Quantitative Airway Assessment of Diffuse Idiopathic Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Cell Hyperplasia (DIPNECH) on CT as a Novel Biomarker
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. CT Acquisition
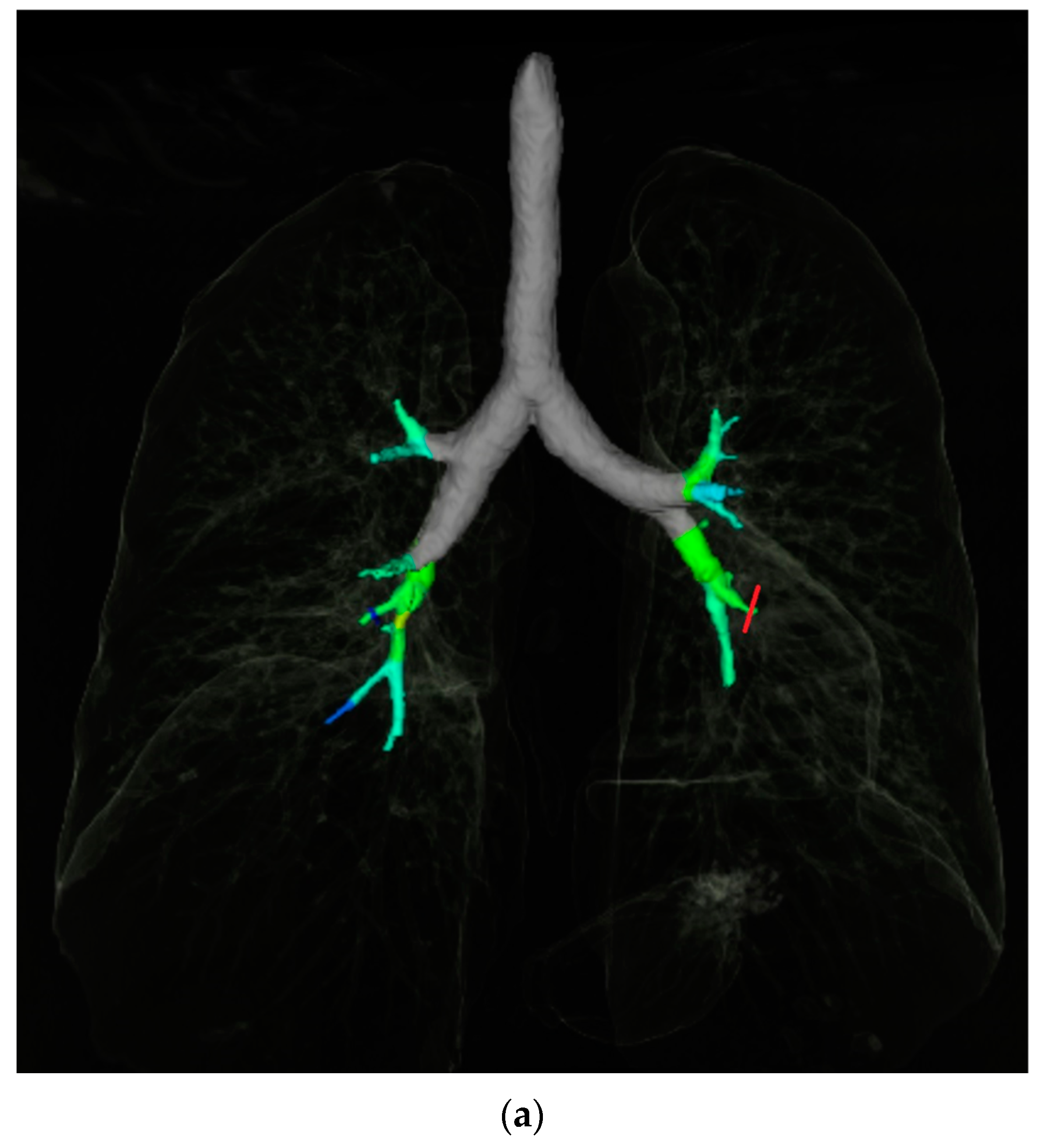
2.3. Quantitative Airway Measurement
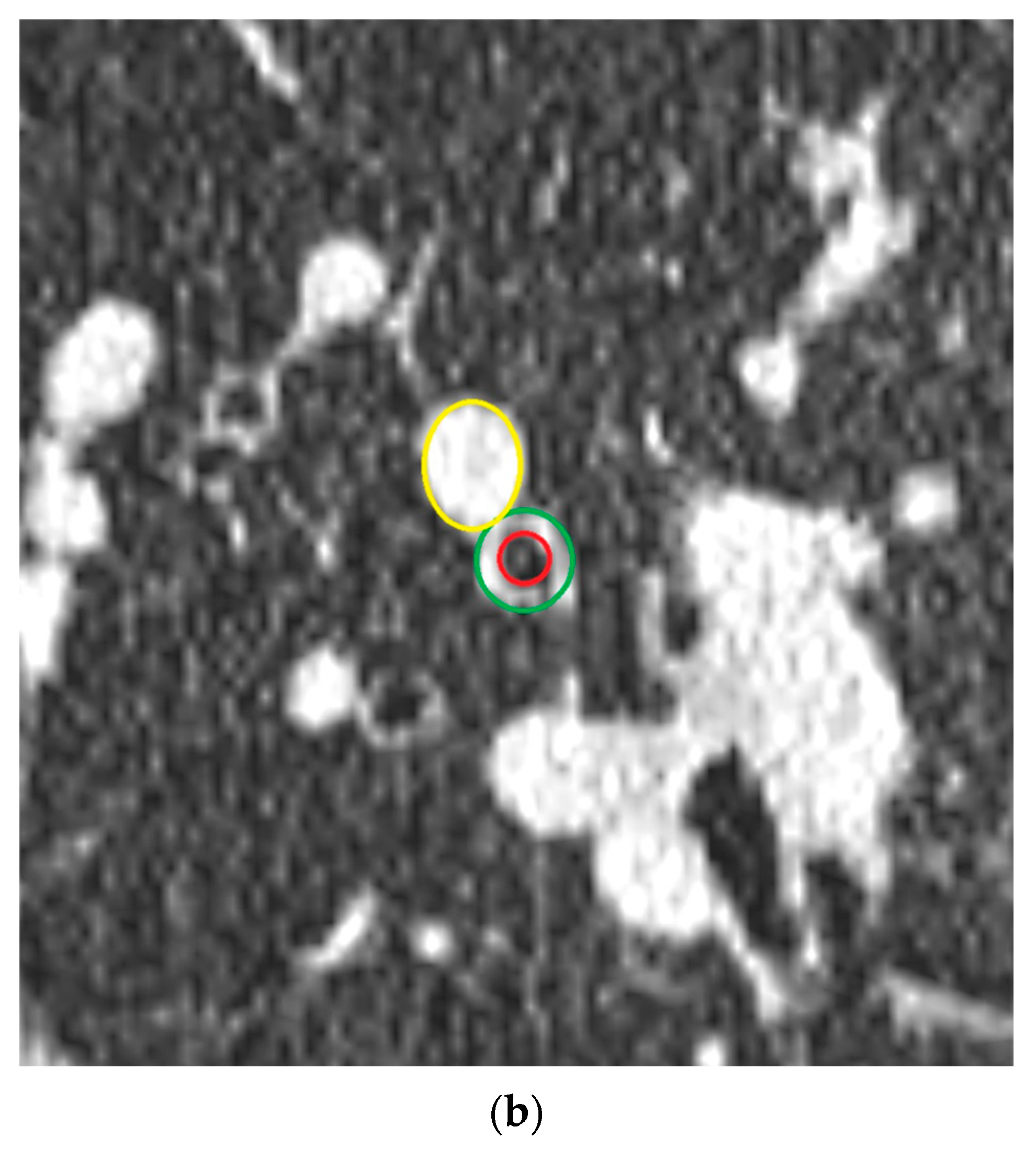
2.4. Airway-Artery Pair Analysis
2.5. Mosaic Attenuation
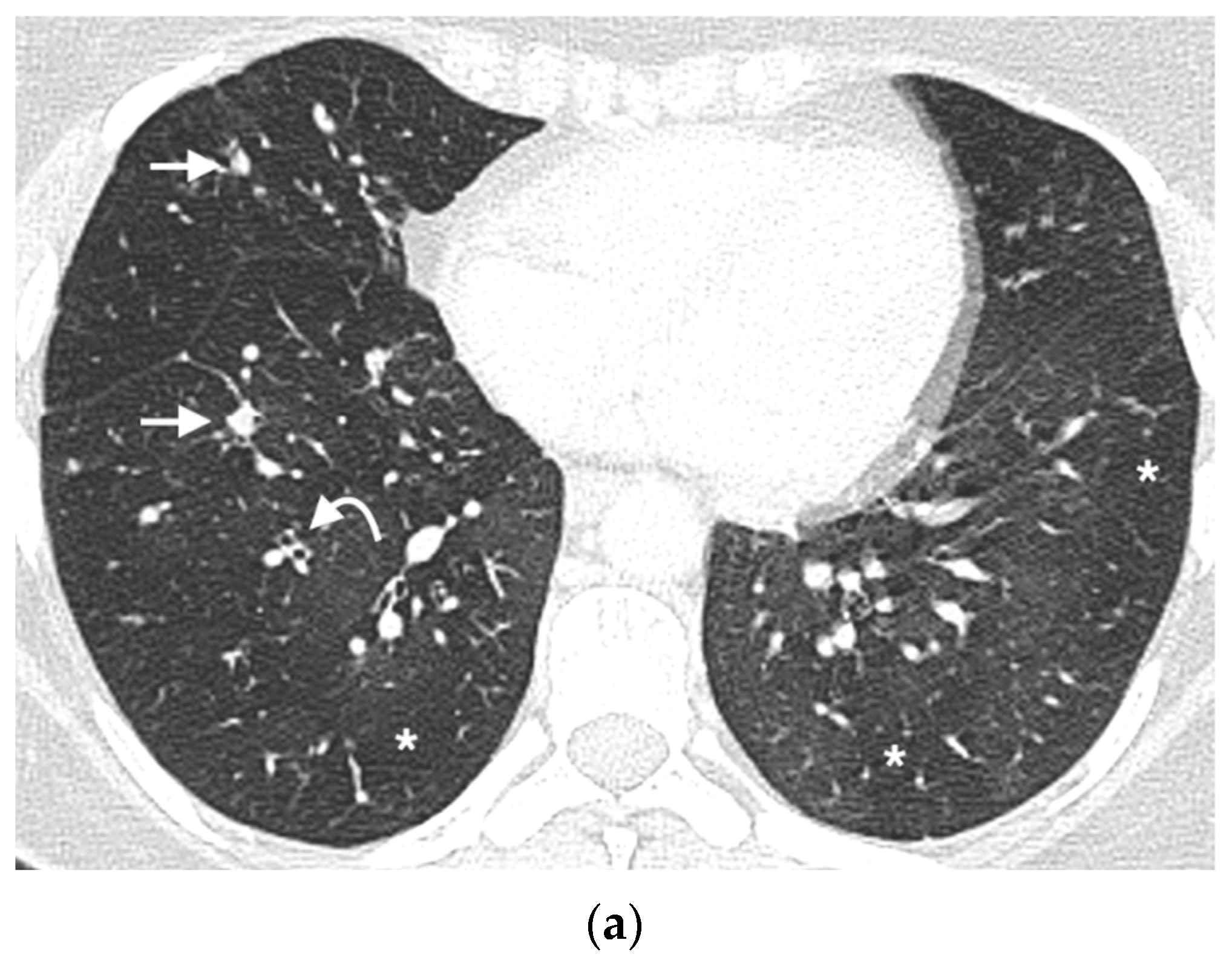
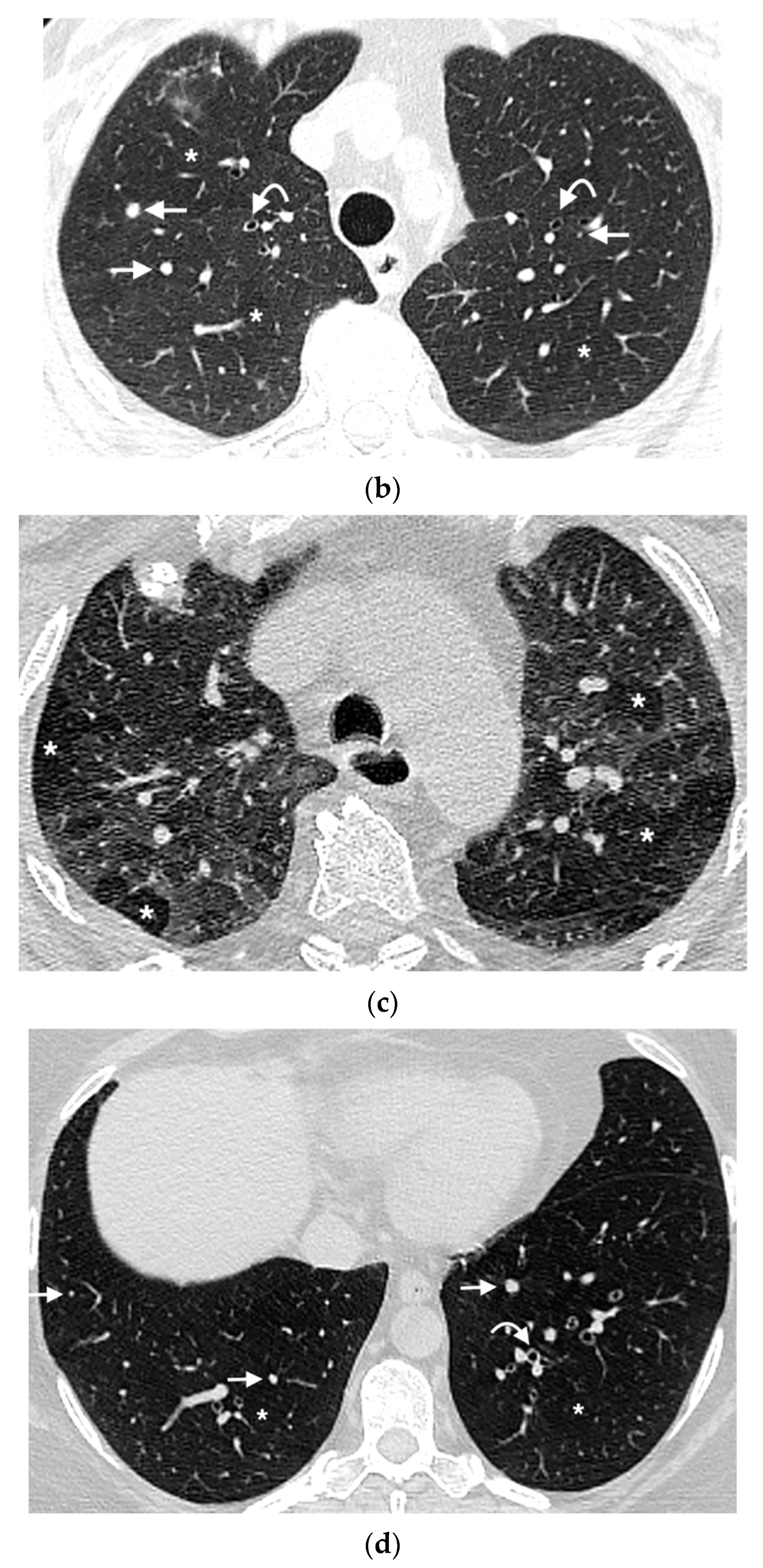
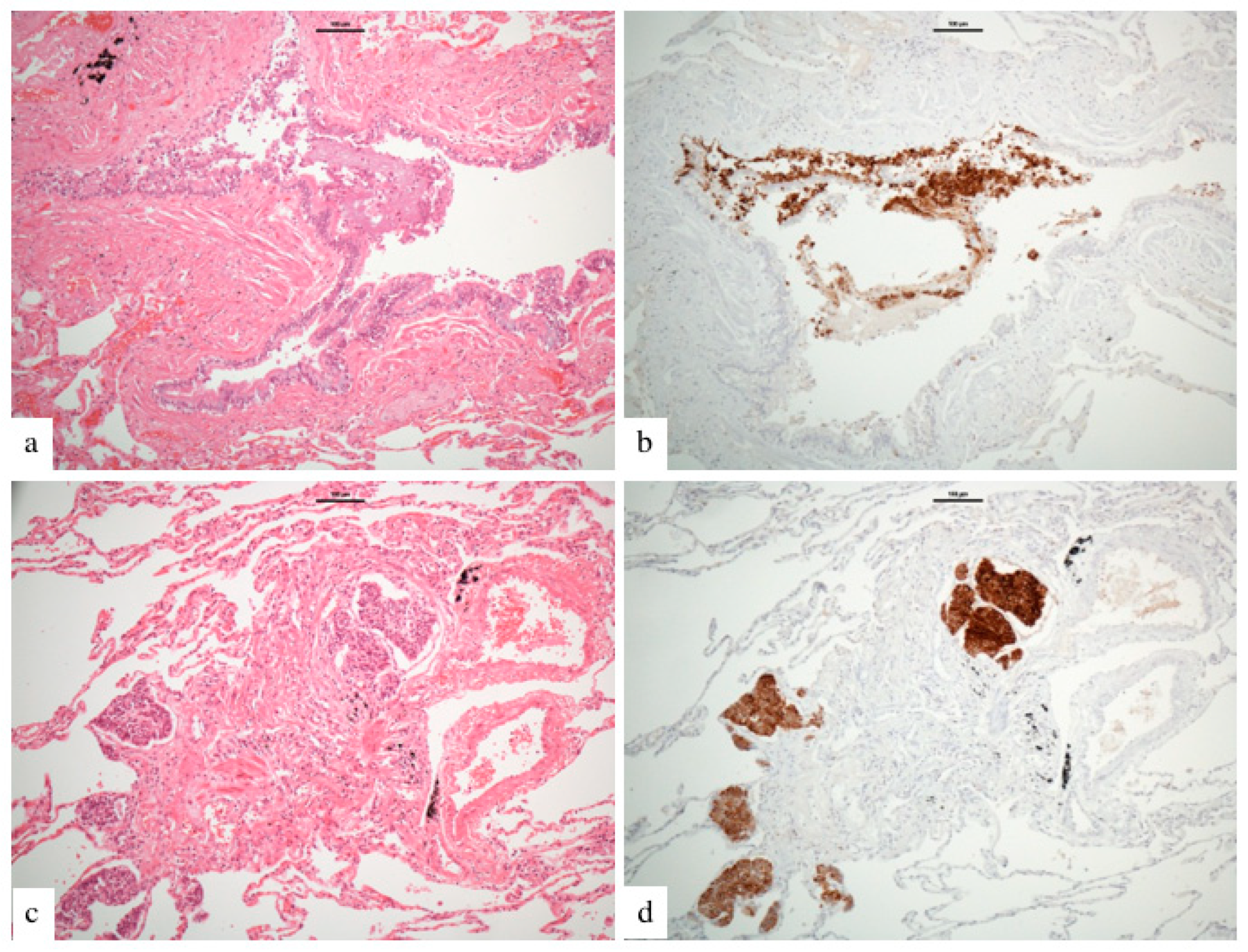
2.6. Nodule Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Airway Wall Thickness and Airway Artery Ratios
3.2. Absolute Airway, Artery Measurements & Wall Area Percentage
3.3. Mosaic Attenuation
3.4. Nodule Characteristics
3.5. Clinical Markers
3.6. Diagnostic Performance (Table 4)
| CT Metric | Cut-Off | Sensitivity | Specificity | Positive LR | Negative LR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nodule Number | ≥5 | 0.81 | 0.87 | 6.2 | 0.2 |
| Airway-artery ratio | ≥1.0 | 0.69 | 0.47 | 1.3 | 0.6 |
| Airway wall thickness-artery ratio | ≥0.73 | 0.71 | 0.68 | 2.2 | 0.4 |
| Wall Area Percentage (%) | ≥60 | 0.75 | 0.51 | 1.5 | 0.5 |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AA ratio | Airway:artery ratio |
| AWTA ratio | Airway wall thickness:artery ratio |
| AUC | Area under the curve |
| DIPNECH | Diffuse idiopathic pulmonary neuroendocrine cell hyperplasia |
| CAD | Computer aided detection |
| CF | Cystic fibrosis |
| COPD | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| DLCO | Diffusion capacity |
| FEV1 | Forced expiratory volume in 1 second |
| FVC | Forced vital capacity |
| LR | Likelihood ratio |
| MA | Mosaic attenuation |
| PFT | Pulmonary function test |
| PNEC | Pulmonary neuroendocrine cells |
| ROC | Receiver operating curve |
| SSA | Somatostatin analogue |
| WAP | Wall area percentage |
References
- Chassagnon, G.; Favelle, O.; Marchand-Adam, S.; Muret, A.D.; Revel, M.P. DIPNECH: When to Suggest This Diagnosis on CT. Clin. Radiol. 