Clinical Value of Neutrophil CD64 Index, PCT, and CRP in Acute Pancreatitis Complicated with Abdominal Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.1.1. Inclusion Criteria
2.1.2. Exclusion Criteria
2.1.3. Diagnostic Criteria for Abdominal Infection
2.2. Flow Cytometric Detection of CD64 Index
2.3. PCT and CRP Index
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Comparison of Infection Indexes
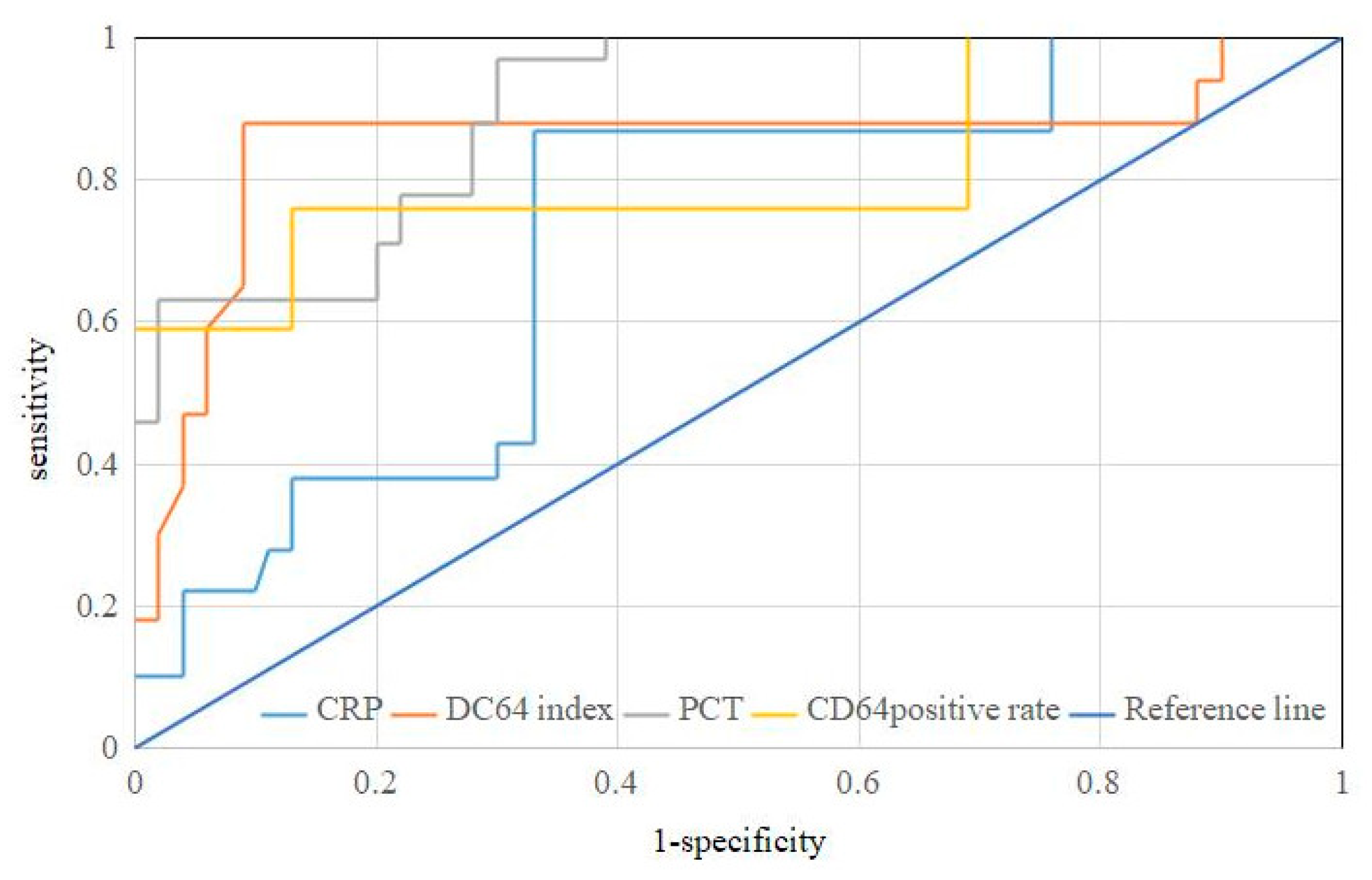
3.2. Evaluation of Diagnostic Efficacy of Acute Pancreatitis with Abdominal Infection
3.3. Evaluation of Diagnostic Efficacy of Acute Pancreatitis with Sepsis
3.4. Combined Diagnosis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johnson, C.D.; Besselink, M.G.; Carter, R. Acute pancreatitis. Bmj Br. Med. J. 2014, 349, g4859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boxhoorn, L.; Voermans, R.P.; Bouwense, S.A.; Bruno, M.J.; Verdonk, R.C.; Boermeester, M.A.; van Santvoort, H.C.; Besselink, M.G. Acute pancreatitis. Lancet 2020, 396, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Waele, E.; Malbrain, M.L.; Spapen, H.D. How to deal with severe acute pancreatitis in the critically ill. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2019, 25, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banks, P.A.; Bollen, T.L.; Dervenis, C.; Gooszen, H.G.; Johnson, C.D.; Sarr, M.G.; Tsiotos, G.G.; Vege, S.S. Classification of acute pancreatitis—2012: Revision of the Atlanta classification and definitions by international consensus. Gut 2013, 62, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, B.R.; Jensen, K.K.; Bakis, G.; Shaaban, A.M.; Coakley, F.V. Revised Atlanta Classification for Acute Pancreatitis: A Pictorial Essay. RadioGraphics 2016, 36, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheshwari, R.; Subramanian, R.M. Severe acute pancreatitis and necrotizing pancreatitis. Critical care clinics 2016, 32, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boxhoorn, L.; van Dijk, S.M.; van Grinsven, J.; Verdonk, R.C.; Boermeester, M.A.; Bollen, T.L.; Bouwense, S.A.; Bruno, M.J.; Cappendijk, V.C.; Dejong, C.H. Immediate versus Postponed Intervention for Infected Necrotizing Pancreatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1372–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gliem, N.; Ammer-Herrmenau, C.; Ellenrieder, V.; Neesse, A. Management of severe acute pancreatitis: An update. Digestion 2021, 102, 503–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morató, O.; Poves, I.; Ilzarbe, L.; Radosevic, A.; Vázquez-Sánchez, A.; Sánchez-Parrilla, J.; Burdío, F.; Grande, L. Minimally