Interrater Reliability of 99mTc-DMSA Scintigraphy Performed as Planar Scan vs. SPECT/Low Dose CT for Diagnosing Renal Scarring in Children
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
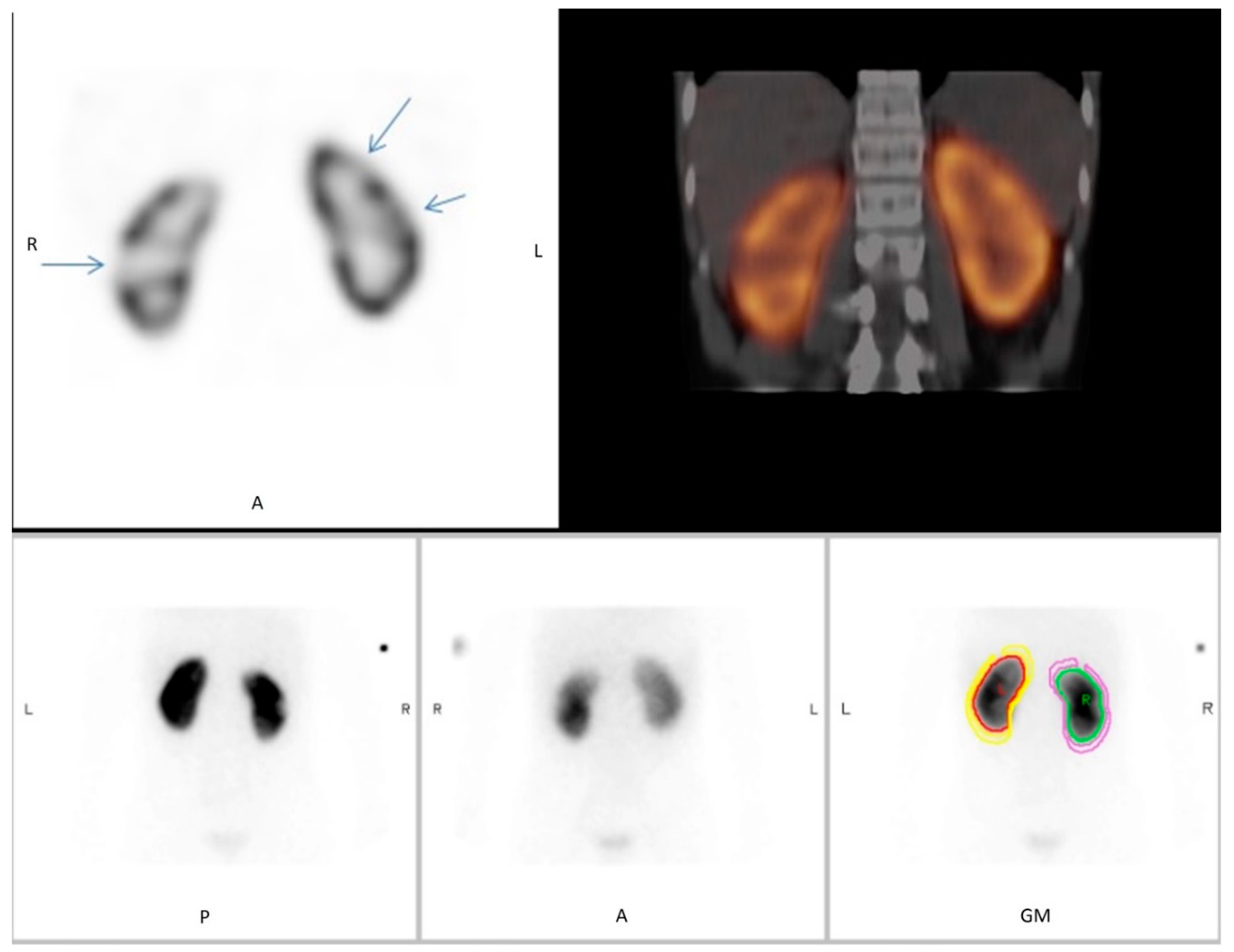
2.1. Scan Protocols and Reconstruction Methods
2.2. DMSA Scintigraphy Readings
2.3. Statistics
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lim, R. Vesicoureteral reflux and urinary tract infection: Evolving practices and current controversies in pediatric imaging. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2009, 192, 1197–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendichovszky, I.; Solar, B.T.; Smeulders, N.; Easty, M.; Biassoni, L. Nuclear medicine in pediatric nephro-urology: An overview. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2017, 47, 204–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piepsz, A.; Colarinha, P.; Gordon, I.; Hahn, K.; Olivier, P.; Roca, I.; Sixt, R.; van Velzen, J. Revised Guidelines on 99mTc-DMSA Scintigraphy in Children. European Association of Nuclear Medicine. Available online: https://eanm.org/publications/guidelines/gl_paed_dmsa_scin.pdf (accessed on 3 October 2009).