2015, 70, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, S.J.; Gosney, J.R.; Hansell, D.M.; Wells, A.U.; du Bois, R.M.; Burke, M.M.; Sheppard, M.N.; Nicholson, A.G. Diffuse Idiopathic Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Cell Hyperplasia: An under-Recognised Spectrum of Disease. Thorax 2007, 62, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koo, C.W.; Baliff, J.P.; Torigian, D.A.; Litzky, L.A.; Gefter, W.B.; Akers, S.R. Spectrum of Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Cell Proliferation: Diffuse Idiopathic Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Cell Hyperplasia, Tumorlet, and Carcinoids. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2010, 195, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mengoli, M.C.; Rossi, G.; Cavazza, A.; Franco, R.; Marino, F.Z.; Migaldi, M.; Gnetti, L.; Silini, E.M.; Ampollini, L.; Tiseo, M.; et al. Diffuse Idiopathic Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Cell Hyperplasia (DIPNECH) Syndrome and Carcinoid Tumors With/Without NECH: A Clinicopathologic, Radiologic and Immunomolecular Comparison Study. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2018, 42, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Travis, W.D.; Brambilla, E.; Nicholson, A.G.; Yatabe, Y.; Austin, J.H.M.; Beasley, M.B.; Chirieac, L.R.; Dacic, S.; Duhig, E.; Flieder, D.B.; et al. The 2015 World Health Organization Classification of Lung Tumors: Impact of Genetic, Clinical and Radiologic Advances Since the 2004 Classification. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 1243–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, J.; Copland, I.; Post, M.; Yeger, H.; Cutz, E. Mechanical Stretch-Induced Serotonin Release from Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Cells: Implications for Lung Development. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2006, 290, L185–L193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gorshtein, A.; Gross, D.J.; Barak, D.; Strenov, Y.; Refaeli, Y.; Shimon, I.; Grozinsky-Glasberg, S. Diffuse Idiopathic Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Cell Hyperplasia and the Associated Lung Neuroendocrine Tumors. Cancer 2012, 118, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguayo, S.M.; Miller, Y.E.; Waldron, J.A.; Bogin, R.M.; Sunday, M.E.; Staton, G.W.; Beam, W.R.; King, T.E. Idiopathic Diffuse Hyperplasia of Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Cells and Airways Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1992, 327, 