Neonatal Sepsis Caused by Streptococcus gallolyticus Complicated with Pulmonary Hypertension: A Case-Report and a Systematic Literature Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Case Presentation
3. Literature Review
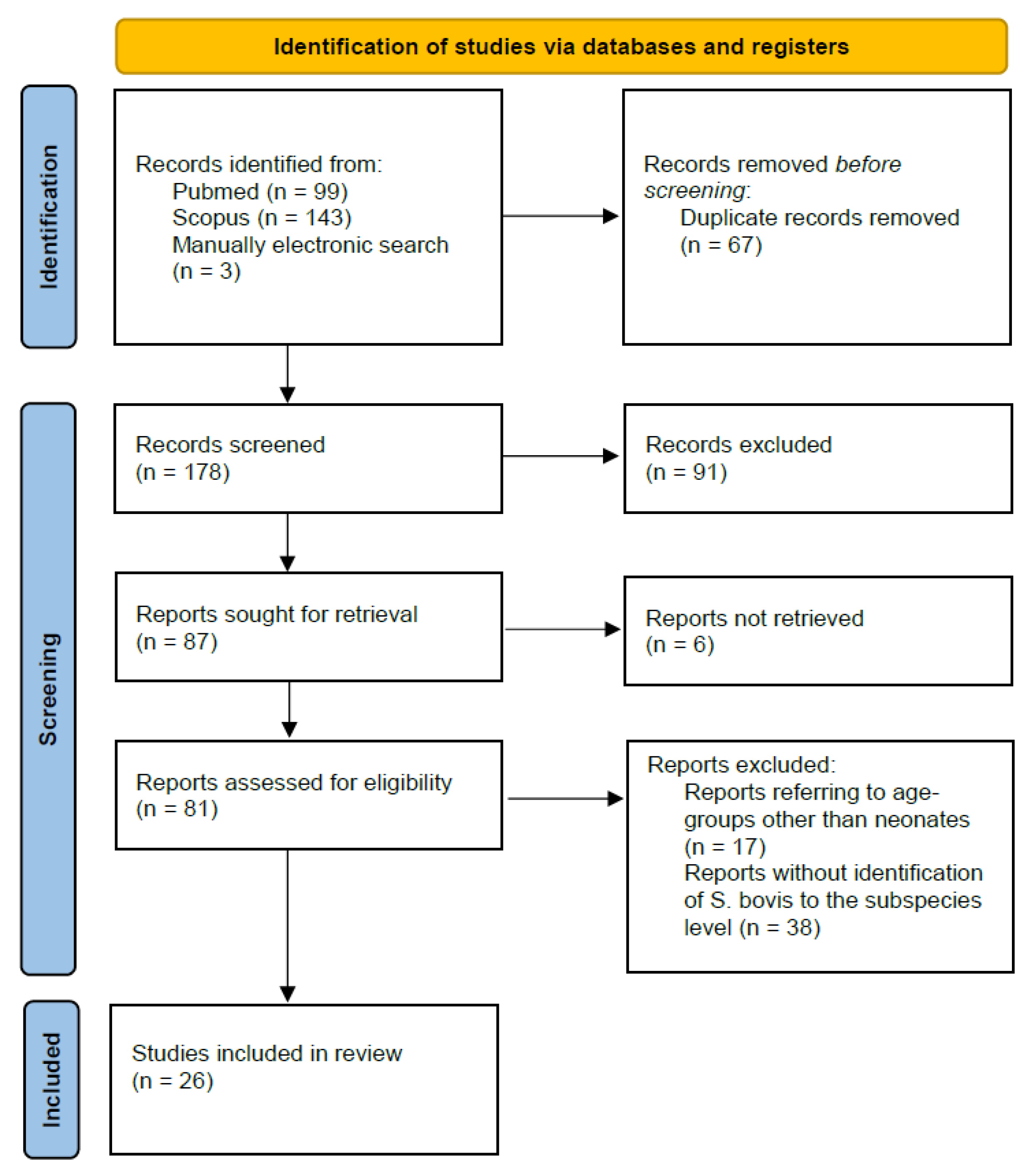
3.1. Materials and Methods
3.2. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dekker, J.P.; Lau, A.F. An Update on the Streptococcus bovis Group: Classification, Identification, and Disease Associations. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 1694–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saegeman, V.; Cossey, V.; Loens, K.; Schuermans, A.; Glaser, P. Streptococcus gallolyticus subsp. Pasteurianus Infection in A Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2016, 35, 1272–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, M.; Pelot, M.; Nadarajah, R.; Kohl, S. Neonate with Late Onset Streptococcus bovis Meningitis: Case Report and Review of the Literature. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2000, 19, 891–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, T.H.; Ho, S. Streptococcus bovis Meningitis in a Neonate with Ivemark Syndrome. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2002, 34, 63–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavin, P.J.; Thomson, R.B.; Horng, S.J.; Yogev, R. Neonatal sepsis caused by Streptococcus bovis variant (biotype 11/2): Report of a case and review. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 3433–3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onoyama, S.; Ogata, R.; Wada, A.; Saito, M.; Okada, K.; Harada, T. Neonatal bacterial meningitis caused by Streptococcus gallolyticus subsp. pasteurianus. J. Med. Microbiol. 2009, 58, 1252–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A. Relative Penicillin Resistance in Streptococcus bovis. A Case of Neonatal Meningitis. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2009, 45, 474–475. [Google Scholar]
- Floret, N.; Bailly, P.; Thouverez, M.; Blanchot, C.; Alez-Martin, D.; Menget, A.; Thiriez, G.; Hoen, B.; Talon, D.; Bertrand, X. A cluster of bloodstream infections caused by Streptococcus gallolyticus subspecies pasteurianus that involved 5 preterm neonates in a university hospital during a 2-month period. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2010, 31, 194–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klatte, J.M.; Clarridge, J.E.; Bratcher, D.; Selvarangan, R. A longitudinal case series description of meningitis due to Streptococcus gallolyticus subsp. pasteurianus in infants. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagamatsu, M.; Takagi, T.; Ohyanagi, T.; Yamazaki, S.; Nobuoka, S.; Takemura, H.; Akita, H.; Miyai, M.; Ohkusu, K. Neonatal meningitis caused by Streptococcus gallolyticus subsp. pasteurianus. J. Infect. Chemother. 2012, 18, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thatrimontrichai, A.; Chanvitan, P.; Janjindamai, W.; Dissaneevate, S.; Maneenil, G. Early onset neonatal bacterial meningitis caused by streptococcus gallolyticus subsp. pasteurianus. Southeast Asian J. Trop Med. Public Health 2012, 43, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tarakçi, N.; Daǎi, H.T.; Uǧur, A.R.; Tuncer, I.; Taştekin, A. Late-onset Streptococcus pasteurianus sepsis in a preterm baby in a neonatal intensive care unit. Turk. Arch. Pediatr. 2014, 49, 157–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hede, S.V.; Olarte, L.; Chandramohan, L.; Kaplan, S.L.; Hulten, G. Streptococcus gallolyticus subsp. pasteurianus infection in twin infants. