Bile Acids Quantification by Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry: Method Validation, Reference Range, and Interference Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Analytical Standards and Solvents
2.2. Calibrators, Quality Control Samples, and Internal Standard Solution
2.3. Sample Collection
2.4. Sample Preparation
2.5. LC–MS/MS Settings
2.6. Validation Procedures
2.7. Reference Ranges
2.8. Interference Study
2.8.1. In Vitro Study
2.8.2. In Vivo Study
3. Results
3.1. LC–MS/MS Optimization
3.2. Method Validation
3.3. Reference Ranges
3.4. Interference Study
3.4.1. In Vitro Study
3.4.2. In Vivo Study
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chiang, J.Y.L. Bile acid metabolism and signaling. Compr. Physiol. 2013, 3, 1191–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, J.Y.L. Bile acids: Regulation of synthesis. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, 1955–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staley, C.; Weingarden, A.R.; Khoruts, A.; Sadowsky, M.J. Interaction of gut microbiota with bile acid metabolism and its influence on disease states. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 47–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Aguiar Vallim, T.Q.; Tarling, E.J.; Edwards, P.A. Pleiotropic Roles of Bile Acids in Metabolism. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kühn, T.; Stepien, M.; López-Nogueroles, M.; Damms-Machado, A.; Sookthai, D.; Johnson, T.; Roca, M.; Hüsing, A.; Maldonado, S.G.; Cross, A.J.; et al. Prediagnostic Plasma Bile Acid Levels and Colon Cancer Risk: A Prospective Study. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2019, 112, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, M.L.; Tomaro-Duchesneau, C.; Prakash, S. The gut microbiome, probiotics, bile acids axis, and human health. Trends Microbiol. 2014, 22, 306–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenman, L.K.; Holma, R.; Eggert, A.; Korpela, R. A novel mechanism for gut barrier dysfunction by dietary fat: Epithelial disruption by hydrophobic bile acids. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2013, 304, G227–G234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duboc, H.; Rajca, S.; Rainteau, D.; Benarous, D.; Maubert, M.-A.; Quervain, E.; Thomas, G.; Barbu, V.; Humbert, L.; Despras, G.; et al. Connecting dysbiosis, bile-acid dysmetabolism and gut inflammation in inflammatory bowel diseases. Gut 2013, 62, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Lu, S.; Zeng, Z.; Liu, Q.; Dong, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Hong, Z.; Zhang, T.; Du, G.; et al. Characterization of Gut Microbiota, Bile Acid Metabolism, and Cytokines in Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatology 2020, 71, 893–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugita, T.; Amano, K.; Nakano, M.; Masubuchi, N.; Sugihara, M.; Matsuura, T. Analysis of the Serum Bile Acid Composition for Differential Diagnosis in Patients with Liver Disease. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2015, 2015, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Aubrecht, J.; Li, D.; Warner, R.L.; Johnson, K.J.; Kenny, J.; Colangelo, J.L. Assessment of serum bile acid profiles as biomarkers of liver injury and liver disease in humans. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danese, E.; Ruzzenente, A.; Montagnana, M.; Lievens, P.M.-J. Current and future roles of mucins in cholangiocarcinoma—recent evidences for a possible interplay with bile acids. Ann. Transl. Med. 2018, 6, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danese, E.; Salvagno, G.L.; Negrini, D.; Brocco, G.; Montagnana, M.; Lippi, G. Analytical evaluation of three enzymatic assays for measuring total bile acids in plasma using a fully-automated clinical chemistry platform. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rejchrt, S.; Hroch, M.; Repak, R.; Fejfar, T.; Douda, T.; Kohoutova, D.; Peterova, E.; Bures, J. Investigation of 23 Bile Acids in Liver Bile in Benign and Malignant Biliary Stenosis: A Pilot Study. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2019, 2019, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, K.L. CLSI C62-A: A New Standard for Clinical Mass Spectrometry. Clin. Chem. 2016, 62, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippi, G.; Cadamuro, J.; Danese, E.; Gelati, M.; Montagnana, M.; von Meyer, A.; Salvagno, G.L.; Simundic, A.-M. Internal quality assurance of HIL indices on Roche Cobas c702. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippi, G. Interference studies: Focus on blood cell lysates preparation and testing. Clin. Lab. 2012, 58, 351–355. [Google Scholar]
- Salvagno, G.L.; Favaloro, E.J.; Demonte, D.; Gelati, M.; Poli, G.; Targher, G.; Lippi, G. Influence of hypertriglyceridemia, hyperbilirubinemia and hemolysis on thrombin generation in human plasma. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2019, 57, 1784–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Xiao, Y.; Golden, J.; Niu, S.; Gayer, C.P. Serum bile acids profiling by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) and its application on pediatric liver and intestinal diseases. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2020, 58, 787–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Succop, P.A.; Clark, S.; Chen, M.; Galke, W. Imputation of data values that are less than a detection limit. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2004, 1, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Cañaveras, J.C.; Donato, M.T.; Castell, J.V.; Lahoz, A. Targeted profiling of circulating and hepatic bile acids in human, mouse, and rat using a UPLC-MRM-MS-validated method. J. Lipid Res. 2012, 53, 2231–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wegner, K.; Just, S.; Gau, L.; Mueller, H.; Gérard, P.; Lepage, P.; Clavel, T.; Rohn, S. Rapid analysis of bile acids in different biological matrices using LC-ESI-MS/MS for the investigation of bile acid transformation by mammalian gut bacteria. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 1231–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humbert, L.; Maubert, M.A.; Wolf, C.; Duboc, H.; Mahé, M.; Farabos, D.; Seksik, P.; Mallet, J.M.; Trugnan, G.; Masliah, J.; et al. Bile acid profiling in human biological samples: Comparison of extraction procedures and application to normal and cholestatic patients. