Clues for Improving the Pathophysiology Knowledge for Endometriosis Using Plasma Micro-RNA Expression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Plasma Sample Collection
2.3. RNA Sample Extraction, Preparation, and Quality Control
3. Bioinformatics
3.1. Raw Data Preprocessing (Raw, Filtered, Aligned Reads) and Quality Control
3.2. Differential Expression Analysis of the miRNAs
3.3. Study of the miRNA Accuracy
3.4. Sources and Search Strategy
4. Results
4.1. Demographic Characteristics of the Population
4.2. Comparison of miRNAs Expressed in Patients with and without Endometriosis
4.3. Relation between miRNA Expression and Signaling Pathways Known in Endometriosis
4.4. Relation between miRNA Expression and Signaling Pathways Involved in Disorders Other Than Endometriosis
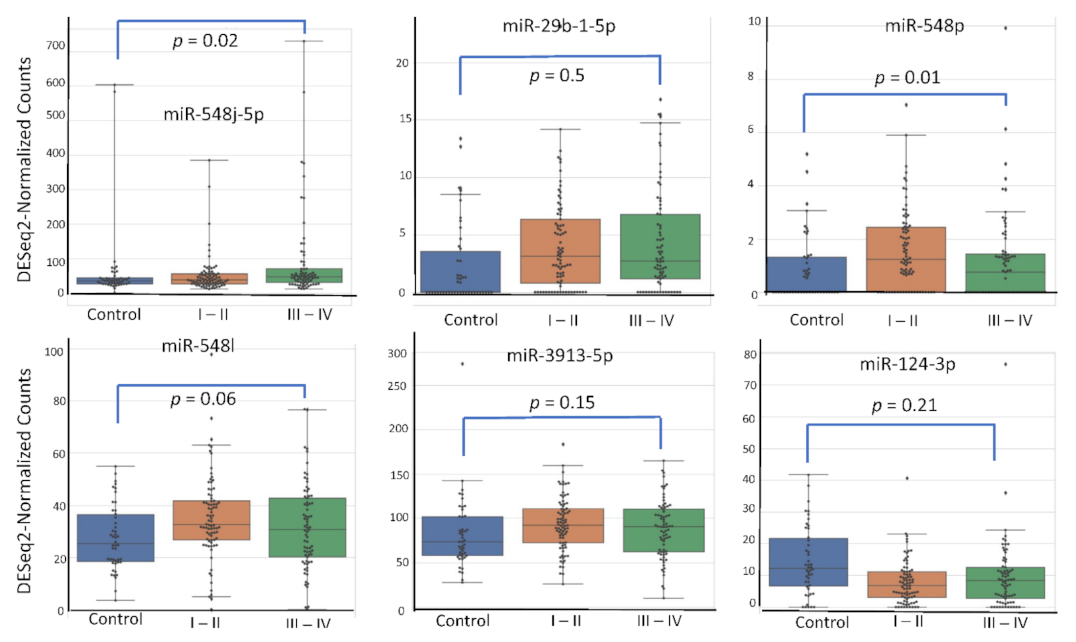
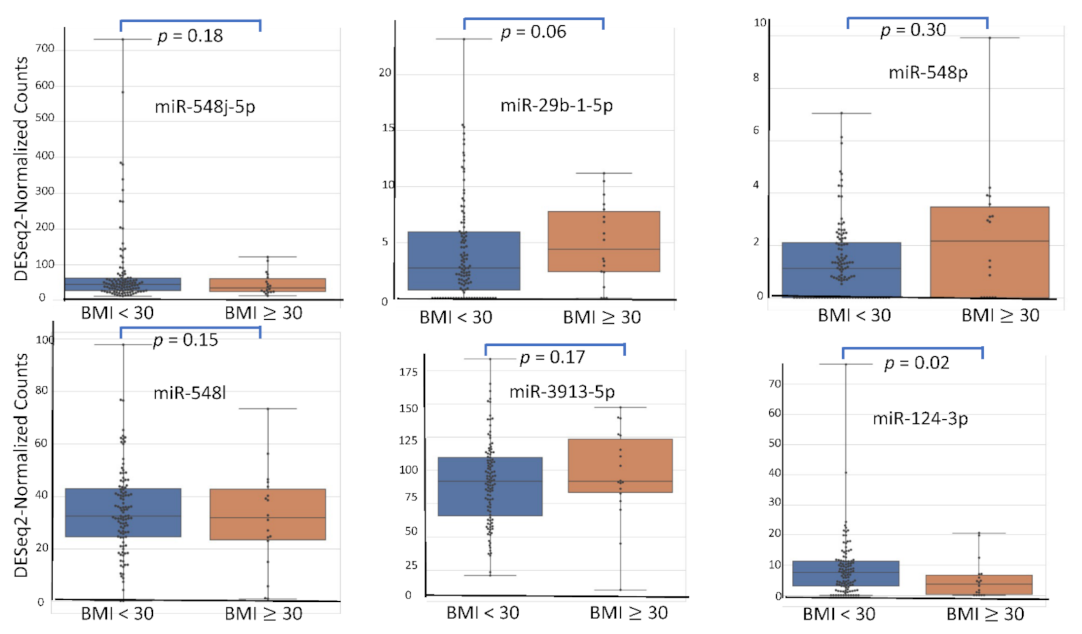
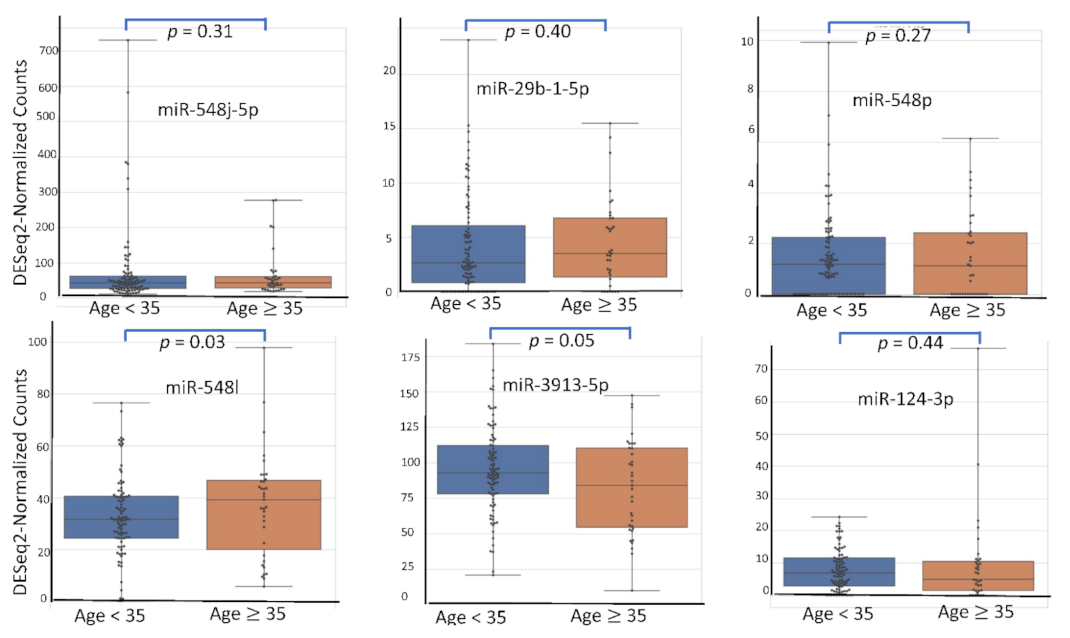
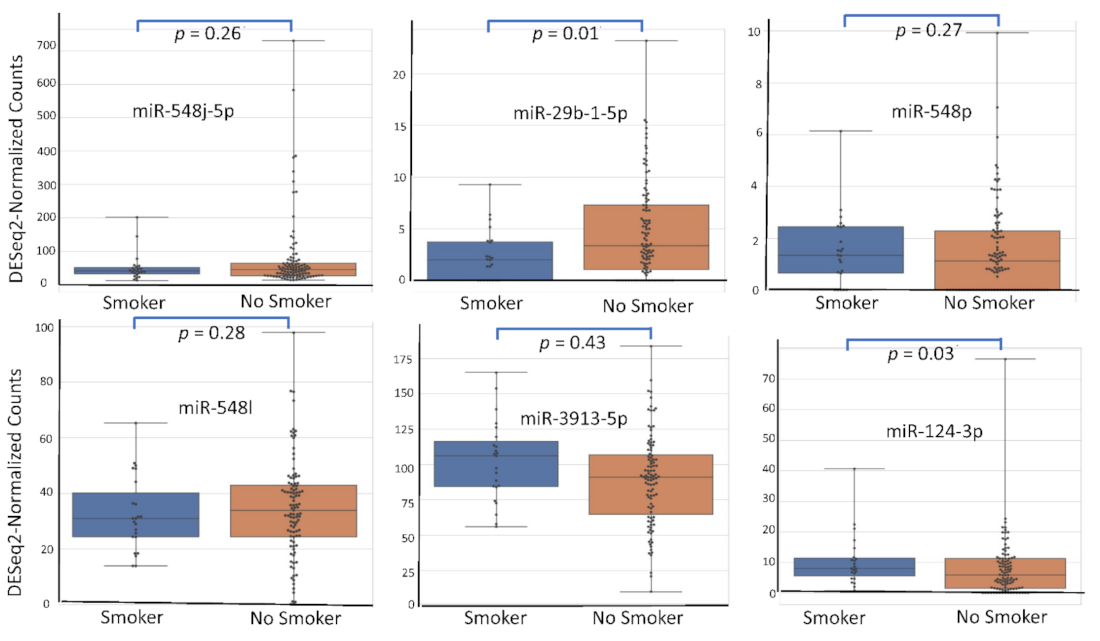
4.5. miRNA Expression Level According to Patient’s Characteristics
5. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ITGB3 | Integrin Subunit Beta 3 |
| PDE4B | Phosphodiesterase 4B |
| EGR2 | Early Growth Response 2 |
| CRKL | CRK Like Proto-Oncogene, Adaptor Protein |
| ABCA2 | ATP Binding Cassette Subfamily A Member 2 |
| MGAT5 | Alpha-1,6-Mannosylglycoprotein 6-Beta-N-Acetylglucosaminyltransferase |
| Fra-2 | Fos-related antigen 2 |
| ANXA7 | Annexin A7 |
| CD1/CDK6 | Cell division protein kinase 6 |
| EZH2 | Enhancer of zeste homolog 2 |
| EDNRB | Endothelin Receptor Type B |
| DAPK1 | Death Associated Protein Kinase 1 |
| FIP200 | FAK family kinase-interacting protein of 200 kDa |
| TRIM14 | Tripartite Motif Containing 14 |
| mTor | mammalian target of rapamycin |
| STAT3 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 |
| PI3K/Akt | Phosphoinositide 3-kinases/Protein kinase B |
| NF–KB | nuclear factor-kappa B |
| ERK | extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| PLGF/ROS | Placental Growth Factor/Reactive oxygen species |
| FGF2–EGFR | fibroblast growth factor/Epidermal Growth Factor |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinases |
| GSK3B/Beta catenine | Glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta/β-catenine |
References
- Secosan, C.; Balulescu, L.; Brasoveanu, S.; Balint, O.; Pirtea, P.; Dorin, G.; Pirtea, L. Endometriosis in Menopause-Renewed Attention on a Controversial Disease. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, D.; Chvatal, R.; Reichert, B.; Renner, S.; Shebl, O.; Binder, H.; Wurm, P.; Oppelt, P. Endometriosis: A premenopausal disease? Age pattern in 42,079 patients with endometriosis. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2012, 286, 667–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matta, K.; Vigneau, E.; Cariou, V.; Mouret, D.; Ploteau, S.; Le Bizec, B.; Antignac, J.