Clinical Significance of Circulating Tumor Cells in Gastrointestinal Carcinomas
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
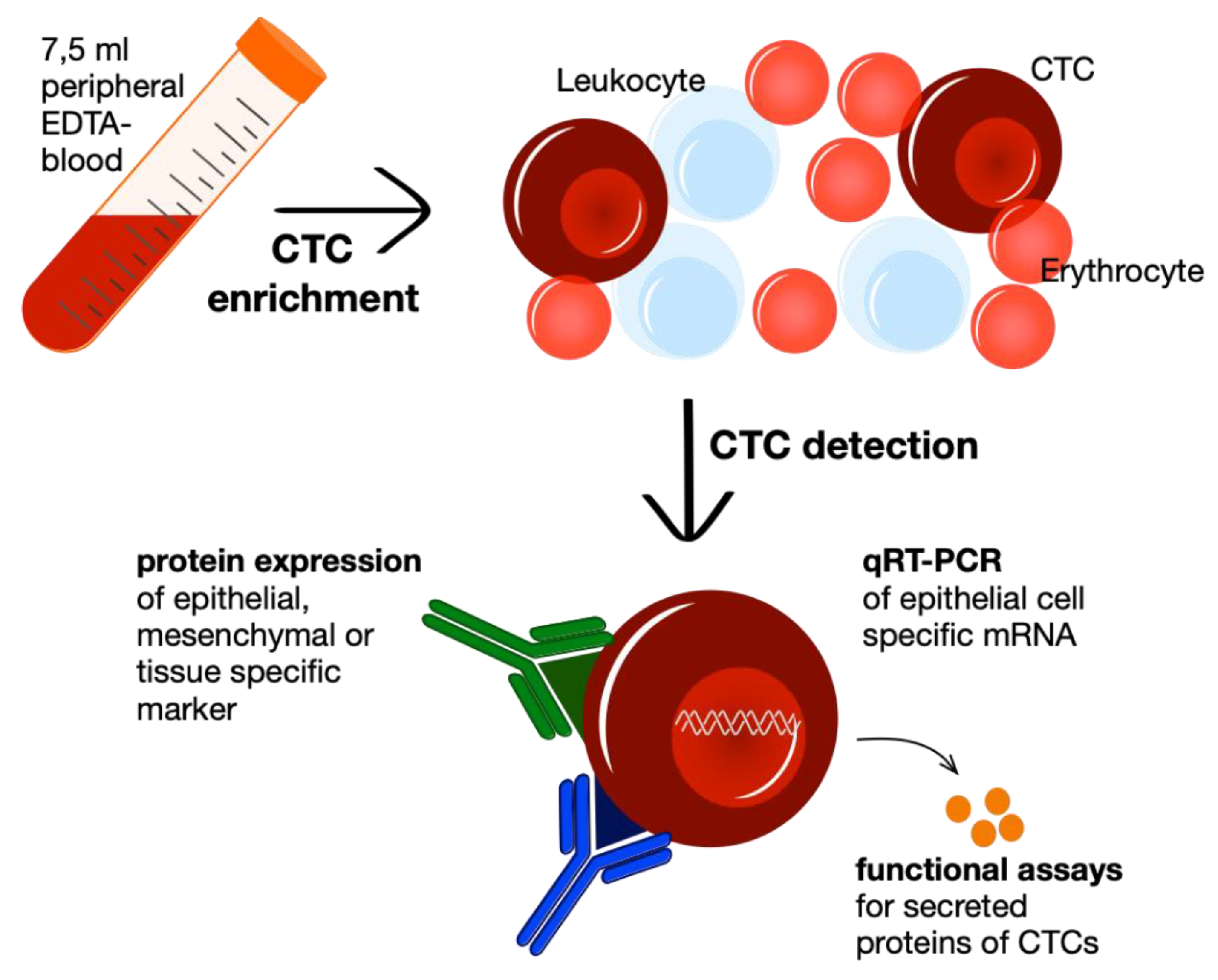
3. CTC Enrichment and Detection Methods
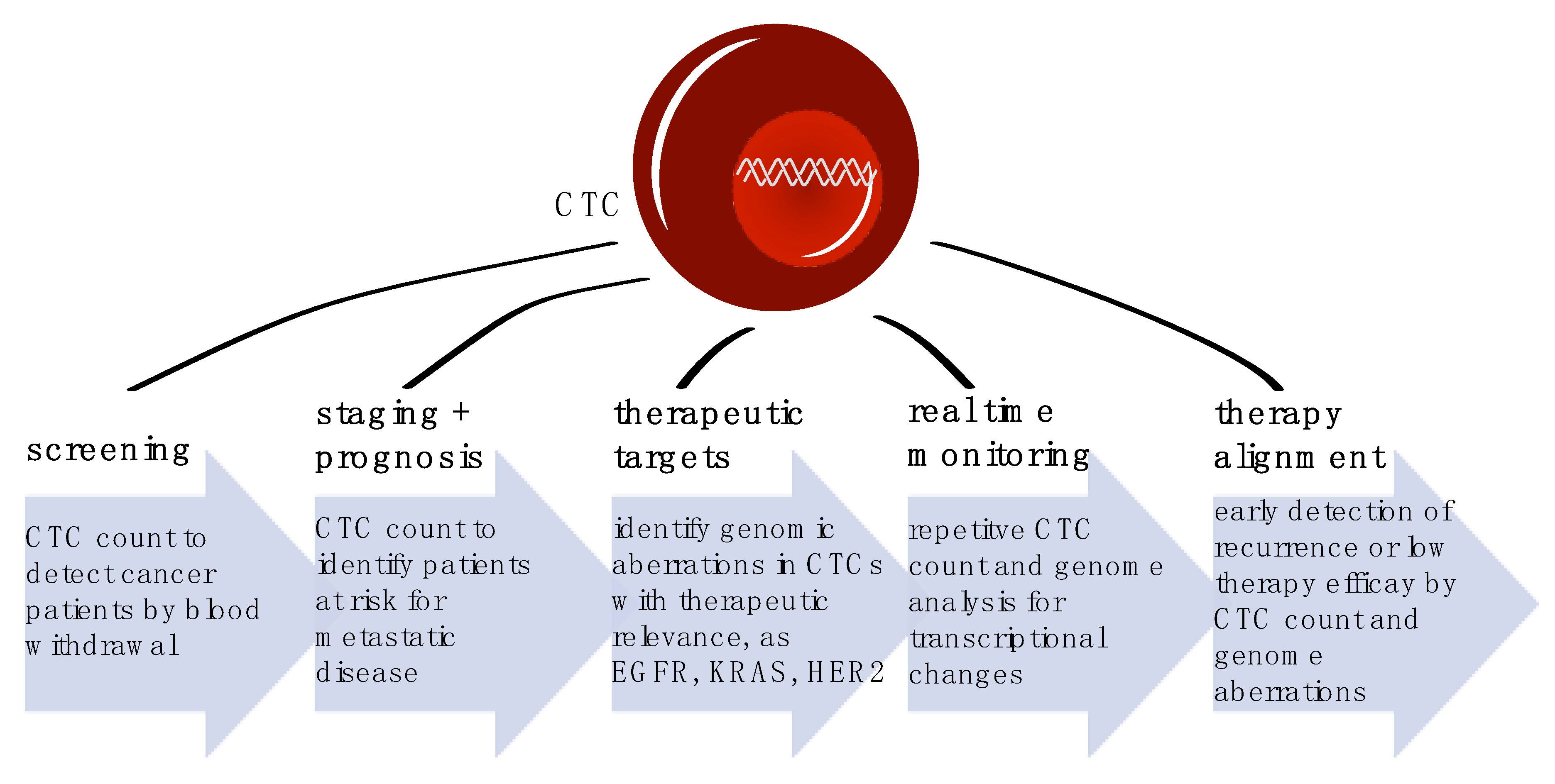
4. CTCs as Screening Tool
5. Cancer Staging and Patients’ Prognosis
6. Therapy Alignment
7. Longitudinal Therapy Monitoring
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantel, K.; Alix-Panabieres, C.; Riethdorf, S. Cancer micrometastases. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 6, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantel, K.; Brakenhoff, R.H. Dissecting the metastatic cascade. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaffer, C.L.; Weinberg, R.A. A perspective on cancer cell metastasis. Science 2011, 331, 1559–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joosse, S.A.; Gorges, T.M.; Pantel, K. Biology, detection, and clinical implications of circulating tumor cells. EMBO Mol. Med. 2015, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deneve, E.; Riethdorf, S.; Ramos, J.; Nocca, D.; Coffy, A.; Daurès, J.P.; Maudelonde, T.; Fabre, J.M.; Pantel, K.; Alix-Panabières, C. Capture of viable circulating tumor cells in the liver of colorectal cancer patients. Clin. Chem. 2013, 59, 1384–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.M.; Kim, G.H.; Jeon, H.K.; Kim, D.H.; Jeon, T.Y.; Park, D.Y.; Jeong, H.; Chun, W.J.; Kim, M.H.; Park, J.; et al. Circulating tumor cells detected by lab-on-a-disc: Role in early diagnosis of gastric cancer. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sefrioui, D.; Blanchard, F.; Toure, E.; Basile, P.; Beaussire, L.; Dolfus, C.; Perdrix, A.; Paresy, M.; Antonietti, M.; Iwanicki-Caron, I.; et al. Diagnostic value of CA19.9, circulating tumour DNA and circulating tumour cells in patients with solid pancreatic tumours. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 117, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenbaum, M.W.; Cauley, C.E.; Kulemann, B.; Liss, A.S.; Castillo, C.F.; Warshaw, A.L.; Lillemoe, K.D.; Thayer, S.P.; Pitman, M.B. Cytologic characteristics of circulating epithelioid cells in pancreatic disease. Cancer Cytopathol. 2017, 125, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, J.; Sanchez, L.; Nuñez, M.T.; Lu, M.; Castro, T.; Sharifi, H.R.; Ericsson, C. Screening Circulating Tumor Cells as a Noninvasive Cancer Test in 3388 Individuals from High-Risk Groups (ICELLATE2). Dis. Markers 2018, 2018, 4653109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Zhang, N.; Wang, S.; Shi, D.; Zhang, C.; Liu, K.; Xiong, B. Wedge-shaped microfluidic chip for circulating tumor cells isolation and its clinical significance in gastric cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2018, 16, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, Y.; Li, J.; Shi, C.; Wang, W.; Qu, X.; Xiong, M.; Sun, Y.; Li, D.