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 1419–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.W.; Eun, S.H.; Kim, E.C.; Seong, M.W.; Kim, Y.K. Neonatal invasive Streptococcus gallolyticus subsp. pasteurianus infection with delayed central nervous system complications. Korean J. Pediatr. 2015, 58, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, G.J.; Kavanagh, K.L.; Kashimawo, L.A.; Cripe, P.J.; Steele, R.W. An Unlikely Cause of Neonatal Sepsis. Clin. Pediatr. 2015, 54, 1017–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beneteau, A.; Levy, C.; Foucaud, P.; Béchet, S.; Cohen, R.; Raymond, J.; Dommergues, M.-A. Childhood meningitis caused by Streptococcus bovis group: Clinical and biologic data during a 12-year period in France. J. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. 2015, 34, 136–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parain, D.; De La Villeon, G.; Pinto Cardoso, G.; Abily Donval, L.; Marret, S.; Pinquier, D. Neonatal Meningoencephalitis Caused by Streptococcus gallolyticus. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2016, 35, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamura, Y.; Mihara, Y.; Nakatani, K.; Nishiguchi, T.; Ikebe, T. Unexpected Ventriculitis Complication of Neonatal Meningitis Caused by Streptococcus gallolyticus subsp. pasteurianus: A Case Report. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 71, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mettananda, S.; Kamalanathan, P.; Namalie, K.D. Streptococcus bovis—Unusual etiology of meningitis in a neonate with Down syndrome: A case report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2018, 12, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, M.T.; Idriss, S.; Guzman, E.; De Oliveira, E.R. Neonatal meningitis, endocarditis, and pneumonitis due to Streptococcus gallolyticus subsp. pasteurianus: A case report. BMC Pediatr. 2019, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sim, J.Y.; Wang, L.-W.; Chow, J.C.; Hsu, W.-Y.; Chen, Y.-C.; Chang, Y.-H.; Chou, Y.; Chen, W.-Y.; Tang, H.-J.; Chang, T.-H. Streptococcus Gallolyticus—A potentially neglected pathogen causing neonatal sepsis not covered by routine group B streptococcus screening. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2021, 54, 1190–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.-C.; Lee, P.-I.; Lin, H.-C.; Chang, L.-Y.; Lee, T.-F.; Chen, J.-M.; Hsueh, P.-R. Clustering of Streptococcus gallolyticus subspecies pasteurianus bacteremia and meningitis in neonates. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2021, 54, 1078–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geetha, O.; Cherie, C.; Natalie, T.W.H.; Merchant, K.; Chien, C.M.; Chandran, S. Streptococcus gallolyticus subspecies pasteurianus causing early onset neonatal sepsis complicated by solitary liver abscess in a preterm infant. Access Microbiol. 2021, 3, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srour, N.; Dasnadi, S.; Korulla, A.; Shah, P.J. Early-onset neonatal ventriculomeningitis due to Streptococcus gallolyticus: A case report. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2022, 63, 430–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, C.; Sakaria, R.P.; Pourcyrous, M. Early-Onset Fulminant Sepsis in a Preterm Neonate due to Streptococcus gallolyticus: A Case Report and Literature Review. AJP Rep. 2022, 12, E117–E122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orbea, M.; Desai, N.; Foster, C. Invasive Streptococcus gallolyticus Infections in Infants At Texas Children’s Hospital: A 9-Year Retrospective Review. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2022, 41, e494–e497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasi, S.; Abid FBen Wilson, G.J.; Zaqout, A.; Nair, A.P.; Chitrambika, P. Intrauterine infection and postpartum bacteremia due to Streptococcus gallolyticus subsp. gallolyticus: An emerging concern. IDCases. 2022, 29, e01562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlegel, L.; Grimont, F.; Ageron, E.; Grimont, P.A.D.; Bouvet, A. Reappraisal of the taxonomy of the Streptococcus bovis/Streptococcus equinus complex and related species: Description of Streptococcus gallolyticus subsp. gallolyticus subsp. nov., S. gallolyticus subsp. macedonicus subsp. nov. and S. gallolyticus subsp. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2003, 53, 631–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, M.; Frodl, R.; Funke, G. Comprehensive study of strains previously designated Streptococcus bovis consecutively isolated from human blood cultures and emended description of Streptococcus gallolyticus and Streptococcus infantarius subsp. coli. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 2966–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funke, G.; Funke-Kissling, P. Performance of the new VITEK 2 GP card for identification of medically relevant gram-positive cocci in a routine clinical laboratory. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, B.; Morosini, M.-I.; Loza, E.; Rodríguez-Baños, M.; Navas, E.; Cantón, R.; del Campo, R. Reidentification of Streptococcus bovis isolates causing bacteremia according to the new taxonomy criteria: Still an issue? J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 3228–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumke, J.; Vollmer, T.; Akkermann, O.; Knabbe, C.; Dreier, J. Case-control study: Determination of potential risk factors for the colonization of healthy volunteers with Streptococcus gallolyticus subsp. gallolyticus. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Simonsen, K.A.; Anderson-berry, A.L.; Delair, S.F.; Davies, D.H. Early-Onset Neonatal Sepsis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 21–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fikar, C.R.; Levy, J. Streptococcus bovis meningitis in a neonate. Am. J. Dis. Child. 1979, 133, 1149–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binghuai, L.; Wenjun, S.; Xinxin, L. Intrauterine infection and post-partum bacteraemia due to Streptococcus gallolyticus subsp. pasteurianus. J. Med. Microbiol. 2013, 62 Pt 10, 1617–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakshminrusimha, S.; Keszler, M. Persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn. Neoreviews 2015, 16, 680–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshpande, S.; Suryawanshi, P.; Holkar, S.; Singh, Y.; Yengkhom, R.; Klimek, J.; Gupta, S. Pulmonary hypertension in late onset neonatal sepsis using functional echocardiography: A prospective study. J. Ultrasound. 2022, 25, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohsen, A.A.; Amin, A. Risk factors and outcomes of persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn in neonatal intensive care unit of al-minya university hospital in Egypt. J. Clin. Neonatol. 2013, 2, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Russa, R.; Maiese, A.; Viola, R.V.; De Matteis, A.; Pinchi, E.; Frati, P.; Fineschi, V. Searching for highly sensitive and specific biomarkers for sepsis: State-of-the-art in post-mortem diagnosis of sepsis through immunohistochemical analysis. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2019, 33, 2058738419855226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MMaiese, A.; Del Nonno, F.; Dell’Aquila, M.; Moauro, M.; Baiocchini, A.; Mastracchio, A.; Bolino, G. Postmortem diagnosis of sepsis: A preliminary immunohistochemical study with an anti-procalcitonin antibody. Leg Med. 2017, 28, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| First Author, Publication Year | GA | Birth Weight (Grams) | Mode of Delivery | Length of Rupture of Membranes | Maternal Vaginal Cultures | Maternal Peripartum Antibiotics | Symptoms Onset Time (Days) | Clinical Signs and Symptoms | Site of Isolation | Diagnosis | Microorganism | Complications | Definitive Antibiotic Treatment | Patient Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gavin, 2003 [5] | Term | 3.925 | Vaginal delivery | <18 h | GBS (-) | N/A | 3 | Fever, irritability, poor oral intake, decreased urine output | Blood, CSF | Biochemical tests (RapID STR, Vitek 2, API 20 Strep, CFA profile) | S. bovis biotype II/2 | Meningitis, Seizure-like episodes | Penicillin G for 14 days | Full recovery |
| Khan, 2009 [7] | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 3 | Apnoeic episodes, lethargy | Blood, CSF | Biochemical tests (API 20 Strep kit) | S. gallolyticus subsp. pasteurianus | Meningitis | Penicillin and gentamicin for 14 days | Recovery |
| Klatte, 2012 [9] | Term | N/A | Vaginal delivery | 3 h | N/A | N/A | 2 | Poor feeding, lethargy, seizure activity | Blood, CSF | Βiochemical tests (Vitek 2), molecular tests (16S rRNA sequencing) | S. gallolyticus subsp. pasteurianus | Meningitis | Ampicillin for 16 days, cefotaxime for 6 days | Recovery |
| Thatrimontrichai, 2012 [11] | 39 weeks | 3.188 | Vaginal delivery | <18 h | Gamma Streptococci not in group D (after onset of neonatal symptoms) | N/A | 2 | Fever, lethargy, poor feeding, slightly bulging anterior fontanel | CSF, maternal urine | N/A | S. gallolyticus subsp. pasteurianus | Meningitis, right IVH grade I | Cefotaxime for 14 days and gentamicin for 5 days | Recovery |
| Beneteau, 2015 [16] | 10 preterm and 5 term neonates * | 2.160 (1.860–3.430) for neonates with symptoms onset <4 days, 2.240 (1.480–3.570) for neonates with symptoms onset >4 and ≤28 days | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 3 neonates ≤ 4 days, 12 neonates >4 and ≤28 days | Fever, hypothermia, digestive signs, respiratory signs, irritability, neurologic signs, sepsis | Blood and/or CSF | N/A | S. gallolyticus pasteurianus in 8 cases and S. gallolyticus gallolyticus in 2 cases ** | Meningitis | Amoxicillin and/or 3rd generation cephalosporin and aminoglycocide for 10–25 days | All neonates survived |
| Nguyen, 2019 [20] | 39+1 weeks | 4.195 | Vaginal delivery | 12 h | GBS (-) | N/A | 1 | Respiratory distress | Blood | N/A | S. gallolyticus subsp. pasteurianus | Meningitis, endocarditis | Cefepime for 28 days and gentamicin for 14 days | Recovery without sequelae |
| 40+1 weeks | 3.250 | Vaginal delivery | 4 h | GBS unknown | No | 1 | Poor respiratory effort, irritability | Blood | N/A | S. gallolyticus subsp. pasteurianus | Septic shock, PPHN | Cefepime and clindamycin for 14 days | Recovery without sequelae | |
| Sim, 2021 [21] | 39 weeks | 3.374 | Vaginal delivery | <18 h | GBS (-) | No | 1 | Respiratory distress | Blood, CSF | Βiochemical tests (MALDI-TOF) | S. gallolyticus | Meningitis | Vancomycin | Recovery without sequelae |
