Quantification and Classification of Contrast Enhanced Ultrasound Breast Cancer Data: A Preliminary Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Imaging Protocol
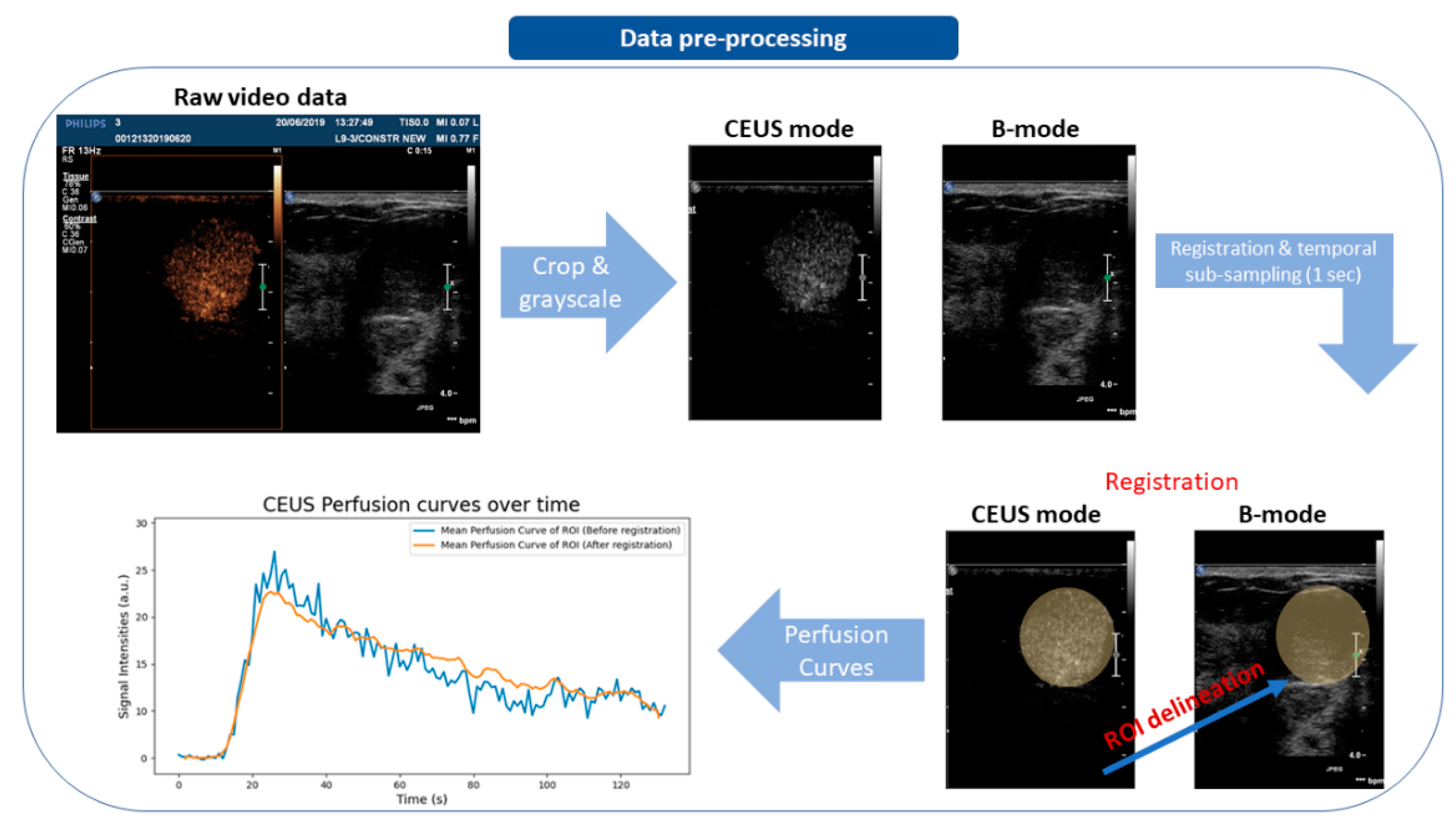
2.3. Data Pre-Processing
2.4. CEUS Quantification, Parametric Mapping
2.5. Goodness of Fit
2.6. Machine-Learning Pipeline
2.6.1. Feature Extraction
2.6.2. Feature Selection
2.6.3. Classification
2.6.4. Model Evaluation Metrics
3. Results
3.1. Goodness of Fit
3.2. Machine Learning
3.2.1. Feature Selection
3.2.2. Classification Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harbeck, N.; Gnant, M. Breast cancer. Lancet 2017, 389, 1134–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooley, R.J.; Greenberg, K.L.; Stackhouse, R.M.; Geisel, J.L.; Butler, R.S.; Philpotts, L.E. Screening US in patients with mammographically dense breasts: Initial experience with Connecticut public act 09-41. Radiology 2012, 265, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Yi, A.; Jang, M.J.; Chang, J.M.; Cho, N.; Moon, W.K. Supplemental screening breast us in women with negative mammographic findings: Effect of routine axillary scanning. Radiology 2018, 286, 830–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprague, B.L.; Stout, N.K.; Schechter, C.; Van Ravesteyn, N.T.; Cevik, M.; Alagoz, O.; Lee, C.I.; Van Den Broek, J.J.; Miglioretti, D.L.; Mandelblatt, J.S.; et al. Benefits, harms, and cost-effectiveness of supplemental ultrasonography screening for women with dense breasts. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 162, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.L.; Zhou, J.Q.; Chen, Q.; Deng, Y.C. Comparison of the sensitivity of mammography, ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging and combinations of these imaging modalities for the detection of small (≤2 cm) breast cancer. Medicine 2021, 100, e26531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobsen, K.K.; O’Meara, E.S.; Key, D.; Buist, D.S.M.; Kerlikowske, K.; Vejborg, I.; Sprague, B.L.; Lynge, E.; Von Euler-Chelpin, M. Comparing sensitivity and specificity of screening mammography in the United States and Denmark. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 137, 2198–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shao, S.H.; Li, C.X.; Yao, M.H.; Li, G.; Li, X.; Wu, R. Incorporation of contrast-enhanced ultrasound in the differential diagnosis for breast lesions with inconsistent results on mammography and conventional ultrasound. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2020, 74, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Dong, L.; Jiang, Q.; Guan, X.; Wu, H.; Luo, B. Incorporating Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound into the BI-RADS Scoring System Improves Accuracy in Breast Tumor Diagnosis: A Preliminary Study in China. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2016, 42, 2630–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Ou, B.; Yang, H.; Wu, H.; Luo, B. Breast Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound: Is a Scoring System Feasible? A Preliminary Study in China. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.C.; Le, J.; Zhou, J.; Huang, Y.X.; Qian, L.; Chang, C. The Role of Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound in the Diagnosis and Pathologic Response Prediction in Breast Cancer: A Meta-analysis and Systematic Review. Clin. Breast Cancer 2020, 20, e490–e509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Z.; Quan, J.; Yunxiao, Z.; Jian, C.; Zhu, H.; Liping, G. Diagnostic value of contrast-enhanced ultrasound parametric imaging in breast tumors. J. Breast Cancer 2013, 16, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saracco, A.; Szabó, B.K.; Aspelin, P.; Leifland, K.; Wilczek, B.; Celebioglu, F.; Axelsson, R. Differentiation between benign and malignant breast tumors using kinetic features of real-time harmonic contrast-enhanced ultrasound. Acta Radiol. 2012, 53, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.R.; Wu, Y.; Chen, M.; Gu, X.G. Application of contrast-enhanced ultrasound in the diagnosis of small breast lesions. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2018, 70, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.L.; Guan, J.; Li, M.Z.; Liu, M.J.; Guo, Y.; Zheng, Y.L.; Yang, Z.; Yang, J.Y. Adjunctive targeted contrast-enhanced ultrasonography for the work-up of Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System category 3 and 4 lesions. J. Med. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2016, 60, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnall, M.D.; Blume, J.; Bluemke, D.A.; DeAngelis, G.A.; DeBruhl, N.; Harms, S.; Heywang-Köbrunner, S.H.; Hylton, N.; Kuhl, C.K.; Pisano, E.D.; et al. Diagnostic architectural and dynamic features at breast MR imaging: Multicenter study. Radiology 2006, 238, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, D.M.; Hylton, N.M.; Kinkel, K.; Hochman, M.G.; Kuhl, C.K.; Kaiser, W.A.; Weinreb, J.C.; Smazal, S.F.; Degani, H.; Viehweg, P.; et al. Development, standardization, and testing of a lexicon for reporting contrast-enhanced breast magnetic resonance imaging studies. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2001, 13, 889–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, R.; Sansone, M.; Filice, S.; Carone, G.; Amato, D.M.; Sansone, C.; Petrillo, A. Pattern Recognition Approaches for Breast Cancer DCE-MRI Classification: A Systematic Review. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 2016, 36, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fusco, R.; Sansone, M.; Filice, S.; Granata, V.; Catalano, O.; Amato, D.M.; Di Bonito, M.; D’Aiuto, M.; Capasso, I.; Rinaldo, M.; et al. Integration of DCE-MRI and DW-MRI Quantitative Parameters for Breast Lesion Classification. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 237863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzacheva, A.A.; Najarian, K.; Brockway, J.P. Breast cancer detection in gadolinium-enhanced MR images by static region descriptors and neural networks. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2003, 17, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agner, S.C.; Soman, S.; Libfeld, E.; McDonald, M.; Thomas, K.; Englander, S.; Rosen, M.A.; Chin, D.; Nosher, J.; Madabhushi, A. Textural Kinetics: A Novel Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced (DCE)-MRI Feature for Breast Lesion Classification. J. Digit. Imaging 2011, 24, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schlossbauer, T.; Leinsinger, G.; Wismuller, A.; Lange, O.; Scherr, M.; Meyer-Baese, A.; Reiser, M. Classification of Small Contrast Enhancing Breast Lesions in Dynamic Magnetic Resonance Imaging Using a Combination of Morphological Criteria and Dynamic Analysis Based on Unsupervised Vector-Quantization. Investig. Radiol. 