-P.; Cano-Sancho, G. Associations between persistent organic pollutants and endometriosis: A multipollutant assessment using machine learning algorithms. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 114066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Fang, X.; Huang, H.; Huang, W.; Wang, L.; Xia, X. Construction and topological analysis of an endometriosis-related exosomal circRNA-miRNA-mRNA regulatory network. Aging 2021, 13, 12607–12630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammond, S.M. RNAi, microRNAs, and human disease. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2006, 58 (Suppl. 1), s63–s68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panir, K.; Schjenken, J.E.; Robertson, S.A.; Hull, M.L. Non-coding RNAs in endometriosis: A narrative review. Hum. Reprod. Update 2018, 24, 497–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monnaka, V.U.; Hernandes, C.; Heller, D.; Podgaec, S. Overview of miRNAs for the non-invasive diagnosis of endometriosis: Evidence, challenges and strategies. A systematic review. Einstein Sao Paulo Braz. 2021, 19, eRW5704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhie, A.; O, D.; Peterse, D.; Beckers, A.; Cuéllar, A.; Fassbender, A.; Meuleman, C.; Mestdagh, P.; D’Hooghe, T. Plasma miRNAs as biomarkers for endometriosis. Hum. Reprod. Oxf. Engl. 2019, 34, 1650–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maged, A.M.; Deeb, W.S.; El Amir, A.; Zaki, S.S.; El Sawah, H.; Al Mohamady, M.; Metwally, A.A.; Katta, M.A. Diagnostic accuracy of serum miR-122 and miR-199a in women with endometriosis. Int. J. Gynaecol. Obstet. Off. Organ. Int. Fed. Gynaecol. Obstet. 2018, 141, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misir, S.; Hepokur, C.; Oksasoglu, B.; Yildiz, C.; Yanik, A.; Aliyazicioglu, Y. Circulating serum miR-200c and miR-34a-5p as diagnostic biomarkers for endometriosis. J. Gynecol. Obstet. Hum. Reprod. 2021, 50, 102092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosar, E.; Mamillapalli, R.; Ersoy, G.S.; Cho, S.; Seifer, B.; Taylor, H.S. Serum microRNAs as diagnostic markers of endometriosis: A comprehensive array-based analysis. Fertil. Steril. 2016, 106, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javadi, M.; Rad, J.S.; Farashah, M.S.G.; Roshangar, L. An Insight on the Role of Altered Function and Expression of Exosomes and MicroRNAs in Female Reproductive Diseases. Reprod. Sci. Thousand Oaks Calif 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, P.; Zhou, J.; Ma, X.; Zhang, G.; Li, Y. Expression, regulation and function of MicroRNAs in endometriosis. Die Pharm.-Int. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 71, 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendifallah, S. Evaluation of miRNAs in Endometriosis. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ (accessed on 28 August 2021).
