Yield of Rare Variants Detected by Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing in a Cohort of Romanian Index Patients with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Genetic Testing
2.3. Variant Assessment
2.4. Variant Databases and In Silico Tools
2.5. Statistical Analysis
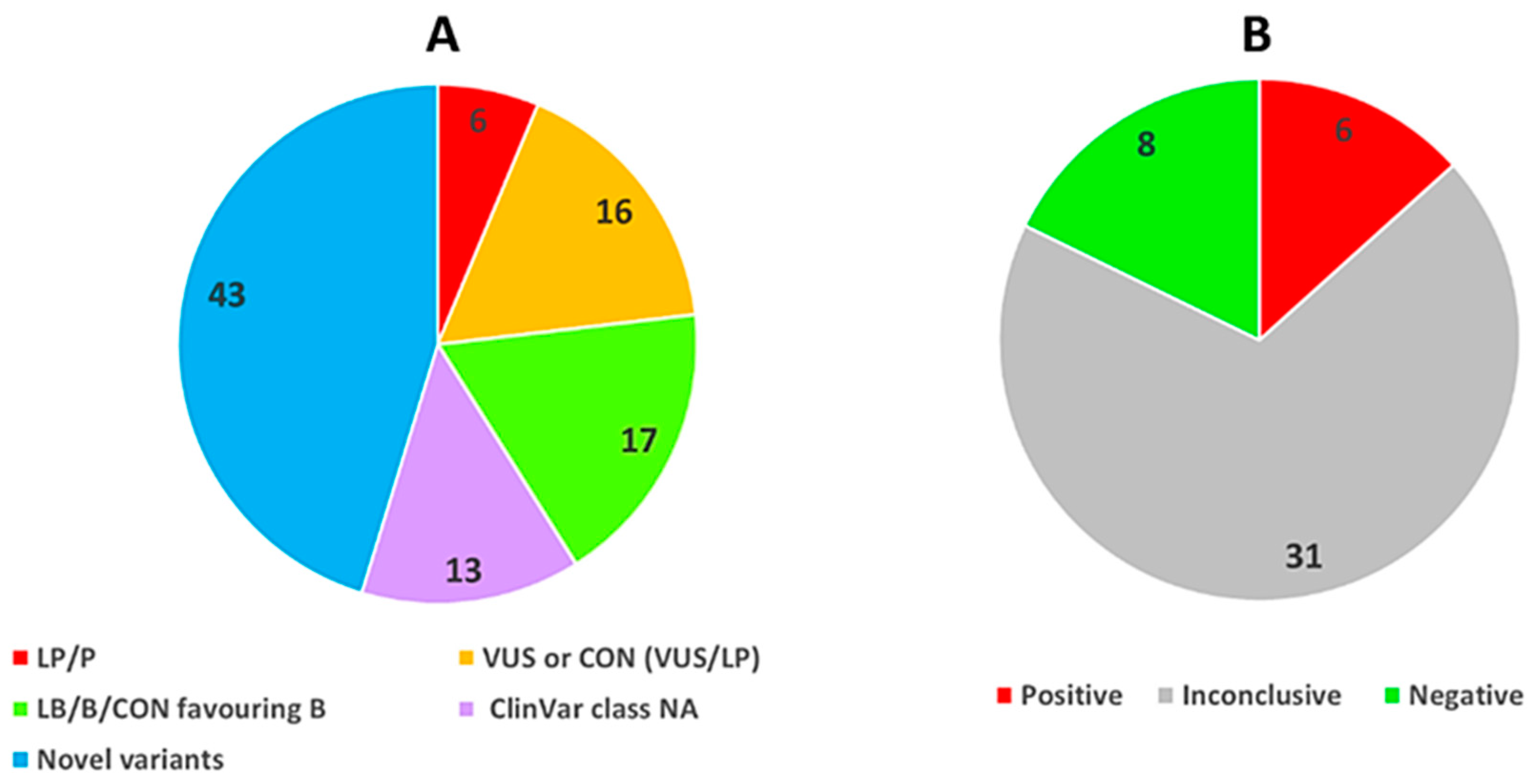
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
3.2. Genes and Variants
4. Discussion
- HCM caused by rare variants in unknown genes for HCM. In the quest to identify putative causative variants outside of recognized HCM genes, various groups used extended next-generation sequencing gene panels or even whole exome/genome sequencing (WES/WGS) as a first/second-line genetic test. In a Dutch study including 453 HCM patients, the sensitivity of genetic testing only slightly improved with the increasing number of genes sequenced, but prompted primarily the yield of class 3 variants (49%) [13]. Likewise, considerable increased detection of VUS (99%) was reported by Thomson and colleagues after examining 51 genes in 240 sarcomere gene negative HCM individuals and 6229 controls, with negligible incremental diagnostic yield [38]. In light of aforementioned findings, one can assert that expanded gene panels appear to offer limited additional sensitivity, most of genes within diagnostic tests lacking robust evidence of disease association [7,35].
- HCM caused by rare variants in regulatory non-coding regions of already recognized causal genes. In a paper published in 2018 by Bagnall and colleagues, it has been demonstrated that variation within deep intronic regions of MYBPC3 can explain up to 9% of gene-elusive HCM cases [39].
