Preoperative AI-Driven Fluorescence Diagnosis of Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
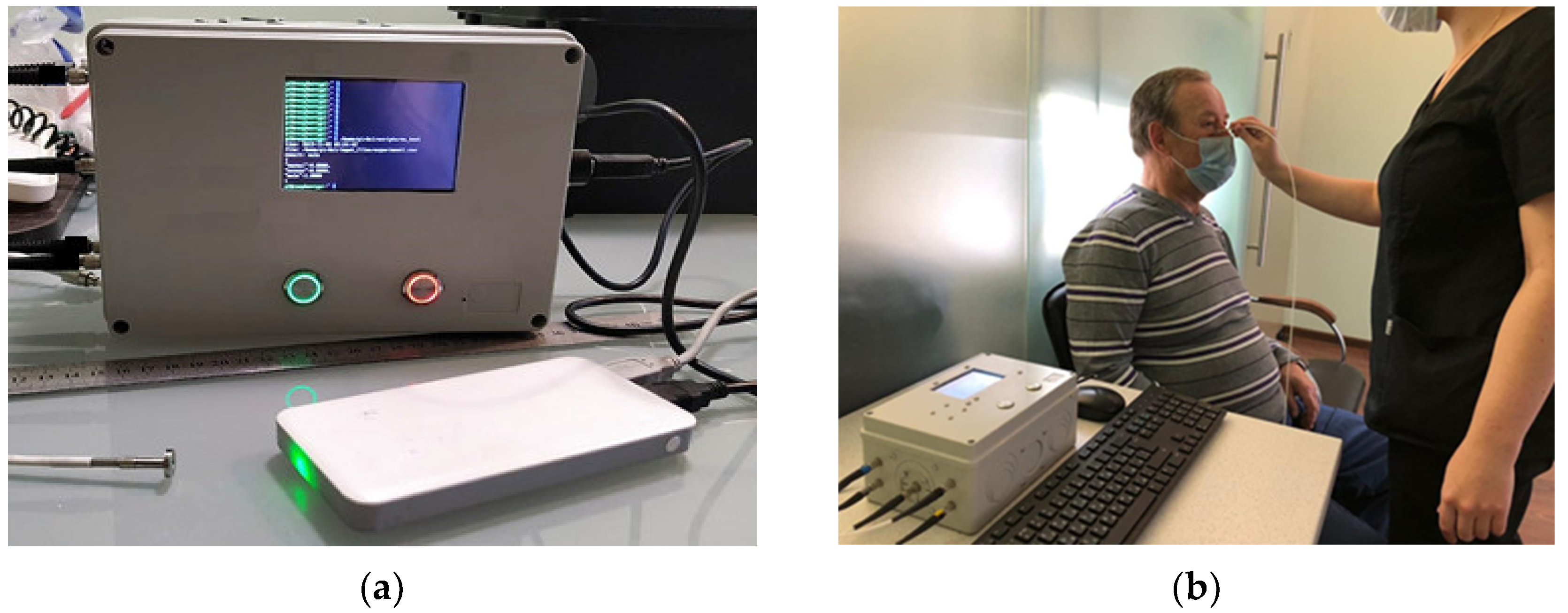
2.2. Fluorescence Measurements and Data Preparation
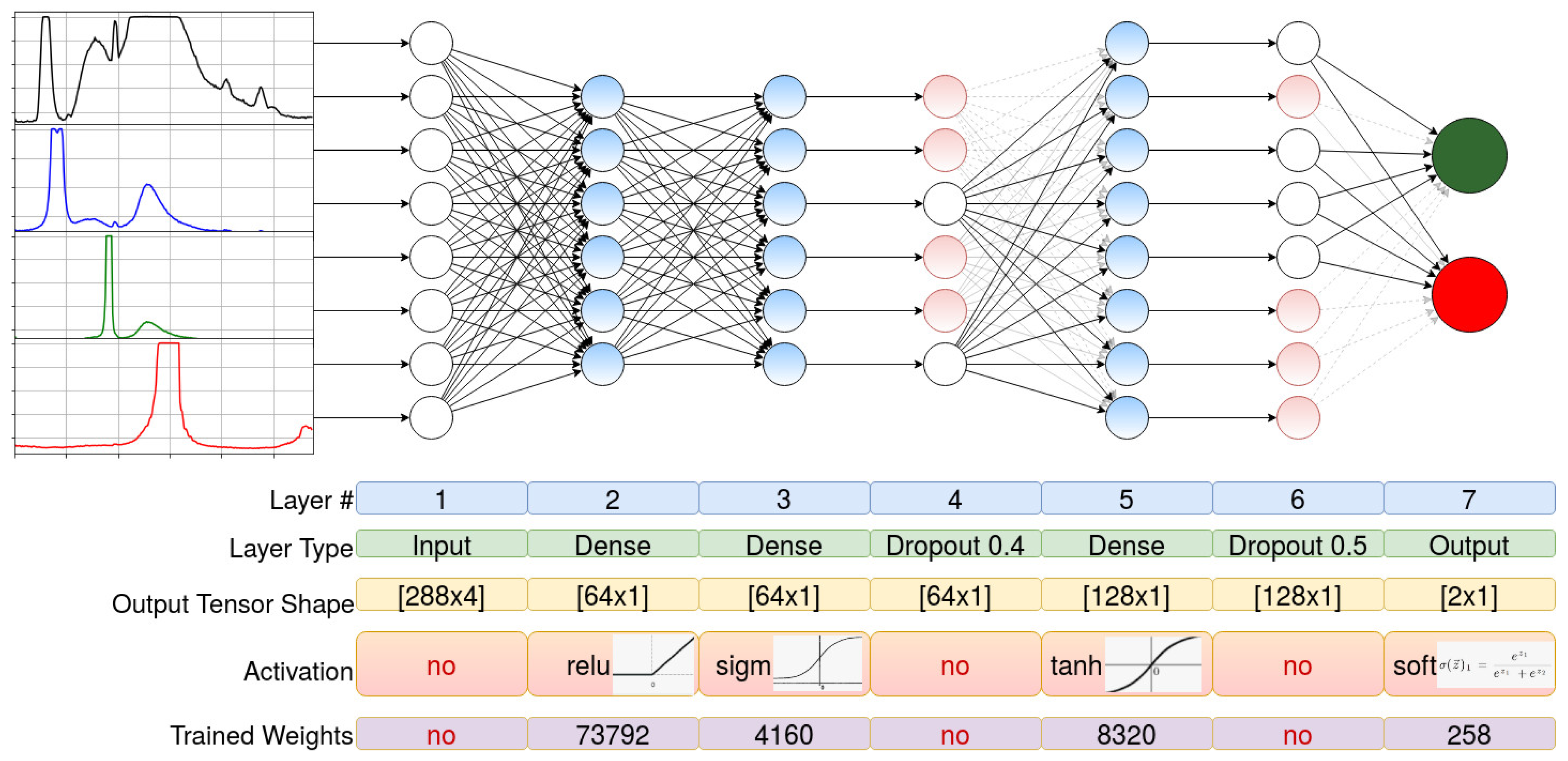
2.3. Dataset Preparation, Experimental Setup, the Architecture of the NN and Training Algorithm
- Input (288 × 4)
- Dense (64, activation = relu)
- Dense (64, activation = sigmoid)
- Dropout (0.4)
- Dense (128, activation = tanh)
- Dropout (0.5)
- Output Dense (2, activation = softmax).
- loss: categorical_crossentropy
- learning_rate: 1 × 10−6
- learning rate decay: 1 × 10−6
- momentum: 0.9
- nesterov: True
- epochs: 15,000
- batch size: 32
- -
- monitor: val_loss
- -
- patience: 5000 epochs.
- -
- es: early stopping
- -
- mc: Model Checkpoint, monitor: val_loss, save_best
- -
- validation_data: X_test, Y_test.
- -
- Run the 50 independent experiments of:
- -
- Split the 286 cases randomly into 3 parts: train (229), test (29), and validation (28);
- -
- Run training on the train set, using loss on the test set for early stopping;
- -
- Evaluate sensitivity and specificity on the validation set by using the “best-by-accuracy-on-test-set” model saved in the “mc-checkpoint”.
