Direct-RT-qPCR Detection of SARS-CoV-2 without RNA Extraction as Part of a COVID-19 Testing Strategy: From Sample to Result in One Hour
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
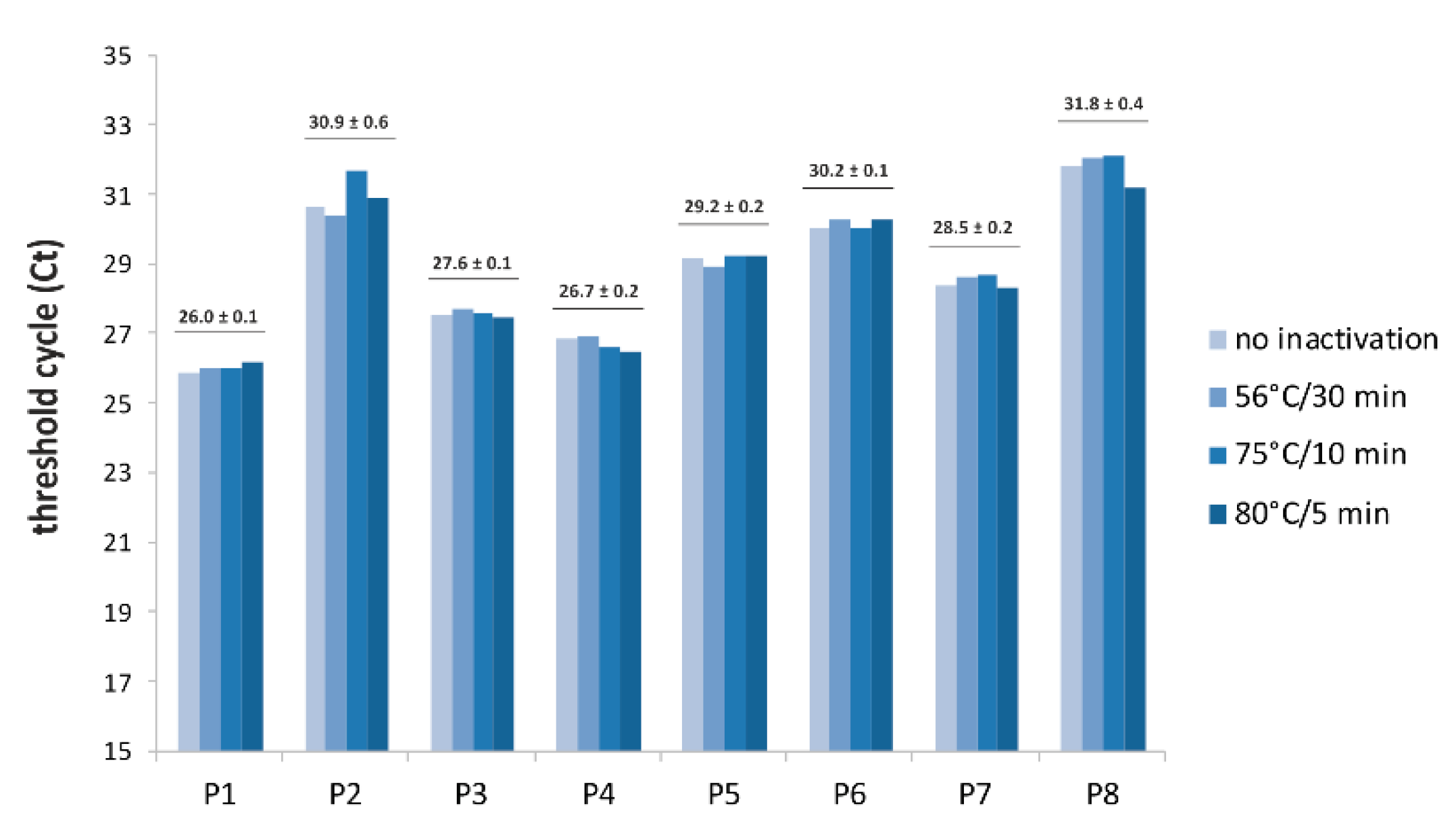
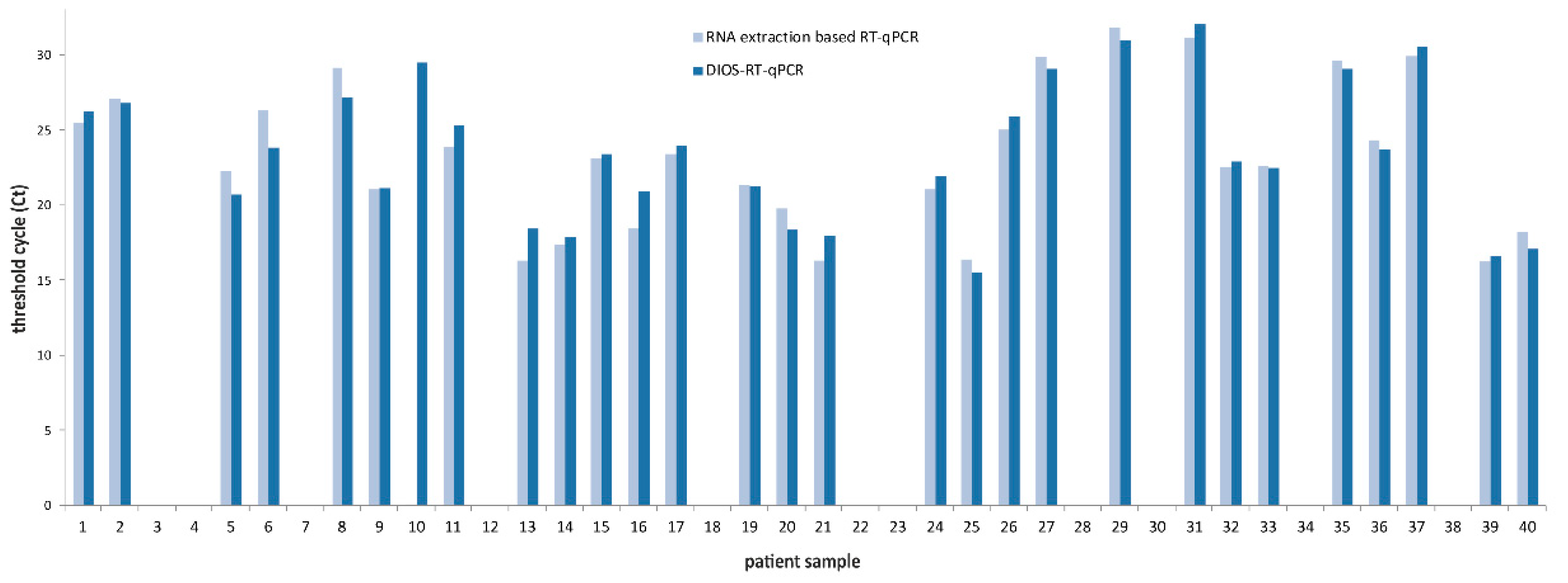
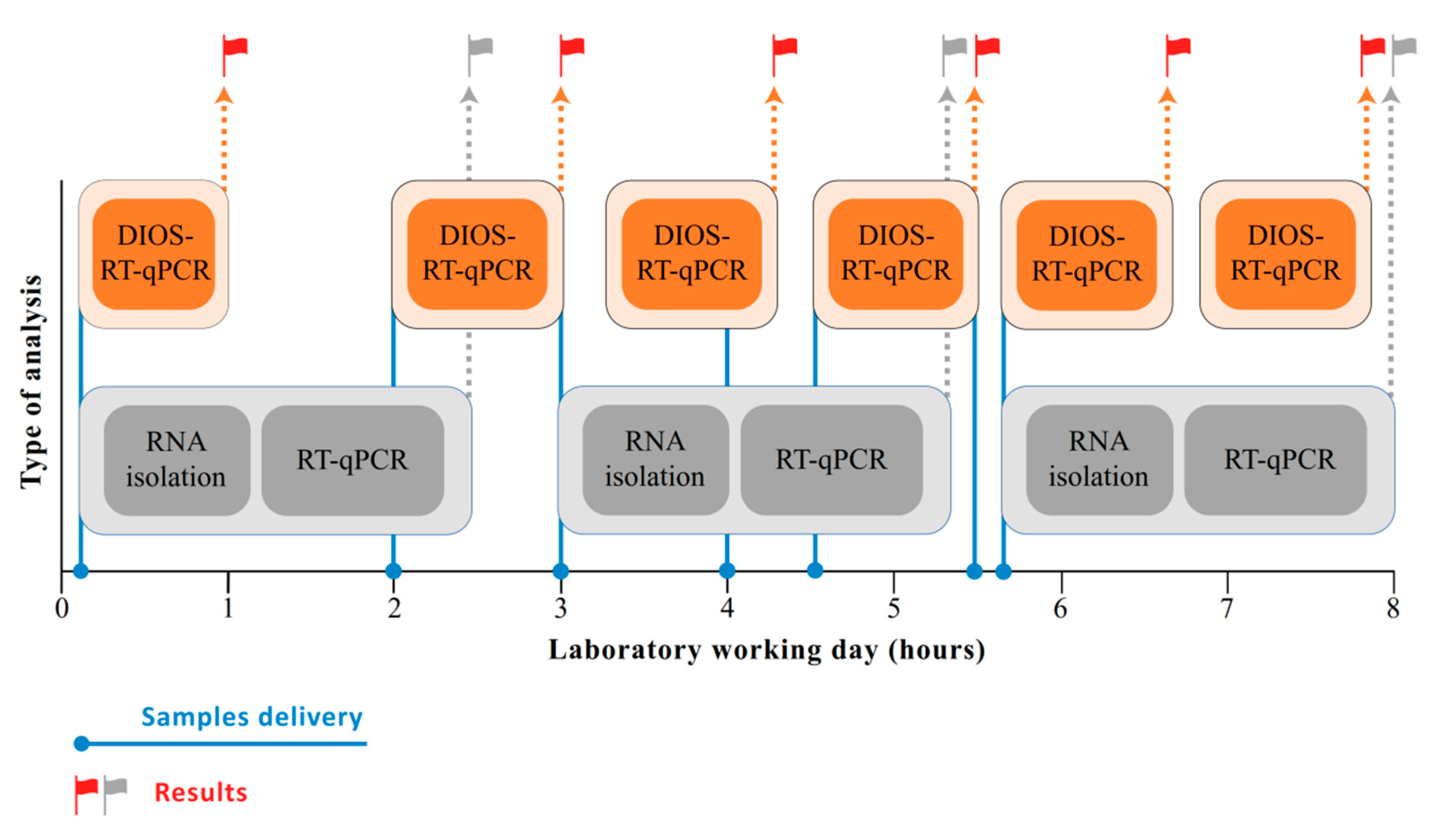
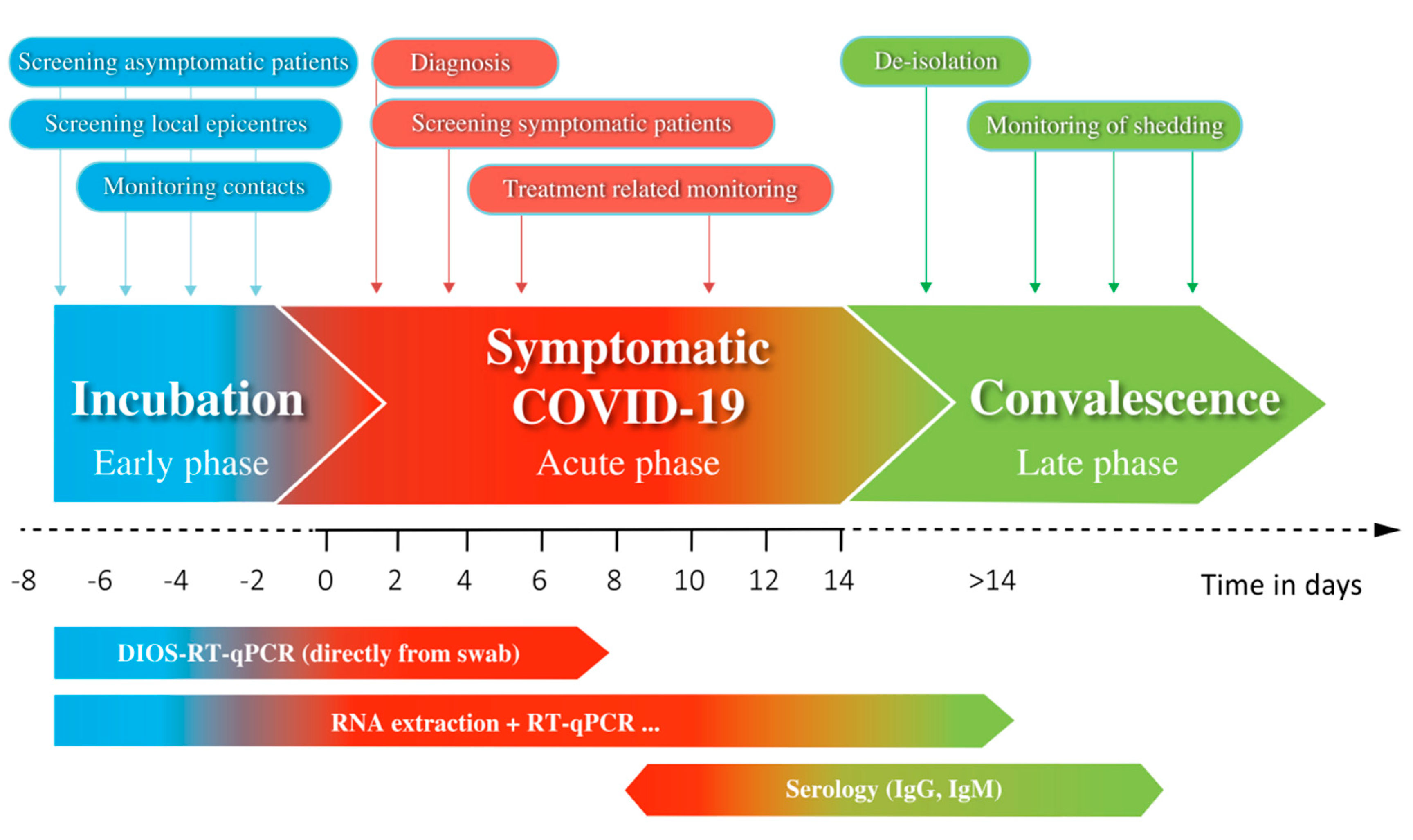
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Statement of Ethical Assurance
Ethics
References
- Johns Hopkins University. Available online: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu (accessed on 30 July 2020).
- Corman, V.M.; Landt, O.; Kaiser, M.; Molenkamp, R.; Meijer, A.; Chu, D.K.; Bleicker, T.; Brünink, S.; Schneider, J.; Schmidt, M.L.; et al. Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) by real-time RT-PCR. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25, 2000045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubina, R.; Dziedzic, A. Molecular and Serological Tests for COVID-19 a Comparative Review of SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus Laboratory and Point-of-Care Diagnostics. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Research Use only 2019-Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) Real-time RT-PCR Primers and Probes. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/lab/rt-pcr-panel-primer-probes.html (accessed on 28 June 2020).
- Hasan, M.R.; Mirza, F.; Al-Hail, H.; Sundararaju, S.; Xaba, T.; Iqbal, M.; Alhussain, H.; Yassine, H.M.; Perez-Lopez, A.; Tang, P. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA by direct RT-qPCR on nasopharyngeal specimens without extraction of viral RNA. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0236564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; He, J.A.; Wang, W.; Xia, Y.; Song, L.; Chen, Z.H.; Zuo, H.Z.; Tan, X.P.; Ho, A.H.; Kong, S.K.; et al. Development of a Direct Reverse-Transcription Quantitative PCR (dirRT-qPCR) Assay for Clinical Zika Diagnosis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 85, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruce, E.A.; Huang, M.L.; Perchetti, G.A.; Tighe, S.; Laaguiby, P.; Hoffman, J.J.; Gerrard, D.L.; Nalla, A.K.; Wei, Y.; Greninger, A.L.; et al. Direct RT-qPCR detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA from patient nasopharyngeal swabs without an RNA extraction step. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fomsgaard, A.S.; Rosenstierne, M.W. An alternative workflow for molecular detection of SARS-CoV-2—Escape from the NA extraction kit-shortage. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltran-Pavez, C.; Marquez, C.L.; Munoz, G.; Valiente-Echeverria, F.; Gaggero, A.; Soto-Rifo, R.; Barriga, G.P. SARS-CoV-2 detection from nasopharyngeal swab samples without RNA extraction. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, P.R.; Turner, M.A.; Shin, G.Y.; Nastouli, E.; Levett, L.J. Extraction-free COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2) diagnosis by RT-PCR to increase capacity for national testing programmes during a pandemic. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Zhang, D.; Yang, P.; Poon, L.L.M.; Wang, Q. Viral load of SARS-CoV-2 in clinical samples. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 411–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wölfel, R.; Corman, V.M.; Guggemos, W.; Seilmaier, M.; Zange, S.; Müller, M.A.; Niemeyer, D.; Jones, T.C.; Vollmar, P.; Rothe, C.; et al. Virological assessment of hospitalized patients with COVID-2019. Nature 2020, 581, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Yan, L.; Wang, N.; Yang, S.; Wang, L.; Tang, Y.; Gao, G.; Wang, S.; Ma, C.; Xie, R.; et al. Quantitative Detection and Viral Load Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 in Infected Patients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA, U.S. Policy for Coronavirus Disease-2019 Tests During the Public Health Emergency (Revised). Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/135659/download (accessed on 28 June 2020).
