Pre-Dialysis B-Line Quantification at Lung Ultrasound Is a Useful Method for Evaluating the Dry Weight and Predicting the Risk of Intradialytic Hypotension
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Cohort
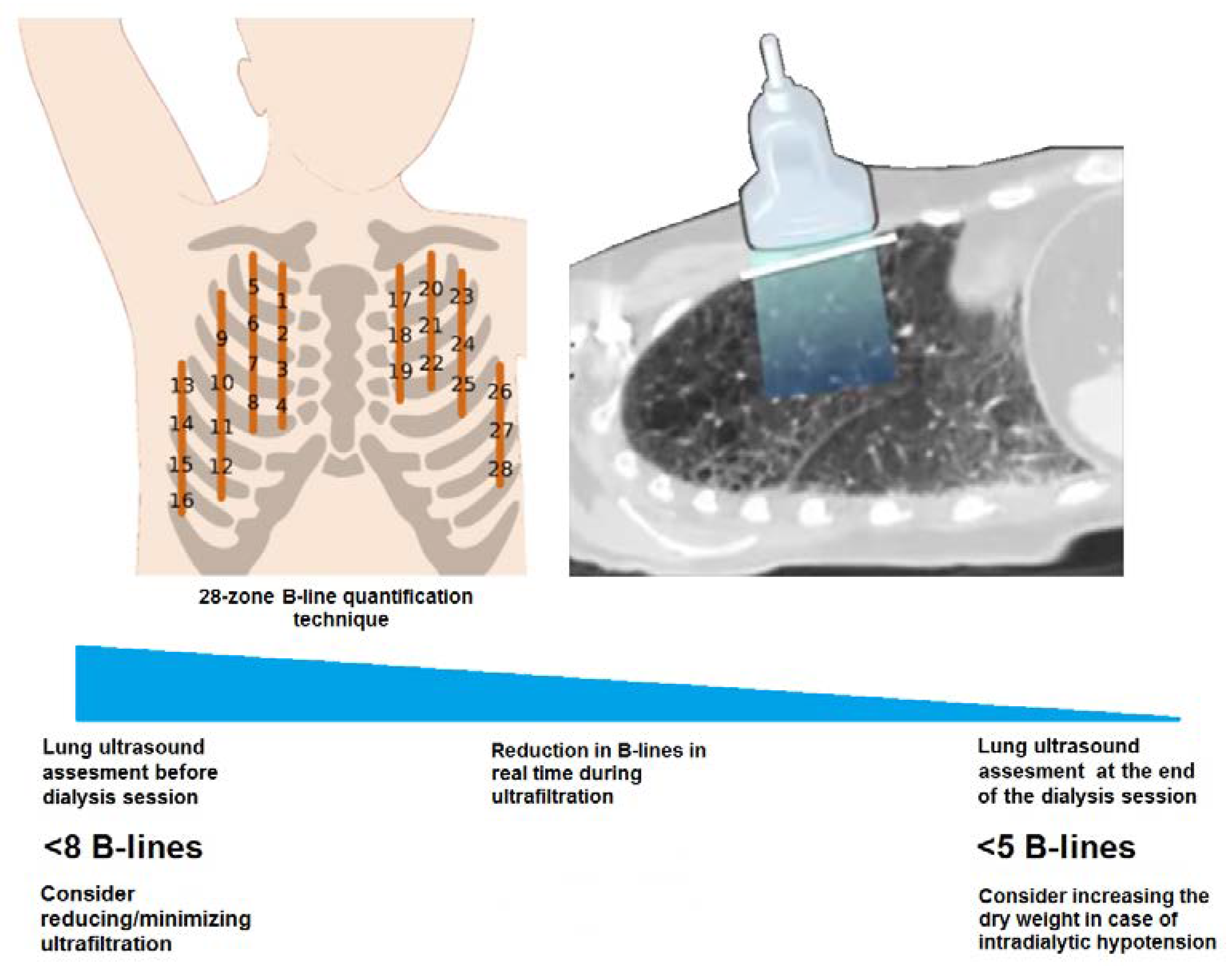
2.2. Ultrasound Evaluation
2.3. Chest X-ray
2.4. Blood Volume Monitoring
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
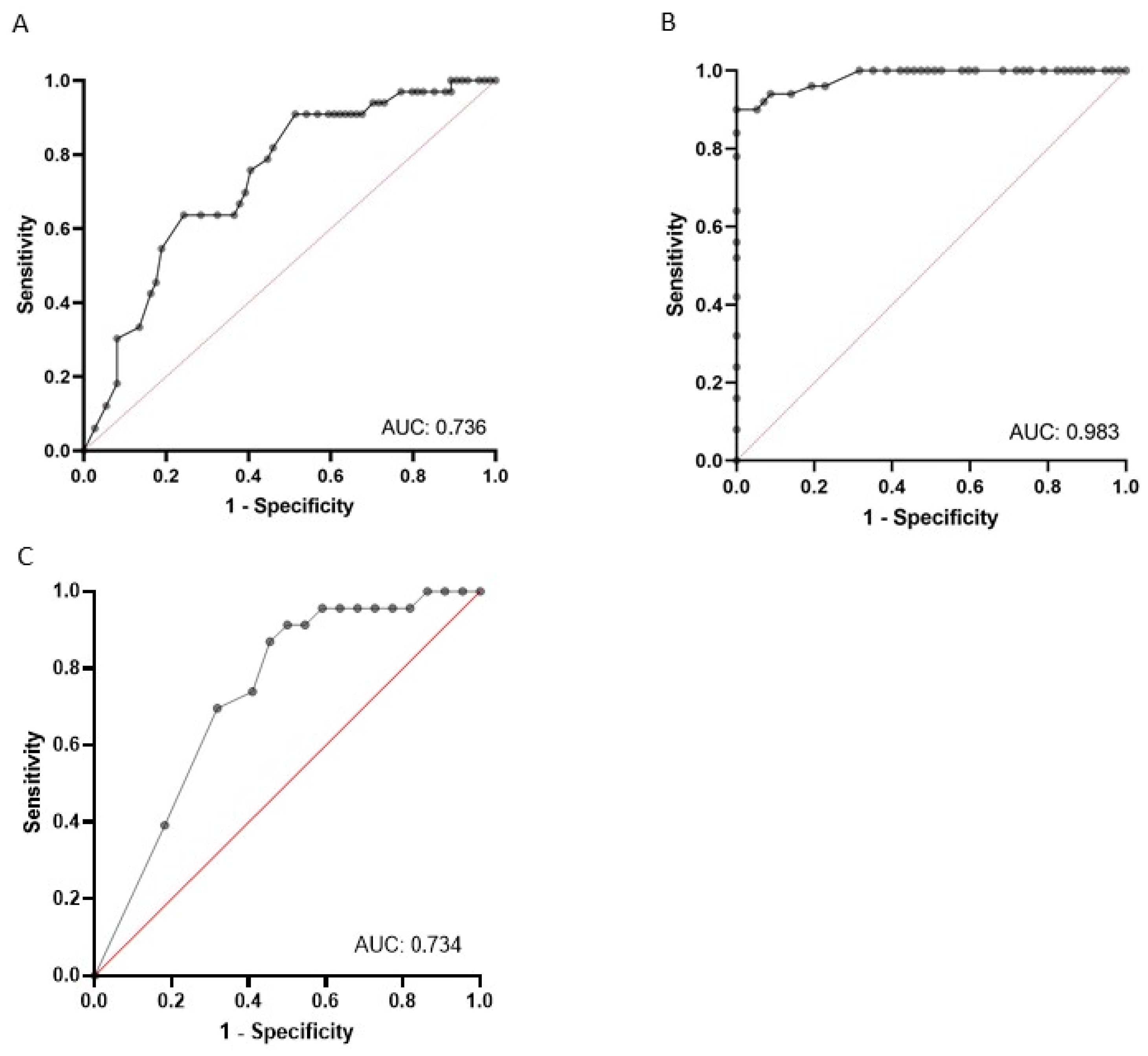
3.2. LUS Yields a High Sensitivity in Fluid Overload Diagnosis
3.3. The Number of B-Lines Predicts the Risk of IDH
3.4. The Number of B-Lines Predicts the Risk of IDH, Even in Patients with Heart Failure
3.5. The Number of B-Lines Correlates with NT-proBNP and Serum Albumin
3.6. Hypoalbuminemia, Low Pre-Dialysis Systolic BP and a Low Number of B-Lines Are Independent Risk Factors for IDH
3.7. IDH and Pre-Dialysis B-Lines Are Not Associated with a Higher Mortality
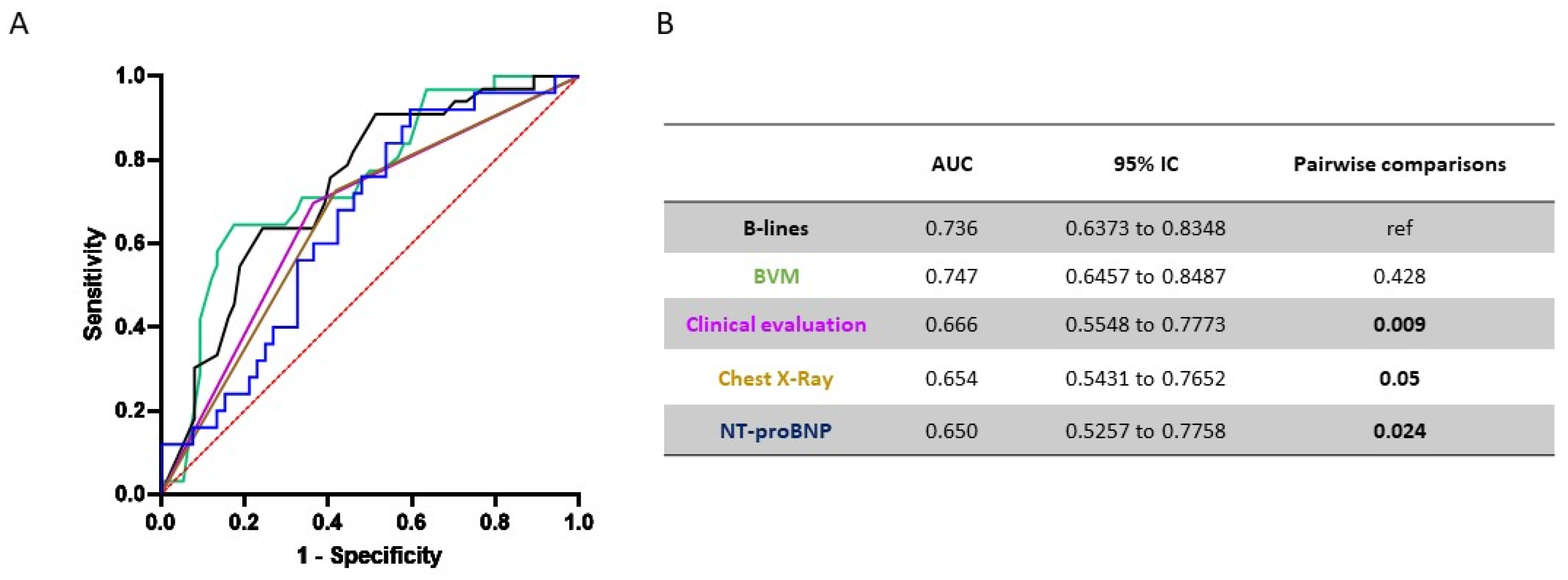
3.8. Overall Performance of Selected Items to Predict IDH
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- K/DOQI Workgroup. K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for cardiovascular disease in dialysis patients. Am. J. Kidney Dis. Off. J. Natl. Kidney Found. 2005, 45, S1–S153. [Google Scholar]
- Orofino, L.; Marcen, R.; Quereda, C.; Villafruela, J.; Sabater, J.; Matesanz, R.; Pascual, J.; Ortuño, J. Epidemiology of Symptomatic Hypotension in Hemodialysis: Is Cool Dialysate Beneficial for All Patients? Am. J. Nephrol. 1990, 10, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, J.A.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Mathew, A.T. A brief review of intradialytic hypotension with a focus on survival. Semin. Dial. 2017, 30, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meredith, D.J.; Pugh, C.W.; Sutherland, S.; Tarassenko, L.; Birks, J. The relationship between symptoms and blood pressure during maintenance hemodialysis. Hemodial. Int. Int. Symp. Home Hemodial. 2015, 19, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cedeño, S.; Vega, A.; Macías, N.; Sánchez, L.; Abad, S.; López-Gómez, J.M.; Luño, J. Intradialytic hypotension definitions with mortality prediction capacity in a cohort of haemodialysis patients. Nefrología 2020, 40, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daugirdas, J.T. Pathophysiology of dialysis hypotension: An update. Am. J. Kidney Dis. Off. J. Natl. Kidney Found. 