- Ito, T.E.; Abi Khalil, E.D.; Taffel, M.; Moawad, G.N. Magnetic resonance imaging correlation to intraoperative findings of deeply infiltrative endometriosis. Fertil. Steril. 2017, 107, e11–e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazot, M.; Daraï, E. Diagnosis of deep endometriosis: Clinical examination, ultrasonography, magnetic resonance imaging, and other techniques. Fertil. Steril. 2017, 108, 886–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazot, M.; Darai, E.; Hourani, R.; Thomassin, I.; Cortez, A.; Uzan, S.; Buy, J.-N. Deep pelvic endometriosis: MR imaging for diagnosis and prediction of extension of disease. Radiology 2004, 232, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revised American Society for Reproductive Medicine classification of endometriosis: 1996. Fertil. Steril. 1997, 67, 817–821. [CrossRef]
- de Foucher, T.; Sbeih, M.; Uzan, J.; Bendifallah, S.; Lefevre, M.; Chabbert-Buffet, N.; Aractingi, S.; Uzan, C.; Abd Alsalam, I.; Mitri, R.; et al. Identification of micro-RNA expression profile related to recurrence in women with ESMO low-risk endometrial cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2018, 16, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canlorbe, G.; Wang, Z.; Laas, E.; Bendifallah, S.; Castela, M.; Lefevre, M.; Chabbert-Buffet, N.; Daraï, E.; Aractingi, S.; Méhats, C.; et al. Identification of microRNA expression profile related to lymph node status in women with early-stage grade 1-2 endometrial cancer. Mod. Pathol. Off. J. U. S. Can. Acad. Pathol. Inc. 2016, 29, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canlorbe, G.; Castela, M.; Bendifallah, S.; Wang, Z.; Lefevre, M.; Chabbert-Buffet, N.; Aractingi, S.; DaraÏ, E.; Méhats, C.; Ballester, M. Micro-RNA signature of lymphovascular space involvement in type 1 endometrial cancer. Histol. Histopathol. 2017, 32, 941–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyvyte, U.; Kupcinskas, J.; Juzenas, S.; Inciuraite, R.; Poskiene, L.; Salteniene, V.; Link, A.; Fassan, M.; Franke, A.; Kupcinskas, L.; et al. Identification of long intergenic non-coding RNAs (lincRNAs) deregulated in gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0209342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gyvyte, U.; Juzenas, S.; Salteniene, V.; Kupcinskas, J.; Poskiene, L.; Kucinskas, L.; Jarmalaite, S.; Stuopelyte, K.; Steponaitiene, R.; Hemmrich-Stanisak, G.; et al. MiRNA profiling of gastrointestinal stromal tumors by next-generation sequencing. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 37225–37238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Rincon, A.; Mendoza-Maldonado, L.; Martinez-Archundia, M.; Schönhuth, A.; Kraneveld, A.D.; Garssen, J.; Tonda, A. Machine Learning-Based Ensemble Recursive Feature Selection of Circulating miRNAs for Cancer Tumor Classification. Cancers 2020, 12, 1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Trapnell, C.; Pop, M.; Salzberg, S.L. Ultrafast and memory-efficient alignment of short DNA sequences to the human genome. Genome Biol. 2009, 10, R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths-Jones, S.; Saini, H.K.; van Dongen, S.; Enright, A.J. miRBase: Tools for microRNA genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, D154–D158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Zhang, L. Construction and comprehensive analysis of a ceRNA network to reveal potential prognostic biomarkers for lung adenocarcinoma. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potla, P.; Ali, S.A.; Kapoor, M. A bioinformatics approach to microRNA-sequencing analysis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. Open 2021, 3, 100131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, G.; Bao, Y.; Wu, Y.; You, Q. Evaluation and application of tools for the identification of known microRNAs in plants. Appl. Plant Sci. 2021, 9, e11414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargaje, R.; Hariharan, M.; Scaria, V.; Pillai, B. Consensus miRNA expression profiles derived from interplatform normalization of microarray data. RNA 2010, 16, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrell, F.E.; Lee, K.L.; Mark, D.B. Multivariable prognostic models: Issues in developing models, evaluating assumptions and adequacy, and measuring and reducing errors. Stat. Med. 1996, 15, 361–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steyerberg, E.W.; Eijkemans, M.J.; Harrell, F.E.; Habbema, J.D. Prognostic modelling with logistic regression analysis: A comparison of selection and estimation methods in small data sets. Stat. Med. 2000, 19, 1059–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Zhu, D. Circ_0017956 promotes the proliferation and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer through regulating miR-515-5p/ITGB8 axis. Cell Cycle Georget. Tex 2021, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shi, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Zheng, P.; Li, H. Circ_0057553/miR-515-5p Regulates Prostate Cancer Cell Proliferation, Apoptosis, Migration, Invasion and Aerobic Glycolysis by Targeting YES1. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 11289–11299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Lu, L.; Xia, H.; Xiang, Q.; Sun, J.; Xue, J.; Xiao, T.; Cheng, C.; Liu, Q.; Shi, A. Circ0061052 regulation of FoxC1/Snail pathway via miR-515-5p is involved in the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of epithelial cells during cigarette smoke-induced airway remodeling. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 746, 141181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.-X.; Zheng, T.; Zhang, Y.; Hao, P. CircFOXM1 silencing represses cell proliferation, migration and invasion by regulating miR-515-5p/ADAM10 axis in prostate cancer. Anticancer Drugs 2021, 33, e573–e583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, H.; Zeng, Q.; Xu, P.; Liu, M.; Yang, N. Circular RNA circ-MAT2B facilitates glycolysis and growth of gastric cancer through regulating the miR-515-5p/HIF-1α axis. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.W.; Yan, T.Q.; Tong, H. Effect of miR-515-5p on Proliferation and Drug Sensitivity of Retinoblastoma Cells. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 12087–12098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, P.; Lv, X.; Aizemaiti, R.; Cheng, J.; Xia, P.; Di, M. H3K27ac-activated LINC00519 promotes lung squamous cell carcinoma progression by targeting miR-450b-5p/miR-515-5p/YAP1 axis. Cell Prolif. 