Automated Screening for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm in CT Scans under Clinical Conditions Using Deep Learning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
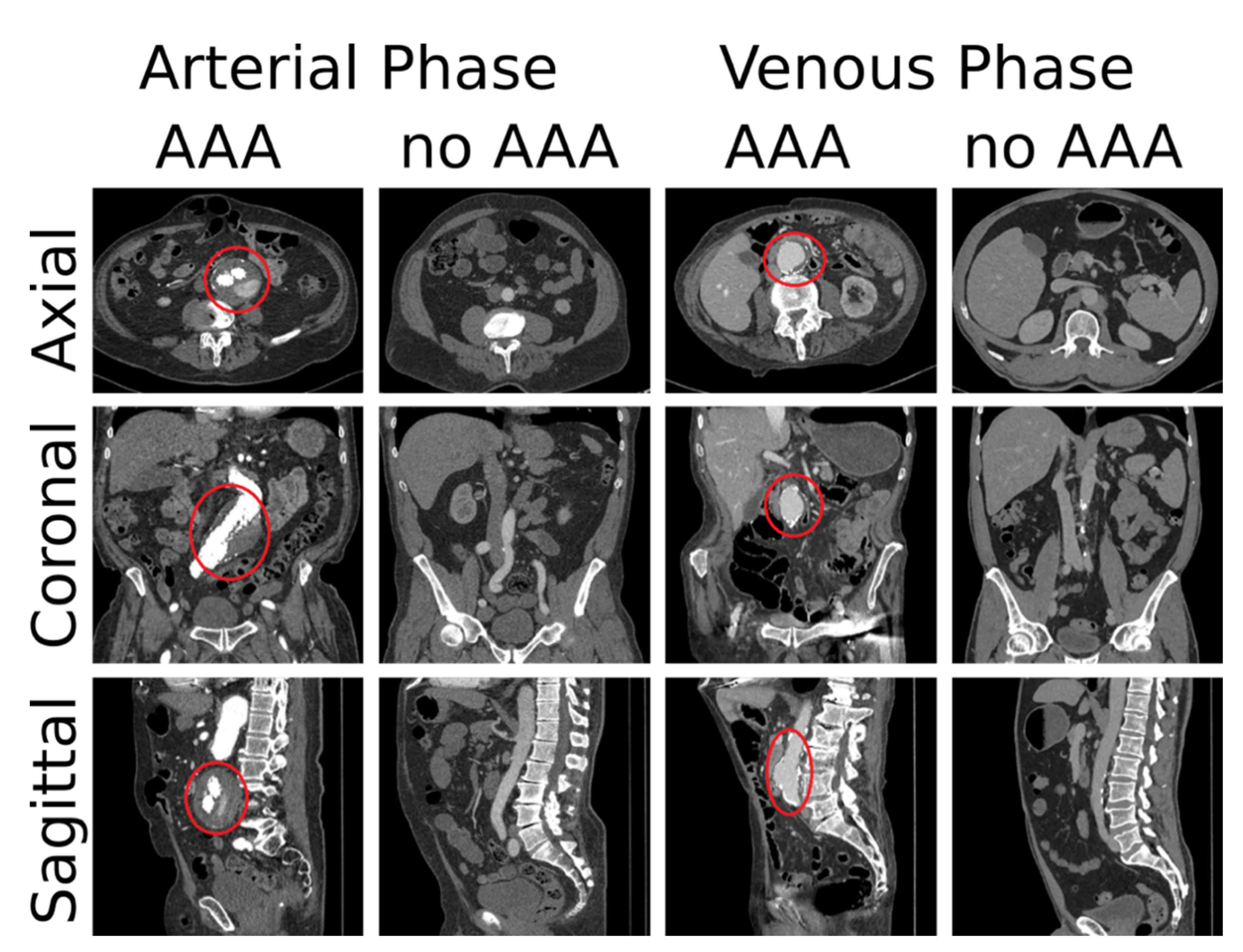
2.1. Patients and Data Sets
2.2. Networks, Preprocessing and Training
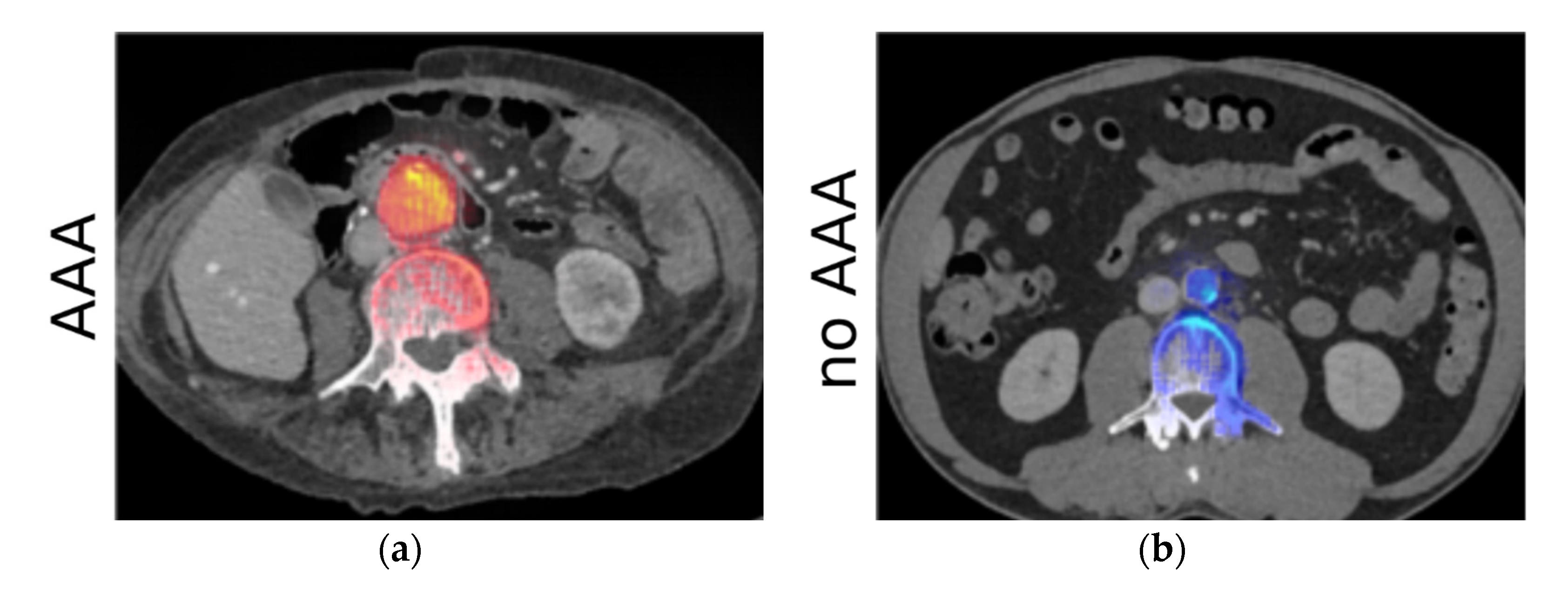
2.3. Layer-Wise Relevance Propagation
2.4. Fully Automatic Screening
2.5. Evaluation
3. Results
3.1. Results of the First Experiment (Network Comparison)
3.2. Results of the Second Experiment (LRP Maps)
3.3. Results of the Third Experiment (Repeated Training of the Best Network) and the Fourth Experiment (Verification on a Additional Dataset)
4. Discussion
4.1. Limitations
4.2. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations and Acronyms
| AAA | Abdominal aortic aneurysm |
| AUC | Area under the curve |
| CNN | Convolutional neural network |
| CT | Computed tomography |
| CTA | Computed tomography angiography |
| DT | Discrimination threshold |
| ECMO | Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation |
| EVAR | Endovascular aneurysm repair |
| LRP | Layer-wise relevance propagation |
| PACS | Picture archiving and communication system |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristic |
| ROI | Region of interest |
| RIS | Radiology information system |
Appendix A. Data Aggregation and Dataset
Appendix B. Networks

Appendix C. Implementation
References
- Nordon, M.; Hinchliffe, R.J.; Loftus, I.M.; Thompson, M.M. Pathophysiology and epidemiology of abdominal aortic aneurysms. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2011, 8, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaikof, E.L.; Dalman, R.L.; Eskandari, M.K.; Jackson, B.M.; Lee, W.A.; Mansour, M.A.; Mastracci, T.M.; Mell, M.; Murad, M.H.; Nguyen, L.L.; et al. The Society for Vascular Surgery practice guidelines on the care of patients with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. J. Vasc. Surg. 2018, 67, 2–77.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turton, E.; Scott, D.; Delbridge, M.; Snowden, S.; Kester, R. Ruptured Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm: A Novel Method of Outcome Prediction Using Neural Network Technology. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2000, 19, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmitz-Rixen, T.; Keese, M.; Hakimi, M.; Peters, A.; Böckler, D.; Nelson, K.; Grundmann, R.T. Ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm—epidemiology, predisposing factors, and biology. Langenbeck’s Arch. Surg. 2016, 401, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, A.S.; Hakimi, M.; Erhart, P.; Keese, M.; Schmitz-Rixen, T.; Wortmann, M.; Bischoff, M.S.; Böckler, D. Current treatment strategies for ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm. Langenbeck’s Arch. Surg. 2016, 401, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindholt, J.S.; Søgaard, R.; Laustsen, J. Prognosis of ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms in Denmark from 1994–2008. Clin. Epidemiol. 2012, 4, 111–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Claridge, R.; Arnold, S.; Morrison, N.; van Rij, A.M. Measuring abdominal aortic diameters in routine abdominal computed tomography scans and implications for abdominal aortic aneurysm screening. J. Vasc. Surg. 2017, 65, 1637–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oliver-Williams, C.; Sweeting, M.; Jacomelli, J.; Summers, L.; Stevenson, A.; Lees, T.; Earnshaw, J.J. Safety of Men With Small and Medium Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms Under Surveillance in the NAAASP. Circulation 2019, 139, 1371–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salata, K.; Hussain, M.A.; de Mestral, C.; Greco, E.; Aljabri, B.A.; Mamdani, M.; Forbes, T.L.; Bhatt, D.L.; Verma, S.; Al-Omran, M. Comparison of outcomes in elective endovascular aortic repair vs open surgical repair of abdominal aortic aneurysms. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lundervold, S.; Lundervold, A. An overview of deep learning in medical imaging focusing on mri. Z. Med. Phys. 2019, 29, 102–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, S.; Mohammadi, M.; Dehlaghi, V.; Ahmadi, A. Automatic segmentation, detection, and diagnosis of abdominal aortic aneurysm (aaa) using convolutional neural networks and hough circles algorithm. Cardiovasc. Eng. Technol. 2019, 10, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Linares, K.; Aranjuelo, N.; Kabongo, L.; Maclair, G.; Lete, N.; Ceresa, M.; García-Familiar, A.; Macía, I.; González Ballester, M.A. Fully automatic detection and segmentation of abdominal aortic thrombus in post-operative cta images using deep convolutional neural networks. Med. Image Anal. 2018, 46, 202–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Habijan, M.; Galić, I.; Leventić, H.; Romić, K.; Babin, D. Abdominal aortic aneurysm segmentation from ct images using modified 3d u-net with deep supervision. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2020 International Symposium ELMAR, Zadar, Croatia, 14–15 September 2020; pp. 123–128. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Jiang, Z.; Choi, J.; Lim, C.Y.; Maiti, T.; Baek, S. Patient-Specific Prediction of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Expansion Using Bayesian Calibration. IEEE J. Biomed. Heal. Inform. 2019, 23, 2537–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, H.N.; Ijaz, A.; Gharahi, H.; Zambrano, B.; Choi, J.; Lee, W.; Baek, S.; Choi, J. Prediction of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Growth Using Dynamical Gaussian Process Implicit Surface. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 66, 609–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, G.; Maiora, J.; Tapia, A.; De Blas, M. Evaluation of Texture for Classification of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm after Endovascular Repair. J. Digit. Imaging 2012, 25, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harris, R.J.; Kim, S.; Lohr, J.; Towey, S.; Velichkovich, Z.; Kabachenko, T.; Driscoll, I.; Baker, B. Classification of aortic dissection and rupture on post-contrast ct images using a convolutional neural network. J. Digit. Imaging 2019, 32, 939–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Shi, R.; Ge, Y.; Xing, L.; Zuo, P.; Jia, Y.; Liu, J.; He, Y.; Wang, X.; Luan, S.; et al. Fully automatic segmentation of type B aortic dissection from CTA images enabled by deep learning. Eur. J. Radiol. 2019, 121, 108713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, S.; Perry, M.; Wshah, S.; Morris, C.S.; Bertges, D.J. SS26. Machine Deep Learning Accurately Detects Endoleak After Endovascular Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair. J. Vasc. Surg. 2019, 69, e202–e203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, H.A.; Sheikh, U.U. Automatic detection, segmentation and classification of abdominal aortic aneurysm using deep learning. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 12th International Colloquium on Signal Processing & Its Applications (CSPA), Melaka, Malaysia, 4–6 March 2016; pp. 242–246. [Google Scholar]