2001, 38, S11–S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, T.I.; Paik, J.; Greene, T.; Desai, M.; Bech, F.; Cheung, A.K.; Chertow, G.M. Intradialytic Hypotension and Vascular Access Thrombosis]. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 1526–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ronco, C.; Brendolan, A.; Milan, M.; Rodeghiero, M.P.; Zanella, M.; La Greca, G. Impact of biofeedback-induced cardiovascular stability on hemodialysis tolerance and efficiency. Kidney Int. 2000, 58, 800–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mc Causland, F.R.; Tumlin, J.A.; Roy-Chaudhury, P.; Koplan, B.A.; Costea, A.I.; Kher, V.; Williamson, D.; Pokhariyal, S.; Charytan, D.M. Intradialytic Hypotension and Cardiac Arrhythmias in Patients Undergoing Maintenance Hemodialysis: Results from the Monitoring in Dialysis Study. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. CJASN 2020, 15, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefánsson, B.V.; Brunelli, S.M.; Cabrera, C.; Rosenbaum, D.; Anum, E.; Ramakrishnan, K.; Jensen, D.E.; Stålhammar, N.O. Intradialytic hypotension and risk of cardiovascular disease. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 9, 2124–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Assimon, M.M.; Wang, L.; Flythe, J.E. Cumulative Exposure to Frequent Intradialytic Hypotension Associates With New-Onset Dementia Among Elderly Hemodialysis Patients. Kidney Int. Rep. 2019, 4, 603–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoji, T.; Tsubakihara, Y.; Fujii, M.; Imai, E. Hemodialysis-associated hypotension as an independent risk factor for two-year mortality in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int. 2004, 66, 1212–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jansen, M.A.; Hart, A.A.; Korevaar, J.C.; Dekker, F.W.; Boeschoten, E.W.; Krediet, R.T. Predictors of the rate of decline of residual renal function in incident dialysis patients. Kidney Int. 2002, 62, 1046–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mizumasa, T.; Hirakata, H.; Yoshimitsu, T.; Hirakata, E.; Kubo, M.; Kashiwagi, M.; Tanaka, H.; Kanai, H.; Fujimi, S.; Iida, M. Dialysis-related hypotension as a cause of progressive frontal lobe atrophy in chronic hemodialysis patients: A 3-year prospective study. Nephron 2004, 97, c23–c30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedeño, S.; Desco, M.; Aleman, Y.; Macías, N.; Fernández-Pena, A.; Vega, A.; Abad, S.; López-Gómez, J.M. Intradialytic hypotension and relationship with cognitive function and brain morphometry. Clin. Kidney J. 2021, 14, 1156–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flythe, J.E.; Assimon, M.M.; Overman, R.A. Target weight achievement and ultrafiltration rate thresholds: Potential patient implications. BMC Nephrol. 