Chronic Pain Diagnosis Using Machine Learning, Questionnaires, and QST: A Sensitivity Experiment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
2.1. Participants
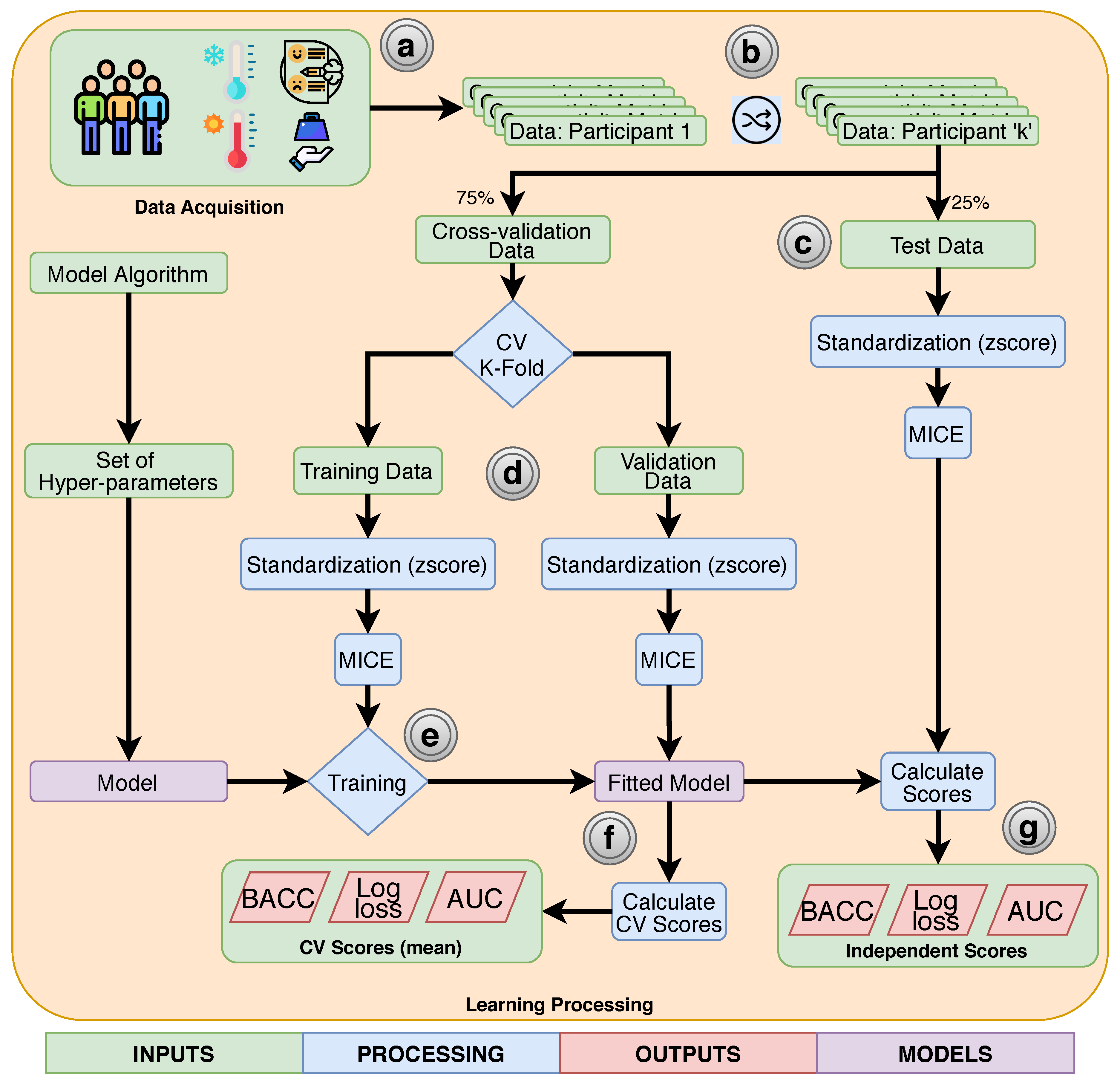
2.2. Data Acquisition
2.3. Data Preprocessing
2.4. Classifiers
2.5. Training and Evaluation
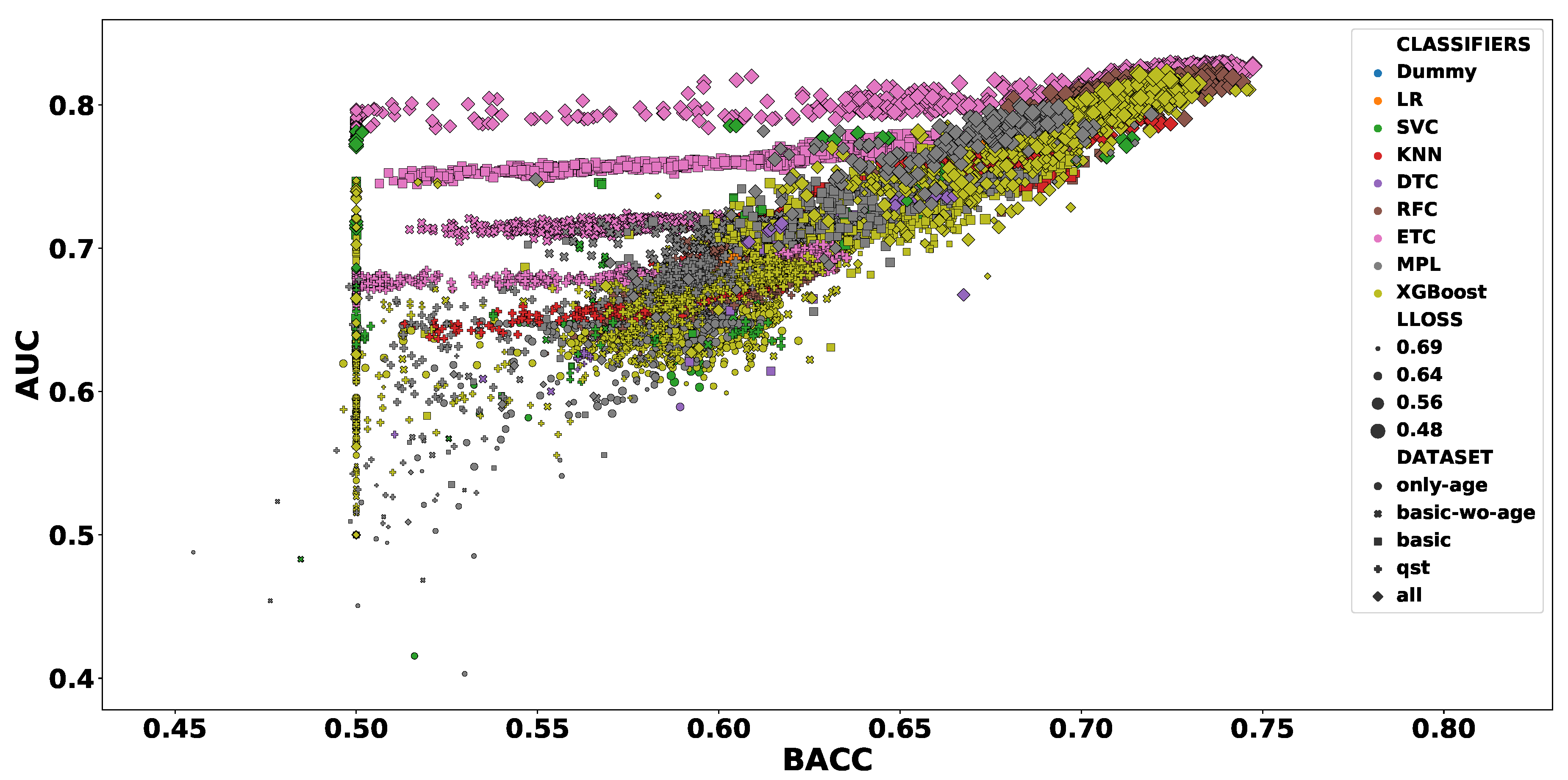
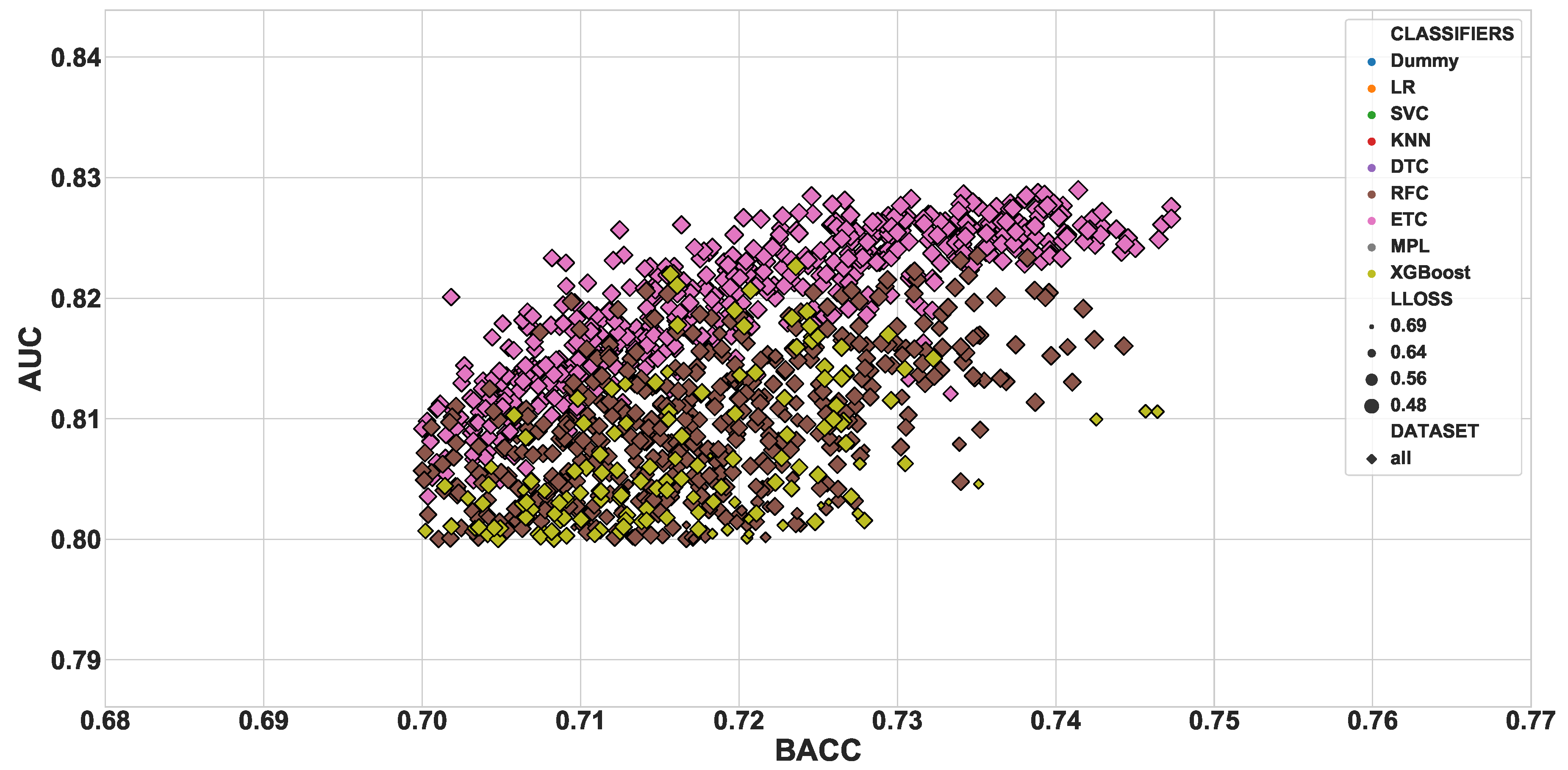
3. Results
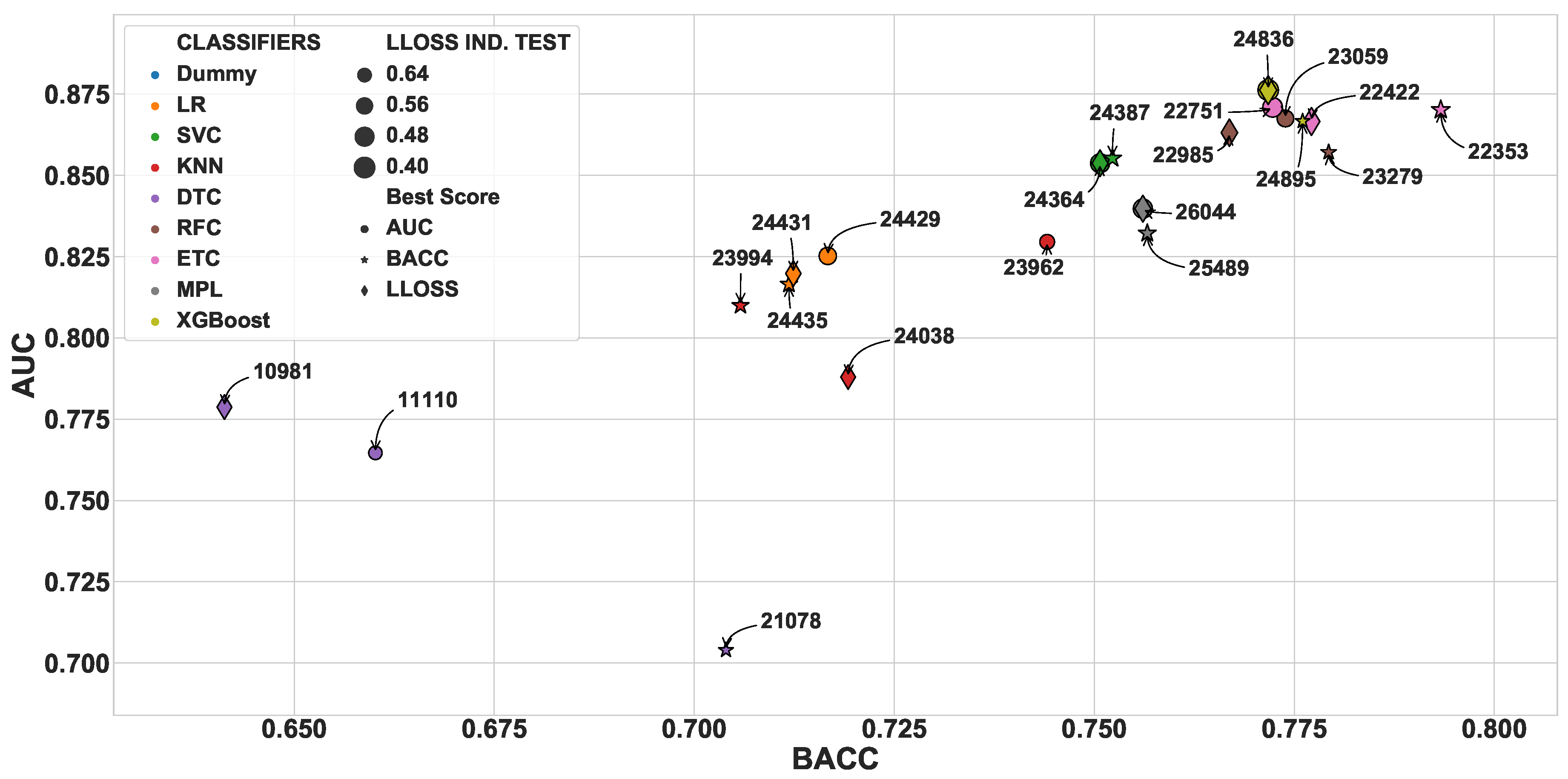
3.1. Independent Test Scores
3.2. Model Interpretation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Albe-Fessar, D.; Berkley, K.; Kruger, L.; Ralston, H., III; Willis, W., Jr. Diencephalic mechanisms of pain sensation. Brain Res. Rev. 1985, 9, 217–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, P.; Larbig, W.; Braun, C.; Preissl, H.; Birbaumer, N. Influence of Social Support and Emotional Context on Pain Processing and Magnetic Brain Responses in Fibromyalgia. Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 50, 4035–4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bevers, K.; Watts, L.; Kishino, N.D.; Gatchel, R.J. The biopsychosocial model of theassessment, prevention, and treatment of chronic pain. Eur. Neurol. Rev. 2016, 12, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treede, R.D.; Rief, W.; Barke, A.; Aziz, Q.; Bennett, M.I.; Benoliel, R.; Cohen, M.; Evers, S.; Finnerup, N.B.; First, M.B.; et al. Chronic pain as a symptom or a disease: The IASP Classification of Chronic Pain for the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-11). Pain 2019, 160, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merskey, H.; Addison, R.G.; Beric, A.; Blumberg, H.; Bogduk, N.; Boivie, J.; Bond, M.R.; Bonica, J.J.; Boyd, D.B.; Deathe, A.B.; et