| Chen, 2021 [22] | 35+1 weeks | N/A | Cesarean section | N/A | N/A | N/A | 3 | Apnea, desaturation | Blood | Βiochemical tests (MALDI-TOF), molecular tests (16S rRNA and sodA gene sequencing, PCR-RFLP assays of groESL gene) | S. gallolyticus subsp. pasteurianus | None | Ampicillin and cefotaxime for 14 days | Recovery without sequelae |
| 37+3 weeks | N/A | Cesarean section | N/A | GBS (+) | No | 2 | Tachypnea, desaturation, poor activity, fever | Blood, CSF | Βiochemical tests (MALDI-TOF), molecular tests (16S rRNA and sodA gene sequencing, PCR-RFLP assays of groESL gene) | S. gallolyticus subsp. pasteurianus | Meningitis | Ampicillin and cefotaxime for 14 days | Recovery without sequelae | |
| Geetha, 2021 [23] | 36+6 weeks | 3.776 | Vaginal delivery | <18 h | GBS (-) | No | 1 | Respiratory distress | Blood | Biochemical tests (MALDI-TOF, Vitek) | S. gallolyticus subsp. pasteurianus | Liver abscess | Cefotaxime for 5 weeks, co-amoxiclav for 3 weeks | Recovery without sequelae |
| Srour, 2022 [24] | 36+4 weeks | 3.720 | Vaginal delivery | <18 h | GBS (-) | N/A | 1 | Intermittent cyanosis, hypothermia, tachypnea | Blood, CSF | N/A | S. gallolyticus | Meningitis, ventriculitis, seizure-like activity | Penicillin G for 21 days | Recovery without sequelae |
| Williams, 2022 [25] | 26 weeks | 950 | Vaginal delivery | PPROM 12 days | GBS (-) | IV ampicillin for 2 days and pos amoxicillin for 5 days and a single dose of azithromycin | 1 | Poor respiratory effort, metabolic and respiratory acidosis | Blood | Βiochemical tests (MALDI-TOF) | S. gallolyticus | Septic shock | Ampicillin and gentamicin (empirical treatment) | Deceased neonate |
| Orbea, 2022 [26] | N/A (9 neonates) *** | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | Median age 24 days (1–74 days) | Fever, irritability, difficulty feeding, lethargy, respiratory distress, apnea, seizure-like activity, emesis, diarrhea | Blood and/or CSF | Biochemical tests (MALDI-TOF, Vitek) | S. gallolyticus, S. gallolyticus subsp. pasteurianus **** | Meningitis (11 infants), bilateral grade III IVH (1neonate), ventriculitis and subdural collection and/or subarachnoid debris (3 neonates) ***** | Antibiotic therapy for a median of 14 days (9–28 days) | One deceased neonate, one neonate with neurologic complications |
| Sasi, 2022 [27] | 37 weeks | 3.125 | Vaginal delivery | N/A | N/A | N/A | 1 | Tachycardia, tachypnea, poor sucking | Maternal blood cultures, placental tissue culture, no growth in neonatal blood culture | Biochemical tests (MALDI-TOF) | S. gallolyticus subsp. gallolyticus | None | Ampicillin and amikacin for 5 days | Recovery without sequelae |
| 38 weeks | 2.670 | Vaginal delivery | 3 h | N/A | N/A | 1 | Tachycardia, tachypnea | Maternal blood cultures, no growth in neonatal blood culture | Biochemical tests (MALDI-TOF) | S. gallolyticus subsp. gallolyticus | None | Ampicillin and amikacin for 7 days | Recovery without sequelae | |
| 39 weeks | 3.620 | Cesarean section | N/A | N/A | N/A | 1 | Respiratory distress | Maternal blood and urine cultures, no growth in neonatal blood culture | Biochemical tests (MALDI-TOF) | S. gallolyticus subsp. gallolyticus | Meningitis | Ampicillin and amikacin for 10 days | Recovery without sequelae | |
| 41 weeks | 4.170 | Cesarean section | N/A | N/A | N/A | 1 | Fever, tachycardia, respiratory distress | Maternal blood cultures, placental tissue culture, no growth in neonatal blood culture | Biochemical tests (MALDI-TOF) | S. gallolyticus subsp. gallolyticus | Pneumonia | Ampicillin and amikacin for 5 days | Recovery without sequelae | |