- Non-Mendelian HCM. A growing body of evidence indicates that genotype-negative HCM cases are most likely to represent non-Mendelian forms of disease, with less severe prognosis and lower risk to relatives [42]. The ability to accurately identify and characterize such candidate variants is encumbered by the necessity to perform genome-wide association studies in large cohorts assessing both variant frequency in the population and phenotypic effect size in patients [37].
Strengths and Limitations of the Study
- Use of a comprehensive panel including 47 genes associated with HCM.
- Screening for the first time of a cohort of Romanian index cases.
- Validation of the identified variants through Sanger sequencing.
- Expanding the study cohort.
- Performing segregation analyses both for known and novel variants.
- Conducting functional studies for novel detected variants.
- Checking for rare variants in the remaining genes of the TruSight Cardio Sequencing panel.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACMG | American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics |
| ACTA1 | Actin alpha skeletal muscle |
| ACTC1 | Actin alpha cardiac muscle 1 |
| ACTN2 | Actinin alpha 2 |
| ANKRD1 | Ankyrin repeat domain-containing protein 1 |
| AMP | Association for Molecular Pathology |
| B | benign |
| BRAF | Serine/threonine-protein kinase B-raf |
| BWA-MEM | Burrows-Wheeler Aligner-Maximal Exact Match |
| CALR3 | Calreticulin 3 |
| CASQ2 | Calsequestrin 2 |
| CAV3 | Caveolin-3 |
| COX15 | Cytochrome c oxidase assembly protein COX15 homolog |
| CRYAB | Alpha-crystallin B chain |
| CSRP3 | Cysteine and glycine-rich protein 3 |
| DES | Desmin |
| DNA | deoxyribonucleic acid |
| ESC | European Society of Cardiology |
| FHL1 | Four and a half LIM domains protein 1 |
| FXN | Frataxin |
| GAA | Lysosomal alpha-glucosidase |
| GATK | Genome Analysis Toolkit |
| GLA | Alpha-galactosidase A |
| HCM | hypertrophic cardiomyopathy |
| HGMD | Human Gene Mutation Database |
| JPH2 | Junctophilin-2 |
| KLF10 | Krueppel-like factor 10 |
| LAMP2 | Lysosome-associated membrane glycoprotein 2 |
| LB | likely benign |
| LDB3 | LIM domain-binding protein 3 |
| LP | likely pathogenic |
| LV | left ventricle |
| LVH | left ventricular hypertrophy |
| MAP2K1 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 |
| MAP2K2 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 2 |
| mtDNA | mitochondrial DNA |
| MYBPC3 | cardiac myosin binding protein C |
| MYH6 | Myosin heavy chain 6 |
| MYH7 | β-myosin heavy chain |
| MYL2 | Myosin regulatory light chain 2 |
| MYL3 | Myosin light chain 3 |
| MYLK2 | Myosin light chain kinase 2 |
| MYO6 | Myosin-VI |
| MYOZ2 | Myozenin-2 |
| MYPN | Myopalladin |
| NEXN | Nexilin |
| NGS | next generation sequencing |
| P | pathogenic |
| PDLIM3 | PDZ and LIM domain protein 3 |
| PLN | Cardiac phospholamban |
| PRKAG2 | 5′-AMP-activated protein kinase subunit gamma-2 |
| PTPN11 | Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 11 |
| RAF1 | RAF proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase |
| SLC25A4 | ADP/ATP translocase 1 |
| SOS1 | Son of sevenless homolog 1 |
| TCAP | Telethonin |
| TNNC | Troponin C |
| TNNI3 | Troponin I |
| TNNT2 | Troponin T |
| TPM1 | Tropomyosin alpha-1 chain |
| TRIM63 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRIM63 |
| TTN | Titin |
| VCF | variant call format |
| VCL | vinculin |
| VUS | variant of uncertain significance |
References
- Semsarian, C.; Ingles, J.; Maron, M.S.; Maron, B.J. New Perspectives on the Prevalence of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 65, 1249–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geske, J.B.; Ommen, S.R.; Gersh, B.J. Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: Clinical Update. JACC Heart Fail. 2018, 6, 364–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, P.; Andersson, B.; Arbustini, E.; Bilinska, Z.; Cecchi, F.; Charron, P.; Dubourg, O.; Kuhl, U.; Maisch, B.; McKenna, W.J.; et al. Classification of the cardiomyopathies: A position statement from the european society of cardiology working group on myocardial and pericardial diseases. Eur. Heart J. 2007, 29, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popa-Fotea, N.M.; Micheu, M.M.; Bataila, V.; Scafa-Udriste, A.; Dorobantu, L.; Scarlatescu, A.I.; Zamfir, D.; Stoian, M.; Onciul, S.; Dorobantu, M. Exploring the continuum