Diagnostic AI and Cardiac Diseases
Abstract
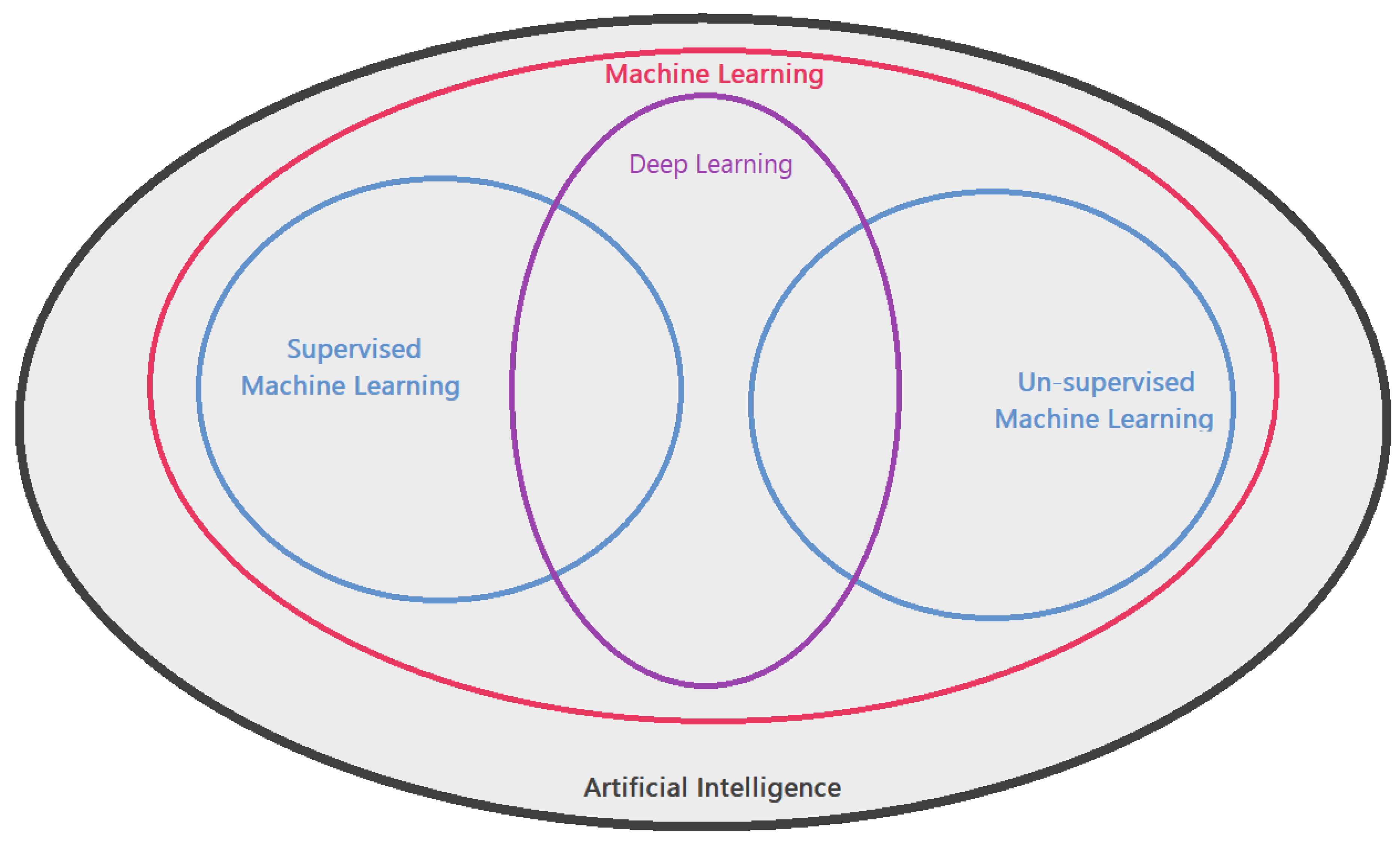
:1. Introduction
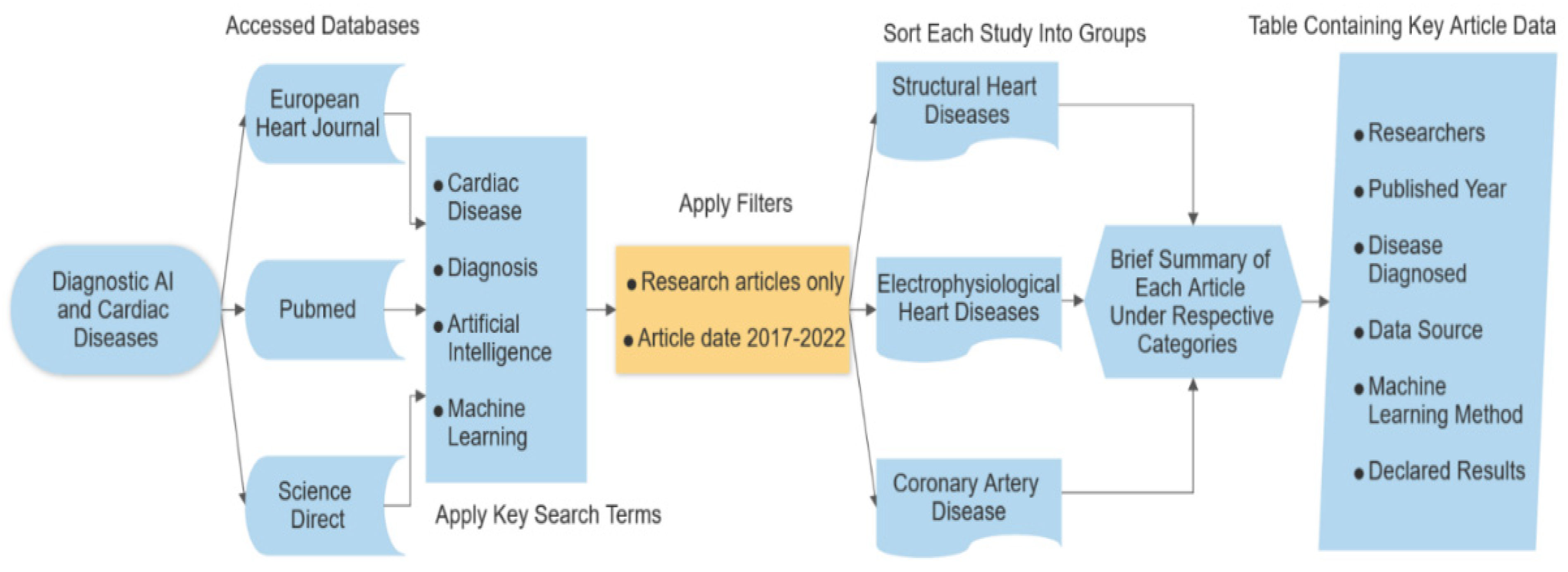
2. Method
3. Results
3.1. Structural Heart Diseases
3.2. Electrophysiological Heart Diseases
3.3. Coronary Artery Disease
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AF | Atrial fibrillation |
| AFL | Atrial flutter |
| AI | Artificial intelligence |
| AUC | Area under curve |
| AV | Aortic valve |
| AV | Atrioventricular |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| BP | Blood pressure |
| CAD | Coronary artery disease |
| CCTA | Coronary computerized tomography angiography |
| CDC | Centers for Disease Control and Prevention |
| CNN | Convolutional neural network |
| CT | Computerized tomography |
| DL | Deep learning |
| ECG | Electrocardiogram |
| EF | Ejection Fraction |
| EGB | Extreme gradient boosting |
| FFR | Fractional flow reserve |
| GLS | Global longitudinal strain |
| HF | Heart failure |
| ICU | Intensive care unit |
| IHS | Integrated healthcare system |
| IVUS | Intravascular ultrasound |
| K-NN | K-nearest neighbor |
| LR | Logistic regression |
| LV | Left ventricule |
| LVEF | Left ventricular ejection fraction |
| MI | Myocardial infarction |
| ML | Machine learning |
| MPI | Myocardial perfusion imaging |
| NN | Neural network |
| NPV | Negative predictive value |
| PPG | Photoplethysmographic |
| PPV | Positive predictive value |
| PVC | Premature ventricular complex |
| QCT | Quantitative computerized tomography |
| RF | Random forest |
| SPECT | Single photon emission computerized tomography |
| SV | Supraventricular |
| SVM | Support vector machine |
| SVT | Supraventricular tachycardia |
| TAVI | Transcatheter aortic valve implantation |
| TET | Treadmill exercise test |
| TTE | Transthoracic echocardiography |
| VCG | Vectorcardiography |
References
- Heart Disease Statistics. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 2022. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/fastats/heart-disease.htm (accessed on 5 October 2022).
