White Matter Microstructural Differences between Hallucinating and Non-Hallucinating Schizophrenia Spectrum Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Image Acquisition
2.3. Image Processing
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Group Comparison of the Original FA-Skeletons
3.2. Hemispheric Asymmetry Comparisons
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 4D | Four Dimensional |
| ANOVA | Analysis of Variance |
| AVH | Auditory Verbal Hallucinations |
| BET | Brain Extraction Tool |
| DDD | Defined Daily Dose |
| DMN | Default Mode Network |
| DTI | Diffusion Tensor Imaging |
| ERC | European Research Council |
| FA | Fractional Anisotropy |
| FMRIB | Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Brain |
| FSL | FMRIB Software Library |
| FWE | Familywise Error |
| GE | General Electrics |
| HD | High-definition |
| ICD | International Classification of Diseases |
| P3 | Positive three |
| PANSS | Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| TBSS | Tract Based Special Statistics |
| TE | Echo Time |
| TFCE | Threshold Free Cluster Enhancement |
| TR | Repetition Time |
References
- Chaudhury, S. Hallucinations: Clinical aspects and management. Ind. Psychiatry J. 2010, 19, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knapp, M.; Mangalore, R.; Simon, J. The Global Costs of Schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 2004, 30, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toh, W.L.; Thomas, N.; Hollander, Y.; Rossell, S.L. On the phenomenology of auditory verbal hallucinations in affective and non-affective psychosis. Psychiatry Res. 2020, 290, 113147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larøi, F.; Thomas, N.; Aleman, A.; Fernyhough, C.; Wilkinson, S.; Deamer, F.; McCarthy-Jones, S. The ice in voices: Understanding negative content in auditory-verbal hallucinations. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2019, 67, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, S.M.; Schanda, H.; Karakula, H.; Olajossy-Hilkesberger, L.; Rudaleviciene, P.; Okribelashvili, N.; Chaudhry, H.R.; Idemudia, S.E.; Gscheider, S.; Ritter, K.; et al. Culture and the prevalence of hallucinations in schizophrenia. Compr. Psychiatry 2011, 52, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ćurčić-Blake, B.; Ford, J.M.; Hubl, D.; Orlov, N.D.; Sommer, I.E.; Waters, F.; Allen, P.; Jardri, R.; Woodruff, P.W.; David, O.; et al. Interaction of language, auditory and memory brain networks in auditory verbal hallucinations. Prog. Neurobiol. 2017, 148, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugdahl, K.; Løberg, E.-M.; Nygård, M. Left temporal lobe structural and functional abnormality underlying auditory hallucinations. Front. Neurosci. 2009, 3, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, S.; Johnsen, E.; Kroken, R.A.; Løberg, E.-M.; Kandilarova, S.; Stoyanov, D.; Kompus, K.; Hugdahl, K. Dynamic Functional Connectivity Patterns in Schizophrenia and the Relationship with Hallucinations. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrity, A.; Pearlson, G.D.; McKiernan, K.; Lloyd, D.; Kiehl, K.; Calhoun, V. Aberrant “Default Mode” Functional Connectivity in Schizophrenia. Am. J. Psychiatry 2007, 164, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambataro, F.; Blasi, G.; Fazio, L.; Caforio, G.; Taurisano, P.; Romano, R.; Di Giorgio, A.; Gelao, B.; Bianco, L.L.; Papazacharias, A.; et al. Treatment with Olanzapine is Associated with Modulation of the Default Mode Network in Patients with Schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology 2009, 35, 904–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Weijer, A.D.; Mandl, R.; Diederen, K.; Neggers, S.; Kahn, R.S.; Pol, H.H.; Sommer, I. Microstructural alterations of the arcuate fasciculus in