al. Classification of Chronic Pain: Descriptions of Chronic Pain Syndromes and Definitions of Pain Terms; IASP Press: Seattle, WA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe, F.; Clauw, D.J.; Fitzcharles, M.A.; Goldenberg, D.L.; Häuser, W.; Katz, R.L.; Mease, P.J.; Russell, A.S.; Russell, I.J.; Walitt, B. 2016 Revisions to the 2010/2011 fibromyalgia diagnostic criteria. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2016, 46, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatchel, R.J.; Peng, Y.B.; Peters, M.L.; Fuchs, P.N.; Turk, D.C. The Biopsychosocial Approach to Chronic Pain: Scientific Advances and Future Directions. Psychol. Bull. 2010, 133, 581–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traeger, A.C.; Henschke, N.; Hübscher, M.; Williams, C.M.; Kamper, S.J.; Maher, C.G.; Moseley, G.L.; McAuley, J.H. Estimating the Risk of Chronic Pain: Development and Validation of a Prognostic Model (PICKUP) for Patients with Acute Low Back Pain. PLoS Med. 2016, 13, e1002019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagé, I.; Abboud, J.; O’Shaughnessy, J.; Laurencelle, L.; Descarreaux, M. Chronic low back pain clinical outcomes present higher associations with the STarT Back Screening Tool than with physiologic measures: A 12-month cohort study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2015, 16, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Almeida, Y.; Fillingim, R.B. Can quantitative sensory testing move us closer to mechanism-based pain management? Pain Med. 2014, 15, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cámara, R.J.A.; Merz, C.; Wegmann, B.; Stauber, S.; Von Känel, R.; Egloff, N. Cost-saving early diagnosis of functional pain in nonmalignant pain: A noninferiority study of diagnostic accuracy. Pain Res. Treat. 