Primary Central Nervous System Lymphomas: A Diagnostic Overview of Key Histomorphologic, Immunophenotypic, and Genetic Features
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Epidemiology
3. Clinical Presentation
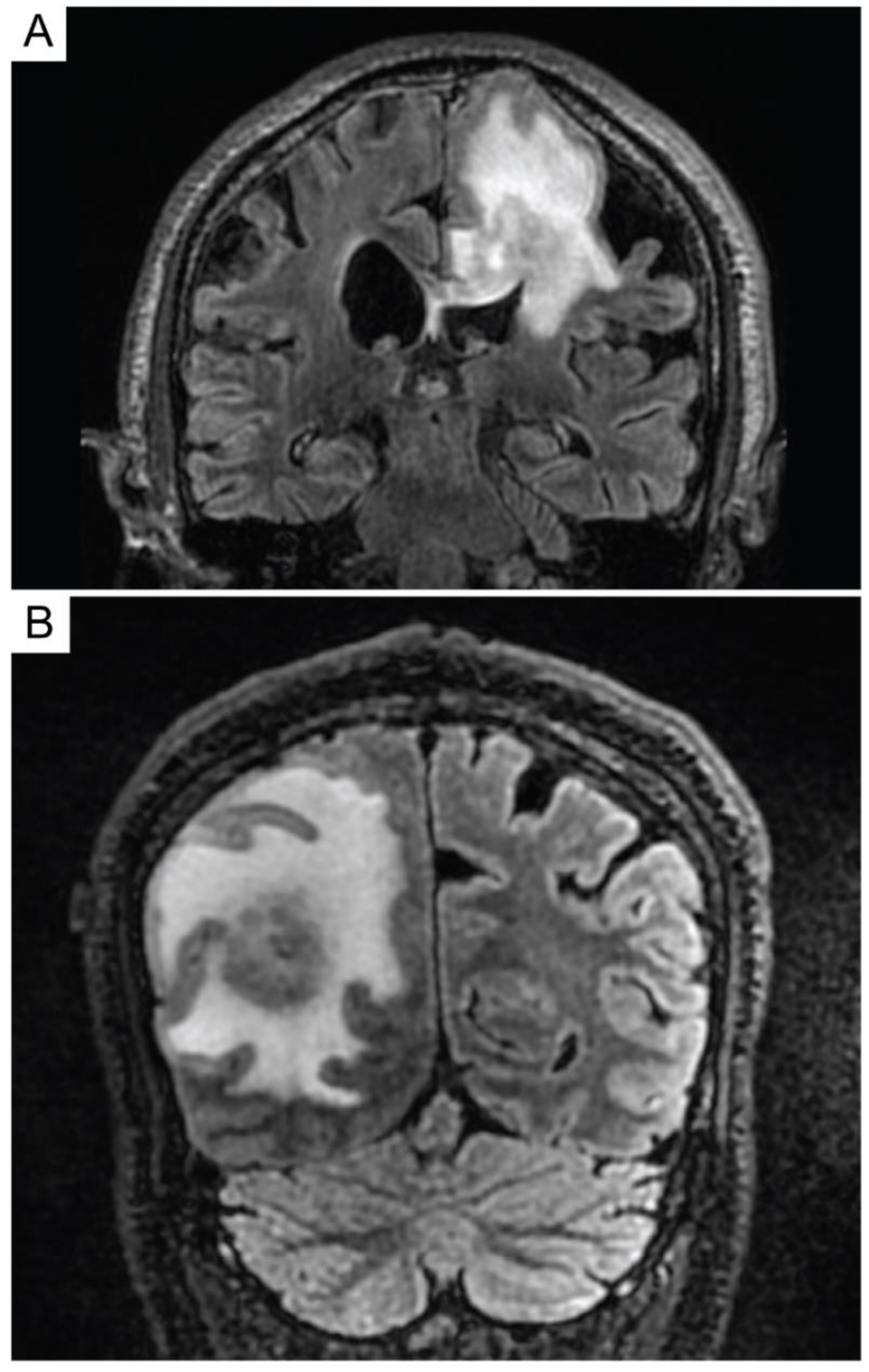
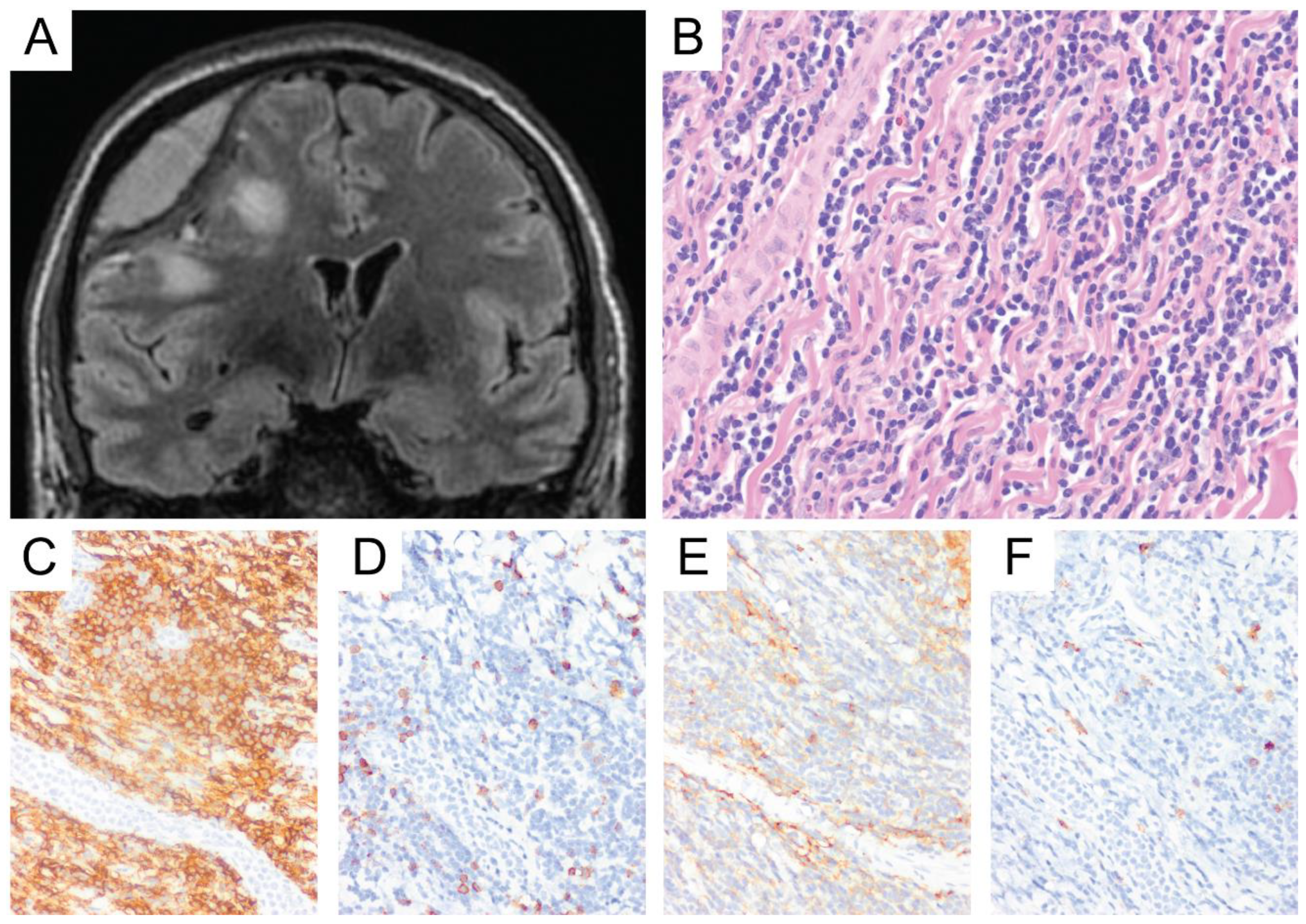
4. Diagnosis and Staging
5. PCNSL in the Pediatric Population
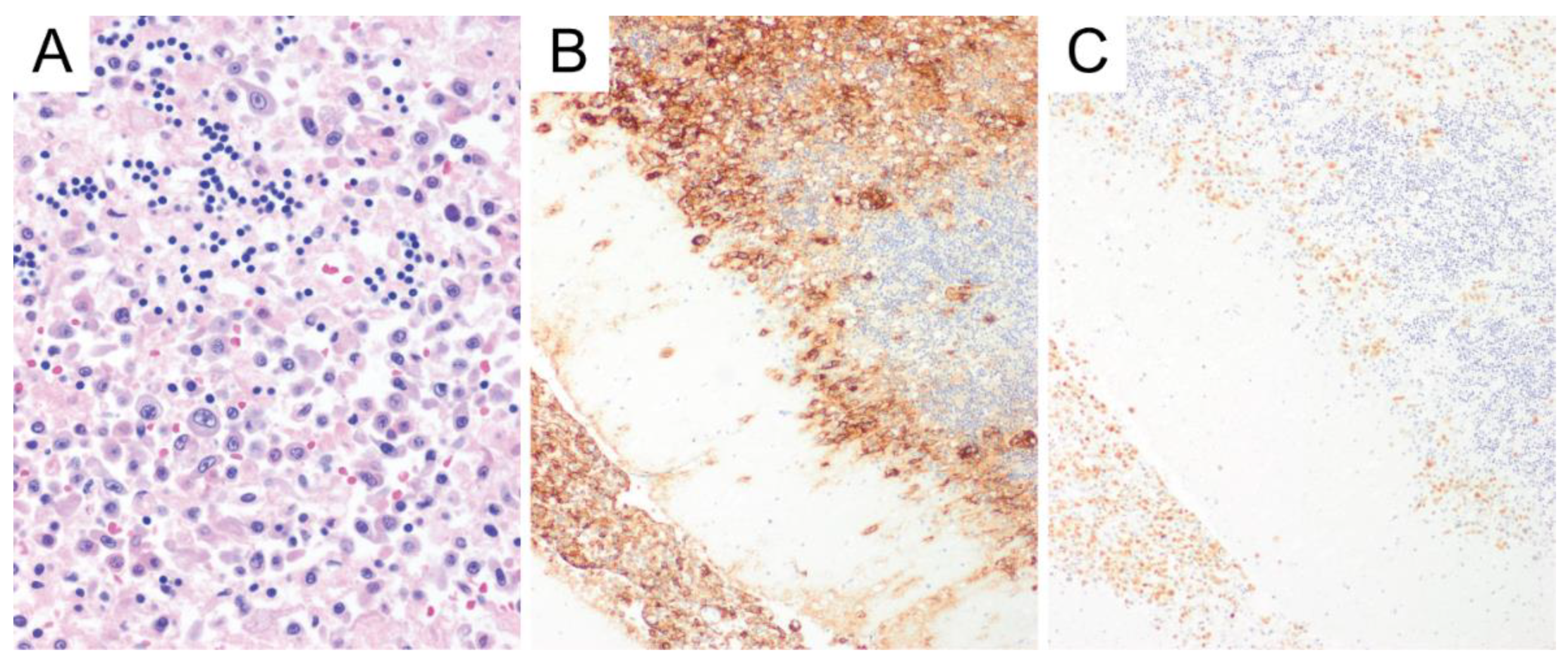
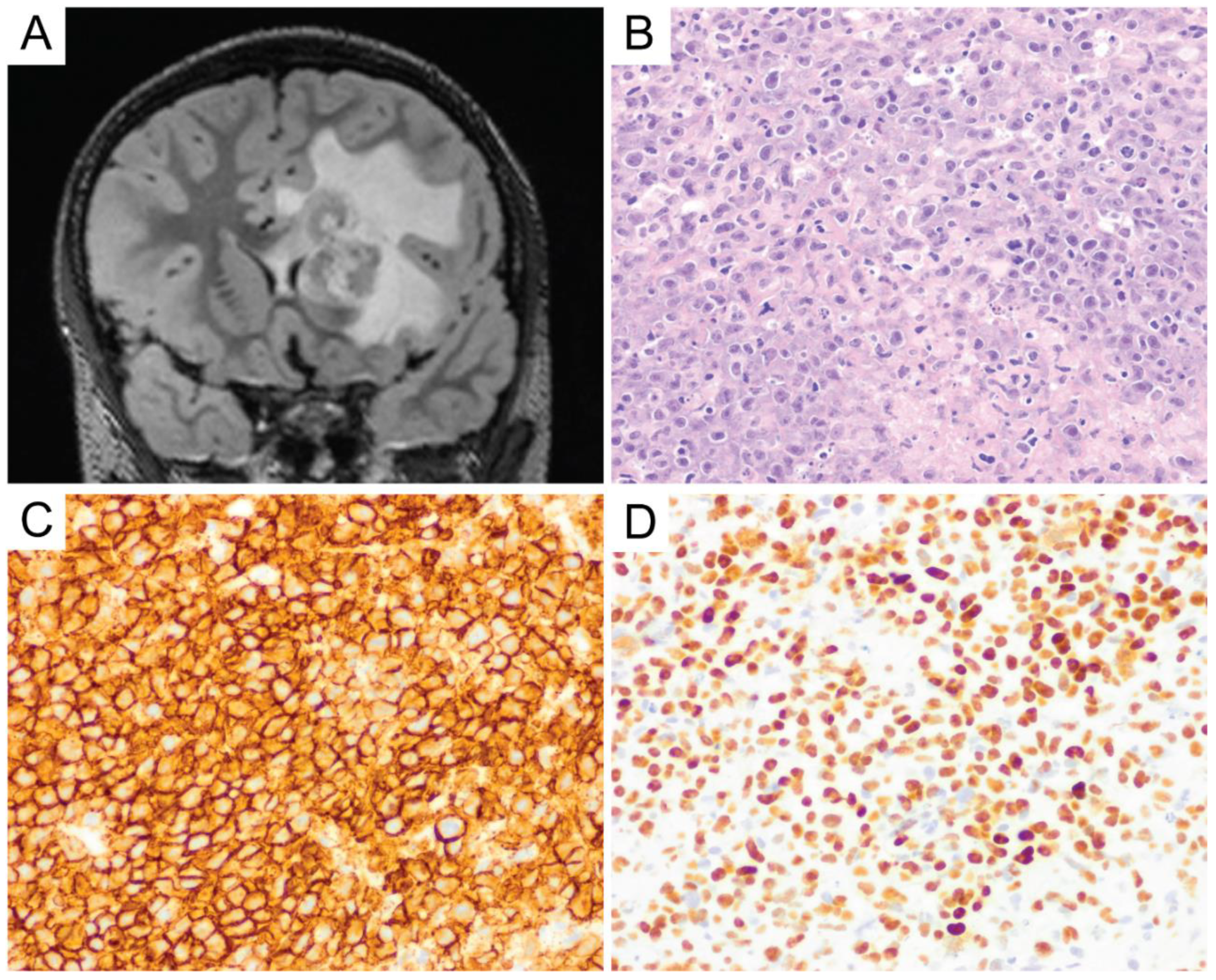
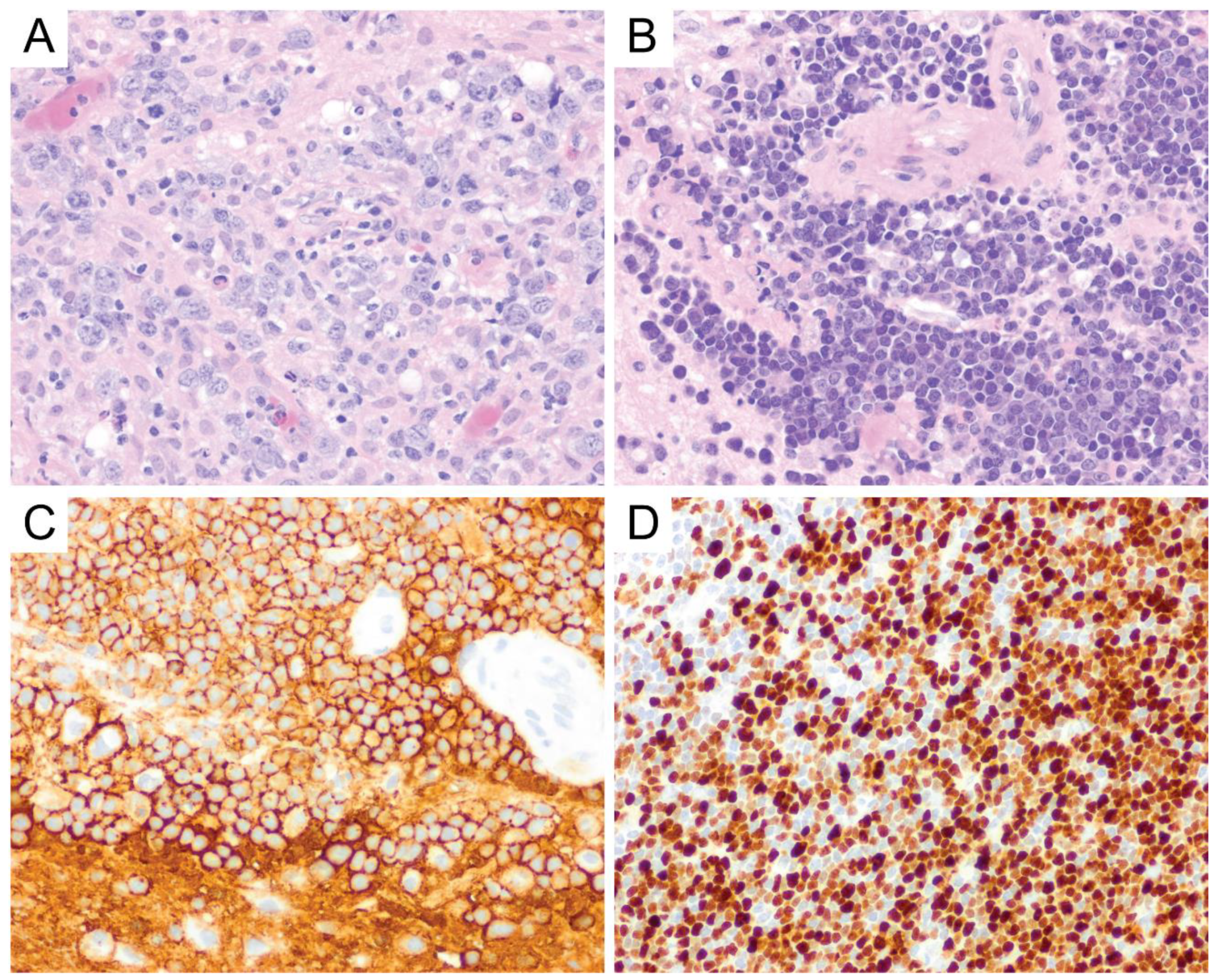
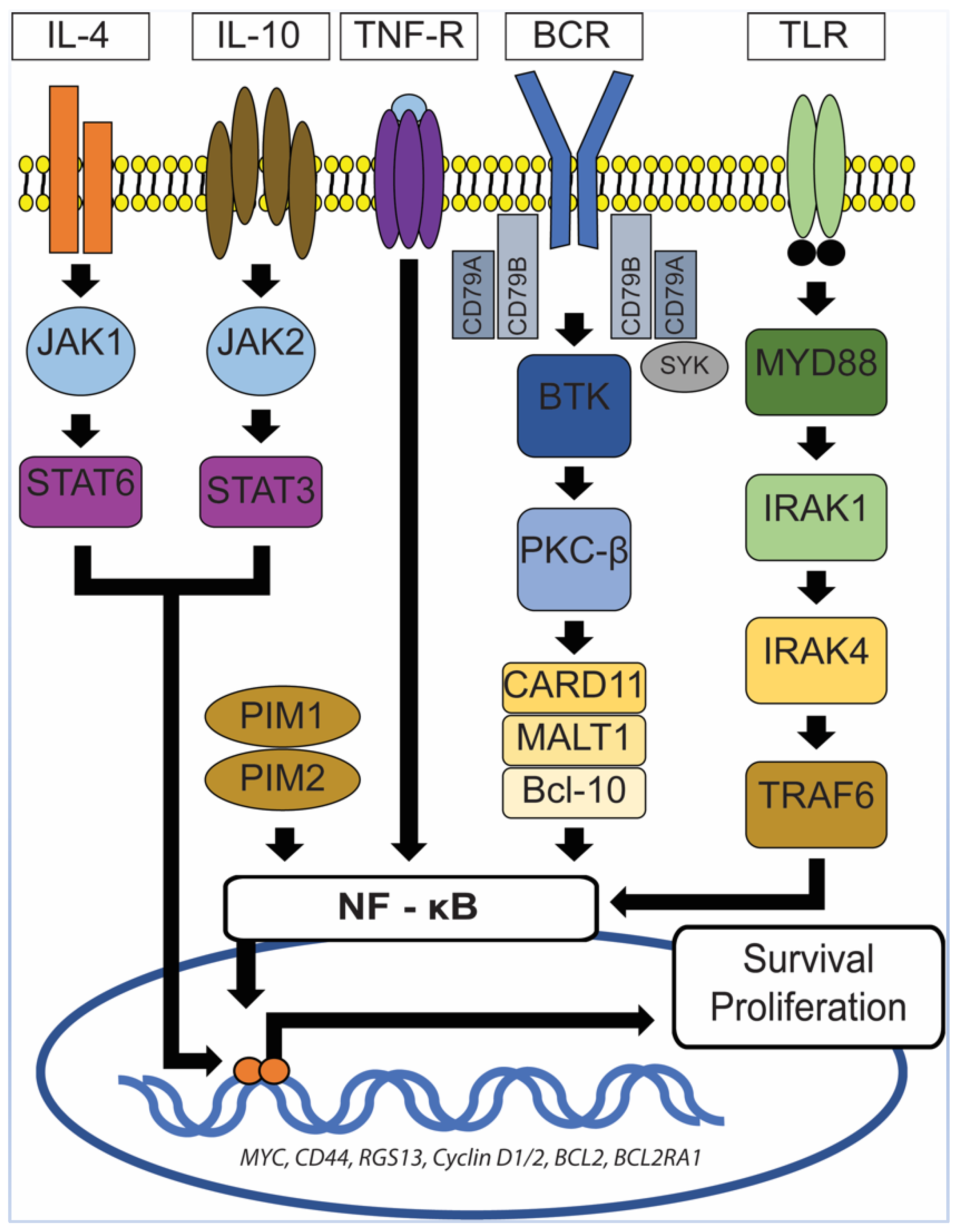
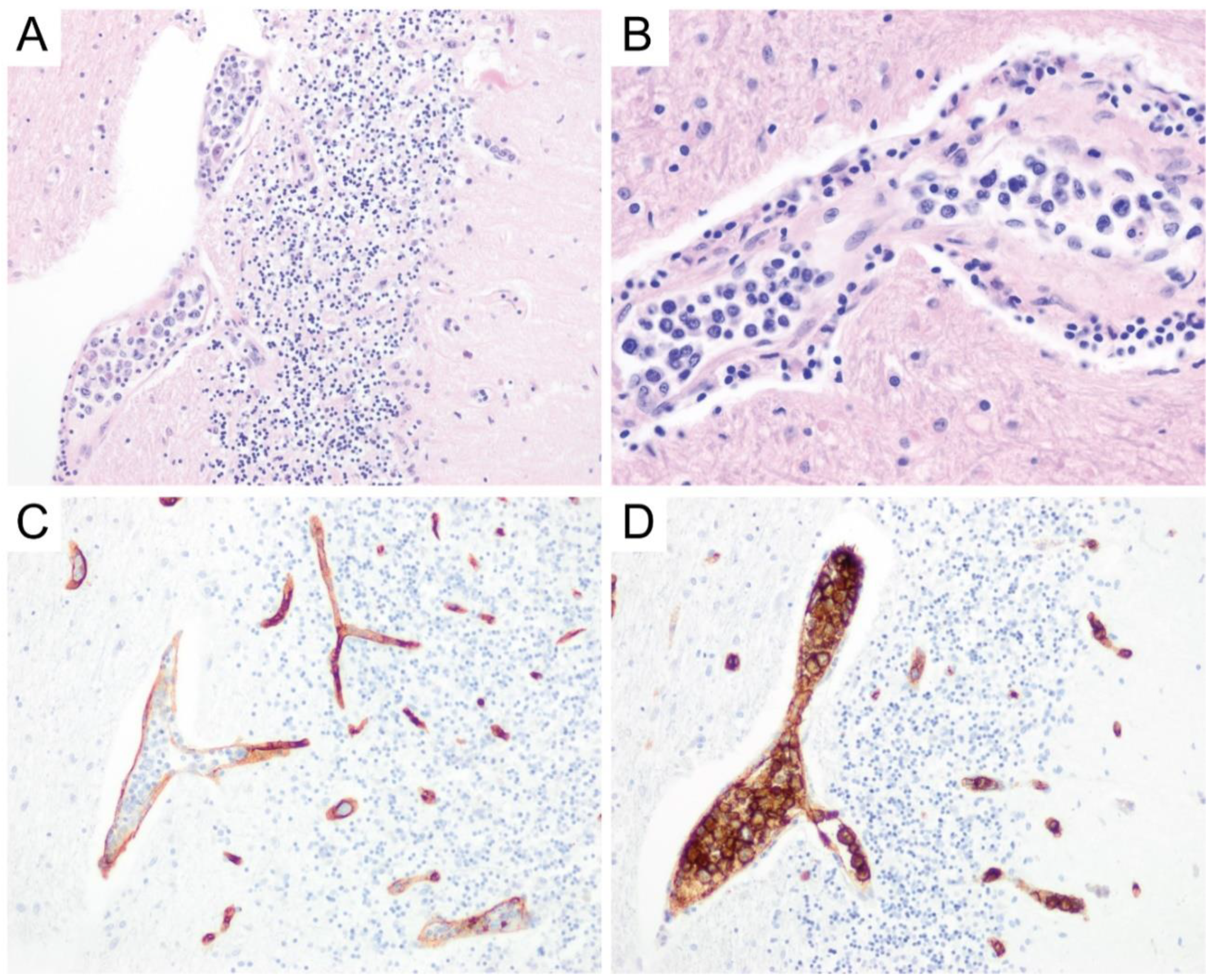
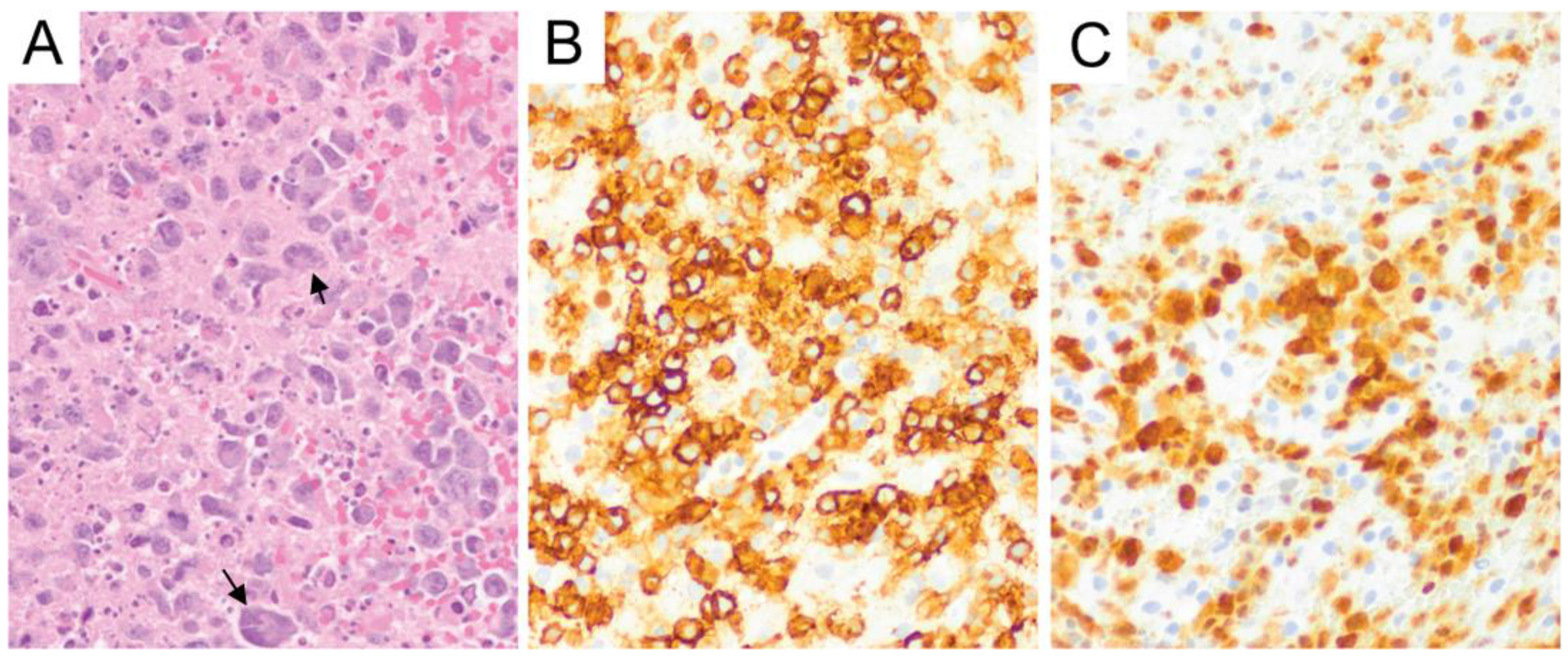
6. Primary Central Nervous System Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (PCNS DLBCL)
7. Intravascular Large B-Cell Lymphoma
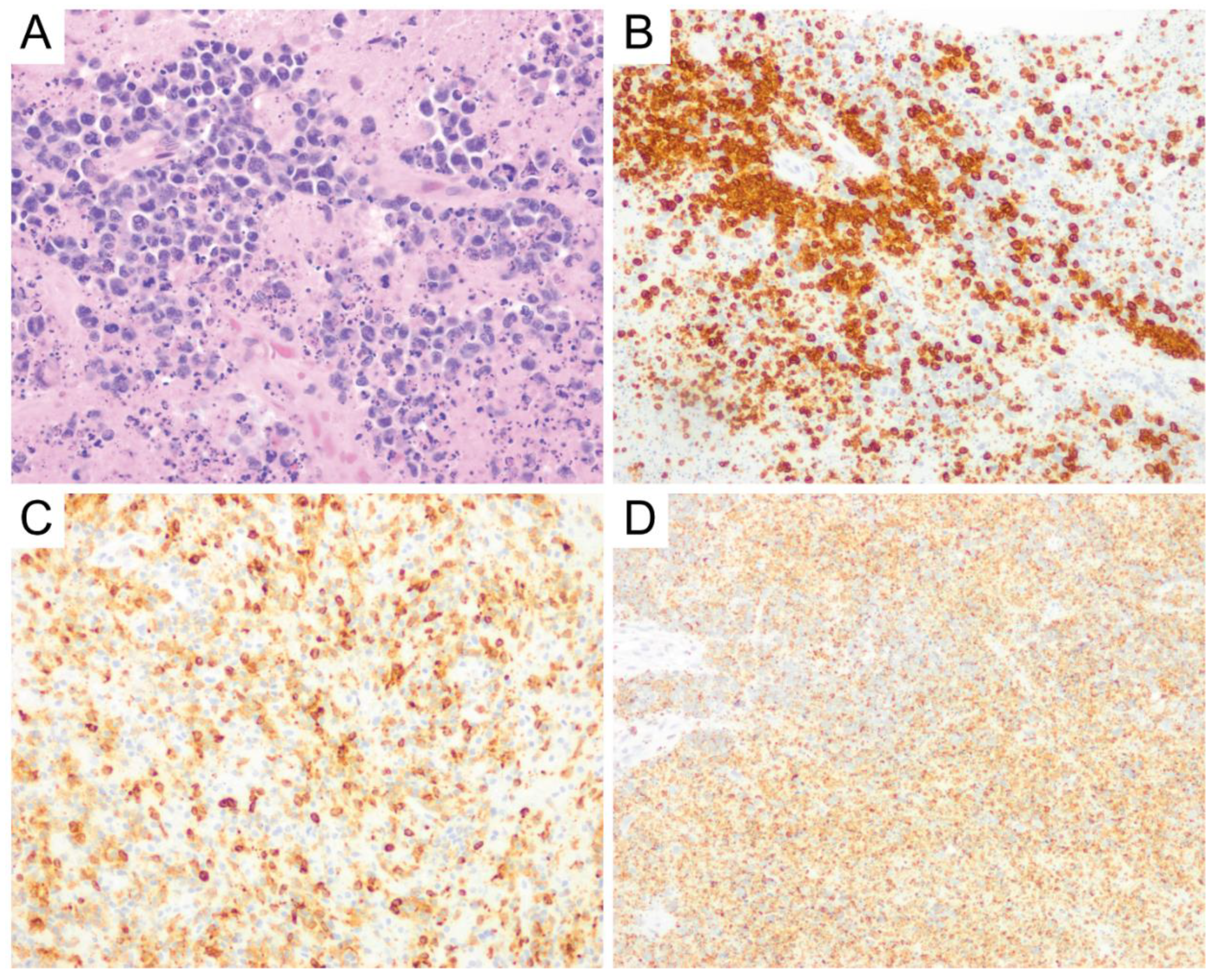
8. Burkitt Lymphoma
9. Low-Grade B-Cell Lymphomas and T-Cell Lymphomas
10. Dural Marginal Zone Lymphoma (MZL)
11. Peripheral T-Cell Lymphoma, not Otherwise Specified (PTCL, NOS) and Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (ALCL)
12. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- King, R.L.; Goodlad, J.R.; Calaminici, M.; Dotlic, S.; Montes-Moreno, S.; Oschlies, I.; Ponzoni, M.; Traverse-Glehen, A.; Ott, G.; Ferry, J.A. Lymphomas arising in immune-privileged sites: Insights into biology, diagnosis, and pathogenesis. Virchows Archiv 2019, 476, 647–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surawicz, T.S.; McCarthy, B.J.; Kupelian, V.; Jukich, P.J.; Bruner, J.M.; Davis, F.G. Descriptive epidemiology of primary brain and CNS tumors: Results from the Central Brain Tumor Registry of the United States, 1990–1994. Neuro Oncol. 1999, 1, 14–25. [Google Scholar]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Gittleman, H.; Xu, J.; Kromer, C.; Wolinsky, Y.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2009–2013. Neuro Oncol. 2016, 18 (Suppl. 5), v1–v75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cote, T.R.; Manns, A.; Hardy, C.R.; Yellin, F.J.; Hartge, P. AIDS/Cancer Study Group Epidemiology of Brain Lymphoma Among People With or Without Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1996, 88, 675–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandachi, D.; Ostrom, Q.T.; Chong, I.; Serpa, J.A.; Giordano, T.P.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S.; Fowler, N.; Colen, R.R.; Morón, F.E. Primary central nervous system lymphoma in patients with and without HIV infection: A multicenter study and comparison with U.S national data. Cancer Causes Control. 2019, 30, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matinella, A.; Lanzafame, M.; Bonometti, M.A.; Gajofatto, A.; Concia, E.; Vento, S.; Monaco, S.; Ferrari, S. Neurological complications of HIV infection in pre-HAART and HAART era: A retrospective study. J. Neurol. 2015, 262, 1317–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopal, S.; Patel, M.R.; Yanik, E.L.; Cole, S.R.; Achenbach, C.J.; Napravnik, S.; Burkholder, G.A.; Reid, E.G.; Rodriguez, B.; Deeks, S.G.; et al. Temporal Trends in Presentation and Survival for HIV-Associated Lymphoma in the Antiretroviral Therapy Era. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2013, 105, 1221–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bataille, B.; Delwail, V.; Menet, E.; Vandermarcq, P.; Ingrand, P.; Wager, M.; Guy, G.; Lapierre, F. Primary intracerebral malignant lymphoma: Report of 248 cases. J. Neurosurg. 