Quantification of Liver Fat Content after Radiofrequency Ablation for Liver Cancer: Correlation with Hepatic Perfusion Disorders
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical Data
2.2. Equipment and Methods
2.3. Image Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, X.; Luo, Y.; Peng, Y.L.; Cai, W.; Lu, Q.; Lin, L.; Sha, X.X.; Li, Y.Z.; Zhu, M. Hepatic perfusion disorder associated with focal liver lesions: Contrast-enhanced US patterns—Correlation study with contrast-enhanced CT. Radiology 2011, 260, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiroga, S.; Sebastia, C.; Pallisa, E.; Castellà, E.; Pérez-Lafuente, M.; Alvarez-Castells, A. Improved diagnosis of hepatic perfusion disorders: Value of hepatic arterial phase imaging during helical CT. Radiographics 2001, 21, 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gryspeerdt, S.; Van Hoe, L.; Marchal, G.; Baert, A.L. Evaluation of hepatic perfusion disorders with double-phase spiral CT. Radiographics 1997, 17, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rijzewijk, L.J.; van der Meer, R.W.; Lubberink, M.; Lamb, H.J.; Romijn, J.A.; de Roos, A.; Twisk, J.W.; Heine, R.J.; Lammertsma, A.A.; Smit, J.W.; et al. Liver fat content in type 2 diabetes: Relationship with hepatic perfusion and substrate metabolism. Diabetes 2010, 59, 2747–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, L.; Wu, P.H.; Lin, H.G.; Li, J.-Q.; Mo, Y.-X.; Zheng, L.; Lu, L.-X.; Ruan, C.-M.; Chen, L. Findings of non-pathologic perfusion defects by CT arterial portography and non-pathologic enhancement of CT hepatic arteriography. World J. Gastroenterol. 1998, 4, 513–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.H.; Yu, J.-S.; Chung, J.; Chung, J.-J.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, K.W. Transient hepatic attenuation difference (THAD) following transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for hepatic malignancy: Changes on serial CT examinations. Eur. Radiol. 2008, 18, 1596–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karcaaltincaba, M.; Akhan, O. Imaging of hepatic steatosis and fatty sparing. Eur. J. Radiol. 2007, 61, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dioguardi Burgio, M.; Bruno, O.; Agnello, F.; Torrisi, C.; Vernuccio, F.; Cabibbo, G.; Soresi, M.; Petta, S.; Calamia, M.; Papia, G.; et al. The cheating liver: Imaging of focal steatosis and fatty sparing. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 10, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, R.; Zhao, R.Z.; Zhang, J.; Yang, F.; Wen, H.