invasive surgery in the era of step-up approach for treatment of severe acute pancreatitis. Int. J. Surg. 2018, 51, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.A.; Hore, T.A.; Phillips, A.R.; Windsor, J.A.; Petrov, M.S. A systematic review of the extra-pancreatic infectious complications in acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2014, 14, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windsor, J.; De-Madaria, E. Critical acute pancreatitis: A category with clinical relevance. Dig. Liver Dis. 2021, 53, 1588–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Lu, B.; Xue, H.-d.; Yang, H.; Qian, J.-m.; Lee, P.; Windsor, J.A. Validation of Modified Determinant-Based Classification of severity for acute pancreatitis in a tertiary teaching hospital. Pancreatology 2019, 19, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Huang, Y.; Xiao, J.; Qin, G.; Liu, H.; Peng, J. Risk Factors for Mortality Among Critical Acute Pancreatitis Patients with Carbapenem-Resistant Organism Infections and Drug Resistance of Causative Pathogens. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2022, 11, 1089–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Shen, B.; Cen, D.; Yu, H.; Cai, X. Minimally Invasive Treatment for Severe Acute Pancreatitis With Superior Mesenteric Vein and Common Bile Duct Stenosis: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Pancreas 2019, 48, e61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, W.; Wan, J.; Chen, J.; He, W.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, N.; Xia, L. Elevated arterial lactate level as an independent risk factor for pancreatic infection in moderately severe acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2019, 19, 653–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Chen, W.; Tang, G.; Liang, Z.; Qin, M.; Qin, M.; Tang, Y.; Qin, H.; Chang, R. Optimal timing of contrast-enhanced computed tomography in an evaluation of severe acute pancreatitis-associated complications. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 18, 1029–1038. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Prashant, A.; Vishwanath, P.; Kulkarni, P.; Sathya Narayana, P.; Gowdara, V.; Nataraj, S.M.; Nagaraj, R. Comparative assessment of cytokines and other inflammatory markers for the early diagnosis of neonatal sepsis–a case control study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vugt, M.J.; Heijnen, I.; Capel, P.; Park, S.Y.; Ra, C.; Saito, T.; Verbeek, J.S.; van De Winkel, J. FcR gamma-chain is essential for both surface expression and function of human Fc gamma RI (CD64) in vivo. Blood 1996, 87, 3593–3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Li, S.B.; Zhou, Y.; Teng, S.J.; Guo, J.J. Determination of CD64 for the diagnosis of bacterial chronic prostatitis. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2015, 74, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, S.; Lewis, S.; Gant, V.; Treacher, D.; Davis, B.; Brown, K. Increased distribution and expression of CD64 on blood polymorphonuclear cells from patients with the systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS). Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2001, 125, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, G.; Singh, H.; Chaturvedi, S.; Hatti, M.; Kumar, A.; Mishra, R.; Mishra, P.; Krishna, V.; Bhadauria, A.; Mohindra, S. Utility of neutrophil CD64 in distinguishing bacterial infection from inflammation in severe alcoholic hepatitis fulfilling SIRS criteria. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danikas, D.; Karakantza, M.; Theodorou, G.; Sakellaropoulos, G.; Gogos, C. Prognostic value of phagocytic activity of neutrophils and monocytes in sepsis. Correlation to CD64 and CD14 antigen expression. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2008, 154, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayan, A.L.; Ravindran, S.; Saikant, R.; Lakshmi, S.; Kartik, R. Procalcitonin: A promising diagnostic marker for sepsis and antibiotic therapy. J. Intensive Care 2017, 5, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuzbasioglu, Y.; Duymaz, H.; Tanrikulu, C.S.; Halhalli, H.C.; Koc, M.O.; Tandoğan, M.; Coskun, F. Role of procalcitonin in evaluation of the severity of acute cholecystitis. Eurasian J. Med. 2016, 48, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Vaz, P.; Abrantes, A.M.; Castelo-Branco, M.; Gouveia, A.; Botelho, M.F.; Tralhão, J.G. Multifactorial Scores and Biomarkers of Prognosis of Acute Pancreatitis: Applications to Research and Practice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crockett, S.D.; Wani, S.; Gardner, T.B.; Falck-Ytter, Y.; Barkun, A.N.; Crockett, S.; Feuerstein, J.; Flamm, S.; Gellad, Z.; Gerson, L. American Gastroenterological Association Institute guideline on initial management of acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 1096–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leppäniemi, A.; Tolonen, M.; Tarasconi, A.; Segovia-Lohse, H.; Gamberini, E.; Kirkpatrick, A.W.; Ball, C.G.; Parry, N.; Sartelli, M.; Wolbrink, D. 