2017, 18, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daugirdas, J.T.; Greene, T.; Rocco, M.V.; A Kaysen, G.; Depner, T.A.; Levin, N.W.; Chertow, G.M.; Ornt, D.B.; Raimann, J.G.; Larive, B.; et al. Effect of frequent hemodialysis on residual kidney function. Kidney Int. 2013, 83, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Odudu, A.; Eldehni, M.T.; McCann, G.P.; McIntyre, C.W. Randomized Controlled Trial of Individualized Dialysate Cooling for Cardiac Protection in Hemodialysis Patients. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. CJASN 2015, 10, 1408–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Locatelli, F.; Altieri, P.; Andrulli, S.; Bolasco, P.; Sau, G.; Pedrini, L.A.; Basile, C.; David, S.; Feriani, M.; Montagna, G.; et al. Hemofiltration and hemodiafiltration reduce intradialytic hypotension in ESRD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2010, 21, 1798–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alexandrou, M.E.; Theodorakopoulou, M.P.; Sarafidis, P.A. Lung Ultrasound as a Tool to Evaluate Fluid Accumulation in Dialysis Patients. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2022, 47, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, D.W.; Abbasi, M.M.; Jhaveri, K.D.; Sachdeva, M.; Miller, I.; Barnett, R.; Narasimhan, M.; Mayo, P.; Merzkani, M.; Mathew, A.T. Lung ultrasonography in end-stage renal disease: Moving from evidence to practice—A narrative review. Clin. Kidney J. 2017, 11, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoccali, C. Lung Ultrasound in the Management of Fluid Volume in Dialysis Patients: Potential Usefulness. Semin. Dial. 2017, 30, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loutradis, C.; Sarafidis, P.A.; Ekart, R.; Papadopoulos, C.; Sachpekidis, V.; Alexandrou, M.E.; Papadopoulou, D.; Efstratiadis, G.; Papagianni, A.; London, G.; et al. The effect of dry-weight reduction guided by lung ultrasound on ambulatory blood pressure in hemodialysis patients: A randomized controlled trial. Kidney Int. 2019, 95, 1505–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loutradis, C.; Papadopoulos, C.E.; Sachpekidis, V.; Ekart, R.; Krunic, B.; Karpetas, A.; Bikos, A.; Tsouchnikas, I.; Mitsopoulos, E.; Papagianni, A.; et al. Lung Ultrasound–Guided Dry Weight Assessment and Echocardiographic Measures in Hypertensive Hemodialysis Patients: A Randomized Controlled Study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. Off. J. Natl. Kidney Found. 