of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy—From DNA to clinical expression. Medicine 2019, 55, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, E.; Aris, A.; Michael, B.; Martin, B.; Cecchi, F.; Charron, P.; Alain Hagege, A.; Lafont, A.; Limongelli, G.; Mahrholdt, H.; et al. 2014 ESC guidelines on diagnosis and management of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy The Task Force for the Diagnosis and Management of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur. Heart J. 2014, 35, 2733–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, M.A.; Cook, S.A.; Seidman, J.G.; Seidman, C.E. Clinical and Mechanistic Insights Into the Genetics of Cardiomyopathy. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 2871–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingles, J.; Goldstein, J.; Thaxton, C.; Caleshu, C.; Corty, E.W.; Crowley, S.B.; Dougherty, K.; Harrison, S.M.; McGlaughon, J.; Milko, L.V.; et al. Evaluating the Clinical Validity of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Genes. Circ. Genom. Precis. Med. 2019, 12, e002460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musunuru, K.; Hershberger, R.E.; Day, S.M.; Klinedinst, N.J.; Landstrom, A.P.; Parikh, V.N.; Prakash, S.; Semsarian, C.; Sturm, A.C. Genetic testing for inherited cardiovascular diseases: A scientific statement from the american heart association. Circ. Genom. Precis. Med. 2020, 13, e000067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landry, L.G.; Rehm, H.L. Association of Racial/Ethnic Categories With the Ability of Genetic Tests to Detect a Cause of Cardiomyopathy. JAMA Cardiol. 2018, 3, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, L.R.; Zekavati, A.; Syrris, P.; Hubank, M.; Giambartolomei, C.; Dalageorgou, C.; Jenkins, S.; McKenna, W.; Plagnol, V.; Elliott, P.M.; et al. Genetic complexity in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy revealed by high-throughput sequencing. J. Med. Genet. 2013, 50, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adalsteinsdottir, B.; Teekakirikul, P.; Maron, B.J.; Burke, M.A.; Gudbjartsson, D.F.; Holm, H.; Stefansson, K.; DePalma, S.R.; Mazaika, E.; McDonough, B.; et al. Nationwide study on hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in iceland evidence of a MYBPC3 founder mutation. Circulation 2014, 130, 1158–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jääskeläinen, P.; Vangipurapu, J.; Raivo, J.; Kuulasmaa, T.; Heliö, T.; Aalto-Setälä, K.; Kaartinen, M.; Ilveskoski, E.; Vanninen, S.; Hämäläinen, L.; et al. Genetic basis and outcome in a nationwide study of Finnish patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. ESC Heart Fail. 2019, 6, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Lint, F.H.M.; Mook, O.R.F.; Alders, M.; Bikker, H.; Lekanne dit Deprez, R.H.; Christiaans, I. Large next-generation sequencing gene panels in genetic heart disease: Yield of pathogenic variants and variants of unknown significance. Netherlands Heart J. 2019, 27, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micheu, M.M.; Popa-Fotea, N.M.; Oprescu, N.; Dorobantu, M.; Ratiu, A.C.; Ecovoiu, A.A. NGS data validated by Sanger sequencing reveal a puzzling small deletion of MYBPC3 gene associated with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Rom. Biotechnol. Lett. 2019, 24, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H. Aligning sequence reads, clone sequences and assembly contigs with BWA-MEM. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1303.3997. [Google Scholar]
- Den Dunnen, J.T.; Dalgleish, R.; Maglott, D.R.; Hart, R.K.; Greenblatt, M.S.; Mcgowan-Jordan, J.; Roux, A.F.; Smith, T.; Antonarakis, S.E.; Taschner, P.E.M. HGVS Recommendations for the Description of Sequence Variants: 2016 Update. Hum. Mutat. 2016, 37, 564–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopanos, C.; Tsiolkas, V.; Kouris, A.; Chapple, C.E.; Albarca Aguilera, M.; Meyer, R.; Massouras, A. VarSome: The human genomic variant search engine. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 1978–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionilă, P.; Jurcuţ, R.; Ferariu, N.; Roşca, M.; Chivulescu, M.; Mursă, A.; Militaru, S.; Ionescu, A.A.; Căldăraru, C.; Fruntelată, A.G.; et al. Romanian Registry of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy—Overview of general characteristics and therapeutic choices at a national level. Rom. J. Intern. Med. 2018, 56, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maron, B.J.; Maron, M.S.; Semsarian, C. Genetics of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy after 20 years: Clinical perspectives. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 60, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canepa, M.; Fumagalli, C.; Tini, G.; Vincent-Tompkins, J.; Day, S.M.; Ashley, E.A.; Mazzarotto, F.; Ware, J.S.; Michels, M.; Jacoby, D.; et al. Temporal Trend of Age at Diagnosis in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: An Analysis of the International Sarcomeric Human Cardiomyopathy Registry. Circ. Heart Fail. 2020, 13, e007230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfares, A.A.; Kelly, M.A.; McDermott, G.; Funke, B.H.; Lebo, M.S.; Baxter, S.B.; Shen, J.; McLaughlin, H.M.; Clark, E.H.; Babb, L.J.; et al. Results of clinical genetic testing of 2,912 probands with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: Expanded panels offer limited additional sensitivity. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 880–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, C.; Bagnall, R.D.; Lam, L.; Semsarian, C.; Ingles, J. Multiple Gene Variants in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy in the Era of Next-Generation Sequencing. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2017, 10, e001666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, R.; Thomson, K.L.; Ware, J.S.; Funke, B.H.; Woodley, J.; McGuire, K.J.; Mazzarotto, F.; Blair, E.; Seller, A.; Taylor, J.C.; et al. Reassessment of Mendelian gene pathogenicity using 7,855 cardiomyopathy cases and 60,706 reference samples. Genet. Med. 2017, 19, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofman, N.; Tan, H.L.; Alders, M.; Kolder, I.; De Haij, S.; Mannens, M.M.A.M.; Lombardi, M.P.; Dit Deprez, R.H.L.; Van Langen, I.; Wilde, A.A.M. Yield of molecular and clinical testing for arrhythmia syndromes: Report of 15 years’ experience. Circulation 2013, 128, 1513–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Militaru, S.; Saftoiu, A.; Streubel, B.; Jurcut, R. New Fabry disease mutation confirms cardiomyopathy aetiology: A case report. Eur. Heart J. Case Rep. 2018, 2, yty133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giucǎ, A.; Mitu, C.; Popescu, B.O.; Bastian, A.E.; Capsą, R.; Mursǎ, A.; Rǎdoi, V.; Popescu, B.A.; Jurcuţ, R. Novel FHL1 mutation variant identified in a patient with nonobstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and myopathy—A case report. BMC Med. Genet. 2020, 21, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jercan, A.; Ene, A.; Jurcut, R.; Draghici, M.; Badelita, S.; Dragomir, M.; Dobrea, C.; Popescu, M.; Jardan, D.; Stoica, E.; et al. Clinical characteristics in patients with hereditary amyloidosis with Glu54Gln transthyretin identified in the Romanian population. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2020, 15, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecchi, F.; Iascone, M.; Maurizi, N.; Pezzoli, L.; Binaco, I.; Biagini, E.; Fibbi, M.L.; Olivotto, I.; Pieruzzi, F.; Fruntelata, A.; et al. Intraoperative Diagnosis of Anderson-Fabry Disease in Patients With Obstructive Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Undergoing Surgical Myectomy. JAMA Cardiol. 2017, 2, 1147–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdmann, J.; Daehmlow, S.; Wischke, S.; Senyuva, M.; Werner, U.; Raible, J.; Tanis, N.; Dyachenko, S.; Hummel, M.; Hetzer, R.; et al. Mutation spectrum in a large cohort of unrelated consecutive patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Clin. Genet. 2003, 64, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaski, J.P.; Syrris, P.; Esteban, M.T.T.; Jenkins, S.; Pantazis, A.; Deanfield, J.E.; McKenna, W.J.; Elliott, P.M. Prevalence of sarcomere protein gene mutations in preadolescent children with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2009, 2, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millat, G.; Bouvagnet, P.; Chevalier, P.; Dauphin, C.; Simon Jouk, P.; Da Costa, A.; Prieur, F.; Bresson, J.L.; Faivre, L.; Eicher, J.C.; et al. Prevalence and spectrum of mutations in a cohort of 192 unrelated patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2010, 53, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidman, C.E.; Seidman, J.G. Identifying