2008, 43, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amit, G.; Ben-Ari, R.; Hadad, O.; Monovich, E.; Granot, N.; Hashoul, S. Classification of Breast MRI Lesions Using Small-Size Training Sets: Comparison of Deep Learning Approaches. In Proceedings of the SPIE 10134, Medical Imaging 2017: Computer-Aided Diagnosis, Orlando, FL, USA, 11–16 February 2017; p. 101341H. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Baloch, S.; Englander, S.; Schnall, M.D.; Shen, D. Segmentation and Classification of Breast Tumor Using Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MR Images. Med. Image Comput. Comput. Assist. Interv. 2007, 10, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McLaren, C.E.; Chen, W.P.; Nie, K.; Su, M.Y. Prediction o Malignant Breast Lesions from MRI Features: A Comparison of Artificial Neural Network and Logistic Regression Techniques. Acad. Radiol. 2009, 16, 842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Mao, N.; Duan, S.; Li, Q.; Li, R.; Jiang, T.; Wang, Z.; Xie, H.; Gu, Y. Radiomic Analysis of Contrast-Enhanced Mammography with Different Image Types: Classification of Breast Lesions. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, T.R.; Cerviño, L.I.; Boone, J.M.; Lindfors, K.K. Classification of breast computed tomography data. Med. Phys. 2008, 35, 1078–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shima, H.; Okuno, T.; Nakamura, T.; Noro, A.; Noma, M.; Sato, M.; Kaga, T.; Mituzuka, Y.; Kamei, K.; Imayoshi, Y.; et al. Comparing the extent of breast cancer tumors through contrast-enhanced ultrasound vs B-mode, opposed with pathology: Evergreen study. Breast Cancer 2021, 28, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, Y.; Ito, T.; Takada, E.; Omoto, K.; Hirai, T.; Moriyasu, F. Efficacy of Sonazoid (perflubutane) for contrast-enhanced ultrasound in the differentiation of focal breast lesions: Phase 3 multicenter clinical trial. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2014, 202, W400–W407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanan, C.; Cottrell, G.W. Color-to-Grayscale: Does the Method Matter in Image Recognition? PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thévenaz, P.; Ruttimann, U.E.; Unser, M. A pyramid approach to subpixel registration based on intensity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 1998, 7, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marquardt, D.W. An algorithm for least-squares estimation of nonlinear parameters. J. Soc. Ind. Appl. Math. 1963, 11, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sourbron, S.; Luypaert, R.; Morhard, D.; Seelos, K.; Reiser, M.; Peller, M. Deconvolution of bolus-tracking data: A comparison of discretization methods. Phys. Med. Biol. 2007, 52, 6761–6778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannidis, G.S.; Christensen, S.; Nikiforaki, K.; Trivizakis, E.; Perisinakis, K.; Hatzidakis, A.; Karantanas, A.; Reyes, M.; Lansberg, M.; Marias, K. Cerebral CT Perfusion in Acute Stroke: The Effect of Lowering the Tube Load and Sampling Rate on the Reproducibility of Parametric Maps. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madsen, K.; Nielsen, H.B.; Tingleff, O. Methods for Non-Linear Least Squares Problems; University of Denmark: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Madsen, M.T. A simplified formulation of the gamma variate function. Phys. Med. Biol. 1992, 37, 1597–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannidis, G.S.; Nikiforaki, K.; Karantanas, A. Correlation of DWI and DCE MRI Markers for the Study of Perfusion of the Lower Limb in Patients with Peripheral Arterial Disease. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 19th International Conference on Bioinformatics and Bioengineering (BIBE), Athens, Greece, 28–30 October 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 433–438. [Google Scholar]
- Ioannidis, G.S.; Maris, T.G.; Nikiforaki, K.; Karantanas, A.; Marias, K. Investigating the Correlation of Ktrans with Semi-Quantitative MRI Parameters Towards More Robust and Reproducible Perfusion Imaging Biomarkers in Three Cancer Types. IEEE J. Biomed. Heal. Inform. 2019, 23, 1855–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioannidis, G.S.; Marias, K.; Galanakis, N.; Perisinakis, K.; Hatzidakis, A.; Tsetis, D.; Karantanas, A.; Maris, T.G. A correlative study between diffusion and perfusion MR imaging parameters on peripheral arterial disease data. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 55, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.; Long, F.; Ding, C. Feature selection based on mutual information criteria of max-dependency, max-relevance, and min-redundancy. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2005, 27, 1226–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Müller, A.; Nothman, J.; Louppe, G.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2012, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Patlak, C.S.; Blasberg, R.G.; Fenstermacher, J.D. Graphical Evaluation of Blood-to-Brain Transfer Constants from Multiple-Time Uptake Data. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1983, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sourbron, S.P.; Buckley, D.L. On the scope and interpretation of the Tofts models for DCE-MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2011, 66, 735–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekkar, M.; Kheliouane Djemaa, D.; Akrouf Alitouche, D. Evaluation Measures for Models Assessment over Imbalanced Data Sets. J. Inf. Eng. Appl. 2013, 3, 27–38. [Google Scholar]
- Batuwita, R.; Palade, V. A New Performance Measure for Class Imbalance Learning. Application to Bioinformatics Problems. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications, Miami, FL, USA, 13–15 December 2009; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 545–550. [Google Scholar]
- Ta, C.N.; Kono, Y.; Barback, C.V.; Mattrey, R.F.; Kummel, A.C. Automating tumor classification with pixel-by-pixel contrast-enhanced ultrasound perfusion kinetics. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B Nanotechnol. Microelectron. Mater. Process. Meas. Phenom. 2012, 30, 02C103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kapetas, P.; Clauser, P.; Woitek, R.; Wengert, G.J.; Lazar, M.; Pinker, K.; Helbich, T.H.; Baltzer, P.A.T. Quantitative Multiparametric Breast Ultrasound: Application of Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound and Elastography Leads to an Improved Differentiation of Benign and Malignant Lesions. Investig. Radiol. 