- Harnad, S. The Annotation Game: On Turing (1950) on Computing, Machinery and Intelligence Archived 18 October 2017 at the Wayback Machine. In Parsing the Turing Test: Philosophical and Methodological Issues in the Quest for the Thinking Computer; Epstein, R., Peters, G., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, S.J.; Norvig, P. Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach, 4th ed.; Pearson: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021; ISBN 9780134610993. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, T.M. Machine Learning; McGraw-Hilll: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, C.M. Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; ISBN 978-1-4939-3843-8. [Google Scholar]
- Mohri, M.; Rostamizadeh, A.; Talwalkar, A. Foundations of Machine Learning; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012; ISBN 9780262018258. [Google Scholar]
- Nichols, J.A.; Chan, H.W.H.; Baker, M.A.B. Machine learning: Applications of artificial intelligence to imaging and diagnosis. Biophys. Rev. 2019, 11, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quer, G.; Arnaout, R.; Henne, M.; Arnaout, R. Machine Learning and the Future of Cardiovascular Care: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2021, 77, 300–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.W.; Soto, J.T.; Glicksberg, B.S.; Shameer, K.; Miotto, R.; Ali, M.; Ashley, E.; Dudley, J.T. Artificial Intelligence in Cardiology. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 2668–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asselbergs, F.W.; Fraser, A.G. Artificial intelligence in cardiology: The debate continues. Eur. Heart J. Digit. Health 2021, 2, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiang, C.-W.; Lin, C.; Liu, W.-C.; Chang, W.-C.; Hsu, H.-H.; Huang, G.-S.; Lou, Y.-S.; Lee, C.-C.; Wang, C.-H.; Fang, W.-H. Detection of Left Ventricular Systolic Dysfunction Using an Artificial Intelligence–Enabled Chest X-Ray. Can. J. Cardiol. 2022, 38, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salte, I.M.; Østvik, A.; Smistad, E.; Melichova, D.; Nguyen, T.M.; Karlsen, S.; Brunvand, H.; Haugaa, K.H.; Edvardsen, T.; Lovstakken, L.; et al. Artificial Intelligence for Automatic Measurement of Left Ventricular Strain in Echocardiography. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2021, 14, 1918–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahado-Singh, R.; Friedman, P.; Talbot, C.; Aydas, B.; Southekal, S.; Mishra, N.K.; Guda, C.; Yilmaz, A.; Radhakrishna, U.; Vishweswaraiah, S. cfDNA in maternal blood and Artificial Intelligence: Accurate Prenatal Detection of Fetal Congenital Heart Defects. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2022, 2, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheema, B.; Mutharasan, R.K.; Sharma, A.; Jacobs, M.; Powers, K.; Lehrer, S.; Wehbe, F.H.; Ronald, J.; Pifer, L.; Rich, J.D.; et al. Augmented Intelligence to Identify Patients With Advanced Heart Failure in an Integrated Health System. JACC Adv. 2022, 1, 100123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, S.; Cohen-Shelly, M.; Attia, Z.I.; Rosenbaum, A.N.; Wang, L.; Giudicessi, J.R.; Redfield, M.; Bailey, K.; Lopez-Jimenez, F.; Lin, G.; et al. Artificial Intelligence-Enabled Electrocardiography to Screen Patients with Dilated Cardiomyopathy. Am. J. Cardiol. 2021, 155, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J.-M.; Kim, K.-H.; Akkus, Z.; Jeon, K.-H.; Park, J.; Oh, B.-H. Artificial intelligence for detecting mitral regurgitation using electrocardiography. J. Electrocardiol. 2020, 59, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jentzer, J.C.; Kashou, A.H.; Attia, Z.I.; Lopez-Jimenez, F.; Kapa, S.; Friedman, P.A.; Noseworthy, P.A. Left ventricular systolic dysfunction identification using artificial intelligence-augmented electrocardiogram in cardiac intensive care unit patients. Int. J. Cardiol. 