2016, 2016, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracely, R.H.; Grant, M.A.; Giesecke, T. Evoked pain measures in fibromyalgia. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2003, 17, 593–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaillant, J.; Pons, C.; Balaguier, R.; Dumolard, A.; Vuillerme, N. In patients with fibromyalgia, there are 18 tender points that are more sensitive than in healthy subjects. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2017, 60, e95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ultsch, A.; Lötsch, J. Machine-learned cluster identification in high-dimensional data. J. Biomed. Inform. 2016, 66, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ablin, J.N.; Buskila, D. Update on the genetics of the fibromyalgia syndrome. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2015, 29, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diatchenko, L.; Slade, G.D.; Nackley, A.G.; Bhalang, K.; Sigurdsson, A.; Belfer, I.; Goldman, D.; Xu, K.; Shabalina, S.A.; Shagin, D.; et al. Genetic basis for individual variations in pain perception and the development of a chronic pain condition. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2005, 14, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraschiv-Ionescu, A.; Perruchoud, C.; Buchser, E.; Aminian, K. Barcoding human physical activity to assess chronic pain conditions. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo, B.; Gilliaux, M.; Poncin, W.; Detrembleur, C. Reliability and validity of a kinematic spine model during active trunk movement in healthy subjects and patients with chronic non-specific low back pain. J. Rehabil. Med. 2012, 44, 756–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo, B.; Nielens, H.; Gilliaux, M.; Hall, T.; Detrembleur, C.; Christine, P.; Gilliaux, M.; Hall, T.; Detrembleur, C. Use of kinematic algorithms to distinguish people with chronic non-specific low back pain from asymptomatic subjects: A validation study. J. Rehabil. Med. 2014, 46, 819–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, I.D.S.; Gamundí, A.; Miranda, J.G.V.; França, L.G.S.; De Santana, C.N.; Montoya, P. Altered functional performance in patients with fibromyalgia. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, E.S.D.S.; de Queirós, F.C.; Montoya, P.; Santos, C.L.; do Nascimento, M.A.; Ito, C.H.; Silva, M.; Nunes Santos, D.B.; Benevides, S.; Miranda, J.G.V.; et al. Electroencephalographic Patterns in Chronic Pain: A Systematic Review of the Literature. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt-Wilcke, T. Neuroimaging of chronic pain. Best Pract. Rese. Clin. Rheumatol. 2015, 29, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, K.D.; Racine, E.; Collett, B. Neuroethical issues related to the use of brain imaging: Can we and should we use brain imaging as a biomarker to diagnose chronic pain? Pain 2012, 153, 1555–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santana, A.N.; Cifre, I.; De Santana, C.N.; Montoya, P. Using Deep Learning and Resting-State fMRI to Classify Chronic Pain Conditions. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Martinez, D.; Peng, K.; Lee, A.; Borsook, D.; Picard, R. Pain Detection with fNIRS-Measured Brain Signals: A Personalized Machine Learning Approach Using the Wavelet Transform and Bayesian Hierarchical Modeling with Dirichlet Process Priors. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Affective Computing and Intelligent Interaction (ACII) Workshop on Recognition, Treatment and Management of Pain and Distress, Cambridge, UK, 3 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Dodick, D.W.; Loder, E.W.; Manack Adams, A.; Buse, D.C.; Fanning, K.M.; Reed, M.L.; Lipton, R.B. Assessing barriers to chronic migraine consultation, diagnosis, and treatment: Results from the Chronic Migraine Epidemiology and Outcomes (CaMEO) study. Head. J. Head Face Pain 2016, 56, 821–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kress, H.G.; Aldington, D.; Alon, E.; Coaccioli, S.; Collett, B.; Coluzzi, F.; Huygen, F.; Jaksch, W.; Kalso, E.; Kocot-Kepska, M.; et al. A holistic approach to chronic pain management that involves all stakeholders: Change is needed. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2015, 31, 1743–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalonde, L.; Leroux-Lapointe, V.; Choinière, M.; Martin, E.; Lussier, D.; Berbiche, D.; Lamarre, D.; Thiffault, R.; Jouini, G.; Perreault, S. Knowledge, attitudes and beliefs about chronic noncancer pain in primary care: A Canadian survey of physicians and pharmacists. Pain Res. Manag. 