| This case | 38+1 weeks | 3.250 | Cesarean section | 10 h | GBS (-) | No | 1 | Respiratory distress, poor feeding, fever | Blood | Biochemical tests (Vitek 2) | S. gallolyticus | PPHN | Ampicillin and cefotaxime for 10 days | Recovery |
| First Author, Publication Year | GA | Birth Weight (Grams) | Mode of Delivery | Length of Rupture of Membranes | Maternal Vaginal Cultures | Maternal Peripartum Antibiotics | Symptoms Onset Time (Days) | Clinical Signs and Symptoms | Site of Isolation | Diagnosis | Microorganism | Complications | Definitive Antibiotic Treatment | Patient Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cheung, 2000 [3] | 32 weeks | 2.340 | Vaginal delivery | N/A | N/A | Prophylactic clindamycin | 28 | Lethargy, possible seizure activity, apnea | Blood, CSF | Biochemical tests (API 20 strep, cellular fatty acid profile) | S. bovis biotype II | Meningitis | Ampicillin and gentamicin changed to penicillin for 18 days | Recovery without sequelae |
| Koh, 2002 [4] | 34 weeks | 1.675 | Cesarean section | N/A | N/A | N/A | 19 | Lethargy, apnea | Blood, CSF | Biochemical tests (API 20 strep test) | S. bovis biotype II | Meningitis | Penicillin G for 14 days | Recovery without sequelae |
| Onoyama, 2009 [6] | Term | 3.192 | Vaginal delivery | <18 h | GBS (-) | N/A | 4 | Fever, poor activity | Blood, CSF | Biochemical tests (API 20 Strep test), molecular tests (16S rRNA and sodA gene sequencing) | S. gallolyticus subsp. pasteurianus | Meningitis | Cefotaxime for 14 days | Recovery without sequelae |
| Floret, 2010 [8] | 5 preterm | N/A | 3 vaginal deliveries, 2 cesarean sections | N/A | N/A | N/A | Median age 18 days (13–56) | Abdominal distention, diarrhea, signs of umbilical inflammation | Blood | Molecular tests (sodA gene sequencing, 16S rRNA gene sequencing, PFGE) | S. gallolyticus subsp. pasteurianus | N/A | Cefotaxime for 10 days | All neonates survived |
| Klatte, 2012 [9] | Term | N/A | Vaginal delivery | N/A | N/A | N/A | 12 | Congestion, increased work of breathing, lethargy | CSF | Βiochemical tests (Vitek 2), molecular tests (16S rRNA sequencing) | S. gallolyticus subsp. pasteurianus | Meningitis | Cefotaxime for 16 days | Recovery |
| Term | N/A | Vaginal delivery | N/A | N/A | N/A | 4 | Fever, seizure-like activity | Blood, CSF | Βiochemical tests (Vitek 2), molecular tests (16S rRNA sequencing) | S. gallolyticus subsp. pasteurianus | Meningitis | Ampicillin for 14 days | Recovery | |
| Post-term | N/A | Vaginal delivery | 13 h | N/A | N/A | 4 | Fever, rhinorrhea, fussiness | Blood, CSF | Βiochemical tests (Vitek 2), molecular tests (16S rRNA sequencing) | S. gallolyticus subsp. pasteurianus | Meningitis | Cefotaxime for 14 days | Recovery | |
| Nagamatsu, 2012 [10] | Term | 3.092 | Vaginal delivery | N/A | N/A | N/A | 8 | Superior tonic eye deviation, fever, irritability, decreased oral intake | CSF | Βiochemical tests (API Rapid ID 32 Strep, VITEK 2), molecular tests (16S rRNA gene sequencing) | S. gallolyticus subsp. pasteurianus | Meningitis, seizures | Ampicillin for 20 days and panipenem/ betamipron for 14 days | Recovery without sequelae |
| Tarakci, 2014 [12] | 30 weeks | 1.300 | Cesarean section | N/A | N/A | N/A | 37 | Apnea, lethargy, cyanosis, superficial respiration | Blood | N/A | S. gallolyticus subsp. pasteurianus | None | Meropenem for 14 days | Recovery |