-Q.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.-L. Quantification of fat deposition in the testis and epididymis using mDIXON Quant sequence: Correlation with age and ejaculation. Abdom. Radiol. 2018, 44, 1528–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Blake, G.M.; Li, K.; Liang, W.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, L.; Wang, L.; Brown, J.K.; Cheng, X.; et al. Liver Fat Content Measurement with Quantitative CT Validated against MRI Proton Density Fat Fraction: A Prospective Study of 400 Healthy Volunteers. Radiology 2020, 294, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, S.; Jiang, S.S.; Liu, S.S.; Dong, Q.; Xin, Y.; Xuan, S. Noninvasive Quantitative Detection Methods of Liver Fat Content in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2018, 6, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, J.; Liu, S.; Du, S.; Zhang, Q.; Xiao, J.; Dong, Q.; Xin, Y. Diagnostic value of MRI-PDFF for hepatic steatosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A meta-analysis. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 3564–3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stine, J.G.; Munaganuru, N.; Barnard, A.; Wang, J.L.; Kaulback, K.; Argo, C.K.; Singh, S.; Fowler, K.J.; Sirlin, C.B.; Loomba, R. Change in MRI-PDFF and Histologic Response in Patients With Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 19, 2274–2283.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Yan, L.; Cheng, Z.; Wu, H.; Du, L.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; Zeng, Y. A Randomized Trial Comparing Radiofrequency Ablation and Surgical Resection for HCC Conforming to the Milan Criteria. Ann. Surg. 2010, 252, 903–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kromrey, M.; Ittermann, T.; Berning, M.; Kolb, C.; Hoffmann, R.; Lerch, M.M.; Völzke, H.; Kühn, J.-P. Accuracy of ultrasonography in the assessment of liver fat compared with MRI. Clin. Radiol. 2019, 74, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Si, G.Y.; He, Q.Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, S.; Xian, R.; Zhang, J.; Yu, F.; Guan, J. Multislice Computed Tomographic Manifestation of Transient Hepatic Attenuation Difference in the Left Lobe of the Liver: A Retrospective Study. Adv. Ther. 2020, 37, 3954–3966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desser, T.S. Understanding Transient Hepatic Attenuation Differences. Semin. Ultrasound CT MRI 2009, 30, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, J.