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, D. Prognostic value of circulating tumor cells in the peripheral blood of patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. OncoTargets Ther. 2017, 10, 1363–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pernot, S.; Badoual, C.; Terme, M.; Castan, F.; Cazes, A.; Bouche, O.; Bennouna, J.; Francois, E.; Ghiringhelli, F.; De La Fouchardiere, C.; et al. Dynamic evaluation of circulating tumour cells in patients with advanced gastric and oesogastric junction adenocarcinoma: Prognostic value and early assessment of therapeutic effects. Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 79, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konczalla, L.; Ghadban, T.; Effenberger, K.E.; Wöstemeier, A.; Riethdorf, S.; Uzunoglu, F.G.; Izbicki, J.R.; Pantel, K.; Bockhorn, M.; Reeh, M. Prospective Comparison of the Prognostic Relevance of Circulating Tumor Cells in Blood and Disseminated Tumor Cells in Bone Marrow of a Single Patient’s Cohort With Esophageal Cancer. Ann. Surg. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeh, M.; Effenberger, K.E.; Koenig, A.M.; Riethdorf, S.; Eichstädt, D.; Vettorazzi, E.; Uzunoglu, F.G.; Vashist, Y.K.; Izbicki, J.R.; Pantel, K.; et al. Circulating Tumor Cells as a Biomarker for Preoperative Prognostic Staging in Patients With Esophageal Cancer. Ann. Surg. 2015, 261, 1124–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Effenberger, K.E.; Schroeder, C.; Hanssen, A.; Wolter, S.; Eulenburg, C.; Tachezy, M.; Gebauer, F.; Izbicki, J.R.; Pantel, K.; Bockhorn, M.; et al. Improved Risk Stratification by Circulating Tumor Cell Counts in Pancreatic Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 2844–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buscail, E.; Alix-Panabières, C.; Quincy, P.; Cauvin, T.; Chauvet, A.; Degrandi, O.; Caumont, C.; Verdon, S.; Lamrissi, I.; Moranvillier, I.; et al. High Clinical Value of Liquid Biopsy to Detect Circulating Tumor Cells and Tumor Exosomes in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Patients Eligible for Up-Front Surgery. Cancers 2019, 11, 1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amantini, C.; Morelli, M.B.; Nabissi, M.; Piva, F.; Marinelli, O.; Maggi, F.; Bianchi, F.; Bittoni, A.; Berardi, R.; Giampieri, R.; et al. Expression Profiling of Circulating Tumor Cells in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Patients: Biomarkers Predicting Overall Survival. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.D.; Yuan, X.; Xue, J.J.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Z.R.; Tong, J.D. Clinical significance of carcinoembryonic antigen-, cytokeratin 19-, or survivin-positive circulating tumor cells in the peripheral blood of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients treated with radiotherapy. Dis. Esophagus 2012, 25, 750–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brabender, J.; Vallböhmer, D.; Grimminger, P.; Hoffmann, A.C.; Ling, F.; Lurje, G.; Bollschweiler, E.; Schneider, P.M.; Hölscher, A.H.; Metzger, R. ERCC1 RNA expression in peripheral blood predicts minor histopathological response to neoadjuvant radio-chemotherapy in patients with locally advanced cancer of the esophagus. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2008, 12, 1815–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lankiewicz, S.; Zimmermann, S.; Hollmann, C.; Hillemann, T.; Greten, T.F. Circulating tumour cells as a predictive factor for response to systemic chemotherapy in patients with advanced colorectal cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2008, 2, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazzaniga, P.; Gradilone, A.; Petracca, A.; Nicolazzo, C.; Raimondi, C.; Iacovelli, R.; Naso, G.; Cortesi, E. Molecular markers in circulating tumour cells from metastatic colorectal cancer patients. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2010, 14, 2073–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, K.; Yamada, T.; Takahashi, G.; Iwai, T.; Ueda, K.; Kuriyama, S.; Koizumi, M.; Matsuda, A.; Shinji, S.; Ohta, R.; et al. Analysis of colorectal cancer-related mutations by liquid biopsy: Utility of circulating cell-free DNA and circulating tumor cells. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 3497–3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwatsuki, M.; Toyoshima, K.; Watanabe, M.; Hayashi, N.; Ishimoto, T.; Eto, K.; Iwagami, S.; Baba, Y.; Yoshida, N.; Hayashi, A.; et al. Frequency of HER2 expression of circulating tumour cells in patients with metastatic or recurrent gastrointestinal cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 109, 2829–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolodziejczyk, P.; Pituch-Noworolska, A.; Drabik, G.; Kulig, J.; Szczepanik, A.; Sierzega, M.; Gurda, A.; Popiela, T.; Zembala, M. The effects of preoperative chemotherapy on isolated tumour cells in the blood and bone marrow of gastric cancer patients. Br. J. Cancer 2007, 97, 589–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Neki, K.; Kawahara, H.; Watanabe, K.; Toyama, Y.; Akiba, T.; Yanaga, K. Usefulness of circulating tumor cells after preliminary chemotherapy for prediction of response to further anticancer therapy in patients with initially unresectable metastatic colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res. 2013, 33, 1769–1772. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, C.Y.; Uen, Y.H.; Tsai, H.L.; Chuang, S.C.; Hou, M.F.; Wu, D.C.; Juo, S.H.; Lin, S.R.; Wang, J.Y. Molecular detection of persistent postoperative circulating tumour cells in stages II and III colon cancer patients via multiple blood sampling: Prognostic significance of detection for early relapse. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 104, 1178–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tol, J.; Koopman, M.; Miller, M.C.; Tibbe, A.; Cats, A.; Creemers, G.J.; Vos, A.H.; Nagtegaal, I.D.; Terstappen, L.W.; Punt, C.J. Circulating tumour cells early predict progression-free and overall survival in advanced colorectal cancer patients treated with chemotherapy and targeted agents. Ann. Oncol. 