2019, 54, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janu, E.; Krikavova, L.; Little, J.; Dvorak, K.; Brancikova, D.; Jandakova, E.; Pavlik, T.; Kovalcikova, P.; Kazda, T.; Valek, V. Prospective evaluation of contrast-enhanced ultrasound of breast BI-RADS 3–5 lesions. BMC Med. Imaging 2020, 20, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, A.Y.; Kwon, M.; Woo, O.H.; Cho, K.R.; Park, E.K.; Cha, S.H.; Song, S.E.; Lee, J.H.; Cha, J.; Son, G.S.; et al. A prospective study on the value of ultrasound microflow assessment to distinguish malignant from benign solid breast masses: Association between ultrasound parameters and histologic microvessel densities. Korean J. Radiol. 2019, 20, 759–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Characteristics | n |
|---|---|
| Total patients | 25 |
| Women | 25 |
| Age (in years) | |
| Mean | 52.3 |
| Median | 50 |
| Range | 28–79 |
| Histopathological grades | |
| BIRADS IV | 25 |
| Benign lesions | 14 |
| Malignant lesions | 11 |
| Number of benign voxels | 22,446 |
| Number of malignant voxels | 65,762 |
| Classifiers | Sensitivity | Specificity | Gmean | AUROC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| QDA | 69.7 ± 20.8 | 88.5 ± 12.0 | 76.8 ± 10.9 | 89.7 ± 5.4 |
| GaussianNB | 69.0 ± 22.1 | 90.7 ± 11.2 | 77.2 ± 12.5 | 89.8 ± 7.4 |
| AdaBoost | 87.4 ± 11.9 | 62.6 ± 21.5 | 72.2 ± 11.4 | 87.9 ± 9.7 |
| Random forest | 88.3 ± 11.8 | 70.3 ± 17.5 | 77.6 ± 9.2 | 87.1 ± 9.8 |
| KNeighbors | 85.4 ± 11.5 | 55.6 ± 15.1 | 67.9 ± 9.1 | 76.7 ± 9.2 |
| Logistic regression | 89.2 ± 10.7 | 70.0 ± 18.5 | 77.1 ± 8.6 | 91.0 ± 6.6 |
| SVM | 88.1 ± 11.4 | 68.6 ± 18.6 | 76.7 ± 11.1 | 87.9 ± 10.8 |
| Classifiers | Sensitivity | Specificity | Gmean | AUROC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| QDA | 70.4 ± 21.5 | 83.8 ± 18.6 | 74.2 ± 12.5 | 87.6 ± 7.1 |
| GaussianNB | 67.8 ± 23.0 | 87.6 ± 19.3 | 74.2 ± 14.4 | 88.8 ± 6.6 |
| AdaBoost | 89.2 ± 11.3 | 57.1 ± 20.1 | 69.5 ± 10.6 | 86.6 ± 9.8 |
| Random forest | 90.4 ± 10.1 | 60.8 ± 25.8 | 71.9 ± 14.3 | 86.5 ± 11.8 |
| KNeighbors | 86.6 ± 9.8 | 52.9 ± 15.8 | 66.3 ± 8.7 | 76.1 ± 7.5 |
| Logistic regression | 88.5 ± 13.3 | 66.3 ± 22.4 | 74.6 ± 11.8 | 89.0 ± 11.0 |
| SVM | 89.2 ± 10.3 | 56.2 ± 25.1 | 68.1 ± 15.9 | 85.8 ± 9.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ioannidis, G.S.; Goumenakis, M.; Stefanis, I.; Karantanas, A.; Marias, K. Quantification and Classification of Contrast Enhanced Ultrasound Breast Cancer Data: A Preliminary Study. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 425. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12020425
Ioannidis GS, Goumenakis M, Stefanis I, Karantanas A, Marias K. Quantification and Classification of Contrast Enhanced Ultrasound Breast Cancer Data: A Preliminary Study. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(2):425. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12020425
Chicago/Turabian StyleIoannidis, Georgios S., Michalis Goumenakis, Ioannis Stefanis, Apostolos Karantanas, and Kostas Marias. 2022. "Quantification and Classification of Contrast Enhanced Ultrasound Breast Cancer Data: A Preliminary Study" Diagnostics 12, no. 2: 425. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12020425
APA StyleIoannidis, G. S., Goumenakis, M., Stefanis, I., Karantanas, A., & Marias, K. (2022). Quantification and Classification of Contrast Enhanced Ultrasound Breast Cancer Data: A Preliminary Study. Diagnostics, 12(2), 425. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12020425