2021, 326, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Choi, B.; Lee, M.S.; Jin, U.; Yoon, S.; Jo, Y.-Y.; Kwon, J.-M. An artificial intelligence electrocardiogram analysis for detecting cardiomyopathy in the peripartum period. Int. J. Cardiol. 2022, 352, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thalappillil, R.; Datta, P.; Datta, S.; Zhan, Y.; Wells, S.; Mahmood, F.; Cobey, F.C. Artificial Intelligence for the Measurement of the Aortic Valve Annulus. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesthesia 2020, 34, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.-M.; Shih, E.S.; Chen, J.-Y.; Huang, C.-H.; Wu, I.-C.; Chen, P.-F.; Higa, S.; Yagi, N.; Hu, Y.-F.; Hwang, M.-J.; et al. Artificial Intelligence-Enabled Electrocardiogram Improves the Diagnosis and Prediction of Mortality in Patients With Pulmonary Hypertension. JACC Asia 2022, 2, 258–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Qiu, Y.; Guo, H.; Hua, Y.; Shao, B.; Qiao, Y.; Guo, J.; Ding, H.; Zhang, Z.; Miao, L.; et al. A method to screen left ventricular dysfunction through ECG based on convolutional neural network. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2021, 32, 1095–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, W.R.; Reinisch, A.J.; Unterberger, M.J.; Schriefl, A.J. Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Auscultation of Heart Murmurs: Validation by Virtual Clinical Trial. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2019, 40, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmon, D.M.; Carter, R.E.; Cohen-Shelly, M.; Svatikova, A.; Adedinsewo, D.A.; Noseworthy, P.A.; Kapa, S.; Lopez-Jimenez, F.; Friedman, P.A.; Attia, Z.I. Real-world performance, long-term efficacy, and absence of bias in the artificial intelligence enhanced electrocardiogram to detect left ventricular systolic dysfunction. Eur. Heart J. Digit. Health 2022, 3, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makimoto, H.; Shiraga, T.; Kohlmann, B.; Magnisali, C.E.; Gerguri, S.; Motoyama, N.; Clasen, L.; Bejinariu, A.; Klein, K.; Makimoto, A.; et al. Efficient screening for severe aortic valve stenosis using understandable artificial intelligence: A prospective diagnostic accuracy study. Eur. Heart J. Digit. Health 2022, 3, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, Z.I.; Dugan, J.; Rideout, A.; Maidens, J.N.; Venkatraman, S.; Guo, L.; Noseworthy, P.A.; Pellikka, P.A.; Pham, S.L.; Kapa, S.; et al. Automated Detection of Low Ejection Fraction from a One-lead Electrocardiogram: Application of an AI algorithm to an ECG-enabled Digital Stethoscope. Eur. Heart J. Digit. Health 2022, 3, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanayim, T.; Lupu, L.; Naveh, S.; Bachner-Hinenzon, N.; Adler, D.; Adawi, S.; Banai, S.; Shiran, A. Artificial Intelligence-Based Stethoscope for the Diagnosis of Aortic Stenosis. Am. J. Med. 2022, 135, 1124–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, D.; Yamamoto, A.; Ehara, S.; Iwata, S.; Abo, K.; Walston, S.L.; Matsumoto, T.; Shimazaki, A.; Yoshiyama, M.; Miki, Y. Artificial intelligence-based detection of aortic stenosis from chest radiographs. Eur. Heart J. Digit. Health 2022, 3, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Nagata, Y.; Nitta, G.; Okata, S.; Nagase, M.; Mitsui, K.; Watanabe, K.; Miyazaki, R.; Kaneko, M.; Nagamine, S.; et al. Prediction of premature ventricular complex origins using artificial intelligence–enabled algorithms. Cardiovasc. Digit. Health J. 2020, 2, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, E.; Jiang, J.; Su, R.; Gao, M.; Zhu, S.; Zhou, J.; Huo, Y. A new smart wristband equipped with an artificial intelligence algorithm to detect atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm 2020, 17, 847–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sau, A.; Ibrahim, S.; Ahmed, A.; Handa, B.; Kramer, D.B.; Waks, J.W.; Arnold, A.D.; Howard, J.P.; Qureshi, N.; Koa-Wing, M.; et al. Artificial intelligence-enabled electrocardiogram to distinguish cavotricuspid isthmus dependence from other atrial tachycardia mechanisms. Eur. Heart J. Digit. Health 2022, 3, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, Y.