Clinical Performance Evaluation of the NeuMoDx Flu A-B/RSV/SARS-CoV-2 Vantage Assay
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sample and Setting
2.2. NeuMoDx Flu A-B/RSV/SARS-CoV-2 Vantage Assay
2.3. Influenza Type A and B RT-PCR
2.4. RSV RT-Nested PCR
2.5. Abbott RealTime SARS-CoV-2 Assay
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Worldometer-Coronavirus. Available online: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus (accessed on 25 July 2022).
- Guan, W.J.; Ni, Z.Y.; Hu, Y.; Liang, W.H.; Ou, C.Q.; He, J.X.; Liu, L.; Shan, H.; Lei, C.L.; Hui, D.S.C.; et al. Clinical characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1708–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO Director-General’s Opening Remarks at the Media Briefing on COVID-19—16 March. Available online: https://www.who.int/director-general/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-remarks-at-the-media-briefing-on-covid-19---16-march-2020 (accessed on 25 July 2022).
- Olsen, S.J.; Winn, A.K.; Budd, A.P.; Prill, M.M.; Steel, J.; Midgley, C.M.; Kniss, K.; Burns, E.; Rowe, T.; Foust, A.; et al. Changes in influenza and other respiratory virus activity during the COVID-19 pandemic—United States, 2020. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2021, 70, 1013–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ujiie, M.; Tsuzuki, S.; Nakamoto, T.; Iwamoto, N. Resurgenceof Respiratory Syncytial Virus infections during COVID-19 pandemic, Tokyo, Japan. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 2969–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grochowska, M.; Ambrożej, D.; Wachnik, A.; Demkow, U.; Podsiadły, E.; Feleszko, W. The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic lockdown on pediatric infections—A single-center retrospective study. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pappa, S.; Haidopoulou, K.; Zarras, C.; Theodorakou, E.; Papadimitriou, E.; Iosifidis, E.; Gkeka, I.; Stoikou, K.; Vagdatli, E.; Skoura, L.; et al. Early initiation of the respiratory syncytial virus season in 2021–2022, Greece. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 3453–3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Influenza Virus Characterization Summary Europe, March. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/sites/default/files/documents/Influenza-characterisation-report-march-2022.pdf (accessed on 25 July 2022).
- Pinky, L.; Hana, M.; Dobrovolny, H. Epidemiological Consequences of Viral Interference: A Mathematical Modeling Study of Two Interacting Viruses. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 830423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenhalgh, T.; Jimenez, J.; Prather, K.; Tufekci, Z.; Fisman, D.; Schoole, R. Ten scientific reasons in support of airborne transmission of SARS-CoV-2. Lancet 2021, 397, 1603–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, J.; Rhinehart, E.; Jackson, M.; Chiarello, L. Health Care Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee. 2007 Guideline for Isolation Precautions: Preventing Transmission of Infectious Agents in Health Care Settings. Am. J. Infect. Control. 2007, 35 (Suppl. S2), S65–S164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyeki, T.; Bernstein, H.; Bradley, J.; Englund, J.; File, T.; Fry, A.; Gravenstein, S.; Hayden, F.; Harper, S.; Hirshon, J.; et al. Clinical Practice Guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America: 2018 Update on Diagnosis, Treatment, Chemoprophylaxis, and Institutional Outbreak Management of Seasonal Influenza. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 68, e1–e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swets, M.; Russell, C.; Harrison, E.; Docherty, A.; Lone, N.; Girvan, M.; Hardwick, H.; ISARIC4C Investigators; Visser, L.; Openshaw, P.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 co-infection with influenza viruses, respiratory syncytial virus, or adenoviruses. Lancet 2022, 399, 1463–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, S.; Safamanesh, S.; Ghasemzadeh-Moghaddam, H.; Ghafouri, M.; Azimian, A. High prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 and influenza A virus (H1N1) coinfection in dead patients in Northeastern Iran. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 1008–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, H.; Zhang, M.; Xing, L.; Wang, K.; Rao, X.; Liu, H.; Tian, J.; Zhou, P.; Yan Deng, Y.; Shang, J. The epidemiology and clinical characteristics of co-infection of SARS-CoV-2 and influenza viruses in patients during COVID-19 outbreak. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 2870–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control: Testing Strategies for SARS-CoV-2. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/covid-19/surveillance/testing-strategies (accessed on 25 July 2022).
