Paper-Based Detection Device for Alzheimer’s Disease—Detecting β-amyloid Peptides (1–42) in Human Plasma
Abstract
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary File 1Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| P-ELISA | Paper-based ELISA |
| Aβ42 | β-amyloid peptide 1–42 |
| MCI | Mild cognitive impairment |
| NINCDS-ADRDA | National Institute of Neurological and Communicative Disorders and Stroke AD and Related Disorders Association |
| DSM | Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of the American Psychiatric Association |
| NIA-AA | National Institute on Aging and the Alzheimer’s Association |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| POC | Point-of-care |
| SPR | Surface plasmon resonance |
| Aβ | ββrface plpeptide |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
| NC16A | Noncollagenous 16A |
| LOD | Limit of detection |
| CSF | Cerebrospinal fluid |
| HRP | Horseradish peroxidase |
| IgG | Immunoglobulin G |
| SPES | Screen-printed electrochemical sensors |
| PE | Plasma exchange |
| APOE | Apolipoprotein E |
References
- Alzheimer’s Association. 2018 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2018, 14, 367–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, R.; Lewis, D.A.; Michels, R.; Pine, D.S.; Schultz, S.K.; Tamminga, C.A.; Gabbard, G.O.; Gau, S.S.; Javitt, D.C.; Oquendo, M.A.; et al. The initial field trials of DSM-5: New blooms and old thorns. Am. J. Psychiatry 2013, 170, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bateman, R.J.; Xiong, C.; Benzinger, T.L.S.; Fagan, A.M.; Goate, A.; Fox, N.C.; Marcus, D.S.; Cairns, N.J.; Xie, X.; Tyler, M.S.; et al. Clinical and biomarker changes in dominantly inherited Alzheimer’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 795–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bature, F.; Guinn, B.A.; Pang, D.; Pappas, Y. Signs and symptoms preceding the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: A systematic scoping review of literature from 1937 to 2016. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e015746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaushik, A.; Jayant, R.D.; Tiwari, S.; Vashist, A.; Nair, M. Nano-biosensors to detect beta-amyloid for Alzheimer’s disease management. Biosens Bioelectron 2016, 80, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stravalaci, M.; Bastone, A.B.M.; Cagnotto, A.; Colombo, L.; Fede, D.G.; Tagliavini, F.; Cantu, L.; Del, F.E.; Mazzanti, M.C.R.; Salmona, M.; et al. Specific recognition of biologically active amyloid-beta oligomers by a new surface plasmon resonance-based immunoassay and an in vivo assay in Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 27796–27805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.M.; Martinez, A.W.; Gong, J.; Mace, C.R.; Phillips, S.T.; Carrilho, E.; Mirica, K.A.; Whitesides, G.M. Paper-based ELISA. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2010, 49, 4771–4774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, M.Y.; Hung, Y.C.; Hwang, D.K.; Lin, S.C.; Lin, K.H.; Wang, C.Y.; Choi, H.Y.; Wang, Y.P.; Cheng, C.M. Detection of aqueous VEGF concentrations before and after intravitreal injection of anti-VEGF antibody using low-volume sampling paper-based ELISA. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, B.; Zhao, C.; Li, L.; Song, X.; Xu, K.