-L.; Zhang, J.-S. Hepatic perfusion disorders: Etiopathogenesis and related diseases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 3265–3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Li, Q.L.; Wen, H.Q.; Xie, W.-J.; Shen, L.-S.; Luo, X.-W.; Zhang, Y.-F.; Guo, R.-M. Quantification of penile fat infiltration using the mDIXON Quant sequence: A pilot study on the correlation with penis hardness and erectile dysfunction. Br. J. Radiol. 2021, 94, 20201400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köseoğlu, K.; Taskin, F.; Ozsunar, Y.; Cildağ, B.; Karaman, C. Transient hepatic attenuation differences at biphasic spiral CT examinations. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2005, 11, 96–101. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Q.Y.; Zou, Z.M.; Wang, Q.; He, C.; Zou, Q.; Wang, B. MRI manifestations of hepatic perfusion disorders. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 15, 5199–5204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brandt, A.H.; Ewertsen, C.; Hansen, K.L. The Impact of Transient Hepatic Attenuation Differences in the Diagnosis of Pseudoaneurysm and Arteriovenous Fistula on Follow-Up CT Scans after Blunt Liver Trauma. Diagnostics 2014, 4, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramanathan, S.; Raghu, V.; Virmani, V.; Sheikh, A.; Al Heidous, M.; Tirumani, S. Unveiling the unreal: Comprehensive imaging review of hepatic pseudolesions. Clin. Imaging 2021, 80, 439–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupescu, I.G.; Grasu, M.; Capsa, R.; Pitrop, A.; A Georgescu, S. Hepatic perfusion disorders: Computer-tomographic and magnetic resonance imaging. J. Gastrointest. Liver Dis. 2006, 15, 273–279. [Google Scholar]
- Pickhardt, P.J.; Graffy, P.M.; Reeder, S.B.; Hernando, D.; Li, K. Quantification of Liver Fat Content With Unenhanced MDCT: Phantom and Clinical Correlation With MRI Proton Density Fat Fraction. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2018, 211, W151–W157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


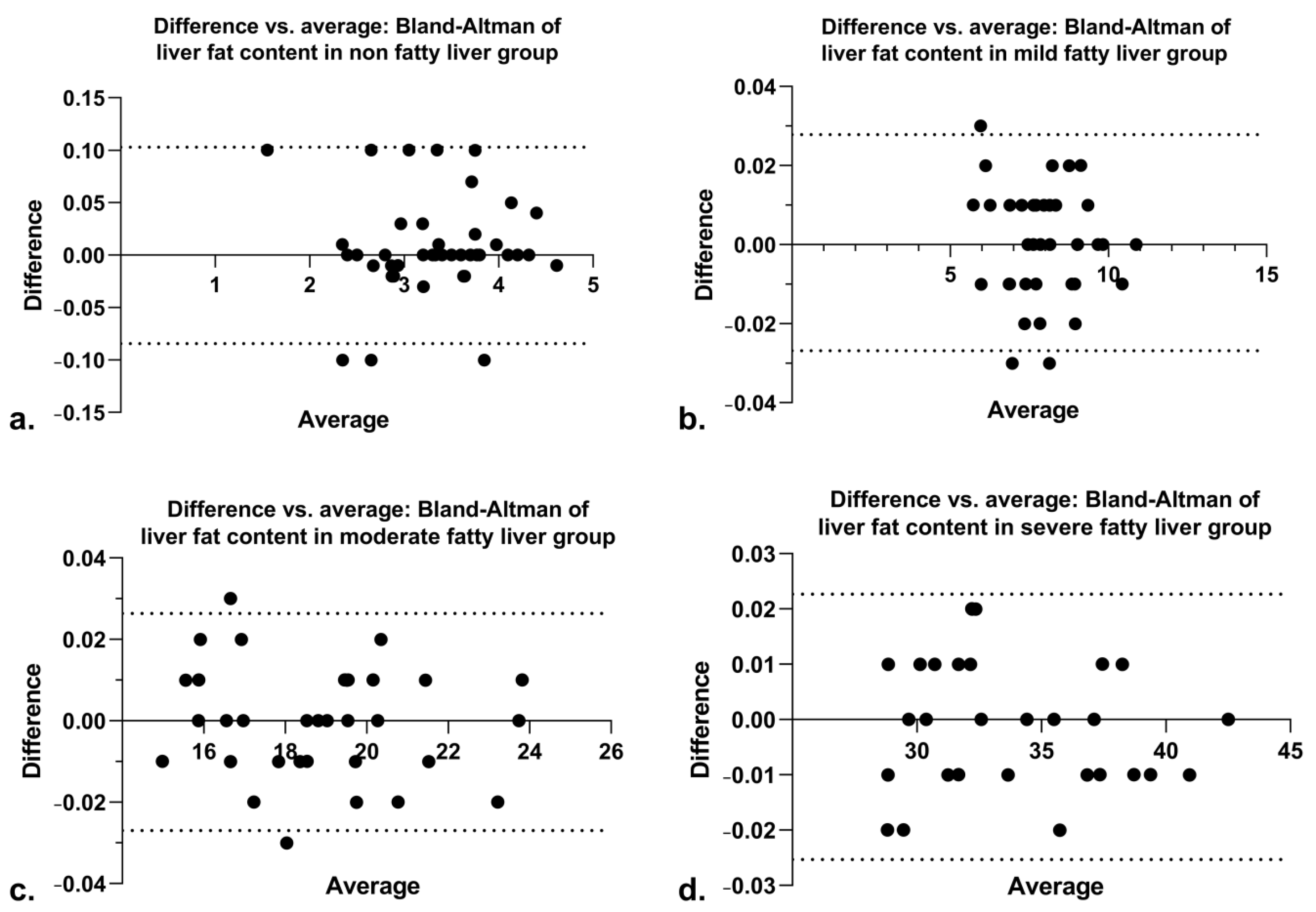
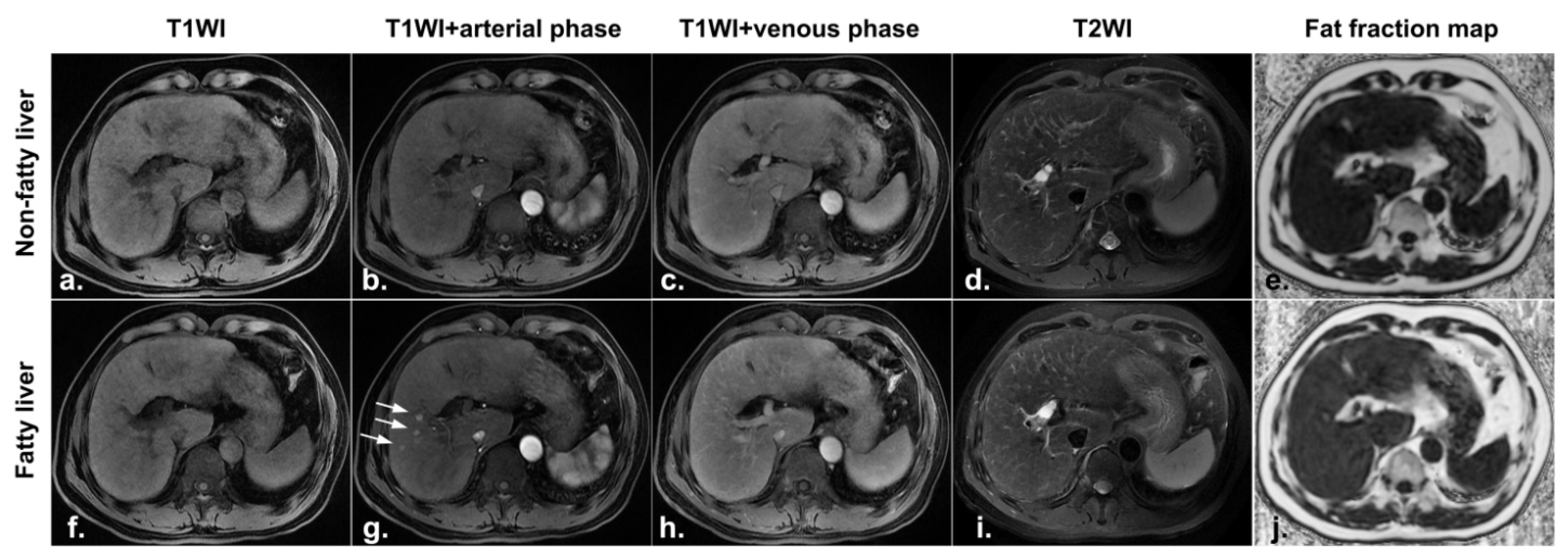

| Group | Number | Sex | Mean Age | Hepatitis Virus Infection | Number of Liver Cancer in Each Liver Segment | Alpha-Fetoprotein Levels (ng/mL) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | Female | HBV | HCB | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S7 | S8 | Preoperative | Postoperative | |||