1285–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, R.E.C.; Rosado-de-Christenson, M.L.; Martinez-Jimenez, S.; Kunin, J.R.; Pettavel, P.P. Spectrum of Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Proliferations and Neoplasms. Radiographics 2013, 33, 1631–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, C.; Tirukonda, P.; Bishop, R.; Mulatero, C.; Scarsbrook, A. Diffuse Idiopathic Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Cell Hyperplasia (DIPNECH) Masquerading as Metastatic Carcinoma with Multiple Pulmonary Deposits. Clin. Imag. 2012, 36, 833–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, B.P.; Junn, J.C.; Zheng, K.S.; Sanchez, F.W.; Henry, T.S.; Veeraraghavan, S.; Berkowitz, E.A. Diffuse Idiopathic Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Cell Hyperplasia: Imaging and Clinical Features of a Frequently Delayed Diagnosis. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2020, 215, 1312–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.R.; Müller, N.L. Neuroendocrine Cell Hyperplasia and Obliterative Bronchiolitis in Patients with Peripheral Carcinoid Tumors. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1995, 19, 653–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, M.J.; English, J.; Müller, N.L. Bronchiolitis Obliterans Due to Neuroendocrine Hyperplasia: High-Resolution CT--Pathologic Correlation. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1997, 168, 1561–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Toubah, T.; Strosberg, J.; Halfdanarson, T.R.; Oleinikov, K.; Gross, D.J.; Haider, M.; Sonbol, M.B.; Almquist, D.; Grozinsky-Glasberg, S. Somatostatin Analogs Improve Respiratory Symptoms in Patients with Diffuse Idiopathic Neuroendocrine Cell Hyperplasia. Chest 2020, 158, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hackx, M.; Gyssels, E.; Garcia, T.S.; Meulder, I.D.; Alard, S.; Bruyneel, M.; Muylem, A.V.; Ninane, V.; Gevenois, P.A. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: CT Quantification of Airway Dimensions, Numbers of Airways to Measure, and Effect of Bronchodilation. Radiology 2015, 277, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackx, M.; Bankier, A.A.; Gevenois, P.A. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: CT Quantification of Airways Disease. Radiology 2012, 265, 34–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, W.; Andrinopoulou, E.