Choroidal Changes of Long-Term Type 1 Diabetic Patients without Retinopathy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kempen, J.H.; O’Colmain, B.J.; Leske, M.C.; Haffner, S.M.; Klein, R.; Moss, S.E.; Taylor, H.R.; Hamman, R.F.; Group EDPR. The prevalence of diabetic retinopathy among adults in the United States. Arch Ophthalmol. 2004, 122, 552–563. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nickla, D.L.; Wallman, J. The multifunctional choroid. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2010, 29, 144–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spaide, R.F.; Koizumi, H.; Pozzoni, M.C.; Pozonni, M.C. Enhanced depth imaging spectral-domain optical coherence tomography. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2008, 146, 496–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coscas, G.; Zhou, Q.; Coscas, F.; Zucchiatti, I.; Rispoli, M.; Uzzan, J.; De Benedetto, U.; Savastano, M.C.; Soules, K.; Goldenberg, D.; et al. Choroid thickness measurement with RTVue optical coherence tomography in emmetropic eyes, mildly myopic eyes, and highly myopic eyes. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2012, 22, 992–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalewska, Z.; Michalewski, J.; Nawrocki, J. New OCT technologies take imaging deeper and wider. Adding the possibility of imaging the choroid, retina, and vitreous. Retin. Physician 2013, 10, 42–48. [Google Scholar]
- Maruko, I.; Iida, T.; Sugano, Y.; Oyamada, H.; Sekiryu, T.; Fujiwara, T.; Spaide, R.F. Subfoveal choroidal thickness after treatment of Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada disease. Retina 2011, 31, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruko, I.; Iida, T.; Sugano, Y.; Ojima, A.; Sekiryu, T. Subfoveal choroidal thickness in fellow eyes of patients with central serous chorioretinopathy. Retina 2011, 31, 1603–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruko, I.; Iida, T.; Sugano, Y.; Oyamada, H.; Akiba, M.; Sekiryu, T. Morphologic analysis in pathologic myopia using high-penetration optical coherence tomography. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 3834–3838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Xu, L.; Chen, C.X.; Yang, L.H.; Du, K.F.; Wang, S.; Zhou, J.Q.; Wang, Y.X.; You, Q.S.; Jonas, J.B.; et al. Reproducibility of subfoveal choroidal thickness measurements with enhanced depth imaging by spectral-domain optical coherence tomography. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 230–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melancia, D.; Vicente, A.; Cunha, J.P.; Abegão Pinto, L.; Ferreira, J. Diabetic choroidopathy: A review of the current literature. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2016, 254, 1453–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.T.; Lee, D.H.; Joe, S.G.; Kim, J.G.; Yoon, Y.H. Changes in choroidal thickness in relation to the severity of retinopathy and macular edema in type 2 diabetic patients. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 3378–3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmaeelpour, M.; Považay, B.; Hermann, B.; Hofer, B.; Kajic, V.; Hale, S.L.; North, R.V.; Drexler, W.; Sheen, N.J. Mapping choroidal and retinal thickness variation in type 2 diabetes using three-dimensional 1060-nm optical coherence tomography. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 5311–5316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vujosevic, S.; Martini, F.; Cavarzeran, F.; Pilotto, E.; Midena, E. Macular and peripapillary choroidal thickness in diabetic patients. Retina 2012, 32, 1781–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha-Vaz, J.; Faria de Abreu, J.R.; Campos, A.J. Early breakdown of the blood-retinal barrier in diabetes. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1975, 59, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciulla, T.A.; Harris, A.; Latkany, P.; Piper, H.C.; Arend, O.; Garzozi, H.; Martin, B. Ocular perfusion abnormalities in diabetes. Acta Ophthalmol. Scand. 2002, 80, 468–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study Research G. Photocoagulation for diabetic macular edema. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1985, 103, 1796–1806. [Google Scholar]
- Orduna, E.; Sanchez-Cano, A.; Luesma, M.J.; Perez-Navarro, I.; Abecia, E.; Pinilla, I. Interocular symmetry of choroidal thickness and volume in healthy eyes on optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmic. Res. 2018, 59, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Cano, A.; Orduna, E.; Segura, F.; Lopez, C.; Cuenca, N.; Abecia, E.; Pinilla, I. Choroidal thickness and volume in healthy young white adults and the relationships between them and axial length, ammetropy and sex. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2014, 158, 574–583.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agawa, T.; Miura, M.; Ikuno, Y.; Makita, S.; Fabritius, T.; Iwasaki, T.; Goto, H.; Nishida, K.; Yasuno, Y. Choroidal thickness measurement in healthy Japanese subjects by three-dimensional high-penetration optical coherence tomography. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2011, 249, 1485–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barteselli, G.; Chhablani, J.; El-Emam, S.; Wang, H.; Chuang, J.; Kozak, I.; Cheng, L.; Bartsch, D.U.; Freeman, W.R. Choroidal volume variations with age, axial length, and sex in healthy subjects: A three-dimensional analysis. Ophthalmology 2012, 119, 2572–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, L.; Perez-Navarro, I.; Sanchez-Cano, A.; Perez-Garcia, D.; Remon, L.; Almenara, C.; Caramello, C.; Cristóbal, J.A.; Pinilla, I. Choroidal thickness and volume in a healthy pediatric population and its relationship with age, axial length, ametropia, and sex. Retina 2015, 35, 2574–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.Q.; Larsen, M.; Munch, I.C. Subfoveal choroidal thickness in relation to sex and axial length in 93 Danish university students. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 8438–8441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regatieri, C.V.; Branchini, L.; Carmody, J.; Fujimoto, J.G.; Duker, J.S. Choroidal thickness in patients with diabetic retinopathy analyzed by spectral-domain optical coherence tomography. Retina 2012, 32, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unsal, E.; Eltutar, K.; Zirtiloğlu, S.; Dinçer, N.; Ozdoğan Erkul, S.; Güngel, H. Choroidal thickness in patients with diabetic retinopathy. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2014, 8, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philip, A.M.; Gerendas, B.S.; Zhang, L.; Faatz, H.; Podkowinski, D.; Bogunovic, H.; Abramoff, M.D.; Hagmann, M.; Leitner, R.; Simader, C.; et al. Choroidal thickness maps from spectral domain and swept source optical coherence tomography: Algorithmic versus ground truth annotation. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 100, 1372–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares Ferreira, J.; Proença, R.; Alves, M.; Dias-Santos, A.; Santos, B.O.; Cunha, J.P.; Papoila, A.L.; Abegão Pinto, L. Retina and choroid of diabetic patients without observed retinal vascular changes: A longitudinal study. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2017, 176, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeelpour, M.; Brunner, S.; Ansari-Shahrezaei, S.; Shahrezaei, S.A.; Nemetz, S.; Povazay, B.; Kajic, V.; Drexler, W.; Binder, S. Choroidal thinning in diabetes type 1 detected by 3-dimensional 1060 nm optical coherence tomography. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 6803–6809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeelpour, M.; Povazay, B.; Hermann, B.; Hofer, B.; Kajic, V.; Kapoor, K.; Sheen, N.J.; North, R.V.; Drexler, W. Three-dimensional 1060-nm OCT: Choroidal thickness maps in normal subjects and improved posterior segment visualization in cataract patients. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 5260–5266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Querques, G.; Lattanzio, R.; Querques, L.; Del Turco, C.; Forte, R.; Pierro, L.; Souied, E.H.; Bandello, F. Enhanced depth imaging optical coherence tomography in type 2 diabetes. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 6017–6024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Xu, L.; Du, K.F.; Shao, L.; Chen, C.X.; Zhou, J.Q.; Wang, Y.X.; You, Q.S.; Jonas, J.B.; Wei, W.B. Subfoveal choroidal thickness in diabetes and diabetic retinopathy. Ophthalmology 2013, 120, 2023–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muir, E.R.; Rentería, R.C.; Duong, T.Q. Reduced ocular blood flow as an early indicator of diabetic retinopathy in a mouse model of diabetes. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 6488–6494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagaoka, T.; Kitaya, N.; Sugawara, R.; Yokota, H.; Mori, F.; Hikichi, T.; Fujio, N.; Yoshida, A. Alteration of choroidal circulation in the foveal region in patients with type 2 diabetes. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2004, 88, 1060–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abadia, B.; Suñen, I.; Calvo, P.; Bartol, F.; Verdes, G.; Ferreras, A. Choroidal thickness measured using swept-source optical coherence tomography is reduced in patients with type 2 diabetes. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malerbi, F.K.; Regatieri, C.V.; de Sa, J.R.; Morales, P.H.; Farah, M.E.; Dib, S.A. Microalbuminuria is associated with increased choroidal thickness in type 1 diabetes mellitus patients without diabetic retinopathy. Acta Ophthalmol. 2018, 96, e95–e97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhi, M.; Brewer, E.; Waheed, N.K.; Duker, J.S. Analysis of morphological features and vascular layers of choroid in diabetic retinopathy using spectral-domain optical coherence tomography. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2013, 131, 1267–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, G.E.; Cho, H.Y.; Kim, Y.T. Change in subfoveal choroidal thickness after argon laser panretinal photocoagulation. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2013, 6, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margolis, R.; Spaide, R.F. A pilot study of enhanced depth imaging optical coherence tomography of the choroid in normal eyes. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2009, 147, 811–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayess, N.; Rahimy, E.; Ying, G.S.; Bagheri, N.; Ho, A.C.; Regillo, C.D.; Vander, J.F.; Hsu, J. Baseline choroidal thickness as a predictor for response to anti-vascular endothelial growth factor therapy in diabetic macular edema. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 159, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
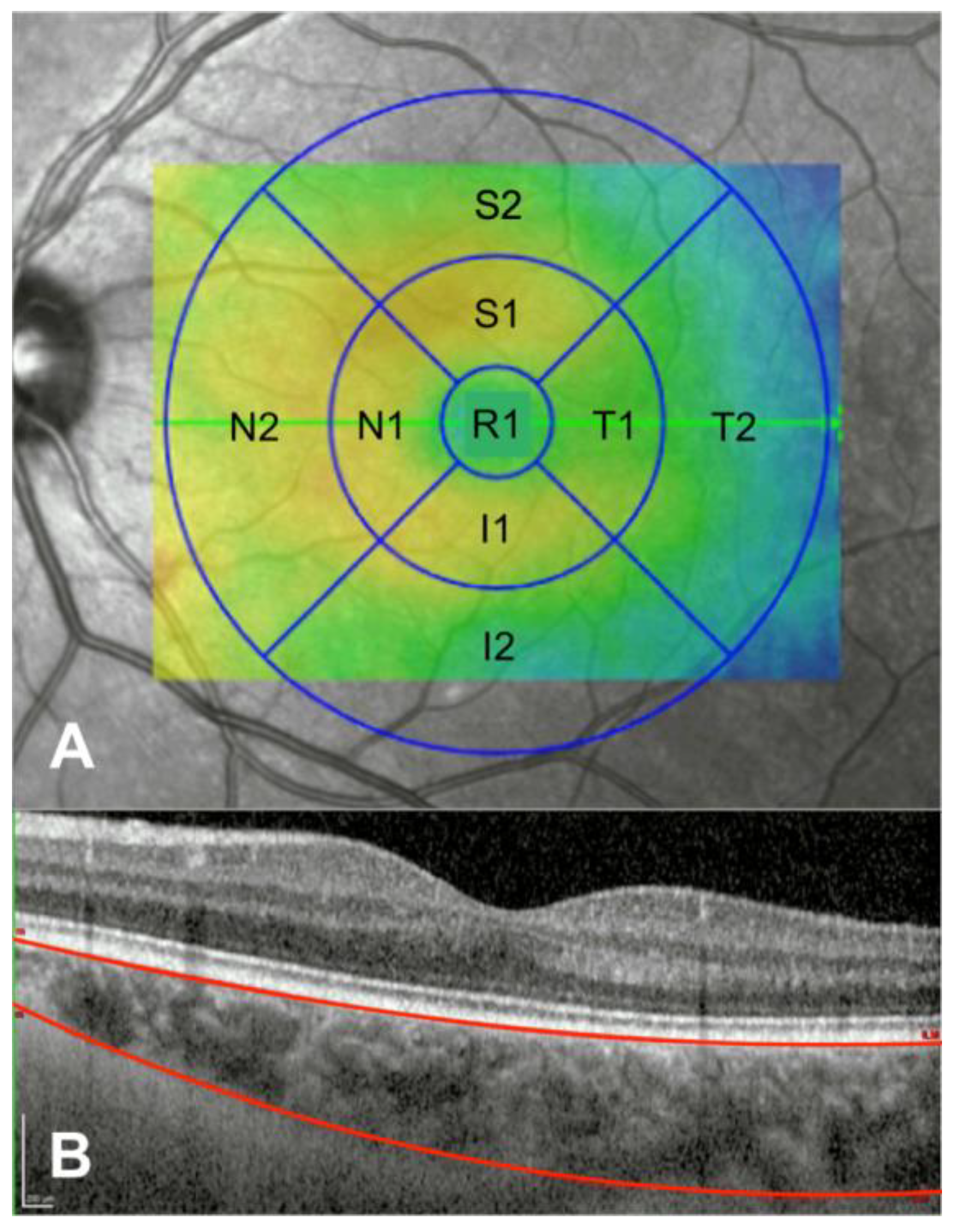


| DM1 Group (n = 90) | Control Group (n = 60) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 41.52 ± 13.05 (22–65) | 42.41 ± 13.56 (26–68) | 0.361 |