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2012, 899, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkard, I.; von Eckardstein, A.; Rentsch, K.M. Differentiated quantification of human bile acids in serum by high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2005, 826, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiner, C.; von Eckardstein, A.; Rentsch, K.M. Quantification of the 15 major human bile acids and their precursor 7α-hydroxy-4-cholesten-3-one in serum by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2010, 878, 2870–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarafian, M.H.; Lewis, M.R.; Pechlivanis, A.; Ralphs, S.; McPhail, M.J.W.; Patel, V.C.; Dumas, M.-E.; Holmes, E.; Nicholson, J.K. Bile Acid Profiling and Quantification in Biofluids Using Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 9662–9670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, M.; Gnewuch, C.; Schmitz, G.; Liebisch, G. Rapid quantification of bile acids and their conjugates in serum by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2009, 877, 3920–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inagaki, T.; Moschetta, A.; Lee, Y.-K.; Peng, L.; Zhao, G.; Downes, M.; Yu, R.T.; Shelton, J.M.; Richardson, J.A.; Repa, J.J.; et al. Regulation of antibacterial defense in the small intestine by the nuclear bile acid receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 3920–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCauley-Myers, D.L.; Eichhold, T.H.; Bailey, R.E.; Dobrozsi, D.J.; Best, K.J.; Hayes, J.W.; Hoke, S.H. Rapid bioanalytical determination of dextromethorphan in canine plasma by dilute-and-shoot preparation combined with one minute per sample LC-MS/MS analysis to optimize formulations for drug delivery. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2000, 23, 825–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salihović, S.; Dickens, A.M.; Schoultz, I.; Fart, F.; Sinisalu, L.; Lindeman, T.; Halfvarson, J.; Orešič, M.; Hyötyläinen, T. Simultaneous determination of perfluoroalkyl substances and bile acids in human serum using ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 2251–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, D.S.; Partridge, S.J.; Handley, S.A.; Couchman, L.; Morgan, P.E.; Flanagan, R.J. LC–MS/MS of some atypical antipsychotics in human plasma, serum, oral fluid and haemolysed whole blood. Forensic Sci. Int. 2013, 229, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Salen, G.; Shefer, S.; Tint, G.S.; Nguyen, L.B.; Parker, T.T.; Chen, T.S.; Roberts, J.; Kong, X.; Greenblatt, D. Regulation of classic and alternative bile acid synthesis in hypercholesterolemic rabbits: Effects of cholesterol feeding and bile acid depletion. J. Lipid Res. 1998, 39, 1608–1615. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Granado-Serrano, A.B.; Martín-Garí, M.; Sánchez, V.; Riart Solans, M.; Berdún, R.; Ludwig, I.A.; Rubió, L.; Vilaprinyó, E.; Portero-Otín, M.; Serrano, J.C.E. Faecal bacterial and short-chain fatty acids signature in hypercholesterolemia. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charach, G.; Karniel, E.; Novikov, I.; Galin, L.; Vons, S.; Grosskopf, I.; Charach, L. Reduced bile acid excretion is an independent risk factor for stroke and mortality: A prospective follow-up study. Atherosclerosis 2020, 293, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, A.; Chen, T.; Ni, Y.; Wong, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, C.; et al. Profiling of Serum Bile Acids in a Healthy Chinese Population Using UPLC–MS/MS. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 850–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Faden, H.S.; Zhu, L. The Response of the Gut Microbiota to Dietary Changes in the First Two Years of Life. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jusakul, A.; Khuntikeo, N.; Haigh, W.G.; Kuver, R.; Ioannou, G.N.; Loilome, W.; Namwat, N.; Bhudhisawasdi, V.; Pugkhem, A.; Pairojkul, C.; et al. Identification of biliary bile acids in patients with benign biliary diseases, hepatocellular carcinoma and cholangiocarcinoma. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2012, 13 Suppl., 77–82. [Google Scholar]
- Rees, D.O.; Crick, P.J.; Jenkins, G.J.; Wang, Y.; Griffiths, W.J.; Brown, T.H.; Al-Sarireh, B. Comparison of the composition of bile acids in bile of patients with adenocarcinoma of the pancreas and benign disease. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 174, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, W.J.; Sjövall, J. Bile acids: Analysis in biological fluids and tissues. J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 23–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
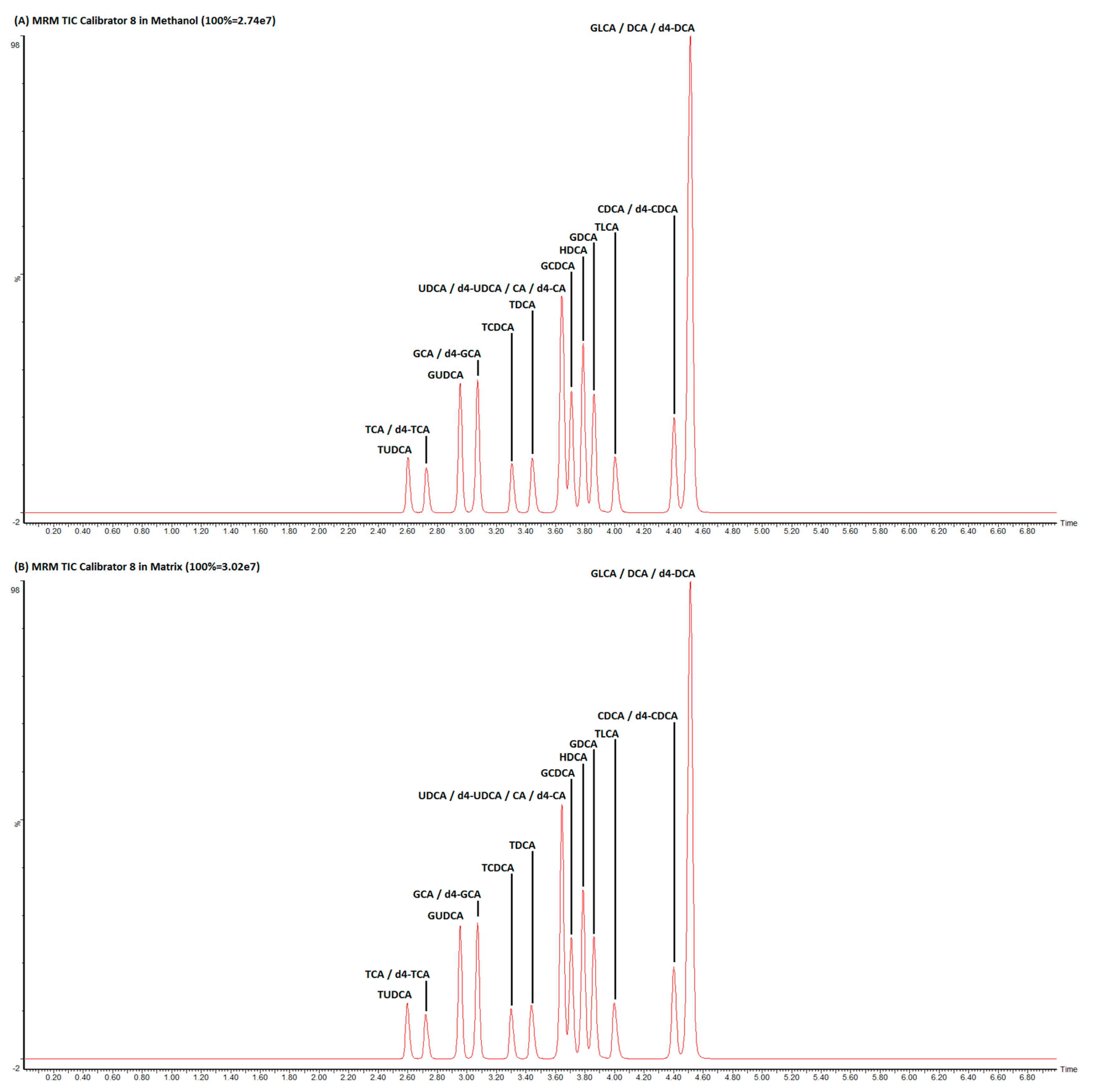
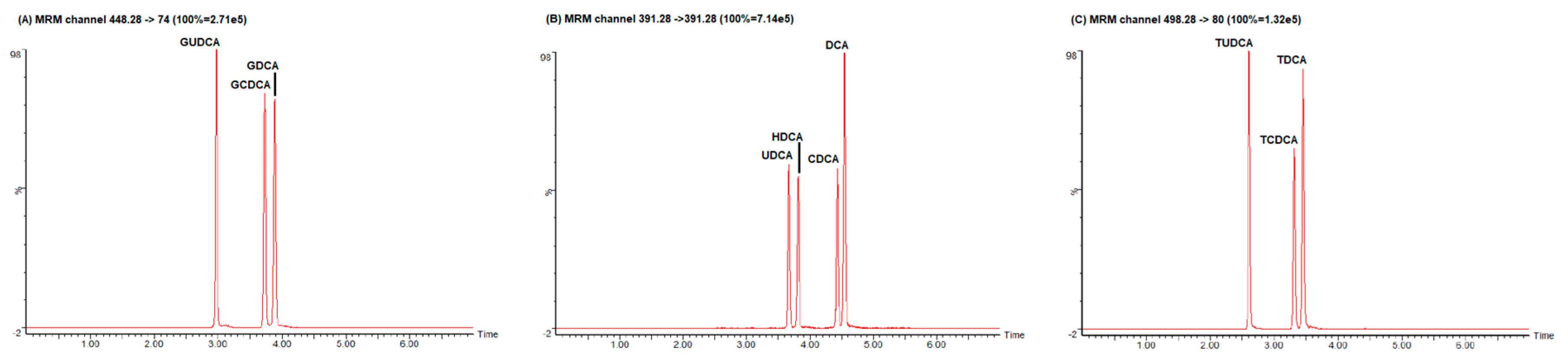


| Type | Bile Acid | Internal Standard | Precursor Ion m/z | Retention Time (min) | Product Ion m/z | Collision Voltage (V) | Calibration Linearity in Methanol (r2) | Calibration Linearity in Steroid-Free Serum (r2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| STD | Tauroursodeoxycholic acid (TUDCA) | d4-GCA | 498.28 | 2.58 | 80.00 | 60 | 0.998387 | 0.999016 |
| STD | Taurocholic acid (TCA) | d4-TCA | 514.28 | 2.7 | 80.00 | 64 | 0.999312 | 0.999820 |
| STD | Glycoursodeoxycholic acid (GUDCA) | d4-GCA | 448.28 | 2.92 | 74.00 | 35 | 0.997775 | 0.999103 |
| STD | Glycocholic acid (GCA) | d4-GCA | 464.28 | 3.06 | 74.00 | 34 | 0.998718 | 0.999051 |
| STD | Taurochenodeoxycholic acid (TCDCA) | d4-GCA | 498.28 | 3.3 | 80.00 | 60 | 0.997292 | 0.998966 |
| STD | Taurodeoxycholic acid (TDCA) | d4-GCA | 498.28 | 3.46 | 80.00 | 60 | 0.998165 | 0.998822 |
| STD | Cholic acid (CA) | d4-CA | 407.28 | 3.64 | 343.28 | 34 | 0.999410 | 0.999722 |
| STD | Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) | d4-UDCA | 391.28 | 3.65 | 391.28 | 16 | 0.999290 | 0.999731 |
| STD | Glycochenodeoxycholic acid (GCDCA) | d4-CA | 448.28 | 3.67 | 74.00 | 35 | 0.998938 | 0.999806 |
| STD | Hyodeoxycholic acid (HDCA) | d4-CA | 391.28 | 3.77 | 391.28 | 16 | 0.999384 | 0.999745 |
