Glaucoma Is Associated with the Risk of Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Population-Based Nationwide Cohort Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statements
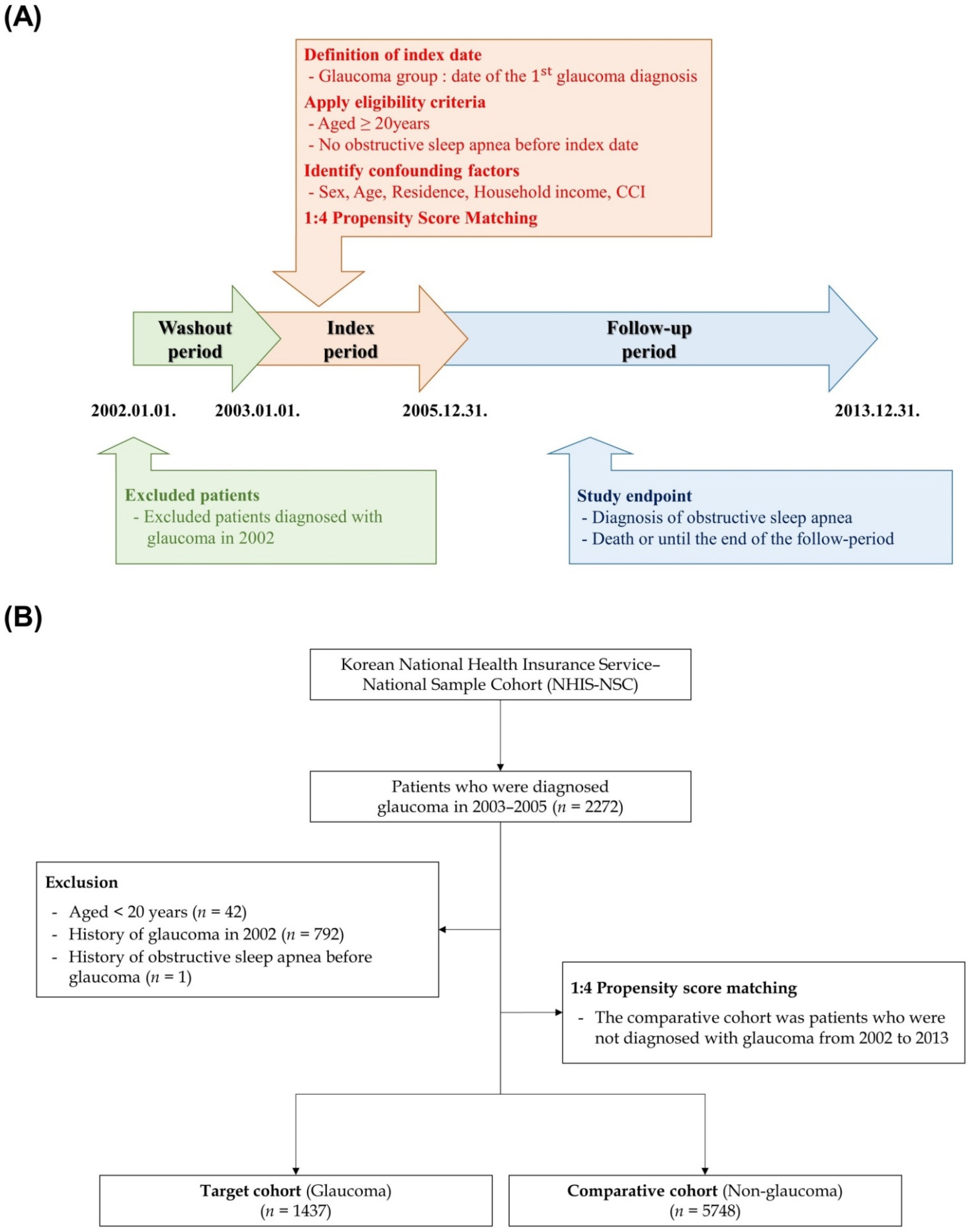
2.2. Study Design and Participants
2.3. Predictor and Outcome Variables
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Clinical Characteristics
3.2. Effect of Glaucoma on the Risk of Subsequent Development of Obstructive Sleep Apnea
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tham, Y.C.; Li, X.; Wong, T.Y.; Quigley, H.A.; Aung, T.; Cheng, C.Y. Global prevalence of glaucoma and projections of glaucoma burden through 2040: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ophthalmology 2014, 121, 2081–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cedrone, C.; Mancino, R.; Cerulli, A.; Cesareo, M.; Nucci, C. Epidemiology of primary glaucoma: Prevalence, incidence, and blinding effects. Prog. Brain Res. 2008, 173, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwase, A.; Sawaguchi, S.; Araie, M. Differentiating diagnosed and undiagnosed primary angle-closure glaucoma and open-angle glaucoma: A population-based study. Ophthalmol. Glaucoma 2022, 5, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, A.C.; Baio, G.; Gazzard, G.; Bunce, C.; Azuara-Blanco, A.; Munoz, B.; Friedman, D.S.; Foster, P.J. The prevalence of primary angle closure glaucoma in European derived populations: A systematic review. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2012, 96, 1162–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.W.; Zong, Y.; Zeng, Y.Y.; Wei, R.L. The prevalence of primary angle closure glaucoma in adult Asians: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stein, J.D.; Kim, D.S.; Niziol, L.M.; Talwar, N.; Nan, B.; Musch, D.C.; Richards, J.E. Differences in rates of glaucoma among Asian Americans and other racial groups, and among various Asian ethnic groups. Ophthalmology 2011, 118, 1031–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, H.K.; Kee, C. Population-based glaucoma prevalence studies in Asians. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2014, 59, 434–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, T.D.; Floras, J.S. Obstructive sleep apnoea and its cardiovascular consequences. Lancet 2009, 373, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drager, L.F.; Martinez-Garcia, M.A. Thoracic aortic aneurysms: Expanding the potential cardiovascular consequences of obstructive sleep apnoea. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 57, 2004440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, K.M.; Kamat, R.; Tomfohr, L.M.; Ancoli-Israel, S.; Dimsdale, J.E. Obstructive sleep apnea and neurocognitive performance: The role of cortisol. Sleep Med. 2014, 15, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seda, G.; Han, T.S. Effect of obstructive sleep apnea on neurocognitive performance. Sleep Med. Clin. 2020, 15, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedlander, A.H.; Graves, L.L.; Chang, T.I.; Kawakami, K.K.; Lee, U.K.; Grabich, S.C.; Fang, Z.T.; Zeidler, M.R.; Giaconi, J.A. Prevalence of primary open-angle glaucoma among patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2018, 126, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Liu, H. Obstructive sleep apnea/hypopnea syndrome increases glaucoma risk: Evidence from a meta-analysis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 297–303. [Google Scholar]
