Urinary MicroRNA-21-5p as Potential Biomarker of Interstitial Fibrosis and Tubular Atrophy (IFTA) in Kidney Transplant Recipients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. MicroRNA Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
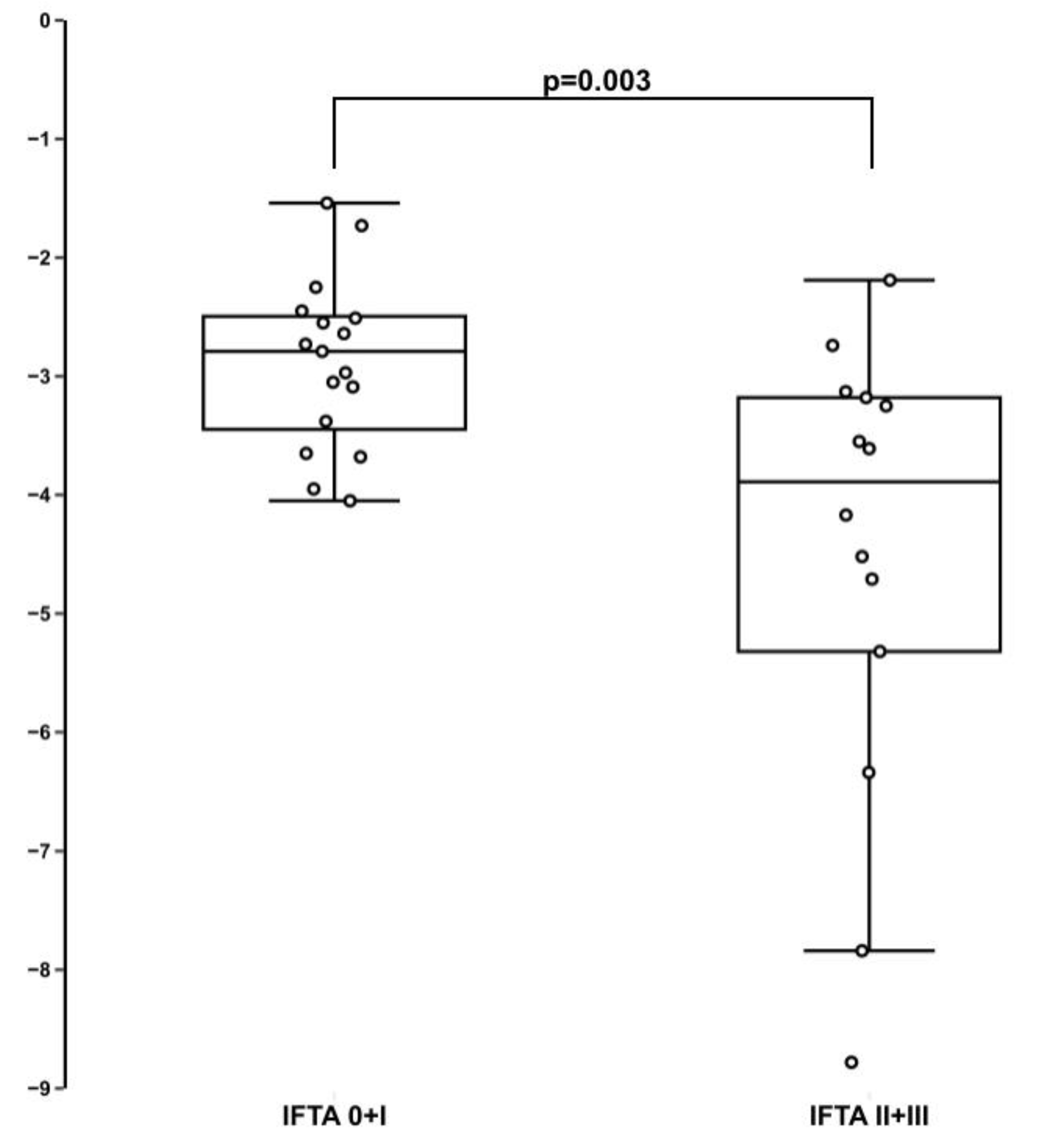
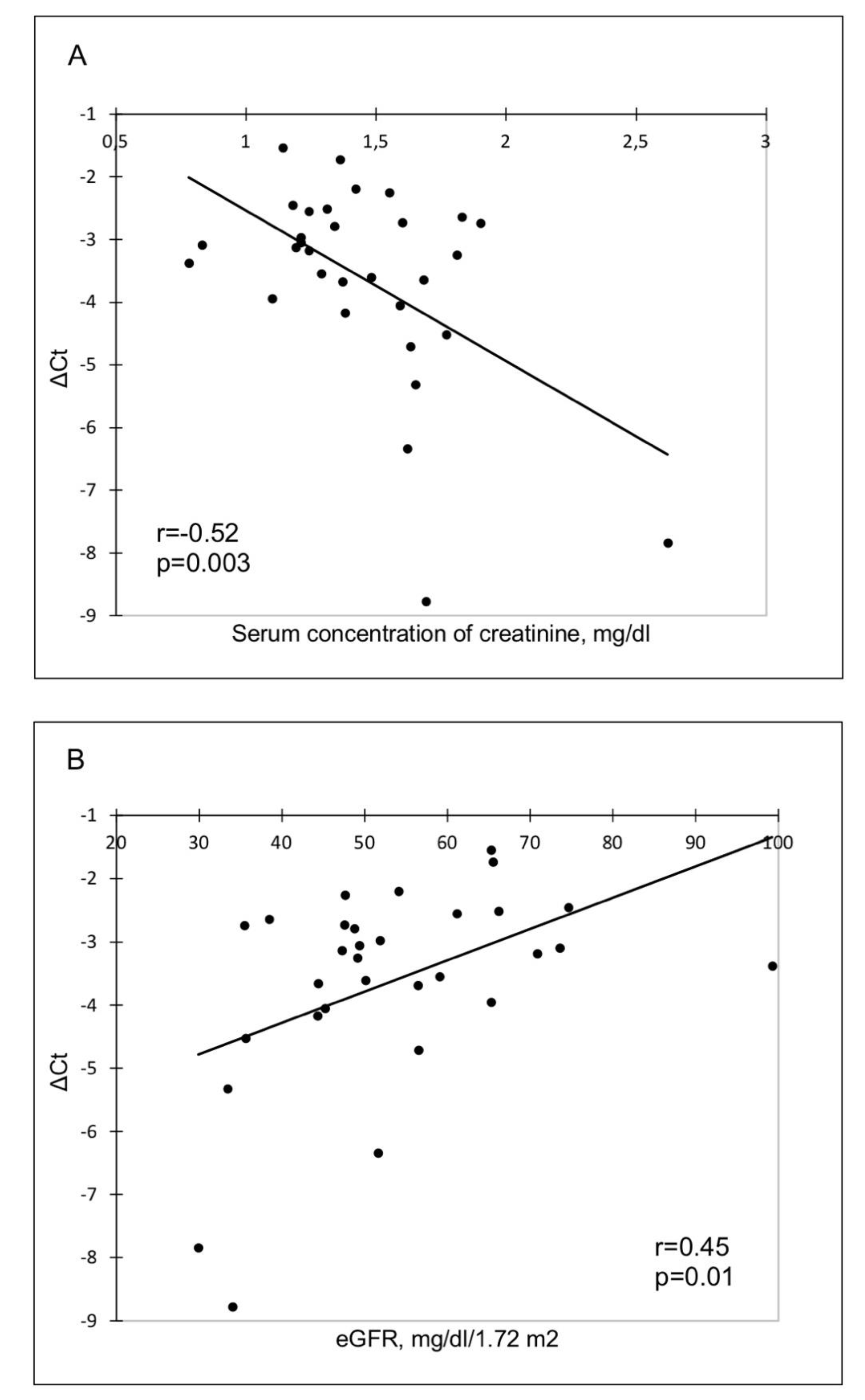
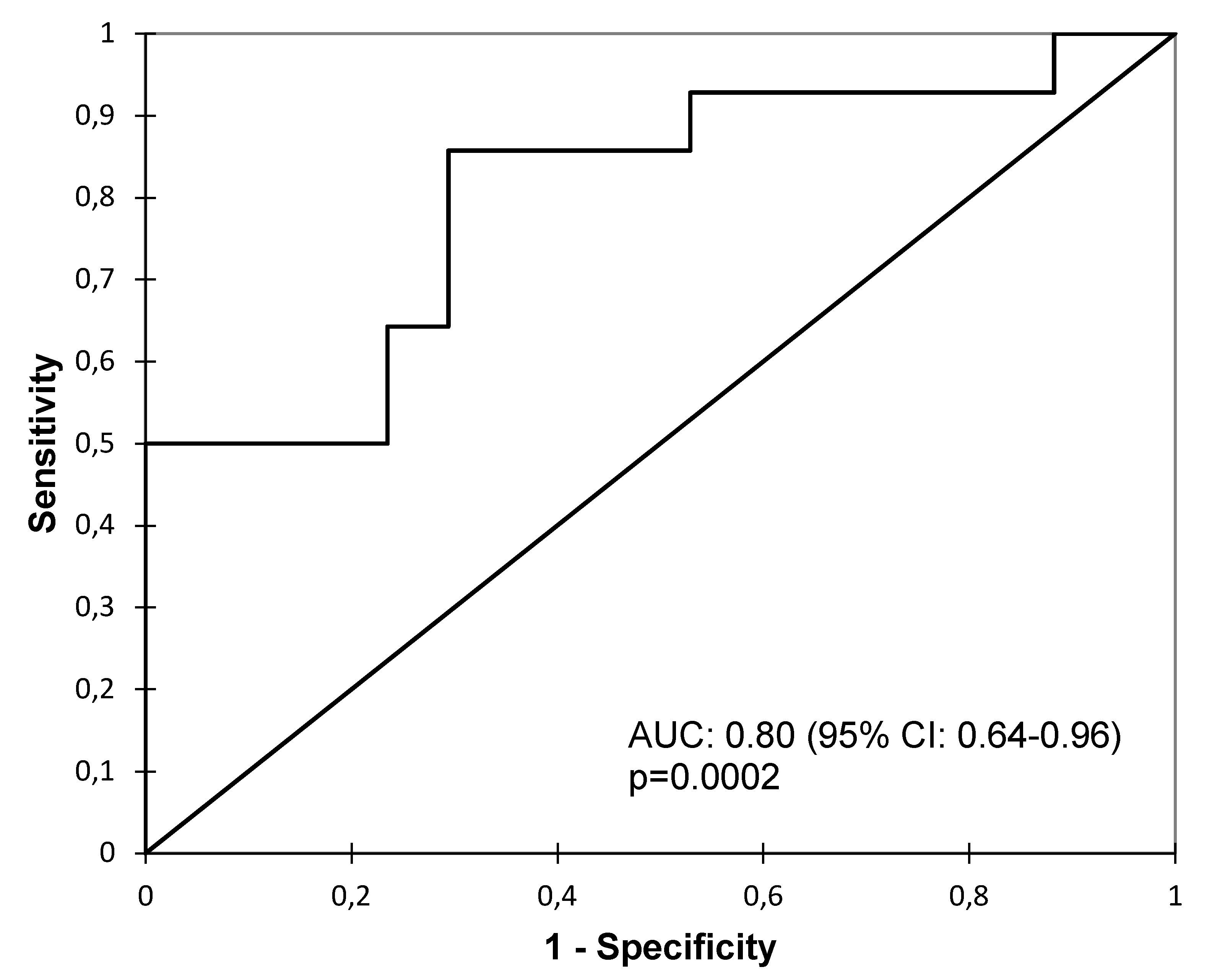
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Voora, S.; Adey, D.B. Management of Kidney Transplant Recipients by General Nephrologists: Core Curriculum 2019. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2019, 73, 866–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racusen, L.C.; Regele, H. The pathology of chronic allograft dysfunction. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, R.J.; Weng, F.L.; Kandula, P. Acute and Chronic Allograft Dysfunction in Kidney Transplant Recipients. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 100, 487–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual, J.; Perez-Saez, M.J.; Mir, M.; Crespo, M. Chronic renal allograft injury: Early detection, accurate diagnosis and management. Transplant. Rev. 2012, 26, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chand, S.; Atkinson, D.; Collins, C.; Briggs, D.; Ball, S.; Sharif, A.; Skordilis, K.; Vydianath, B.; Neil, D.; Borrows, R. The Spectrum of Renal Allograft Failure. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roufosse, C.; Simmonds, N.; Clahsen-van Groningen, M.; Haas, M.; Henriksen, K.J.; Horsfield, C.; Loupy, A.; Mengel, M.; Perkowska-Ptasinska, A.; Rabant, M.; et al. A 2018 Reference Guide to the Banff Classification of Renal Allograft Pathology. Transplantation 2018, 102, 1795–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, B.M.; Haylor, J. Biological pathways and potential targets for prevention and therapy of chronic allograft nephropathy. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 482438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giral, M.; Renaudin, K.; Naesens, M.; Luning, R.; Anglicheau, D.; Morelon, E.; Huneau, A.; Paul, C.; Brouard, S.; Couvrat-Desvergnes, G.; et al. The 1-year Renal Biopsy Index: A scoring system to drive biopsy indication at 1-year post-kidney transplantation. Transpl. Int. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, L.K.; Nankivell, B.J.; Chapman, J.R. Surveillance protocol kidney transplant biopsies: Their evolving role in clinical practice. Am. J. Transplant. 2011, 11, 1570–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, T.A.; Chandran, S.; Burger, I.M.; Zhang, C.A.; Goldstein, R.B. Complications of Ultrasound-Guided Renal Transplant Biopsies. Am. J. Transplant. 2016, 16, 1298–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brachemi, S.; Bollee, G. Renal biopsy practice: What is the gold standard? World J. Nephrol. 2014, 3, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scian, M.J.; Maluf, D.G.; David, K.G.; Archer, K.J.; Suh, J.L.; Wolen, A.R.; Mba, M.U.; Massey, H.D.; King, A.L.; Gehr, T.; et al. MicroRNA profiles in allograft tissues and paired urines associate with chronic allograft dysfunction with IF/TA. Am. J. Transplant. 2011, 11, 2110–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Vrie, M.; Deegens, J.K.; Eikmans, M.; van der Vlag, J.; Hilbrands, L.B. Urinary MicroRNA as Biomarker in Renal Transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2017, 17, 1160–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staszel, T.; Zapala, B.; Polus, A.; Sadakierska-Chudy, A.; Kiec-Wilk, B.; Stepien, E.; Wybranska, I.; Chojnacka, M.; Dembinska-Kiec, A. Role of microRNAs in endothelial cell pathophysiology. Pol. Arch. Med. Wewn 2011, 121, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Wan, X.; Ruan, Q. The MicroRNA-21 in Autoimmune Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Akker, E.K.; Dor, F.J.; JN, I.J.; de Bruin, R.W. MicroRNAs in Kidney Transplantation: Living up to Their Expectations? J. Transplant. 2015, 2015, 354826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Glowacki, F.; Savary, G.; Gnemmi, V.; Buob, D.; Van der Hauwaert, C.; Lo-Guidice, J.M.; Bouye, S.; Hazzan, M.; Pottier, N.; Perrais, M.; et al. Increased circulating miR-21 levels are associated with kidney fibrosis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennino, M.F.; Buob, D.; Van der Hauwaert, C.; Gnemmi, V.; Jomaa, Z.; Pottier, N.; Savary, G.; Drumez, E.; Noel, C.; Cauffiez, C.; et al. miR-21-5p renal expression is associated with fibrosis and renal survival in patients with IgA nephropathy. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakhia, R.; Hajarnis, S.; Williams, D.; Aboudehen, K.; Yheskel, M.; Xing, C.; Hatley, M.E.; Torres, V.E.; Wallace, D.P.; Patel, V. MicroRNA-21 Aggravates Cyst Growth in a Model of Polycystic Kidney Disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 2319–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, X. Key Genes Involved in Diabetic Nephropathy Investigated by Microarray Analysis. J. Comput. Biol. 2019, 26, 1438–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nalewajska, M.; Gurazda, K.; Styczynska-Kowalska, E.; Marchelek-Mysliwiec, M.; Pawlik, A.; Dziedziejko, V. The Role of MicroRNAs in Selected Forms of Glomerulonephritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci 2019, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, B.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, R.; Sun, M.; Sun, M.; Yuan, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, X.; Chen, Z.; et al. MicroRNA21 contributes to renal cell carcinoma cell invasiveness and angiogenesis via the PDCD4/cJun (AP1) signalling pathway. Int. J. Oncol. 2020, 56, 178–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalid, U.; Newbury, L.J.; Simpson, K.; Jenkins, R.H.; Bowen, T.; Bates, L.; Sheerin, N.S.; Chavez, R.; Fraser, D.J. A urinary microRNA panel that is an early predictive biomarker of delayed graft function following kidney transplantation. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zununi Vahed, S.; Poursadegh Zonouzi, A.; Ghanbarian, H.; Ghojazadeh, M.; Samadi, N.; Omidi, Y.; Ardalan, M. Differential expression of circulating miR-21, miR-142-3p and miR-155 in renal transplant recipients with impaired graft function. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2017, 49, 1681–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegall, M.D.; Park, W.D.; Larson, T.S.; Gloor, J.M.; Cornell, L.D.; Sethi, S.; Dean, P.G.; Prieto, M.; Amer, H.; Textor, S.; et al. The histology of solitary renal allografts at 1 and 5 years after transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2011, 11, 