Different Biomarker Kinetics in Critically Ill Patients with High Lactate Levels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Protocol
2.2. Measurement of Lactate, IL-6, NGAL, and HMGB1 Levels
2.3. Statistical Analysis
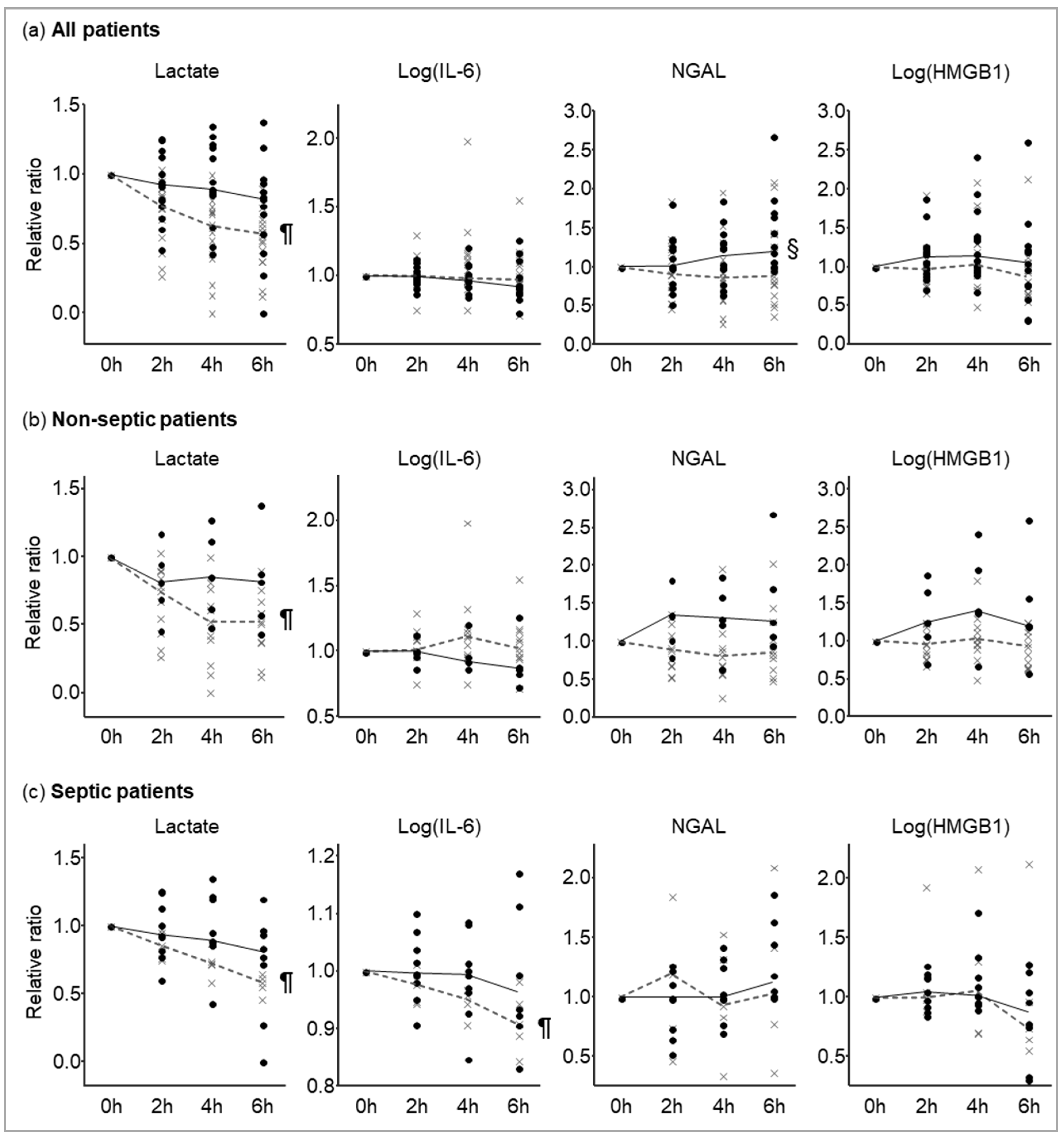
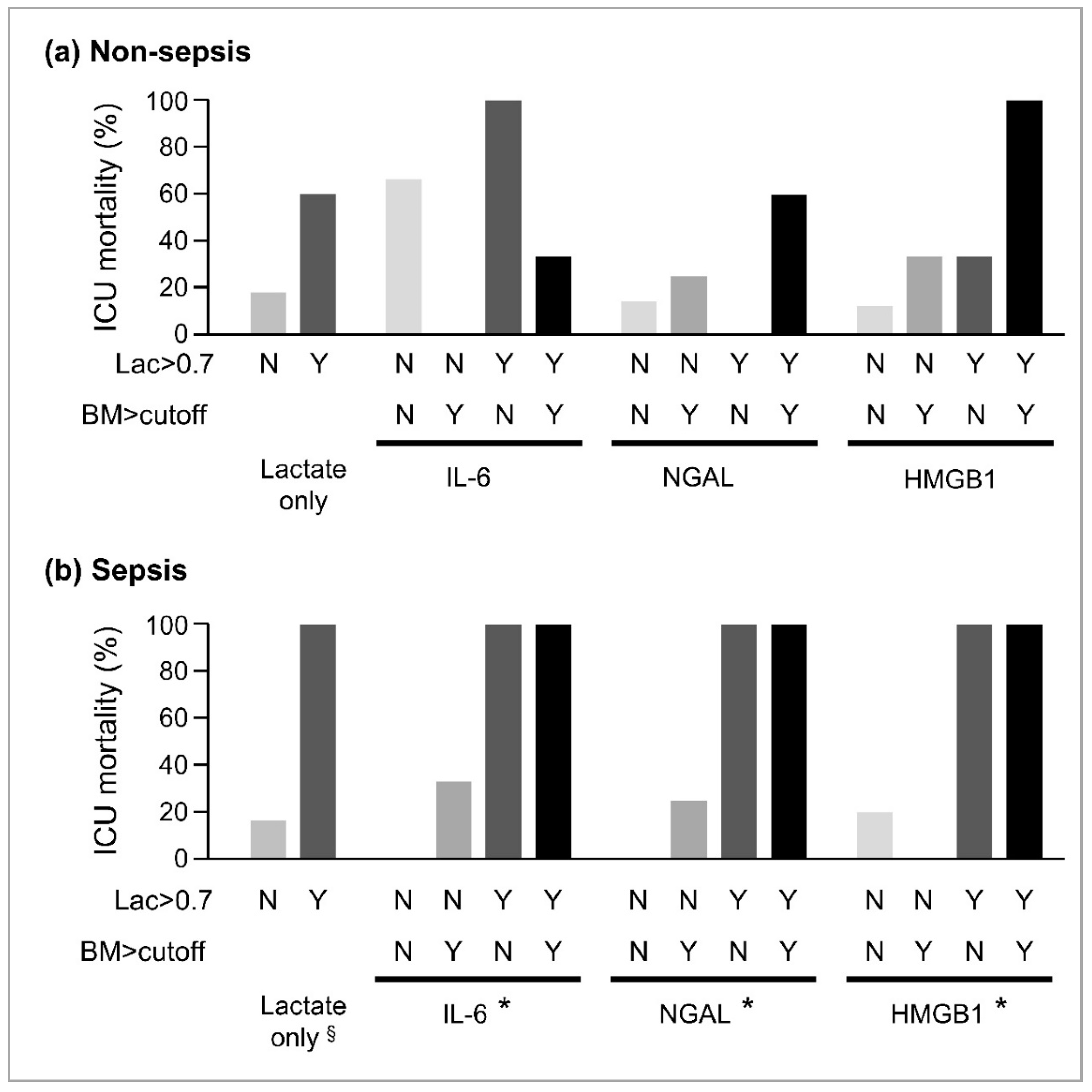
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Sepsis and Inflammatory Biomarkers at ICU Admission
3.3. Biomarker Kinetics and ICU Mortality
3.4. Combination of Biomarkers and ICU Mortality
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Harrison, D.A.; Brady, A.R.; Rowan, K. Case mix, outcome and length of stay for admissions to adult, general critical care units in England, Wales and Northern Ireland: The Intensive Care National Audit & Research Centre Case Mix Programme Database. Crit. Care 2004, 8, R99–R111. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wallace, D.J.; Angus, D.C.; Barnato, A.E.; Kramer, A.A.; Kahn, J.M. Nighttime intensivist staffing and mortality among critically ill patients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 2093–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Power, G.S.; Harrison, D.A. Why try to predict ICU outcomes? Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2014, 20, 544–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahn, J.M. Predicting outcome in critical care: Past, present and future. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2014, 20, 542–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.B.; Corbett, S.W.; Steele, R.; Banta, J.; Clark, R.T.; Hayes, S.R.; Edwards, J.; Cho, T.W.; Wittlake, W.A. Implementation of a bundle of quality indicators for the early management of severe sepsis and septic shock is associated with decreased mortality. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 35, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.B.; Rivers, E.P.; Knoblich, B.P.; Jacobsen, G.; Muzzin, A.; Ressler, J.A.; Tomlanovich, M.C. Early lactate clearance is associated with improved outcome in severe sepsis and septic shock. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 32, 1637–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, T.C.; van Bommel, J.; Schoonderbeek, F.J.; Sleeswijk Visser, S.J.; van der Klooster, J.M.; Lima, A.P.; Willemsen, S.P.; Bakker, J. Early lactate-guided therapy in intensive care unit patients: A multicenter, open-label, randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 182, 752–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, X. Lactate clearance is a useful biomarker for the prediction of all-cause mortality in critically ill patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis*. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 42, 2118–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zhang, H.; Yin, Y.