- WHO. Recommendations for National SARS-CoV-2 Testing Strategies and Diagnostic Capacities. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-2019-nCoV-lab-testing-2021.1-eng (accessed on 25 July 2022).
- QIAGEN Launches NeuMoDx Multiplex Test to Complete Range of SARS-CoV-2 Testing Solutions in Europe and Other Markets. Available online: https://corporate.qiagen.com/newsroom/press-releases/press-release-details/2020/QIAGEN-launches-NeuMoDx-multiplex-test-to-complete-range-of-SARS-CoV-2-testing-solutions-in-Europe-and-other-markets/default.aspx (accessed on 25 July 2022).
- NeuMoDx™ Flu A-B/RSV/SARS-CoV-2 Vantage Test Strip. Available online: https://www.neumodx.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/IFU_300900_NeuMoDx%E2%84%A2-Flu-A-B-RSV-SARS-CoV-2-Vantage-Test-Strip_40600444_B_US-Export.pdf (accessed on 25 July 2022).
- Coiras, M.T.; Perez-Brena, P.; Garcia, M.L.; Casas, I. Simultaneous detection of influenza A, B, and C viruses, respiratory syncytial virus, and adenoviruses in clinical samples by multiplex reverse transcription nested-PCR assay. J. Med. Virol. 2003, 69, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peret, T.C.; Hall, C.B.; Schnabel, K.C.; Golub, J.A.; Anderson, L.J. Circulation patterns of genetically distinct group A and B strains of human respiratory syncytial virus in a community. J. Gen. Virol. 1998, 79, 2221–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott RealTime SARS-CoV-2. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/136258/download (accessed on 25 July 2022).
- Fox, A.S.; Rao, S.N. Syndromic testing for the diagnosis of infectious diseases: The right test if used for the right patient. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2021, 76, iii2–iii3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protonotariou, E.; Mantzana, P.; Meletis, G.; Tychala, A.; Kassomenaki, A.; Vasilaki, O.; Kagkalou, G.; Gkeka, I.; Archonti, M.; Kati, S.; et al. Microbiological characteristics of bacteremias among COVID-19 hospitalized patients in a tertiary referral hospital in Northern Greece during the second epidemic wave. FEMS Microbes 2021, 2, xtab021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinton, M.; Geahr, M.; Gluck, L.; Jarrett, J.; Mostafa, H.H. Evaluation of the respiratory NeuMoDx™ Flu A-B/RSV/SARS-CoV-2 Vantage and Alinity m Resp-4-Plex assays. J. Clin. Virol. 