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Fu, K.; Bao, H.; Song, D.; et al. Development of a low-cost paper-based ELISA method for rapid Escherichia coli O157:H7 detection. Anal. Biochem. 2017, 542, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.K.; Huang, H.Y.; Chen, W.R.; Nishie, W.; Ujiie, H.; Natsuga, K.; Fan, S.T.; Wang, H.K.; Lee, J.Y.; Tsai, W.L.; et al. Paper-based ELISA for the detection of autoimmune antibodies in body fluid-the case of bullous pemphigoid. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 4605–4610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barage, S.H.; Sonawane, K.D. Amyloid cascade hypothesis: Pathogenesis and therapeutic strategies in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropeptides 2015, 52, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouras, G.K.; Olsson, T.T.; Hansson, O. β-Amyloid peptides and amyloid plaques in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurotherapeutics 2015, 12, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, R.F.; Shineman, D.W.; Steele, J.W.; Lee LB, H.; Fillit, H.M. Beyond amyloid: The future of therapeutics for Alzheimer’s disease. In Advances in Pharmacology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012; Volume 64, pp. 213–271. [Google Scholar]
- Henriksen, K.; O’Bryant, S.E.; Hampel, H.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Montine, T.J.; Jeromin, A.; Blennow, K.; Lonneborg, A.; Wyss-Coray, T.; Soares, H.; et al. The future of blood-based biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement 2014, 10, 115–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laske, C.; Sohrabi, H.R.; Frost, S.M.; Lopez-de-Ipina, K.; Garrard, P.; Buscema, M.; Dauwels, J.; Soekadar, S.R.; Mueller, S.; Linnemann, C.; et al. Innovative diagnostic tools for early detection of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2015, 11, 561–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poljak, A.; Crawford, J.D.; Smythe, G.F.; Brodaty, H.; Slavin, M.J.; Kochan, N.A.; Trollor, J.N.; Wen, W.; Mather, K.A.; Assareh, A.A.; et al. The relationship between plasma abeta levels, cognitive function and brain volumetrics: Sydney memory and ageing study. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2016, 13, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.M.; Kim, H.V.; Lee, S.; Kim, H.Y.; Kim, W.; Kim, T.S.; Kim, D.J.; Kim, Y. Correlations of amyloid-beta concentrations between CSF and plasma in acute Alzheimer mouse model. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janelidze, S.; Stomrud, E.; Palmqvist, S.; Zetterberg, H.; van Westen, D.; Jeromin, A.; Song, L.; Hanlon, D.; Tan Hehir, C.A.; Baker, D.; et al. Plasma beta-amyloid in Alzheimer’s disease and vascular disease. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawarabayashi, T.; Shoji, M. Plasma biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 2008, 21, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovheim, H.; Elgh, F.; Johansson, A.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; Hallmans, G.; Eriksson, S. Plasma concentrations of free amyloid beta cannot predict the development of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2017, 13, 778–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Park, D.; Baek, S.Y.; Yang, S.-H.; Kim, Y.; Lim, S.M.; Kim, J.; Hwang, K.S. Dielectrophoresis-based filtration effect and detection of amyloid beta in plasma for Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis. Biosensors Bioelectron. 