Mortality Risk Assessment in Peripheral Arterial Disease—The Burden of Cardiovascular Risk Factors over the Years: A Single Center’s Experience
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and PAD Diagnosis
2.2. Measurements
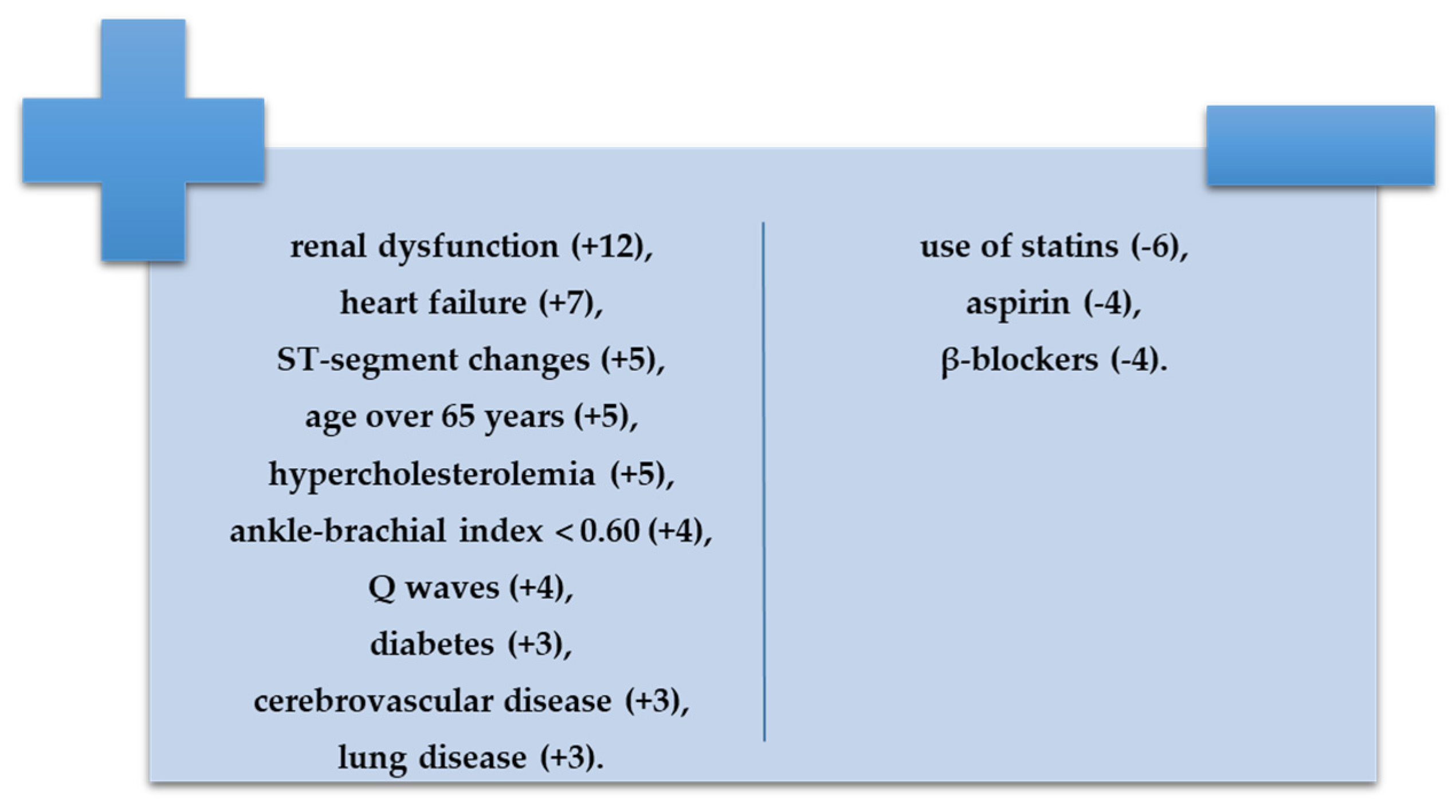
- With negative prognostic value, renal dysfunction (+12), heart failure (+7), ST-segment changes (+5), age over 65 years (+5), hypercholesterolemia (+5), ankle-brachial index less than 0. 60 (+4), Q waves (+4), diabetes (+3), cerebrovascular disease (+3), and lung disease (+3);
- With positive prognostic value, use of statins (−6), aspirin (−4), or β-blockers (−4).
