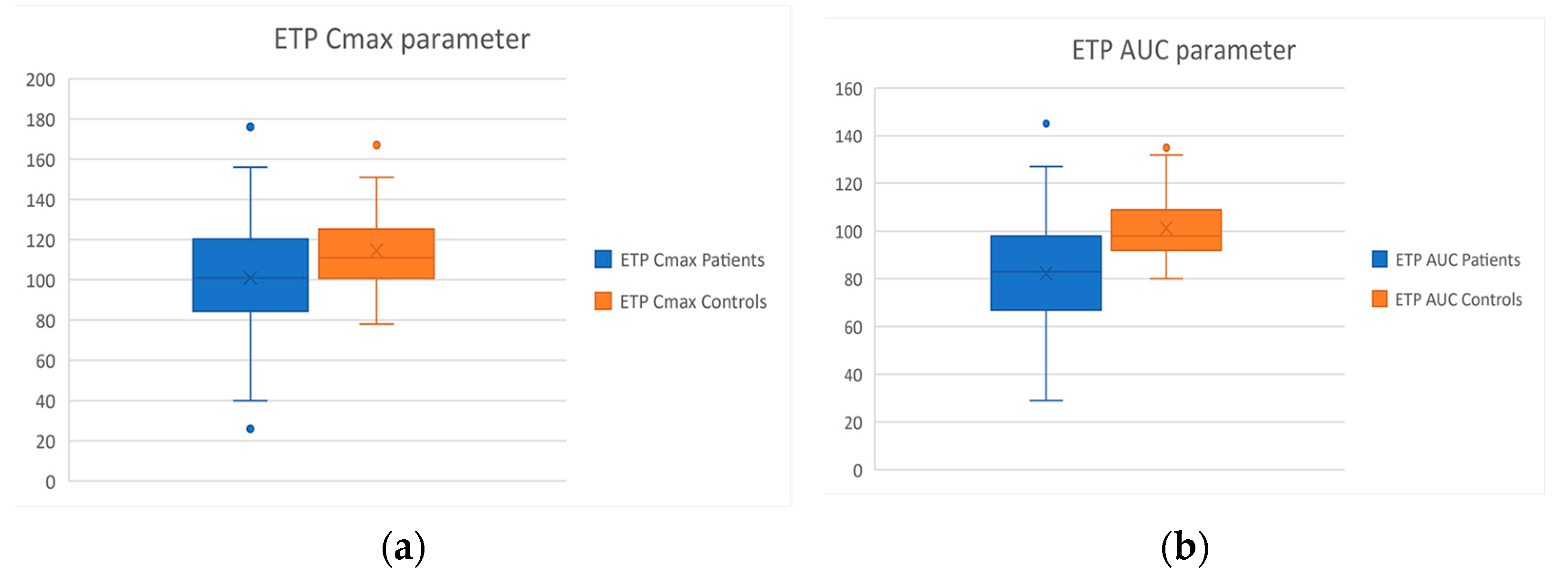
| Cmax (%) | 114.7 ± 20.3 | 101 ± 29.7 | p = 0.03 |
| AUC (%) | 114.6 ± 20.3 | 82.3 ± 26.7 | p < 0.001 |
| Healthy Controls | CTEPH Patients | Significance | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Serotonin (ng/mL) | 242.9 ± 96.9 | 267.9 ± 174.7 | p = 0.47 |
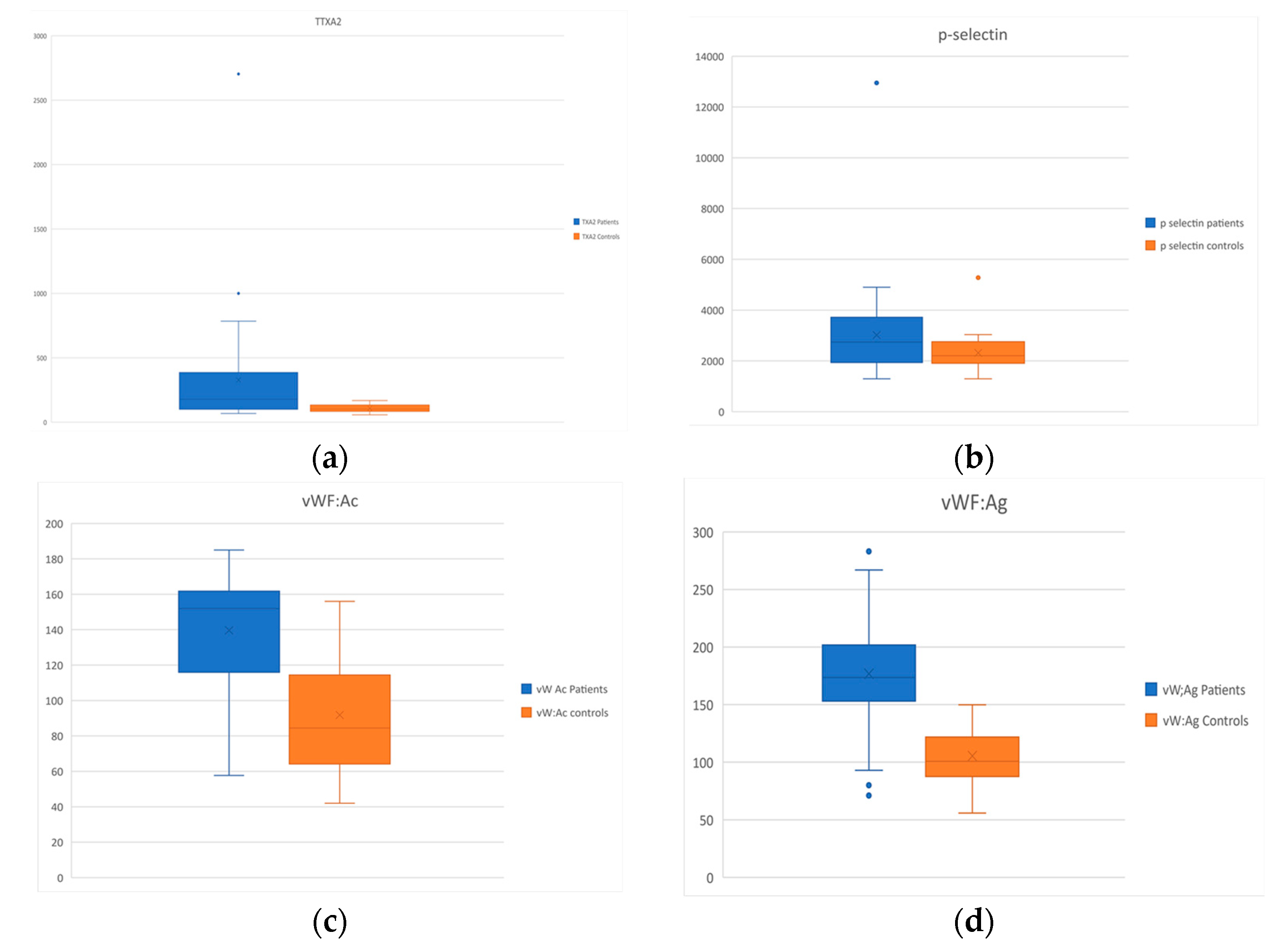
| Thromboxane A2 (pg/mL) | 108.1 ± 31.9 | 327.8 ± 449.6 | p = 0.006 |
| Soluble p-selectin (pg/mL) | 2314.6 ± 686 | 3019.9 ± 1888.6 | p = 0.04 |
| vW:Ac (%) | 91.8 ± 33.7 | 139.6 ± 32 | p < 0.001 |
| vW Ag (%) | 105.4 ± 25 | 176.7 ± 51.8 | p < 0.001 |
| D-dimers (ng/mL) | 318 ± 173 | 535.2 ± 552.9 | p = 0.1 |
| Fibrinogen (mg/dL) | 284.6 ± 91.6 | 353.6 ± 165.5 | p = 0.04 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vrigkou, E.; Tsantes, A.; Konstantonis, D.; Rapti, E.; Maratou, E.; Pappas, A.; Halvatsiotis, P.; Tsangaris, I. Platelet, Fibrinolytic and Other Coagulation Abnormalities in Newly-Diagnosed Patients with Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1238. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12051238
Vrigkou E, Tsantes A, Konstantonis D, Rapti E, Maratou E, Pappas A, Halvatsiotis P, Tsangaris I. Platelet, Fibrinolytic and Other Coagulation Abnormalities in Newly-Diagnosed Patients with Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(5):1238. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12051238
Chicago/Turabian StyleVrigkou, Eleni, Argirios Tsantes, Dimitrios Konstantonis, Evdoxia Rapti, Eirini Maratou, Athanasios Pappas, Panagiotis Halvatsiotis, and Iraklis Tsangaris. 2022. "Platelet, Fibrinolytic and Other Coagulation Abnormalities in Newly-Diagnosed Patients with Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension" Diagnostics 12, no. 5: 1238. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12051238
APA StyleVrigkou, E., Tsantes, A., Konstantonis, D., Rapti, E., Maratou, E., Pappas, A., Halvatsiotis, P., & Tsangaris, I. (2022). Platelet, Fibrinolytic and Other Coagulation Abnormalities in Newly-Diagnosed Patients with Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension. Diagnostics, 12(5), 1238. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12051238








