The Pathophysiology and the Management of Radiocontrast-Induced Nephropathy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Terminology and Definition
3. Risk Factors
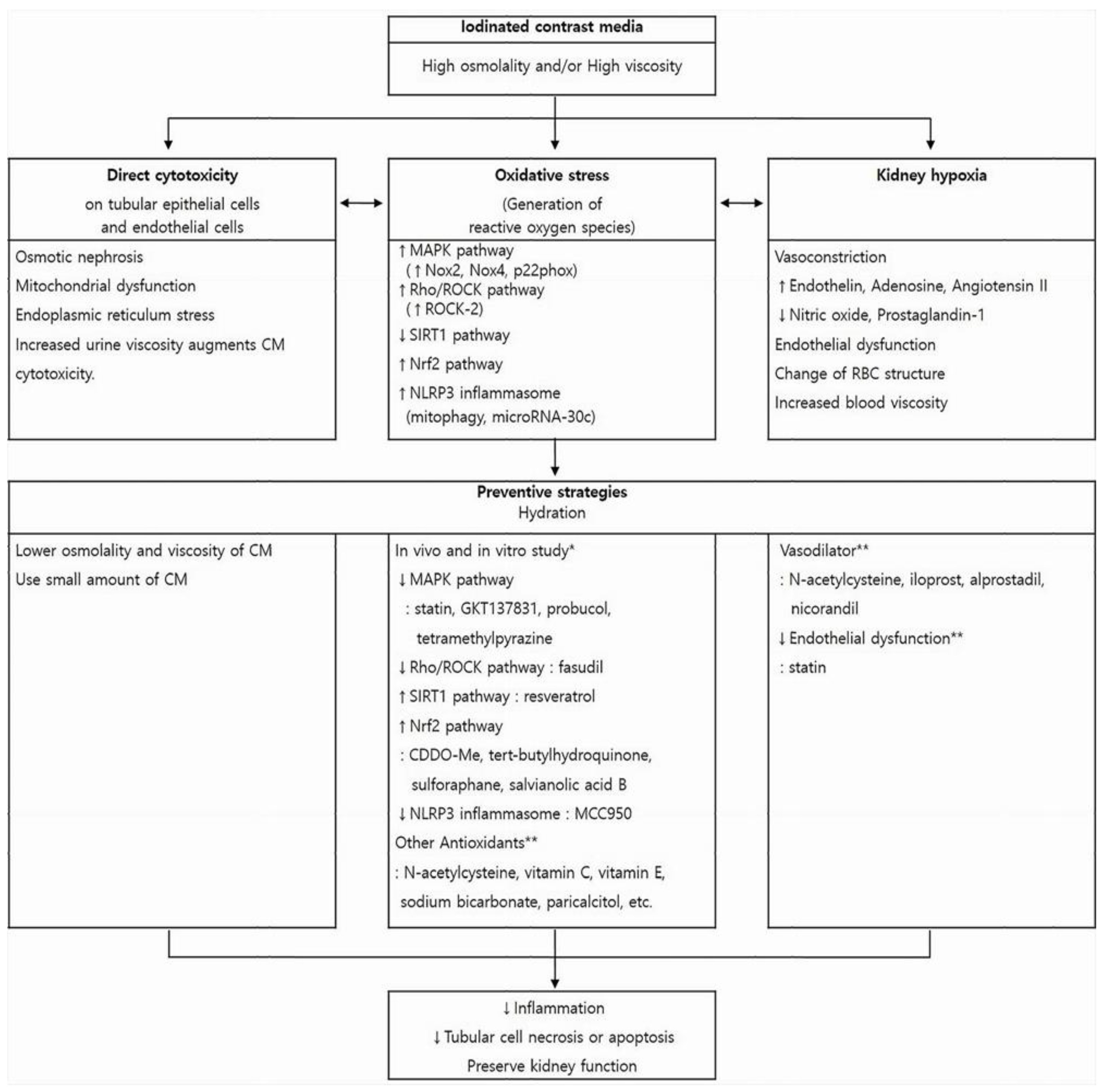
4. Pathophysiology
5. Management
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hou, S.H.; Bushinsky, D.A.; Wish, J.B.; Cohen, J.J.; Harrington, J.T. Hospital-acquired renal insufficiency: A prospective study. Am. J. Med. 1983, 74, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, K.; Hafeez, A.; Hou, S. Hospital-acquired renal insufficiency. Am. J. Kidney Dis. Off. J. Natl. Kidney Found. 2002, 39, 930–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, M.; Morimoto, T.; Akao, M.; Furukawa, Y.; Nakagawa, Y.; Shizuta, S.; Ehara, N.; Taniguchi, R.; Doi, T.; Nishiyama, K.; et al. Relation of contrast-induced nephropathy to long-term mortality after percutaneous coronary intervention. Am. J. Cardiol. 2014, 114, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzalini, L.; Kalra, S. Contrast-Induced Acute Kidney Injury-Definitions, Epidemiology, and Implications. Interv. Cardiol. Clin. 2020, 9, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haveman, J.W.; Gansevoort, R.T.; Bongaerts, A.H.; Nijsten, M.W. Low incidence of nephropathy in surgical ICU patients receiving intravenous contrast: A retrospective analysis. Intensive Care Med. 2006, 32, 1199–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kooiman, J.; Pasha, S.M.; Zondag, W.; Sijpkens, Y.W.; van der Molen, A.J.; Huisman, M.V.; Dekkers, O.M. Meta-analysis: Serum creatinine changes following contrast enhanced CT imaging. Eur. J. Radiol. 2012, 81, 2554–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chousterman, B.G.; Bouadma, L.; Moutereau, S.; Loric, S.; Alvarez-Gonzalez, A.; Mekontso-Dessap, A.; Laissy, J.P.; Rahmouni, A.; Katsahian, S.; Brochard, L.; et al. Prevention of contrast-induced nephropathy by N-acetylcysteine in critically ill patients: Different definitions, different results. J. Crit. Care 2013, 28, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ACR_Committee_on_Drugs_Contrast_Media. In ACR Manual on Contrast Media; American College of Radiology: Reston, VA, USA, 2021; Volume 128.