-Y.; Kwon, J.-M.; Jeon, K.-H.; Cho, Y.-H.; Shin, J.-H.; Lee, Y.-J.; Jung, M.-S.; Ban, J.-H.; Kim, K.-H.; Lee, S.Y.; et al. Artificial intelligence to diagnose paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia using electrocardiography during normal sinus rhythm. Eur. Heart J. Digit. Health 2021, 2, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.-C.; Hsieh, P.-H.; Wu, M.-Y.; Wang, Y.-C.; Wei, J.-T.; Shih, E.S.C.; Hwang, M.-J.; Lin, W.-Y.; Lee, K.-J.; Wang, T.-H. Usefulness of multi-labelling artificial intelligence in detecting rhythm disorders and acute ST-elevation myocardial infarction on 12-lead electrocardiogram. Eur. Heart J. Digit. Health 2021, 2, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au-Yeung, W.-T.M.; Sevakula, R.K.; Sahani, A.K.; Kassab, M.; Boyer, R.; Isselbacher, E.M.; Armoundas, A.A. Real-time machine learning-based intensive care unit alarm classification without prior knowledge of the underlying rhythm. Eur. Heart J. Digit. Health 2021, 2, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-C.; Chen, C.-Y.; Lee, S.-J.; Lee, M.-C.; Tsai, C.-Y.; Chen, S.-T.; Li, Y.-J. Exploiting exercise electrocardiography to improve early diagnosis of atrial fibrillation with deep learning neural networks. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 146, 105584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, S.K.; Janghel, R.R.; Vani, V. Patient Specific Machine Learning Models for ECG Signal Classification. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2020, 167, 2181–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Cheng, C.; Yin, H.; Li, X.; Zuo, P.; Ding, J.; Lin, F.; Wang, J.; Zhou, B.; Li, Y.; et al. Automatic multilabel electrocardiogram diagnosis of heart rhythm or conduction abnormalities with deep learning: A cohort study. Lancet Digit. Health 2020, 2, e348–e357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otaki, Y.; Singh, A.; Kavanagh, P.; Miller, R.J.; Parekh, T.; Tamarappoo, B.K.; Sharir, T.; Einstein, A.J.; Fish, M.B.; Ruddy, T.D.; et al. Clinical Deployment of Explainable Artificial Intelligence of SPECT for Diagnosis of Coronary Artery Disease. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2022, 15, 1091–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, T.; Spiliopoulos, S.; Veltman, C.; Hergesell, V.; Passow, A.; Tenderich, G.; Borggrefe, M.; Koerner, M.M. Detection of myocardial ischemia due to clinically asymptomatic coronary artery stenosis at rest using supervised artificial intelligence-enabled vectorcardiography—A five-fold cross validation of accuracy. J. Electrocardiol. 2020, 59, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xiong, J.; Hou, Y.; Zhu, M.; Lu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Teliewubai, J.; Liu, W.; Xu, X.; Li, X.; et al. Early detection of ST-segment elevated myocardial infarction by artificial intelligence with 12-lead electrocardiogram. Int. J. Cardiol. 2020, 317, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.J.; Park, M.J.; Ko, Y.; Soh, M.-S.; Kim, H.M.; Kim, C.H.; Lee, E.; Kim, J. Artificial intelligence versus physicians on interpretation of printed ECG images: Diagnostic performance of ST-elevation myocardial infarction on electrocardiography. Int. J. Cardiol. 2022, 363, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Kang, S.-J.; Min, H.-S.; Lee, J.-G.; Kim, W.-J.; Kang, S.H.; Kang, D.-Y.; Lee, P.H.; Ahn, J.-M.; Park, D.