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.4. Ethics
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Campia, U.; Gerhard-Herman, M.; Piazza, G.; Goldhaber, S.Z. Peripheral Artery Disease: Past, Present, and Future. Am. J. Med. 2019, 132, 1133–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shammas, N.W. Epidemiology, Classification, and Modifiable Risk Factors of Peripheral Arterial Disease. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2007, 3, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aday, A.W.; Matsushita, K. Epidemiology of Peripheral Artery Disease and Polyvascular Disease. Circ. Res. 2021, 128, 1818–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, G.A.; Mensah, G.A.; Johnson, C.O.; Addolorato, G.; Ammirati, E.; Baddour, L.M.; Barengo, N.C.; Beaton, A.Z.; Benjamin, E.J.; Benziger, C.P.; et al. Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk Factors, 1990–2019. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 2982–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pabon, M.; Cheng, S.; Altin, S.E.; Sethi, S.S.; Nelson, M.D.; Moreau, K.L.; Hamburg, N.; Hess, C.N. Sex Differences in Peripheral Artery Disease. Circ. Res. 2022, 130, 496–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Rudan, D.; Zhu, Y.; Fowkes, F.J.I.; Rahimi, K.; Fowkes, F.G.R.; Rudan, I. Global, Regional, and National Prevalence and Risk Factors for Peripheral Artery Disease in 2015: An Updated Systematic Review and Analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2019, 7, e1020–e1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colantonio, L.D.; Hubbard, D.; Monda, K.L.; Mues, K.E.; Huang, L.; Dai, Y.; Jackson, E.A.; Brown, T.M.; Rosenson, R.S.; Woodward, M.; et al. Atherosclerotic Risk and Statin Use Among Patients With Peripheral Artery Disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, M.G.; Klarin, D.; Assimes, T.L.; Freiberg, M.S.; Ingelsson, E.; Lynch, J.; Natarajan, P.; O’Donnell, C.; Rader, D.J.; Tsao, P.S.; et al. Genetics of Smoking and Risk of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Diseases: A Mendelian Randomization Study. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2034461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aponte, J. The Prevalence of Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) and PAD Risk Factors among Different Ethnic Groups in the US Population. J. Vasc. Nurs. 2012, 30, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elfghi, M.; Jordan, F.; Dunne, D.; Gibson, I.; Jones, J.; Flaherty, G.; Sultan, S.; Tawfick, W. The Effect of Lifestyle and Risk Factor Modification on Occlusive Peripheral Arterial Disease Outcomes: Standard Healthcare vs Structured Programme—For a Randomised Controlled Trial Protocol. Trials 2021, 22, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, A.T.; Criqui, M.H.; Treat-Jacobson, D.; Regensteiner, J.G.; Creager, M.A.; Olin, J.W.; Krook, S.H.; Hunninghake, D.B.; Comerota, A.J.; Walsh, M.E.; et al. Peripheral Arterial Disease Detection, Awareness, and Treatment in Primary Care. JAMA 2001, 286, 1317–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, G.J.; McClenny, T.E.; Kovacs, M.E.; Raabe, R.D.; Katzen, B.T. The Importance of Increasing Public and Physician Awareness of Peripheral Arterial Disease. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2002, 13, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meru, A.V.; Mittra, S.; Thyagarajan, B.; Chugh, A. Intermittent Claudication: An Overview. Atherosclerosis 2006, 187, 221–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, B.; Mancia, G.; Spiering, W.; Agabiti Rosei, E.; Azizi, M.; Burnier, M.; Clement, D.L.; Coca, A.; de Simone, G.; Dominiczak, A.; et al. 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the Management of Arterial Hypertension. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 3021–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonagh, T.A.; Metra, M.; Adamo, M.; Gardner, R.S.; Baumbach, A.; Böhm, M.; Burri, H.; Butler, J.; Čelutkienė, J.; Chioncel, O.; et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute and Chronic Heart Failure. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 3599–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, P.E. Evaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease: Synopsis of the Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes 2012 Clinical Practice Guideline. Ann. Intern. Med. 2013, 158, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khwaja, A. KDIGO Clinical Practice Guidelines for Acute Kidney Injury. Nephron 2012, 120, c179–c184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association. 6. Glycemic Targets: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2020. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, S66–S76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feringa, H.H.H. A Prognostic Risk Index for Long-Term Mortality in Patients With Peripheral Arterial Disease. Arch. Intern. Med. 2007, 167, 2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buliga-Finis, O.; Ouatu, A.; Badescu, M.C.; Dima, N.; Tănase, D.; Richter, P.; Rezuş, C. Beyond the Cardiorenal Syndrome: Pathophysiological Approaches and Biomarkers for Renal and Cardiac Crosstalk. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreau, K.L.; Hildreth, K.L.; Meditz, A.L.; Deane, K.D.; Kohrt, W.M. Endothelial Function Is Impaired across the Stages of the Menopause Transition in Healthy Women. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, 4692–4700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celermajer, D.S.; Sorensen, K.E.; Spiegelhalter, D.J.; Georgakopoulos, D.; Robinson, J.; Deanfield, J.E. Aging Is Associated with Endothelial Dysfunction in Healthy Men Years before the Age-Related Decline in Women. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1994, 24, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davignon, J.; Ganz, P. Role of Endothelial Dysfunction in Atherosclerosis. Circulation 2004, 109, III-27–III-32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, M.A.; Ho, E.; Denenberg, J.O.; Langer, R.D.; Newman, A.B.; Fabsitz, R.R.; Criqui, M.H. Ethnic-Specific Prevalence of Peripheral Arterial Disease in the United States. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2007, 32, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erb, W. Klinische Beitrage Zur Pathologie Des Intermittierenden Hinkens. Munch Med. Wochenschr 1911, 2, 2487. [Google Scholar]
- Willigendael, E.M.; Teijink, J.A.W.; Bartelink, M.-L.; Kuiken, B.W.; Boiten, J.; Moll, F.L.; Büller, H.R.; Prins, M.H. Influence of Smoking on Incidence and Prevalence of Peripheral Arterial Disease. J. Vasc. Surg. 2004, 40, 1158–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Group, T. working Management of Peripheral Arterial Disease: Transatlantic Inter-Society Consensus. J. Vasc. Surg. 2000, 31, S192–S273. [Google Scholar]
- Hooi, J.D.; Kester, A.D.; Stoffers, H.E.; Overdijk, M.M.; van Ree, J.W.; Knottnerus, J.A. Incidence of and Risk Factors for Asymptomatic Peripheral Arterial Occlusive Disease: A Longitudinal Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2001, 153, 666–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingolfsson, I.O.; Sigurdsson, G.; Sigvaldason, H.; Thorgeirsson, G.; Sigfusson, N. A Marked Decline in the Prevalence and Incidence of Intermittent Claudication in Icelandic Men 1968-1986: A Strong Relationship to Smoking and Serum Cholesterol--the Reykjavik Study. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1994, 47, 1237–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera-Guarderas, F.; Carrasco-Tenezaca, F.; De la Torre-Cisneros, K. Peripheral Artery Disease in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Survival Analysis of an Ecuadorian Population in Primary Care. J. Prim. Care Community Health 2020, 11, 2150132720957449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva Filho, P.J.; Teodoro, E.C.M.; Pereira, E.C.A.; dos Reis Miranda, V.C. Prevalence of Peripheral Arterial Disease and Associated Factors in People with Type 2 Diabetes. Fisioter. Mov. 2021, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowkes, F.G.R.; Rudan, D.; Rudan, I.; Aboyans, V.; Denenberg, J.O.; McDermott, M.M.; Norman, P.E.; Sampson, U.K.A.; Williams, L.J.; Mensah, G.A.; et al. Comparison of Global Estimates of Prevalence and Risk Factors for Peripheral Artery Disease in 2000 and 2010: A Systematic Review and Analysis. Lancet 2013, 382, 1329–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyelade, B.O.; OlaOlorun, A.D.; Odeigah, L.O.; Amole, I.O.; Adediran, O.S. The Prevalence of Peripheral Arterial Disease in Diabetic Subjects in South-West Nigeria. Afr. J. Prim. Health Care Fam. Med. 2012, 4, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Barnes, J.A.; Eid, M.A.; Creager, M.A.; Goodney, P.P. Epidemiology and Risk of Amputation in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus and Peripheral Artery Disease. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, 1808–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schamp, K.B.C.; Meerwaldt, R.; Reijnen, M.M.P.J.; Geelkerken, R.H.; Zeebregts, C.J. The Ongoing Battle between Infrapopliteal Angioplasty and Bypass Surgery for Critical Limb Ischemia. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2012, 26, 1145–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckman, J.A.; Creager, M.A.; Libby, P. Diabetes and Atherosclerosis: Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, and Management. JAMA 2002, 287, 2570–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favaretto, E.; Sartori, M.; Pacelli, A.; Conti, E.; Cosmi, B. Coronary Artery Disease and Restenosis after Peripheral Endovascular Intervention Are Predictors of Poor Outcome in Peripheral Arterial Disease. Acta Cardiol. 2020, 75, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, E.J.; Bishu, K.; Waldo, S.W. Endovascular Treatment of Infrapopliteal Peripheral Artery Disease. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2016, 18, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laird, J.R.; Jain, A.; Zeller, T.; Feldman, R.; Scheinert, D.; Popma, J.J.; Armstrong, E.J.; Jaff, M.R. Complete SE Investigators Nitinol Stent Implantation in the Superficial Femoral Artery and Proximal Popliteal Artery: Twelve-Month Results from the Complete SE Multicenter Trial. J. Endovasc. Ther. 2014, 21, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saia, F.; Lemos, P.A.; Lee, C.H.; Arampatzis, C.A.; Hoye, A.; Degertekin, M.; Tanabe, K.; Sianos, G.; Smits, P.C.; McFadden, E.; et al. Sirolimus-Eluting Stent Implantation in ST-Elevation Acute Myocardial Infarction: A Clinical and Angiographic Study. Circulation 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalano, M.; Scandale, G.; Carzaniga, G.; Cinquini, M.; Minola, M.; Antoniazzi, V.; Dimitrov, G.; Carotta, M. Aortic Augmentation Index in Patients With Peripheral Arterial Disease. J. Clin. Hypertens 2014, 16, 782–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabia, J.; Torguet, P.; Garcia, I.; Martin, N.; Mate, G.; Marin, A.; Molina, C.; Valles, M. The Relationship between Renal Resistive Index, Arterial Stiffness, and Atherosclerotic Burden: The Link between Macrocirculation and Microcirculation. J. Clin. Hypertens 2014, 16, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijer, W.T.; Grobbee, D.E.; Hunink, M.G.M.; Hofman, A.; Hoes, A.W. Determinants of Peripheral Arterial Disease in the Elderly: The Rotterdam Study. Arch. Intern. Med. 2000, 160, 2934–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clement, D.L.; De Buyzere, M.L.; Duprez, D.A. Hypertension in Peripheral Arterial Disease. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2004, 10, 3615–3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Ballew, S.H.; Tanaka, H.; Szklo, M.; Heiss, G.; Coresh, J.; Matsushita, K. 2017 ACC/AHA Blood Pressure Classification and Incident Peripheral Artery Disease: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2020, 27, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez Muñoz-Torrero, J.F.; Escudero-Sánchez, G.; Calderón-García, J.F.; Rico-Martín, S.; Robles, N.R.; Bacaicoa, M.A.; Alcalá-Pedrajas, J.N.; Gil-Fernández, G.; Monreal, M.; On Behalf of the Frena Investigators. Systolic Blood Pressure and Outcomes in Stable Outpatients with Recent Symptomatic Artery Disease: A Population-Based Longitudinal Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hicks, C.W.; Yang, C.; Ndumele, C.E.; Folsom, A.R.; Heiss, G.; Black, J.H.; Selvin, E.; Matsushita, K. Associations of Obesity With Incident Hospitalization Related to Peripheral Artery Disease and Critical Limb Ischemia in the ARIC Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, e008644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freiberg, M.S.; Pencina, M.J.; D’Agostino, R.B.; Lanier, K.; Wilson, P.W.F.; Vasan, R.S. BMI vs. Waist Circumference for Identifying Vascular Risk. Obesity 2008, 16, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heffron, S.P.; Dwivedi, A.; Rockman, C.B.; Xia, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhong, J.; Berger, J.S. Body Mass Index and Peripheral Artery Disease. Atherosclerosis 2020, 292, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cronin, O.; Morris, D.R.; Walker, P.J.; Golledge, J. The Association of Obesity with Cardiovascular Events in Patients with Peripheral Artery Disease. Atherosclerosis 2013, 228, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Schutter, A.; Lavie, C.J.; Milani, R.V. The Impact of Obesity on Risk Factors and Prevalence and Prognosis of Coronary Heart Disease—The Obesity Paradox. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2014, 56, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsiki, N.; Giannoukas, A.D.; Athyros, V.G.; Mikhailidis, D.P. Lipid-Lowering Treatment in Peripheral Artery Disease. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2018, 39, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murabito, J.M.; Evans, J.C.; Nieto, K.; Larson, M.G.; Levy, D.; Wilson, P.W.F. Prevalence and Clinical Correlates of Peripheral Arterial Disease in the Framingham Offspring Study. Am. Heart J. 2002, 143, 961–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bainton, D.; Sweetnam, P.; Baker, I.; Elwood, P. Peripheral Vascular Disease: Consequence for Survival and Association with Risk Factors in the Speedwell Prospective Heart Disease Study. Br. Heart J. 1994, 72, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hageman, S.H.J.; de Borst, G.J.; Dorresteijn, J.A.N.; Bots, M.L.; Westerink, J.; Asselbergs, F.W.; Visseren, F.L.J. UCC-SMART Study Group Cardiovascular Risk Factors and the Risk of Major Adverse Limb Events in Patients with Symptomatic Cardiovascular Disease. Heart 2020, 106, 1686–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, C.; Saulnier, P.-J.; Potier, L.; Croyal, M.; Blanchard, V.; Gand, E.; Ragot, S.; Schneider, F.; Bocock, O.; Baillet-Blanco, L.; et al. Plasma Concentrations of Lipoproteins and Risk of Lower-Limb Peripheral Artery Disease in People with Type 2 Diabetes: The SURDIAGENE Study. Diabetologia 2021, 64, 668–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, J.; Jhund, P.S.; Lund, L.H.; Padmanabhan, S.; Claggett, B.L.; Shen, L.; Petrie, M.C.; Abraham, W.T.; Desai, A.S.; Dickstein, K.; et al. Prognostic Models Derived in PARADIGM-HF and Validated in ATMOSPHERE and the Swedish Heart Failure Registry to Predict Mortality and Morbidity in Chronic Heart Failure. JAMA Cardiol. 2020, 5, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samsky, M.D.; Hellkamp, A.; Hiatt, W.R.; Fowkes, F.G.R.; Baumgartner, I.; Berger, J.S.; Katona, B.G.