698–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egidi, M.G.; Cochetti, G.; Guelfi, G.; Zampini, D.; Diverio, S.; Poli, G.; Mearini, E. Stability Assessment of Candidate Reference Genes in Urine Sediment of Prostate Cancer Patients for miRNA Applications. Dis. Mark. 2015, 2015, 973597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrami, C.; Simpson, K.; Jesky, M.; Wonnacott, A.; Carrington, C.; Holmans, P.; Newbury, L.; Jenkins, R.; Ashdown, T.; Dayan, C.; et al. Association of Elevated Urinary miR-126, miR-155, and miR-29b with Diabetic Kidney Disease. Am. J. Pathol. 2018, 188, 1982–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Marian, C.; Makambi, K.H.; Kosti, O.; Kallakury, B.V.; Loffredo, C.A.; Zheng, Y.L. MicroRNA-9 as potential biomarker for breast cancer local recurrence and tumor estrogen receptor status. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, I.O.; Lerman, L.O. Urinary microRNA in kidney disease: Utility and roles. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2019, 316, F785–F793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoeven, J.; Boer, K.; Van Schaik, R.H.N.; Manintveld, O.C.; Huibers, M.M.H.; Baan, C.C.; Hesselink, D.A. Liquid Biopsies to Monitor Solid Organ Transplant Function: A Review of New Biomarkers. Ther. Drug Monit. 2018, 40, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Dov, I.Z.; Muthukumar, T.; Morozov, P.; Mueller, F.B.; Tuschl, T.; Suthanthiran, M. MicroRNA sequence profiles of human kidney allografts with or without tubulointerstitial fibrosis. Transplantation 2012, 94, 1086–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chau, B.N.; Xin, C.; Hartner, J.; Ren, S.; Castano, A.P.; Linn, G.; Li, J.; Tran, P.T.; Kaimal, V.; Huang, X.; et al. MicroRNA-21 promotes fibrosis of the kidney by silencing metabolic pathways. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 121ra118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, H.; Li, X.; Wu, Q.; Hao, L. Overexpression of microRNA-21 mediates Ang II-induced renal fibrosis by activating the TGF-beta1/Smad3 pathway via suppressing PPARalpha. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 141, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Xu, T.; Chen, Y.; Qu, W.; Sun, D.; Song, X.; Yuan, Q.; Yao, L. Pioglitazone attenuates kidney fibrosis via miR-21-5p modulation. Life Sci. 2019, 232, 116609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandenbussche, C.; Van der Hauwaert, C.; Dewaeles, E.; Franczak, J.; Hennino, M.F.; Gnemmi, V.; Savary, G.; Tavernier, Q.; Nottet, N.; Paquet, A.; et al. Tacrolimus-induced nephrotoxicity in mice is associated with microRNA deregulation. Arch. Toxicol. 2018, 92, 1539–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zmijewska, A.; Zhi, D.; Mannon, R.B. Cyclosporine-mediated allograft fibrosis is associated with micro-RNA-21 through AKT signaling. Transpl. Int. 2015, 28, 232–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, N.; Ghosh-Choudhury, N.; Kasinath, B.S.; Choudhury, G.G. TGFbeta-stimulated microRNA-21 utilizes PTEN to orchestrate AKT/mTORC1 signaling for mesangial cell hypertrophy and matrix expansion. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClelland, A.D.; Herman-Edelstein, M.; Komers, R.; Jha, J.C.; Winbanks, C.E.; Hagiwara, S.; Gregorevic, P.; Kantharidis, P.; Cooper, M.E. miR-21 promotes renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy by targeting PTEN and SMAD7. Clin. Sci. 2015, 129, 1237–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zununi Vahed, S.; Omidi, Y.; Ardalan, M.; Samadi, N. Dysregulation of urinary miR-21 and miR-200b associated with interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy (IFTA) in renal transplant recipients. Clin. Biochem. 2017, 50, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| IFTA 0 + I (n = 17) | IFTA II + III (n = 14) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age at biopsy, years, mean (SD) | 54.76 (10.74) | 48.38 (14.95) | 0.18 |
| Male sex, n (%) | 12 (70.59) | 8 (57.14) | 0.31 |
| Body mass index, kg/m2, mean (SD) | 25.48 (3.48) | 23.58 (4.06) | 0.18 |
| First transplantation, n (%) | 15 (88.24) | 14 (100.00) | 0.49 |
| Cold ischemia time, min, mean (SD) | 1249.33 (420.32) | 1262.14 (530.34) | 0.95 |
| Warm ischemia time, min, mean (SD) | 35.08 (7.47) | 32.08 (5.33) | 0.25 |
| Delayed graft function, n (%) | 5 (29.41) | 5 (35.71) | 0.71 |
| Time of biopsy after transplantation | 0.82 | ||