sarcomere gene mutations in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: A personal history. Circ. Res. 2011, 108, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, C.Y.; Day, S.M.; Ashley, E.A.; Michels, M.; Pereira, A.C.; Jacoby, D.; Cirino, A.L.; Fox, J.C.; Lakdawala, N.K.; Ware, J.S.; et al. Genotype and Lifetime Burden of Disease in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: Insights from the Sarcomeric Human Cardiomyopathy Registry (SHaRe). Circulation 2018, 138, 1387–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzarotto, F.; Girolami, F.; Boschi, B.; Barlocco, F.; Tomberli, A.; Baldini, K.; Coppini, R.; Tanini, I.; Bardi, S.; Contini, E.; et al. Defining the diagnostic effectiveness of genes for inclusion in panels: The experience of two decades of genetic testing for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy at a single center. Genet. Med. 2018, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, R.; Buchan, R.; Wilk, A.; John, S.; Felkin, L.E.; Thomson, K.L.; Chiaw, T.H.; Loong, C.C.W.; Pua, C.J.; Raphael, C.; et al. Defining the genetic architecture of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: Re-evaluating the role of non-sarcomeric genes. Eur. Heart J. 2017, 38, 3461–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, R.; Tadros, R.; Bezzina, C.R. When genetic burden reaches threshold. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 3849–3855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, K.L.; Ormondroyd, E.; Harper, A.R.; Dent, T.; McGuire, K.; Baksi, J.; Blair, E.; Brennan, P.; Buchan, R.; Bueser, T.; et al. Analysis of 51 proposed hypertrophic cardiomyopathy genes from genome sequencing data in sarcomere negative cases has negligible diagnostic yield. Genet. Med. 2019, 21, 1576–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnall, R.D.; Ingles, J.; Dinger, M.E.; Cowley, M.J.; Ross, S.B.; Minoche, A.E.; Lal, S.; Turner, C.; Colley, A.; Rajagopalan, S.; et al. Whole Genome Sequencing Improves Outcomes of Genetic Testing in Patients With Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 72, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagen, C.M.; Aidt, F.H.; Havndrup, O.; Hedley, P.L.; Jensen, M.K.; Kanters, J.K.; Pham, T.T.; Bundgaard, H.; Christiansen, M. Private mitochondrial DNA variants in Danish patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargaran, P.K.; Evans, J.M.; Bodbin, S.E.; Smith, J.G.W.; Nelson, T.J.; Denning, C.; Mosqueira, D. Mitochondrial DNA: Hotspot for Potential Gene Modifiers Regulating Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzarotto, F.; Olivotto, I.; Boschi, B.; Girolami, F.; Poggesi, C.; Barton, P.J.R.; Walsh, R. Contemporary Insights Into the Genetics of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: Toward a New Era in Clinical Testing? J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e015473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Driest, S.L.; Vasile, V.C.; Ommen, S.R.; Will, M.L.; Tajik, A.J.; Gersh, B.J.; Ackerman, M.J. Myosin binding protein C mutations and compound heterozygosity in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2004, 44, 1903–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingles, J.; Doolan, A.; Chiu, C.; Seidman, J.; Seidman, C.; Semsarian, C. Compound and double mutations in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: Implications for genetic testing and counselling. J. Med. Genet. 2005, 42, e59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girolami, F.; Ho, C.Y.; Semsarian, C.; Baldi, M.; Will, M.L.; Baldini, K.; Torricelli, F.; Yeates, L.; Cecchi, F.; Ackerman, M.J.; et al. Clinical Features and Outcome of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Associated with Triple Sarcomere Protein Gene Mutations. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 55, 1444–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maron, B.J.; Maron, M.S.; Semsarian, C. Double or compound sarcomere mutations in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: A potential link to sudden death in the absence of conventional risk factors. Hear. Rhythm 2012, 9, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene | Chromosome | Encoding Protein | Number of Rare Variants Identified |
|---|---|---|---|
| ACTA1 | 1 | Actin alpha skeletal muscle | 1 |