-L.; Guo, W.-Z.; Ma, Y.-Q.; Wang, Y.-B.; Shu, C.; Dong, L.-Q. Role of interleukin-6 to differentiate sepsis from non-infectious systemic inflammatory response syndrome. Cytokine 2016, 88, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klag, T.; Cantara, G.; Sechtem, U.; Athanasiadis, A. Interleukin-6 Kinetics can be Useful for Early Treatment Monitoring of Severe Bacterial Sepsis and Septic Shock. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2016, 8, 6213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagshaw, S.M.; Bennett, M.; Haase, M.; Haase-Fielitz, A.; Egi, M.; Morimatsu, H.; D’amico, G.; Goldsmith, D.; Devarajan, P.; Bellomo, R. Plasma and urine neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in septic versus non-septic acute kidney injury in critical illness. Intensive Care Med. 2010, 36, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angus, D.C.; Yang, L.; Kong, L.; Kellum, J.A.; Delude, R.L.; Tracey, K.J.; Weissfeld, L. Circulating high-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) concentrations are elevated in both uncomplicated pneumonia and pneumonia with severe sepsis. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 35, 1061–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibot, S.; Massin, F.; Cravoisy, A.; Barraud, D.; Nace, L.; Levy, B.; Bollaert, P.-E. High-mobility group box 1 protein plasma concentrations during septic shock. Intensive Care Med. 2007, 33, 1347–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, A.; Evans, L.E.; Alhazzani, W.; Levy, M.M.; Antonelli, M.; Ferrer, R.; Kumar, A.; Sevransky, J.E.; Sprung, C.L.; Nunnally, M.E.; et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: International Guidelines for Management of Sepsis and Septic Shock: 2016. Intensive Care Med. 2017, 43, 304–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nichol, A.D.; Egi, M.; Pettila, V.; Bellomo, R.; French, C.; Hart, G.; Davies, A.; Stachowski, E.; Reade, M.C.; Bailey, M.; et al. Relative hyperlactatemia and hospital mortality in critically ill patients: A retrospective multi-centre study. Crit. Care 2010, 14, R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunnerson, K.J.; Saul, M.; He, S.; Kellum, J.A. Lactate versus non-lactate metabolic acidosis: A retrospective outcome evaluation of critically ill patients. Crit. Care 2006, 10, R22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Section 2: AKI Definition. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2012, 2, 19–36. [CrossRef]