schizophrenia patients with frequent auditory verbal hallucinations. Schizophr. Res. 2011, 130, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellison-Wright, I.; Bullmore, E. Meta-analysis of diffusion tensor imaging studies in schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2009, 108, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, S.; Jahanshad, N.; Zalesky, A.; Kochunov, P.; Agartz, I.; Alloza, C.; Andreassen, O.A.; Arango, C.; Banaj, N.; Bouix, S.; et al. Widespread white matter microstructural differences in schizophrenia across 4322 individuals: Results from the ENIGMA Schizophrenia DTI Working Group. Mol. Psychiatry 2018, 23, 1261–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubicki, M.; McCarley, R.; Westin, C.-F.; Park, H.-J.; Maier, S.; Kikinis, R.; Jolesz, F.A.; Shenton, M.E. A review of diffusion tensor imaging studies in schizophrenia. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2007, 41, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leroux, E.; Delcroix, N.; Dollfus, S. Abnormalities of language pathways in schizophrenia patients with and without a lifetime history of auditory verbal hallucinations: A DTI-based tractography study. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2017, 18, 528–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oestreich, L.K.; Australian Schizophrenia Research Bank; McCarthy-Jones, S.; Whitford, T.J. Decreased integrity of the fronto-temporal fibers of the left inferior occipito-frontal fasciculus associated with auditory verbal hallucinations in schizophrenia. Brain Imaging Behav. 2016, 10, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seok, J.-H.; Park, H.-J.; Chun, J.-W.; Lee, S.-K.; Cho, H.S.; Kwon, J.S.; Kim, J.-J. White matter abnormalities associated with auditory hallucinations in schizophrenia: A combined study of voxel-based analyses of diffusion tensor imaging and structural magnetic resonance imaging. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2007, 156, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ćurčić-Blake, B.; Nanetti, L.; Van Der Meer, L.; Cerliani, L.; Renken, R.; Pijnenborg, G.H.M.; Aleman, A. Not on speaking terms: Hallucinations and structural network disconnectivity in schizophrenia. Brain Struct. Funct. 2013, 220, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shergill, S.S. A diffusion tensor imaging study of fasciculi in schizophrenia. Am. J. Psychiatry 2007, 164, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühn, S.; Gallinat, J. Quantitative Meta-Analysis on State and Trait Aspects of Auditory Verbal Hallucinations in Schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 2010, 38, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugdahl, K.; Sommer, I.E. Auditory Verbal Hallucinations in Schizophrenia from a Levels of Explanation Perspective. Schizophr. Bull. 2018, 44, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Psomiades, M.; Fonteneau, C.; Mondino, M.; Luck, D.; Haesebaert, F.; Suaud-Chagny, M.-F.; Brunelin, J. Integrity of the arcuate fasciculus in patients with schizophrenia with auditory verbal hallucinations: A DTI-tractography study. NeuroImage Clin. 2016, 12, 970–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Case, M.; Stauffer, V.L.; Ascher-Svanum, H.; Conley, R.; Kapur, S.; Kane, J.M.; Kollack-Walker, S.; Jacob, J.; Kinon, B.J. The heterogeneity of antipsychotic response in the treatment of schizophrenia. Psychol. Med. 2010, 41, 1291–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, S.Z.; Rabinowitz, J.; Faries, D.; Lawson, A.H.; Ascher-Svanum, H. Treatment response trajectories and antipsychotic medications: Examination of up to 18months of treatment in the CATIE chronic schizophrenia trial. Schizophr. Res. 2012, 137, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kay, S.R.; Fiszbein, A.; Opler, L.A. The Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) for Schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 1987, 13, 261–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirnstein, M.; Hugdahl, K. Excess of non-right-handedness in schizophrenia: Meta-analysis of gender effects and potential biases in handedness assessment. Br. J. Psychiatry 2014, 205, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilder, R.M.; Wu, H.; Bogerts, B.; Degreef, G.; Ashtari, M.; Alvir, J.M.; Snyder, P.J.; Lieberman, J.A. Absence of regional hemispheric volume asymmetries in first-episode schizophrenia. Am. J. Psychiatry 1994, 151, 1437–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkai, P. Loss of sylvian fissure asymmetry in schizophrenia: A quantitative post mortem study. Schizophr. Res. 1992, 7, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takao, H.; Abe, O.; Yamasue, H.; Aoki, S.; Kasai, K.; Ohtomo, K. Cerebral asymmetry in patients with schizophrenia: A voxel-based morphometry (VBM) and diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) study. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2009, 31, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dollfus, S.; Razafimandimby, A.; Delamillieure, P.; Brazo, P.; Joliot, M.; Mazoyer, B.; Tzourio-Mazoyer, N. Atypical hemispheric specialization for language in right-handed schizophrenia patients. Biol. Psychiatry 2005, 57, 1020–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oertel-Knöchel, V.; Linden, D.E.J. Cerebral Asymmetry in Schizophrenia. Neuroscience 2011, 17, 456–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy-Jones, S.; Oestreich, L.K.; Whitford, T. Reduced integrity of the left arcuate fasciculus is specifically associated with auditory verbal hallucinations in schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2015, 162, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falkenberga, L.E.; Westerhausen, R.; Johnsen, E.; Kroken, R.; Løberg, E.-M.; Beresniewicz, J.; Kazimierczak, K.; Kompus, K.; Ersland, L.; Sandøy, L.B.; et al. Hallucinating schizophrenia patients have longer left arcuate fasciculus fiber tracks: A DTI tractography study. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2020, 302, 111088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy-Jones, S.; Smailes, D.; Corvin, A.; Gill, M.; Morris, D.W.; Dinan, T.G.; Murphy, K.C.; O’neill, F.A.; Waddington, J.L.; null Australian Schizophrenia Research Bank; et al. Occurrence and co-occurrence of hallucinations by modality in schizophrenia-spectrum disorders. Psychiatry Res. 2017, 252, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayani, T.H.; David, A.S. The auditory hallucination: A phenomenological survey. Psychol. Med. 1996, 26, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinn, A.K.; Pfaff, D.; Young, S.; Lewandowski, K.E.; Cohen, B.M.; Öngür, D. Auditory hallucinations in a cross-diagnostic sample of psychotic disorder patients: A descriptive, cross-sectional study. Compr. Psychiatry 2012, 53, 718–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.M. Fast robust automated brain extraction. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2002, 17, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.M.; Jenkinson, M.; Woolrich, M.W.; Beckmann, C.F.; Behrens, T.E.; Johansen-Berg, H.; Bannister, P.R.; De Luca, M.; Drobnjak, I.; Flitney, D.E.; et al. Advances in functional and structural MR image analysis and implementation as FSL. NeuroImage 2004, 23, S208–S219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.M.; Jenkinson, M.; Johansen-Berg, H.; Rueckert, D.; Nichols, T.E.; Mackay, C.E.; Watkins, K.E.; Ciccarelli, O.; Cader, M.Z.; Matthews, P.M.; et al. Tract-based spatial statistics: Voxelwise analysis of multi-subject diffusion data. NeuroImage 2006, 31, 1487–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkinson, M. TBSS User Guide. 2013. Available online: https://fsl.fmrib.ox.ac.uk/fsl/fslwiki/TBSS/UserGuide#Testing_left_vs._right_in_TBSS (accessed on 1 January 2019).