2010, 21, 1006–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merker, J.D.; Oxnard, G.R.; Compton, C.; Diehn, M.; Hurley, P.; Lazar, A.J.; Lindeman, N.; Lockwood, C.M.; Rai, A.J.; Schilsky, R.L.; et al. Circulating Tumor DNA Analysis in Patients With Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology and College of American Pathologists Joint Review. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 1631–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaldson, J.; Park, B.H. Circulating Tumor DNA: Measurement and Clinical Utility. Annu. Rev. Med. 2018, 69, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Pei, R. High-purity capture of CTCs based on micro-beads enhanced isolation by size of epithelial tumor cells (ISET) method. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 102, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coumans, F.A.; van Dalum, G.; Beck, M.; Terstappen, L.W.M.M. Filtration parameters influencing circulating tumor cell enrichment from whole blood. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alix-Panabieres, C.; Mader, S.; Pantel, K. Epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity in circulating tumor cells. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 95, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paoletti, C.; Larios, J.M.; Muniz, M.C.; Aung, K.; Cannell, E.M.; Darga, E.P.; Kidwell, K.M.; Thomas, D.G.; Tokudome, N.; Brown, M.E.; et al. Heterogeneous estrogen receptor expression in circulating tumor cells suggests diverse mechanisms of fulvestrant resistance. Mol. Oncol. 2016, 10, 1078–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, J.; Carpenter, E.; Issadore, D. Detection and isolation of circulating exosomes and microvesicles for cancer monitoring and diagnostics using micro-/nano-based devices. Analyst 2016, 141, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastoraki, S.; Strati, A.; Tzanikou, E.; Chimonidou, M.; Politaki, E.; Voutsina, A.; Psyrri, A.; Georgoulias, V.; Lianidou, E. ESR1 Methylation: A Liquid Biopsy-Based Epigenetic Assay for the Follow-up of Patients with Metastatic Breast Cancer Receiving Endocrine Treatment. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 1500–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler, A.; Cayrefourcq, L.; Mazel, M.; Alix-Panabières, C. EpCAM-Independent Enrichment and Detection of Viable Circulating Tumor Cells Using the EPISPOT Assay. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1634, 263–276. [Google Scholar]