- Kim, G.E.; Park, J.H.; Kim, J.S.; Won, K.S.; Kim, H.W. Comparison of Tc-99m DMSA renal planar scan and SPECT for detection of cortical defects in infants with suspected acute pyelonephritis. Indian J. Pediatr. 2019, 86, 797–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagni, B.; Orsolon, P.; Fattori, A.; Guerra, U.P. Renal SPECT with Tc-99m DMSA in children with upper urinary tract infections using a triple-headed gamma camera. Clin. Nucl. Med. 1997, 22, 838–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenner, M.; Bonta, D.; Eslamy, H.; Ziessman, H.A. Comparison of 99mTc-DMSA dual-head SPECT versus high-resolution parallel-hole planar imaging for the detection of renal cortical defects. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2009, 193, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association of Nuclear Medicine Dosage Calculator. Available online: https://www.eanm.org/publications/dosage-calculator (accessed on 1 November 2008).
- Reichkendler, M.H.; Berg, R.M.G.; de Nijs, R.; Nørgaard, H.; Schmidt, I.M.; Borgwardt, L. Planar scan vs. SPECT/low-dose CT for estimating split renal function by 99mTc-DMSA scintigraphy in children. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2020, 47, 729–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everaert, H.; Flamen, P.; Franken, P.R.; Peeters, P.; Bossuyt, A.; Piepsz, A. 99Tcm-DMSA renal scintigraphy for acute pyelonephritis in adults: Planar and/or SPET imaging? Nucl. Med. Commun. 1996, 17, 884–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beslic, N.; Milardovic, R.; Sadija, A.; Dzananovic, L.; Cavaljuga, S. Interobserver variability in interpretation of planar and SPECT Tc-99m-DMSA renal scintigraphy in children. Acta Inform. Med. 2017, 25, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Reader 1 | Reader 2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Planar Scintigraphy | ||
| Evidence of renal scarring | 20 (43%) | 7 (15%) |
| No evidence of renal scarring | 26 (57%) | 39 (85%) |
| Unconfident about diagnosis | 16 (35%) | 20 (43%) |
| SPECT/ldCT | ||
| Evidence of renal scarring | 13 (28%) | 12 (26%) |
| No evidence of renal scarring | 33 (72%) | 34 (74%) |
| Unconfident about diagnosis | 1 (2%) | 4 (9%) |
| Planar Scintigraphy vs. SPECT/ldCT | ||
| Concordant diagnoses between modalities | 37 (85%) | 35 (76%) |
| Evidence of renal scarring | 12 (32%) | 4 (11%) |
| No evidence of renal scarring | 25 (68%) | 31 (89%) |
| Discordant diagnoses between modalities | 9 (15%) | 11 (24%) |
| Evidence of renal scarring on planar scintigraphy No evidence on SPECT/ldCT | 8 (89%) | 3 (27%) |
| No evidence of renal scarring on planar scintigraphy Evidence on SPECT/ldCT | 1 (11%) | 8 (73%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Einarsdóttir, H.S.; Berg, R.M.G.; Borgwardt, L. Interrater Reliability of 99mTc-DMSA Scintigraphy Performed as Planar Scan vs. SPECT/Low Dose CT for Diagnosing Renal Scarring in Children. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 1101. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10121101
Einarsdóttir HS, Berg RMG, Borgwardt L. Interrater Reliability of 99mTc-DMSA Scintigraphy Performed as Planar Scan vs. SPECT/Low Dose CT for Diagnosing Renal Scarring in Children. Diagnostics. 2020; 10(12):1101. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10121101
Chicago/Turabian StyleEinarsdóttir, Hrefna Sæunn, Ronan Martin Griffin Berg, and Lise Borgwardt. 2020. "Interrater Reliability of 99mTc-DMSA Scintigraphy Performed as Planar Scan vs. SPECT/Low Dose CT for Diagnosing Renal Scarring in Children" Diagnostics 10, no. 12: 1101. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10121101
APA StyleEinarsdóttir, H. S., Berg, R. M. G., & Borgwardt, L. (2020). Interrater Reliability of 99mTc-DMSA Scintigraphy Performed as Planar Scan vs. SPECT/Low Dose CT for Diagnosing Renal Scarring in Children. Diagnostics, 10(12), 1101. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10121101