| STD | Glycodeoxycholic acid (GDCA) | d4-CA | 448.28 | 3.87 | 74.00 | 35 | 0.998329 | 0.999870 |
| STD | Taurolithocholic acid (TLCA) | d4-CDCA | 482.28 | 4.02 | 80.00 | 60 | 0.997170 | 0.999418 |
| STD | Chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA) | d4-CDCA | 391.28 | 4.41 | 391.28 | 16 | 0.999702 | 0.999748 |
| STD | Glycolithocholic acid (GLCA) | d4-DCA | 432.28 | 4.49 | 74.00 | 35 | 0.999886 | 0.998580 |
| STD | Deoxycholic acid (DCA) | d4-DCA | 391.28 | 4.51 | 391.28 | 16 | 0.999446 | 0.999799 |
| IS | Taurocholic acid-d4 (d4-TCA) | 518.28 | 2.7 | 80.00 | 64 | |||
| IS | Glycocholic acid-d4 (d4-GCA) | 468.28 | 3.06 | 74.00 | 34 | |||
| IS | Cholic acid-d4 (d4-CA) | 411.28 | 3.64 | 347.28 | 34 | |||
| IS | Ursodeoxycholic acid-d4 (d4-UDCA) | 395.28 | 3.65 | 395.28 | 16 | |||
| IS | Chenodeoxycholic acid-d4 (d4-CDCA) | 395.28 | 4.41 | 395.28 | 16 | |||
| IS | Deoxycholic acid-d4 (d4-DCA) | 395.28 | 4.51 | 395.28 | 16 |
| BA Species | Mean (ng/mL) | 2.5 Percentile (ng/mL) | 97.5 Percentile (ng/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total BA | 795.4 | 143.2 | 2152.4 |
| TUDCA | <5 | <5 | 5.2 |
| GCDCA | 203.5 | 24.8 | 706.5 |
| HDCA | 6.9 | <5 | 14.1 |
| GDCA | 75.3 | 7.2 | 273.9 |
| TLCA | <5 | <5 | <5 |
| CDCA | 97.4 | 5.1 | 521.3 |
| GLCA | 5.8 | <5 | 21.7 |
| DCA | 161.4 | 9.6 | 542.8 |
| GUDCA | 40.1 | 3.9 | 145.8 |
| TCA | 11.3 | <5 | 65.9 |
| GCA | 77.4 | 8.6 | 415.1 |
| TCDCA | 24.1 | <5 | 92.8 |
| TDCA | 11.7 | <5 | 45.1 |
| UDCA | 17.9 | <5 | 77.7 |
| CA | 71.3 | <5 | 495.0 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Danese, E.; Negrini, D.; Pucci, M.; De Nitto, S.; Ambrogi, D.; Donzelli, S.; Lievens, P.M.-J.; Salvagno, G.L.; Lippi, G. Bile Acids Quantification by Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry: Method Validation, Reference Range, and Interference Study. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 462. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10070462
Danese E, Negrini D, Pucci M, De Nitto S, Ambrogi D, Donzelli S, Lievens PM-J, Salvagno GL, Lippi G. Bile Acids Quantification by Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry: Method Validation, Reference Range, and Interference Study. Diagnostics. 2020; 10(7):462. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10070462
Chicago/Turabian StyleDanese, Elisa, Davide Negrini, Mairi Pucci, Simone De Nitto, Davide Ambrogi, Simone Donzelli, Patricia M.-J. Lievens, Gian Luca Salvagno, and Giuseppe Lippi. 2020. "Bile Acids Quantification by Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry: Method Validation, Reference Range, and Interference Study" Diagnostics 10, no. 7: 462. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10070462
APA StyleDanese, E., Negrini, D., Pucci, M., De Nitto, S., Ambrogi, D., Donzelli, S., Lievens, P. M.-J., Salvagno, G. L., & Lippi, G. (2020). Bile Acids Quantification by Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry: Method Validation, Reference Range, and Interference Study. Diagnostics, 10(7), 462. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10070462