-R.; Perez-Rovira, A.; Ozturk, H.; de Bruijne, M.; Tiddens, H.A.W.M. Objective Airway Artery Dimensions Compared to CT Scoring Methods Assessing Structural Cystic Fibrosis Lung Disease. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2017, 16, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuo, W.; Soffers, T.; Andrinopoulou, E.-R.; Rosenow, T.; Ranganathan, S.; Turkovic, L.; Stick, S.M.; Tiddens, H.A.W.M.; on behalf of AREST CF. Quantitative Assessment of Airway Dimensions in Young Children with Cystic Fibrosis Lung Disease Using Chest Computed Tomography. Pediatr. Pulm. 2017, 52, 1414–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyden, E.A. The Intrahilar and Related Segmental Anatomy of the Lung. Surgery 1945, 18, 706–731. [Google Scholar]
- Achenbach, T.; Weinheimer, O.; Biedermann, A.; Schmitt, S.; Freudenstein, D.; Goutham, E.; Kunz, R.P.; Buhl, R.; Dueber, C.; Heussel, C.P. MDCT Assessment of Airway Wall Thickness in COPD Patients Using a New Method: Correlations with Pulmonary Function Tests. Eur. Radiol. 2008, 18, 2731–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.R.; Xie, X.; de Koning, H.J.; Mali, W.P.; Vliegenthart, R.; Oudkerk, M. NELSON Lung Cancer Screening Study. Cancer Imaging 2011, 11, S79–S84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansell, D.M.; Bankier, A.A.; MacMahon, H.; McLoud, T.C.; Müller, N.L.; Remy, J. Fleischner Society: Glossary of Terms for Thoracic Imaging 1. Radiology 2008, 246, 697–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nassar, A.A.; Jaroszewski, D.E.; Helmers, R.A.; Colby, T.V.; Patel, B.M.; Mookadam, F. Diffuse Idiopathic Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Cell Hyperplasia: A Systematic Overview. Am. J. Resp. Crit. Care 2011, 184, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sazonova, O.; Manem, V.; Béland, C.; Hamel, M.-A.; Lacasse, Y.; Lévesque, M.-H.; Orain, M.; Joubert, D.; Provencher, S.; Simonyan, D.; et al. Development and Validation of Diffuse Idiopathic Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Hyperplasia Diagnostic Criteria. JTO Clin. Res. Rep. 2020, 1, 100078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foran, P.J.; Hayes, S.A.; Blair, D.J.; Zakowski, M.F.; Ginsberg, M.S. Imaging Appearances of