| Refractive error (D) | −1.03 ± 2.23 (−5.00/+ 3.25) | −0.76 ± 2.68 (−5.00/+ 5.00) | 0.394 |
| ACD (mm) | 3.19 ± 0.51 (2.38–4.10) | 3.29 ± 0.33 (2.59–4.00) | 0.999 |
| AL (mm) | 23.71 ± 2.73 (21.84–26.51) | 23.51 ± 1.15 (21.78–26.00) | 0.908 |
| SPECTRALIS SD-OCT | DRI-TRITON SS-OCT | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DM1 (n = 90) | CONTROL (n = 60) | p | DM1 (n = 90) | CONTROL (n = 60) | p | |
| Foveal Center (Central ETDRS Region: R1, 1 mm) | ||||||
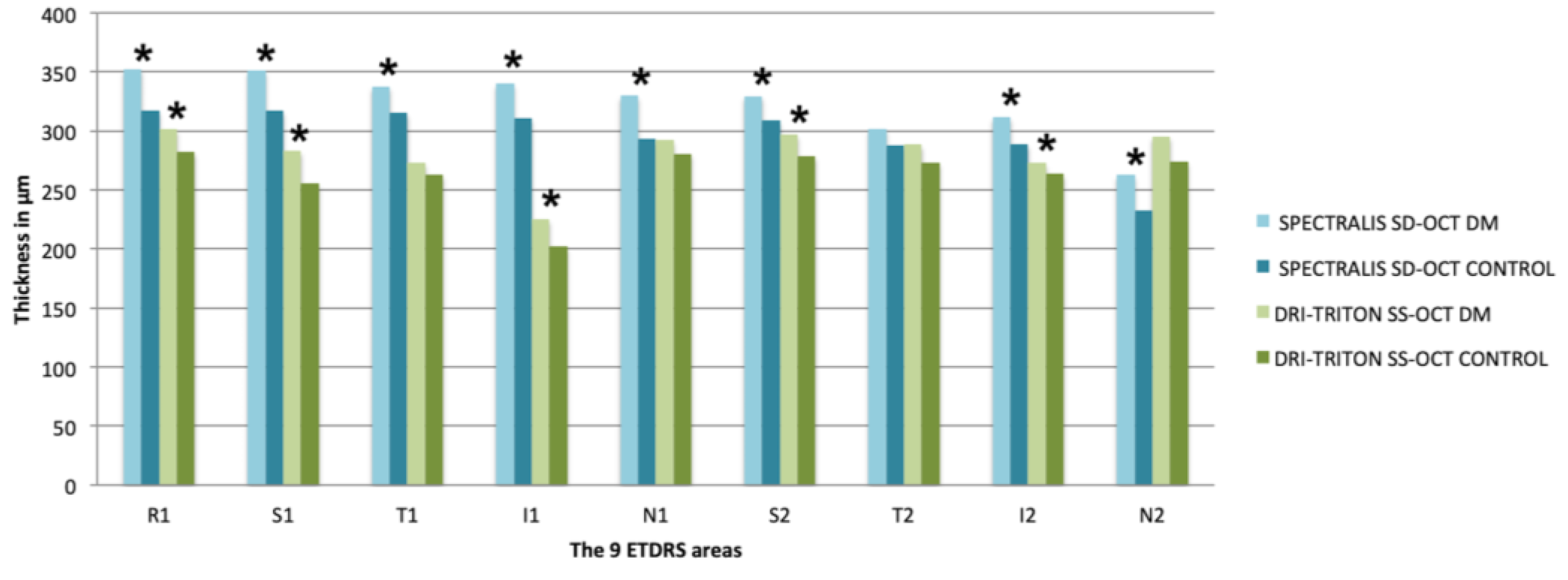
| Central R1 | 352.55 ± 88.20 (126–525) | 317.42 ± 80.05 (170–549) | 0.004 * | 301.30 ± 64.55 (107.17–443.40) | 282.32 ± 74.26 (143.01–492.05) | 0.025 * |
| Inner Circle (Parafoveal ETDRS Region: 3 mm) | ||||||
| Superior S1 | 351.23 ± 85.20 (160–562) | 317.32 ± 71.92 (192–567) | 0.003 * | 283.18 ± 68.26 (81.35–415.32) | 255.81 ± 76.83 (115.78–468.45) | 0.014 * |
| Temporal T1 | 337.60 ± 80.46 (145–484) | 315.59 ± 71.85 (171–536) | 0.046 * | 272.87 ± 60.20 (106.91–463.28) | 263.23 ± 59.71 (141.78–406.01) | 0.310 |
| Inferior I1 | 340.09 ± 88.13 (133–487) | 311.12 ± 82.85 (149–557) | 0.028 * | 225.23 ± 63.27 (71.77–344.04) | 202.09 ± 72.93 (84.56–409.92) | 0.016 * |
| Nasal N1 | 329.70 ± 86.61 (109–501) | 292.93 ± 83.58 (145–562) | 0.001 * | 292.06 ± 61.95 (116.55–463.760) | 280.80 ± 66.03 (147.06–466.31) | 0.097 |
| Outer Circle (Perifoveal ETDRS Region: 6 mm) | ||||||
| Superior S2 | 329.64 ± 81.53 (132–490) | 308.72 ± 68.00 (186–552) | 0.018 * | 297.05 ± 69.55 (105.17–424.30) | 278.77 ± 79.90 (129.04–477.19) | 0.040 * |
| Temporal T2 | 302.07 ± 71.46 (139–469) | 287.75 ± 60.22 (182–497) | 0.107 | 288.40 ± 66.21 (110.66–414.31) | 273.15 ± 62.76 (155.06–454.61) | 0.133 |
| Inferior I2 | 311.53 ± 87.62 (106–466) | 288.95 ± 79.35 (137–561) | 0.016 * | 272.65 ± 73.86 (91.53–403.04) | 263.54 ± 75.29 (109.90–486.64) | 0.036 * |
| Nasal N2 | 262.60 ± 75.21 (92–410) | 232.91 ± 78.20 (115–502) | 0.007 * | 295.42 ± 64.15 (129.61–433.49) | 274.11 ± 62.93 (152.67–457.2) | 0.076 |
| Volume | 8.82 ± 2.09 (3.62–12.60) | 8.12 ± 1.92 (4.48–15) | 0.003 * | 7.69 ± 1.65 (2.96–11.09) | 7.25 ± 1.78 (3.58–12.62) | 0.135 |
| DM1 Group <24 Years (n = 46) | DM1 Group ≥24 Years (n = 44) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 35.65 ± 12.87 (22–63) | 45.59 ± 9.96 (32–65) | <0.001 * |
| Refractive error (D) | −1.27 ± 2.38 (−5.00/+ 3.25) | −0.78 ± 2.08 (−5.00/+ 3.25) | 0.387 |
| ACD (mm) | 3.20 ± 0.31 (2.59–3.72) | 3.18 ± 0.44 (2.38–4.10) | 0.225 |
| AL (mm) | 23.63 ± 1.25 (21.84–26.51) | 23.78 ± 1.00 (22.24–26.71) | 0.070 |
| SPECTRALIS SD-OCT | DRI-TRITON SS-OCT | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DM <24 (n = 46) | DM ≥24 (n = 44) | p | DM <24 (n = 46) | DM ≥24 (n = 44) | p | |