-W.; et al. Intravascular ultrasound-based deep learning for plaque characterization in coronary artery disease. Atherosclerosis 2021, 324, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuckey, T.D.; Gammon, R.S.; Goswami, R.; Depta, J.P.; Steuter, J.A.; Iii, F.J.M.; Roberts, M.C.; Singh, N.; Ramchandani, S.; Burton, T.; et al. Cardiac Phase Space Tomography: A novel method of assessing coronary artery disease utilizing machine learning. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.; Lee, J.-G.; Kang, S.-J.; Kim, W.-J.; Choi, S.-Y.; Ko, J.; Min, H.-S.; Choi, G.-H.; Kang, D.-Y.; Lee, P.H.; et al. Angiography-Based Machine Learning for Predicting Fractional Flow Reserve in Intermediate Coronary Artery Lesions. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, e011685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.-H.; Tsai, T.-H.; Chen, J.-H.; Huang, C.-J.; Chiang, C.-E.; Chen, C.-H.; Cheng, H.-M. Machine learning of treadmill exercise test to improve selection for testing for coronary artery disease. Atherosclerosis 2022, 340, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipkin, I.; Telluri, A.; Kim, Y.; Sidahmed, A.; Krepp, J.M.; Choi, B.G.; Jonas, R.; Marques, H.; Chang, H.-J.; Choi, J.H.; et al. Coronary CTA With AI-QCT Interpretation: Comparison with Myocardial Perfusion Imaging for Detection of Obstructive Stenosis Using Invasive Angiography as Reference Standard. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2022, 219, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurata, A.; Fukuyama, N.; Hirai, K.; Kawaguchi, N.; Tanabe, Y.; Okayama, H.; Shigemi, S.; Watanabe, K.; Uetani, T.; Ikeda, S.; et al. On-Site Computed Tomography-Derived Fractional Flow Reserve Using a Machine-Learning Algorithm—Clinical Effectiveness in a Retrospective Multicenter Cohort. Circ. J. 2019, 83, 1563–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, C.X.; Wang, Y.N.; Zhou, F.; Schoepf, U.J.; van Assen, M.; Stroud, R.E.; Li, J.H.; Zhang, X.L.; Lu, M.J.; Zhou, C.S.; et al. Diagnostic performance of fractional flow reserve derived from coronary CT angiography for detection of lesion-specific ischemia: A multi-center study and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Radiol. 2019, 116, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, A.D.; Marques, H.; Kumar, V.; Griffin, W.F.; Rahban, H.; Karlsberg, R.P.; Zeman, R.K.; Katz, R.J.; Earls, J.P. CT Evaluation by Artificial Intelligence for Atherosclerosis, Stenosis and Vascular Morphology (CLARIFY): A Multi-center, international study. J. Cardiovasc. Comput. Tomogr. 2021, 15, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, I.; Na, W.; Kwon, O.; Yang, D.H.; Park, G.-M.; Gwon, H.; Kang, H.J.; Jeong, Y.U.; Yoo, J.; Kim, Y.; et al. CardioNet: A manually curated database for artificial intelligence-based research on cardiovascular diseases. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2021, 21, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardiovascular Disease Dataset. Kaggle. 2022. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/sulianova/cardiovascular-disease-dataset (accessed on 14 November 2022).
- Heart Disease Data Set. UC Irvine Machine Learning Repository. 2022. Available online: https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/heart+disease (accessed on 14 November 2022).
| Authors (et al.) | Year | Disease Diagnosed | Data Source | Machine Learning Method | Reported Results (Accuracy, Sensitivity, Specificity, PPV, NPV, AUC, F1) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hsiang [11] | 2022 | Low EF | Chest X-ray | Deep Learning | 0.867 | ||||||
| Salte [12] | 2021 | LV dysfunction | Echocardiography | Deep Learning | GLS for: AI −12.0 ± 4.1%, Reference −13.5 ± 5.3% | ||||||
| Bahado-Singh [13] | 2022 | Fetal congenital heart defects | Cell-free DNA | RF, SVM, DL | 98% | 94% | 0.97 | ||||
| Cheema [14] | 2022 | Heart Failure | IHS Data | Deep Learning | 83% | ||||||
