Precision Medicine for Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Right Drug for the Right Patient—Companion Diagnostics
Abstract
1. Introduction
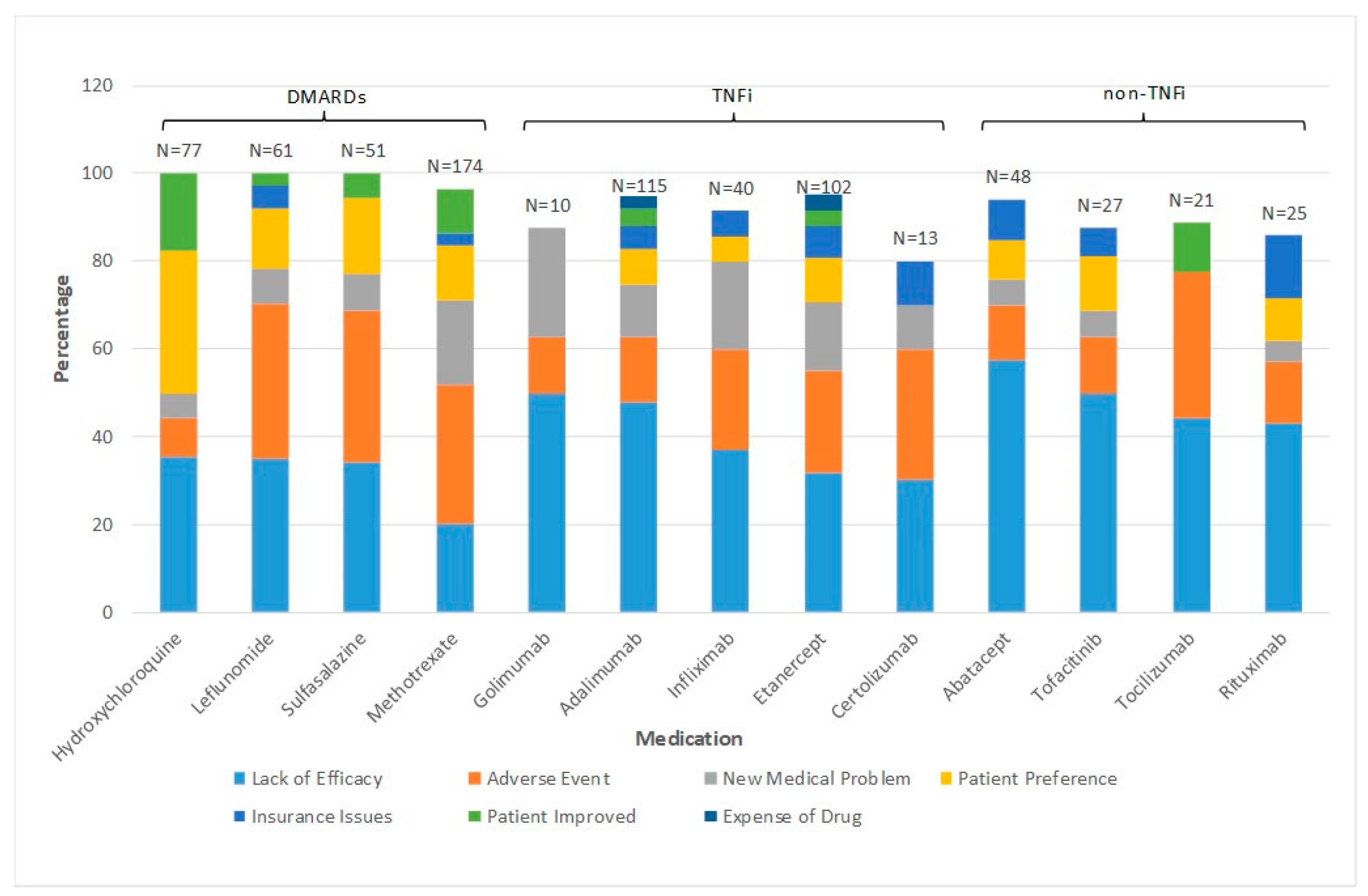
2. How Often and Why Do RA Patients Change bDMARD and Small Molecule Drugs?
3. Commonly Used Biomarkers in Rheumatology
4. Peripheral Blood as a Source of CDx Biomarkers
5. Autoantibody Profiling
6. Synovial Fluid as a Source of CDx Biomarkers
7. Synovial Tissue as a Source of CDx Biomarkers
8. Potential Additional Promising New Technologies for CDx
9. Additional Genetic Based Platforms
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smolen, J.S.; Aletaha, D.; McInnes, I.B. Rheumatoid Arthritis. Lancet 2016, 388, 2023–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, J.T. Companion diagnostics: The key to personalized medicine. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2015, 15, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, G.P. Endotyping asthma new insights into key pathogenic mechanisms in a complex, heterogeneous disease. Lancet 2008, 372, 1107–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadoun, S.; Zeboulin-Ktorza, N.; Combescure, C.; Elahi, M.; Rozenberg, S.; Gossec, L.; Fautrl, B. Mortality in rheumatoid arthritis over the last fifty years: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Jt. Bone Spine 2013, 80, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulman, K.A.; Richman, B.D. The Evolving Pharmaceutical Benefits Market. JAMA 2018, 319, 2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mewar, D.; Wilson, A.G. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with tumor necrosis factor inhibitors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 162, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, J.D.; Reed, G.; Decktor, D.; Harrold, L.; Furst, D.; Gibofsky, A.; DeHoratius, R.; Kishimoto, M.; Kremer, J.M. A comparative effectiveness study of adalimumab, etanercept and infliximab in biologically naive and switched rheumatoid arthritis patients: Results from the US CORRONA registry. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 71, 1134–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barton, A. Stratified medicine in rheumatoid arthritis-the MATURA programme. Rheumatology 2017, 56, 1247–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cope, A.; The RA-MAP Consortium; Barnes, M.; Belson, A.; Binks, M.; Brockbank, S.; Bonachela-Capdevila, F.; Carini, C.; Fisher, B.A.; Goodyear, C.S.; et al. The RA-MAP Consortium: A working model for academia–industry collaboration. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2017, 14, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, S. Biologic Agents. In Rheumatology Secrets, 4th ed.; Elsevier: Philidelphia PA, USA, 2019; Chapter 85; ISBN 978-0-323-64186-98. [Google Scholar]
- Aletaha, D.; Smolen, J. The Simplified Disease Activity Index (SDAI) and the Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI): A review of their usefulness and validity in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2005, 23, S100–S108. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Erickson, S.J. High-resolution imaging of the musculoskeletal system. Radiology 1997, 205, 593–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cyteval, C. Doppler Ultrasonography and Dynamic Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Assessment of Synovitis in the Hand and Wrist of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Semin. Musculoskelet. Radiol. 