- Levy, M.M.; Fink, M.P.; Marshall, J.C.; Abraham, E.; Angus, D.; Cook, D.; Cohen, J.; Opal, S.M.; Vincent, J.-L.; Ramsay, G. 2001 SCCM/ESICM/ACCP/ATS/SIS International Sepsis Definitions Conference. Intensive Care Med. 2003, 29, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, K.; Ohba, T.; Ishii, K.; Jung, G.; Haro, H.; Matsuda, K. Development of a quick serum IL-6 measuring system in rheumatoid arthritis. Cytokine 2017, 95, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruopp, M.D.; Perkins, N.J.; Whitcomb, B.W.; Schisterman, E.F. Youden Index and optimal cut-point estimated from observations affected by a lower limit of detection. Biom. J. 2008, 50, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, N.R.; Ridker, P.M. Advances in measuring the effect of individual predictors of cardiovascular risk: The role of reclassification measures. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 150, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pencina, M.J.; D’Agostino, R.B.S.; D’Agostino, R.B.J.; Vasan, R.S. Evaluating the added predictive ability of a new marker: From area under the ROC curve to reclassification and beyond. Stat. Med. 2008, 27, 112–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dellinger, R.P.; Levy, M.M.; Rhodes, A.; Annane, D.; Gerlach, H.; Opal, S.M.; Sevransky, J.E.; Sprung, C.L.; Douglas, I.S.; Jaeschke, R.; et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: International guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock: 2012. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 41, 580–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mat-Nor, M.B.; Md Ralib, A.; Abdulah, N.Z.; Pickering, J.W. The diagnostic ability of procalcitonin and interleukin-6 to differentiate infectious from noninfectious systemic inflammatory response syndrome and to predict mortality. J. Crit. Care 2016, 33, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Geus, H.R.H.; Betjes, M.G.; Schaick, R.v.; Groeneveld, J.A.B.J. Plasma NGAL similarly predicts acute kidney injury in sepsis and nonsepsis. Biomark. Med. 2013, 7, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katagiri, D.; Doi, K.; Matsubara, T.; Negishi, K.; Hamasaki, Y.; Nakamura, K.; Ishii, T.; Yahagi, N.; Noiri, E. New biomarker panel of plasma neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin and endotoxin activity assay for detecting sepsis in acute kidney injury. J. Crit. Care 2013, 28, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Chen, G.; Zhang, J.; Xue, J.; Cao, Y.; Wu, Y. Increased Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin is Associated with Mortality and Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome in Severe Sepsis and Septic Shock. Shock 2015, 44, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, H.E.; Andersson, U.; Pisetsky, D.S. HMGB1: A multifunctional alarmin driving autoimmune and inflammatory disease. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2012, 8, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angus, D.C.; van der Poll, T. Severe sepsis and septic shock. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 840–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristics | n = 30 |