2020, 53, e12797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilam, A.; Edry, L.; Mamluk-Morag, E.; Bar-Ilan, D.; Avivi, C.; Golan, D.; Laitman, Y.; Barshack, I.; Friedman, E.; Shomron, N. Involvement of IGF-1R regulation by miR-515-5p modifies breast cancer risk among BRCA1 carriers. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2013, 138, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, K.; Ning, S.; Wan, L.; Wu, H.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Xu, S.; Pang, D. LINC00673 is activated by YY1 and promotes the proliferation of breast cancer cells via the miR-515-5p/MARK4/Hippo signaling pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. CR 2019, 38, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, G.; Huang, C.; Yang, J.; Jin, L.; Fu, K.; Yuan, F.; Zhu, J.; Xue, B. LncRNA SNHG3 promotes bladder cancer proliferation and metastasis through miR-515-5p/GINS2 axis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 9231–9243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gao, L.; Zhang, C.; Meng, J. LncRNA SNHG3 Promotes Proliferation and Metastasis of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells Through miR-515-5p/SUMO2 Axis. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 20, 15330338211019376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Q.; Li, F.; Shen, K.; Luo, C.; Song, G. LOXL1-AS1/miR-515-5p/STAT3 Positive Feedback Loop Facilitates Cell Proliferation and Migration in Atherosclerosis. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2020, 76, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rong, F.; Liu, L.; Zou, C.; Zeng, J.; Xu, Y. MALAT1 Promotes Cell Tumorigenicity Through Regulating miR-515-5p/EEF2 Axis in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 7691–7701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, J.; Xue, D.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Dong, L. MiR-515-5p acts as a tumor suppressor via targeting TRIP13 in prostate cancer. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 129, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.-S.; Zheng, H.; Ou, Y.-L.; Tao, Y.-P.; Wang, Z.-G.; Song, L.-H.; Yan, H.-L.; Zhou, W.-P. miR-515-5p suppresses HCC migration and invasion via targeting IL6/JAK/STAT3 pathway. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 34, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Li, F.; Xie, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H. PVT1 Mediates Cell Proliferation, Apoptosis and Radioresistance in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Through Regulating miR-515-5p/PIK3CA Axis. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 10077–10090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wan, Q.; Zhou, H. Targeted-regulating of miR-515-5p by LncRNA LOXL1-AS1 on the proliferation and migration of trophoblast cells. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2021, 118, 104588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, D.; Hong, S.; Yang, J.; San, P. The Effects of microRNA-515-5p on the Toll-Like Receptor 4 (TLR4)/JNK Signaling Pathway and WNT1-Inducible-Signaling Pathway Protein 1 (WISP-1) Expression in Rheumatoid Arthritis Fibroblast-Like Synovial (RAFLS) Cells Following Treatment with Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor-kappa-B Ligand (RANKL). Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2020, 26, e920611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, R.; Du, Y.; Niu, X.; Zang, R. ZFPM2-AS1 transcriptionally mediated by STAT1 regulates thyroid cancer cell growth, migration and invasion via miR-515-5p/TUSC3. J. Cancer 2021, 12, 3393–3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Blasio, A.; Di Fiore, R.; Pratelli, G.; Drago-Ferrante, R.; Saliba, C.; Baldacchino, S.; Grech, G.; Scerri, C.; Vento, R.; Tesoriere, G. A loop involving NRF2, miR-29b-1-5p and AKT, regulates cell fate of MDA-MB-231 triple-negative breast cancer cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, A.; Mizushima, T.; Wu, X.; Okuzaki, D.; Kambara, N.; Ishikawa, S.; Wang, J.; Qian, Y.; Hirose, H.; Yokoyama, Y.; et al. A miR-29b Byproduct Sequence Exhibits Potent Tumor-Suppressive Activities via Inhibition of NF-κB Signaling in KRAS-Mutant Colon Cancer Cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 977–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Ouyang, H.; Wang, Z.; Chen, B.; Nie, Q. A Novel Circular RNA Generated by FGFR2 Gene Promotes Myoblast Proliferation and Differentiation by Sponging miR-133a-5p and miR-29b-1-5p. Cells 2018, 7, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmansi, A.M.; Hussein, K.A.; Herrero, S.M.; Periyasamy-Thandavan, S.; Aguilar-Pérez, A.; Kondrikova, G.; Kondrikov, D.; Eisa, N.H.; Pierce, J.L.; Kaiser, H.; et al. Age-related increase of kynurenine enhances miR29b-1-5p to decrease both CXCL12 signaling and the epigenetic enzyme Hdac3 in bone marrow stromal cells. Bone Rep. 2020, 12, 100270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Q.; Sun, B.; Wang, D.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y. Circ6401, a novel circular RNA, is implicated in repair of the damaged endometrium by Wharton’s jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells through regulation of the miR-29b-1-5p/RAP1B axis. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2020, 11, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, H.; Li, Z.; Chang, Y.; Fang, B.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, H. Downregulation of Long Noncoding RNA TUG1 Attenuates MTDH-Mediated Inflammatory Damage via Targeting miR-29b-1-5p After Spinal Cord Ischemia Reperfusion. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2021, 80, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Zhang, Q.; Cheng, W.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Ge, J. Effect of miR-29b-1* and miR-29c knockdown on cell growth of the bladder cancer cell line T24. J. Int. Med. Res. 2013, 41, 1803–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datta, C.; Subuddhi, A.; Kumar, M.; Lepcha, T.T.; Chakraborty, S.; Jana, K.; Ghosh, Z.; Mukhopadhyay, A.K.; Basu, J.; Kundu, M. Genome-wide mRNA-miRNA profiling uncovers a role of the microRNA miR-29b-1-5p/PHLPP1 signalling pathway in Helicobacter pylori-driven matrix metalloproteinase production in gastric epithelial cells. Cell. Microbiol. 2018, 20, e12859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, B.; Li, N.; Xu, X.-X.; Li, X.-X.; Xu, X.-J.; Guo, D.; Zhang, D.; Wu, Z.-H.; Zhang, S.-Y. Long noncoding RNA FTX regulates cardiomyocyte apoptosis by targeting miR-29b-1-5p and Bcl2l2. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 495, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drago-Ferrante, R.; Pentimalli, F.; Carlisi, D.; De Blasio, A.; Saliba, C.; Baldacchino, S.; Degaetano, J.; Debono, J.; Caruana-Dingli, G.; Grech, G.; et al. Suppressive role exerted by microRNA-29b-1-5p in triple negative breast cancer through SPIN1 regulation. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 28939–28958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurihara-Shimomura, M.; Sasahira, T.; Shimomura, H.; Nakashima, C.; Kirita, T. The Oncogenic Activity of miR-29b-1-5p Induces the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Song, X.; Li, Y.; Su, P.; Han, D.; Ma, T.; Guo, R.; Chen, B.; Zhao, W.; Sang, Y.; et al. circKDM4C suppresses tumor progression and attenuates doxorubicin resistance by regulating miR-548p/PBLD axis in breast cancer. Oncogene 2019, 38, 6850–6866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chang, Y.; Xu, L.; Qin, L. Elevated expression of circular RNA circ_0008450 predicts dismal prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma and regulates cell proliferation, apoptosis, and invasion via sponging miR-548p. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 9487–9494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Hussain, M.M. Human MicroRNA-548p Decreases Hepatic Apolipoprotein B Secretion and Lipid Synthesis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2017, 37, 786–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.-M.; Yan, X.-H.; Hu, Y.-W.; Huang, J.-L.; Cao, S.-W.; Ren, T.-Y.; Tang, Y.-T.; Lin, L.; Zheng, L.; Wang, Q. miRNA-548p suppresses hepatitis B virus X protein associated hepatocellular carcinoma by downregulating oncoprotein hepatitis B x-interacting protein. Hepatol. Res. Off. J. Jpn. Soc. Hepatol. 2016, 46, 804–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yang, H.; Xu, Z.; Li, D.; Zhou, M.; Xiao, K.; Shi, Z.; Zhu, L.; Yang, L.; Zhou, R. microRNA-548l is involved in the migration and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer by targeting the AKT1 signaling pathway. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 141, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, H.; Zhou, H.; Miao, Y.; Li, N.; Zhao, L.; Jia, L. MiRNA expression profiles reveal the involvement of miR-26a, miR-548l and miR-34a in hepatocellular carcinoma progression through regulation of ST3GAL5. Lab. Investig. J. Tech. Methods Pathol. 2017, 97, 530–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Trillo, C.; Aroca-Aguilar, J.-D.; Ferre-Fernández, J.-J.; Méndez-Hernández, C.-D.; Morales, L.; García-Feijoo, J.; Escribano, J. The Role of hsa-miR-548l Dysregulation as a Putative Modifier Factor for Glaucoma-Associated FOXC1 Mutations. MicroRNA Shariqah United Arab Emir. 2015, 4, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, C.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Sun, W.; Shen, K.; Lv, Y.; Zhu, S.; Zhan, P.; Lv, T.; et al. Elevated exosome-derived miRNAs predict osimertinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Jiao, D.; Liu, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhou, X.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Han, X. Novel miRNA Predicts Survival and Prognosis of Cholangiocarcinoma Based on RNA-seq Data and In Vitro Experiments. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 5976127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepeler, T.; Holm, A.; Halvey, P.; Nordentoft, I.; Lamy, P.; Riising, E.M.; Christensen, L.L.; Thorsen, K.; Liebler, D.C.; Helin, K.; et al. Attenuation of the beta-catenin/TCF4 complex in colorectal cancer cells induces several growth-suppressive microRNAs that target cancer promoting genes. Oncogene 2012, 31, 2750–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, A.; Yang, Y.; He, H.; Sun, J.; Chang, Q.; Xue, Q. Inhibition of Long Non-Coding RNA KCNQ1OT1 Attenuates Neuroinflammation and Neuronal Apoptosis Through Regulating NLRP3 Expression via Sponging miR-30e-3p. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 14, 1731–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Wang, X.; He, H.; Cao, Y. LINC02308 promotes the progression of glioma through activating mTOR/AKT-signaling pathway by targeting miR-30e-3p/TM4SF1 axis. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2021, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Ding, L.; Yu, L.; Zhang, B.; Wei, D. LncRNA MEG3 suppressed the progression of ovarian cancer via sponging miR-30e-3p and regulating LAMA4 expression. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Ma, F.; Su, L.; Shao, G. MicroRNA-30e-3p inhibits cell invasion and migration in clear cell renal cell carcinoma by targeting Snail1. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 2053–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramantieri, L.; Pollutri, D.; Gagliardi, M.; Giovannini, C.; Quarta, S.; Ferracin, M.; Casadei-Gardini, A.; Callegari, E.; De Carolis, S.; Marinelli, S.; et al. MiR-30e-3p Influences Tumor Phenotype through MDM2/TP53 Axis and Predicts Sorafenib Resistance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 1720–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Wang, X.; Sun, Y.; Long, M.; Zheng, J.; Wu, W.; Li, L. miR-30e-3p Promotes Cardiomyocyte Autophagy and Inhibits Apoptosis via Regulating Egr-1 during Ischemia/Hypoxia. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 7231243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeap, S.K.; Mohd Ali, N.; Akhtar, M.N.; Razak, N.A.; Chong, Z.X.; Ho, W.Y.; Boo, L.; Zareen, S.; Kurniawan, T.A.; Avtar, R.; et al. Induction of Apoptosis and Regulation of MicroRNA Expression by (2E,6E)-2,6-bis-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidene)-cyclohexanone (BHMC) Treatment on MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells. Molecules 2021, 26, 1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintanilha, J.C.F.; Cursino, M.A.; Borges, J.B.; Torso, N.G.; Bastos, L.B.; Oliveira, J.M.; Cobaxo, T.S.; Pincinato, E.C.; Hirata, M.H.; Geraldo, M.V.; et al. MiR-3168, miR-6125, and miR-4718 as potential predictors of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in patients with head and neck cancer. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ormseth, M.J.; Solus, J.F.; Sheng, Q.; Chen, S.-C.; Ye, F.; Wu, Q.; Oeser, A.M.; Allen, R.; Raggi, P.; Vickers, K.C.; et al. Plasma miRNAs improve the prediction of coronary atherosclerosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 40, 2211–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedorchak, G.; Rangnekar, A.; Onks, C.; Loeffert, A.C.; Loeffert, J.; Olympia, R.P.; DeVita, S.; Leddy, J.; Haider, M.N.; Roberts, A.; et al. Saliva RNA biomarkers predict concussion duration and detect symptom recovery: A comparison with balance and cognitive testing. J. Neurol. 