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Norgren, L.; Blomster, J.I.; et al. Association of Heart Failure With Outcomes Among Patients With Peripheral Artery Disease: Insights From EUCLID. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e018684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, H.; Miura, T.; Minamisawa, M.; Ueki, Y.; Abe, N.; Hashizume, N.; Mochidome, T.; Harada, M.; Shimizu, K.; Shoin, W.; et al. Prognostic Value of Ankle Brachial Index for Future Incident Heart Failure in Patients without Previous Heart Failure: Data from the Impressive Predictive Value of Ankle Brachial Index for Clinical Long Term Outcome in Patients with Cardiovascular Disease Examined by ABI Study. Heart Vessels 2017, 32, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, D.K.; Skali, H.; Claggett, B.; Kasabov, R.; Cheng, S.; Shah, A.M.; Loehr, L.R.; Heiss, G.; Nambi, V.; Aguilar, D.; et al. Heart Failure Risk Across the Spectrum of Ankle-Brachial Index. JACC Heart Fail. 2014, 2, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasada, S.; Shah, S.J.; Michos, E.D.; Polak, J.F.; Greenland, P. Ankle–Brachial Index and Incident Heart Failure with Reduced versus Preserved Ejection Fraction: The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. Vasc. Med. 2019, 24, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unkart, J.T.; Allison, M.A.; Araneta, M.R.G.; Ix, J.H.; Matsushita, K.; Criqui, M.H. Burden of Peripheral Artery Disease on Mortality and Incident Cardiovascular Events. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2020, 189, 951–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyun, S.; Forbang, N.I.; Allison, M.A.; Denenberg, J.O.; Criqui, M.H.; Ix, J.H. Ankle-Brachial Index, Toe-Brachial Index, and Cardiovascular Mortality in Persons with and without Diabetes Mellitus. J. Vasc. Surg. 2014, 60, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagt, V.L.; Hazenberg, C.E.V.B.; Kapelle, J.; Cramer, M.J.; Visseren, F.L.J.; Westerink, J.; on behalf of the UCC-SMART Study Group. Screen-Detected Abnormal Ankle Brachial Index: A Risk Indicator for Future Cardiovascular Morbidity and Mortality in Patients with Manifest Cardiovascular Disease. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0265050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Guo, X.; Li, J.; Hu, D.; Zhao, D.; Ma, H.; Mou, Q.; Liu, J.; Xu, Y. Predictive Value of Ankle-Brachial Index to All-Cause Mortality and Cardiovascular Mortality in Chinese Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Vasa 2012, 41, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mlekusch, W.; Exner, M.; Sabeti, S.; Amighi, J.; Schlager, O.; Wagner, O.; Minar, E.; Schillinger, M. Serum Creatinine Predicts Mortality in Patients with Peripheral Artery Disease: Influence of Diabetes and Hypertension. Atherosclerosis 2004, 175, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez, J.A.; Aday, A.W.; Patel, M.R.; Jones, W.S. Polyvascular Disease: Reappraisal of the Current Clinical Landscape. Circ Cardiovasc. Interv. 2019, 12, e007385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, J.A.; Mulder, H.; Jones, W.S.; Rockhold, F.W.; Baumgartner, I.; Berger, J.S.; Blomster, J.I.; Fowkes, F.G.R.; Held, P.; Katona, B.G.; et al. Polyvascular Disease and Risk of Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Peripheral Artery Disease: A Secondary Analysis of the EUCLID Trial. JAMA Netw. Open 2018, 1, e185239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
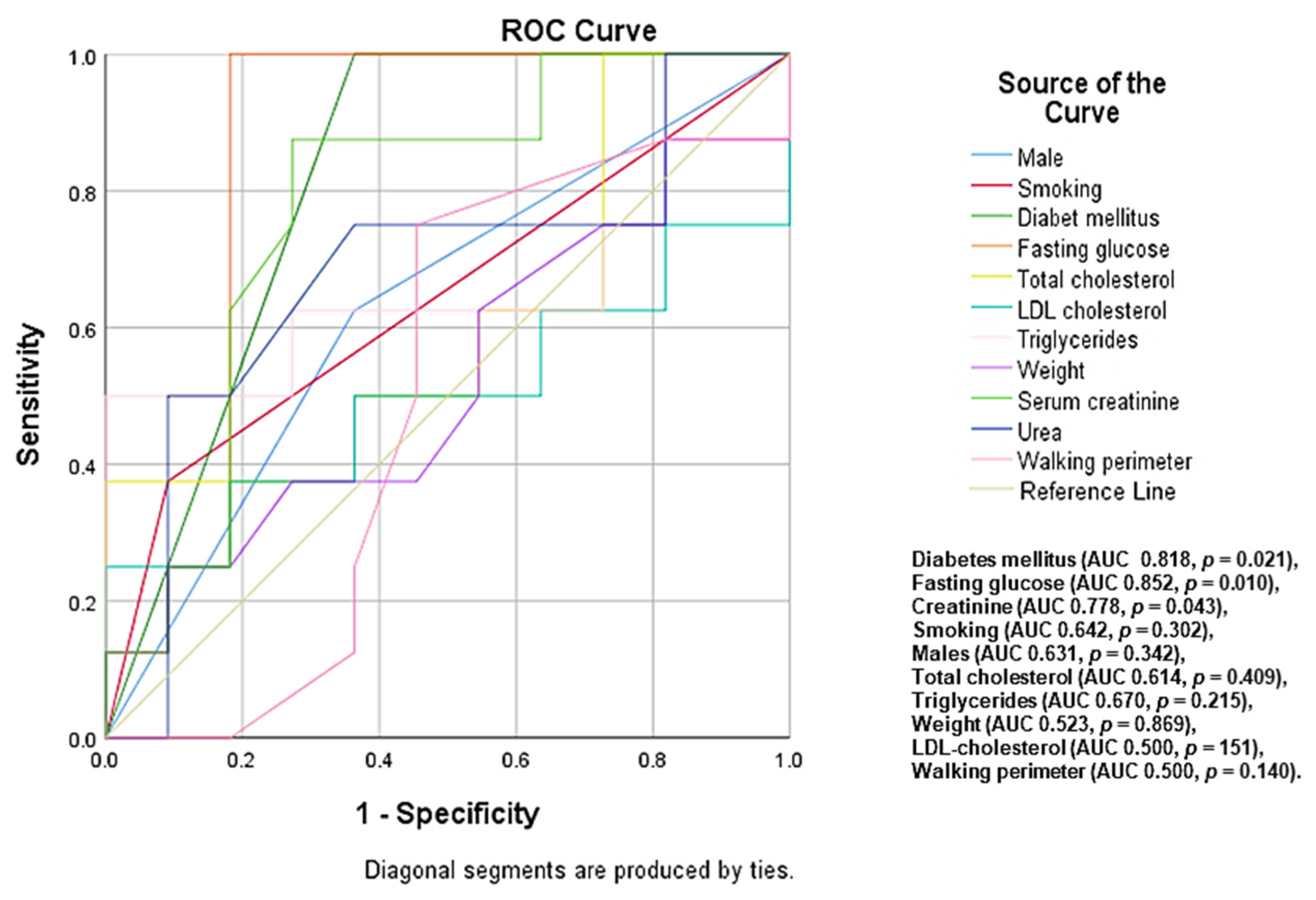
| Paremeters | Total Group (n = 101) | Low and Low-Intermediate Risk Group (n = 49) | High-Intermediate and High-Risk Group (n = 52) | p-Value | p*-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographics | |||||
| Males | 52 (51.5%) | 30 (61.2%) | 22 (42.3%) | 0.270 | 0.289 |
| Urban environment | 38 (37.6%) | 14 (28.6%) | 24 (46.2%) | 0.021 | 0.029 |