- Andreucci, M.; Solomon, R.; Tasanarong, A. Side effects of radiographic contrast media: Pathogenesis, risk factors, and prevention. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 741018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Molen, A.J.; Reimer, P.; Dekkers, I.A.; Bongartz, G.; Bellin, M.F.; Bertolotto, M.; Clement, O.; Heinz-Peer, G.; Stacul, F.; Webb, J.A.W.; et al. Post-contrast acute kidney injury—Part 1: Definition, clinical features, incidence, role of contrast medium and risk factors: Recommendations for updated ESUR Contrast Medium Safety Committee guidelines. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 2845–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidney Disease: Improving_Global_Outcomes_(KDIGO)_Acute_Kidney_Injury_Work_Group. KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for Acute Kidney Injury: Section 2: AKI definition. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2012, 2, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ad-hoc Working Group of ERBP; Fliser, D.; Laville, M.; Covic, A.; Fouque, D.; Vanholder, R.; Juillard, L.; Van Biesen, W. A European Renal Best Practice (ERBP) position statement on the Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) clinical practice guidelines on acute kidney injury: Part 1: Definitions, conservative management and contrast-induced nephropathy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 27, 4263–4272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slocum, N.K.; Grossman, P.M.; Moscucci, M.; Smith, D.E.; Aronow, H.D.; Dixon, S.R.; Share, D.; Gurm, H.S. The changing definition of contrast-induced nephropathy and its clinical implications: Insights from the Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan Cardiovascular Consortium (BMC2). Am. Heart J. 2012, 163, 829–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budano, C.; Levis, M.; D’Amico, M.; Usmiani, T.; Fava, A.; Sbarra, P.; Burdese, M.; Segoloni, G.P.; Colombo, A.; Marra, S. Impact of contrast-induced acute kidney injury definition on clinical outcomes. Am. Heart J. 2011, 161, 963–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amore, C.; Nuzzo, S.; Briguori, C. Biomarkers of Contrast-Induced Nephropathy:: Which Ones are Clinically Important? Interv. Cardiol. Clin. 2020, 9, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shams, E.; Mayrovitz, H.N. Contrast-Induced Nephropathy: A Review of Mechanisms and Risks. Cureus 2021, 13, e14842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kane-Gill, S.L.; Meersch, M.; Bell, M. Biomarker-guided management of acute kidney injury. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2020, 26, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zdziechowska, M.; Gluba-Brzozka, A.; Franczyk, B.; Rysz, J. Biochemical Markers in the Prediction of Contrast-induced Acute Kidney Injury. Curr. Med. Chem. 2021, 28, 1234–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parikh, C.R.; Liu, C.; Mor, M.K.; Palevsky, P.M.; Kaufman, J.S.; Thiessen Philbrook, H.; Weisbord, S.D. Kidney Biomarkers of Injury and Repair as Predictors of Contrast-Associated AKI: A Substudy of the PRESERVE Trial. Am. J. Kidney Dis. Off. J. Natl. Kidney Found. 2020, 75, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccalandro, F.; Shreyder, K.; Harmon, L.; Dhindsa, M.; Fahim, T.; Sheikh, S. Five-Year Follow-Up of Patients With Radio-Contrast-Induced Acute Renal Injury: Can Intravenous Sodium Bicarbonate Improve Long-Term Outcomes? Cardiovasc. Revascularization Med. Incl. Mol. Interv. 2021, 31, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehran, R.; Aymong, E.D.; Nikolsky, E.; Lasic, Z.; Iakovou, I.; Fahy, M.; Mintz, G.S.; Lansky, A.J.; Moses, J.W.; Stone, G.W.; et al. A simple risk score for prediction of contrast-induced nephropathy after percutaneous coronary intervention: Development and initial validation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2004, 44, 1393–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.A.; Costanzo, E.; Cosentino, J.; Patel, C.; Qaisar, H.; Singh, V.; Khan, T.; Cheng, J.S.; Asif, A.; Vachharajani, T.J. Contrast-induced nephropathy: Pathophysiology, risk factors, and prevention. Saudi J. Kidney Dis. Transplant. Off. Publ. Saudi Cent. Organ Transplant. Saudi Arab. 2018, 29, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, K.; Xie, X.; Song, B. Contrast-associated acute kidney injury: An update of risk factors, risk factor scores, and preventive measures. Clin. Imaging 2021, 69, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kooiman, J.; Klok, F.A.; Mos, I.C.; van der Molen, A.; de Roos, A.; Sijpkens, Y.W.; Huisman, M.V. Incidence and predictors of contrast-induced nephropathy following CT-angiography for clinically suspected acute pulmonary embolism. J. Thromb. Haemost. JTH 2010, 8, 409–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzberg, R.W.; Newhouse, J.H. Intravenous contrast medium-induced nephrotoxicity: Is the medical risk really as great as we have come to believe? Radiology 2010, 256, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manske, C.L.; Sprafka, J.M.; Strony, J.T.; Wang, Y. Contrast nephropathy in azotemic diabetic patients undergoing coronary angiography. Am. J. Med. 1990, 89, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.H.; Hsieh, C.H.; Chan, Y.L.; Wong, Y.C.; Kuo, C.F.; Li, C.H.; Lee, C.C.; Chen, H.Y. Intravenous CT Contrast Media and Acute Kidney Injury: A Multicenter Emergency Department-based Study. Radiology 2021, 301, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, S.; Bez, C.; Hinterleitner, C.; Horger, M. Incidence of contrast-induced acute kidney injury (CI-AKI) in high-risk oncology patients undergoing contrast-enhanced CT with a reduced dose of the iso-osmolar iodinated contrast medium iodixanol. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0233433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ren, K. The Mechanism of Contrast-Induced Acute Kidney Injury and Its Association with Diabetes Mellitus. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2020, 2020, 3295176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delp, M.D.; Behnke, B.J.; Spier, S.A.; Wu, G.; Muller-Delp, J.M. Ageing diminishes endothelium-dependent vasodilatation and tetrahydrobiopterin content in rat skeletal muscle arterioles. J. Physiol. 2008, 586, 1161–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolignano, D.; Mattace-Raso, F.; Sijbrands, E.J.; Zoccali, C. The aging kidney revisited: A systematic review. Ageing Res. Rev. 2014, 14, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morcos, R.; Kucharik, M.; Bansal, P.; Al Taii, H.; Manam, R.; Casale, J.; Khalili, H.; Maini, B. Contrast-Induced Acute Kidney Injury: Review and Practical Update. Clin. Med. Insights. Cardiol. 2019, 13, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehran, R.; Dangas, G.D.; Weisbord, S.D. Contrast-Associated Acute Kidney Injury. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2146–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grainger, R.G. Osmolality of intravascular radiological contrast media. Br. J. Radiol. 1980, 53, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faucon, A.L.; Bobrie, G.; Clement, O. Nephrotoxicity of iodinated contrast media: From pathophysiology to prevention strategies. Eur. J. Radiol. 2019, 116, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buschur, M.; Aspelin, P. Contrast Media: History and Chemical Properties. Interv. Cardiol. Clin. 2014, 3, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, R. Contrast media: Are there differences in nephrotoxicity among contrast media? BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 934947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Lei, R.; Yang, S.K.; Luo, M.; Cheng, W.; Xiao, Y.Q.; Li, X.W.; Guo, J.; Duan, S.B. Comparative effect of iso-osmolar versus low-osmolar contrast media on the incidence of contrast-induced acute kidney injury in diabetic patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Imaging Off. Publ. Int. Cancer Imaging Soc. 2019, 19, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Jiang, L.; Tang, X.; Gao, Z.; Xu, B.; Yuan, J. Contrast Induced Nephropathy and 2-Year Outcomes of Iso-Osmolar Compared with Low-Osmolar Contrast Media after Elective Percutaneous Coronary Intervention. Korean Circ. J. 2021, 51, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.F.; Zhang, X.X.; Liu, K.M.; Tan, H.; Zhang, Q. Contrast-induced nephropathy in patients with diabetes mellitus between iso- and low-osmolar contrast media: A meta-analysis of full-text prospective, randomized controlled trials. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Rui, Q.; Chen, M.; Zhang, N.; Yang, H.; Zhou, Y. Iodixanol versus iopromide in patients with renal insufficiency undergoing coronary angiography with or without PCI. Medicine 2018, 97, e0617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.Q.; Luo, W.L.; Tan, X.; Fang, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Yu, X.F.; Cai, J.R.; Ding, X.Q. A novel contrast-induced acute kidney injury model based on the 5/6-nephrectomy rat and nephrotoxicological evaluation of iohexol and iodixanol in vivo. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2014, 2014, 427560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Zhou, L.Y.; Li, D.Y.; Cheng, W.J.; Yin, W.J.; Hu, C.; Xie, Y.L.; Wang, J.L.; Zuo, S.R.; Chen, L.H.; et al. A novel rat model of contrast-induced nephropathy based on dehydration. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 141, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, B.; Fang, L.; Li, Y.; Meng, S. Iso-Osmolar Iodixanol Induces Less Increase in Circulating Endothelial Microparticles In Vivo and Less Endothelial Apoptosis In Vitro Compared with Low-Osmolar Iohexol. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2018, 2018, 8303609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, J.S.; McDonald, R.J.; Comin, J.; Williamson, E.E.; Katzberg, R.W.; Murad, M.H.; Kallmes, D.F. Frequency of acute kidney injury following intravenous contrast medium administration: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Radiology 2013, 267, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, J.S.; McDonald, R.J.; Carter, R.E.; Katzberg, R.W.; Kallmes, D.F.; Williamson, E.E. Risk of intravenous contrast material-mediated acute kidney injury: A propensity score-matched study stratified by baseline-estimated glomerular filtration rate. Radiology 2014, 271, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elias, A.; Aronson, D. Risk of Acute Kidney Injury after Intravenous Contrast Media Administration in Patients with Suspected Pulmonary Embolism: A Propensity-Matched Study. Thromb. Haemost. 2021, 121, 800–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; Jiao, Z.; Liu, T.; Guo, F.; Li, G. Effect of administration route on the renal safety of contrast agents: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Nephrol. 2012, 25, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tziakas, D.; Chalikias, G.; Stakos, D.; Altun, A.; Sivri, N.; Yetkin, E.; Gur, M.; Stankovic, G.; Mehmedbegovic, Z.; Voudris, V.; et al. Validation of a new risk score to predict contrast-induced nephropathy after percutaneous coronary intervention. Am. J. Cardiol. 2014, 113, 1487–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurm, H.S.; Seth, M.; Dixon, S.R.; Michael Grossman, P.; Sukul, D.; Lalonde, T.; Cannon, L.; West, D.; Madder, R.D.; Adam Lauver, D. Contemporary use of and outcomes associated with ultra-low contrast volume in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary interventions. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. Off. J. Soc. Card. Angiogr. Interv. 2019, 93, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Molen, A.J.; Reimer, P.; Dekkers, I.A.; Bongartz, G.; Bellin, M.F.; Bertolotto, M.; Clement, O.; Heinz-Peer, G.; Stacul, F.; Webb, J.A.W.; et al. Post-contrast acute kidney injury. Part 2: Risk stratification, role of hydration and other prophylactic measures, patients taking metformin and chronic dialysis patients: Recommendations for updated ESUR Contrast Medium Safety Committee guidelines. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 2856–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamoulakis, C.; Tsarouhas, K.; Fragkiadoulaki, I.; Heretis, I.; Wilks, M.F.; Spandidos, D.A.; Tsitsimpikou, C.; Tsatsakis, A. Contrast-induced nephropathy: Basic concepts, pathophysiological implications and prevention strategies. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 180, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, D.B.; Valentovic, M.A. Contrast Induced Acute Kidney Injury and Direct Cytotoxicity of Iodinated Radiocontrast Media on Renal Proximal Tubule Cells. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2019, 370, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCullough, P.A.; Choi, J.P.; Feghali, G.A.; Schussler, J.M.; Stoler, R.M.; Vallabahn, R.C.; Mehta, A. Contrast-Induced Acute Kidney Injury. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 1465–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caiazza, A.; Russo, L.; Sabbatini, M.; Russo, D. Hemodynamic and tubular changes induced by contrast media. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 578974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.Z.; Viegas, V.U.; Perlewitz, A.; Lai, E.Y.; Persson, P.B.; Patzak, A.; Sendeski, M.M. Iodinated contrast media differentially affect afferent and efferent arteriolar tone and reactivity in mice: A possible explanation for reduced glomerular filtration rate. Radiology 2012, 265, 762–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heyman, S.N.; Khamaisi, M.; Zorbavel, D.; Rosen, S.; Abassi, Z. Role of Hypoxia in Renal Failure Caused by Nephrotoxins and Hypertonic Solutions. Semin. Nephrol. 2019, 39, 530–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leisman, S. Radiocontrast Toxicity. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2020, 27, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sendeski, M.M.; Persson, A.B.; Liu, Z.Z.; Busch, J.F.; Weikert, S.; Persson, P.B.; Hippenstiel, S.; Patzak, A. Iodinated contrast media cause endothelial damage leading to vasoconstriction of human and rat vasa recta. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2012, 303, F1592–F1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.Z.; Schmerbach, K.; Lu, Y.; Perlewitz, A.; Nikitina, T.; Cantow, K.; Seeliger, E.; Persson, P.B.; Patzak, A.; Liu, R.; et al. Iodinated contrast media cause direct tubular cell damage, leading to oxidative stress, low nitric oxide, and impairment of tubuloglomerular feedback. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2014, 306, F864–F872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.H.; Lee, T.S.; Lin, S.J.; Yeh, Y.C.; Lu, T.M.; Hsu, C.P. DDAH-2 alleviates contrast medium iopromide-induced acute kidney injury through nitric oxide synthase. Clin. Sci. 2019, 133, 2361–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusirisin, P.; Chattipakorn, S.C.; Chattipakorn, N. Contrast-induced nephropathy and oxidative stress: Mechanistic insights for better interventional approaches. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisani, A.; Riccio, E.; Andreucci, M.; Faga, T.; Ashour, M.; Di Nuzzi, A.; Mancini, A.; Sabbatini, M. Role of reactive oxygen species in pathogenesis of radiocontrast-induced nephropathy. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 868321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, B.Y.; Lee, H.Y.; Park, C.G.; Kang, J.; Yu, S.L.; Choi, D.R.; Han, S.Y.; Park, M.H.; Cho, S.; Lee, S.Y.; et al. Oxidative stress caused by activation of NADPH oxidase 4 promotes contrast-induced acute kidney injury. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.L.; Lei, R.; Duan, S.B.; Tang, M.M.; Luo, M.; Xu, Q. Atorvastatin alleviates iodinated contrast media-induced cytotoxicity in human proximal renal tubular epithelial cells. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 14, 3309–3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gong, X.; Wang, Q.; Tang, X.; Wang, Y.; Fu, D.; Lu, H.; Wang, G.; Norgren, S. Tetramethylpyrazine prevents contrast-induced nephropathy by inhibiting p38 MAPK and FoxO1 signaling pathways. Am. J. Nephrol. 2013, 37, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amano, M.; Nakayama, M.; Kaibuchi, K. Rho-kinase/ROCK: A key regulator of the cytoskeleton and cell polarity. Cytoskeleton 2010, 67, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Ying, Z.; Webb, R.C. Activation of Rho/Rho kinase signaling pathway by reactive oxygen species in rat aorta. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2004, 287, H1495–H1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Z.; Miao, D.; Zhang, D. Rho Kinase Inhibitor, Fasudil, Attenuates Contrast-induced Acute Kidney Injury. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2018, 122, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaleel, S.A.; Raslan, N.A.; Alzokaky, A.A.; Ewees, M.G.; Ashour, A.A.; Abdel-Hamied, H.E.; Abd-Allah, A.R. Contrast media (meglumine diatrizoate) aggravates renal inflammation, oxidative DNA damage and apoptosis in diabetic rats which is restored by sulforaphane through Nrf2/HO-1 reactivation. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2019, 309, 108689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.A.; Bae, S.Y.; Ahn, S.Y.; Kim, J.; Kwon, Y.J.; Jung, W.Y.; Ko, G.J. Resveratrol Ameliorates Contrast Induced Nephropathy Through the Activation of SIRT1-PGC-1alpha-Foxo1 Signaling in Mice. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2017, 42, 641–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.E.; Bae, S.Y.; Ahn, S.Y.; Kwon, Y.J.; Ko, G.J. The role of nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2 expression in radiocontrast-induced nephropathy. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Liao, G.; Zhou, Q.; Lv, D.; Holthfer, H.; Zou, H. Sulforaphane Attenuates Contrast-Induced Nephropathy in Rats via Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 9825623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Wang, X.; Shao, X.; Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Ke, X.; Xiong, C.; Wei, L.; Zou, H. tert-Butylhydroquinone Treatment Alleviates Contrast-Induced Nephropathy in Rats by Activating the Nrf2/Sirt3/SOD2 Signaling Pathway. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 4657651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morigi, M.; Perico, L.; Benigni, A. Sirtuins in Renal Health and Disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2018, 29, 1799–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Wang, H.; Xu, Y.; Zheng, D.; Zhang, Q.; Li, W. Protective effect of astaxanthin against contrast-induced acute kidney injury via SIRT1-p53 pathway in rats. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2019, 51, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, B.; Qi, X.; Zhang, X.; Ren, K. Resveratrol Protects Against Post-Contrast Acute Kidney Injury in Rabbits With Diabetic Nephropathy. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tongqiang, L.; Shaopeng, L.; Xiaofang, Y.; Nana, S.; Xialian, X.; Jiachang, H.; Ting, Z.; Xiaoqiang, D. Salvianolic Acid B Prevents Iodinated Contrast Media-Induced Acute Renal Injury in Rats via the PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 Pathway. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 7079487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.; Yao, S.; Zheng, D.; Xuan, Y.; Li, W. Astaxanthin attenuates contrast-induced acute kidney injury in rats via ROS/NLRP3 inflammasome. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, W.; Zhao, F.; Tang, C.Y.; Li, X.W.; Luo, M.; Duan, S.B. Comparison of iohexol and iodixanol induced nephrotoxicity, mitochondrial damage and mitophagy in a new contrast-induced acute kidney injury rat model. Arch. Toxicol. 2018, 92, 2245–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Wang, L.; Jiang, N.; Mou, S.; Zhang, M.; Gu, L.; Shao, X.; Wang, Q.; Qi, C.; Li, S.; et al. NLRP3 inflammasome mediates contrast media-induced acute kidney injury by regulating cell apoptosis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Li, S.; Jiang, N.; Jin, H.; Shao, X.; Zhu, X.; Wu, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, J.; et al. Inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome attenuates apoptosis in contrast-induced acute kidney injury through the upregulation of HIF1A and BNIP3-mediated mitophagy. Autophagy 2021, 17, 2975–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Zheng, X.; Huang, Z.; Lin, J.; Xie, C.; Lin, Y. Involvement of S100A8/A9-TLR4-NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway in Contrast-Induced Acute Kidney Injury. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Int. J. Exp. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 43, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Q.; Li, S.; Jiang, N.; Shao, X.; Zhang, M.; Jin, H.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, W.; et al. PINK1-parkin pathway of mitophagy protects against contrast-induced acute kidney injury via decreasing mitochondrial ROS and NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Redox Biol. 2019, 26, 101254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Ma, L.; Fu, P. MicroRNA-30c attenuates contrast-induced acute kidney injury by suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 87, 106457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.; Cao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Ping, K.; Tan, M.T.; Tan, N.; Chen, J.; Chen, P. A New Preprocedure Risk Score for Predicting Contrast-Induced Acute Kidney Injury. Can. J. Cardiol. 2017, 33, 714–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.; Liang, Y.; Xie, N.; Liu, J.; Sun, G.; Chen, S.; Ye, J.; He, Y.; Guo, W.; Tan, N.; et al. Simple pre-procedure risk stratification tool for contrast-induced nephropathy. J. Thorac. Dis. 2019, 11, 1597–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, J.F.; Chen, S.Q.; Ye, J.F.; Chen, Y.; Lei, L.; Liu, X.Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lin, J.J.; Chen, J.Y. A simple risk score model for predicting contrast-induced nephropathy after coronary angiography in patients with diabetes. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2019, 23, 969–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Z.F.; Shen, H.; Tang, M.N.; Yan, Y.; Ge, J.B. A novel risk assessment model of contrast-induced nephropathy after percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with diabetes. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2021, 128, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranucci, M.; Castelvecchio, S.; Menicanti, L.; Frigiola, A.; Pelissero, G. Risk of assessing mortality risk in elective cardiac operations: Age, creatinine, ejection fraction, and the law of parsimony. Circulation 2009, 119, 3053–3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.H.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.L.; He, P.C.; Yu, D.Q.; Li, L.W.; Xie, N.J.; Guo, W.; Tan, N.; Chen, J.Y. Comparison of Different Risk Scores for Predicting Contrast Induced Nephropathy and Outcomes After Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in Patients With ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction. Am. J. Cardiol. 2016, 117, 1896–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khwaja, A. KDIGO clinical practice guidelines for acute kidney injury. Nephron Clin. Pract. 