Diffuse Idiopathic Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Cell Hyperplasia. Clin. Imag. 2015, 39, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, L.L.; Chung, J.H.; Achcar, R.D.; Lesic, Z.; Rho, J.Y.; Yagihashi, K.; Tate, R.M.; Swigris, J.J.; Kern, J.A. The Clinical Course of Diffuse Idiopathic Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Cell Hyperplasia. Chest 2015, 147, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubry, M.-C.; Thomas, C.F.; Jett, J.R.; Swensen, S.J.; Myers, J.L. Significance of Multiple Carcinoid Tumors and Tumorlets in Surgical Lung Specimens Analysis of 28 Patients. Chest 2007, 131, 1635–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, W.; Bruijne, M.; Petersen, J.; Nasserinejad, K.; Ozturk, H.; Chen, Y.; Perez-Rovira, A.; Tiddens, H.A.W.M. Diagnosis of Bronchiectasis and Airway Wall Thickening in Children with Cystic Fibrosis: Objective Airway-Artery Quantification. Eur. Radiol. 2017, 27, 4680–4689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, L.; Wang, Z.; Qi, X. Diffuse Idiopathic Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Cell Hyperplasia. Medicine (Baltimore) 2018, 97, e13806-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, C.C.W.; Moosavi, S.M.; Bubb, K.J. The Regulation of Pulmonary Vascular Tone by Neuropeptides and the Implications for Pulmonary Hypertension. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amaral, J.L.M.; Lopes, A.J.; Veiga, J.; Faria, A.C.D.; Melo, P.L. High-Accuracy Detection of Airway Obstruction in Asthma Using Machine Learning Algorithms and Forced Oscillation Measurements. Comput. Meth. Prog. Bio. 2017, 144, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchevsky, A.M.; Wirtschafter, E.; Walts, A.E. The spectrum of changes in adults with multifocal pulmonary neuroendocrine proliferations: What is the minimum set of pathologic criteria to diagnose DIPNECH? Hum. Pathol. 2015, 2, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robin, X.; Turck, N.; Hainard, A.; Tiberti, N.; Lisacek, F.; Sanchez, J.-C.; Müller, M. pROC: An open-source package for R and S+ to analyze and compare ROC curves. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 1, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| DIPNECH (n = 216) | Control (n = 209) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Airway wall thickness-artery ratio | |||