| Foveal Center (Central ETDRS Region: R1, 1 mm) | ||||||
| Central R1 | 359,87 ± 83.43 (126–525) | 344.91 ± 77.59 (158–485) | 0.304 | 308.67 ± 71.58 (107.17–443.40) | 293.59 ± 56.07 (139.10–397.35) | 0.152 |
| Inner Circle (Parafoveal ETDRS Region: 3 mm) | ||||||
| Superior S1 | 346.39 ± 77.73 (160–522) | 356.30 ± 77.34 (168–500) | 0.783 | 285.93 ± 75.76 (81.35–415.32) | 280.31 ± 60.17 (123.97–374.02) | 0.692 |
| Temporal T1 | 347.47 ± 73.55 (145–484) | 327.27 ± 71.09 (156–481) | 0.238 | 280.07 ± 61.93 (115.20–463.28) | 265.34 ± 58.08 (106.91–342.31) | 0.434 |
| Inferior I1 | 354.93 ± 82.00 (136–487) | 324.57 ± 77.96 (133–485) | 0.031 * | 224.40 ± 66.39 (73.44–344.04) | 226.10 ± 60.59 (71.77–326.64) | 0.881 |
| Nasal N1 | 333.54 ± 85.37 (109–507) | 325.68 ± 74.44 (137–452) | 0.557 | 299.75 ± 68.46 (116.55–463.76) | 284.04 ± 53.95 (125.83–367.94) | 0.178 |
| Outer Circle (Perifoveal ETDRS Region: 6 mm) | ||||||
| Superior S2 | 323.52 ± 77.85 (158–490) | 336.05 ± 70.62 (132–465) | 0.044 * | 310.51 ± 71.24 (105.17–424.30) | 282.98 ± 65.60 (121.24–398.88) | 0.016 * |
| Temporal T2 | 313.13 ± 64.14 (139–469) | 290.52 ± 63.38 (140–433) | 0.166 | 279.68 ± 68.15 (132.03–414.31) | 297.51 ± 63.62 (110.66–412.02) | 0.063 |
| Inferior I2 | 330.56 ± 82.35 (126–466) | 291.64 ± 77.12 (106–436) | 0.036 * | 285.04 ± 72.33 (91.53–371.42) | 259.70 ± 74.04 (93.75–403.40) | 0.045 * |
| Nasal N2 | 263.61 ± 72.50 (100–378) | 261.55 ± 68.92 (92–410) | 0.981 | 296.36 ± 70.69 (129.61–433.49) | 294.43 ± 57.31 (145.27–389.12) | 0.977 |
| Volume | 9.03 ± 81.95 (3.89–12.58) | 8.64 ± 1.78 (3.62–12.60) | 0.708 | 7.78 ± 1.74 (3.02–11.09) | 7.58 ± 1.56 (2.96–9.94) | 0.523 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Orduna-Hospital, E.; Perdices, L.; Sanchez-Cano, A.; Acha, J.; Cuenca, N.; Pinilla, I. Choroidal Changes of Long-Term Type 1 Diabetic Patients without Retinopathy. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10040235
Orduna-Hospital E, Perdices L, Sanchez-Cano A, Acha J, Cuenca N, Pinilla I. Choroidal Changes of Long-Term Type 1 Diabetic Patients without Retinopathy. Diagnostics. 2020; 10(4):235. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10040235
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrduna-Hospital, Elvira, Lorena Perdices, Ana Sanchez-Cano, Javier Acha, Nicolás Cuenca, and Isabel Pinilla. 2020. "Choroidal Changes of Long-Term Type 1 Diabetic Patients without Retinopathy" Diagnostics 10, no. 4: 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10040235
APA StyleOrduna-Hospital, E., Perdices, L., Sanchez-Cano, A., Acha, J., Cuenca, N., & Pinilla, I. (2020). Choroidal Changes of Long-Term Type 1 Diabetic Patients without Retinopathy. Diagnostics, 10(4), 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10040235






