Segmental Distribution of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Cirrhotic Livers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
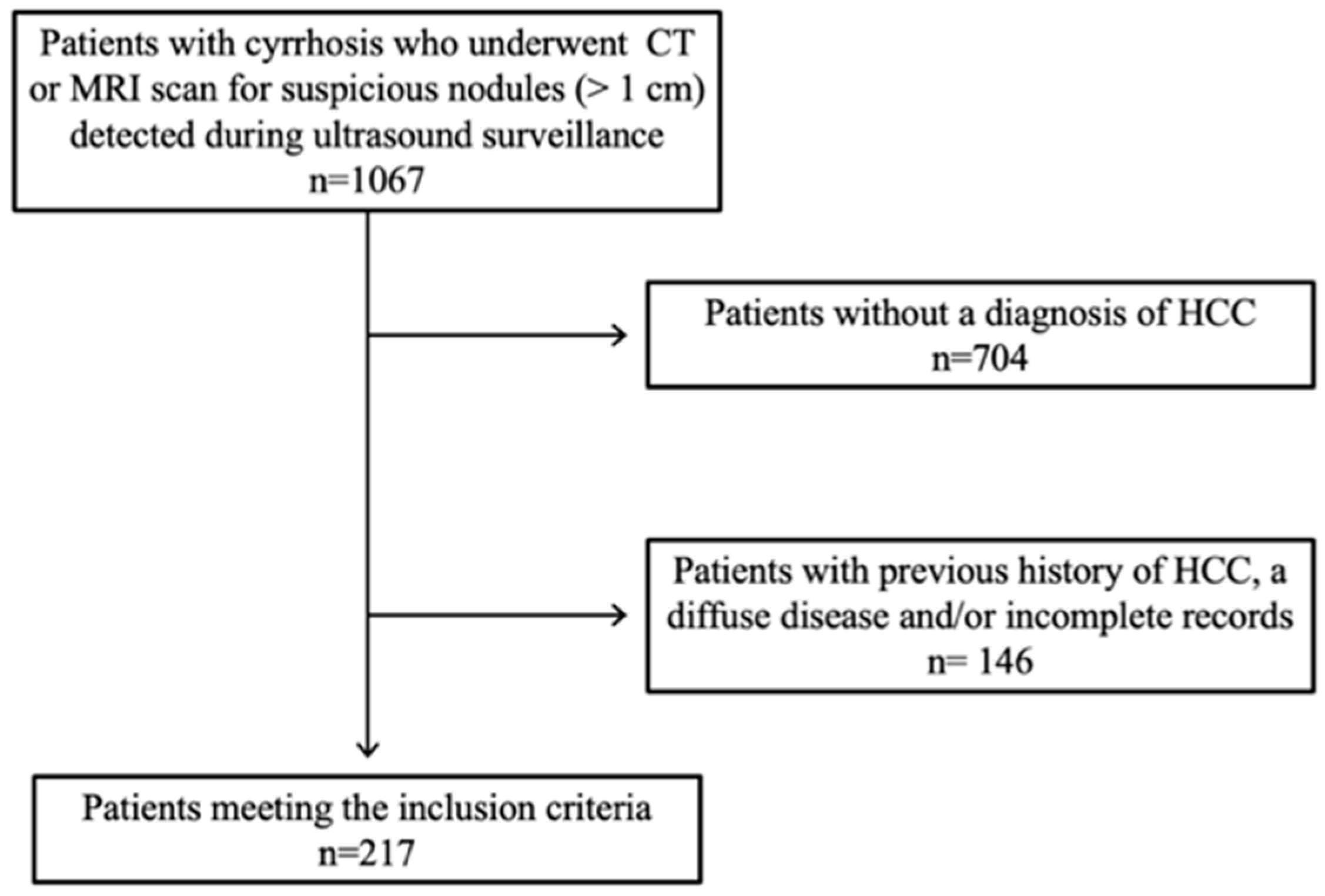
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Characteristics and Imaging Technique
2.2. Image Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
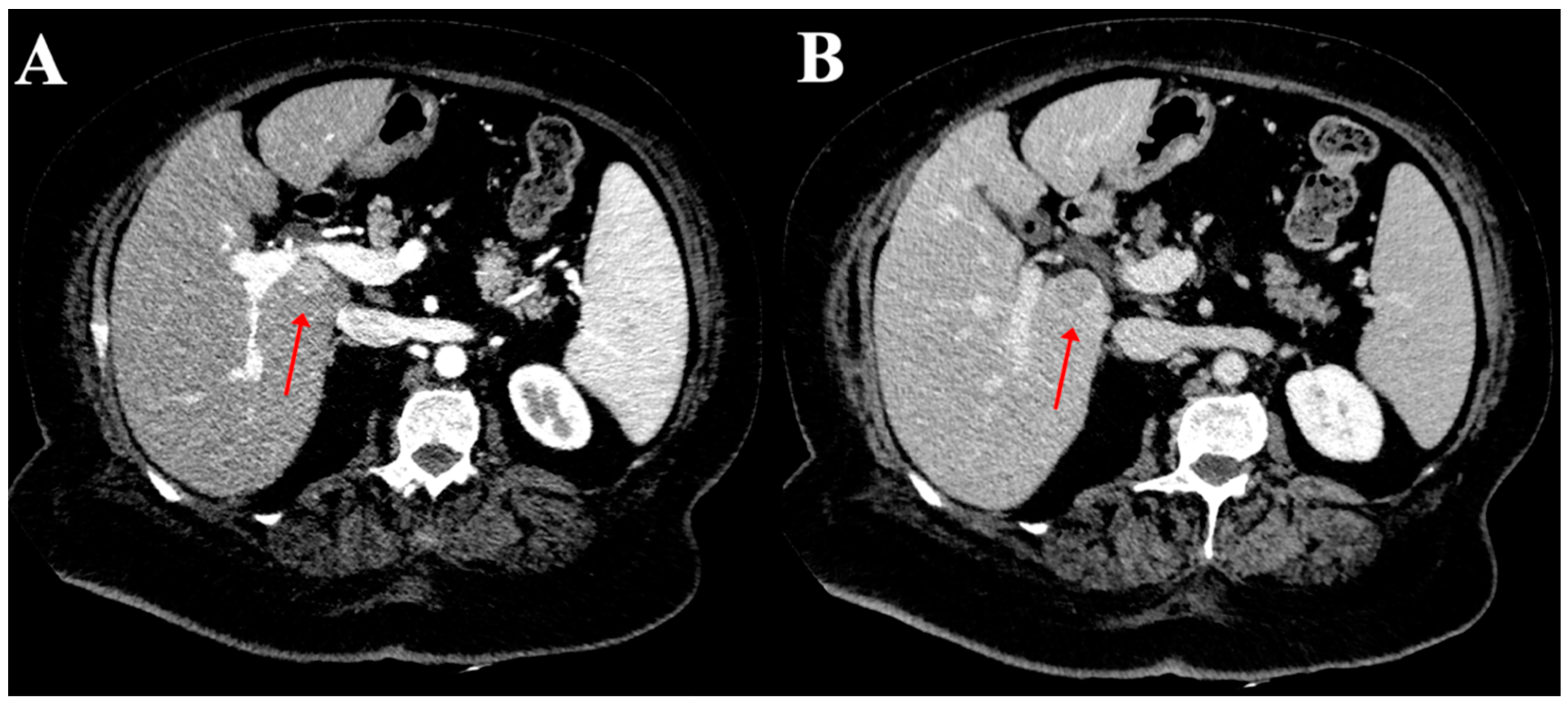
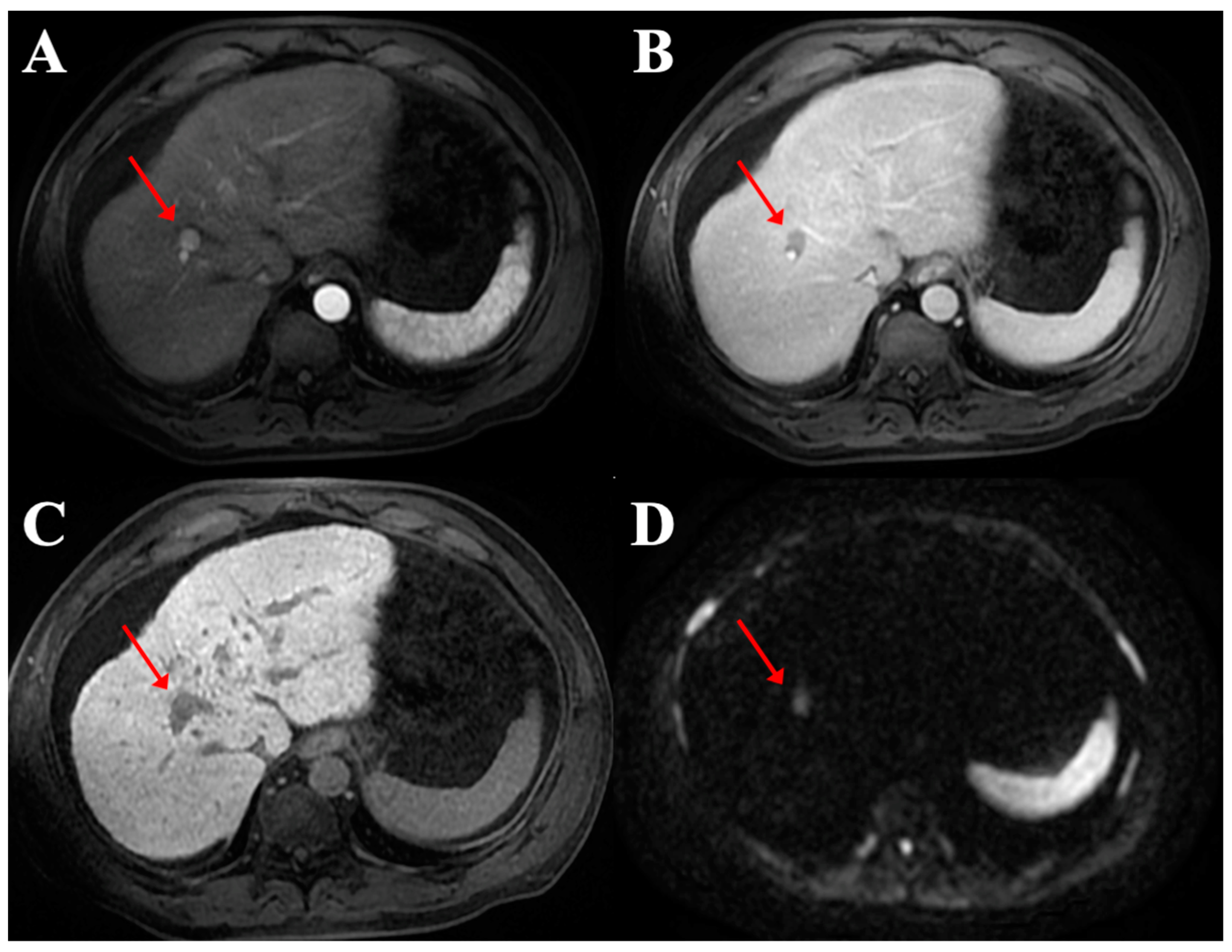
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Cucchetti, A.; Trevisani, F.; Cescon, M.; Ercolani, G.; Farinati, F.; Poggio, P.D.; Rapaccini, G.; Nolfo, M.; Benvegnù, L.; Zoli, M.; et al. Italian Liver Cancer (ITA.LI.CA) Group. Cost-effectiveness of semi-annual surveillance for hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhotic patients of the Italian Liver Cancer population. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 1089–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renzulli, M.; Golfieri, R.; Bologna Liver Oncology Group (BLOG). Proposal of a new diagnostic algorithm for hepatocellular carcinoma based on the Japanese guidelines but adapted to the Western world for patients under surveillance for chronic liver disease. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 31, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Al-Azzawi, Y.; Rouanet, E.; Hendrix, R.J.; Spaho, L.; Malik, H.; Devuni, D.; Szabo, G.; Barnard, G. Segmental Distribution of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Correlates with Microvascular Invasion in Liver Explants Undergoing Transplantation. J. Cancer Epidemiol. 2019, 2019, 8534372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Facciorusso, A.; Licinio, R.; Muscatiello, N.; Di Leo, A.; Barone, M. Transarterial chemoembolization: Evidences from the literature and applications in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. World J. Hepatol. 2015, 7, 2009–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tovoli, F.; Renzulli, M.; Negrini, G.; Brocchi, S.; Ferrarini, A.; Andreone, A.; Benevento, F.; Golfieri, R.; Morselli-Labate, A.M.; Mastroroberto, M.; et al. Inter-operator variability and source of errors in tumour response assessment for hepatocellular carcinoma treated with sorafenib. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 3611–3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tovoli, F.; Ielasi, L.; Casadei-Gardini, A.; Granito, A.; Foschi, F.G.; Rovesti, G.; Negrini, G.; Orsi, G.; Renzulli, M.; Piscaglia, F. Management of adverse events with tailored sorafenib dosing prolongs survival of hepatocellular carcinoma patients. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 1175–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Terzi, E.; Terenzi, L.; Venerandi, L.; Croci, L.; Renzulli, M.; Mosconi, C.; Allegretti, G.; Granito, A.; Golfieri, R.; Bolondi, L.; et al. The ART score is not effective to select patients for transarterial chemoembolization retreatment in an Italian series. Dig. Dis. 2014, 32, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granito, A.; Facciorusso, A.; Sacco, R.; Bartalena, L.; Mosconi, C.; Cea, U.V.; Cappelli, A.; Antonino, M.; Modestino, F.; Brandi, N.; et al. TRANS-TACE: Prognostic Role of the Transient Hypertransaminasemia after Conventional Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Jang, H.Y.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, S.J.; Won, H.J.; Byun, J.H.; Choi, S.H.; Lee, S.S.; An, J.; Lim, Y.S. Non-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging as a surveillance tool for hepatocellular carcinoma: Comparison with ultrasound. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 718–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golfieri, R.; Garzillo, G.; Ascanio, S.; Renzulli, M. Focal lesions in the cirrhotic liver: Their pivotal role in gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI and recognition by the Western guidelines. Dig. Dis. 2014, 32, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compagnone, G.; Giampalma, E.; Domenichelli, S.; Renzulli, M.; Golfieri, R. Calculation of conversion factors for effective dose for various interventional radiology procedures. Med. Phys. 2012, 39, 2491–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Germain, T.; Favelier, S.; Cercueil, J.P.; Denys, A.; Krausé, D.; Guiu, B. Liver segmentation: Practical tips. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2014, 95, 1003–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mise, Y.; Satou, S.; Shindoh, J.; Conrad, C.; Aoki, T.; Hasegawa, K.; Sugawara, Y.; Kokudo, N. Three-dimensional volumetry in 107 normal livers reveals clinically relevant inter-segment variation in size. HPB 2014, 16, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baran, B.; Ozupek, N.M.; Tetik, N.Y.; Acar, E.; Bekcioglu, O.; Baskin, Y. Difference Between Left-Sided and Right-Sided Colorectal Cancer: A Focused Review of Literature. Gastroenterol. Res. 2018, 11, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Levi Sandri, G.B.; Ettorre, G.M.; Aldrighetti, L.; Cillo, U.; Dalla Valle, R.; Guglielmi, A.; Mazzaferro, V.; Ferrero, A.; Di Benedetto, F.; Gruttadauria, S.; et al. I Go MILS Group on HCC. Laparoscopic liver resection of hepatocellular carcinoma located in unfavorable segments: A propensity score-matched analysis from the I Go MILS (Italian Group of Minimally Invasive Liver Surgery) Registry. Surg. Endosc. 2019, 33, 1451–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, D.I.; Kang, T.W.; Song, K.D.; Lee, M.W.; Rhim, H.; Lim, H.K.; Sinn, D.H.; Kim, K. Radiofrequency ablation for subcardiac hepatocellular carcinoma: Therapeutic outcomes and risk factors for technical failure. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 2706–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledoux, G.; Amroun, K.; Rhaiem, R.; Cagniet, A.; Aghaei, A.; Bouche, O.; Hoeffel, C.; Sommacale, D.; Piardi, T.; Kianmanesh, R. Fully laparoscopic thermo-ablation of liver malignancies with or without liver resection: Tumor location is an independent local recurrence risk factor. Surg. Endosc. 2021, 35, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakuraoka, Y.; Kubota, K.; Tanaka, G.; Shimizu, T.; Tago, K.; Park, K.H.; Matsumoto, T.; Shiraki, T.; Mori, S.; Iso, Y.; et al. Is left-sided involvement of hepatocellular carcinoma an important preoperative predictive factor of poor outcome? World J. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 18, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, J.P.; Han, Z.Y.; Cheng, Z.G.; Liu, F.Y.; Yu, X.L.; Yu, J.; Liang, P. The effect of tumor location on long-term results of microwave ablation for early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma. Abdom. Radiol. 2020, 45, 3923–3933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, E.H.; Zahra, H.F.; Soumaya, B.M.; Maria, L.; Nada, L.; Hakima, A.; Samira, E.F.; Meriem, H.; Badreddine, A.; Youssef, H.; et al. Study of predictive factors of complete response after chemoembolization for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma in 162 patients. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2020, 6, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livingston, A.J.; Bailey, C.E. Invited Editorial: Does Side Really Matter? Survival Analysis among Patients with Right- Versus Left-Sided Colon Cancer: A Propensity Score-Adjusted Analysis. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2022, 29, 9–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.S.; Menter, D.G.; Kopetz, S. Right Versus Left Colon Cancer Biology: Integrating the Consensus Molecular Subtypes. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2017, 15, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Peng, K.; Hu, D.; Shen, J.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, L.; Chen, J.; Pan, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Tumor Location Influences Oncologic Outcomes of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Undergoing Radiofrequency Ablation. Cancers 2018, 10, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, W.; Yan, K.; Wu, G.X.; Wu, W.; Fu, Y.; Lee, J.C.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Wang, S.; Chen, M.H. Radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma in difficult locations: Strategies and long-term outcomes. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 1554–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. Electronic address: Easloffice@easloffice.eu, European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 182–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver, European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer. EASL-EORTC clinical practice guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 908–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Couinaud, C. Liver anatomy: Portal (and suprahepatic) or biliary segmentation. Dig. Surg. 1999, 16, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.M.; Lee, S.H.; Shin, W.Y.; Lee, K.Y.; Kim, J.M.; Ahn, S.I. Intrahepatic recurrence of single nodular hepatocellular carcinoma after surgical resection: An analysis by segmental distribution. ANZ J. Surg. 2018, 88, E840–E844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, A.; Morales, R.R.; Zanus, G.; Farinati, F.; Burra, P.; Angeli, P.; Frigo, A.C.; Del Poggio, P.; Rapaccini, G.; Di Nolfo, M.A.; et al. Italian Liver Cancer group. Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer staging and transplant survival benefit for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: A multicentre, cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2011, 12, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuffer, Z.; Marini, T.; Rupasov, A.; Kwak, S.; Bhatt, S. The Best Single Measurement for Assessing Splenomegaly in Patients with Cirrhotic Liver Morphology. Acad. Radiol. 2017, 24, 1510–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparchez, Z.; Mocan, T. Contemporary role of liver biopsy in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Hepatol. 2018, 10, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trochsler, M.I.; Ralph, Q.; Bridgewater, F.; Kanhere, H.; Maddern, G.J. Technical note: Facilitating laparoscopic liver biopsy by the use of a single-handed disposable core biopsy needle. HPB Surg. 2013, 2013, 462498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamwal, R.; Krishnan, V.; Kushwaha, D.S.; Khurana, R. Hepatocellular carcinoma in non-cirrhotic versus cirrhotic liver: A clinico-radiological comparative analysis. Abdom. Radiol. 2020, 45, 2378–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Saraswat, M.K.; Sharma, B.C.; Sakhuja, P.; Sarin, S.K. Characteristics of hepatocellular carcinoma in India: A retrospective analysis of 191 cases. QJM 2008, 101, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.; Jang, Y.J.; Ryeom, H.; Lee, S.M.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, G.C.; Kim, H.J. Variation in hepatic segmental volume distribution according to different causes of liver cirrhosis: CT volumetric evaluation. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2012, 36, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apisarnthanarak, P.; Wongsawaeng, D.; Muangsomboon, K. Correlation between the severity of hepatitis B cirrhosis and CT volumetry-based hepatic segmental anatomic changes. J. Med. Assoc. Thail. 2014, 97, 856–862. [Google Scholar]