2000, 92, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grommes, C.; Rubenstein, J.L.; DeAngelis, L.M.; Ferreri, A.J.M.; Batchelor, T.T. Comprehensive approach to diagnosis and treatment of newly diagnosed primary CNS lymphoma. Neuro Oncol. 2019, 21, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisariu, S.; Avni, B.; Batchelor, T.T.; Bent, M.J.V.D.; Bokstein, F.; Schiff, D.; Kuittinen, O.; Chamberlain, M.C.; Roth, P.; Nemets, A.; et al. Neurolymphomatosis: An International Primary CNS Lymphoma Collaborative Group report. Blood 2010, 115, 5005–5011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, S.A.; Pulido, J.S.; Jahnke, K.; Schiff, D.; Hall, A.J.; Shenkier, T.N.; Siegal, T.; Doolittle, N.D.; Batchelor, T.T.; Herrlinger, U.; et al. Primary intraocular lymphoma: An International Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma Collaborative Group Report. Ann. Oncol. 2007, 18, 1851–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Harris, N.L.; Jaffe, E.S.; Pileri, S.A.; Stein, H.; Thiele, J.; Arber, D.A.; Hasserjian, R.P.; Le Beau, M.M.; et al. (Eds.) WHO Classification of Tumours of Hematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues, Revised, 4th ed.; IARC Press: Lyon, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Abrey, L.E.; Batchelor, T.T.; Ferreri, A.J.; Gospodarowicz, M.; Pulczynski, E.J.; Zucca, E.; Smith, J.R.; Korfel, A.; Soussain, C.; DeAngelis, L.M.; et al. Report of an International Workshop to Standardize Baseline Evaluation and Response Criteria for Primary CNS Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 5034–5043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booman, M.; Douwes, J.; Legdeur, M.-C.; Van Baarlen, J.; Schuuring, E.; Kluin, P.M. From brain to testis: Immune escape and clonal selection in a B cell lymphoma with selective outgrowth in two immune sanctuaries [correction of sanctuariesy]. Haematologica 2007, 92, e69–e71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Schmidt, S.; Rainer, J.; Ploner, C.; Presul, E.; Riml, S.; Kofler, R. Glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis and glucocorticoid resistance: Molecular mechanisms and clinical relevance. Cell Death Differ. 2004, 11, S45–S55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geppert, M.; Ostertag, C.B.; Seitz, G.; Kiessling, M. Glucocorticoid therapy obscures the diagnosis of cerebral lymphoma. Acta Neuropathol. 1990, 80, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrantes-Freer, A.; Engel, A.S.; Rodríguez-Villagra, O.A.; Winkler, A.; Bergmann, M.; Mawrin, C.; Kuempfel, T.; Pellkofer, H.; Metz, I.; Bleckmann, A.; et al. Diagnostic red flags: Steroid-treated malignant CNS lymphoma mimicking autoimmune inflammatory demyelination. Brain Pathol. 2017, 28, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alakeel, F.; DePalma, L.; Wu, X. 205 The Challenge of Necrotic Tissue for Lymphoma Work-Up. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2018, 149, S87–S88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannini, C.; Dogan, A.; Salomão, D.R. CNS Lymphoma: A Practical Diagnostic Approach. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2014, 73, 478–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadan-Lottick, N.S.; Skluzacek, M.C.; Gurney, J.G. Decreasing incidence rates of primary central nervous system lymphoma. Cancer 2002, 95, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abla, O.; Weitzman, S.; Blay, J.-Y.; O’Neill, B.P.; Abrey, L.E.; Neuwelt, E.; Doolittle, N.D.; Baehring, J.; Pradhan, K.; Martin, S.E.; et al. Primary CNS lymphoma in children and adolescents: A descriptive analysis from the International Primary CNS Lymphoma Collaborative Group (IPCG). Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Attarbaschi, A.; Abla, O.; Ronceray, L.; Bansil, S.; Bomken, S.; Burkhardt, B.; Ceppi, F.; Chiang, A.K.S.; Dave, H.; Fedorova, A.; et al. Primary central nervous system lymphoma: Initial features, outcome, and late effects in 75 children and adolescents. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 4291–4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochberg, J.; El-Mallawany, N.K.; Abla, O. Adolescent and young adult non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2016, 173, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulus, W.; Jellinger, K.; Hallas, C.; Ott, G.; Müller-Hermelink, H.K. Human herpesvirus-6 and Epstein-Barr virus genome in primary cerebral lymphomas. Neurology 1993, 43, 1591–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deckert, M.; Hans, V.H.; Eis-Hübinger, A.M.; Prinz, M.; Schaller, C.; Van Roost, D.; Aguzzi, A.; Wiestler, O.D.; Deckert, M. Human herpes virus-8 is not associated with primary central nervous system lymphoma in HIV-negative patients. Acta Neuropathol. 2001, 102, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montesinos-Rongen, M.; Besleaga, R.; Heinsohn, S.; Siebert, R.; Kabisch, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Deckert, M. Absence of simian virus 40 DNA sequences in primary central nervous system lymphoma in HIV-negative patients. Virchows Archiv 2004, 444, 436–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, J.; Morgello, S. Polyomaviruses and primary central nervous system lymphomas. Neurology 2004, 63, 1299–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponzoni, M.; Berger, F.; Chassagne-Clement, C.; Tinguely, M.; Jouvet, A.; Ferreri, A.J.M.; Dell’Oro, S.; Terreni, M.R.; Doglioni, C.; Weis, J.; et al. Reactive perivascular T-cell infiltrate predicts survival in primary central nervous system B-cell lymphomas. Br. J. Haematol. 2007, 138, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino, K.; Nakamura, H.; Shinojima, N.; Kuroda, J.-I.; Yano, S.; Mikami, Y.; Mukasa, A. BCL2 expression is associated with a poor prognosis independent of cellular origin in primary central nervous system diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2018, 140, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilleri-Broët, S.; Crinière, E.; Broët, P.; Delwail, V.; Mokhtari, K.; Moreau, A.; Kujas, M.; Raphaël, M.; Iraqi, W.; Sautès-Fridman, C.; et al. A uniform activated B-cell–like immunophenotype might explain the poor prognosis of primary central nervous system lymphomas: Analysis of 83 cases. Blood 2005, 107, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-H.; Kuo, K.; Chuang, S.-S.; Kuo, S.-H.; Chang, J.H.; Chang, K.-C.; Hsu, H.-C.; Tien, H.; Cheng, A.-L. Comparison of the Expression and Prognostic Significance of Differentiation Markers between Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma of Central Nervous System Origin and Peripheral Nodal Origin. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 1152–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattab, E.M.; Martin, S.E.; Al-Khatib, S.M.; Kupsky, W.J.; Vance, G.H.; Stohler, R.A.; Czader, M.; Al-Abbadi, M.A. Most primary central nervous system diffuse large B-cell lymphomas occurring in immunocompetent individuals belong to the nongerminal center subtype: A retrospective analysis of 31 cases. Mod. Pathol. 