| Age, y | 70.67 ± 9.24 | 69.71 ± 10.01 | 71.58 ± 8.45 | 0.411 | 0.704 |
| Height, m | 1.65 ± 0.08 | 1.66 ± 0.07 | 1.64 ± 0.09 | 0.385 | 0.522 |
| Weight, kg | 76.53 ± 16.33 | 75.98 ± 13.95 | 79.06 ± 18.43 | 0.047 | 0.041 |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 27.97 ± 4.88 | 27.55 ± 4.27 | 29.36 ± 5.40 | 0.049 | 0.031 |
| Resting hemodynamics | |||||
| Systolic BP, mmHg | 144.18 ± 19.44 | 142.29 ± 21.39 | 145.96 ± 17.43 | 0.345 | 0.754 |
| Diastolic BP, mmHg | 81.73 ± 7.40 | 80.71 ± 5.95 | 82.69 ± 8.49 | 0.181 | 0.557 |
| Heart rate, bpm | 82.55 ± 15.95 | 80.59 ± 13.05 | 84.40 ± 18.19 | 0.232 | 0.767 |
| Prognostic index risk factors | |||||
| Renal dysfunction | 17 (16.83%) | 3 (6.1%) | 14 (26.92%) | 0.024 | 0.033 |
| Heart failure | 26 (25.74%) | 9 (18.4%) | 17 (32.69%) | 0.019 | 0.038 |
| Age > 65 years | 69 (68.3%) | 31 (63.3%) | 38 (73.1%) | 0.289 | 0.692 |
| Hypercholesterolemia | 59 (58.4%) | 25 (51.0%) | 34 (65.4%) | <0.001 | 0.031 |
| ST-segment changes | 37 (36.6%) | 22 (44.9%) | 15 (28.8%) | 0.094 | 0.748 |
| ABI < 0.6 | 21 (20.8%) | 8 (16.3%) | 13 (25.0%) | 0.028 | 0.043 |
| Q-waves | 38 (37.6%) | 16 (32.7%) | 22 (42.3%) | 0.317 | 0.387 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 13 (12.9%) | 7 (14.3%) | 6 (11.5%) | 0.427 | 0.574 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 38 (37.6%) | 15 (30.6%) | 23 (44.2%) | 0.051 | 0.046 |
| COPD | 27 (26.7%) | 12 (24.5%) | 15 (28.8%) | 0.621 | 0.830 |
| Other cardiovascular risk factors | |||||
| Prior CAD or MI | 24 (23.8%) | 13 (26.5%) | 11 (21.2%) | 0.712 | 0.842 |
| Smoking | 43 (42.57%) | 16 (32.7%) | 27 (51.92%) | 0.018 | 0.007 |
| Obesity | 50 (49.5%) | 19 (38.8%) | 31 (59.61%) | 0.041 | 0.037 |
| Hypertension | 77 (76.2%) | 30 (61.2%) | 47 (90.4%) | 0.046 | 0.021 |
| Symptoms and clinical signs | |||||
| Intermittent claudication | 25 (24.8%) | 9 (18.4%) | 16 (30.8%) | 0.149 | 0.303 |
| Rest leg pain | 24 (23.8%) | 11 (22.4%) | 13 (25.0%) | 0.763 | 0.842 |
| Subcutaneous atrophy | 11 (10.9%) | 4 (8.2%) | 7 (13.5%) | 0.393 | 0.298 |
| Erythema | 7 (6.9%) | 2 (4.1%) | 5 (9.6%) | 0.274 | 0.019 |
| Ulcers | 3 (3.0%) | 2 (4.1%) | 1 (1.9%) | 0.523 | 0.231 |
| Necrosis | 2 (2.0%) | 1 (2.0%) | 1 (1.9%) | 0.956 | 0.331 |
| Heart murmur | 40 (39.6%) | 17 (34.7%) | 23 (44.2%) | 0.327 | 0.006 |
| Right pedal pulse–absent | 25 (24.8%) | 14 (28.6%) | 11 (21.2%) | 0.388 | 0.341 |
| Left pedal pulse–absent | 22 (21.8%) | 10 (20.4%) | 12 (23.1%) | 0.745 | 0.293 |
| Right posterior tibial artery pulse–absent | 15 (14.9%) | 8 (16.3%) | 7 (13.5%) | 0.686 | 0.098 |
| Left posterior tibial artery pulse–absent | 15 (14.9%) | 5 (10.2%) | 10 (19.2%) | 0.202 | 0.176 |
| Arterial murmur | 4 (4.0%) | 2 (4.1%) | 2 (3.8%) | 0.952 | 0.769 |
| Parameters | Total Group (n = 101) | Low and Low-Intermediate Risk Group (n = 49) | High-Intermediate and High Risk Group (n = 52) | p-Value | p*-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blood biochemistry | |||||
| Total cholesterol, mg/dL | 193.51 ± 47.65 | 183.76 ± 47.20 | 202.71 ± 46.68 | 0.045 | 0.020 |
| LDL-cholesterol, mg/dL | 117.95 ± 41.37 | 111.24 ± 41.18 | 134.27 ± 40.93 | 0.005 | 0.018 |
| HDL-cholesterol, mg/dL | 48.63 ± 12.52 | 46.77 ± 11.79 | 50.39 ± 13.04 | 0.147 | 0.293 |
| Triglycerides, mg/dL | 142.68 ± 101.02 | 140.41 ± 59.5 | 150.27 ± 56.2 | 0.058 | 0.046 |
| Uric acid, mg/dL | 5.94 ± 2.22 | 5.65 ± 1.96 | 6.25 ± 2.49 | 0.021 | 0.044 |
| Creatinine, mg/dL | 0.95 ± 0.35 | 0.90 ± 0.26 | 1.33 ± 0.41 | 0.047 | 0.038 |
| Fasting glucose, mg/dL | 122.66 ± 54.33 | 114.18 ± 38.35 | 130.65 ± 65.35 | 0.013 | 0.028 |
| Urea, mg/dL | 48.68 ± 22.45 | 49 ± 19.19 | 53.38 ± 25.33 | 0.051 | 0.059 |
| Fibrinogen | 385.33 ± 83.41 | 368.92 ± 67.39 | 400.79 ± 94.15 | 0.055 | 0.043 |
| Hematocrit | 40.83 ± 5.78 | 41.42 ± 5.95 | 40.27 ± 5.62 | 0.320 | 0.114 |
| Platelets | 242,554.46 ± 77,639.74 | 247,795.92 ± 88,404.84 | 237,615.38 ± 66,426.77 | 0.513 | 0.519 |