| Shrivastava [15] | 2021 | Dilated Cardiomyopathy | ECG | N/A | 98.8% | 44.8% | 1.8% | 100% | 0.955 | ||
| Kwon [16] | 2020 | Mitral Regurgitation | ECG | N/A | 0.816 | ||||||
| Jentzer [17] | 2021 | LV dysfunction | ECG | N/A | 76% | 0.83 | |||||
| Lee [18] | 2022 | LV dysfunction | ECG | Deep Learning | 0.833 | 0.809 | 0.352 | 0.975 | 0.877 | ||
| Thalappillil [19] | 2020 | Aortic Annulus Size | Echocardiography | N/A | −4.62 to 1.26 mm difference for derived area and −4.51 to 1.45 mm for derived perimeter value | ||||||
| Liu [20] | 2022 | Pulmonary Hypertension | ECG, TTE | Cross Validation DL | 81% | 79.6% | 0.88 | ||||
| Sun [21] | 2021 | Low EF | ECG, TTE | CNN Deep Learning | 73.9% | 69.2% | 70.50% | 70.1% | 69.9% | ||
| Thompson [22] | 2019 | Valvular, congenital | Digital Stethoscope | N/A | 88% | 93% | 81% | ||||
| Harmon [23] | 2022 | LV dysfunction | ECG | CNN Deep Learning | 0.93 | ||||||
| Makimoto [24] | 2022 | AV Stenosis | Digital Stethoscope | CNN Cross Validation | 95.7% | 97.6% | 94.4% | 0.93 | |||
| Attia [25] | 2022 | Low EF | Digital Stethoscope | CNN | 0.89 | ||||||
| Ghanayim [26] | 2022 | AV Stenosis | Digital Stethoscope | N/A | 84% | 92% | |||||
| Ueda [27] | 2021 | AV Stenosis | Chest X-ray | Deep Learning Ensemble | 0.71 | 0.78 | 0.71 | 0.18 | 0.97 | 0.83 | |
| Nakamura [28] | 2021 | PVC Origin | ECG | SVM, CNN | 0.85 | ||||||
| Chen [29] | 2020 | AF | 1-Lead ECG, PPG | CNN Deep Learning | 93.27% | 88% | 96.41% | ||||
| Sau [30] | 2022 | AFL/SVT | ECG | N/A | 86% | ||||||
| Jo [31] | 2021 | Paroxisymal SVT | Sinus ECG | Deep Learning | 0.97 | 0.868 | 0.972 | 0.255 | 0.998 | ||
| Chang [32] | 2021 | Arrhythmia | ECG | Recurrent NN | 0.987 | 0.997 | |||||
| Au-Yeung [33] | 2021 | Arrhythmia | ECG, BP, PPG | Random Forest | 81.54% | ||||||
| Lee [34] | 2022 | AF | Exercise ECG | Deep Learning | N/A | ||||||
| Pandey [35] | 2020 | Arrhythmia | ECG | Ensemble SVM | 94.4% | ||||||
| Zhu [36] | 2020 | Arrhythmia | ECG | CNN | 0.887 | ||||||
| Otaki [37] | 2022 | CAD | SPECT | Deep Learning | 0.83 | ||||||
| Braun [38] | 2020 | CAD | VCG | Supervised ML | 82.5% | 90.20% | 74.4% | ||||
| Zhao [39] | 2020 | ST elevated MI | ECG | N/A | 99.01% | 96.75% | 99.2% | 0.995 | 0.937 | ||
| Choi [40] | 2022 | ST elevated MI | ECG Image | N/A | 0.919 | ||||||
| Cho [41] | 2021 | Plaque Type | IVUS | Deep Learning | 96% | 86% | 97% | ||||
| Stuckey [42] | 2018 | CAD | CT | Supervised ML | 92% | 62% | 46% | 96% | |||
| Cho [43] | 2019 | CAD | C. Angiography FFR | Supervised ML | 81% | 0.87 | |||||
| Lee [44] | 2021 | CAD | Treadmill Test | RF, SVM, LR, K-NN, EGB | 85% | 0.74 | |||||
| Lipkin [45] | 2022 | CAD | AI CCTA | N/A | 0.88 | ||||||
| Kurata [46] | 2019 | CAD | CT FFR | N/A | 0.907 | ||||||
| Tang [47] | 2019 | CAD | CCTA FFR | N/A | 0.9 | 0.85 | 0.94 | ||||
| Choi [48] | 2021 | CAD | AI CCTA | CNN Deep Learning | 94.80% | 80% | 97% | 80% | 97% | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Uzun Ozsahin, D.; Ozgocmen, C.; Balcioglu, O.; Ozsahin, I.; Uzun, B. Diagnostic AI and Cardiac Diseases. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2901. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12122901
Uzun Ozsahin D, Ozgocmen C, Balcioglu O, Ozsahin I, Uzun B. Diagnostic AI and Cardiac Diseases. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(12):2901. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12122901
Chicago/Turabian StyleUzun Ozsahin, Dilber, Cemre Ozgocmen, Ozlem Balcioglu, Ilker Ozsahin, and Berna Uzun. 2022. "Diagnostic AI and Cardiac Diseases" Diagnostics 12, no. 12: 2901. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12122901
APA StyleUzun Ozsahin, D., Ozgocmen, C., Balcioglu, O., Ozsahin, I., & Uzun, B. (2022). Diagnostic AI and Cardiac Diseases. Diagnostics, 12(12), 2901. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12122901