| Total lung | 0.57 +/− 0.42 | 0.38 +/− 0.23 | <0.001 |
| Right lung | 0.61 +/− 0.52 | 0.39 +/− 0.30 | <0.001 |
| Right upper lobe | 0.56 +/− 0.30 | 0.37 +/− 0.33 | 0.0057 |
| Right middle lobe | 0.56 +/− 0.26 | 0.33 +/− 0.11 | <0.001 |
| Right lower lobe | 0.65 +/− 0.68 | 0.41 +/− 0.27 | 0.01 |
| Left lung | 0.50 +/− 0.17 | 0.37 +/− 0.14 | <0.001 |
| Left upper lobe | 0.52 +/− 0.14 | 0.41 +/− 0.18 | 0.002 |
| Left lower lobe | 0.49 +/− 0.20 | 0.35 +/− 0.12 | <0.001 |
| Airway-artery ratio | |||
| Total lung | 1.18 +/− 0.53 | 1.03 +/− 0.29 | <0.001 |
| Right lung | 1.22 +/− 0.64 | 1.03 +/− 0.35 | 0.007 |
| Right upper lobe | 1.23 +/− 0.43 | 1.09 +/− 0.43 | 0.124 |
| Right middle lobe | 1.24 +/− 0.46 | 0.93 +/− 0.16 | 0.004 |
| Right lower lobe | 1.21 +/− 0.49 | 0.99 +/− 0.30 | 0.045 |
| Left lung | 1.10 +/− 0.27 | 1.00 +/− 0.20 | 0.013 |
| Left upper lobe | 1.13 +/− 0.33 | 1.06 +/− 0.30 | 0.298 |
| Left lower lobe | 1.07 +/− 0.21 | 1.05 +/− 0.40 | 0.78 |
| DIPNECH (n = 216) | Control (n = 209) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Airway outer diameter (cm) | |||
| Total lung | 0.55 +/− 0.10 | 0.55 +/− 0.11 | 0.91 |
| Right lung | 0.55 +/− 0.10 | 0.54 +/− 0.12 | 0.37 |
| Right upper lobe | 0.54 +/− 0.09 | 0.57 +/− 0.14 | 0.19 |
| Right middle lobe | 0.56 +/− 0.17 | 0.56 +/− 0.08 | 0.92 |
| Right lower lobe | 0.55 +/− 0.09 | 0.50 +/− 0.15 | 0.04 |
| Left lung | 0.55 +/− 0.09 | 0.57 +/− 0.09 | 0.33 |
| Left upper lobe | 0.56 +/− 0.07 | 0.57 +/− 0.79 | 0.62 |
| Left lower lobe | 0.55 +/− 0.12 | 0.57 +/− 0.10 | 0.37 |
| Airway inner diameter (cm) | |||
| Total lung | 0.30 +/− 0.09 | 0.36 +/− 0.08 | <0.001 |
| Right lung | 0.30 +/− 0.09 | 0.361+/− 0.09 | <0.001 |
| Right upper lobe | 0.30 +/− 0.08 | 0.38 +/− 0.12 | 0.0013 |
| Right middle lobe | 0.30+/− 0.11 | 0.36 +/− 0.07 | 0.0156 |
| Right lower lobe | 0.30 +/− 0.09 | 0.35 +/− 0.07 | 0.0031 |
| Left lung | 0.30 +/− 0.09 | 0.36 +/− 0.09 | <0.001 |
| Left upper lobe | 0.31 +/− 0.09 | 0.34 +/− 0.08 | 0.027 |
| Left lower lobe | 0.29 +/− 0.09 | 0.38 +/− 0.10 | <0.001 |
| Airway wall thickness (cm) | |||
| Total | 0.26 +/− 0.09 | 0.22 +/− 0.08 | <0.001 |
| Right lung | 0.25 +/− 0.07 | 0.20 +/− 0.06 | <0.001 |
| Right upper lobe | 0.24 +/− 0.06 | 0.12 +/− 0.06 | 0.01 |