- Eyer, K.; Doineau, R.C.L.; Castrillon, C.E.; Briseño-Roa, L.; Menrath, V.; Mottet, G.; England, P.; Godina, A.; Brient-Litzler, E.; Nizak, C.; et al. Single-cell deep phenotyping of IgG-secreting cells for high-resolution immune monitoring. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 977–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, W.J.; Matera, J.; Miller, M.C.; Repollet, M.; Connelly, M.C.; Rao, C.; Tibbe, A.G.J.; Uhr, J.W.; Terstappen, L.W.M.M. Tumor cells circulate in the peripheral blood of all major carcinomas but not in healthy subjects or patients with nonmalignant diseases. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 6897–6904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, W.J.; Terstappen, L.W. CCR 20th Anniversary Commentary: Paving the Way for Circulating Tumor Cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 2883–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagwat, N.; Dulmage, K.; Pletcher, C.H., Jr.; Wang, L.; DeMuth, W.; Sen, M.; Balli, D.; Yee, S.S.; Sa, S.; Tong, F.; et al. An integrated flow cytometry-based platform for isolation and molecular characterization of circulating tumor single cells and clusters. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGranahan, N.; Swanton, C. Clonal Heterogeneity and Tumor Evolution: Past, Present, and the Future. Cell 2017, 168, 613–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, D.F. Biomarker validation and testing. Mol. Oncol. 2015, 9, 960–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettegowda, C.; Sausen, M.; Leary, R.J.; Kinde, I.; Wang, Y.; Agrawal, N.; Bartlett, B.R.; Wang, H.; Luber, B.; Alani, R.M.; et al. Detection of circulating tumor DNA in early- and late-stage human malignancies. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 224ra24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchoa Guimaraes, C.T.; Ferreira Martins, N.N.; da Silva Oliveira, K.C.; Almeida, C.M.; Pinheiro, T.M.; Gigek, C.O.; de Araújo Cavallero, S.R.; Assumpção, P.P.; Cardoso Smith, M.A.; Burbano, R.R.; et al. Liquid biopsy provides new insights into gastric cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 15144–15156. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J.D.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Thoburn, C.; Afsari, B.; Danilova, L.; Douville, C.; Javed, A.A.; Wong, F.; Mattox, A.; et al. Detection and localization of surgically resectable cancers with a multi-analyte blood test. Science 2018, 359, 926–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, D.; Nahm, C.; Chua, T.; Gill, A.; Mittal, A.; de Reuver, P.; Samra, J. Circulating and disseminated tumor cells in pancreatic cancer and their role in patient prognosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 107223–107236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Ge, H.Y. Micrometastasis in gastric cancer. Cancer Lett. 2013, 336, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuno, H.; Zacharakis, E.; Aziz, O.; Rao, C.; Deeba, S.; Paraskeva, P.; Ziprin, P.; Athanasiou, T.; Darzi, A. Does the presence of circulating tumor cells in the venous drainage of curative colorectal cancer resections determine prognosis? A meta-analysis. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2008, 15, 3083–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tie, J.; Cohen, J.D.