2010, 23, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hans, C.P.; Weisenburger, D.D.; Greiner, T.C.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Delabie, J.; Ott, G.; Müller-Hermelink, H.K.; Campo, E.; Braziel, R.M.; Jaffe, E.S.; et al. Confirmation of the molecular classification of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by immunohistochemistry using a tissue microarray. Blood 2004, 103, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montesinos-Rongen, M.; Schmitz, R.; Courts, C.; Stenzel, W.; Bechtel, D.; Niedobitek, G.; Blumcke, I.; Reifenberger, G.; Von Deimling, A.; Jungnickel, B.; et al. Absence of Immunoglobulin Class Switch in Primary Lymphomas of the Central Nervous System. Am. J. Pathol. 2005, 166, 1773–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunn, A.; Nagel, I.; Montesinos-Rongen, M.; Klapper, W.; Vater, I.; Paulus, W.; Hans, V.; Blümcke, I.; Weis, J.; Siebert, R.; et al. Frequent triple-hit expression of MYC, BCL2, and BCL6 in primary lymphoma of the central nervous system and absence of a favorable MYClowBCL2low subgroup may underlie the inferior prognosis as compared to systemic diffuse large B cell lymphomas. Acta Neuropathol. 2013, 126, 603–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, K.Z.; Iwamoto, F.; Allen, A.; Hoehn, D.; Murty, V.V.; Alobeid, B.; Bhagat, G. MYC Protein Expression in Primary Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma of the Central Nervous System. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cady, F.M.; O’Neill, B.P.; Law, M.E.; Decker, P.A.; Kurtz, D.M.; Giannini, C.; Porter, A.B.; Kurtin, P.J.; Johnston, P.B.; Dogan, A.; et al. Del(6)(q22) and BCL6 Rearrangements in Primary CNS Lymphoma Are Indicators of an Aggressive Clinical Course. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 4814–4819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montesinos-Rongen, M.; Zühlke-Jenisch, R.; Gesk, S.; Martín-Subero, J.I.; Schaller, C.; Van Roost, D.; Wiestler, O.D.; Deckert, M.; Siebert, R. Interphase Cytogenetic Analysis of Lymphoma-Associated Chromosomal Breakpoints in Primary Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphomas of the Central Nervous System. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2002, 61, 926–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.-Y.; Feng, X.; Bao, W.; Ma, J.; Lv, J.-H.; Wang, X.; Rao, Q.; Shi, Q.-L. MYC/BCL2 Co-Expression Is a Stronger Prognostic Factor Compared With the Cell-of-Origin Classification in Primary CNS DLBCL. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2017, 76, 942–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Nam, S.J.; Kwon, D.; Kim, H.; Lee, E.; Kim, T.M.; Heo, D.S.; Park, S.H.; Kim, C.W.; Jeon, Y.K. MYC and BCL2 overexpression is associated with a higher class of Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center prognostic model and poor clinical outcome in primary diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the central nervous system. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia, G.; Baptista, M.-J.; Muñoz-Marmol, A.-M.; Gaafar, A.; Puente-Pomposo, M.; Garcia, O.; Marginet-Flinch, R.; Sanz, C.; Navarro, J.-T.; Sancho, J.-M.; et al. MYC protein expression is associated with poor prognosis in primary diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the central nervous system. APMIS 2015, 123, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukumura, K.; Kawazu, M.; Kojima, S.; Ueno, T.; Sai, E.; Soda, M.; Ueda, H.; Yasuda, T.; Yamaguchi, H.; Lee, J.; et al. Genomic characterization of primary central nervous system lymphoma. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.-M.; Ha, S.-Y.; Yoo, H.-Y.; Oh, D.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, W.-S.; Ko, Y.-H. Prognostic impact of MYC protein expression in central nervous system diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: Comparison with MYC rearrangement and MYC mRNA expression. Mod. Pathol. 2016, 30, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Cui, Q.; Ji, N.; Sun, S.; Wang, B.; Wang, Y.; Sun, X.; et al. Immunohistochemical profile and prognostic significance in primary central nervous system lymphoma: Analysis of 89 cases. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 5505–5512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Bai, Q.; Rohr, J.M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, K.; Yu, K.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z. Clinicopathological features of primary diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the central nervous system-strong EZH2 expression implying diagnostic and therapeutic implication. APMIS 2016, 124, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montesinos-Rongen, M.; Küppers, R.; Schlüter, D.; Spieker, T.; Van Roost, D.; Schaller, C.; Reifenberger, G.; Wiestler, O.D.; Deckert-Schlüter, M. Primary Central Nervous System Lymphomas Are Derived from Germinal-Center B Cells and Show a Preferential Usage of the V4–34 Gene Segment. Am. J. Pathol. 1999, 155, 2077–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharathkumar, B.; Jon, D.W. Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2008, 132, 1830–1834. [Google Scholar]
- Rubenstein, J.L.; Fridlyand, J.; Shen, A.; Aldape, K.; Ginzinger, D.; Batchelor, T.; Treseler, P.; Berger, M.; McDermott, M.; Prados, M.; et al. Gene expression and angiotropism in primary CNS lymphoma. Blood 2006, 107, 3716–3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montesinos-Rongen, M.; Godlewska, E.; Brunn, A.; Wiestler, O.D.; Siebert, R.; Deckert, M. Activating L265P mutations of the MYD88 gene are common in primary central nervous system lymphoma. Acta Neuropathol. 2011, 122, 791–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwindt, H.; Vater, I.; Kreuz, M.; Montesinos-Rongen, M.; Brunn, A.; Richter, J.; Gesk, S.; Ammerpohl, O.; Wiestler, O.D.; Hasenclever, D.; et al. Chromosomal imbalances and partial uniparental disomies in primary central nervous system lymphoma. Leukemia 2009, 23, 1875–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ngo, V.N.; Young, R.M.; Schmitz, R.; Jhavar, S.; Xiao, W.; Lim, K.-H.; Kohlhammer, H.; Xu, W.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, H.; et al. Oncogenically active MYD88 mutations in human lymphoma. Nature 2011, 470, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreri, A.J.M.; Dognini, G.P.; Campo, E.; Willemze, R.; Seymour, J.F.; Bairey, O.; Martelli, M.; De Renz, A.O.; Doglioni, C.; Montalbán, C.; et al. Variations in clinical presentation, frequency of hemophagocytosis and clinical behavior of intravascular lymphoma diagnosed in different geographical regions. Haematologica 2007, 92, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, S.E.; Kim, W.S.; Kim, S.J. Asian variant of intravascular large B-cell lymphoma: A comparison of clinical features based on involvement of the central nervous system. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2020, 35, 946–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahsili-Fahadan, P.; Rashidi, A.; Cimino, P.J.; Bucelli, R.C.; Keyrouz, S.G. Neurologic manifestations of intravascular large B-cell lymphoma. Neurol. Clin. Pr. 2015, 6, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsue, K.; Abe, Y.; Narita, K.; Kobayashi, H.; Kitadate, A.; Takeuchi, M.; Miura, D.; Takeuchi, K. Diagnosis of intravascular large B cell lymphoma: Novel insights into clinicopathological features from 42 patients at a single institution over 20 years. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 187, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimada, K.; Murase, T.; Matsue, K.; Okamoto, M.; Ichikawa, N.; Tsukamoto, N.; Niitsu, N.; Miwa, H.; Asaoku, H.; Kosugi, H.; et al. Central nervous system involvement in intravascular large B-cell lymphoma: A retrospective analysis of 109 patients. Cancer Sci. 2010, 101, 1480–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponzoni, M.; Arrigoni, G.; Gould, V.E.; Del Curto, B.; Maggioni, M.; Scapinello, A.; Paolino, S.; Cassisa, A.; Patriarca, C. Lack of CD 29 (beta1 integrin) and CD 54 (ICAM-1) adhesion molecules in intravascular lymphomatosis. Hum Pathol. 2000, 31, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrader, A.M.R.; Jansen, P.M.; Willemze, R.; Vermeer, M.H.; Cleton-Jansen, A.-M.; Somers, S.F.; Veelken, H.; Van Eijk, R.; Kraan, W.; Kersten, M.J.; et al. High prevalence of MYD88 and CD79B mutations in intravascular large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2018, 131, 2086–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bower, K.; Shah, N. Primary CNS Burkitt Lymphoma: A Case Report of a 55-Year-Old Cerebral Palsy Patient. Case Rep. Oncol. Med. 2018, 2018, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesin, N.; Lam, C.; Margolin, E. Central Nervous System Burkitt Lymphoma Presenting as Atypical Guillain-Barre Syndrome. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 2019, 47, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, H.; Sano, T.; Ii, K.; Hizawa, K.; Li, K. Primary Burkitt-type lymphoma of the central nervous system. Acta Neuropathol. 1984, 64, 12–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leucci, E.; Cocco, M.; Onnis, A.; De Falco, G.; Van Cleef, P.; Bellan, C.; Van Rijk, A.; Nyagol, J.; Byakika, B.; Lazzi, S.; et al. MYC translocation-negative classical Burkitt lymphoma cases: An alternative pathogenetic mechanism involving miRNA deregulation. J. Pathol. 2008, 216, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kretzmer, H.; Project, I.M.-S.; Bernhart, S.H.; Wang, W.; Haake, A.; Weniger, M.A.; Bergmann, A.K.; Betts, M.J.; Carrillo-De-Santa-Pau, E.; Doose, G.; et al. DNA methylome analysis in Burkitt and follicular lymphomas identifies differentially methylated regions linked to somatic mutation and transcriptional control. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1316–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, C.; Sun, Z.; Jima, D.D.; Li, G.; Zhang, J.; Miles, R.R.; Richards, K.L.; Dunphy, C.H.; Choi, W.W.L.; Srivastava, G.; et al. The genetic landscape of mutations in Burkitt lymphoma. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 1321–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Project, T.I.M.-S.; Richter, J.; Schlesner, M.; Hoffmann, S.; Kreuz, M.; Leich, E.; Burkhardt, B.; Rosolowski, M.; Ammerpohl, O.; Wagener, R.; et al. Recurrent mutation of the ID3 gene in Burkitt lymphoma identified by integrated genome, exome and transcriptome sequencing. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 1316–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giulino-Roth, L.; Wang, K.; Macdonald, T.Y.; Mathew, S.; Tam, Y.; Cronin, M.T.; Palmer, G.; Lucena-Silva, N.; Pedrosa, F.; Pedrosa, M.; et al. Targeted genomic sequencing of pediatric Burkitt lymphoma identifies recurrent alterations in antiapoptotic and chromatin-remodeling genes. Blood 2012, 120, 5181–5184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagener, R.; Aukema, S.M.; Schlesner, M.; Haake, A.; Burkhardt, B.; Claviez, A.; Drexler, H.G.; Hummel, M.; Kreuz, M.; Loeffler, M.; et al. ThePCBP1gene encoding poly(rc) binding protein i is recurrently mutated in Burkitt lymphoma. Genes Chromosom. Cancer 2015, 54, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahnke, K.; Korfel, A.; O’Neill, B.P.; Blay, J.-Y.; Abrey, L.E.; Martus, P.; Poortmans, P.M.P.; Shenkier, T.N.; Batchelor, T.T.; Neuwelt, E.A.; et al. International study on low-grade primary central nervous system lymphoma. Ann. Neurol. 2006, 59, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanicolau-Sengos, A.; Wang-Rodriguez, J.; Wang, H.-Y.; Lee, R.R.; Wong, A.; Hansen, L.A.; Mahooti, S.; Rashidi, H.H. Rare case of a primary non-dural central nervous system low grade B-cell lymphoma and literature review. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2012, 5, 89–95. [Google Scholar]
- Nomani, L.; Cotta, C.V.; Hsi, E.D.; A Ferry, J.; Cook, J.R. Extranodal Marginal Zone Lymphoma of the Central Nervous System Includes Parenchymal-Based Cases With Characteristic Features. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2020, 154, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treon, S.P.; Xu, L.; Yang, G.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, X.; Cao, Y.; Sheehy, P.; Manning, R.J.; Patterson, C.J.; Tripsas, C.; et al. MYD88 L265P somatic mutation in Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Kuzu, I.; Dogan, A.; Dirnhofer, S.; Chan, J.K.C.; Sander, B.; Ott, G.; Xerri, L.; Quintanilla-Martinez, L.; Campo, E. The many faces of small B cell lymphomas with plasmacytic differentiation and the contribution of MYD88 testing. Virchows Archiv 2016, 468, 259–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganapathi, K.A.; Jobanputra, V.; Iwamoto, F.; Jain, P.; Chen, J.; Cascione, L.; Nahum, O.; Levy, B.; Xie, Y.; Khattar, P.; et al. The genetic landscape of dural marginal zone lymphomas. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 43052–43061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Kumar, D.; Kaldjian, E.P.; Bauserman, S.; Raffeld, M.; Jaffe, E.S. Primary low-grade B-cell lymphoma of the dura: A mucosa associated lymphoid tissue-type lymphoma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1997, 21, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, P.; Giannini, C.; Judkins, A.R.; Schwalb, J.M.; Burack, R.; O’Neill, B.P.; Yachnis, A.T.; Burger, P.C.; Scheithauer, B.W.; Perry, A. Clinicopathologic and Genetic Profile of Intracranial Marginal Zone Lymphoma: A Primary Low-Grade CNS Lymphoma That Mimics Meningioma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 5718–5727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matmati, K.S.; Matmati, N.; Hannun, Y.A.; Rumboldt, Z.; Patel, S.; Lazarchick, J.; Stuart, R.; Giglio, P. Dural MALT lymphoma with disseminated disease. Hematol. Rep. 2010, 2, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamoto, F.M.; DeAngelis, L.M.; Abrey, L.E. Primary dural lymphomas: A clinicopathologic study of treatment and outcome in eight patients. Neurol. 