2022, 150–151, 105164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sluimer, J.; Goderski, G.; van den Brink, S.; Broeders, M.; Rahamat-Langendoen, J.; Then, E.; Wijsman, L.; Wolters, F.; van de Bovenkamp, J.; Melchers, W.J.; et al. Multi-center evaluation of Cepheid Xpert® Xpress SARS-CoV-2/Flu/RSV molecular point-of-care test. J. Clin. Virol. Plus 2021, 1, 100042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; AlMutawa, F. Tracheal Aspirate and Bronchoalveolar Lavage as Potential Specimen Types for COVID-19 Testing Using the Cepheid Xpert Xpress SARS-CoV-2/Flu/RSV. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0039922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farfour, E.; Yung, T.; Baudoin, R.; Vasse, M. Evaluation of Four Fully Integrated Molecular Assays for the Detection of Respiratory Viruses during the Co-Circulation of SARS-CoV-2, Influenza and RSV. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriger, O.; Gefen-Halevi, S.; Leshem, E.; Smollan, G.; Belausov, N.; Egbarye, A.; Khashab, R.; Odeh, M.; Saffia, A.; Barak, Y.; et al. Viral co-pathogens in COVID-19 acute respiratory syndrome—What did we learn from the first year of pandemic? Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 116, 226–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherman, A.C.; Babiker, A.; Sieben, A.J.; Pyden, A.; Steinberg, J.; Kraft, C.S.; Koelle, K.; Kanjilal, S. The effect of SARS-CoV-2 mitigation strategies on seasonal respiratory viruses: A tale of two large metropolitan centers in the United States. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 72, e154–e157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozinska, A.; Wegrzynska, K.; Komiazyk, M.; Walory, J.; Wasko, I.; Baraniak, A. Viral Etiological Agent(s) of Respiratory Tract Infections in Symptomatic Individuals during the Second Wave of COVID-19 Pandemic: A Single Drive-Thru Mobile Collection Site Study. Pathogens 2022, 11, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.C.; Wang, C.Y.; Hsueh, P.R. Co-infections among patients with COVID-19: The need for combination therapy with non-anti-SARS-CoV-2 agents? J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2020, 53, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Liu, L.; Zhang, M.; Hu, Y.; Yang, Q.; Guo, J.; Guo, Y.; Dai, Y.; Xu, Y.; Cai, Y.; et al. Co-infections of SARS-CoV-2 with multiple common respiratory pathogens in infected patients. Sci. China Life Sci. 2020, 63, 606–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lansbury, L.; Lim, B.; Baskaran, V.; Lim, W.S. Co-infections in people with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Infect. 2020, 81, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidmann, M.D.; Berry, G.J.; Green, D.A.; Wu, F. Prevalence and clinical disease severity of respiratory coinfections during the Coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic. Adv. Mol. Path. 2022, 5, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omoush, S.A.; Alzyoud, J.A.M. The Prevalence and Impact of Coinfection and Superinfection on the Severity and Outcome of COVID-19 Infection: An Updated Literature Review. Pathogens 2022, 11, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, J. COVID-19: Researchers call for routine flu testing of hospital inpatients with SARS-CoV-2 infection. BMJ 2022, 376, o809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumbein, H.; Kümmel, L.S.; Fragkou, P.C.; Thölken, C.; Hünerbein, B.L.; Reiter, R.; Papathanasiou, K.A.; Renz, H.; Skevaki, C. Respiratory viral co-infections in patients with COVID-19 and associated outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Rev. Med. Virol. 2022, e2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meletis, G.; Pappa, S.; Gioula, G.; Exindari, M.; Haidopoulou, K.; Roilides, E.; Papadopoulou-Alataki, E.; Christoforidi, M.; Papa, A. Acute respiratory tract infections in SARS-CoV-2-negative children during the COVID-19 pandemic. Acta Microbiol. Hell. 2022, 67, 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- Papa, A.; Kotrotsiou, T.; Papadopoulou, E.; Reusken, C.; GeurtsvanKessel, C.; Koopmans, M. Challenges in laboratory diagnosis of acute viral central nervous system infections in the era of emerging infectious diseases: The syndromic approach. Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2016, 14, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
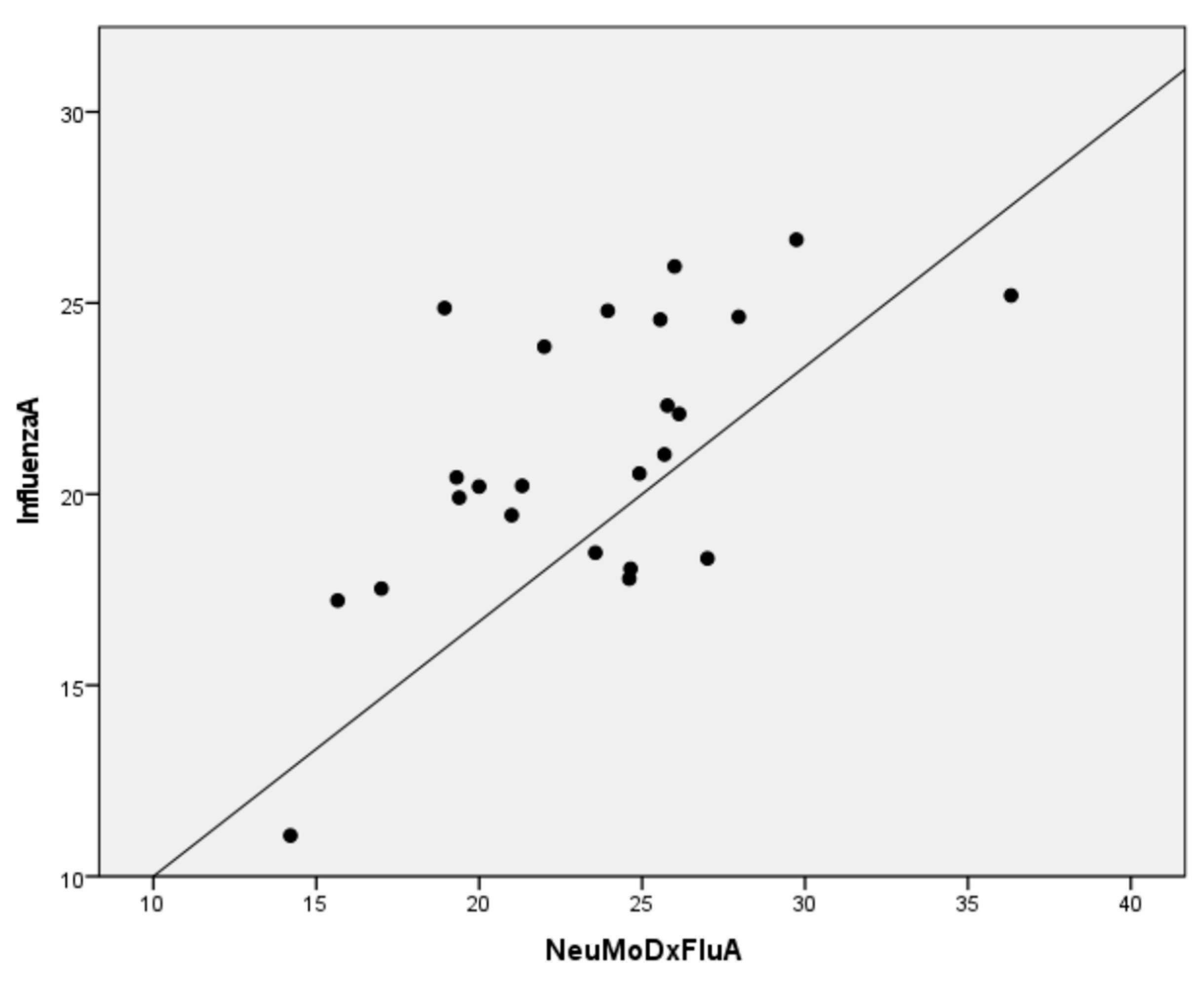
| Sample ID | Virus Type | Influenza A and B RT-PCR | NeuMoDx Flu A | NeuMoDx Flu B |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 69802 | AH3Ν2 | 20.22 | 21.32 | negative |
| 69931 | AH3Ν2 | 20.44 | 19.31 | negative |
| 70467 | AH3Ν2 | 11.07 | 14.21 | negative |
| 70393 | AH3Ν2 | 20.20 | 20.00 | negative |
| 70214 | AH3Ν2 | 25.96 | 26.00 | negative |
| 70310 | AH3Ν2 | 19.45 | 21.00 | negative |
| 70342 | AH3Ν2 | 23.86 | 22.00 | negative |
| 70381 | AH3Ν2 | 17.53 | 17.00 | negative |
| 70427 | AH3Ν2 | 19.91 | 19.39 | negative |
| 89962 | AH3Ν2 | 18.32 | 27.01 | negative |
| 89963 | AH3Ν2 | 22.32 | 25.78 | negative |
| 89965 | AH3Ν2 | 26.66 | 29.74 | negative |
| 89967 | AH3Ν2 | 22.10 | 26.14 | negative |
| 89968 | AH3Ν2 | 24.80 | 23.95 | negative |
| 89971 | AH3Ν2 | 24.87 | 18.94 | negative |
| 89950 | B | 20.63 | negative | 28.68 |
| 89955 | AH3Ν2 | 20.54 | 24.92 | negative |
| 89956 | AH3Ν2 | 24.64 | 27.97 | negative |
| 89958 | AH3Ν2 | 18.05 | 24.65 | negative |
| 89960 | AH3Ν2 | 21.04 | 25.69 | negative |
| 89961 | AH3Ν2 | 18.47 | 23.57 | negative |
| 89945 | AH3Ν2 | 17.79 | 24.61 | negative |
| 89946 | AH3Ν2 | 25.20 | 36.33 | negative |
| 89947 | AH3Ν2 | 24.57 | 25.56 | negative |
| 89948 | AH3Ν2 | 17.22 | 15.66 | negative |
| Sample ID | Virus Type | NeuMoDx RSV | NeuMoDx SARS-CoV-2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 83515 | RSV-A OΝ1 | 22.54 | negative |
| 83521 | RSV-A OΝ1 | 12.22 | negative |
| 83523 | RSV-A OΝ1 | 17.01 | negative |
| 83524 | RSV-A OΝ1 | 15.76 | negative |
| 83528 | RSV-A OΝ1 | 17.17 | negative |
| 83529 | RSV-A OΝ1 | 28.01 | negative |
| 83530 | RSV-A OΝ1 | 21.42 | negative |