2021, 268, 4349–4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondal, T.; Brunetto, M.R.; Cavallone, D.; Mikkelsen, M.; Thorsen, M.; Mang, Y.; Pinheiro, H.; Bonino, F.; Mouritzen, P. Genome-Wide Comparison of Next-Generation Sequencing and qPCR Platforms for microRNA Profiling in Serum. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1580, 21–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hicks, S.D.; Onks, C.; Kim, R.Y.; Zhen, K.J.; Loeffert, J.; Loeffert, A.C.; Olympia, R.P.; Fedorchak, G.; DeVita, S.; Rangnekar, A.; et al. Diagnosing mild traumatic brain injury using saliva RNA compared to cognitive and balance testing. Clin. Transl. Med. 2020, 10, e197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.H.; Hong, X.; Mathur, S.C.; Sharma, M.; Rastogi, A.; Sharma, P.; Christenson, L.K.; Bansal, A. A detailed analysis of next generation sequencing reads of microRNA expression in Barrett’s esophagus: Absolute versus relative quantification. BMC Res. Notes 2014, 7, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- ’t Hoen, P.A.C.; Ariyurek, Y.; Thygesen, H.H.; Vreugdenhil, E.; Vossen, R.H.A.M.; de Menezes, R.X.; Boer, J.M.; van Ommen, G.-J.B.; den Dunnen, J.T. Deep sequencing-based expression analysis shows major advances in robustness, resolution and inter-lab portability over five microarray platforms. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, e141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.; Tapmeier, T.; Rahmioglu, N.; Kirtley, S.; Zondervan, K.; Becker, C. The miRNA Mirage: How Close Are We to Finding a Non-Invasive Diagnostic Biomarker in Endometriosis? A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setti, G.; Pezzi, M.E.; Viani, M.V.; Pertinhez, T.A.; Cassi, D.; Magnoni, C.; Bellini, P.; Musolino, A.; Vescovi, P.; Meleti, M. Salivary MicroRNA for Diagnosis of Cancer and Systemic Diseases: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moustafa, S.; Burn, M.; Mamillapalli, R.; Nematian, S.; Flores, V.; Taylor, H.S. Accurate diagnosis of endometriosis using serum microRNAs. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 223, 557.e1–557.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Shoorei, H.; Taheri, M. Role of Non-coding RNAs in the Pathogenesis of Endometriosis. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marí-Alexandre, J.; Sánchez-Izquierdo, D.; Gilabert-Estellés, J.; Barceló-Molina, M.; Braza-Boïls, A.; Sandoval, J. miRNAs Regulation and Its Role as Biomarkers in Endometriosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, X.; Hou, X.; Zhao, W.; Yang, C.; Wan, W.; Chen, L. miR-548b-3p functions as a tumor suppressor in lung cancer. Lasers Med. Sci. 2020, 35, 833–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sha, M.-X.; Huang, X.-W.; Yin, Q. MiR-548b-3p inhibits proliferation and migration of breast cancer cells by targeting MDM2. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 3105–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.-C.; Li, L.-C.; Ng, H.-Y.; Lin, P.-T.; Chiou, T.T.-Y.; Kuo, W.-H.; Lee, C.-T. Urinary Exosomal MicroRNA Signatures in Nephrotic, Biopsy-Proven Diabetic Nephropathy. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Lacarte, M.; Mansego, M.L.; Zulet, M.A.; Martinez, J.A.; Milagro, F.I. miR-1185-1 and miR-548q Are Biomarkers of Response to Weight Loss and Regulate the Expression of GSK3B. Cells 2019, 8, 1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, X.-H.; Zhang, M.-L.; Zhao, X.-S.; Zhao, H.-Y.; Suzuki, T.; Wen, J.-K. A Novel Regulatory Mechanism of Smooth Muscle α-Actin Expression by NRG-1/circACTA2/miR-548f-5p Axis. Circ. Res. 2017, 121, 628–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chacolla-Huaringa, R.; Moreno-Cuevas, J.; Trevino, V.; Scott, S.-P. Entrainment of Breast Cell Lines Results in Rhythmic Fluctuations of MicroRNAs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Liu, X.-L.; Wang, W.; Dong, H.-L.; Xia, Y.-F.; Ruan, L.-P.; Liu, L.-P. Expression of MMIF, HIF-1α and VEGF in Serum and Endometrial Tissues of Patients with Endometriosis. Curr. Med. Sci. 2018, 38, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herington, J.L.; Bruner-Tran, K.L.; Lucas, J.A.; Osteen, K.G. Immune interactions in endometriosis. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2011, 7, 611–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Králíčková, M.; Vetvicka, V. Immunological aspects of endometriosis: A review. Ann. Transl. Med. 2015, 3, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milewski, Ł.; Barcz, E.; Dziunycz, P.; Radomski, D.; Kamiński, P.; Roszkowski, P.I.; Korczak-Kowalska, G.; Malejczyk, J. Association of leptin with inflammatory cytokines and lymphocyte subpopulations in peritoneal fluid of patients with endometriosis. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2008, 79, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keenan, J.A.; Chen, T.T.; Chadwell, N.L.; Torry, D.S.; Caudle, M.R. IL-1 beta, TNF-alpha, and IL-2 in peritoneal fluid and macrophage-conditioned media of women with endometriosis. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 1995, 34, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gmyrek, G.B.; Sieradzka, U.; Goluda, M.; Gabrys, M.; Sozanski, R.; Jerzak, M.; Zbyryt, I.; Chrobak, A.; Chełmonska-Soyta, A. Flow cytometric evaluation of intracellular cytokine synthesis in peripheral mononuclear cells of women with endometriosis. Immunol. Investig. 2008, 37, 43–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.-H.; Sun, H.S.; Lin, C.-C.; Hsiao, K.-Y.; Chuang, P.-C.; Pan, H.-A.; Tsai, S.-J. Distinct mechanisms regulate cyclooxygenase-1 and -2 in peritoneal macrophages of women with and without endometriosis. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2002, 8, 1103–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laganà, A.S.; Salmeri, F.M.; Ban Frangež, H.; Ghezzi, F.; Vrtačnik-Bokal, E.; Granese, R. Evaluation of M1 and M2 macrophages in ovarian endometriomas from women affected by endometriosis at different stages of the disease. Gynecol. Endocrinol. Off. J. Int. Soc. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2020, 36, 441–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulun, S.E.; Monsavais, D.; Pavone, M.E.; Dyson, M.; Xue, Q.; Attar, E.; Tokunaga, H.; Su, E.J. Role of estrogen receptor-β in endometriosis. Semin. Reprod. Med. 2012, 30, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kästingschäfer, C.S.; Schäfer, S.D.; Kiesel, L.; Götte, M. miR-142-3p is a novel regulator of cell viability and proinflammatory signalling in endometrial stroma cells. Reprod. Biomed. Online 2015, 30, 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, M.; Nasu, K.; Abe, W.; Aoyagi, Y.; Kawano, Y.; Kai, K.; Moriyama, M.; Narahara, H. Enhanced miR-210 expression promotes the pathogenesis of endometriosis through activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3. Hum. Reprod. Oxf. Engl. 2015, 30, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, W.; Nasu, K.; Nakada, C.; Kawano, Y.; Moriyama, M.; Narahara, H. miR-196b targets c-myc and Bcl-2 expression, inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in endometriotic stromal cells. Hum. Reprod. Oxf. Engl. 2013, 28, 750–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, E.-M.; Wang, Y.-S.; Lin, C.-S.; Lin, W.-Y.; Hsi, E.; Wu, M.-T.; Juo, S.-H.H. A microRNA-520 mirSNP at the MMP2 gene influences susceptibility to endometriosis in Chinese women. J. Hum. Genet. 2013, 58, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laganà, A.S.; Salmeri, F.M.; Vitale, S.G.; Triolo, O.; Götte, M. Stem Cell Trafficking During Endometriosis: May Epigenetics Play a Pivotal Role? Reprod. Sci. 2018, 25, 978–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, M.K.O.; Ferriani, R.A.; Rosa e Silva, J.C.; Japur de Sá Rosa e Silva, A.C.; Vieira, C.S.; Cândido dos Reis, F.J. The levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system and endometriosis staging. Fertil. Steril. 2007, 87, 1231–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laschke, M.W.; Menger, M.D. Anti-angiogenic treatment strategies for the therapy of endometriosis. Hum. Reprod. Update 2012, 18, 682–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laschke, M.W.; Menger, M.D. In vitro and in vivo approaches to study angiogenesis in the pathophysiology and therapy of endometriosis. Hum. Reprod. Update 2007, 13, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousa, N.A.; Bedaiwy, M.A.; Casper, R.F. Aromatase inhibitors in the treatment of severe endometriosis. Obstet. Gynecol. 2007, 109, 1421–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedaiwy, M.A.; Allaire, C.; Alfaraj, S. Long-term medical management of endometriosis with dienogest and with a gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist and add-back hormone therapy. Fertil. Steril. 2017, 107, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Andres, M.P.; Lopes, L.A.; Baracat, E.C.; Podgaec, S. Dienogest in the treatment of endometriosis: Systematic review. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2015, 292, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papkoff, J.; Rubinfeld, B.; Schryver, B.; Polakis, P. Wnt-1 regulates free pools of catenins and stabilizes APC-catenin complexes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1996, 16, 2128–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clevers, H.; Nusse, R. Wnt/β-catenin signaling and disease. Cell 2012, 149, 1192–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janda, C.Y.; Dang, L.T.; You, C.; Chang, J.; de Lau, W.; Zhong, Z.A.; Yan, K.S.; Marecic, O.; Siepe, D.; Li, X.; et al. Surrogate Wnt agonists that phenocopy canonical Wnt and β-catenin signalling. Nature 2017, 545, 234–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licht-Murava, A.; Paz, R.; Vaks, L.; Avrahami, L.; Plotkin, B.; Eisenstein, M.; Eldar-Finkelman, H. A unique type of GSK-3 inhibitor brings new opportunities to the clinic. Sci. Signal. 2016, 9, ra110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eldar-Finkelman, H.; VanHook, A.M. Science Signaling Podcast for 15 November 2016: A new type of kinase inhibitor. Sci. Signal. 2016, 9, c22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, A.; Varelas, X.; Guan, K.-L. Targeting the Hippo pathway in cancer, fibrosis, wound healing and regenerative medicine. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 19, 480–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanconato, F.; Cordenonsi, M.; Piccolo, S. YAP/TAZ at the Roots of Cancer. Cancer Cell 2016, 29, 783–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, S.; Saito, A.; Nagase, T. YAP/TAZ Signaling as a Molecular Link between Fibrosis and Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, V.J.; Ahmad, S.F.; Duncan, W.C.; Horne, A.W. The role of TGF-β in the pathophysiology of peritoneal endometriosis. Hum. Reprod. Update 2017, 23, 548–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, S.; Li, C.; Hao, Q.; Miao, H.; Zhang, L.; Li, L.; Zhou, Z. VGLL4 targets a TCF4-TEAD4 complex to coregulate Wnt and Hippo signalling in colorectal cancer. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Lin, F.; Wu, W.; Liu, Y.; Huang, W. Verteporfin inhibits YAP-induced bladder cancer cell growth and invasion via Hippo signaling pathway. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 15, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.-C.; Yang, Y.-J.; Zheng, J.-F.; Zhang, J.-Q.; Guo, M.; Yang, X.; Jiang, X.-L.; Xiang, L.; Li, Y.; Ping, H.; et al. Silencing of long noncoding RNA HOXA11-AS inhibits the Wnt signaling pathway via the upregulation of HOXA11 and thereby inhibits the proliferation, invasion, and self-renewal of hepatocellular carcinoma stem cells. Exp. Mol. Med. 2019, 51, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poncelet, C.; Leblanc, M.; Walker-Combrouze, F.; Soriano, D.; Feldmann, G.; Madelenat, P.; Scoazec, J.-Y.; Daraï, E. Expression of cadherins and CD44 isoforms in human endometrium and peritoneal endometriosis. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2002, 81, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graesslin, O.; Cortez, A.; Uzan, C.; Birembaut, P.; Quereux, C.; Daraï, E. Endometrial tumor invasiveness is related to metalloproteinase 2 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 2 expressions. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer Off. J. Int. Gynecol. Cancer Soc. 2006, 16, 1911–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.I.; Kim, J.J. Influence of AKT on progesterone action in endometrial diseases. Biol. Reprod. 2014, 91, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kacan, T.; Yildiz, C.; Baloglu Kacan, S.; Seker, M.; Ozer, H.; Cetin, A. Everolimus as an mTOR Inhibitor Suppresses Endometriotic Implants: An Experimental Rat Study. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 2017, 77, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Li, H.; Yuan, M.; Li, D.; Sun, C.; Wang, G. Serum Exosomal MicroRNAs as Potential Circulating Biomarkers for Endometriosis. Dis. Markers 2020, 2020, 2456340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.; Mutlu, L.; Grechukhina, O.; Taylor, H.S. Circulating microRNAs as potential biomarkers for endometriosis. Fertil. Steril. 