- World Health Organisation. Laboratory Biosafety Guidance Related to Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/331138/WHO-WPE-GIH-2020.1-eng.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y (accessed on 4 July 2020).
- Kampf, G.; Voss, A.; Scheithauer, S. Inactivation of coronaviruses by heat. J. Hosp. Infect. 2020, 105, 348–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lista, M.J.; Page, R.; Sartkaya, H.; Matos, P.M.; Ortiz-Zapater, E.; Maguire, T.J.A.; Poulton, K.; O’Byrne, A.; Bouton, C.; Dickenson, R.E.; et al. Resilient SARS-CoV-2 diagnostics workflows including viral heat inactivation. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Wu, X.; Wan, Z.; Li, Y.; Jin, X.; Zhang, C. A Novel Reverse Transcription Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Method for Rapid Detection of SARS-CoV-2. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Odiwuor, N.; Xiong, J.; Sun, L.; Nyaruaba, R.O.; Wei, H.; Tanner, N.A. Rapid Molecular Detection of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) Virus RNA Using Colorimetric LAMP. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joung, J.; Ladha, A.; Saito, M.; Segel, M.; Bruneau, R.; Huang, M.W.; Kim, N.G.; Yu, X.; Li, J.; Walker, B.D.; et al. Point-of-care testing for COVID-19 using SHERLOCK diagnostics. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arizti-Sanz, J.; Freije, C.A.; Stanton, A.C.; Boehm, C.K.; Petros, B.A.; Siddiqui, S.; Shaw, B.M.; Adams, G.; Kosoko-Thoroddsen, T.S.F.; Kemball, M.E.; et al. Integrated sample inactivation, amplification, and Cas13-based detection of SARS-CoV-2. Version 1. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikramaratna, P.; Paton, R.S.; Ghafari, M.; Lourenco, J. Estimating false-negative detection rate of SARS-CoV-2 by RT-PCR. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Specimen Collection Guidelines. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/urdo/downloads/SpecCollectionGuidelines.pdf (accessed on 28 June 2020).
- Wyllie, A.L.; Fournier, J.; Casanovas-Massana, A.; Campbell, M.; Tokuyama, M.; Vijayakumar, P.; Geng, B.; Muenker, M.C.; Moore, A.J.; Vogels, C.B.F.; et al. Saliva is more sensitive for SARS-CoV-2 detection in COVID-19 patients than nasopharyngeal swap. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, M.; Shen, C.; Wang, F.; Yuan, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Z.; Xing, L.; Wei, J.; et al. Evaluating the accuracy of different respiratory specimens in the laboratory diagnosis and monitoring the viral shedding of 2019-nCoV infections. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, A.W.H.; Chu, J.T.S.; Perera, M.R.A.; Hui, K.P.Y.; Yen, H.-L.; Chan, M.C.W.; Peiris, M.; Poon, L.L.M. Stability of SARS-CoV-2 in different environmental conditions. Lancet Microbe 2020, 1, e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organisation. First Data on Stability and Resistance of SARS Coronavirus Complied by Members of WHO Laboratory Network. Available online: https://www.who.int/csr/sars/survival_2003_05_04/en/ (accessed on 17 July 2020).