2019, 128, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayeux, R.; Tang, M.-X.; Jacobs, D.M.; Manly, J.; Bell, K.; Merchant, C.; Small, S.A.; Stern, Y.; Wisniewski, H.M.; Mehta, P.D. Plasma amyloid β-peptide 1–42 and incipient Alzheimer’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 1999, 46, 412–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayeux, R.; Honig, L.S.; Tang, M.X.; Manly, J.; Stern, Y.; Schupf, N.; Mehta, P.D. Plasma Aβ40 and Aβ42 and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 2003, 61, 1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toledo, J.B.; Shaw, L.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q. Plasma amyloid beta measurements—A desired but elusive Alzheimer’s disease biomarker. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2013, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thambisetty, M.; Lovestone, S. Blood-based biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease: Challenging but feasible. Biomark Med. 2010, 4, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H. Understanding biomarkers of neurodegeneration: Ultrasensitive detection techniques pave the way for mechanistic understanding. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 217–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H. Biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease: Current status and prospects for the future. J. Intern. Med. 2018, 284, 643–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mufson, E.J.; Ikonomovic, M.D.; Counts, S.E.; Perez, S.E.; Malek-Ahmadi, M.; Scheff, S.W.; Ginsberg, S.D. Molecular and cellular pathophysiology of preclinical Alzheimer’s disease. Behav. Brain Res. 2016, 311, 54–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperling, R.A.; Karlawish, J.; Johnson, K.A. Preclinical Alzheimer disease-the challenges ahead. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2013, 9, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, A.; Kaneko, N.; Villemagne, V.L.; Kato, T.; Doecke, J.; Doré, V.; Fowler, C.; Li, Q.-X.; Martins, R.; Rowe, C.; et al. High performance plasma amyloid-β biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 2018, 554, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garyfallou, G.Z.; Ketebu, O.; Sahin, S.; Mukaetova-Ladinska, E.B.; Catt, M.; Yu, E.H. Electrochemical Detection of Plasma Immunoglobulin as a Biomarker for Alzheimer’s Disease. Sensors 2017, 17, 2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonello, S.; Serpelloni, M.; Lopomo, N.F.; Abate, G.; Uberti, D.L.; Sardini, E. Screen-printed biosensors for the early detection of biomarkers related to alzheimer disease: Preliminary results. Procedia Eng. 2016, 168, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galozzi, S.; Marcus, K.; Barkovits, K. Amyloid-beta as a biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease: Quantification methods in body fluids. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2015, 12, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poljak, A.; Sachdev, P.S. Plasma amyloid beta peptides: An Alzheimer’s conundrum or a more accessible Alzheimer’s biomarker? Expert Rev. Neurother. 