2014, 19, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dworkin, R.H.; Bruehl, S.; Fillingim, R.B.; Loeser, J.D.; Terman, G.W.; Turk, D.C. Multidimensional Diagnostic Criteria for Chronic Pain: Introduction to the ACTTION—American Pain Society Pain Taxonomy (AAPT). J. Pain 2016, 17, T1–T9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markman, J.D.; Czerniecka-Foxx, K.; Khalsa, P.S.; Hayek, S.M.; Asher, A.L.; Loeser, J.D.; Chou, R. AAPT Diagnostic Criteria for Chronic Low Back Pain. J. Pain 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohrbach, R.; Dworkin, S.F. AAPT Diagnostic Criteria for Chronic Painful Temporomandibular Disorders. J. Pain 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, L.M.; Bennett, R.M.; Crofford, L.J.; Dean, L.E.; Clauw, D.J.; Goldenberg, D.L.; Fitzcharles, M.A.; Paiva, E.S.; Staud, R.; Sarzi-Puttini, P.; et al. AAPT Diagnostic Criteria for Fibromyalgia. J. Pain 2019, 20, 611–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, R.; Edwards, R.; Baron, R.; Bruehl, S.; Cruccu, G.; Dworkin, R.H.; Haroutounian, S. AAPT Diagnostic Criteria for Peripheral Neuropathic Pain: Focal and Segmental Disorders. J. Pain 2019, 20, 369–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Wesselmann, U.; Walker, L.; Lee, L.; Zeltzer, L.; Verne, G.N. AAPT Diagnostic Criteria for Chronic Abdominal, Pelvic, and Urogenital Pain: Irritable Bowel Syndrome. J. Pain 2018, 19, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widerström-Noga, E.; Loeser, J.D.; Jensen, T.S.; Finnerup, N.B. AAPT Diagnostic Criteria for Central Neuropathic Pain. J. Pain 2017, 18, 1417–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dampier, C.; Palermo, T.M.; Darbari, D.S.; Hassell, K.; Smith, W.; Zempsky, W. AAPT Diagnostic Criteria for Chronic Sickle Cell Disease Pain. J. Pain 2017, 18, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellor, F.E.; Thomas, P.W.; Thompson, P.; Breen, A.C. Proportional