| ACTC1 | 15 | Actin alpha cardiac muscle 1 | 0 |
| ACTN2 | 1 | Actinin alpha 2 | 3 |
| ANKRD1 | 10 | Ankyrin repeat domain-containing protein 1 | 2 |
| BRAF | 7 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase B-raf | 1 |
| CALR3 | 19 | Calreticulin 3 | 1 |
| CASQ2 | 1 | Calsequestrin 2 | 0 |
| CAV3 | 3 | Caveolin-3 | 1 |
| COX15 | 10 | Cytochrome c oxidase assembly protein COX15 homolog | 0 |
| CRYAB | 11 | Alpha-crystallin B chain | 0 |
| CSRP3 | 11 | Cysteine and glycine-rich protein 3 | 1 |
| DES | 2 | Desmin | 4 |
| FHL1 | X | Four and a half LIM domains protein 1 | 0 |
| FXN | 9 | Frataxin | 0 |
| GAA | 17 | Lysosomal alpha-glucosidase | 3 |
| GLA | X | Alpha-galactosidase A | 0 |
| JPH2 | 20 | Junctophilin-2 | 2 |
| KLF10 | 8 | Krueppel-like factor 10 | 2 |
| LAMP2 | X | Lysosome-associated membrane glycoprotein 2 | 1 |
| LDB3 | 10 | LIM domain-binding protein 3 | 5 |
| MAP2K1 | 15 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 | 1 |
| MAP2K2 | 19 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 2 | 0 |
| MYBPC3 | 11 | Myosin-binding protein C, cardiac-type | 17 |
| MYH6 | 14 | Myosin heavy chain 6 | 3 |
| MYH7 | 14 | Myosin heavy chain 7 | 9 |
| MYL2 | 12 | Myosin regulatory light chain 2 | 1 |
| MYL3 | 3 | Myosin light chain 3 | 0 |
| MYLK2 | 20 | Myosin light chain kinase 2 | 1 |
| MYO6 | 6 | Myosin-VI | 1 |
| MYOZ2 | 4 | Myozenin-2 | 1 |
| MYPN | 10 | Myopalladin | 1 |
| NEXN | 1 | Nexilin | 1 |
| PDLIM3 | 4 | PDZ and LIM domain protein 3 | 1 |
| PLN | 6 | Cardiac phospholamban | 0 |
| PRKAG2 | 7 | 5′-AMP-activated protein kinase subunit gamma-2 | 2 |
| PTPN11 | 12 | Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 11 | 0 |
| RAF1 | 3 | RAF proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase | 0 |
| SLC25A4 | 4 | ADP/ATP translocase 1 | 0 |
| SOS1 | 2 | Son of sevenless homolog 1 | 2 |
| TCAP | 17 | Telethonin | 1 |
| TNNC1 | 3 | Troponin C | 0 |
| TNNI3 | 19 | Troponin I | 1 |
| TNNT2 | 1 | Troponin T | 4 |
| TPM1 | 15 | Tropomyosin alpha-1 chain | 2 |
| TRIM63 | 1 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRIM63 | 1 |
| TTN | 2 | Titin | 17 |
| VCL | 10 | Vinculin | 1 |
| Variable | G+ (n = 6) | G− (n = 39) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age at inclusion, years | 34 ± 10.3 | 53 ± 14.7 | 0.04 |
| Sex: male, n (%) | 6 (100%) | 27 (69.2%) | 0.31 |
| Family history of HCM, n (%) | 2 (33.3%) | 5 (12.82%) | 0.06 |
| Family history of SCD, n (%) | 4 (66.7%) | 10 (25.6%) | 0.065 |
| ICD, n (%) | 1 (16.7%) | 6 (15.4%) | 0.68 |
| Atrial fibrillation, n (%) | 5 (83.33%) | 17 (43.6%) | 0.35 |
| Echocardiographic data | |||
| Maron classification, n (%) | |||
| 1 | 2 (33.3%) | 5 (17.9%) | 0.56 |
| 2 | 1 (16.7%) | 4 (10.3%) | |
| 3 | 3 (50%) | 29 (69.2%) | |
| 4 | 0 | 1 (2.6%) | |
| Presence of LVOTO, n (%) | 1 (16.7%) | 19 (48.7%) | 0.29 |
| LV maximal wall thickness, mm | 18.83 ± 7.28 | 20.97 ± 4.88 | 0.36 |
| LV mass, g | 262.4 ± 113.7 | 275.45 ± 96 | 0.53 |
| LVEDD, mm | 46.2 ± 9 | 39.9 ± 7.17 | 0.13 |
| LVESD, mm | 26 ± 7.29 | 24 ± 10.8 | 0.66 |
| LVEDV, ml | 106.85 ± 37.33 | 121.6 ± 44.22 | 0.43 |
| LVESV, ml | 50.96 ± 26.82 | 55.4 ± 21.3 | 0.64 |
| LVEF, (%) | 58.52 ± 19.9 | 56.6 ± 13.36 | 0.76 |
| LAD, mm | 39.8 ± 5.49 | 40.74 ± 7 | 0.77 |
| LAV, ml | 117.8 ± 68.18 | 83.19 ± 41.9 | 0.12 |
| Consequence | Missense | Stop-Gained | In-Frame | Frameshift | Splice | Synonymous | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Previously reported | 35 | 1 | 2 | - | - | 14 | 52 |
| Novel | 30 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8 | 43 |
| Total | 65 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 22 | 95 |
| Gene | HGVSc | HGVSp | Molecular Consequence | In Silico Predictions | VarSome Class | No. Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACTA1 | c.848G>A | p.Ser283Asn | Missense variant | S: D P: N PP: B MT: DC | LP | 1 |
| ACTN2 | c.411C>A | p.Ile137= | Synonymous variant | S: T P: N PP: NA MT: DC | LB | 1 |
| ACTN2 | c.973G>T | p.Asp325Tyr | Missense variant | S: D P: D PP: PrD MT: DC | VUS | 1 |
| ANKRD1 | c.566C>T | p.Ala189Val | Missense variant | S: D P: D PP: PoD MT: DC | VUS | 1 |
| CALR3 | c.877G>T | p.Glu293Ter | Stop gained | S: D P: NA PP: NA MT: DC | P | 1 |
| DES | c.462C>A | p.Leu154= | Synonymous variant | S: T P: N PP: NA MT: DC | LB | 1 |
| DES | c.1023T>G | p.Thr341= | Synonymous variant | S: T P: N PP: NA MT: DC | LP | 1 |