2020, 75, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoccali, C.; Torino, C.; Mallamaci, F.; Sarafidis, P.; Papagianni, A.; Ekart, R.; Hojs, R.; Klinger, M.; Letachowicz, K.; Fliser, D.; et al. A randomized multicenter trial on a lung ultrasound–guided treatment strategy in patients on chronic hemodialysis with high cardiovascular risk. Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 1325–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siriopol, D.; Onofriescu, M.; Voroneanu, L.; Apetrii, M.; Nistor, I.; Hogas, S.; Kanbay, M.; Sascau, R.; Scripcariu, D.; Covic, A. Dry weight assessment by combined ultrasound and bioimpedance monitoring in low cardiovascular risk hemodialysis patients: A randomized controlled trial. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2017, 49, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortini, A.; Torrigiani, A.; Sbaragli, S.; Forte, A.L.; Crociani, A.; Cecchini, P.; Bruni, G.I.; Faraone, A. COVID-19: Persistence of symptoms and lung alterations after 3–6 months from hospital discharge. Infection 2021, 49, 1007–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basso, F.; Manani, S.M.; Cruz, D.N.; Teixeira, C.; Brendolan, A.; Nalesso, F.; Zanella, M.; Ronco, C. Comparison and Reproducibility of Techniques for Fluid Status Assessment in Chronic Hemodialysis Patients. Cardiorenal Med. 2013, 3, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jambrik, Z.; Monti, S.; Coppola, V.; Agricola, E.; Mottola, G.; Miniati, M.; Picano, E. Usefulness of ultrasound lung comets as a nonradiologic sign of extravascular lung water. Am. J. Cardiol. 2004, 93, 1265–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoccali, C.; Torino, C.; Tripepi, R.; Tripepi, G.; D’Arrigo, G.; Postorino, M.; Gargani, L.; Sicari, R.; Picano, E.; Mallamaci, F.; et al. Pulmonary congestion predicts cardiac events and mortality in ESRD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2013, 24, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heitzman, E.R.; Ziter, F.M., Jr. Acute interstitial pulmonary edema. Am. J. Roentgenol. Radium Ther. Nucl. Med. 1966, 98, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milne, E.N.; Pistolesi, M.; Miniati, M.; Giuntini, C. The radiologic distinction of cardiogenic and noncardiogenic edema. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1985, 144, 879–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosmer, D.W.; Lemeshow, S.; Sturdivant, R.X. Applied Logistic Regression; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuipers, J.; Verboom, L.M.; Ipema, K.J.; Paans, W.; Krijnen, W.P.; Gaillard, C.A.; Westerhuis, R.; Franssen, C.F. The Prevalence of Intradialytic Hypotension in Patients on Conventional Hemodialysis: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Nephrol. 2019, 49, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sands, J.J.; Usvyat, L.A.; Sullivan, T.; Segal, J.H.; Zabetakis, P.; Kotanko, P.; Maddux, F.W.; Diaz-Buxo, J.A. Intradialytic hypotension: Frequency, sources of variation and correlation with clinical outcome. Hemodial. Int. Int. Symp. Home Hemodial. 2014, 18, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hryciw, N.; Joannidis, M.; Hiremath, S.; Callum, J.; Clark, E.G. Intravenous Albumin for Mitigating Hypotension and Augmenting Ultrafiltration during Kidney Replacement Therapy. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. CJASN 2021, 16, 820–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, S.; Pena-Esparragoza, J.K.; Scovner, K.M.; Mc Causland, F.R. Predictors of Intradialytic Symptoms: An Analysis of Data From the Hemodialysis Study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. Off. J. Natl. Kidney Found. 2020, 76, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passos, R.D.H.; Caldas, J.; Ramos, J.G.R.; Melo, E.B.D.S.G.D.; Ribeiro, M.P.D.; Alves, M.F.C.; Batista, P.B.P.; Messeder, O.H.C.; Farias, A.M.D.C.D.; Macedo, E.; et al. Ultrasound-based clinical profiles for predicting the risk of intradialytic hypotension in critically ill patients on intermittent dialysis: A prospective observational study. Crit. Care Soc. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 23, 389. [Google Scholar]
- Khanin, Y.; Hirsch, J.S.; Stalbow, D.; Zhang, M.; Hasan, Z.; Ross, D.W. Intradialytic Hypotension in Critically Ill Patients on Hemodialysis With A-Line versus B-Line Pattern on Lung Ultrasonography. Kidney Int. Rep. 2021, 6, 1969–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picano, E.; Pellikka, P.A. Ultrasound of extravascular lung water: A new standard for pulmonary congestion. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 2097–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trezzi, M.; Torzillo, D.; Ceriani, E.; Costantino, G.; Caruso, S.; Damavandi, P.T.; Genderini, A.; Cicardi, M.; Montano, N.; Cogliati, C. Lung ultrasonography for the assessment of rapid extravascular water variation: Evidence from hemodialysis patients. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2013, 8, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keane, D.F.; Raimann, J.G.; Zhang, H.; Willetts, J.; Thijssen, S.; Kotanko, P. The time of onset of intradialytic hypotension during a hemodialysis session associates with clinical parameters and mortality. Kidney Int. 2021, 99, 1408–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vizioli, L.; Ciccarese, F.; Forti, P.; Chiesa, A.M.; Giovagnoli, M.; Mughetti, M.; Zompatori, M.; Zoli, M. Integrated Use of Lung Ultrasound and Chest X-Ray in the Detection of Interstitial Lung Disease. Respir. Int. Rev. Thorac. Dis. 2017, 93, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| All | No Intradialytic Hypotension Group | Intradialytic Hypotension Group | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of patients | 107 | 74 | 33 | |
| Males, n (%) | 68 (63.6) | 48 (64.9) | 20 (60.6) | 0.672 |
| Age [years, median (IQR)] | 69.1 (58.2–81.3) | 68.2 (58.1–79.6) | 75.8 (59.1–82.1) | 0.324 |
| Comorbidities: | ||||
| Diabetes, n (%) | 28 (26.7%) | 18 (24.3) | 10 (30.3) | 0.516 |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 99 (92.5) | 70 (94.6) | 29 (87.9) | 0.124 |
| Dialysis vintage [years, median (IQR)] | 1.7 (0.2–3.5) | 1.6 (0.5–3.7) | 1.8 (0.2–4.9) | 0.589 |
| Oligoanuria, n (%) | 60 (56.1) | 41 (55.4) | 19 (57.6) | 0.835 |
| LVH, n (%) | 87 (81.3) | 63 (85.1) | 24 (72.7) | 0.128 |
| NYHA ≥ 3, n (%) | 26 (24.3) | 13 (17.6) | 13 (39.4) | 0.015 |
| Anemia, n (%) | 43 (40.1) | 29 (39.2) | 14 (42.4) | 0.753 |
| Hypoalbuminemia, n (%) | 43 (40.1) | 27 (36.5) | 16 (48.5) | 0.242 |
| Pre-dialysis fluid status assessment: | ||||
| SBP before dialysis [mmHg, median (IQR)] | 135 (120–147) | 137 (130–150) | 126 (110–138) | 0.003 |
| Peripheral oedema-pulmonary crackles, n (%) | 42 (39.3) | 31 (41.9) | 11 (33.3) | 0.632 |
| Lung congestion at chest X-ray, n (%) | 52 (47.7) | 43 (58.1) | 9 (27.3) | 0.006 |
| NT-proBNP [pg/mL, median (IQR)] | 8896 (3545–34,500) | 22,249 (3888–63,809.8) | 6306 (2899–20,310.5) | 0.019 |
| Interdialytic weight gain [kg, median (IQR)] | 2.3 (1.3–3.5) | 2.4 (1.5–3.5) | 1.8 (1.0–2.9) | 0.2 |