| Name | Description | Oligonucleotide Sequence (5′ → 3′) | Final Concentration in Reaction |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2019-nCoV_N1 | Forward primer | GACCCCAAAATCAGCGAAAT | 333 nM |
| Reverse primer | TCTGGTTACTGCCAGTTGAATCTG | 333 nM | |
| Probe | FAM-ACCCCGCATTACGTTTGGTGGACC-BHQ-1 | 83 nM | |
| 2019-nCoV_N2 | Forward primer | TTACAAACATTGGCCGCAAA | 200 nM |
| Reverse primer | GCGCGACATTCCGAAGAA | 200 nM | |
| Probe | FAM-ACAATTTGCCCCCAGCGCTTCAG-BHQ-1 | 50 nM | |
| RP | Forward primer | AGATTTGGACCTGCGAGCG | 133 nM |
| Reverse primer | GAGCGGCTGTCTCCACAAGT | 133 nM | |
| Probe | Cy5-TTCTGACCTGAAGGCTCTGCGCG-BHQ-2 | 33 nM |
| Mean Ct ± SD | Virus Copies/ Reaction | Virus Copies/mL in Swabs | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| qTOWER3 | LightCycler 480 | Rotor-Gene Q | ||
| 25.9 ± 0.1 | 28.2 ± 0.2 | 24.0 ± 0.1 | 125 | 8.9 × 103 |
| 26.8 ± 0.1 | 29.4 ± 0.2 | 25.2 ± 0.1 | 63 | 4.5 × 103 |
| 27.5 ± 0.1 | 30.7 ± 0.1 | 25.7 ± 0.1 | 31 | 2.2 × 103 |
| 28.3 ± 0.1 | 31.9 ± 0.2 | 26.9 ± 0.2 | 15.6 | 1.1 × 103 |
| 29.1 ± 0.1 | 32.8 ± 0.1 | 27.9 ± 0.2 | 7.8 | 554 |
| 30.0 ± 0.2 | 33.6 ± 0.2 | 28.8 ± 0.2 | 3.9 | 277 |
| 30.6 ± 0.3 | 34.2 ± 0.3 | 29.4 ± 0.3 | 2 | 141 |
| ND | ND | ND | 0 | 0 |
| QCMD EQA Specimens | DIOS-RT-qPCR Result | Study by Hasan et al. 2020 [5] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample ID | SARS-CoV-2 Result | SARS-CoV-2 Result | qTOWER3 (Ct) | QIAstat-Dx (Ct) | Direct Approach (Ct) |
| S 01 | Positive | Positive | 24.4 | 34.0 | 35.5 |
| S 02 | Negative | Negative | ND | ND | ND |
| S 03 | Positive | Positive | 27.1 | 35.4 | 37.1 |
| S 04 | Negative | Negative | ND | ND | ND |
| S 05 | Negative | Negative | ND | ND | ND |
| S 06 | Positive | Positive | 24.1 | 36.7 | 35.1 |
| S 07 | Positive | Positive | 20.8 | 31.5 | 31.7 |
| S 08 | Borderline | Positive | 30.2 | ND | ND |
| Target Subjects | Result Expected | Key Requirements for Methods Used | DIOS-RT-qPCR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Screening | Local epicentres, contacts of positive cases, business, travelling, risk groups | Positive/negative for COVID-19 | Fast, cost-effective, high throughput, easy performance | Yes, suitable |
| Point-of-care testing | Patients before emergent hospitalisation, surgery, doctor/dentist visits | Positive/negative for COVID-19 | Ultra-fast, on-site | Yes, suitable |
| Diagnostics | Patients with suspected COVID-19 | Viral load, quantification of pathogens, positive/negative for COVID-19 and other respiratory pathogens (panels of targets) | Analysis of multiple targets and genes, ultra-sensitive, quantitative and qualitative evaluation | Not intended |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kriegova, E.; Fillerova, R.; Kvapil, P. Direct-RT-qPCR Detection of SARS-CoV-2 without RNA Extraction as Part of a COVID-19 Testing Strategy: From Sample to Result in One Hour. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 605. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10080605
Kriegova E, Fillerova R, Kvapil P. Direct-RT-qPCR Detection of SARS-CoV-2 without RNA Extraction as Part of a COVID-19 Testing Strategy: From Sample to Result in One Hour. Diagnostics. 2020; 10(8):605. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10080605
Chicago/Turabian StyleKriegova, Eva, Regina Fillerova, and Petr Kvapil. 2020. "Direct-RT-qPCR Detection of SARS-CoV-2 without RNA Extraction as Part of a COVID-19 Testing Strategy: From Sample to Result in One Hour" Diagnostics 10, no. 8: 605. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10080605
APA StyleKriegova, E., Fillerova, R., & Kvapil, P. (2020). Direct-RT-qPCR Detection of SARS-CoV-2 without RNA Extraction as Part of a COVID-19 Testing Strategy: From Sample to Result in One Hour. Diagnostics, 10(8), 605. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10080605