| Hede, 2015 [13] | 32 weeks | 1.474 | Cesarean section | N/A | GBS unknown | No | 24 | Intermittent tachypnea | Blood | Βiochemical tests (Vitek 2), molecular tests (16S rRNA sequencing, PFGE) | S. gallolyticus subsp. pasteurianus | None | Ampicillin for 10 days | Survived |
| 32 weeks | 2.120 | Cesarean section | N/A | GBS unknown | No | 24 | Pale color, loose stools, respiratory distress, hypoxemia, hypothermia | Blood, CSF | Βiochemical tests (Vitek 2), molecular tests (16S rRNA sequencing, PFGE) | S. gallolyticus subsp. pasteurianus | Meningitis, acute respiratory failure, septic shock, seizures, grade III IVH | Ampicillin for 14 days | Survived | |
| Park, 2015 [14] | 38+4 weeks | 3.600 | Vaginal delivery | N/A | N/A | N/A | 27 | Fever, lethargy, moaning sounds | Blood, CSF, urine | Μolecular tests (16S rRNA gene sequencing) | S. gallolyticus subsp. pasteurianus | Meningitis, bilateral reduction in visual evoked potentials, subdural effusion and seizures | Ampicillin and cefotaxime for 21 days, ampicillin and cefotaxime for 31 days due to CNS complications | Discharge, improvement of visual evoked potential in follow-up |
| Kennedy, 2015 [15] | 37 weeks | 3.050 | Vaginal delivery | 6 h | GBS (-) | N/A | 4 | Lethargy, irritability, decreased urine output, poor feeding, fever | Blood, CSF | Βiochemical tests (RapID STR), molecular tests (16S rRNA gene sequencing) | S. gallolyticus subsp. pasteurianus | Meningitis | Ampicillin for 14 days | Recovery without sequelae |
| Beneteau, 2015 [16] | 10 preterm and 5 term neonates * | 2.160 (1.860–3.430) for neonates with symptoms onset <4 days, 2.240 (1.480–3.570) for neonates with symptoms onset >4 and ≤28 days | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 3 neonates ≤ 4 days, 12 neonates >4 and ≤28 days | Fever, hypothermia, digestive signs, respiratory signs, irritability, neurologic signs, sepsis | Blood and/or CSF | N/A | S. gallolyticus pasteurianus in 8 cases and S. gallolyticus gallolyticus in 2 cases ** | Meningitis | Amoxicillin and/or 3rd generation cephalosporin and aminoglycocide for 10–25 days | All neonates survived |
| Parain, 2016 [17] | Term | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 28 | Altered consciousness, hypertonic limbs, bulging fontanel | CSF | N/A | S. gallolyticus | Meningitis, hydrocephalus with tetraventricular dilatation requiring external ventricular drainage, recurrence of hydrocephalus requiring ventriculoperitoneal bypass | Cefotaxime for 17 days and amikacin for 2 days | Recovery with neurologic complications (neuromotor delay with poor spontaneous motor mobilization and hypertonia of the limbs at 9 months) |
| Saegeman, 2016 [2] | 30 weeks | N/A | Vaginal delivery | N/A | N/A | N/A | 7 | Hemodynamic instability | Blood | Βiochemical tests (MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry), molecular tests (PFGE, 16S rRNA gene sequencing) | S. gallolyticus subsp. pasteurianus | Meningitis | N/A | Recovery |
| 32 weeks | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 34 | Septic shock, respiratory failure, pulmonary hemorrhage | Blood | Βiochemical tests (MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry), molecular tests (PFGE, 16S rRNA gene sequencing) | S. gallolyticus subsp. pasteurianus | Septic shock | N/A | Deceased neonate | |
| Yamamura, 2018 [18] | Term | 3.680 | Vaginal delivery | N/A | N/A | N/A | 27 | Fever, lethargy, irritability | Blood, CSF | Βiochemical tests (API 20 Strep test), molecular tests (16s rRNA gene sequencing) | S. gallolyticus subsp. pasteurianus | Meningitis, ventriculitis | Ampicillin for 21 days | Recovery without sequelae |