- Bagabas, N.; Ghazali, W.; Mukhtar, M.; AlQassas, I.; Merdad, R.; Maniyar, A.; Almarzouki, N.; Afreen, H.; Badeeb, O.; Wali, S. Prevalence of glaucoma in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. J. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2019, 9, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leggewie, B.; Gouveris, H.; Bahr, K. A narrative review of the association between obstructive sleep apnea and glaucoma in adults. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, L.H.; Koh, Y.Y.; Chen, H.S.L.; Lo, Y.L.; Yu, C.C.; Yeung, L.; Lai, C.C. Normal tension glaucoma in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome: A structural and functional study. Medicine 2020, 99, e19468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.S.; Sanfilippo, P.G.; Hunter, M.; Yazar, S.; James, A.; Mackey, D.A. Optic disc measures in obstructive sleep apnea: A community-based study of middle-aged and older adults. J. Glaucoma 2020, 29, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsy, N.E.; Amani, B.E.; Magda, A.A.; Nabil, A.J.; Pandi-Perumal, S.R.; BaHammam, A.S.; Spence, D.W.; Lundmark, P.O.; Zaki, N.F. Prevalence and predictors of ocular complications in obstructive sleep apnea patients: A cross-sectional case-control study. Open Respir. Med. J. 2019, 13, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.S.Y.; McArdle, N.; Sanfilippo, P.G.; Yazar, S.; Eastwood, P.R.; Hewitt, A.W.; Li, Q.; Mackey, D.A. Associations between optic disc measures and obstructive sleep apnea in young adults. Ophthalmology 2019, 126, 1372–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.Y.; Su, W.W.; Liu, C.H.; Chen, H.S.; Wu, S.C.; Chang, S.H.L.; Chen, K.J.; Wu, W.C.; Chen, N.H.; Li, H.Y.; et al. Correlation between structural progression in glaucoma and obstructive sleep apnea. Eye 2019, 33, 1459–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uslu, H.; Kanra, A.Y.; Sarac, S. Structural assessment of the optic nerve in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome: Case-control study. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 31, 1741–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davanian, A.; Williamson, L.; Taylor, C.; Harrover, A.; Bollinger, K.; Chaudhary, B.; Taskar, V.; Lee, T.J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Q.; et al. Optical coherence tomography angiography and Humphrey visual field in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2022, 18, 2133–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swaminathan, S.S.; Bhakta, A.S.; Shi, W.; Feuer, W.J.; Abreu, A.R.; Chediak, A.D.; Greenfield, D.S. Is obstructive sleep apnea associated with progressive glaucomatous optic neuropathy? J. Glaucoma 2018, 27, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wozniak, D.; Bourne, R.; Peretz, G.; Kean, J.; Willshire, C.; Harun, S.; Villar, S.; Chiu, Y.D.; Smith, I. Obstructive sleep apnea in patients with primary-open angle glaucoma: No role for a screening program. J. Glaucoma 2019, 28, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, R.F. Aetiology of the anatomical basis for primary angle-closure glaucoma. Biometrical comparisons between normal eyes and eyes with primary angle-closure glaucoma. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1970, 54, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sihota, R.; Ghate, D.; Mohan, S.; Gupta, V.; Pandey, R.M.; Dada, T. Study of biometric parameters in family members of primary angle closure glaucoma patients. Eye 2008, 22, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchini, G.; Pagliarusco, A.; Toscano, A.; Tosi, R.; Brunelli, C.; Bonomi, L. Ultrasound biomicroscopic and conventional ultrasonographic study of ocular dimensions in primary angle-closure glaucoma. Ophthalmology 1998, 105, 2091–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonomi, L.; Marchini, G.; Marraffa, M.; Bernardi, P.; De Franco, I.; Perfetti, S.; Varotto, A. Epidemiology of angle-closure glaucoma: Prevalence, clinical types, and association with peripheral anterior chamber depth in the Egna-Neumarket Glaucoma Study. Ophthalmology 2000, 107, 998–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, P.J. The epidemiology of primary angle closure and associated glaucomatous optic neuropathy. Semin. Ophthalmol. 2002, 17, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, Z.L.; Soh, Z.D.; Tham, Y.C.; Yu, M.; Chee, M.L.; Thakur, S.; Nongpiur, M.E.; Koh, V.; Wong, T.Y.; Aung, T.; et al. Six-year incidence and risk factors for primary angle-closure disease: The Singapore epidemiology of eye diseases study. Ophthalmology 2022, 129, 792–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Wu, H.; Fan, Z. Primary angle closure glaucoma in Chinese and Western populations. Chin. Med. J. 2002, 115, 1706–1715. [Google Scholar]
- Sacca, S.C.; Bolognesi, C.; Battistella, A.; Bagnis, A.; Izzotti, A. Gene-environment interactions in ocular diseases. Mutat. Res. 2009, 667, 98–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.S.; Yin, Z.Q.; Pen, H.M.; Yuan, C.M. Genetic heritability of a shallow anterior chamber in Chinese families with primary angle closure glaucoma. Ophthalmic Genet. 2008, 29, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, Y.; Guo, X.; Liu, X.; Cao, D.; Jia, X.; Xiao, X.; Li, S.; Fang, S.; Zhang, Q. Association of the single nucleotide polymorphisms in the extracellular matrix metalloprotease-9 gene with PACG in southern China. Mol. Vis. 2009, 15, 1412–1417. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, I.J.; Chiang, T.H.; Shih, Y.F.; Lu, S.C.; Lin, L.L.; Shieh, J.W.; Wang, T.H.; Samples, J.R.; Hung, P.T. The association of single nucleotide polymorphisms in the MMP-9 genes with susceptibility to acute primary angle closure glaucoma in Taiwanese patients. Mol. Vis. 2006, 12, 1223–1232. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Wiggs, J.L.; Pasquale, L.R.; Sun, X.; Fan, B.J. Association of matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP9) variants with primary angle closure and primary angle closure glaucoma. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, H.; Li, M.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Wu, X. Association of MYOC and APOE promoter polymorphisms and primary open-angle glaucoma: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 15, 2052–2064. [Google Scholar]