|---|---|
| Age | 68 (51–76) |
| Male/Female | 21/9 |
| Hypertension | 13 (43%) |
| Diabetes mellitus | 9 (30%) |
| Admission type | |
| Medical | 21 (70%) |
| Elective surgical | 3 (10%) |
| Emergent surgical | 6 (20%) |
| Sepsis | 14 (47%) |
| - Blood culture positive | 6 (43%) |
| - Infection site | |
| Gastrointestinal | 8 (57%) |
| Pneumonia | 2 (14%) |
| Urinary tract | 1 (7%) |
| Meningitis | 1 (7%) |
| Cholangitis | 1 (7%) |
| Necrotizing fasciitis | 1 (7%) |
| -Infecting organism | |
| Gram-positive cocci | 4 (28%) |
| Gram-positive rod | 3 (21%) |
| Gram-negative rod | 4 (28%) |
| Charlson comorbidity score | 1 (0–3) |
| APACHE II score | 23 (18–26) |
| SAPS II score | 54 (42–63) |
| SOFA score | 9 (6–12) |
| Mechanical ventilation | 22 (73%) |
| Acute kidney injury | 25 (83%) |
| Dependent on catecholamine | 12 (40%) |
| Duration of hospitalization (days) | 30 (13–66) |
| Length of ICU stay | 8 (4–15) |
| ICU mortality | 14 (47%) |
| Survival days until ICU death (days) | 8 (4–15) |
| In-hospital mortality | 16 (53%) |
| Lactate at ICU admission (mmol/L) | 6.4 (4.8–9.9) |
| Biomarker | Cutoff | AUC (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|
| Lactate | 0.70 | 0.73 (0.48–0.89) |
| IL-6 | 0.94 | 0.63 (0.40–0.81) |
| NGAL | 1.00 | 0.72 (0.49–0.87) |
| HMGB1 | 1.20 | 0.58 (0.35–0.78) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matsuura, R.; Komaru, Y.; Miyamoto, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Yoshimoto, K.; Hamasaki, Y.; Nangaku, M.; Doi, K. Different Biomarker Kinetics in Critically Ill Patients with High Lactate Levels. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 454. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10070454
Matsuura R, Komaru Y, Miyamoto Y, Yoshida T, Yoshimoto K, Hamasaki Y, Nangaku M, Doi K. Different Biomarker Kinetics in Critically Ill Patients with High Lactate Levels. Diagnostics. 2020; 10(7):454. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10070454
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatsuura, Ryo, Yohei Komaru, Yoshihisa Miyamoto, Teruhiko Yoshida, Kohei Yoshimoto, Yoshifumi Hamasaki, Masaomi Nangaku, and Kent Doi. 2020. "Different Biomarker Kinetics in Critically Ill Patients with High Lactate Levels" Diagnostics 10, no. 7: 454. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10070454
APA StyleMatsuura, R., Komaru, Y., Miyamoto, Y., Yoshida, T., Yoshimoto, K., Hamasaki, Y., Nangaku, M., & Doi, K. (2020). Different Biomarker Kinetics in Critically Ill Patients with High Lactate Levels. Diagnostics, 10(7), 454. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10070454