| DES | c.1095C>A | p.Asp365Glu | Missense variant | S: T P: N PP: B MT: DC | LP | 1 |
| DES | c.1104G>T | p.Ala368= | Synonymous variant | S: T P: N PP: NA MT: Pol | LB | 1 |
| GAA | c.352G>A | p.Gln118Lys | Missense variant | S: T P: N PP: B MT: Pol | VUS | 1 |
| JPH2 | c.1683G>T | p.Ala561= | Synonymous variant | S: T P: N PP: NA MT: DC | LB | 1 |
| JPH2 | c.1039G>T | p.Val347Phe | Missense variant | S: D P: D PP: PrD MT: DC | LB | 1 |
| KLF10 | c.1060G>T | p.Ala354Ser | Missense variant | S: T P: N PP: B MT: Pol | VUS | 1 |
| LDB3 | c.563G>A | p.Gly188Asp | Missense variant | S: T P: N PP: B MT: Pol | LB | 1 |
| LDB3 | c.1103C>A | p.Pro368His | Missense variant | S: T P: N PP: NA MT: DC | LB | 1 |
| LDB3 | c.1155C>A | p.Thr385= | Synonymous variant | S: T P: N PP: NA MT: Pol | LB | 1 |
| LDB3 | c.1838C>A | p.Pro613Gln | Missense variant | S: D P: D PP: NA MT: DC | VUS | 1 |
| MYBPC3 | c.2813C>T | p.Ala938Val | Missense variant | S: D P: N PP: PrD MT: DC | LP | 1 |
| MYBPC3 | c.1965A>G | p.Ile655Met | Missense variant | S: T P: N PP: B MT: Pol | VUS | 2 |
| MYBPC3 | c.1957_1962delGGCCGC | p.Gly653_Arg654del | In-frame deletion | S: NA P: D PP: NA MT: Pol | LP | 2 |
| MYBPC3 | c.1252A>C | p.Lys418Gln | Missense variant | S: T P: N PP: B MT: DC | VUS | 1 |
| MYBPC3 | c.1251C>T | p.Ala417= | Synonymous variant | S: T P: N PP: NA MT: DC | LB | 1 |
| MYBPC3 | c.1247_1248insCCAG | p.Ala417GlnfsTer29 | Frameshift variant | S: NA P: NA PP: NA MT: DC | P | 1 |
| MYBPC3 | c.996G>T | p.Glu332Asp | Missense variant | S: T P: N PP: B MT: DC | VUS | 1 |
| MYH6 | c.2571G>T | p.Glu857Asp | Missense variant | S: T P: N PP: PrD MT: DC | LB | 1 |
| MYH6 | c.2346G>T | p.Arg782Ser | Missense variant | S: D P: D PP: B MT: DC | VUS | 1 |
| MYLK2 | c.1431C>A | p.Ser477Arg | Missense variant | S: D P: D PP: PrD MT: DC | VUS | 1 |
| MYOZ2 | c.236C>A | p.Ala79Glu | Missense variant | S: T P: N PP: PoD MT: DC | LB | 1 |
| NEXN | c.44C>A | p.Ser15Tyr | Missense variant | S: D P: N PP: PoD MT: DC | VUS | 1 |
| PRKAG2 | c.1381C>T | p.Pro461Ser | Missense variant | S: D P: D PP: PrD MT: DC | VUS | 1 |
| SOS1 | c.3434A>G | p.Asp1145Gly | Missense variant | S: T P: N PP: B MT: DC | VUS | 1 |
| TCAP | c.68C>A | p.Ala23Glu | Missense variant | S: D P: D PP: PoD MT: DC | VUS | 1 |
| TRIM63 | c.697C>A | p.Gln233Lys | Missense variant | S: T P: N PP: B MT: Pol | LB | 1 |
| TTN | c.44530G>T | p.Ala14844Ser | Missense variant | S: D P: N PP: PrD MT: DC | VUS | 1 |
| TTN | c.30392G>T | p.Cys10131Phe | Missense variant | S: T P: D PP: B MT: DC | VUS | 1 |
| TTN | c.26928G>T | p.Leu8976= | Synonymous variant | S: T P: N PP: NA MT: DC | LB | 1 |
| TTN | c.25185G>T | p.Lys8395Asn | Missense variant | S: D P: D PP: PrD MT: DC | LB | 1 |
| TTN | c.22816+1G>T | Splice donor variant | S: NA P: NA PP: NA MT: DC | P | 1 | |
| TTN | c.16783G>T | p.Val5595Leu | Missense variant | S: T P: N PP: B MT: Pol | LB | 1 |
| TTN | c.11927A>G | p.Lys3976Arg | Missense variant | S: T P: N PP: B MT: Pol | LB | 1 |
| TTN | c.11338G>T | p.Glu3780Ter | Stop gained | S: NA P: NA PP: NA MT: DC | P | 1 |
| TTN | c.2518G>T | p.Ala840Ser | Missense variant | S: D P: N PP: B MT: DC | VUS | 1 |
| TTN | c.49G>T | p.Val17Leu | Missense variant | S: T P: N PP: B MT: DC | VUS | 1 |
| Gene | HGVSc | HGVSp | dbSNP ID | ClinVar ID | ClinVar Class | No. Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACTN2 | c.2445C>T | p.Ile815= | rs397516575 | 43929 | LB | 1 |
| ANKRD1 | c.197G>A | p.Arg66Gln | rs150797476 | 45628 | LB | 1 |
| BRAF | c.95_100dupGCGCCG | p.Gly32_Ala33dup | rs397515331 | 41448 | VUS | 1 |
| CAV3 | c.39C>T | p.Ile13= | rs200562715 | 179005 | LB | 1 |
| CSRP3 | c.208G>T | p.Gly70Trp | rs777211110 | 520335 | VUS | 1 |
| GAA | c.762G>A | p.Ser254= | rs533960093 | 509666 | LB | 1 |
| GAA | c.899C>A | p.Ala300Glu | rs1032949450 | NA | NA | 1 |
| KLF10 | c.973G>A | p.Val325Ile | rs760040811 | NA | NA | 1 |
| LAMP2 | c.37G>T | p.Gly13Trp | rs12853266 | NA | NA | 1 |
| LDB3 | c.610G>A | p.Ala204Thr | rs774976112 | 626705 | CON (LB/VUS) | 1 |
| MAP2K1 | c.315C>T | p.Pro105= | rs144166521 | 44589 | B | 2 |
| MYBPC3 | c.3413G>C | p.Arg1138Pro | rs187705120 | 42712 | VUS | 2 |
| MYBPC3 | c.3294G>A | p.Trp1098Ter | rs767039057 | 520341 | P | 1 |
| MYBPC3 | c.3262C>G | p.Pro1088Ala | rs1263358939 | NA | NA | 1 |
| MYBPC3 | c.2882C>T | p.Pro961Leu | rs373056282 | 42665 | VUS | 1 |