| Nonfatty liver | 45 | 25 | 20 | 51.5 | 44 | 1 | 1 | 7 | 5 | 8 | 3 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 532.36–936.84 | 1.21–7.55 |
| Mild fatty liver | 40 | 20 | 20 | 51.0 | 40 | 0 | 1 | 6 | 5 | 6 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 594.05–914.95 | 1.17–7.32 |
| Moderate fatty liver | 35 | 25 | 10 | 50.5 | 34 | 1 | 0 | 5 | 4 | 6 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 7 | 483.38–969.37 | 1.67–7.19 |
| Severe fatty liver | 30 | 20 | 10 | 49.5 | 30 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 4 | 5 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 492.76–991.65 | 1.52–7.23 |
| Group | Hyperperfusion Abnormalities | Hypoperfusion Abnormalities | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | OR | 95% CI for OR | B | OR | 95% CI for OR | |
| Nonfatty | −0.211 | 0.810 | 0.187 to 3.799 | −1.115 | 0.328 | 0.043 to 2.039 |
| Mild fatty | 0.557 | 1.745 | 0.975 to 3.447 | −0.432 | 0.649 | 0.199 to 1.741 |
| Moderate fatty | 0.369 | 1.446 | 1.046 to 2.153 | −0.226 | 0.798 | 0.337 to 1.518 |
| Severe fatty | 0.228 | 1.256 | 1.017 to 1.635 | −0.052 | 0.949 | 0.571 to 1.371 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, L.-S.; Li, Q.-X.; Luo, X.-W.; Tang, H.-J.; Tang, Y.-J.; Tang, W.-J.; Guo, R.-M. Quantification of Liver Fat Content after Radiofrequency Ablation for Liver Cancer: Correlation with Hepatic Perfusion Disorders. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 2137. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11112137
Shen L-S, Li Q-X, Luo X-W, Tang H-J, Tang Y-J, Tang W-J, Guo R-M. Quantification of Liver Fat Content after Radiofrequency Ablation for Liver Cancer: Correlation with Hepatic Perfusion Disorders. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(11):2137. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11112137
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Li-Shan, Quan-Xi Li, Xiao-Wen Luo, Hui-Jun Tang, You-Jie Tang, Wen-Jie Tang, and Ruo-Mi Guo. 2021. "Quantification of Liver Fat Content after Radiofrequency Ablation for Liver Cancer: Correlation with Hepatic Perfusion Disorders" Diagnostics 11, no. 11: 2137. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11112137
APA StyleShen, L.-S., Li, Q.-X., Luo, X.-W., Tang, H.-J., Tang, Y.-J., Tang, W.-J., & Guo, R.-M. (2021). Quantification of Liver Fat Content after Radiofrequency Ablation for Liver Cancer: Correlation with Hepatic Perfusion Disorders. Diagnostics, 11(11), 2137. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11112137