2006, 66, 1763–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Fuente, M.I.; Haggiagi, A.; Moul, A.; Young, R.J.; Sidani, C.; Markoe, A.; Vega, F.; DeAngelis, L.M.; Lossos, I.S. Marginal zone dural lymphoma: The Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center and University of Miami experiences. Leuk. Lymphoma 2016, 58, 882–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataraman, G.; Rizzo, K.A.; Chavez, J.J.; Streubel, B.; Raffeld, M.; Jaffe, E.S.; Pittaluga, S. Marginal zone lymphomas involving meningeal dura: Possible link to IgG4-related diseases. Mod. Pathol. 2011, 24, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayabuchi, N.; Shibamoto, Y.; Onizuka, Y. Primary central nervous system lymphoma in japan: A nationwide survey. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 1999, 44, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, T.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, K.; Lee, J.-I.; Lim, D.H.; Lee, D.J.; Baek, K.K.; Lee, H.Y.; Han, B.; Uhm, J.E.; et al. Primary CNS lymphoma other than DLBCL: A descriptive analysis of clinical features and treatment outcomes. Ann. Hematol. 2011, 90, 1391–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shenkier, T.N.; Blay, J.-Y.; O’Neill, B.P.; Poortmans, P.; Thiel, E.; Jahnke, K.; Abrey, L.E.; Neuwelt, E.; Tsang, R.; Batchelor, T.; et al. Primary CNS Lymphoma of T-Cell Origin: A Descriptive Analysis From the International Primary CNS Lymphoma Collaborative Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 2233–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villegas, E.; Villà, S.; López-Guillermo, A.; Petit, J.; Ribalta, T.; Graus, F. Primary central nervous system lymphoma of T-cell origin: Description of two cases and review of the literature. J. Neuro-Oncol. 1997, 34, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, M.P.; Nicolae, A.; Meeker, H.; Raffeld, M.; Xi, L.; Jegalian, A.G.; Miller, C.D.; Pittaluga, S.; Jaffe, E.S. Primary CNS T-cell Lymphomas: A Clinical, Morphologic, Immunophenotypic, and Molecular Analysis. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2015, 39, 1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lauw, M.I.S.; Lucas, C.-H.G.; Ohgami, R.S.; Wen, K.W. Primary Central Nervous System Lymphomas: A Diagnostic Overview of Key Histomorphologic, Immunophenotypic, and Genetic Features. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 1076. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10121076
Lauw MIS, Lucas C-HG, Ohgami RS, Wen KW. Primary Central Nervous System Lymphomas: A Diagnostic Overview of Key Histomorphologic, Immunophenotypic, and Genetic Features. Diagnostics. 2020; 10(12):1076. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10121076
Chicago/Turabian StyleLauw, Marietya I. S., Calixto-Hope G. Lucas, Robert S. Ohgami, and Kwun Wah Wen. 2020. "Primary Central Nervous System Lymphomas: A Diagnostic Overview of Key Histomorphologic, Immunophenotypic, and Genetic Features" Diagnostics 10, no. 12: 1076. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10121076
APA StyleLauw, M. I. S., Lucas, C.-H. G., Ohgami, R. S., & Wen, K. W. (2020). Primary Central Nervous System Lymphomas: A Diagnostic Overview of Key Histomorphologic, Immunophenotypic, and Genetic Features. Diagnostics, 10(12), 1076. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10121076



