Volumetric Measurements in Lung Cancer Screening Reduces Unnecessary Low-Dose Computed Tomography Scans: Results from a Single-Center Prospective Trial on 4119 Subjects
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The bioMILD Trial
2.2. Imaging Acquisition
2.3. Study Population
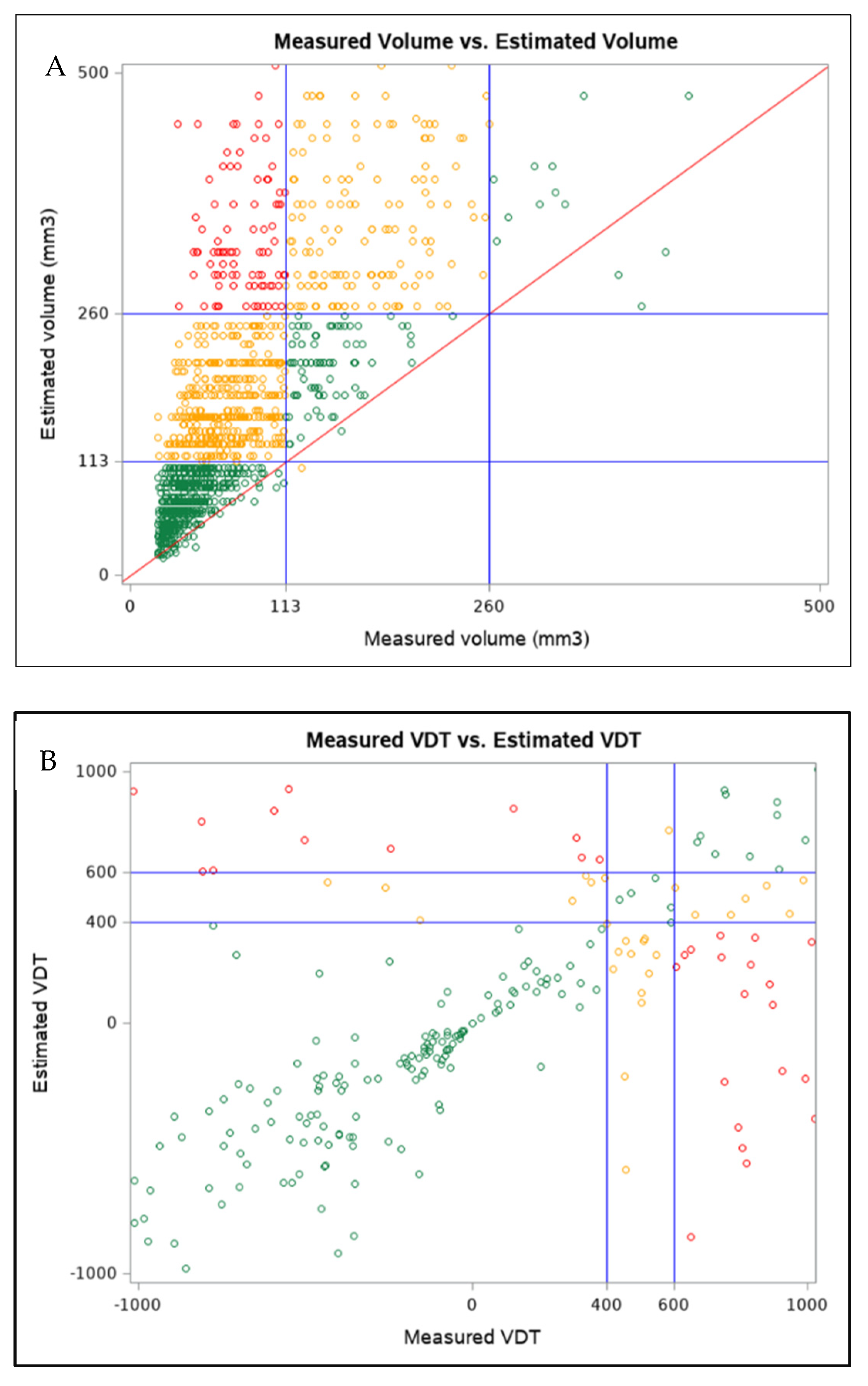
- Negative outcome: PN < 113 mm3
- Indeterminate outcome: PN 113–260 mm3
- Positive outcome: PN > 260 mm3
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
3.2. PN-Based Analysis
3.3. Screenee-Based Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- National Lung Screening Trial Research Team; Aberle, D.R.; Adams, A.M. Reduced lung-cancer mortality with low-dose computed tomographic screening. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 395–409. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- de Koning, H.J.; van der Aalst, C.M.; de Jong, P.A. Reduced Lung-Cancer Mortality with Volume CT Screening in a Randomized Trial. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastorino, U.; Silva, M.; Sestini, S. Prolonged lung cancer screening reduced 10-year mortality in the MILD trial: New confirmation of lung cancer screening efficacy. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ko, J.P.; Berman, E.J.; Kaur, M. Pulmonary Nodules: Growth rate assessment in patients by using serial CT and three-dimensional volumetry. Radiology 2012, 262, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kauczor, H.U.; Baird, A.M.; Blum, T.G. ESR/ERS statement paper on lung cancer screening. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 3277–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ACR. Lung CT Screening Reporting & Data System (Lung-RADS). Available online: https://www.acr.org/Clinical-Resources/Reporting-and-Data-Systems/Lung-Rads (accessed on 5 January 2022).