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Christie, M.; Simons, K.; Elsaleh, H.; Kosmider, S.; Wong, R.; Yip, D.; et al. Serial circulating tumour DNA analysis during multimodality treatment of locally advanced rectal cancer: A prospective biomarker study. Gut 2019, 68, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kin, C.; Kidess, E.; Poultsides, G.A.; Visser, B.C.; Jeffery, S.S. Colorectal cancer diagnostics: Biomarkers, cell-free DNA, circulating tumor cells and defining heterogeneous populations by single-cell analysis. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2013, 13, 581–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pectasides, E.; Stachler, M.D.; Derks, S.; Liu, Y.; Maron, S.; Islam, M.; Alpert, L.; Kwak, H.; Kindler, H.; Polite, B.; et al. Genomic Heterogeneity as a Barrier to Precision Medicine in Gastroesophageal Adenocarcinoma. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoeppner, J.; Lordick, F.; Brunner, T.; Glatz, T.; Bronsert, P.; Röthling, N.; Schmoor, C.; Lorenz, D.; Ell, C.; Hopt, U.T.; et al. ESOPEC: Prospective randomized controlled multicenter phase III trial comparing perioperative chemotherapy (FLOT protocol) to neoadjuvant chemoradiation (CROSS protocol) in patients with adenocarcinoma of the esophagus (NCT02509286). BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Author, Year | Entity | No. of Patients | Detection Method | CTC No. (%) | End-Point | Clinical Significance | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| screening | Kang et al., 2017 [7] | Gastric cancer | 116 | FAST | 99 (85) | - | - |
| Sefrioui et al., 2017 [8] | Pancreatic cancer | 49 | size-based Screencell Cyto filtration | 33 (67) | - | no | |
| Rosenbaum et al., 2017 [9] | Pancreatic cancer | 171 | CellSearch | 115 (67) | - | No, low specificity for PDAC (63%) | |
| Castro et al., 2018 [10] | Healthy people | 3388 | CellSearch | - | - | Ongoing ICELLATE2 study | |
| Yang et al., 2018 [11] | Gastric cancer | 40 | Microfluidic chip | 20 (75) | - | yes | |
| staging & prognosis prediction | Qiao et al., 2017 [12] | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | 103 | FACS | 47/59 (80) | OS; PFS | yes |
| Pernot et al., 2017 [13] | Gastric and esopahgeal junction cancer | 60 | CellSearch | - | OS; PFS; treatment monitoring | yes | |
| Konczalla et al., 2019 [14] | Esophageal cancer | 76 | CellSearch | 15 (20) | OS; PFS | yes, CTC count as predictive marker in non-metastatic disease | |
| Reeh et al., 2015 [15] | Esophageal cancer | 100 | CellSearch | 18 (18) | OS; PFS | yes | |
| Effenberger et al., 2018 [16] | Pancreatic cancer | 69 | CellSearch | 23 (33) | OS; PFS | yes | |
| Buscail et al., 2019 [17] | Pancreatic cancer | 22 PDAC 28 healthy controls | CellSearch/RosettSep/Oncoquick | CellSearch: Peripheral 2 (22); portal vein 5 (22) | OS; PFS | yes, combination of two sampling sites and combination with tumor exosome analysis are sensitive prognosis prediction tools | |
| Amantini et al., 2019 [18] | Pancreatic cancer | 20 | ScreenCell | 20 (20) | OS; PFS; molecular expression pattern | yes | |