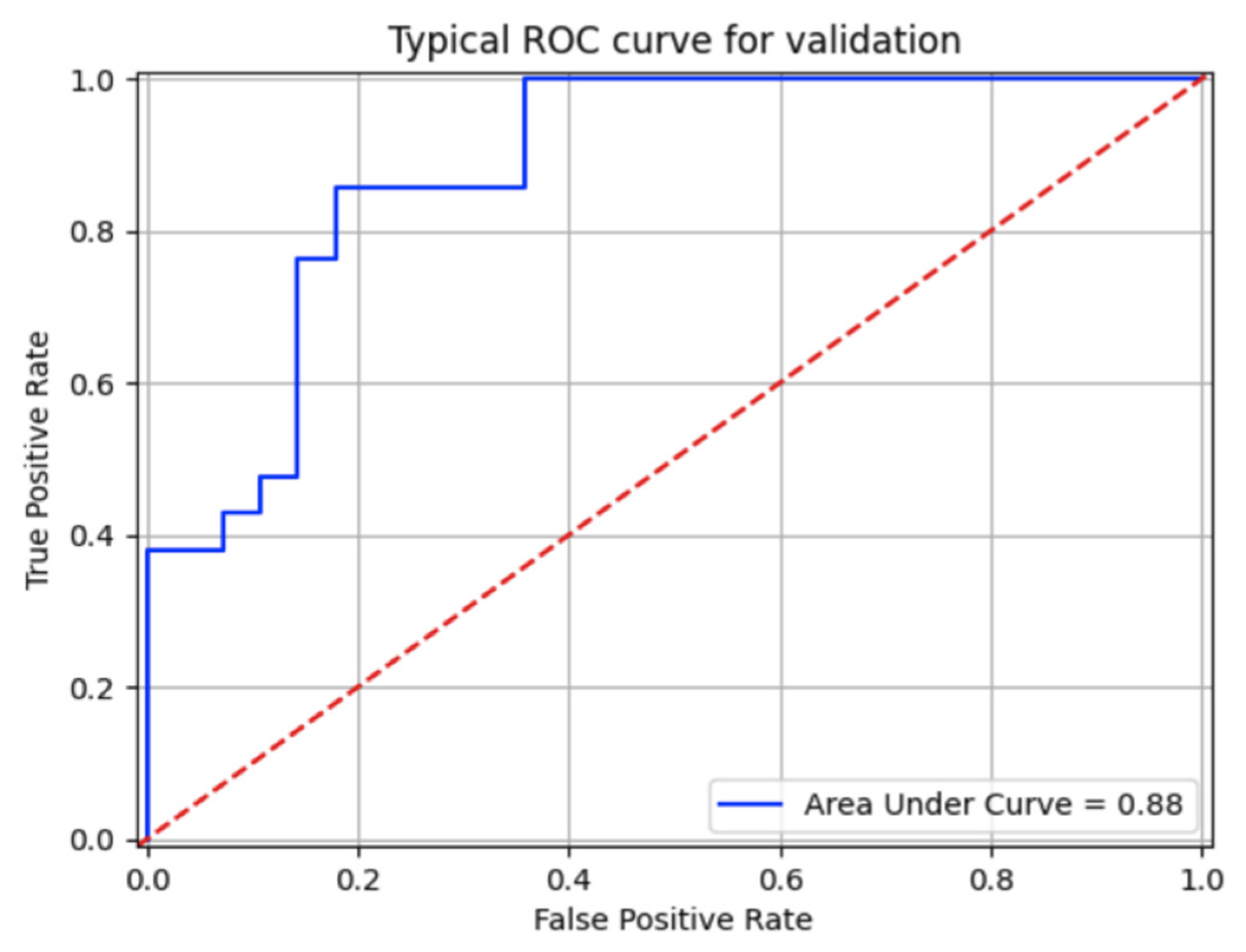
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Madan, V.; Lear, J.T.; Szeimies, R.M. Non-melanoma skin cancer. Lancet 2010, 375, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, R.S.; PUVA Follow-Up Study. The risk of squamous cell and basal cell cancer associated with psoralen and ultraviolet A therapy: A 30-year prospective study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2012, 66, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.; Ratner, D. Cutaneous squamous-cell carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karagas, M.R.; Weinstock, M.A.; Nelson, H.H. Keratinocyte carcinomas (basal and squamous cell carcinomas of the skin). In Cancer Epidemiology and Prevention; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Malvehy, J.; Pellacani, G. Dermoscopy, confocal microscopy and other non-invasive tools for the diagnosis of non-melanoma skin cancers and other skin conditions. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2017, 8, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigurdsson, H.; Agnarsson, B.A. Basal cell carcinoma of the eyelid. Risk of recurrence according to adequacy of surgical margins. Acta Ophthalmol. Scand. 1998, 76, 477–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fransen, M.; Karahalios, A.; Sharma, N.; English, D.R.; Giles, G.G.; Sinclair, R.D. Non-melanoma skin cancer in Australia. Med. J. Aust. 2012, 197, 565–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perera, E.; Gnaneswaran, N.; Staines, C.; Win, A.K.; Sinclair, R. Incidence and prevalence of non-melanoma skin cancer in A ustralia: A systematic review. Australas. J. Dermatol. 2015, 56, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leiter, U.; Eigentler, T.; Garbe, C. Epidemiology of skin cancer. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 810, 120–140. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rowe, C.J.; Khosrotehrani, K. Clinical and biological determinants of melanoma progression: Should all be considered for clinical management? Australas. J. Dermatol. 2016, 57, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Telfer, N.R.; Colver, G.B.; Morton, C.A. Guidelines for the management of basal cell carcinoma. Br. J. Dermatol. 2008, 159, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, L.L.; Ali, F.R.; Lear, J.T. Non-melanoma skin cancer. Clin. Med. 2016, 16, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keiser, G. Biophotonics; Springer: Singapore, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Litvinova, K.S.; Rafailov, I.E.; Dunaev, A.V.; Sokolovski, S.G.; Rafailov, E.U. Non-invasive biomedical research and diagnostics enabled by innovative compact lasers. Prog. Quantum Electron. 2017, 56, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Croce, A.C.; Bottiroli, G. Autofluorescence spectroscopy and imaging: A tool for biomedical research and diagnosis. Eur. J. Histochem. 2014, 58, 2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaram, N.; Aramil, T.J.; Lee, K.; Reichenberg, J.S.; Nguyen, T.H.; Tunnell, J.W. Design and validation of a clinical instrument for spectral diagnosis of cutaneous malignancy. Appl. Opt. 2010, 49, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borisova, E.G.; Bratchenko, I.A.; Khristoforova, Y.A.; Bratchenko, L.A.; Genova, T.I.; Gisbrecht, A.I.; Moryatov, A.A.; Kozlov, S.V.; Troyanova, P.P.; Zakharov, V.P. Near-infrared autofluorescence spectroscopy of pigmented benign and malignant skin lesions. Opt. Eng. 2020, 59, 061616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosny, A.; Parmar, C.; Quackenbush, J.; Schwartz, L.H.; Aerts, H.J.W.L. Artificial intelligence in radiology. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemouri, R.; Omri, N.; Morello, B.; Devalland, C.; Arnould, L.; Zerhouni, N.; Fnaiech, F. Constructive Deep Neural Network for Breast Cancer Diagnosis. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2018, 51, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Xie, L.; Han, J.; Guo, X. The Application of Deep Learning in Cancer Prognosis Prediction. Cancers 2020, 12, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelapu, R.; Devi, G.L.; Rao, K.S. Deep learning based conventional neural network architecture for medical image classification. Traitement Signal 2018, 35, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litjens, G.; Kooi, T.; Bejnordi, B.E.; Setio, A.A.A.; Ciompi, F.; Ghafoorian, M.; Van Der Laak, J.A.; Van Ginneken, B.; Sánchez, C.I. A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Med. Image Anal. 2017, 42, 60–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poplin, R.; Varadarajan, A.V.; Blumer, K.; Liu, Y.; McConnell, M.V.; Corrado, G.S.; Peng, L.; Webster, D.R. Prediction of cardiovascular risk factors from retinal fundus photographs via deep learning. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 2, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Yun, J.; Cho, Y.; Shin, K.; Jang, R.; Bae, H.J.; Kim, N. Deep learning in medical imaging. Neurospine 2019, 16, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1505.04597.
- Litvinova, K. Noninvasive, Multispectral-Fluorescence Characterization of Biological Tissues with Machine/Deep Learning. Patent US20200268252 16/798,001, 27 August 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ramanujam, N. Fluorescence spectroscopy of neoplastic and non-neoplastic tissues. Neoplasia 2000, 2, 89–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrukhina, V.V.; Litvinova, K.S.; Nikitin, A.A.; Spiridonova, N.Z.; Rogatkin, D.A. The first experience in estimation of basal cell carcinoma cryoresistence using noninvasive spectrophotometry. In Proceedings of the Saratov Fall Meeting 2009: International School for Junior Scientists and Students on Optics, Laser Physics, and Biophotonics, Saratov, Russia, 21–24 September 2009; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2010; Volume 7547, p. 75470G. [Google Scholar]
- Smirnova, O.D.; Rogatkin, D.; Litvinova, K. Collagen as in vivo quantitative fluorescent biomarkers of abnormal tissue changes. J. Innov. Opt. Health Sci. 2012, 5, 1250010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Leeuw, J.; van der Beek, N.; Neugebauer, W.D.; Bjerring, P.; Neumann, H.M. Fluorescence detection and diagnosis of non-melanoma skin cancer at an early stage. Lasers Surg. Med. 2009, 41, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calin, M.A.; Parasca, S.V.; Savastru, R.; Calin, M.R.; Dontu, S. Optical techniques for the noninvasive diagnosis of skin cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 139, 1083–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heuke, S.; Vogler, N.; Meyer, T.; Akimov, D.; Kluschke, F.; Röwert-Huber, H.J.; Lademann, J.; Dietzek, B.; Popp, J. Detection and discrimination of non-melanoma skin cancer by multimodal imaging. Healthcare 2013, 1, 64–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galletly, N.P.; McGinty, J.; Dunsby, C.; Teixeira, F.; Requejo-Isidro, J.; Munro, I.; Elson, D.S.; Neil, M.A.A.; Chu, A.C.; French, P.M.W.; et al. Fluorescence lifetime imaging distinguishes basal cell carcinoma from surrounding uninvolved skin. Br. J. Dermatol. 2008, 159, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Que, S.K.T. Research Techniques Made Simple: Noninvasive Imaging Technologies for the Delineation of Basal Cell Carcinomas. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 136, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dascalu, A.; David, E.O. Skin cancer detection by deep learning and sound analysis algorithms: A prospective clinical study of an elementary dermoscope. EBioMedicine 2019, 43, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Saffar, A.A.M.; Tao, H.; Talab, M.A. Review of deep convolution neural network in image classification. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Radar, Antenna, Microwave, Electronics, and Telecommunications (ICRAMET), Jakarta, Indonesia, 23–24 October 2017; pp. 26–31. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, C.Q.; Ibrahim, H.; Abdullah, M.Z.; Abdullah, J.M.; Suandi, S.A.; Azman, A.A. Literature Review on Data Conversion Methods on EEG for Convolution Neural Network Applications. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Robotics, Vision, Signal Processing and Power Applications; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 521–527. [Google Scholar]
- Cha, K.H.; Hadjiiski, L.M.; Samala, R.K.; Chan, H.P.; Cohan, R.H.; Caoili, E.M.; Paramagul, C.; Alva, A.; Weizer, A.Z. Bladder cancer segmentation in CT for treatment response assessment: Application of deep-learning convolution neural network—A pilot study. Tomography 2016, 2, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, A.A.; Hussain, L.; Awan, I.A.; Abbasi, I.; Majid, A.; Nadeem, M.S.A.; Chaudhary, Q.A. Detecting prostate cancer using deep learning convolution neural network with transfer learning approach. Cogn. Neurodyn. 2020, 14, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haj-Hassan, H.; Chaddad, A.; Harkouss, Y.; Desrosiers, C.; Toews, M.; Tanougast, C. Classifications of multispectral colorectal cancer tissues using convolution neural network. J. Pathol. Inform. 2017, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sua, J.N.; Halim, Y.M.; Yulius, M.H.; Su, X.; Yapp, E.K.Y.; Le, N.Q.K.; Yeh, H.-Y.; Chua, M.C.H. Incorporating convolutional neural networks and sequence graph transform for identifying multilabel protein lysine ptm sites. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2020, 206, 104171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, N.Q.K.; Ho, Q.T.; Yapp, E.K.Y.; Ou, Y.Y.; Yeh, H.Y. DeepETC: A deep convolutional neural network architecture for investigating and classifying electron transport chain’s complexes. Neurocomputing 2020, 375, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giambagli, L.; Buffoni, L.; Carletti, T.; Nocentini, W.; Fanelli, D. Machine learning in spectral domain. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| N | Min | Max | Mean | Median | Std | 25th Perc | 75th Perc | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specificity | 50 | 0.34 | 1 | 0.83 | 0.85 | 0.17 | 0.75 | 1 |
| Sensitivity | 50 | 0.16 | 1 | 0.62 | 0.64 | 0.23 | 0.5 | 0.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Andreeva, V.; Aksamentova, E.; Muhachev, A.; Solovey, A.; Litvinov, I.; Gusarov, A.; Shevtsova, N.N.; Kushkin, D.; Litvinova, K. Preoperative AI-Driven Fluorescence Diagnosis of Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12010072
Andreeva V, Aksamentova E, Muhachev A, Solovey A, Litvinov I, Gusarov A, Shevtsova NN, Kushkin D, Litvinova K. Preoperative AI-Driven Fluorescence Diagnosis of Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(1):72. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12010072
Chicago/Turabian StyleAndreeva, Victoriya, Evgeniia Aksamentova, Andrey Muhachev, Alexey Solovey, Igor Litvinov, Alexey Gusarov, Natalia N. Shevtsova, Dmitry Kushkin, and Karina Litvinova. 2022. "Preoperative AI-Driven Fluorescence Diagnosis of Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer" Diagnostics 12, no. 1: 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12010072
APA StyleAndreeva, V., Aksamentova, E., Muhachev, A., Solovey, A., Litvinov, I., Gusarov, A., Shevtsova, N. N., Kushkin, D., & Litvinova, K. (2022). Preoperative AI-Driven Fluorescence Diagnosis of Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer. Diagnostics, 12(1), 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12010072