- Ozaki, K.; Matsui, O.; Kobayashi, S.; Minami, T.; Kitao, A.; Gabata, T. Morphometric changes in liver cirrhosis: Aetiological differences correlated with progression. Br. J. Radiol. 2016, 89, 20150896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, X.P.; Lu, T.; Wei, Y.G.; Chen, X.Z. Liver volume variation in patients with virus-induced cirrhosis: Findings on MDCT. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2007, 189, W153–W159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holbrook, R.F.; Rodriguez-Bigas, M.A.; Ramakrishnan, K.; Blumenson, L.; Petrelli, N.J. Patterns of colorectal liver metastases according to Couinaud’s segments. Dis. Colon Rectum. 1995, 38, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadiyoran, C.; Cizmecioglu, H.A.; Cure, E.; Yildirim, M.A.; Yilmaz, P.D. Liver metastasis in colorectal cancer: Evaluation of segmental distribution. Prz. Gastroenterol. 2019, 14, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, G.E.; Bridenbaugh, R.B. Roentgen demonstration of the venous circulation in the liver; portal venography. Radiology 1951, 57, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wigmore, S.J.; Madhavan, K.; Redhead, D.N.; Currie, E.J.; Garden, O.J. Distribution of colorectal liver metastases in patients referred for hepatic resection. Cancer 2000, 89, 285–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirai, Y.; Wakai, T.; Ohtani, T.; Sakai, Y.; Tsukada, K.; Hatakeyama, K. Colorectal carcinoma metastases to the liver. Does primary tumor location affect its lobar distribution? Cancer 1996, 77, 2213–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lautt, W.W.; Schafer, J.; Legare, D.J. Hepatic blood flow distribution: Consideration of gravity, liver surface, and norepinephrine on regional heterogeneity. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1993, 71, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.F.; Huang, T.L.; Lee, T.Y.; Chen, T.Y.; Chen, C.L. Variation of the intrahepatic portal vein; angiographic demonstration and application in living-related hepatic transplantation. Transplant. Proc. 1996, 28, 1667–1668. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Milosevic, I.; Vujovic, A.; Barac, A.; Djelic, M.; Korac, M.; Spurnic, A.R.; Gmizic, I.; Stevanovic, O.; Djordjevic, V.; Lekic, N.; et al. Gut-Liver Axis, Gut Microbiota, and Its Modulation in the Management of Liver Diseases: A Review of the Literature. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, P.; Chen, K. Gut microbiota and hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatobiliary Surg. Nutr. 2020, 9, 345–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colecchia, A.; Montrone, L.; Scaioli, E.; Bacchi-Reggiani, M.L.; Colli, A.; Casazza, G.; Schiumerini, R.; Turco, L.; Di Biase, A.R.; Mazzella, G.; et al. Measurement of spleen stiffness to evaluate portal hypertension and the presence of esophageal varices in patients with HCV-related cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 2012, 143, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedredal, G.I.; Yin, M.; McKenzie, T.; Lillegard, J.; Luebke-Wheeler, J.; Talwalkar, J.; Ehman, R.; Nyberg, S.L. Portal hypertension correlates with splenic stiffness as measured with MR elastography. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2011, 34, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Renzulli, M.; Dajti, E.; Ierardi, A.M.; Brandi, N.; Berzigotti, A.; Milandri, M.; Rossini, B.; Clemente, A.; Ravaioli, F.; Marasco, G.; et al. Validation of a standardized CT protocol for the evaluation of varices and porto-systemic shunts in cirrhotic patients. Eur. J. Radiol. 2022, 147, 110010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dajti, E.; Renzulli, M.; Colecchia, A.; Bacchi-Reggiani, M.L.; Milandri, M.; Rossini, B.; Ravaioli, F.; Marasco, G.; Alemanni, L.V.; Ierardi, A.M.; et al. Size and location of spontaneous portosystemic shunts predict the risk of decompensation in cirrhotic patients. Dig. Liver Dis. 2022, 54, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiberger, T. The Value of Liver and Spleen Stiffness for Evaluation of Portal Hypertension in Compensated Cirrhosis. Hepatol. Commun. 2021, 11, 1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marasco, G.; Dajti, E.; Ravaioli, F.; Alemanni, L.V.; Capuano, F.; Gjini, K.; Colecchia, L.; Puppini, G.; Cusumano, C.; Renzulli, M.; et al. Spleen stiffness measurement for assessing the response to β-blockers therapy for high-risk esophageal varices patients. Hepatol. Int. 2020, 14, 850–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Liver Lobe | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Left | Right | Caudate | p | |
| Nodule Total (n = 322) | 79 (24.5) | 234 (72.7) | 9 (2.8) | |
| Gender * | ||||
| Male | 62 (78.5) | 198 (84.6) | 7 (77.8) | 0.419 |
| Female | 17 (21.5) | 36 (15.4) | 2 (22.2) | |
| Age § | 64 (±11.9) | 65 (±10.7) | 62 (±8.8) | 0.570 |
| Etiology of cirrhosis | ||||
| Viral | 36 (45.6) | 128 (54.7) | 5 (55.6) | 0.412 |
| Alcohol | 21 (26.6) | 38 (16.2) | 2 (22.2) | |
| NASH-NAFLD | 8 (10.1) | 36 (15.4) | 1 (11.1) | |
| Others | 14 (17.7) | 33 (14.1) | 1 (11.1) | |
| Type of HCC | ||||
| Monofocal | 33 (41.8) | 117 (50) | 5 (55.6) | 0.755 |
| Oligonodular | 15 (19) | 37 (15.8) | 1 (11.1) | |
| Multinodular | 31 (39.2) | 80 (34.2) | 3 (33.3) | |
| Milan criteria | ||||
| Milan in | 64 (81) | 197 (84.2) | 8 (88.9) | 0.731 |
| Milan out | 15 (19) | 37 (15.8) | 1 (11.1) | |
| Nodule size | ||||
| ≤2 cm | 33 (41.8) | 119 (50.9) | 6 (66.7) | 0.213 |
| >2 cm but ≤3 cm | 20 (25.3) | 42 (17.9) | 0 | |