| therapy alignment &monitorig | |||||||
| Yin et al., 2012 [19] | Esophageal cancer | 72 | rT-PCR | - | Radiotherapy (RT) response | Yes, CTC count variation due to RT correlated with response rate | |
| Brabender et al., 200 [20] | Esophageal cancer | 29 | rT-PCR | - | - | Yes, reduced chemotherapy response in patients with ERCC1 positive CTCs | |
| Lankiewicz et al., 2008 [21] | Colorectal cancer | 34 | Multiplex PCR | 20 (59) | - | Yes, CTC cound predicts chemotherapy response, moreover EGFR status of CTCs could predict likelihood of targeted therapy response | |
| Gazzaniga et al., 2010 [22] | Colorectal cancer | 40 | CELLection Dynabeads® | 27 (68) | PFS; OS; molecular expression pattern | Yes, patients with ALDH1, survivin and MRP5 positive CTCs had significantly shorter PFS | |
| Takeda et al., 2019 [23] | Colorectal cancer | 34 | Microfluidic chips | 34 | - | Comparison of mutational status of CTCs, ctDNA and primary tumor tissue revealed great heterogeneity | |
| Iwatsuki et al., 2013 [24] | Gastric cancer | 87 | CellSearch | 62 (71) | - | Yes, 36% of discordant HER2 status between primary tumor and CTCs, predict likelihood of targeted therapy response | |
| Kolodziejczyk et al., 2007 [25] | Gastric cancer | 32 | FACS | - | - | Yes, neo-adjuvant chemotherapy significantly reduces CTC count in responders | |
| Neki et al., 2013 [26] | Colorectal cancer | 14 | CellSearch | 14; 4 (29) after chemotherapy | PFS; OS; | Yes, CTC negative patients after chemotherapy had significantly better treatment response | |
| Lu et al., 2011 [27] | Colorectal cancer | 141 | rT-PCR | 141 (100) | PFS; OS | Yes, CTC persistence after surgical resection was a significant marker for early recurrence | |
| Tol et al., 2009 [28] | Colorectal cancer | 467 | CellSearch | 467 (100) | PFS; OS; | CTC count provides additional information to CT imaging for early recurrence monitoring |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Konczalla, L.; Wöstemeier, A.; Kemper, M.; Karstens, K.-F.; Izbicki, J.; Reeh, M. Clinical Significance of Circulating Tumor Cells in Gastrointestinal Carcinomas. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10040192
Konczalla L, Wöstemeier A, Kemper M, Karstens K-F, Izbicki J, Reeh M. Clinical Significance of Circulating Tumor Cells in Gastrointestinal Carcinomas. Diagnostics. 2020; 10(4):192. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10040192
Chicago/Turabian StyleKonczalla, Leonie, Anna Wöstemeier, Marius Kemper, Karl-Frederik Karstens, Jakob Izbicki, and Matthias Reeh. 2020. "Clinical Significance of Circulating Tumor Cells in Gastrointestinal Carcinomas" Diagnostics 10, no. 4: 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10040192
APA StyleKonczalla, L., Wöstemeier, A., Kemper, M., Karstens, K.-F., Izbicki, J., & Reeh, M. (2020). Clinical Significance of Circulating Tumor Cells in Gastrointestinal Carcinomas. Diagnostics, 10(4), 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10040192