- Winkler, A.M.; Ridgway, G.R.; Webster, M.A.; Smith, S.M.; Nichols, T.E. Permutation inference for the general linear model. NeuroImage 2014, 92, 381–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, T.E.; Holmes, A.P. Nonparametric permutation tests for functional neuroimaging: A primer with examples. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2002, 15, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.M.; Nichols, T.E. Threshold-free cluster enhancement: Addressing problems of smoothing, threshold dependence and localisation in cluster inference. NeuroImage 2009, 44, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bopp, M.; Zöllner, R.; Jansen, A.; Dietsche, B.; Krug, A.; Kircher, T. White matter integrity and symptom dimensions of schizophrenia: A diffusion tensor imaging study. Schizophr. Res. 2017, 184, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Gao, J.; Zhu, F.; Wang, W.; Fan, Y.; Ma, Q.; Ma, X.; Yang, J. Reduced white matter connectivity associated with auditory verbal hallucinations in first-episode and chronic schizophrenia: A diffusion tensor imaging study. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2018, 273, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffau, H.; Gatignol, P.; Mandonnet, E.; Peruzzi, P.; Tzourio-Mazoyer, N.; Capelle, L. New insights into the anatomo-functional connectivity of the semantic system: A study using cortico-subcortical electrostimulations. Brain 2005, 128, 797–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friederici, A.D. Allocating functions to fiber tracts: Facing its indirectness. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2009, 13, 370–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasser, M.F.; Rilling, J.K. DTI Tractography of the Human Brain’s Language Pathways. Cereb. Cortex 2008, 18, 2471–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rilling, J.K.; Glasser, M.F.; Preuss, T.M.; Ma, X.; Zhao, T.; Hu, X.; Behrens, T.E.J. The evolution of the arcuate fasciculus revealed with comparative DTI. Nat. Neurosci. 2008, 11, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geschwind, N. The Organization of Language and the Brain: Language disorders after brain damage help in elucidating the neural basis of verbal behavior. Science 1970, 170, 940–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagmann, P.; Cammoun, L.; Martuzzi, R.; Maeder, P.; Clarke, S.; Thiran, J.-P.; Meuli, R.A. Hand preference and sex shape the architecture of language networks. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2006, 27, 828–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubb, E.J.; Metzler-Baddeley, C.; Aggleton, J.P. The cingulum bundle: Anatomy, function, and dysfunction. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2018, 92, 104–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panksepp, J. Affective Neuroscience: The Foundations of Human and Animal Emotions; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Panksepp, J. Affective consciousness: Core emotional feelings in animals and humans. Conscious. Cogn. 2005, 14, 30–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Peräkylä, J.; Polvivaara, M.; Öhman, J.; Peltola, J.; Lehtimäki, K.; Huhtala, H.; Hartikainen, K.M. Human anterior thalamic nuclei are involved in emotion–attention interaction. Neuropsychology 2015, 78, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyata, J.; Sasamoto, A.; Koelkebeck, K.; Hirao, K.; Ueda, K.; Kawada, R.; Fujimoto, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Kubota, M.; Fukuyama, H.; et al. Abnormal asymmetry of white matter integrity in schizophrenia revealed by voxelwise diffusion tensor imaging. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2011, 33, 1741–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jäncke, L.; Wustenberg, T.; Schulze, K.; Heinze, H.J. Asymmetric hemodynamic responses of the human auditory cortex to monaural and binaural stimulation. Heart Res. 2002, 170, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugdahl, K.; Heiervang, E.; Ersland, L.; Lundervold, A.; Steinmetz, H.; Smievoll, A.I. Significant relation between MR measures of planum temporale area and dichotic processing of syllables in dyslexic children. Neuropsychology 2003, 41, 666–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribolsi, M.; Daskalakis, Z.J.; Siracusano, A.; Koch, G. Abnormal Asymmetry of Brain Connectivity in Schizophrenia. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamali, A.; Flanders, A.E.; Brody, J.; Hunter, J.V.; Hasan, K.M. Tracing superior longitudinal fasciculus connectivity in the human brain using high resolution diffusion tensor tractography. Brain Struct. Funct. 2014, 219, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Rahman, M.F.; Qiu, A.; Woon, P.S.; Kuswanto, C.; Collinson, S.L.; Sim, K. Arcuate Fasciculus Abnormalities and Their Relationship with Psychotic Symptoms in Schizophrenia. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catani, M.; Craig, M.C.; Forkel, S.J.; Kanaan, R.; Picchioni, M.; Toulopoulou, T.; Shergill, S.; Williams, S.; Murphy, D.G.; McGuire, P. Altered Integrity of Perisylvian Language Pathways in Schizophrenia: Relationship to Auditory Hallucinations. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 70, 1143–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugdahl, K.; Løberg, E.-M.; Falkenberg, L.E.; Johnsen, E.; Kompus, K.; Kroken, R.A.; Nygård, M.; Westerhausen, R.; Alptekin, K.; Özgören, M. Auditory verbal hallucinations in schizophrenia as aberrant lateralized speech perception: Evidence from dichotic listening. Schizophr. Res. 2012, 140, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, L.J.; Pasternak, O. Does diffusion MRI tell us anything about the white matter? An overview of methods and pitfalls. Schizophr. Res. 2015, 161, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, S.; Zhang, J. Principles of Diffusion Tensor Imaging and Its Applications to Basic Neuroscience Research. Neuron 2006, 51, 527–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tønnesen, S.; Kaufmann, T.; De Lange, A.-M.G.; Richard, G.; Doan, N.T.; Alnæs, D.; Van Der Meer, D.; Rokicki, J.; Moberget, T.; Maximov, I.I.; et al. Brain Age Prediction Reveals Aberrant Brain White Matter in Schizophrenia and Bipolar Disorder: A Multisample Diffusion Tensor Imaging Study. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2020, 5, 1095–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoyanov, D. A linkage of mind and brain: Towards translational validity between neurobiology and psychiatry. Biomed. Rev. 2014, 22, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]

| AVH+ | AVH- | Cntrl | p (Value) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample size (female/male) | 44 (12/32) | 13 (2/11) | 57 (15/42) | 0.72 Fisher’s Exact test |
| Age (mean ± SD) a | 30.1 ± 11.4 | 29.5 ± 9.3 | 30.7 ± 9.9 | 0.92 ANOVA |
| Handedness (A/L/R) b | 2/4/38 | 1/1/11 | 0/6/51 | 0.35 Fisher’s Exact test |
| Scanning after/before the upgrade | 21/23 | 5/8 | 25/32 | 0.86 Fisher’s Exact test |
| Duration of illness | 3.6 ± 4.7 | 2.2 ± 4.4 | - | 0.40 Welch Two Sample t-test |
| Defined Daily Dose (DDD) | 1.02 ± 0.63 | 0.91 ± 0.41 | - | 0.51 Welch Two Sample t-test |
| Smoking/non-smoking | 28/16 | 10/3 | - | 0.51 Fisher’s Exact test |
| Baseline PANSS c positive | 3.0 ± 0.7 | 2.6 ± 0.7 | - | 0.04 Welch Two Sample t-test |