| >3 but ≤5 cm | 14 (17.7) | 37 (15.8) | 1 (11.1) | |
| >5 cm | 12 (15.2) | 36 (15.4) | 2 (22.2) | |
| Spleen diameter | ||||
| ≤12 cm | 44 (55.7) | 118 (50.4) | 4 (44.4) | 0.657 |
| >12 cm | 35 (44.3) | 116 (49.6) | 5 (55.6) | |
| Spleen stiffness | ||||
| ≤61 kPa | 37 (46.8) | 100 (43.5) | 3 (33.3) | 0.673 |
| >61 kPa | 42 (53.2) | 134 (56.5) | 6 (66.7) | |
| Liver stiffness | ||||
| ≤29 kPa | 37 (46.8) | 85 (36.3) | 5 (55.6) | 0.154 |
| >29 kPa | 42 (53.2) | 149 (63.7) | 4 (44.4) | |
| Nodules in Child–Pugh score | ||||
| Class A (5–6) | 63 (79.7) | 192 (82.1) | 8 (88.9) | 0.559 |
| Class B (7–9) | 14 (17.7) | 38 (16.2) | 1 (11.1) | |
| Class C (10–15) | 2 (2.5) | 4 (1.7) | 0 | |
| HPVG | ||||
| <12 mmHg | 38 (48.1) | 93 (39.7) | 6 (66.7) | 0.143 |
| ≥12 mmHg | 41 (51.9) | 141 (61.3) | 3 (33.3) | |
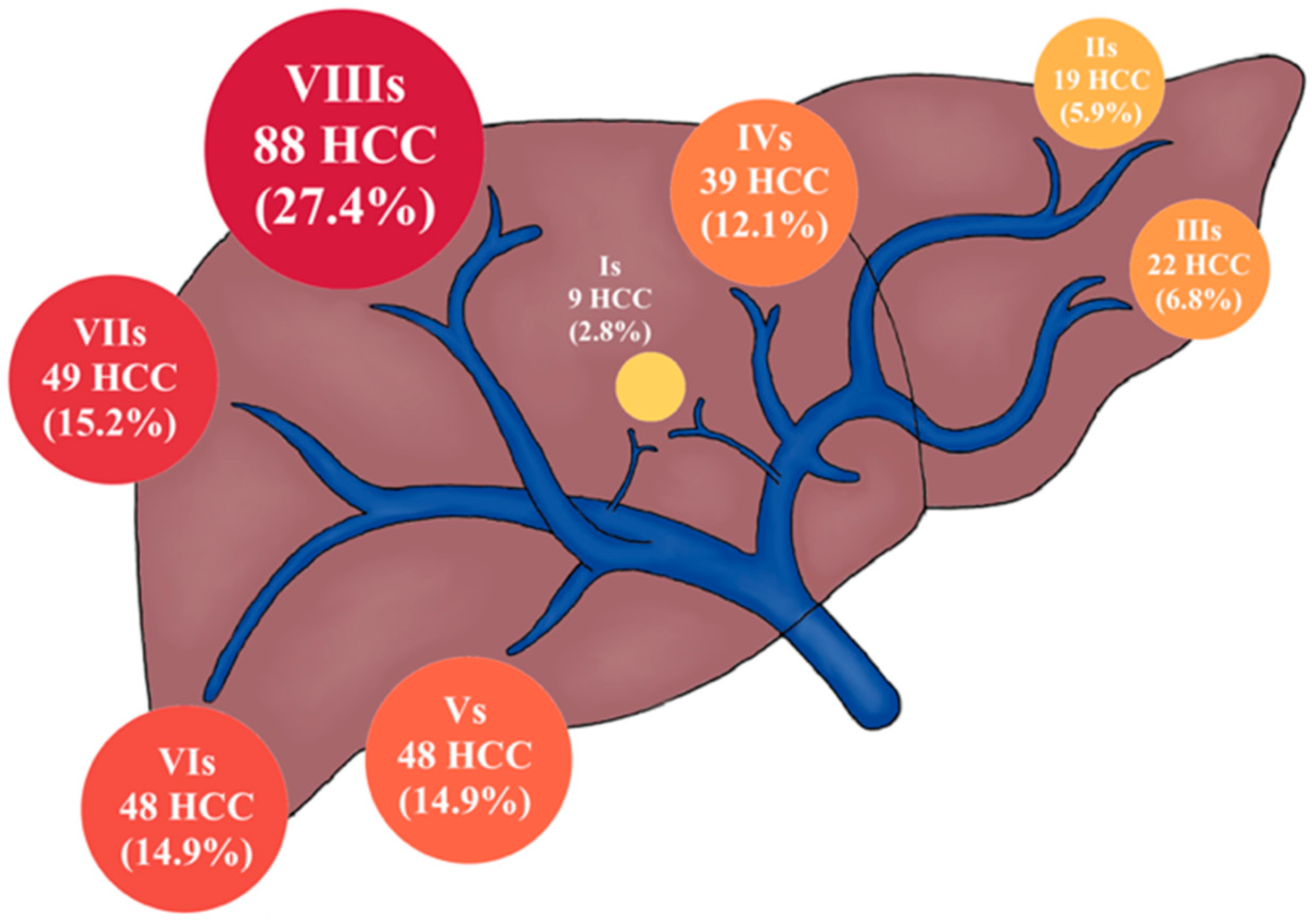
| Liver Segment | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S7 | S8 | p | |
| Nodule Total (n = 322) | 9 (2.8) | 19 (5.9) | 22 (6.8) | 39 (12.1) | 48 (14.9) | 48 (14.9) | 49 (15.2) | 88 (27.4) | |
| Gender * | |||||||||
| Male | 7 (77.8) | 16 (84.2) | 16 (72.7) | 31 (79.5) | 43 (89.6) | 41 (85.4) | 39 (79.6) | 74 (84.1) | 0.743 |
| Female | 2 (22.2) | 3 (15.8) | 6 (27.3) | 8 (20.5) | 5 (10.4) | 7 (14.6) | 10 (20.4) | 14 (15.9) | |
| Age § | 62 (±8.8) | 66 (±9.5) | 66 (10) | 62 (±13.6) | 66 (±10.4) | 65 (±12) | 65 (±10) | 66 (±10.6) | 0.809 |
| Etiology of cirrhosis | |||||||||
| Viral | 5 (55.6) | 11 (57.9) | 10 (45.4) | 16 (41.1) | 32 (66.7) | 26 (54.2) | 24 (49) | 45 (51.1) | 0.771 |
| Alcohol | 2 (22.2) | 4 (21) | 6 (27.3) | 11 (28.2) | 9 (18.7) | 5 (10.4) | 10 (20.4) | 14 (15.9) | |
| NASH-NAFLD | 1 (11.1) | 1 (5.3) | 2 (9.1) | 5 (12.8) | 4 (8.3) | 9 (18.7) | 7 (14.3) | 16 (18.2) | |
| Others | 1 (11.1) | 3 (15.8) | 4 (18.2) | 7 (17.9) | 3 (6.3) | 8 (16.7) | 8 (16.3) | 13 (14.8) | |
| Type of HCC | |||||||||
| Monofocal | 5 (55.6) | 10 (52.6) | 9 (40.9) | 14 (35.9) | 20 (41.7) | 25 (52.1) | 26 (53.1) | 46 (52.3) | 0.860 |
| Oligonodular | 1 (11.1) | 2 (10.5) | 6 (27.3) | 7 (17.9) | 11 (22.9) | 7 (14.6) | 6 (12.2) | 13 (14.8) | |
| Multinodular | 3 (33.3) | 7 (36.8) | 7 (31.8) | 18 (46.2) | 17 (35.4) | 16 (33.3) | 17 (34.7) | 29 (33) | |
| Milan criteria | |||||||||
| Milan in | 8 (88.9) | 17 (89.5) | 16 (72.7) | 32 (82.1) | 37 (77.1) | 41 (85.4) | 43 (87.8) | 75 (85.2) | 0.660 |
| Milan out | 1 (11.1) | 2 (10.5) | 6 (27.3) | 7 (17.9) | 11 (22.9) | 7 (14.6) | 6 (12.2) | 13 (14.8) | |
| Nodule size | |||||||||
| ≤2 cm | 6 (66.7) | 6 (31.6) | 12 (54.5) | 15 (38.5) | 23 (47.9) | 24 (50) | 30 (61.2) | 42 (47.7) | 0.294 |
| >2 but ≤3 cm | 0 | 7 (36.9) | 5 (22.8) | 8 (20.5) | 7 (14.6) | 9 (18.7) | 6 (12.3) | 20 (22.8) | |
| >3 but ≤5 cm | 1 (11.1) | 4 (21) | 2 (9.1) | 9 (23.1) | 13 (27.1) | 7 (14.6) | 5 (10.2) | 11 (12.5) | |