2012, 120, c179–c184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, M.S.; Perazella, M.A.; Yee, J.; Dillman, J.R.; Fine, D.; McDonald, R.J.; Rodby, R.A.; Wang, C.L.; Weinreb, J.C. Use of Intravenous Iodinated Contrast Media in Patients With Kidney Disease: Consensus Statements from the American College of Radiology and the National Kidney Foundation. Kidney Med. 2020, 2, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motes, A.T.; Ratanasrimetha, P.; Wongsaengsak, S.; Vorakunthada, Y.; Mingbunjerdsuk, T.; Pena, C.; Nugent, K. Impact of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors/Angiotensin Receptor Blockers on Renal Function in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients Undergoing Coronary Angiography. Cureus 2021, 13, e12808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Jin, W.; Liu, Y.; Lu, L.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, R. The Effect of Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Blockade Medications on Contrast-Induced Nephropathy in Patients Undergoing Coronary Angiography: A Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Qu, W.; Sun, D.; Liu, X. Meta-analysis of effect of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system blockers on contrast-induced nephropathy. J. Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2020, 21, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shemirani, H.; Pourrmoghaddas, M. A randomized trial of saline hydration to prevent contrast-induced nephropathy in patients on regular captopril or furosemide therapy undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention. Saudi J. Kidney Dis. Transpl. 2012, 23, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rosenstock, J.L.; Bruno, R.; Kim, J.K.; Lubarsky, L.; Schaller, R.; Panagopoulos, G.; DeVita, M.V.; Michelis, M.F. The effect of withdrawal of ACE inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers prior to coronary angiography on the incidence of contrast-induced nephropathy. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2008, 40, 749–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolak, T.; Aliev, E.; Rogachev, B.; Baumfeld, Y.; Cafri, C.; Abu-Shakra, M.; Novack, V. Renal safety and angiotensin II blockade medications in patients undergoing non-emergent coronary angiography: A randomized controlled study. Isr. Med. Assoc. J. 2013, 15, 682–687. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bainey, K.R.; Rahim, S.; Etherington, K.; Rokoss, M.L.; Natarajan, M.K.; Velianou, J.L.; Brons, S.; Mehta, S.R. Effects of withdrawing vs continuing renin-angiotensin blockers on incidence of acute kidney injury in patients with renal insufficiency undergoing cardiac catheterization: Results from the Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibitor/Angiotensin Receptor Blocker and Contrast Induced Nephropathy in Patients Receiving Cardiac Catheterization (CAPTAIN) trial. Am. Heart J. 2015, 170, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaka, Y.; Hayashi, H.; Aonuma, K.; Horio, M.; Terada, Y.; Doi, K.; Fujigaki, Y.; Yasuda, H.; Sato, T.; Fujikura, T.; et al. Guideline on the use of iodinated contrast media in patients with kidney disease 2018. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2020, 24, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFronzo, R.; Fleming, G.A.; Chen, K.; Bicsak, T.A. Metformin-associated lactic acidosis: Current perspectives on causes and risk. Metabolism 2016, 65, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Molen, A.J.; Geenen, R.W.F.; Pels Rijcken, T.H.; Dekker, H.M.; Van den Meiracker, A.H.; Hoogeveen, E.K.; van Straaten, H.M.O.; Sijpkens, Y.W.J.; Kooiman, J.; Cobbaert, C.; et al. Guideline Safe Use of Contrast Media, Part 1. 2017. Available online: https://www.radiologen.nl/kwaliteit/richtlijnen-veilig-gebruik-van-contrastmiddelen-guidelines-safe-use-contrast-media (accessed on 15 December 2021).
- Food and Drug Administration (FDA). FDA Revises Warnings Regarding Use of the Diabetes Medicine Metformin in Certain Patients with Reduced Kidney Function. Available online: http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DrugSafety/ucm493244.htm (accessed on 15 December 2021).
- Nagayama, Y.; Tanoue, S.; Tsuji, A.; Urata, J.; Furusawa, M.; Oda, S.; Nakaura, T.; Utsunomiya, D.; Yoshida, E.; Yoshida, M.; et al. Application of 80-kVp scan and raw data-based iterative reconstruction for reduced iodine load abdominal-pelvic CT in patients at risk of contrast-induced nephropathy referred for oncological assessment: Effects on radiation dose, image quality and renal function. Br. J. Radiol. 2018, 91, 20170632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balemans, C.E.; Reichert, L.J.; van Schelven, B.I.; van den Brand, J.A.; Wetzels, J.F. Epidemiology of contrast material-induced nephropathy in the era of hydration. Radiology 2012, 263, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brar, S.S.; Aharonian, V.; Mansukhani, P.; Moore, N.; Shen, A.Y.J.; Jorgensen, M.; Dua, A.; Short, L.; Kane, K. Haemodynamic-guided fluid administration for the prevention of contrast-induced acute kidney injury: The POSEIDON randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2014, 383, 1814–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, M.A.; McCullough, P.A.; Tobin, K.J.; Speck, J.P.; Westveer, D.C.; Guido-Allen, D.A.; Timmis, G.C.; O’Neill, W.W. A prospective randomized trial of prevention measures in patients at high risk for contrast nephropathy: Results of the P.R.I.N.C.E. Study. Prevention of Radiocontrast Induced Nephropathy Clinical Evaluation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1999, 33, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briguori, C.; D’Amore, C.; De Micco, F.; Signore, N.; Esposito, G.; Napolitano, G.; Focaccio, A.; Investigators, R.I. Renal insufficiency following contrast media administration trial III: Urine flow rate-guided versus left-ventricular end-diastolic pressure-guided hydration in high-risk patients for contrast-induced acute kidney injury. Rationale and design. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2020, 95, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorval, J.F.; Dixon, S.R.; Zelman, R.B.; Davidson, C.J.; Rudko, R.; Resnic, F.S. Feasibility study of the RenalGuard™ balanced hydration system: A novel strategy for the prevention of contrast-induced nephropathy in high risk patients. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 166, 482–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briguori, C.; Visconti, G.; Focaccio, A.; Airoldi, F.; Valgimigli, M.; Sangiorgi, G.M.; Golia, B.; Ricciardelli, B.; Condorelli, G. Renal Insufficiency After Contrast Media Administration Trial II (REMEDIAL II): RenalGuard System in high-risk patients for contrast-induced acute kidney injury. Circulation 2011, 124, 1260–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Guo, Y. RenalGuard system and conventional hydration for preventing contrast-associated acute kidney injury in patients undergoing cardiac interventional procedures: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Cardiol. 2021, 333, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briguori, C.; D’Amore, C.; De Micco, F.; Signore, N.; Esposito, G.; Visconti, G.; Airoldi, F.; Signoriello, G.; Focaccio, A. Left Ventricular End-Diastolic Pressure Versus Urine Flow Rate-Guided Hydration in Preventing Contrast-Associated Acute Kidney Injury. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2020, 13, 2065–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maioli, M.; Toso, A.; Leoncini, M.; Musilli, N.; Grippo, G.; Ronco, C.; McCullough, P.A.; Bellandi, F. Bioimpedance-Guided Hydration for the Prevention of Contrast-Induced Kidney Injury: The HYDRA Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 2880–2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Ye, M.; Dong, X.; Chen, Q.; Hong, H.; Chen, L.; Luo, Y. Prevention of Contrast-Induced Nephropathy by Inferior Vena Cava Ultrasonography-Guided Hydration in Chronic Heart Failure Patients. Cardiology 2021, 146, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahling, M.; Seeliger, E.; Patzak, A.; Persson, P.B. Understanding and preventing contrast-induced acute kidney injury. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, J.; Yang, B.; Wu, K.; Lin, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Wang, H.; Zeng, C.; Chen, X.; et al. Effectiveness of oral hydration in preventing contrast-induced acute kidney injury in patients undergoing coronary angiography or intervention: A pairwise and network meta-analysis. Coron. Artery Dis. 2018, 29, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiremath, S.; Akbari, A.; Shabana, W.; Fergusson, D.A.; Knoll, G.A. Prevention of contrast-induced acute kidney injury: Is simple oral hydration similar to intravenous? A systematic review of the evidence. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastia, C.; Paez-Carpio, A.; Guillen, E.; Pano, B.; Garcia-Cinca, D.; Poch, E.; Oleaga, L.; Nicolau, C. Oral hydration compared to intravenous hydration in the prevention of post-contrast acute kidney injury in patients with chronic kidney disease stage IIIb: A phase III non-inferiority study (NICIR study). Eur. J. Radiol. 2021, 136, 109509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.G.; Hou, Y.F.; Ma, L.L.; Yao, D.K.; Wang, L.X. Comparison of oral and intravenous hydration strategies for the prevention of contrast-induced nephropathy in patients undergoing coronary angiography or angioplasty: A randomized clinical trial. Acta Cardiol. 2012, 67, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijssen, E.C.; Rennenberg, R.J.; Nelemans, P.J.; Essers, B.A.; Janssen, M.M.; Vermeeren, M.A.; Ommen, V.V.; Wildberger, J.E. Prophylactic hydration to protect renal function from intravascular iodinated contrast material in patients at high risk of contrast-induced nephropathy (AMACING): A prospective, randomised, phase 3, controlled, open-label, non-inferiority trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 1312–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Chen, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, N.; Yang, H.; Yao, J.; Zhou, Y. Meta-analysis of prophylactic hydration versus no hydration on contrast-induced acute kidney injury. Coron. Artery Dis. 2017, 28, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, P.; Amione-Guerra, J.; Sheikh, O.; Jameson, L.C.; Bansal, S.; Prasad, A. Meta-analysis of intravascular volume expansion strategies to prevent contrast-associated acute kidney injury following invasive angiography. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2021, 98, 1120–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.; Jing, R.; Zhang, W.; Tang, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, T. Hydration Strategies for Preventing Contrast-Induced Acute Kidney Injury: A Systematic Review and Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis. J. Interv. Cardiol. 2020, 2020, 7292675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Kim, D.K.; Jung, H.Y.; Kim, C.D.; Cho, J.H.; Cha, R.H.; Jeong, J.C.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.J.; Ban, T.H.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of a Balanced Salt Solution Versus a 0.9% Saline Infusion for the Prevention of Contrast-Induced Acute Kidney Injury After Contrast-Enhanced Computed Tomography. Kidney Med. 2020, 2, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, D.N.; Goh, C.Y.; Marenzi, G.; Corradi, V.; Ronco, C.; Perazella, M.A. Renal replacement therapies for prevention of radiocontrast-induced nephropathy: A systematic review. Am. J. Med. 2012, 125, 66–78.e63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marenzi, G.; Lauri, G.; Campodonico, J.; Marana, I.; Assanelli, E.; De Metrio, M.; Grazi, M.; Veglia, F.; Fabbiocchi, F.; Montorsi, P.; et al. Comparison of two hemofiltration protocols for prevention of contrast-induced nephropathy in high-risk patients. Am. J. Med. 2006, 119, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marenzi, G.; Marana, I.; Lauri, G.; Assanelli, E.; Grazi, M.; Campodonico, J.; Trabattoni, D.; Fabbiocchi, F.; Montorsi, P.; Bartorelli, A.L. The prevention of radiocontrast-agent-induced nephropathy by hemofiltration. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 1333–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.J.; Yoon, J.W.; Han, S.J.; Choi, H.H.; Song, Y.R.; Kim, S.G.; Oh, J.E.; Lee, Y.K.; Seo, J.W.; Kim, H.J.; et al. The prevention of contrast-induced nephropathy by simultaneous hemofiltration during coronary angiographic procedures: A comparison with periprocedural hemofiltration. Int. J. Cardiol. 2014, 176, 941–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyamada, N.; Hamanaka, I.; Fujioka, A.; Iwasaku, T.; Minami, T.; Fujie, H.; Ueda, K. Effectiveness of high flow-volume intermittent hemodiafiltration during and after intervention to prevent contrast-induced nephropathy in patients with advanced chronic kidney disease: A pilot study. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2020, 96, 1174–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recio-Mayoral, A.; Chaparro, M.; Prado, B.; Cózar, R.; Méndez, I.; Banerjee, D.; Kaski, J.C.; Cubero, J.; Cruz, J.M. The reno-protective effect of hydration with sodium bicarbonate plus N-acetylcysteine in patients undergoing emergency percutaneous coronary intervention: The RENO Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2007, 49, 1283–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisbord, S.D.; Gallagher, M.; Jneid, H.; Garcia, S.; Cass, A.; Thwin, S.S.; Conner, T.A.; Chertow, G.M.; Bhatt, D.L.; Shunk, K.; et al. Outcomes after Angiography with Sodium Bicarbonate and Acetylcysteine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ACT Investigators. Acetylcysteine for prevention of renal outcomes in patients undergoing coronary and peripheral vascular angiography: Main results from the randomized Acetylcysteine for Contrast-induced nephropathy Trial (ACT). Circulation 2011, 124, 1250–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Xie, X.; Liu, L.; Lv, J.; Song, F.; Perkovic, V.; Zhang, H. Comparative Effectiveness of 12 Treatment Strategies for Preventing Contrast-Induced Acute Kidney Injury: A Systematic Review and Bayesian Network Meta-analysis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2017, 69, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.Q.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Han, X.Q.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, N.F. Comparative efficacy of pharmacological interventions for contrast-induced nephropathy prevention after coronary angiography: A network meta-analysis from randomized trials. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2018, 50, 1085–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, R.; Zuo, C.; Zeng, J.; Su, B.; Tao, Y.; Huang, S.; Zeng, R. Atorvastatin attenuates experimental contrast-induced acute kidney injury: A role for TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway. Ren. Fail. 2017, 39, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, S.O.; Budoff, M. Effect of statins on atherosclerotic plaque. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2019, 29, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Otaibi, K.E.; Al Elaiwi, A.M.; Tariq, M.; Al-Asmari, A.K. Simvastatin attenuates contrast-induced nephropathy through modulation of oxidative stress, proinflammatory myeloperoxidase, and nitric oxide. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2012, 2012, 831748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.L.; Chen, L.Q.; Du, X.G. Efficacy of short-term moderate or high-dose statin therapy for the prevention of contrast-induced nephropathy in high-risk patients with chronic kidney disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Clinics 2021, 76, e1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, S.H.; Koo, B.K.; Park, J.S.; Kang, H.J.; Cho, Y.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Youn, T.J.; Chung, W.Y.; Chae, I.H.; Choi, D.J.; et al. Prevention of radiocontrast medium-induced nephropathy using short-term high-dose simvastatin in patients with renal insufficiency undergoing coronary angiography (PROMISS) trial—A randomized controlled study. Am. Heart J. 2008, 155, 499.e1–499.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Patient-Related | Impaired renal function Diabetes mellitus Effective intravascular volume depletion: dehydration, blood loss, congestive heart failure, liver cirrhosis, nephrosis Advanced age Female gender Cardiovascular disease including hypertension Malignancy Inflammation Anemia Hyperuricemia Nephrotoxic medications: diuretics, nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs, aminoglycosides, amphotericin B, antiviral drugs such as acyclovir, cyclosporine A, cisplatin |
| Procedure-Related | Route of CM administration: intra-arterial vs. intravenous administration Type of procedure: catheter-based procedure Type of CM Volume of CM Repeated CM administration within 24–72 h |
| Patient-related | Risk stratification of individual patients Evaluate and correct patient’s volume status Correct modifiable factors including cessation of nephrotoxic drugs |
| Procedure-related | Use low-osmolar or iso-osmolar contrast media Minimize the volume of contrast media - limit maximum contrast volume - consider the interval of contrast administration |
| Pathophysiology-related | Hydration * Pharmaceutical agents targeting pathogenic process including oxidative stress |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cho, E.; Ko, G.-J. The Pathophysiology and the Management of Radiocontrast-Induced Nephropathy. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12010180
Cho E, Ko G-J. The Pathophysiology and the Management of Radiocontrast-Induced Nephropathy. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(1):180. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12010180
Chicago/Turabian StyleCho, Eunjung, and Gang-Jee Ko. 2022. "The Pathophysiology and the Management of Radiocontrast-Induced Nephropathy" Diagnostics 12, no. 1: 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12010180
APA StyleCho, E., & Ko, G.-J. (2022). The Pathophysiology and the Management of Radiocontrast-Induced Nephropathy. Diagnostics, 12(1), 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12010180