2015, 103, 1252–1260.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.-T.; Zhao, Y.-N.; Han, B.-W.; Hong, S.-J.; Chen, Y.-Q. Circulating microRNAs identified in a genome-wide serum microRNA expression analysis as noninvasive biomarkers for endometriosis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisenblat, V.; Sharkey, D.J.; Wang, Z.; Evans, S.F.; Healey, M.; Ohlsson Teague, E.M.C.; Print, C.G.; Robertson, S.A.; Hull, M.L. Plasma miRNAs Display Limited Potential as Diagnostic Tools for Endometriosis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 104, 1999–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nothnick, W.B.; Falcone, T.; Joshi, N.; Fazleabas, A.T.; Graham, A. Serum miR-451a Levels Are Significantly Elevated in Women With Endometriosis and Recapitulated in Baboons (Papio anubis) With Experimentally-Induced Disease. Reprod. Sci. 2017, 24, 1195–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talbi, S.; Hamilton, A.E.; Vo, K.C.; Tulac, S.; Overgaard, M.T.; Dosiou, C.; Le Shay, N.; Nezhat, C.N.; Kempson, R.; Lessey, B.A.; et al. Molecular phenotyping of human endometrium distinguishes menstrual cycle phases and underlying biological processes in normo-ovulatory women. Endocrinology 2006, 147, 1097–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, L.C.; Germeyer, A.; Tulac, S.; Lobo, S.; Yang, J.P.; Taylor, R.N.; Osteen, K.; Lessey, B.A.; Giudice, L.C. Expression profiling of endometrium from women with endometriosis reveals candidate genes for disease-based implantation failure and infertility. Endocrinology 2003, 144, 2870–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Controls N (%) N = 47 | Endometriosis N (%) N = 153 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age:mean (SD) | 30.92 (13.79) | 31.17 (10.78) | 0.19 |
| BMI: mean (SD) | 24.84 (11.10) | 24.36 (8.38) | 0.53 |
| Tobacco use | 22 (14.4) | 0 (0) | <0.01 |
| rASRM classification - I–II - III–IV | - - | 80 (52) 73 (48) | - |
| Control diagnoses - No abnormality - Leiomyoma - Cystadenoma - Teratoma - Other gynecological disorders | 24 (51) 1 (2) 5 (11) 11 (23) 6 (13) | - | - |
| Dysmenorrhea | 47 (100) | 153 (100) | |
| Abdominal pain outside menstruation | 21 (44) | 89 (58.2) | 0.70 |
| Pain suggesting sciatica | 10 (21) | 70 (45.6) | 0.02 |
| Dyspareunia: mean (SD) | 4.95 (3.52) | 5.28 (3.95) | <0.01 |
| Lower back pain outside menstruation | 20 (42) | 101 (66.0) | 0.049 |
| Painful defecation: mean (SD) | 2.84 (2.76) | 4.35 (3.47) | <0.01 |
| Right shoulder pain near or during menstruation | 3 (9) | 26 (17.0) | 0.22 |
| Urinary pain during menstruation: mean (SD) | 2.84 (2.76) | 4.35(3.36) | <0.01 |
| Blood in the stools during menstruation | 4 (12) | 30 (19.6) | 0.24 |
| Blood in urine during menstruation | 8 (17) | 21 (13.7) | 0.42 |
| Mode of diagnostic | - | ||
| Surgery | 47 (100) | 83 (54.2) | - |
| Magnetic Resonance Imaging | - | 70 (45.8) | - |
| miRNAs | Up/Down Regulated | Benign Disorders | Malignant Disorders |
|---|---|---|---|
| miR-515-5p [36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54] | Up | Atherosclerosis | Hepato-cellular carcinoma, retinoblastoma, prostate cancer, Breast cancer, Lung cancer |
| miR-29b-1-5p [55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65] | Up | Helicobacter Pilori (Gastric cells), Spinal cord injury, | Breast cancer, Colon cancer, Oral squamous cell carcinoma, Bladder cancer |
| miR-548p [66,67,68,69] | - | - | Hepatitis B-mediated hepatocarcinoma |
| miR-548l [70,71,72] | - | Glaucoma | Hepatocellular carcinoma, Lung cancer |
| miR-3913-5p [73,74] | - | - | Lung cancer, Cholangiocarcinoma |
| miR-30e-3p [75,76,77,78,79,80,81] | - | - | Glioma, Hepatocellular carcinoma, ovarian cancer, colorectal cancer, clear cell renal cell carcinoma |
| miR-6813-5p [82] | - | - | Breast cancer |
| miR-3168 [83,84] | Down | Coronary atherosclerosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis | - |
| miR-548j-5p | - | Never reported | Never reported |
| miR-6502-5p | Up | Never reported | Never reported |
| miR-4748 | Up | Never reported | Never reported |
| miR-3137 | Down | Never reported | Never reported |
| mirRNAs | Ad/ Inv | Prolif | Apopt | Angio | Inf | EMR | Met/Mig | Immune Resp/escT | Neuro f | LTP | Ster/Horm | Therap sens | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-29b-1-5p [55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65] | - | X | X | X | X | X | - | - | - | - | - | - | EMT |
| miR-548p [66,67,68,69] | X | X | X | - | - | - | X | - | - | - | - | X | Decreases Hepatic Apolipoprotein B Secretion and Lipid Synthesis |
| miR-548l [70,71,72] | X | - | - | - | - | - | X | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| miR-3913-5p [73,74] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | X | - |
| miR-30e-3p [75,76,77,78,79,80,81] | - | X | X | - | X | - | - | - | X | - | - | - | Cardiomyocyte autophagy |
| miR-6813-5p [82] | - | - | X | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| miR-3168 [83,84] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| miR-548j-5p | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| miR-6502-5p | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| miR-4748 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| miR-3137 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dabi, Y.; Suisse, S.; Jornea, L.; Bouteiller, D.; Touboul, C.; Puchar, A.; Daraï, E.; Bendifallah, S. Clues for Improving the Pathophysiology Knowledge for Endometriosis Using Plasma Micro-RNA Expression. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 175. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12010175
Dabi Y, Suisse S, Jornea L, Bouteiller D, Touboul C, Puchar A, Daraï E, Bendifallah S. Clues for Improving the Pathophysiology Knowledge for Endometriosis Using Plasma Micro-RNA Expression. Diagnostics. 2022; 12(1):175. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12010175
Chicago/Turabian StyleDabi, Yohann, Stéphane Suisse, Ludmila Jornea, Delphine Bouteiller, Cyril Touboul, Anne Puchar, Emile Daraï, and Sofiane Bendifallah. 2022. "Clues for Improving the Pathophysiology Knowledge for Endometriosis Using Plasma Micro-RNA Expression" Diagnostics 12, no. 1: 175. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12010175
APA StyleDabi, Y., Suisse, S., Jornea, L., Bouteiller, D., Touboul, C., Puchar, A., Daraï, E., & Bendifallah, S. (2022). Clues for Improving the Pathophysiology Knowledge for Endometriosis Using Plasma Micro-RNA Expression. Diagnostics, 12(1), 175. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12010175