- Maiora, J.; Graña, M. A Hybrid Segmentation of Abdominal CT Images. In Hybrid Artificial Intelligent Systems; Corchado, E., Snášel, V., Abraham, A., Woźniak, M., Graña, M., Cho, S.B., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 7209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, H.; Farag, A.; Turkbey, E.B.; Lu, L.; Liu, J.; Summers, R.M. Data From Pancreas-CT. In The Cancer Imaging Archive; The University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences: Little Rock, AR, USA, 2016; Available online: https://wiki.cancerimagingarchive.net/display/Public/Pancreas-CT#225140400c26eab54502412cbbd0e1c0fddd917b (accessed on 1 November 2021). [CrossRef]
- Soler, L.; Hostettler, A.; Agnus, V.; Charnoz, A.; Fasquel, J.B.; Moreau, J.; Osswald, A.B.; Bouhadjar, M.; Marescaux, J. 3D Image Reconstruction for Comparison of Algorithm Database: A Patient Specific Anatomical and Medical Image Database; Les Hôpitaux Universitaires: Strasbourg, France, 2010; Available online: https://www.ircad.fr/fr/recherche/3d-ircadb-01-fr/ (accessed on 21 October 2021).
- Kavur, E.; Selver, M.A.; Dicle, O.; Barış, M.; Gezer, N.S. CHAOS-Combined (CT-MR) Healthy Abdominal Organ Segmentation Challenge Data (Version v1.03) [Data Set]; Zenodo, European Organization for Nuclear Research and OpenAIRE: Genève, Switzerland, 2019; Available online: http://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3362844 (accessed on 21 October 2021).
- Landman, A.; Xu, Z.; Igelsias, J.E.; Styner, M.; Langerak, T.R.; Klein, A. MICCAI Multi-Atlas Labeling beyond the Cranial Vault-workshop and Challenge; Synapse, Sage Bionetworks: Seattle, WA, USA, 2015; Available online: https://doi.org/10.7303/syn3193805 (accessed on 21 October 2021).
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the NIPS 2012, Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 3–6 December 2012; Pereira, F., Burges, C.J.C., Bottou, L., Weinberger, K.Q., Eds.; Curran Associates Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 2012; Volume 25, pp. 1097–1105. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2015, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015; Bengio, Y., LeCun, Y., Eds.; International Conference on Representation Learning: La Jolla, CA, USA, 2015. Available online: https://dblp.org/db/conf/iclr/iclr2015.html (accessed on 21 October 2021).