| Baseline PANSS negative | 2.4 ± 0.8 | 2.0 ± 0.7 | - | 0.99 Welch Two Sample t-test |
| Baseline PANSS total | 2.7± 0.6 | 2.3 ± 0.6 | - | 0.03 Welch Two Sample t-test |
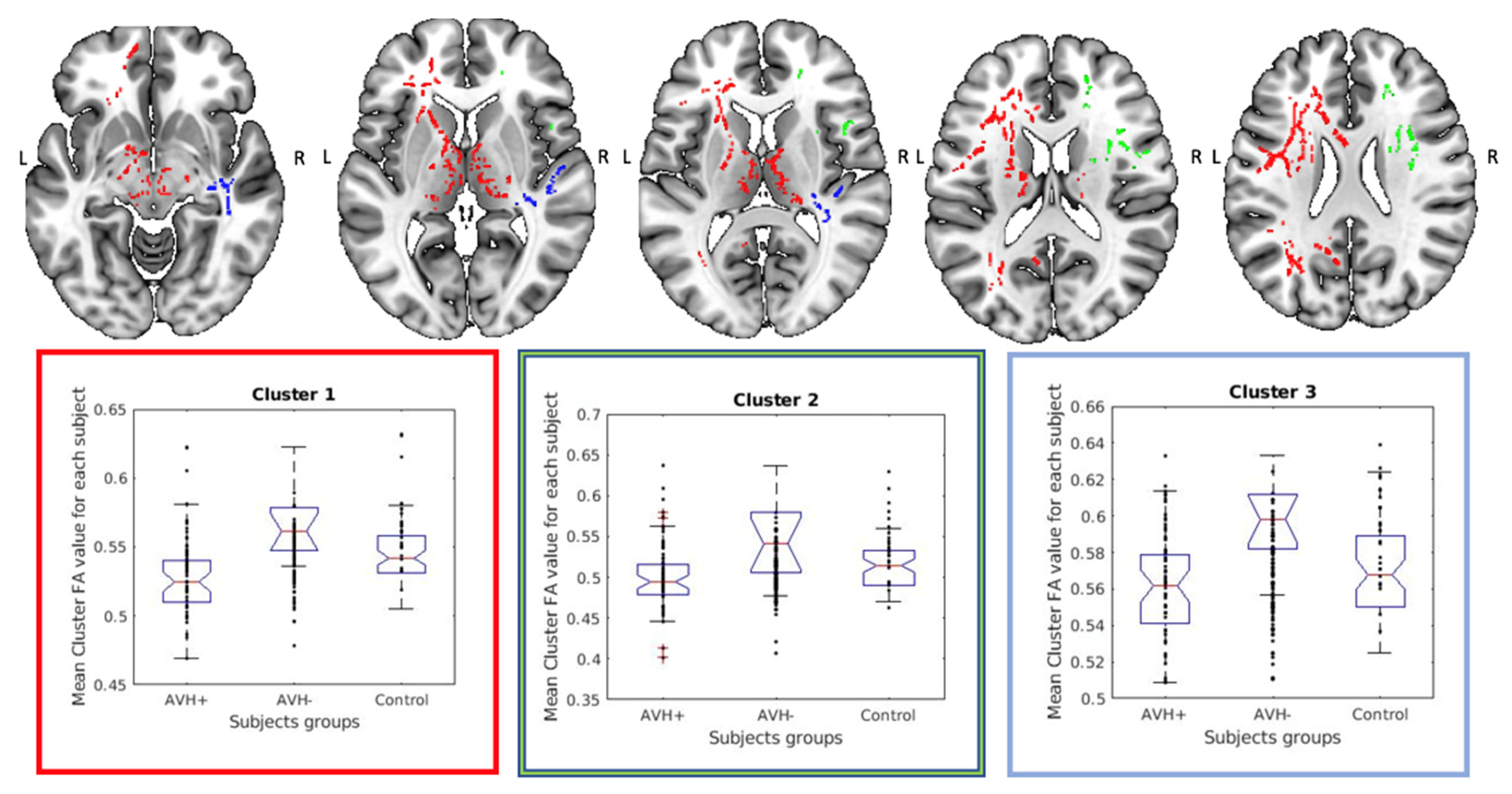
| Number of Voxels | X (mm) a | Y (mm) | Z (mm) | Major Tracts Included in a Cluster b |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13231 | −36 | −1 | 28 | Anterior thalamic radiation L c: 5.9 Anterior thalamic radiation R: 2.7 Corticospinal tract L: 1.8 Corticospinal tract R: 1.0 Forceps minor: 2.0 Inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus L: 1.4 Superior longitudinal fasciculus L: 2.2 |
| 1752 | 32 | 7 | 28 | Anterior thalamic radiation R: 1.2 Forceps minor: 3.8 Superior longitudinal fasciculus R: 6.4 Superior longitudinal fasciculus (temporal part) R: 2.4 |
| 948 | 45 | −22 | 5 | Inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus R: 14.4 Inferior longitudinal fasciculus R: 9.8 |
| 530 | 34 | −59 | 29 | Superior longitudinal fasciculus R: 7.5 Superior longitudinal fasciculus (temporal part) R: 1.3 |
| 295 | 17 | −52 | 25 | Cingulum (cingulate gyrus) R: 1.3 |
| 275 | 12 | 4 | −7 | Anterior thalamic radiation R: 14.8 |
| 89 | 49 | −4 | −12 | Inferior longitudinal fasciculus R: 6.8 |
| 53 | 31 | −32 | 37 | Superior longitudinal fasciculus R: 16.3 |
| 46 | 24 | −54 | 24 | Inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus R: 5.0 Inferior longitudinal fasciculus R: 1.7 Superior longitudinal fasciculus R: 1.3 |
| 38 | 34 | −11 | −5 | Inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus R:3 9.4 Inferior longitudinal fasciculus R: 1.2 |
| 30 | 36 | −4 | −5 | Inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus R: 8.7 Superior longitudinal fasciculus R: 3.8 Superior longitudinal fasciculus (temporal part) R: 2.3 |
| 25 | 23 | −50 | 32 | Anterior thalamic radiation R: 1.9 Inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus R: 2.9 Superior longitudinal fasciculus R: 1.6 |
| 15 | 19 | −47 | 35 | Cingulum (cingulate gyrus) R: 4.2 |
| Cluster Index | Number of Voxels | X a (mm) | Y (mm) | Z (mm) | Major Tracts Included in a Cluster b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 22 | −38 | 5 | 20 | Superior longitudinal fasciculus: 13.2 Superior longitudinal fasciculus (temporal part): 6.9 (marked in green on Figure 2) |
| 2 | 20 | −38 | −9 | 34 | Superior longitudinal fasciculus: 15.4 Superior longitudinal fasciculus (temporal part): 7.0 (marked in red on Figure 2) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Beresniewicz, J.; Craven, A.R.; Hugdahl, K.; Løberg, E.-M.; Kroken, R.A.; Johnsen, E.; Grüner, R. White Matter Microstructural Differences between Hallucinating and Non-Hallucinating Schizophrenia Spectrum Patients. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11010139
Beresniewicz J, Craven AR, Hugdahl K, Løberg E-M, Kroken RA, Johnsen E, Grüner R. White Matter Microstructural Differences between Hallucinating and Non-Hallucinating Schizophrenia Spectrum Patients. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(1):139. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11010139
Chicago/Turabian StyleBeresniewicz, Justyna, Alexander R. Craven, Kenneth Hugdahl, Else-Marie Løberg, Rune Andreas Kroken, Erik Johnsen, and Renate Grüner. 2021. "White Matter Microstructural Differences between Hallucinating and Non-Hallucinating Schizophrenia Spectrum Patients" Diagnostics 11, no. 1: 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11010139
APA StyleBeresniewicz, J., Craven, A. R., Hugdahl, K., Løberg, E.-M., Kroken, R. A., Johnsen, E., & Grüner, R. (2021). White Matter Microstructural Differences between Hallucinating and Non-Hallucinating Schizophrenia Spectrum Patients. Diagnostics, 11(1), 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11010139