| Right middle lobe | 0.26 +/− 0.85 | 0.20 +/− 0.06 | 0.006 |
| Right lower lobe | 0.25 +/− 0.07 | 0.21 +/− 0.49 | 0.006 |
| Left lung | 0.28 +/− 0.11 | 0.23 +/− 0.09 | 0.004 |
| Left upper lobe | 0.32 +/− 0.114 | 0.27 +/− 0.11 | 0.051 |
| Left lower lobe | 0.25 +/− 0.01 | 0.19 +/− 0.05 | 0.002 |
| Wall Area Percentage (%) | |||
| Total | 68.8 +/− 13.6 | 58.3 +/− 12.2 | 0.003 |
| Right lung | 68.6 +/− 14.3 | 58.1 +/− 12.9 | 0.012 |
| Right upper lobe | 68.1 +/− 12.3 | 56.8 +/− 15.5 | <0.001 |
| Right middle lobe | 66.5 +/− 18.6 | 53.1 +/− 16.5 | 0.03 |
| Right lower lobe | 68.8 +/− 14.8 | 60.6 +/− 9.0 | <0.001 |
| Left lung | 67.9 +/− 15.0 | 57.4 +/− 12.2 | <0.001 |
| Left upper lobe | 69.4 +/− 13.5 | 59.5 +/− 13 | <0.001 |
| Left lower lobe | 66.5 +/− 16.2 | 55.3 +/− 11 | <0.001 |
| Artery diameter (cm) | |||
| Total lung | 0.51 +/− 0.13 | 0.54 +/− 0.15 | 0.01 |
| Right lung | 0.49 +/− 0.13 | 0.52 +/− 0.17 | 0.09 |
| Right upper lobe | 0.47 +/− 0.14 | 0.56 +/− 0.15 | 0.007 |
| Right middle lobe | 0.46 +/− 0.08 | 0.61 +/− 0.09 | <0.001 |
| Right lower lobe | 0.51 +/− 0.13 | 0.46 +/− 0.19 | 0.09 |
| Left lung | 0.52 +/− 0.14 | 0.56+/− 0.10 | 0.02 |
| Left upper lobe | 0.52 +/− 0.12 | 0.55 +/− 0.10 | 0.3 |
| Left lower lobe | 0.51 +/− 0.15 | 0.57 +/− 0.11 | 0.03 |
| DIPNECH (n = 16) | Controls (n = 16) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nodule number | |||
| Total Number | 22.4 +/− 32.6 | 3.6 +/− 3.6 | 0.03 |
| Right lung | 4.2 +/− 6.8 | 0.6 +/− 1.0 | <0.001 |
| Right upper lobe | 4.3 +/− 7.3 | 0.7 +/− 0.9 | 0.059 |
| Right middle lobe | 2.1 +/− 2.2 | 0.4 +/− 0.7 | 0.006 |
| Right lower lobe | 6.3 +/− 8.6 | 0.8 +/− 1.4 | 0.018 |
| Left lung | 2.8 +/− 5.2 | 0.5 +/− 0.8 | <0.001 |
| Left upper lobe | 2.1 +/− 2.9 | 0.3 +/− 0.6 | 0.002 |
| Left lower lobe | 4.9 +/− 8.1 | 0.8 +/− 1.1 | 0.053 |
| Nodule Location (%) | |||
| Peripheral | 36 | 41 | 0.5 |
| Central | 35 | 37 | 0.7 |
| Perifissural | 12 | 16 | 0.47 |
| Subpleural | 18 | 6 | 0.06 |
| Nodule shape (%) | |||
| Spherical | 67 | 59 | 0.35 |
| Ovoid | 22 | 22 | 1.0 |
| Triangular | 10 | 20 | 0.3 |
| Other | 1 | 0 | 1.0 |
| Nodule Distribution (%) | |||
| Centrilobular | 20 | - | |
| Peribronchiolar | 47 | - | |
| Random | 33 | - | |
| Largest Nodule Diameter (mm) | |||