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the CVPR 2016, Los Alamitos, CA, USA, June 2016; IEEE Computer Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Bach, S.; Binder, A.; Montavon, G.; Klauschen, F.; Müller, K.-R.; Samek, W. On pixel-wise explanations for non-linear classifier decisions by layer-wise relevance propagation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chlebus, G.; Abolmaali, N.; Schenk, A.; Meine, H. Relevance analysis of mri sequences for automatic liver tumor segmentation. In Proceedings of the MIDL 2019, London, UK, 8–10 July 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Schnurr, A.-K.; Schöben, M.; Hermann, I.; Schmidt, R.; Chlebus, G.; Schad, L.R.; Zöllner, F.G. Relevance analysis of mri sequences for ms lesion detection. In Proceedings of the 2020 ESMRMB Congress, Online; 2020; pp. 77–78. [Google Scholar]
- Hossin, M.; Sulaiman, M. A review on evaluation metrics for data classification evaluations. Int. J. Data Min. Knowl. Manag. Process. 2015, 5, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Likert, R. A technique for the measurement of attitudes. Arch. Psychol. 1932, 22, 55. [Google Scholar]
- Bains, P.; Oliffe, J.L.; Mackay, M.H.; Kelly, M.T. Screening older adult men for abdominal aortic aneurysm: A. scoping review. Am. J. Mens Health 2021, 15, 15579883211001204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweeting, M.; Marshall, J.; Glover, M.; Nasim, A.; Bown, M.J. Evaluating the cost-effectiveness of changes to the surveillance intervals in the uk abdominal aortic aneurysm screening programme. Value Health 2021, 24, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasaka, K.; Abe, O. Deep learning and artificial intelligence in radiology: Current applications and future directions. PLoS Med. 2018, 15, e1002707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saba, L.; Biswas, M.; Kuppili, V.; Cuadrado Godia, E.; Suri, H.S.; Edla, D.R.; Omerzu, T.; Laird, J.R.; Khanna, N.N.; Mavrogeni, S.; et al. The present and future of deep learning in radiology. Eur. J. Radiol. 2019, 114, 14–24. [Google Scholar]
- Ghesu, F.; Georgescu, B.; Zheng, Y.; Grbic, S.; Maier, A.; Hornegger, J.; Comaniciu, D. Multi-scale deep reinforcement learning for real-time 3dlandmark detection in ct scans. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2019, 41, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmuelling, L.; Franzeck, F.C.; Nickel, C.H.; Mansella, G.; Bingisser, R.; Schmidt, N.; Stieltjes, B.; Bremerich, J.; Sauter, A.W.; Weikert, T.; et al. Deep Learning-based Automated Detection of Pulmonary Embolism on CT Pulmonary Angiograms: No Significant Effects on Report Communication Times and Patient Turnaround in the Emergency Department Nine Months after Technical Implementation. Eur. J. Radiol. 2021, 141, 109816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffort, J.; Adam, C.; Carrier, M.; Ballaith, A.; Coscas, R.; Jean-Baptiste, E.; Hassen-Khodja, R.; Chakf´e, N.; Lareyre, F. Artificial intelligence in abdominal aortic aneurysm. J. Vasc. Surg. 2020, 72, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lareyre, F.; Adam, C.; Carrier, M.; Dommerc, C.; Mialhe, C.; Raffort, J. A fully automated pipeline for mining abdominal aortic aneurysm using image segmentation. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirata, K.; Nakaura, T.; Nakagawa, M.; Kidoh, M.; Oda, S.; Utsunomiya, D.; Yamashita, Y. Machine learning to predict the rapid growth of small abdominal aortic aneurysm. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2020, 44, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polat, H.; Danaei Mehr, H. Classification of pulmonary ct images by using hybrid 3d-deep convolutional neural network architecture. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, D.; Kumar, V.; Kaur, M. Classification of covid-19 patients from chest ct images using multi-objective differential evolution–based convolutional neural networks. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 39, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golla, K.; Bauer, D.F.; Schmidt, R.; Russ, T.; Nörenberg, D.; Chung, K.; Tönnes, C.; Schad, L.R.; Zöllner, F.G. Convolutional neural network ensemble segmentation with ratio-based sampling for the arteries and veins in abdominal ct scans. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 68, 1518–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioffe, S.; Szegedy, C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In Proceedings of the ICML 2015, Lille, France, 6–11 July 2015; pp. 448–456. [Google Scholar]
- Abadi, M.; Agarwal, A.; Barham, P.; Brevdo, E.; Chen, Z.; Citro, C.; Corrado, G.S.; Davis, A.; Dean, J.; Devin, M.; et al. TensorFlow: Large-Scale Machine Learning on Heterogeneous Systems. 2015. Available online: Tensorflow.Org (accessed on 21 October 2021).