| >5 cm | 2 (22.2) | 2 (10.5) | 3 (13.6) | 7 (17.9) | 5 (10.4) | 8 (16.7) | 8 (16.3) | 15 (17) | |
| Spleen diameter | |||||||||
| ≤12 cm | 4 (44.4) | 12 (63.2) | 13 (59.1) | 20 (51.3) | 23 (47.9) | 26 (54.2) | 21 (42.6) | 47 (53.4) | 0.828 |
| >12 cm | 5 (55.6) | 7 (36.8) | 9 (40.9) | 19 (48.7) | 25 (52.1) | 22 (45.8) | 28 (57.1) | 41 (46.6) | |
| Spleen stiffness | |||||||||
| ≤61 kPa | 3 (33.3) | 10 (52.6) | 11 (50) | 17 (43.6) | 16 (33.3) | 21 (43.7) | 19 (38.8) | 43 (48.9) | 0.673 |
| >61 kPa | 6 (66.7) | 9 (47.4) | 11 (50) | 22 (56.4) | 32 (66.7) | 27 (56.2) | 30 (61.2) | 45 (51.1) | |
| Liver stiffness | |||||||||
| ≤29 kPa | 5 (55.6) | 9 (47.4) | 11 (50) | 18 (46.2) | 15 (31.2) | 20 (83.3) | 15 (30.6) | 34 (38.6) | 0.504 |
| >29 kPa | 4 (44.4) | 10 (52.6) | 11 (50) | 21 (53.8) | 33 (68.8) | 28 (58.3) | 34 (69.4) | 54 (61.4) | |
| Nodules in Child–Pugh score | |||||||||
| Class A (5–6) | 8 (88.9) | 13 (68.5) | 16 (72.7) | 35 (89.7) | 42 (87.5) | 39 (81.3) | 37 (75.5) | 73 (83) | 0.577 |
| Class B (7–9) | 1 (11.1) | 5 (26.2) | 6 (27.3) | 3 (7.7) | 6 (12.5) | 7 (14.6) | 10 (20.4) | 15 (17.0) | |
| Class C (10–15) | 0 | 1 (5.3) | 0 | 1 (2.5) | 0 | 2 (4.2) | 2 (4.1) | 0 | |
| HPVG | |||||||||
| <12 mmHg | 6 (66.7) | 10 (52.6) | 14 (63.6) | 15 (38.5) | 21 (43.7) | 23 (47.9) | 14 (28.6) | 34 (38.6) | 0.092 |
| ≥12 mmHg | 3 (33.3) | 9 (47.4) | 8 (36.4) | 24 (61.5) | 27 (56.2) | 25 (52.1) | 35 (71.4) | 54 (61.4) | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Renzulli, M.; Brandi, N.; Pecorelli, A.; Pastore, L.V.; Granito, A.; Martinese, G.; Tovoli, F.; Simonetti, M.; Dajti, E.; Colecchia, A.; et al. Segmental Distribution of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Cirrhotic Livers. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12040834
Renzulli M, Brandi N, Pecorelli A, Pastore LV, Granito A, Martinese G, Tovoli F, Simonetti M, Dajti E, Colecchia A, et al. Segmental Distribution of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Cirrhotic Livers. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(4):834. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12040834
Chicago/Turabian StyleRenzulli, Matteo, Nicolò Brandi, Anna Pecorelli, Luigi Vincenzo Pastore, Alessandro Granito, Giuseppe Martinese, Francesco Tovoli, Mario Simonetti, Elton Dajti, Antonio Colecchia, and et al. 2022. "Segmental Distribution of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Cirrhotic Livers" Diagnostics 12, no. 4: 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12040834
APA StyleRenzulli, M., Brandi, N., Pecorelli, A., Pastore, L. V., Granito, A., Martinese, G., Tovoli, F., Simonetti, M., Dajti, E., Colecchia, A., & Golfieri, R. (2022). Segmental Distribution of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Cirrhotic Livers. Diagnostics, 12(4), 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12040834