2017, 17, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Boada, M.; Anaya, F.; Ortiz, P.; Olazaran, J.; Shua-Haim, J.R.; Obisesan, T.O.; Hernandez, I.; Munoz, J.; Buendia, M.; Alegret, M.; et al. Efficacy and safety of plasma exchange with 5% albumin to modify cerebrospinal fluid and plasma amyloid-beta concentrations and cognition outcomes in alzheimer’s disease patients: A multicenter, randomized, controlled clinical trial. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2017, 56, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, H.M.; Carrillo, M.C.; Grodstein, F.; Henriksen, K.; Jeromin, A.; Lovestone, S.; Mielke, M.M.; O’Bryant, S.; Sarasa, M.; Sjøgren, M.; et al. Developing novel blood-based biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2014, 10, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sher, M.; Zhuang, R.; Demirci, U.; Asghar, W. Paper-based analytical devices for clinical diagnosis: Recent advances in the fabrication techniques and sensing mechanisms. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2017, 17, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K.; Shibata, H.; Suzuki, K.; Citterio, D. Toward practical application of paper-based microfluidics for medical diagnostics: State-of-the-art and challenges. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 1206–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Grijalba, V.; Fandos, N.; Canudas, J.; Insua, D.; Casabona, D.; Lacosta, A.M.; Montanes, M.; Pesini, P.; Sarasa, M. Validation of immunoassay-based tools for the comprehensive quantification of abeta40 and abeta42 peptides in Plasma. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2016, 54, 751–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG H and L (Cat. No.: Ab6702) | Anti-Rabbit IgG, HRP-Linked Antibody (Cat. No.: 7074) | |
|---|---|---|
| Host Species | Goat | Goat |
| Target Species | Rabbit | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG | IgG |
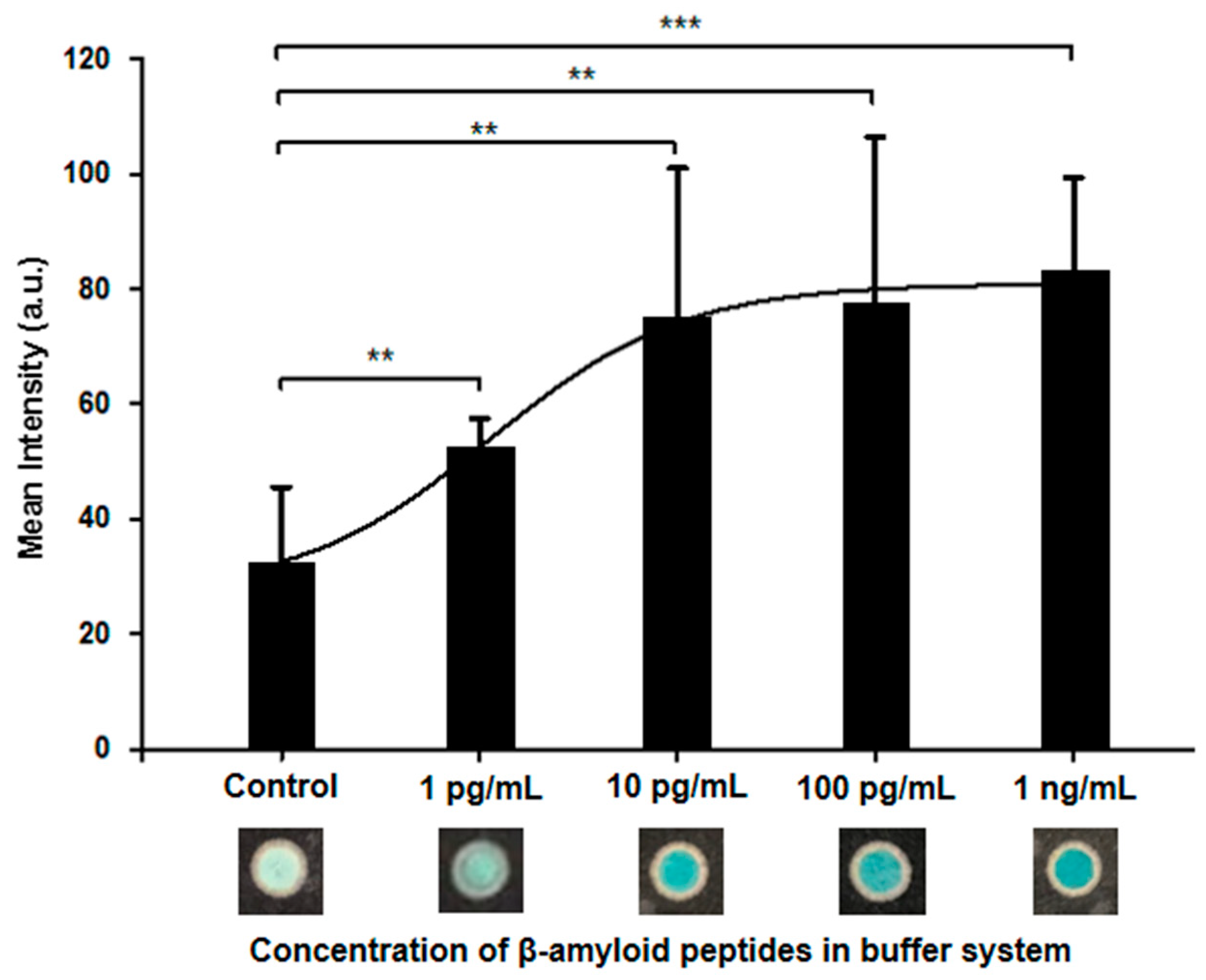
| Performance | 10 pg/mL | 100 pg/mL |
| Brand | Abcam | Cell Signaling Technology |
| Paper-based ELISA (P-ELISA) | Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) [25,39] | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Time | 1.5 h | 6–8 h (at least) | |
| Sample Volume (per Test Zone) | 3 μL | 75 μL | 100−370 μL |
| Sample Source | Buffer | Plasma | CSF |
| Limit of Detection | 63.04 pg/mL | 5.71 pg/mL | 312 pg/mL |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sung, W.-H.; Hung, J.-T.; Lu, Y.-J.; Cheng, C.-M. Paper-Based Detection Device for Alzheimer’s Disease—Detecting β-amyloid Peptides (1–42) in Human Plasma. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10050272
Sung W-H, Hung J-T, Lu Y-J, Cheng C-M. Paper-Based Detection Device for Alzheimer’s Disease—Detecting β-amyloid Peptides (1–42) in Human Plasma. Diagnostics. 2020; 10(5):272. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10050272
Chicago/Turabian StyleSung, Wei-Hsuan, Jung-Tung Hung, Yu-Jen Lu, and Chao-Min Cheng. 2020. "Paper-Based Detection Device for Alzheimer’s Disease—Detecting β-amyloid Peptides (1–42) in Human Plasma" Diagnostics 10, no. 5: 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10050272
APA StyleSung, W.-H., Hung, J.-T., Lu, Y.-J., & Cheng, C.-M. (2020). Paper-Based Detection Device for Alzheimer’s Disease—Detecting β-amyloid Peptides (1–42) in Human Plasma. Diagnostics, 10(5), 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10050272