| Total Lung | 7.1 +/− 4.1 | 5.4 +/− 2.6 | 0.005 |
| Right Lung | 7.2 +/− 4.9 | 5.56 +/− 2.7 | 0.048 |
| Right upper lobe | 6.1 +/− 2.4 | 4.8 +/− 3 | 0.11 |
| Right middle lobe | 8.5 +/− 6.2 | 5.4 +/− 1.4 | 0.09 |
| Right lower lobe | 7.3 +/− 4.4 | 6.3 +/− 3.1 | 0.27 |
| Left Lung | 7 +/− 3.4 | 5.3 +/− 2.6 | 0.02 |
| Left upper lobe | 6.9 +/− 2.8 | 5.8 +/− 2 | 0.16 |
| Left lower lobe | 7.1 +/− 3.9 | 4.8 +/− 2.4 | 0.03 |
| Mosaic attenuation | |||
| Overall | 16 | 4 | <0.0001 |
| Mild | 11 | 4 | 0.035 |
| Moderate | 5 | 0 | 0.04 |
| Severe | 0 | 0 | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
O’Brien, C.; Duignan, J.A.; Gleeson, M.; O’Carroll, O.; Franciosi, A.N.; O’Toole, D.; Fabre, A.; Crowley, R.K.; McCarthy, C.; Dodd, J.D.; et al. Quantitative Airway Assessment of Diffuse Idiopathic Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Cell Hyperplasia (DIPNECH) on CT as a Novel Biomarker. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 3096. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123096
O’Brien C, Duignan JA, Gleeson M, O’Carroll O, Franciosi AN, O’Toole D, Fabre A, Crowley RK, McCarthy C, Dodd JD, et al. Quantitative Airway Assessment of Diffuse Idiopathic Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Cell Hyperplasia (DIPNECH) on CT as a Novel Biomarker. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(12):3096. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123096
Chicago/Turabian StyleO’Brien, Cormac, John A. Duignan, Margaret Gleeson, Orla O’Carroll, Alessandro N. Franciosi, Dermot O’Toole, Aurelie Fabre, Rachel K. Crowley, Cormac McCarthy, Jonathan D. Dodd, and et al. 2022. "Quantitative Airway Assessment of Diffuse Idiopathic Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Cell Hyperplasia (DIPNECH) on CT as a Novel Biomarker" Diagnostics 12, no. 12: 3096. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123096
APA StyleO’Brien, C., Duignan, J. A., Gleeson, M., O’Carroll, O., Franciosi, A. N., O’Toole, D., Fabre, A., Crowley, R. K., McCarthy, C., Dodd, J. D., & Murphy, D. J. (2022). Quantitative Airway Assessment of Diffuse Idiopathic Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Cell Hyperplasia (DIPNECH) on CT as a Novel Biomarker. Diagnostics, 12(12), 3096. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123096