2009, 13, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.M. Editorial: The Multi-Biomarker Disease Activity Test for Rheumatoid Arthritis: Is It a Valid Measure of Disease Activity? Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 2061–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, C.; Hyrich, K.L.; Tracey, A.; Lunt, M.; Plant, D.; Symmons, D.; Thomson, W.; Worthington, J.; Emery, P.; Morgan, A.; et al. Association of rheumatoid factor and anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide positivity, but not carriage of shared epitope or PTPN22 susceptibility variants, with anti-tumour necrosis factor response in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2008, 68, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mini, E.; Nobili, S. Pharmacogenetics: Implementing personalized medicine. Clin. Cases Miner. Bone Metab. 2009, 6, 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Benucci, M.; Gobbi, F.L.; Meacci, F.; Manfredi, M.; Infantino, M.; Severino, M.; Atzeni, F.; Testi, S.; Sarzi-Puttini, P.; Ricci, C. Antidrug antibodies against TNF-blocking agents: Correlations between disease activity, hypersensitivity reactions, and different classes of immunoglobulins. Biol. Targets Ther. 2015, 9, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Garcês, S.; Demengeot, J.; Benito-Garcia, E. The immunogenicity of anti-TNF therapy in immune-mediated inflammatory diseases: A systematic review of the literature with a meta-analysis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 72, 1947–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hueber, W.; Tomooka, B.; Bartliwalla, F.; Wentian, L.; Monach, P.A.; Tibshirani, R.J.; Van Vollenhoven, R.F.; Lampa, J.; Saito, K.; Tanaka, Y.; et al. Blood autoantibody and cytokine profiles predict respnse to anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy in rehumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2009, 11, R76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaschke, S.; Rinke, K.; Maring, M.; Flad, T.; Patschan, S.; Jahn, O.; Mueller, C.A.; Mueller, G.A.; Dihazi, H. Haptoglobin-α1, -α2, vitamin D-binding protein and apolipoprotein C-III as predictors of etanercept drug response in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Mellors, T.; Whithers, J.A.; Ameli, A.; Jones, A.; Wang, M.; Zhang, L.; Sanchez, H.; Santolini, M.; Do Valle, I.; Sebek, M.; et al. Clinical validation of a blood based predictive test for stratification of response to anti-TNF therapies in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Netw. Syst. Med. 2020, 3, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber, K.; Nocturne, G.; Cornec, D.; Daïen, C.I. Lymphocytes as Biomarkers of Therapeutic Response in Rheumatic Autoimmune Diseases, Is It a Realistic Goal? Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2017, 53, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodenmiller, B.; Zunder, E.R.; Finck, R.; Chen, T.J.; Savig, E.S.; Bruggner, R.V.; Simonds, E.; Bendall, S.C.; Sachs, K.; Krutzik, P.O.; et al. Multiplexed mass cytometry profiling of cellular states perturbed by small-molecule regulators. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 858–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, N.; Mei, H.E.; Chen, S.-Y.; Hale, M.; Nolan, G.P.; Maecker, H.T.; Genovese, M.; Fathman, C.G.; Whiting, C.C. Mass cytometry as a platform for the discovery of cellular biomarkers to guide effective rheumatic disease therapy. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, K.A.; Kulik, L.; Tomooka, B.; Braschler, K.J.; Arend, W.P.; Robinson, W.H.; Holers, V.M. Antibodies against citrullinated proteins enhance tissue injury in experimental autoimmune arthritis. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 961–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolove, J.; Zhao, X.; Chandra, P.E.; Robinson, W.H. Immune complexes containing citrullinated fibrinogen costimulate macrophages via Toll-like receptor 4 and Fc gamma receptor. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uysal, H.; Bockermann, R.; Nandakumar, K.S.; Sehnert, B.; Bajtner, E.; Engström, Å.; Serre, G.; Burkhardt, H.; Thunnissen, M.M.; Holmdahl, R. Structure and pathogenicity of antibodies specific for citrullinated collagen type II in experimental arthritis. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harre, U.; Georgess, D.; Bang, H.; Bozec, A.; Axmann, R.; Ossipova, E.; Jakobsson, P.-J.; Baum, W.; Nimmerjahn, F.; Szarka, E.; et al. Induction of osteoclastogenesis and bone loss by human autoantibodies against citrullinated vimentin. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 1791–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brink, M.; Verheul, M.K.; Rönnelid, J.; Berglin, E.; Holmdahl, R.; Toes, R.E.; Klareskog, L.; Trouw, L.A.; Rantapää-Dahlqvist, S. Anti-carbamylated protein antibodies in the pre-symptomatic phase of rheumatoid arthritis, their relationship with multiple anti-citrulline peptide antibodies and association with radiological damage. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajeganova, S.; Van Steenbergen, H.; Verheul, M.K.; Forslind, K.; Hafstrom, I.; Toes, R.E.M.; Huizinga, T.W.J.; Svensson, B.; Trouw, L.A.; van der Helm-van Mil, A.H.M.; et al. The association between anti-carbamylated protein (anti-CarP) antibodies and radiographic progression in early rheumatoid arthritis: A study exploring replication and the added value to ACPA and rheumatoid factor. Ann. Rheum Dis. 2017, 76, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, M.H.; Petrone, D.; Nemeth, J.F.; Barnathan, E.; Björck, L.; Jordan, R.E. Proteolysis of purified IgGs by human and bacterial enzymes in vitro and the detection of specific proteolytic fragments of endogenous IgG in rheumatoid synovial fluid. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 1837–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van De Stadt, L.A.; De Vrieze, H.; Derksen, N.I.L.; Brouwer, M.; Wouters, D.; Van Schaardenburg, D.; Wolbink, G.J.; Rispens, T. Antibodies to IgG4 Hinge Can Be Found in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients During All Stages of Disease and May Exacerbate Chronic Antibody-Mediated Inflammation. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 1133–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juarez, M.; Bang, H.; Hammar, F.; Reimer, U.; Dyke, B.; Sahbudin, I.; Buckley, C.D.; Fisher, B.A.; Filer, A.; Raza, K. Identification of novel antiacetylated vimentin antibodies in patients with early inflammatory arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 75, 1099–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scher, J.U.; Abramson, S.B. The microbiome and rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2011, 7, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cretu, D.; Diamandis, E.P.; Chandran, V. Delineating the synovial fluid proteome: Recent advancements and ongoing challenges in biomarker research. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2013, 50, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.-J.; Chung, M.K.; Hwang, D.; Kim, W.-U. Proteomics in Rheumatoid Arthritis Research. Immune Netw. 2015, 15, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catterall, J.B.; Stabler, T.V.; Flannery, C.R.; Kraus, V.B. Changes in serum and synovial fluid biomarkers after acute injury (NCT00332254). Arthritis Res. Ther. 2010, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuellar, J.M.; Scuderi, G.J.; Cuellar, V.G.; Golish, S.R.; Yeomans, D.C. Diagnostic Utility of Cytokine Biomarkers in the Evaluation of Acute Knee Pain. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2009, 91, 2313–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osiri, M.; Wongpiyabovorn, J.; Sattayasomboon, Y.; Thammacharoenrach, N. Inflammatory cytokine levels, disease activity, and function of patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with combined conventional disease-modifying and rheumatic drugs or biologics. Clin. Rheumatol. 2016, 5, 1673–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, H.; Bucknall, R.C.; Moots, R.J.; Edwards, S.W. Analysis of SF and plasma cytokines provides insights into the mechanisms of inflammatory arthritis and may predict response to therapy. Rheumatology 2011, 51, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Wu, J.; Kuhn, E.; Chin, W.; Chang, B.; Jones, M.D.; O’Neil, S.; Clauser, K.R.; Karl, J.; Hasler, F.; et al. Use of mass spec-trometry to identify protein biomarkers of disease severity in the synovial fluid and serum of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 50, 3792–3803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekigawa, I.; Yanagida, M.; Iwabuchi, K.; Kaneda, K.; Kaneko, H.; Takasaki, Y.; Jung, G.; Sone, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Ogawa, H.; et al. Protein biomarker analysis by mass spectrometry in patients with rheumatoid arthritis receiving anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha antibody therapy. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2008, 26, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maricar, N.; Parkes, M.; Callaghan, M.; Felso, D.; O’Neill, T. Where and how to inject the knees a systemic review. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 43, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibbitt, W.; Peisajovich, A.; Michael, A.; Park, K.A.; Sibbitt, R.R.; Band, P.; Bankhurst, A.D. Does sonographic needle guidance affect the clinical outcome of intra-articular injections? J. Rheum. 2012, 36, 1892–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhavsar, T.B.; Sibbitt, W.L.; Band, P.A.; Cabacungan, R.J.; Moore, T.S.; Salayandia, L.C.; Fields, R.A.; Kettwich, S.K.; Roldan, L.P.; Emil, N.S.; et al. Improvement in diagnostic and therapeutic arthrocentesis via constant compression. Clin. Rheumatol. 2017, 37, 2251–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meehan, R.; Wilson, C.; Hoffman, E.; Altimier, L.; Kaessner, M.; Regan, E.A. Ultrasound measurement of knee synovial fluid during external pneumatic compression. J. Orthop. Res. 2019, 37, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klaasen, R.; Thurlings, R.; Wijbrandts, C.; van Kuijk, A.W.; Baeten, D.; Gerlag, D.; Tak, P. The relationship between synovial lym-phocyte aggregates and the clinical response to infliximab in rheumatoid arthritis: A prospective study. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavanaugh, A.; Rosengren, S.; Lee, S.J.; Hammaker, D.; Firestein, G.S.; Kalunian, K.; Wei, N.; Boyle, D.L. Assessment of Rituximab’s immunomodulatory synovial effects (ARISE trial). Clinical and synovial biomarker results. Ann. Rheum. 2008, 67, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wei, K.; Slowikowski, K.; Fonseka, C.Y.; Rao, D.A.; Kelly, S.; Goodman, S.M.; Tabechian, D.; Hughes, L.B.; Salo-mon-Escoto, K.; et al. Defining inflammatory cell states in rheumatoid arthritis joint synovial tissues by integrating single-cell transcriptomics and mass cytometry. Nat. Immunol. 2019, 20, 928–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, E.V.; Holweg, C.T.J.; Choy, D.; Kummerfeld, S.; Hackney, J.A.; Teng, Y.K.O.; Townsend, M.; Van Laar, J.M. Pretreatment synovial transcriptional profile is associated with early and late clinical response in rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with rituximab. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 71, 1888–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreas, K.; Häupl, T.; Lübke, C.; Ringe, J.; Morawietz, L.; Wachtel, A.; Sittinger, M.; Kaps, C. Antirheumatic drug response signatures in human chondrocytes: Potential molecular targets to stimulate cartilage regeneration. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2009, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, M.; Balakrishnan, L.; Renuse, S.; Advani, J.; Goel, R.; Sathe, G.; Prasad, T.S.K.; Nair, B.; Jois, R.; Shankar, S.; et al. Synovial fluid proteome in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Proteom. 2016, 13, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, J.; Charles-Schoeman, C.; Miao, Y.; Elashoff, D.; Lee, Y.Y.; Katselis, G.S.; Lee, T.D.; Reddy, S.T. Proteomic profiling following immunoaffinity capture of high-density lipoprotein: Association of acute-phase proteins and complement factors with proinflammatory high-density lipoprotein in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 1828–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, M.; Dotzlaw, H.; Mikkat, S.; Eggert, M.; Neeck, G. Proteomic Analysis of Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells: Selective Protein Processing Observed in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Proteome Res. 2007, 6, 3752–3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Tang, M.-S.; Xu, L.-C.; Li, S.; Ge, Y.; Du, J.-F.; Xie, X.; Tian, J.; Chen, J.-W.; Li, F. Proteomic analysis of biomarkers predicting the response to triple therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 116, 109026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, R.C.; Dhindsa, N.; Krokhin, O.V.; Cortens, J.; Wilkins, J.A.; El-Gabalawy, H.S. The effects of infliximab therapy on the serum proteome of rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2009, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.-J.; Kim, M.; Adamopoulos, I.E.; Tagkopoulos, I. Compendium of synovial signatures identifies pathologic characteristics for predicting treatment response in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Clin. Immunol. 