- Nowak, A.; Majsterek, I.; Przybyłowska-Sygut, K.; Pytel, D.; Szymanek, K.; Szaflik, J.; Szaflik, J.P. Analysis of the expression and polymorphism of APOE, HSP, BDNF, and GRIN2B genes associated with the neurodegeneration process in the pathogenesis of primary open angle glaucoma. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 258281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gozal, D.; Capdevila, O.S.; Kheirandish-Gozal, L.; Crabtree, V.M. APOE epsilon 4 allele, cognitive dysfunction, and obstructive sleep apnea in children. Neurology 2007, 17, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rim, T.H.; Kim, D.W.; Han, J.S.; Chung, E.J. Retinal vein occlusion and the risk of stroke development: A 9-year nationwide population-based study. Ophthalmology 2015, 122, 1187–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-Y.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, M.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, N.-K. Association of Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss with Affective Disorders. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2018, 144, 614–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-Y.; Ko, I.; Kim, D.-K. Association of Obstructive Sleep Apnea with the Risk of Affective Disorders. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2019, 145, 1020–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Ko, I.; Cho, B.J.; Kim, D.K. Association of Obstructive Sleep Apnea With the Risk of Ménière’s Disease and Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss: A Study Using Data From the Korean National Health Insurance Service. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2019, 15, 1293–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.H.; Yu, H.; Ha, S.-S.; Son, G.M.; Park, K.J.; Lee, J.J.; Kim, D.-K. Association between Late-Onset Ménière’s Disease and the Risk of Incident All-Cause Dementia. J. Pers Med. 2021, 31, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-Y.; Ko, I.; Kim, M.S.; Kim, D.W.; Cho, B.-J.; Kim, D.-K. Relationship of Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Asthma, Myocardial Infarction, Stroke, Anxiety, and Depression. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2020, 8, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variable | Comparison (n = 5748) | Glaucoma (n = 1437) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | 1.000 | ||
| Male | 2876 (50.0%) | 719 (50.0%) | |
| Female | 2872 (50.0%) | 718 (50.0%) | |
| Age (years) | 1.000 | ||
| <45 | 1232 (21.4%) | 308 (21.4%) | |
| 45–64 | 2380 (41.4%) | 595 (41.4%) | |
| >64 | 2136 (37.2%) | 534 (37.2%) | |
| Residence | 1.000 | ||
| Seoul | 1272 (22.1%) | 318 (22.1%) | |
| Second area | 1460 (25.4%) | 365 (25.4%) | |
| Third area | 3016 (52.5%) | 754 (52.5%) | |
| Household income | 1.000 | ||
| Low (0–30%) | 1064 (18.5%) | 266 (18.5%) | |