| ABI | 0.87 ± 0.31 | 0.89 ± 0.29 | 0.85 ± 0.32 | 0.519 | 0.269 |
| Walking perimeter (m) | 223.68 ± 292.05 | 352.86 ± 452.10 | 148.33 ± 106.16 | 0.145 | 0.371 |
| Right toe SBP | 94.62 ± 33.23 | 91.63 ± 32.44 | 97.44 ± 34.04 | 0.383 | 0.687 |
| Left toe SBP | 94.34 ± 28.69 | 99.23 ± 28.15 | 89.83 ± 28.71 | 0.102 | 0.265 |
| Left toe-brachial index | 0.70 ± 0.23 | 0.67 ± 0.23 | 0.72 ± 0.22 | 0.301 | 0.452 |
| Right toe-brachial index | 0.70 ± 0.22 | 0.73 ± 0.19 | 0.67 ± 0.23 | 0.230 | 0.656 |
| LV ejection fraction (%) | 54.77 ± 13.78 | 56.98 ± 12.28 | 52.43 ± 14.98 | 0.097 | 0.898 |
| Medication | |||||
| ACE inhibitors | 47 (6.5%) | 22 (44.9%) | 25 (48.1%) | 0.385 | 0.749 |
| Angiotensin receptor blockers | 7 (6.9%) | 2 (4.1%) | 5 (9.6%) | 0.314 | 0.475 |
| Diuretics | 45 (44.6%) | 17 (34.7%) | 28 (53.8%) | 0.822 | 0.601 |
| Calcium blockers | 25 (24.8%) | 12 (24.5%) | 13 (25.0%) | 0.407 | 0.624 |
| Beta-blockers | 46 (45.5%) | 29 (59.2%) | 29 (55.8%) | 0.729 | 0.304 |
| Alpha blockers | 3 (3.0%) | 2 (4.1%) | 1 (1.9%) | 0.279 | 0.769 |
| Aspirin | 60 (59.4%) | 35 (71.4%) | 25 (48.1%) | 0.017 | 0.190 |
| Clopidogrel | 8 (7.9%) | 3 (6.1%) | 5 (9.6%) | 0.672 | 0.724 |
| Warfarin | 11 (10.9%) | 3 (6.1%) | 8 (15.4%) | 0.648 | 0.374 |
| Trifusal | 4 (40%) | 3 (6.1%) | 1 (1.9%) | 0.003 | 0.088 |
| Statins | 41 (40.6%) | 20 (40.8%) | 21 (40.4%) | 0.965 | 0.666 |
| Antidiabetic medication | 20 (19.8%) | 8 (16.3%) | 12 (23.1%) | 0.395 | 0.722 |
| Insulin | 8 (7.9%) | 2 (4.1%) | 6 (11.5%) | 0.165 | 0.246 |
| Angiography | |||||
| Collateral circulation | 16 (15.8%) | 8 (16.3%) | 8 (15.4%) | 0.557 | 0.817 |
| Two-sides disease | 10 (9.9%) | 4 (8.2%) | 6 (11.5%) | 0.575 | 0.043 |
| Severity of lesions | |||||
| Stenosis | 8 (7.9%) | 6 (12.2%) | 2 (3.8%) | 0.567 | 0.791 |
| Complete occlusion | 14 (13.9%) | 5 (10.2%) | 9 (17.3%) | ||
| Location of lesion | |||||
| Suprapopliteal | 16 (84.2%) | 7 (87.5%) | 9 (81.8%) | 0.754 | 0.947 |
| Infrapopliteal | 8 (42.1%) | 3 (37.5%) | 5 (45.5%) | 0.080 | 0.157 |
| Number of lesions | |||||
| Single | 7 (6.8%) | 2 (25.0%) | 5 (45.5%) | 0.390 | 0.238 |
| Multiple | 12 (63.2%) | 6 (75.0%) | 6 (54.5%) | ||
| Invasive treatment | |||||
| Interventional revascularization | 5 (5.0%) | 3 (6.1%) | 2 (3.8%) | 0.598 | 0.682 |
| Surgical revascularization | 13 (12.9%) | 5 (10.2%) | 8 (15.4%) | 0.437 | 0.940 |
| Exercise training | 58 (57.4%) | 26 (53.1%) | 32 (61.5%) | 0.389 | 0.871 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aursulesei Onofrei, V.; Ceasovschih, A.; Marcu, D.T.M.; Adam, C.A.; Mitu, O.; Mitu, F. Mortality Risk Assessment in Peripheral Arterial Disease—The Burden of Cardiovascular Risk Factors over the Years: A Single Center’s Experience. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2499. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12102499
Aursulesei Onofrei V, Ceasovschih A, Marcu DTM, Adam CA, Mitu O, Mitu F. Mortality Risk Assessment in Peripheral Arterial Disease—The Burden of Cardiovascular Risk Factors over the Years: A Single Center’s Experience. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(10):2499. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12102499
Chicago/Turabian StyleAursulesei Onofrei, Viviana, Alexandr Ceasovschih, Dragos Traian Marius Marcu, Cristina Andreea Adam, Ovidiu Mitu, and Florin Mitu. 2022. "Mortality Risk Assessment in Peripheral Arterial Disease—The Burden of Cardiovascular Risk Factors over the Years: A Single Center’s Experience" Diagnostics 12, no. 10: 2499. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12102499
APA StyleAursulesei Onofrei, V., Ceasovschih, A., Marcu, D. T. M., Adam, C. A., Mitu, O., & Mitu, F. (2022). Mortality Risk Assessment in Peripheral Arterial Disease—The Burden of Cardiovascular Risk Factors over the Years: A Single Center’s Experience. Diagnostics, 12(10), 2499. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12102499