| Mettananda, 2018 [19] | 34 weeks | 1.680 | Cesarean section | N/A | N/A | N/A | 25 | Fever, poor sucking, reduced activity | Blood | Βiochemical tests | S. bovis biotype II | Meningitis | Penicillin G and cefotaxime for 21 days | Recovery without sequelae |
| Sim, 2021 [21] | 39 weeks | 3.268 | Vaginal delivery | <18 h | GBS (-) | No | 4 | Fever, respiratory distress | Blood, CSF | Βiochemical tests (MALDI-TOF) | S. gallolyticus | Meningitis | Ampicillin | Recovery without sequelae |
| 39 weeks | 3.194 | Vaginal delivery | <18 h | GBS (-) | No | 23 | Fever, lethargy | Blood | Βiochemical tests (MALDI-TOF) | S. gallolyticus | None | Ampicillin | Recovery without sequelae | |
| 34 weeks | 1.812 | Cesarean section | <18 h | GBS (-) | No | 15 | Fever, poor feeding | Blood | Βiochemical tests (MALDI-TOF) | S. gallolyticus | None | Clindamycin | Recovery without sequelae | |
| Chen, 2021 [22] | 37+3 weeks | N/A | Cesarean section | N/A | GBS (+) | No | 5 | Fever, tachypnea | CSF | Βiochemical tests (MALDI-TOF), molecular tests (16S rRNA and sodA gene sequencing, PCR-RFLP assays of groESL gene) | S. gallolyticus subsp. pasteurianus | Meningitis | Ampicillin and cefotaxime for 14 days | Recovery without sequelae |
| Orbea, 2022 [26] | N/A (9 neonates) *** | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | Median age 24 days (1–74 days) | Fever, irritability, difficulty feeding, lethargy, respiratory distress, apnea, seizure-like activity, emesis, diarrhea | Blood and/or CSF | Biochemical tests (MALDI-TOF, Vitek) | S. gallolyticus, S. gallolyticus subsp. pasteurianus **** | Meningitis (11 infants), bilateral grade III IVH (1neonate), ventriculitis and subdural collection and/or subarachnoid debris (3 neonates) ***** | Antibiotic therapy for a median of 14 days (9–28 days) | One deceased neonate, one neonate with neurologic complications |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iliodromiti, Z.; Tsaousi, M.; Kitsou, K.; Bouza, H.; Boutsikou, T.; Pouliakis, A.; Tsampou, E.; Oikonomidi, S.; Dagre, M.; Sokou, R.; et al. Neonatal Sepsis Caused by Streptococcus gallolyticus Complicated with Pulmonary Hypertension: A Case-Report and a Systematic Literature Review. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 3116. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123116
Iliodromiti Z, Tsaousi M, Kitsou K, Bouza H, Boutsikou T, Pouliakis A, Tsampou E, Oikonomidi S, Dagre M, Sokou R, et al. Neonatal Sepsis Caused by Streptococcus gallolyticus Complicated with Pulmonary Hypertension: A Case-Report and a Systematic Literature Review. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(12):3116. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123116
Chicago/Turabian StyleIliodromiti, Zoi, Marina Tsaousi, Konstantina Kitsou, Helen Bouza, Theodora Boutsikou, Abraham Pouliakis, Efstathia Tsampou, Stavroula Oikonomidi, Maria Dagre, Rozeta Sokou, and et al. 2022. "Neonatal Sepsis Caused by Streptococcus gallolyticus Complicated with Pulmonary Hypertension: A Case-Report and a Systematic Literature Review" Diagnostics 12, no. 12: 3116. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123116
APA StyleIliodromiti, Z., Tsaousi, M., Kitsou, K., Bouza, H., Boutsikou, T., Pouliakis, A., Tsampou, E., Oikonomidi, S., Dagre, M., Sokou, R., Iacovidou, N., & Petropoulou, C. (2022). Neonatal Sepsis Caused by Streptococcus gallolyticus Complicated with Pulmonary Hypertension: A Case-Report and a Systematic Literature Review. Diagnostics, 12(12), 3116. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123116