| 83531 | RSV-A OΝ1 | 24.38 | negative |
| 83532 | RSV-A OΝ1 | 16.36 | negative |
| 83533 | RSV-A OΝ1 | 11.96 | negative |
| 83534 | RSV-A OΝ1 | 23.73 | negative |
| 83535 | RSV-A OΝ1 | 13.24 | negative |
| 83536 | RSV-A OΝ1 | 16.36 | negative |
| 83537 | RSV-A OΝ1 | 20.94 | negative |
| 83538 | RSV-B BA | 16.60 | negative |
| 83539 | RSV-B BA | 16.73 | negative |
| 83541 | RSV-A OΝ1 | 26.91 | negative |
| 83542 | RSV-A OΝ1 | 28.53 | negative |
| 83543 | RSV-A OΝ1 | 20.62 | negative |
| 83545 | RSV-A OΝ1 | 30.17 | negative |
| 83547 | RSV-A OΝ1 | 18.24 | 17.21 |
| 83550 | RSV-A OΝ1 | 24.30 | negative |
| 83552 | RSV-A OΝ1 | 25.69 | negative |
| 83553 | RSV-A OΝ1 | 29.42 | negative |
| 83556 | RSV-A OΝ1 | 20.93 | negative |
| 83558 | RSV-A OΝ1 | 28.64 | negative |
| 83562 | RSV-A OΝ1 | 24.43 | negative |
| 83630 | RSV-A OΝ1 | 12.56 | negative |
| 83564 | RSV-A OΝ1 | 13.71 | negative |
| 83568 | RSV-A OΝ1 | 31.50 | negative |
| 83570 | RSV-B | negative | negative |
| 83572 | RSV-B BA | 30.20 | negative |
| 83574 | RSV-B BA | 30.00 | negative |
| 83576 | RSV-B BA | 29.06 | negative |
| 83597 | RSV-B BA | 29.09 | negative |
| 83578 | RSV-A OΝ1 | 32.11 | negative |
| 83580 | RSV-B BA | 23.16 | negative |
| 83582 | RSV-A OΝ1 | 27.37 | negative |
| 83584 | RSV-A OΝ1 | 28.00 | negative |
| 83586 | RSV-B BA | 30.03 | negative |
| 83588 | RSV-A OΝ1 | 31.35 | negative |
| 83590 | RSV-A OΝ1 | 26.39 | negative |
| 83592 | RSV-A | negative | negative |
| 83593 | RSV-A OΝ1 | 28.97 | negative |
| 83594 | RSV-A OΝ1 | 25.94 | negative |
| 83596 | RSV-B | negative | negative |
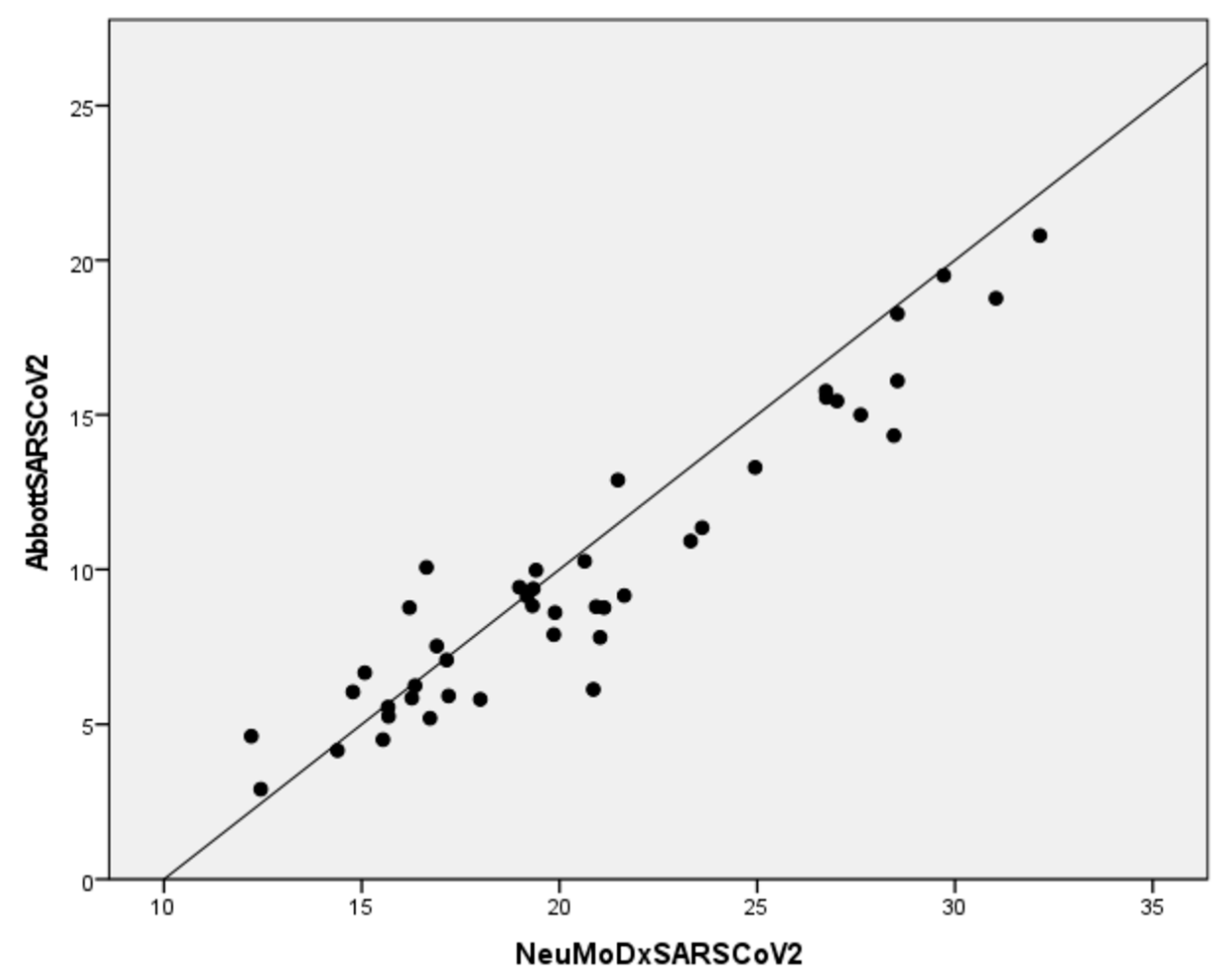
| Sample ID | Abbott RealTime SARS-CoV-2 | NeuMoDx SARS-CoV-2 |
|---|---|---|
| 49437 | 7.90 | 19.86 |
| 49519 | 8.77 | 21.13 |
| 45713 | 7.08 | 17.15 |
| 45714 | 4.51 | 15.54 |
| 45715 | 6.13 | 20.86 |
| 45329 | 8.80 | 20.93 |
| 45216 | 9.38 | 19.34 |
| 44819 | 6.67 | 15.08 |
| 44439 | 9.43 | 18.99 |
| 44061 | 5.26 | 15.68 |
| 44056 | 9.14 | 19.18 |
| 42996 | 5.20 | 16.73 |
| 42478 | 10.07 | 16.64 |
| 42415 | 10.27 | 20.64 |
| 42475 | 5.92 | 17.20 |
| 37996 | 5.56 | 15.67 |
| 37960 | 4.62 | 12.21 |