| Middle (30–70%) | 1920 (33.4%) | 480 (33.4%) | |
| High (70–100%) | 2764 (48.1%) | 691 (48.1%) | |
| CCI | 1.000 | ||
| 0 | 3100 (53.9%) | 775 (53.9%) | |
| 1 | 1244 (21.6%) | 311 (21.6%) | |
| ≥2 | 1404 (24.4%) | 351 (24.4%) |
| Number of Endpoint Events | ||
|---|---|---|
| Event | 26 | |
| Comparison | 19 | |
| Glaucoma | 7 | |
| Total censored (No event) | 7159 | |
| Comparison | 5729 | |
| Glaucoma | 1430 | |
| Termination of study | 5670 | |
| Comparison | 4517 | |
| Glaucoma | 1153 | |
| Loss to follow-up/Drop-out | 1489 | |
| Comparison | 1212 | |
| Glaucoma | 277 | |
| Variable | N | Case | Person-Year | Incidence | Unadjusted HR (95% CI) | Adjusted HR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group | ||||||
| Comparison | 5748 | 19 | 51,545.6 | 0.37 | 1.00 (ref) | 1.00 (ref) |
| Glaucoma | 1437 | 7 | 12,509.0 | 0.56 | 1.50 (0.63–3.57) | 1.52 (0.64–3.62) |
| POAG | 1209 | 4 | 10,550.2 | 0.38 | 1.01 (0.34–2.98) | 0.99 (0.34–2.90) |
| PACG | 228 | 3 | 1958.8 | 1.53 | 4.10 (1.21–13.87) * | 5.65 (1.65–19.41) ** |
| Follow-Up Period (Year) | Number of Participants with Obstructive Sleep Apnea | Adjusted Hazard Ratio (95% Confidence Interval) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Comparison | PACG | ||
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0.00 (0–Inf) |
| 2 | 3 | 0 | 0.00 (0–Inf) |
| 3 | 6 | 0 | 0.00 (0–Inf) |
| 4 | 8 | 0 | 0.00 (0–Inf) |
| 5 | 11 | 1 | 3.09 (0.39–24.38) |
| 6 | 13 | 1 | 2.46 (0.32–19.15) |
| 7 | 14 | 1 | 2.32 (0.30–17.91) |
| 8 | 17 | 1 | 2.02 (0.27–15.34) |
| 9 | 19 | 3 | 5.65 (1.65–19.41) ** |
| 10 | 19 | 3 | 5.65 (1.65–19.41) ** |
| 11 | 19 | 3 | 5.65 (1.65–19.41) ** |
| CCI | <2 | ≥2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Comparison | PACG | Comparison | PACG | |
| Obstructive sleep apnea | ||||
| Unadjusted HR (95% CI) | 1.00 (ref) | 4.98 (1.09–22.73) * | 1.00 (ref) | 3.29 (0.42–25.99) |
| Adjusted HR (95% CI) | 1.00 (ref) | 6.98 (1.47–33.16) * | 1.00 (ref) | 4.76 (0.59–38.71) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.Y.; Yu, H.; Kim, D.-K. Glaucoma Is Associated with the Risk of Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Population-Based Nationwide Cohort Study. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2992. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12122992
Lee SY, Yu H, Kim D-K. Glaucoma Is Associated with the Risk of Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Population-Based Nationwide Cohort Study. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(12):2992. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12122992
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, So Yeon, Hyunjae Yu, and Dong-Kyu Kim. 2022. "Glaucoma Is Associated with the Risk of Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Population-Based Nationwide Cohort Study" Diagnostics 12, no. 12: 2992. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12122992
APA StyleLee, S. Y., Yu, H., & Kim, D.-K. (2022). Glaucoma Is Associated with the Risk of Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Population-Based Nationwide Cohort Study. Diagnostics, 12(12), 2992. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12122992