| 1 year, n (%) | 9 (52.94) | 8 (57.14) | |
| 2 years, n (%) | 8 (47.06) | 6 (42.86) | |
| Serum creatinine, mg/dl, mean (SD) | 1.31 (0.28) | 1.62 (0.35) | 0.01 |
| eGFR (CKD-EPI), mg/dl/1.72 m2, mean (SD) | 58.82 (14.99) | 46.50 (11.77) | 0.02 |
| Human leukocyte antigen (HLA) mismatches, mean (Q1–Q3) | 3.59 (2.50–5.00) | 3.29 (3.00–4.00) | 0.52 |
| Immunosuppressive therapy (tacrolimus, mycophenolate mofetil and corticosteroids), n (%) | 17 (100) | 14 (100) | 1.00 |
| Blood tacrolimus level, ng/mL, mean (SD) | 6.02 (1.79) | 5.72 (1.43) | 0.48 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gniewkiewicz, M.S.; Paszkowska, I.; Gozdowska, J.; Czerwinska, K.; Sadowska-Jakubowicz, A.; Deborska-Materkowska, D.; Perkowska-Ptasinska, A.; Kosieradzki, M.; Durlik, M. Urinary MicroRNA-21-5p as Potential Biomarker of Interstitial Fibrosis and Tubular Atrophy (IFTA) in Kidney Transplant Recipients. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10020113
Gniewkiewicz MS, Paszkowska I, Gozdowska J, Czerwinska K, Sadowska-Jakubowicz A, Deborska-Materkowska D, Perkowska-Ptasinska A, Kosieradzki M, Durlik M. Urinary MicroRNA-21-5p as Potential Biomarker of Interstitial Fibrosis and Tubular Atrophy (IFTA) in Kidney Transplant Recipients. Diagnostics. 2020; 10(2):113. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10020113
Chicago/Turabian StyleGniewkiewicz, Michal S., Izabela Paszkowska, Jolanta Gozdowska, Katarzyna Czerwinska, Anna Sadowska-Jakubowicz, Dominika Deborska-Materkowska, Agnieszka Perkowska-Ptasinska, Maciej Kosieradzki, and Magdalena Durlik. 2020. "Urinary MicroRNA-21-5p as Potential Biomarker of Interstitial Fibrosis and Tubular Atrophy (IFTA) in Kidney Transplant Recipients" Diagnostics 10, no. 2: 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10020113
APA StyleGniewkiewicz, M. S., Paszkowska, I., Gozdowska, J., Czerwinska, K., Sadowska-Jakubowicz, A., Deborska-Materkowska, D., Perkowska-Ptasinska, A., Kosieradzki, M., & Durlik, M. (2020). Urinary MicroRNA-21-5p as Potential Biomarker of Interstitial Fibrosis and Tubular Atrophy (IFTA) in Kidney Transplant Recipients. Diagnostics, 10(2), 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10020113