2019, 202, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latini, A.; Borgiani, P.; Novelli, G.; Ciccacci, C. miRNAs in drug response variability: Potential utility as biomarkers for personalized medicine. Pharmacogenomics 2019, 20, 1049–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derambure, C.; Dzangue-Tchoupou, G.; Berard, C.; Vergne, N.; Hiron, M.; D’Agostino, M.A.; Musette, P.; Vittecoq, O.; Lequerre, T. Pre-silencing of genes involved in the electron transport chain (ECT) pathway is associated with responsiveness to abatacept in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthrits Res. Ther. 2017, 19, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canet, L.; Sanchez-Maldonado, J.; Caliz, R.; Rodriguez-Ramos, A.; Lupianez, C.B.; Canhao, H.; Martinez-Bueno, M.; Escudero, A.; Segura-Catema, J.; Sorensen, S.B.; et al. Polymorphisms at phase I-metabolizing enzyme and hormone receptor loci influence the response to anti-TNF therapy in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Pharm. J. 2019, 19, 83–96. [Google Scholar]
- Folkersen, L.; Brynedal, B.; Diaz-Gallo, L.; Ramskold, D.; Shchetynsky, K.; Westerlind, H.; Sundstrom, Y.; Schepis, D.; Hensvold, A.; Vivar, N.; et al. Integration of known DNA, RNA and protein biomarkers provides prediction of anti-TNF response in rheumatoid arthritis: Results from the COMBINE study. Mol. Med. 2016, 22, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, L.; Ahmed, S.; Jain, A.; Misra, R. Emerging role of metabolomics in rheumatology. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 21, 1468–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuppen, B.V.J.; Fu, J.; Van Wietmarschen, H.A.; Harms, A.C.; Koval, S.; Marijnissen, A.C.A.; Peeters, J.J.W.; Bijlsma, J.W.J.; Tekstra, J.; Van Laar, J.M.; et al. Exploring the Inflammatory Metabolomic Profile to Predict Response to TNF-α Inhibitors in Rheumatoid Arthritis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| TNFi | Mechanism | Auto-Immune Disease Indications |
|---|---|---|
| Etanercept | fusion protein-TNFr | RA, PsA, AS, JIA |
| Infliximab | Chimeric anti-TNF | RA, PsA, AS, Crohn’s, UC |
| Adalimumab | Anti-TNF mAB | RA, PsA, AS, JIA, UC |
| Certolizumab Pegol | pegylated anti-TNF | RA, PsA, AS, Crohn’s, UC |
| Golimumab | anti-TNF mAB | RA, PsA, AS |
| Anti-cytokines | ||
| Anakinra | IL 1 ra | RA, JIA |
| Canakinumab | anti-IL 1 mAB | Systemic JIA |
| Tocilizumab | anti-IL6 mAB | RA, GCA, JIA |
| Sarilumab | anti-IL 6 receptor | RA |
| Anti B Cell | ||
| Rituximab | chimeric anti-CD 20 | RA, GPA, MPA |
| T Cell Costimulation modulator | ||
| Abatacept | CTLA-4 fusion protein | RA, PsA, JIA |
| Small Molecule | ||
| Tofacitinib | JAK inhibitor | RA, PsA, UC, JIA |
| Baricitinib | JAK inhibitor | RA |
| Upadacitinib | JAK inhibitor | RA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meehan, R.T.; Amigues, I.A.; Knight, V. Precision Medicine for Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Right Drug for the Right Patient—Companion Diagnostics. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11081362
Meehan RT, Amigues IA, Knight V. Precision Medicine for Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Right Drug for the Right Patient—Companion Diagnostics. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(8):1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11081362
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeehan, Richard Thomas, Isabelle Anne Amigues, and Vijaya Knight. 2021. "Precision Medicine for Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Right Drug for the Right Patient—Companion Diagnostics" Diagnostics 11, no. 8: 1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11081362
APA StyleMeehan, R. T., Amigues, I. A., & Knight, V. (2021). Precision Medicine for Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Right Drug for the Right Patient—Companion Diagnostics. Diagnostics, 11(8), 1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11081362