| MYBPC3 | c.2441_2443delAGA * | p.Lys814del * | rs727504288 | 177700 | CON (VUS/LP) | 1 |
| MYBPC3 | c.1967C>T | p.Pro656Leu | rs927421140 | NA | NA | 2 |
| MYBPC3 | c.1316G>A | p.Gly439Asp | rs763045718 | 628463 | VUS | 1 |
| MYBPC3 | c.1127G>A | p.Ser376Asn | rs1595846858 | NA | NA | 1 |
| MYBPC3 | c.772G>A | p.Glu258Lys | rs397516074 | 42792 | P | 1 |
| MYBPC3 | c.152C>T | p.Ala51Val | rs746738538 | NA | NA | 1 |
| MYH6 | c.2710G>T | p.Glu904Ter | rs759822161 | NA | NA | 1 |
| MYH7 | c.5736C>T | p.Ile1912= | rs200728597 | 43086 | B | 1 |
| MYH7 | c.5203T>A | p.Ser1735Thr | rs144066768 | 181272 | VUS | 1 |
| MYH7 | c.4377G>T | p.Lys1459Asn | rs201307101 | 43012 | LB | 1 |
| MYH7 | c.4348G>A | p.Asp1450Asn | rs397516211 | 43009 | VUS | 1 |
| MYH7 | c.4212G>T | p.Val1404= | rs397516205 | 43000 | LB | 1 |
| MYH7 | c.2389G>A | p.Ala797Thr | rs3218716 | 42901 | LP/P | 1 |
| MYH7 | c.1755C>T | p.Ile585= | rs201860580 | 194465 | CON (LB/VUS) | 1 |
| MYH7 | c.1108G>A | p.Glu370Lys | NU | 858379 | VUS | 1 |
| MYH7 | c.715G>A | p.Asp239Asn | rs397516264 | 43100 | LP/P | 1 |
| MYL2 | c.374C>T | p.Thr125Met | rs375667565 | 43473 | VUS | 1 |
| MYO6 | c.2322T>C | p.Pro774= | rs947653207 | NA | NA | 1 |
| MYPN | c.1012C>T | p.Arg338Cys | rs140037748 | 201882 | VUS | 1 |
| PDLIM3 | c.334G>A | p.Gly112Arg | rs777447396 | 967683 | VUS | 1 |
| PRKAG2 | c.147C>T | p.Asp49= | rs761196275 | 696154 | LB | 1 |
| SOS1 | c.661C>G | p.Leu221Val | rs1007628403 | NA | NA | 1 |
| TNNI3 | c.557G>A | p.Arg186Gln | rs397516357 | 43395 | LP/P | 1 |
| TNNT2 | c.863G>A | p.Arg288His | rs397516484 | 43674 | VUS | 1 |
| TNNT2 | c.774C>T | p.Phe258= | rs397516481 | 43668 | LB | 1 |
| TNNT2 | c.430C>T | p.Arg144Trp | rs45525839 | 127070 | VUS | 1 |
| TNNT2 | c.341C>T | p.Ala114Val | rs727504245 | 177633 | CON (VUS/LP) | 1 |
| TPM1 | c.574G>A | p.Glu192Lys | rs199476315 | 31882 | P | 1 |
| TPM1 | c.835C>T | p.Leu279= | rs374434837 | 378751 | LB | 1 |
| TTN | c.40423A>G | p.Lys13475Glu | rs775980062 | NA | NA | 1 |
| TTN | c.32736G>A | p.Pro10912= | rs368838709 | NA | NA | 1 |
| TTN | c.29079G>A | p.Ala9693= | rs372997298 | 137775 | CON (B/LB/VUS) | 1 |
| TTN | c.22386T>A | p.Asp7462Glu | rs183482849 | 46699 | CON (B/VUS) | 1 |
| TTN | c.20395C>T | p.Arg6799Trp | rs751534449 | 809053 | VUS | 1 |
| TTN | c.15856G>A | p.Gly5286Ser | rs1409273228 | NA | NA | 1 |
| TTN | c.11959A>G | p.Ile3987Val | rs551387805 | 264496 | CON (LB/VUS) | 1 |
| VCL | c.3186G>A | p.Gln1062= | rs761534024 | 300798 | CON (LB/VUS) | 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Micheu, M.M.; Popa-Fotea, N.-M.; Oprescu, N.; Bogdan, S.; Dan, M.; Deaconu, A.; Dorobantu, L.; Gheorghe-Fronea, O.; Greavu, M.; Iorgulescu, C.; et al. Yield of Rare Variants Detected by Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing in a Cohort of Romanian Index Patients with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 1061. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10121061
Micheu MM, Popa-Fotea N-M, Oprescu N, Bogdan S, Dan M, Deaconu A, Dorobantu L, Gheorghe-Fronea O, Greavu M, Iorgulescu C, et al. Yield of Rare Variants Detected by Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing in a Cohort of Romanian Index Patients with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Diagnostics. 2020; 10(12):1061. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10121061
Chicago/Turabian StyleMicheu, Miruna Mihaela, Nicoleta-Monica Popa-Fotea, Nicoleta Oprescu, Stefan Bogdan, Monica Dan, Alexandru Deaconu, Lucian Dorobantu, Oana Gheorghe-Fronea, Maria Greavu, Corneliu Iorgulescu, and et al. 2020. "Yield of Rare Variants Detected by Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing in a Cohort of Romanian Index Patients with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy" Diagnostics 10, no. 12: 1061. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10121061
APA StyleMicheu, M. M., Popa-Fotea, N.-M., Oprescu, N., Bogdan, S., Dan, M., Deaconu, A., Dorobantu, L., Gheorghe-Fronea, O., Greavu, M., Iorgulescu, C., Scafa-Udriste, A., Ticulescu, R., Vatasescu, R. G., & Dorobanțu, M. (2020). Yield of Rare Variants Detected by Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing in a Cohort of Romanian Index Patients with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Diagnostics, 10(12), 1061. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10121061