| Interdialytic weight gain [%, median (IQR)] | 3.3 (1.9–5.1) | 3.6 (2.0–5.3) | 2.6 (1.5–4.2) | 0.117 |
| UF rate [mL/Kg/hr, median (IQR)] | 10.5 (7.3–12.7) | 10.5 (6.9–13.5) | 10.5 (7.4–11.4) | 0.684 |
| B-lines before dialysis [n, median (IQR)] | 15.0 (6.0–35.0) | 18 (6.9–13.5) | 7.0 (3.0–15.5) | <0.001 |
| B-lines ≤ 5 before dialysis, n (%) | 26 (24.3) | 12 (16.2) | 14 (42.4) | 0.004 |
| B-lines ≥ 15 before dialysis, n (%) | 55 (51.4) | 45 (60.8) | 10 (30.3) | 0.004 |
| Fluid status assessment all along the dialysis session: | ||||
| B-lines after dialysis [n, median (IQR)] | 3.0 (1.0–17.0) | 4.5 (1.0–22.8) | 1.0 (0–3.0) | 0.006 |
| % slope in RBV during first hour of dialysis [n, median (IQR)] | −5.5 (−2.8–−8.5) | −4.6 (−4.2–−6.7) | −7.6 (−4.2–−10) | <0.001 |
| Follow-up | ||||
| 12-month mortality, n (%) | 31/92 (33.7) | 17/60 (28.3) | 14/32 (43.8) | 0.14 |
| All | No intradialytic Hypotension Group | Intradialytic Hypotension Group | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of patients | 26 | 13 | 13 | |
| Males, n (%) | 20 (77) | 10 (77) | 10 (77) | 1.0 |
| Age [years, median (IQR)] | 76.6 (71.7–84.2) | 73.6 (66.5–84.9) | 79.6 (76.0–83.9) | 0.41 |
| Different methods for fluid status assessment before dialysis: | ||||
| SBP before dialysis [mmHg, median (IQR)] | 128 (114–138) | 130 (114–138) | 126 (114–138) | 0.84 |
| Peripheral oedema-pulmonary crackles, n (%) | 15 (57.7) | 9 (69.2) | 6 (46.2) | 0.43 |
| Lung congestion at chest X-ray, n (%) | 18 (69.2) | 12 (92.3) | 6 (46.2) | 0.03 |
| NT-proBNP [pg/mL, median (IQR)] | 49,895 (11,681–82,920) | 76,293 (48,141–84,818) | 21,097 (6279–23,784) | <0.001 |
| B-lines before dialysis [n, median (IQR)] | 28.6 (12.8–47.5) | 41.8 (37–51) | 15.4 (3–18) | 0.001 |
| Different methods for fluid status assessment during the dialysis session: | ||||
| % slope in RBV during first hour of dialysis [n, median (IQR)] | −5.1 (−7.7–−3.0) | −4.1 (−5.5–−2.8) | −6.2 (−9.5–−3.0) | 0.24 |
| B-lines after dialysis [n, median (IQR)] | 9 (3–18) | 24 (10–28) | 3 (0–6) | <0.001 |
| Model 1 | Model 2 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | p | OR | 95% CI | p | |||
| Age (years) | 0.989 | 0.950 | 1.029 | 0.579 | - | - | - | - |
| Gender (M) | 0.666 | 0.211 | 2.100 | 0.487 | - | - | - | - |
| NYHA class | 2.334 | 0.989 | 5.509 | 0.053 | 2.06 | 1.027 | 4.132 | 0.042 |
| Previous cardiovascular events (yes/no) | 0.809 | 0.199 | 3.298 | 0.768 | - | - | - | - |