2019 WSES guidelines for the management of severe acute pancreatitis. World J. Emerg. Surg. 2019, 14, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youden, W.J. Index for rating diagnostic tests. Cancer 1950, 3, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Chen, J.; Qin, G. Partial Youden index and its inferences. J. Biopharm. Stat. 2019, 29, 385–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, P.A.; Bradley, D.; Conwell, D.L.; Dungan, K.; Krishna, S.G.; Wyne, K.; Bellin, M.D.; Yadav, D.; Andersen, D.K.; Serrano, J. Diabetes following acute pancreatitis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 6, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yang, Z.; Tian, F. Risk factors associated with intolerance to enteral nutrition in moderately severe acute pancreatitis: A retrospective study of 568 patients. Saudi J. Gastroenterol. Off. J. Saudi Gastroenterol. Assoc. 2019, 25, 362. [Google Scholar]
- Kitagawa, S.; Sawai, K. Hypertriglyceridemia-induced acute pancreatitis with normal pancreatic enzymes. Am. J. Med. 2018, 131, e299–e300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogina, P.; Stubljar, D.; Lejko-Zupanc, T.; Osredkar, J.; Skvarc, M. Expression of CD64 on neutrophils (CD64 index): Diagnostic accuracy of CD64 index to predict sepsis in critically ill patients. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2015, 53, e89–e91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, D.; Faubion, W.; Sandborn, W. biological activity markers in inflammatory bowel disease. Alimentary pharmacology & therapeutics 2007, 25, 247–255. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, C.; Zhang, S.; Zhong, H.; Gu, Z.; Kang, Y.; Pan, C.; Xu, Z.; Chen, E.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Q. Intra-abdominal infection in acute pancreatitis in eastern China: Microbiological features and a prediction model. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stirling, A.D.; Moran, N.R.; Kelly, M.E.; Ridgway, P.F.; Conlon, K.C. The predictive value of C-reactive protein (CRP) in acute pancreatitis–is interval change in CRP an additional indicator of severity? HPB 2017, 19, 874–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregoriano, C.; Heilmann, E.; Molitor, A.; Schuetz, P. Role of procalcitonin use in the management of sepsis. J. Thorac. Dis. 2020, 12, S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, S.; Ma, T.; Di, X.; Tian, C.; Zhao, M.; Wang, K. Diagnostic value of neutrophil CD64, procalcitonin, and interleukin-6 in sepsis: A meta-analysis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, J.J. Neutrophil CD64: A diagnostic marker for infection and sepsis. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2009, 47, 903–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Zou, H.; Liu, S.; Mei, C.; Chang, X.; Hu, Z.; Yang, H.; Wu, Y. Diagnostic performance of neutrophil CD64 index in patients with sepsis in the intensive care unit. J. Int. Med Res. 2019, 47, 4304–4311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Tang, J.; Chen, D. Meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy of neutrophil CD64 for neonatal sepsis. Ital. J. Pediatrics 2016, 42, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiriet, C.; Mahjoub, K.; Courte, G.; Labroca, P.; Cravoisy, A.; Lemarie, J.; Conrad, M.; Nace, L.; Bollaert, P.-E.; Gibot, S. Automated measurement of neutrophil CD64 expression for diagnosing sepsis in critically ill patients. Minerva Anestesiol. 2019, 85, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

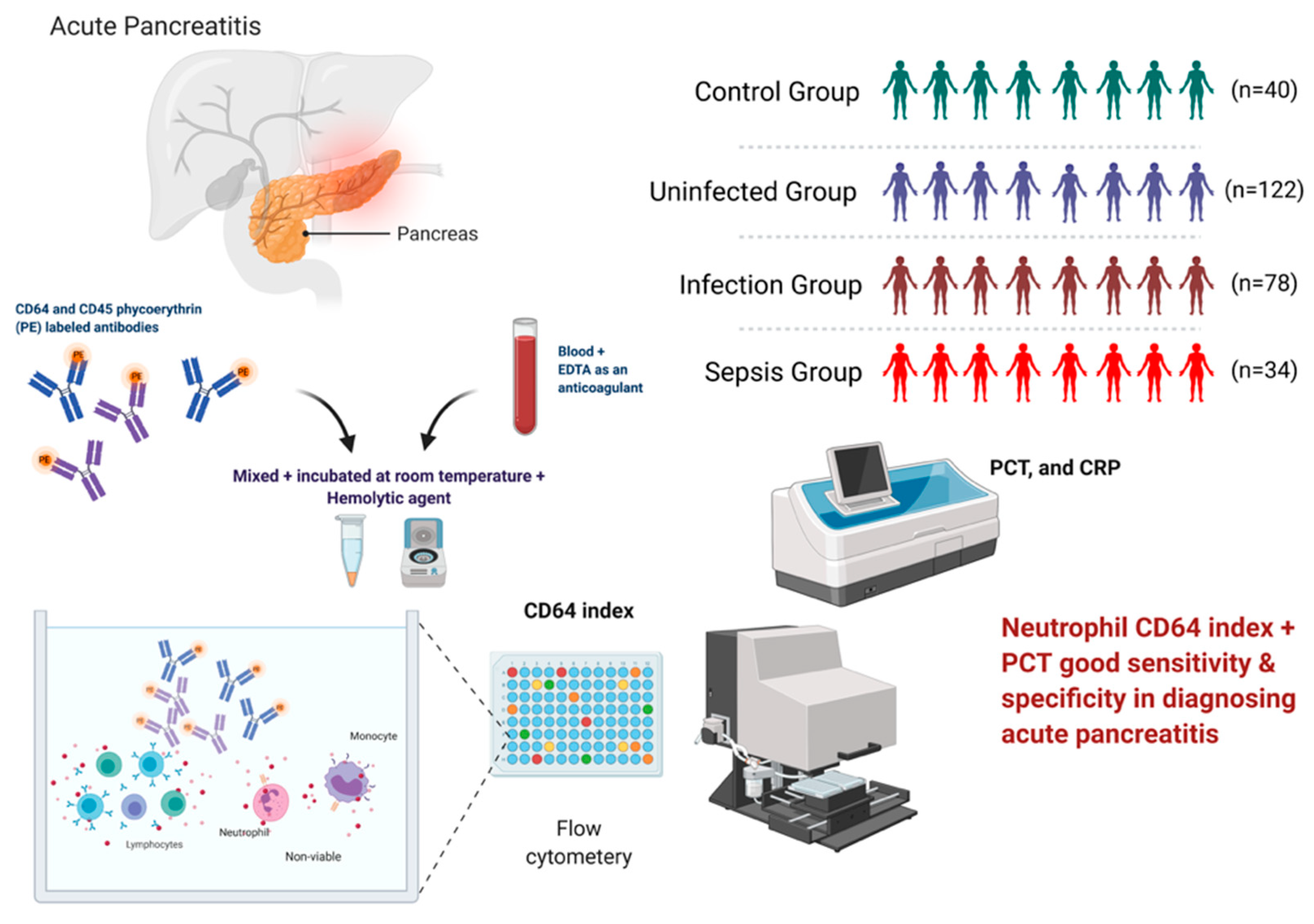
| Group | n | Sex [n (%)] | Age (Years) | Etiology [n (%)] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | Female | (x ± s) | Biliary | Hyperlipidemia | Other Reasons | ||
| Control group | 40 | 27 (67.50) | 13 (32.50) | 45.21 ± 8.24 | |||
| Uninfected group | 122 | 74 (60.66) | 48 (39.34) | 44.49 ± 9.39 | 66 (54.10) | 38 (31.15) | 18 (14.75) |
| Infection group | 78 | 46 (58.97) | 32 (41.03) | 43.61 ± 9.47 | 50 (64.10) | 20 (25.64) | 8 (10.26) |
| Sepsis group | 34 | 22 (64.71) | 12 (35.29) | 44.21 ± 8.26 | 22 (64.71) | 6 (17.65) | 6 (17.65) |
| Statistical test | X2 = 1.001 | F = 0.592 | X2 = 4.089 | ||||
| p-value | 0.801 | 0.555 | 0.394 | ||||
| Group | n | CD64 Positive Rate | CD64 Index | CRP (mg/L) | PCT (μg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control group | 40 | 9.79± 3.56 | 0.76± 0.21 | 2.29 ± 0.81 | 0.12± 0.07 |
| Uninfected group | 122 | 23.41 ± 7.17 a | 1.21 ± 0.35 a | 24.43± 4.61 a | 1.14 ± 0.78 a |
| Infection group | 78 | 43.91 ±15.82 ab | 3.34 ± 0.94 ab | 25.51 ±4.97 a | 2.53 ± 1.25 ab |
| Sepsis group | 34 | 67.71 ±9.64 abc | 5.06 ± 0.36 abc | 29.74 ±4.64 abc | 5.35 ± 1.75 abc |
| F-value | 177.321 | 304.560 | 328.296 | 131.643 | |
| p-value | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Bacteria Types | n | CD64 Ositive Rate | CD64 Index | CRP (mg/L) | PCT (μg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gram-negative bacteria | 89 | 51.91 ± 12.78 | 4.02 ± 0.81 | 27.36 ± 5.19 | 3.91 ±1.11 |