| 37636 | 8.77 | 16.21 |
| 37637 | 7.53 | 16.90 |
| 37416 | 9.16 | 21.64 |
| 37395 | 4.16 | 14.39 |
| 37400 | 5.85 | 16.27 |
| 37413 | 6.05 | 14.78 |
| 37360 | 2.91 | 12.45 |
| 37359 | 6.25 | 16.35 |
| 273620 | 18.77 | 31.04 |
| 273616 | 13.30 | 24.95 |
| 273557 | 19.51 | 29.72 |
| 273615 | 11.35 | 23.61 |
| 273245 | 18.27 | 28.55 |
| 273468 | 16.10 | 28.55 |
| 273457 | 15.56 | 26.75 |
| 273418 | 14.33 | 28.46 |
| 273237 | 12.89 | 21.48 |
| 273076 | 15.77 | 26.74 |
| 273072 | 15.00 | 27.62 |
| 272923 | 5.81 | 18.00 |
| 272565 | 15.45 | 27.02 |
| 271235 | 20.80 | 32.15 |
| 273555 | 9.98 | 19.41 |
| 271076 | 10.92 | 23.32 |
| 271027 | 8.83 | 19.32 |
| 271024 | 8.61 | 19.89 |
| 271023 | 7.81 | 21.03 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meletis, G.; Tychala, A.; Gkeka, I.; Gkotzia, A.; Triantafyllou, A.; Pappa, S.; Exindari, M.; Gioula, G.; Papa, A.; Skoura, L. Clinical Performance Evaluation of the NeuMoDx Flu A-B/RSV/SARS-CoV-2 Vantage Assay. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 3201. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123201
Meletis G, Tychala A, Gkeka I, Gkotzia A, Triantafyllou A, Pappa S, Exindari M, Gioula G, Papa A, Skoura L. Clinical Performance Evaluation of the NeuMoDx Flu A-B/RSV/SARS-CoV-2 Vantage Assay. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(12):3201. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123201
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeletis, Georgios, Areti Tychala, Ioanna Gkeka, Athanasia Gkotzia, Aikaterini Triantafyllou, Styliani Pappa, Maria Exindari, Georgia Gioula, Anna Papa, and Lemonia Skoura. 2022. "Clinical Performance Evaluation of the NeuMoDx Flu A-B/RSV/SARS-CoV-2 Vantage Assay" Diagnostics 12, no. 12: 3201. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123201
APA StyleMeletis, G., Tychala, A., Gkeka, I., Gkotzia, A., Triantafyllou, A., Pappa, S., Exindari, M., Gioula, G., Papa, A., & Skoura, L. (2022). Clinical Performance Evaluation of the NeuMoDx Flu A-B/RSV/SARS-CoV-2 Vantage Assay. Diagnostics, 12(12), 3201. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123201