| Residual diuresis (mL) | 0.999 | 0.998 | 1.00 | 0.192 | - | - | - | - |
| SBP before dialysis (mmHg) | 0.964 | 0.933 | 0.996 | 0.030 | 0.965 | 0.938 | 0.994 | 0.017 |
| Delta weight gain/dry weight (%) | 1.149 | 0.781 | 1.689 | 0.480 | - | - | - | - |
| UF rate (mL/kg/h) | 1.018 | 0.832 | 1.246 | 0.863 | - | - | - | - |
| Peripheral oedema-pulmonary crackles (yes/no) | 4.476 | 0.980 | 21.369 | 0.53 | - | - | - | - |
| Hypoalbuminemia (yes/no) | 0.319 | 0.091 | 1.122 | 0.075 | 0.471 | 0.164 | 1.352 | 0.162 |
| B-lines before dialysis (n) | 0.877 | 0.817 | 0.942 | <0.001 | 0.920 | 0.881 | 0.962 | <0.001 |
| Hb (g/dL) | 1.364 | 0.397 | 4.69 | 0.622 | - | - | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Allinovi, M.; Palazzini, G.; Lugli, G.; Gianassi, I.; Dallari, L.; Laudicina, S.; Gregori, M.; Rossi, F.; Giannerini, D.; Cutruzzulà, R.; et al. Pre-Dialysis B-Line Quantification at Lung Ultrasound Is a Useful Method for Evaluating the Dry Weight and Predicting the Risk of Intradialytic Hypotension. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2990. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12122990
Allinovi M, Palazzini G, Lugli G, Gianassi I, Dallari L, Laudicina S, Gregori M, Rossi F, Giannerini D, Cutruzzulà R, et al. Pre-Dialysis B-Line Quantification at Lung Ultrasound Is a Useful Method for Evaluating the Dry Weight and Predicting the Risk of Intradialytic Hypotension. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(12):2990. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12122990
Chicago/Turabian StyleAllinovi, Marco, Giulia Palazzini, Gianmarco Lugli, Iacopo Gianassi, Lorenzo Dallari, Selene Laudicina, Marco Gregori, Francesco Rossi, Daniele Giannerini, Roberta Cutruzzulà, and et al. 2022. "Pre-Dialysis B-Line Quantification at Lung Ultrasound Is a Useful Method for Evaluating the Dry Weight and Predicting the Risk of Intradialytic Hypotension" Diagnostics 12, no. 12: 2990. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12122990
APA StyleAllinovi, M., Palazzini, G., Lugli, G., Gianassi, I., Dallari, L., Laudicina, S., Gregori, M., Rossi, F., Giannerini, D., Cutruzzulà, R., Dervishi, E., Biagini, M., & Cirami, C. L. (2022). Pre-Dialysis B-Line Quantification at Lung Ultrasound Is a Useful Method for Evaluating the Dry Weight and Predicting the Risk of Intradialytic Hypotension. Diagnostics, 12(12), 2990. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12122990