- Han, D.; Heuvelmans, M.A.; Oudkerk, M. Volume versus diameter assessment of small pulmonary nodules in CT lung cancer screening. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2017, 6, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Revel, M.P.; Bissery, A.; Bienvenu, M. Are two-dimensional CT measurements of small noncalcified pulmonary nodules reliable? Radiology 2004, 231, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Margerie-Mellon, C.; Heidinger, B.H.; Bankier, A.A. 2D or 3D measurements of pulmonary nodules: Preliminary answers and more open questions. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, 547–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Devaraj, A.; van Ginneken, B.; Nair, A. Use of Volumetry for Lung Nodule Management: Theory and Practice. Radiology 2017, 284, 630–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacMahon, H.; Naidich, D.P.; Goo, J.M. Guidelines for Management of Incidental Pulmonary Nodules Detected on CT Images: From the Fleischner Society 2017. Radiology 2017, 284, 228–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Callister, M.E.; Baldwin, D.R.; Akram, A.R. British Thoracic Society guidelines for the investigation and management of pulmonary nodules. Thorax 2015, 70 (Suppl. 2), ii1–ii54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Silva, M.; Milanese, G.; Sestini, S. Lung cancer screening by nodule volume in Lung-RADS v1.1: Negative baseline CT yields potential for increased screening interval. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 31, 1956–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heuvelmans, M.A.; Walter, J.E.; Vliegenthart, R. Disagreement of diameter and volume measurements for pulmonary nodule size estimation in CT lung cancer screening. Thorax 2018, 73, 779–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horeweg, N.; van Rosmalen, J.; Heuvelmans, M.A. Lung cancer probability in patients with CT-detected pulmonary nodules: A prespecified analysis of data from the NELSON trial of low-dose CT screening. Lancet. Oncol. 2014, 15, 1332–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mets, O.M.; de Jong, P.A.; Chung, K. Fleischner recommendations for the management of subsolid pulmonary nodules: High awareness but limited conformance—a survey study. Eur. Radiol. 2016, 26, 3840–3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xie, X.; Willemink, M.J.; de Jong, P.A. Small irregular pulmonary nodules in low-dose CT: Observer detection sensitivity and volumetry accuracy. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2014, 202, W202–W209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milanese, G.; Eberhard, M.; Martini, K. Vessel suppressed chest Computed Tomography for semi-automated volumetric measurements of solid pulmonary nodules. Eur. J. Radiol. 2018, 101, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, M.; Milanese, G.; Seletti, V. Pulmonary quantitative CT imaging in focal and diffuse disease: Current research and clinical applications. Br. J. Radiol. 2018, 2018, 20170644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| PN-Based Analysis | ||||
| EV LDCT Outcome | ||||
| Negative | Indeterminate | Positive | ||
| MV LDCT outcome | Negative | 1308 | 735 | 160 |
| Indeterminate | 3 | 108 | 217 | |
| Positive | 0 | 0 | 184 | |
| PN-Based Analysis | ||||
| EV VDT | ||||
| <400 | 400–600 | >600 | ||
| MV VDT | <400 | 1021 | 29 | 254 |
| 400–600 | 29 | 12 | 11 | |
| >600 | 377 | 73 | 505 | |
| Screenee-Based Analysis | ||||
| EV LDCT Outcome | ||||
| Negative | Indeterminate | Positive | ||
| MV LDCT outcome | Negative | 611 | 445 | 100 |
| Indeterminate | 1 | 83 | 182 | |
| Positive | 0 | 0 | 161 | |
| Screenee-Based Analysis | ||||
| EV VDT | ||||
| >600 | 400–600 | >600 | ||
| MV VDT | <400 | 579 | 15 | 170 |
| 400–600 | 17 | 5 | 5 | |
| >600 | 225 | 40 | 291 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Milanese, G.; Sabia, F.; Ledda, R.E.; Sestini, S.; Marchianò, A.V.; Sverzellati, N.; Pastorino, U. Volumetric Measurements in Lung Cancer Screening Reduces Unnecessary Low-Dose Computed Tomography Scans: Results from a Single-Center Prospective Trial on 4119 Subjects. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12020229
Milanese G, Sabia F, Ledda RE, Sestini S, Marchianò AV, Sverzellati N, Pastorino U. Volumetric Measurements in Lung Cancer Screening Reduces Unnecessary Low-Dose Computed Tomography Scans: Results from a Single-Center Prospective Trial on 4119 Subjects. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(2):229. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12020229
Chicago/Turabian StyleMilanese, Gianluca, Federica Sabia, Roberta Eufrasia Ledda, Stefano Sestini, Alfonso Vittorio Marchianò, Nicola Sverzellati, and Ugo Pastorino. 2022. "Volumetric Measurements in Lung Cancer Screening Reduces Unnecessary Low-Dose Computed Tomography Scans: Results from a Single-Center Prospective Trial on 4119 Subjects" Diagnostics 12, no. 2: 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12020229
APA StyleMilanese, G., Sabia, F., Ledda, R. E., Sestini, S., Marchianò, A. V., Sverzellati, N., & Pastorino, U. (2022). Volumetric Measurements in Lung Cancer Screening Reduces Unnecessary Low-Dose Computed Tomography Scans: Results from a Single-Center Prospective Trial on 4119 Subjects. Diagnostics, 12(2), 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12020229