| Gram-positive bacteria | 23 | 49.93 ± 10.55 | 3.75 ± 0.76 | 25.954 ± 4.74 | 2.64 ± 0.75 |
| F-value | 0.621 | 1.259 | 1.031 | 4.802 | |
| p-value | 0.550 | 0.239 | 0.329 | <0.001 |
| Infection Index | AUC * | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | Youden Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD64 positive rate | 0.669 | 71.44 | 75.42 | 0.469 |
| CD64 index | 0.892 | 82.15 | 88.51 | 0.707 |
| CRP | 0.622 | 58.94 | 81.96 | 0.409 |
| PCT | 0.867 | 67.85 | 95.11 | 0.630 |
| Infection Index | AUC | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | Youden Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD64 positive rate | 0.815 | 76.48 | 87.19 | 0.637 |
| CD64 index | 0.847 | 88.26 | 89.76 | 0.780 |
| CRP | 0.627 | 88.25 | 66.69 | 0.549 |
| PCT | 0.897 | 70.61 | 94.87 | 0.655 |
| Diagnosis of Content | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | Youden Index |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acute pancreatitis with abdominal infection | 89.29 (100/112) | 88.52 (108/122) | 0.778 |
| Acute pancreatitis with sepsis | 94.12 (32/34) | 84.62 (66/78) | 0.787 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, B.; Tang, R.; Wu, S.; Liu, M.; Kanwal, F.; Rehman, M.F.u.; Wu, F.; Zhu, J. Clinical Value of Neutrophil CD64 Index, PCT, and CRP in Acute Pancreatitis Complicated with Abdominal Infection. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2409. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12102409
Wang B, Tang R, Wu S, Liu M, Kanwal F, Rehman MFu, Wu F, Zhu J. Clinical Value of Neutrophil CD64 Index, PCT, and CRP in Acute Pancreatitis Complicated with Abdominal Infection. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(10):2409. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12102409
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Biao, Rongzhu Tang, Shaohong Wu, Ming Liu, Fariha Kanwal, Muhammad Fayyaz ur Rehman, Fang Wu, and Jianping Zhu. 2022. "Clinical Value of Neutrophil CD64 Index, PCT, and CRP in Acute Pancreatitis Complicated with Abdominal Infection" Diagnostics 12, no. 10: 2409. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12102409
APA StyleWang, B., Tang, R., Wu, S., Liu, M., Kanwal, F., Rehman, M. F. u., Wu, F., & Zhu, J. (2022). Clinical Value of Neutrophil CD64 Index, PCT, and CRP in Acute Pancreatitis Complicated with Abdominal Infection. Diagnostics, 12(10), 2409. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12102409