- Lowekamp, B.C.; Chen, D.T.; Ibáñez, L.; Blezek, D. The design of simpleitk. Front. Neuroinform. 2013, 7, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alber, M.; Lapuschkin, S.; Seegerer, P.; Hägele, M.; Schütt, K.T.; Montavon, G.; Samek, W.; Müller, K.-R.; Dähne, S.; Kindermans, P.-J. Innvestigate neural networks! J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2019, 20, 1–8. [Google Scholar]



| Training Set | Verification Set | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TCIA | IRCAD | CHAOS | BTCV | Internal | ||
| Cases (total) | 187 | 23 | 9 | 8 | 10 | 56 |
| Cases in arterial phase | 85 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 31 |
| Cases in venous phase | 102 | 23 | 9 | 8 | 10 | 25 |
| Cases with AAA | 100 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 56 |
| Voxel resolution X/Y | 0.9 ± 0.1 mm | 0.8 ± 0.1 mm | 0.7 ± 0.1 mm | 0.7 ± 0.0 mm | 0.7 ± 0.1 mm | 0.8 ± 0.1 mm |
| Voxel resolution Z | 1.5 ± 0.5 mm | 1.0 ± 0.0 mm | 1.6 ± 0.8 mm | 1 ± 0.4 mm | 3 ± 0.6 mm | 1.5 ± 0.6 mm |
| Slices [min, max] | [101, 2687] | [187, 310] | [79, 260] | [95, 266] | [42, 148] | [101, 1323] |
| Network | A | P | TPR | F1 | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3D AlexNet | 0.769 | 0.773 | 0.810 | 0.791 | 0.899 |
| 3D VGG | 0.769 | 0.800 | 0.762 | 0.780 | 0.860 |
| 3D ResNet | 0.872 | 0.808 | 1.000 | 0.894 | 0.931 |
| Fold | A | P | TPR | F1 | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.872 | 0.808 | 1.000 | 0.894 | 0.931 |
| 2 | 0.821 | 0.850 | 0.810 | 0.829 | 0.929 |
| 3 | 0.838 | 0.850 | 0.850 | 0.850 | 0.919 |
| 4 | 0.944 | 0.947 | 0.947 | 0.947 | 0.961 |
| 5 | 0.806 | 0.773 | 0.895 | 0.829 | 0.885 |
| All | 0.856 | 0.841 | 0.900 | 0.870 | 0.926 |
| Fold | A | P | TPR | F1 | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All | 0.953 | 0.949 | 0.966 | 0.957 | 0.971 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Golla, A.-K.; Tönnes, C.; Russ, T.; Bauer, D.F.; Froelich, M.F.; Diehl, S.J.; Schoenberg, S.O.; Keese, M.; Schad, L.R.; Zöllner, F.G.; et al. Automated Screening for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm in CT Scans under Clinical Conditions Using Deep Learning. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 2131. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11112131
Golla A-K, Tönnes C, Russ T, Bauer DF, Froelich MF, Diehl SJ, Schoenberg SO, Keese M, Schad LR, Zöllner FG, et al. Automated Screening for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm in CT Scans under Clinical Conditions Using Deep Learning. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(11):2131. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11112131
Chicago/Turabian StyleGolla, Alena-K., Christian Tönnes, Tom Russ, Dominik F. Bauer, Matthias F. Froelich, Steffen J. Diehl, Stefan O. Schoenberg, Michael Keese, Lothar R. Schad, Frank G. Zöllner, and et al. 2021. "Automated Screening for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm in CT Scans under Clinical Conditions Using Deep Learning" Diagnostics 11, no. 11: 2131. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11112131
APA StyleGolla, A.-K., Tönnes, C., Russ, T., Bauer, D. F., Froelich, M. F., Diehl, S. J., Schoenberg, S. O., Keese, M., Schad, L. R., Zöllner, F. G., & Rink, J. S. (2021). Automated Screening for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm in CT Scans under Clinical Conditions Using Deep Learning. Diagnostics, 11(11), 2131. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11112131