lumbar spine inter-vertebral motion patterns: A comparison of patients with chronic, non-specific low back pain and healthy controls. Eur. Spine J. 2014, 23, 2059–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dankaerts, W.; O’Sullivan, P.B.; Burnett, A.F.; Straker, L.M.; Danneels, L.A. Reliability of EMG measurements for trunk muscles during maximal and sub-maximal voluntary isometric contractions in healthy controls and CLBP patients. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2004, 14, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rantanen, P.; Nykvist, F. Optimal sagittal motion axis for trunk extension and flexion tests in chronic low back trouble. Clin. Biomech. 2000, 15, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyer, D.; Kletzin, U.; Adler, D.; Adler, S.; Meissner, W.; Blickhan, R. Gait information flow indicates complex motor dysfunction. Physiol. Meas. 2005, 26, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, A.R.; Nargol, A.V.; Jones, A.P.; Ratcliffe, A.A.; Greenough, C.G. The value of electromyography of the lumbar paraspinal muscles in discriminating between chronic-low-back-pain sufferers and normal subjects. Eur. Spine J. 2005, 14, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfving, B.; Dedering, A.; Nemeth, G. Lumbar muscle fatigue and recovery in patients with long-term low-back trouble–electromyography and health-related factors. Clin. Biomech. 2003, 18, 619–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neblett, R.; Brede, E.; Mayer, T.G.; Gatchel, R.J. What is the best surface EMG measure of lumbar flexion-relaxation for distinguishing chronic low back pain patients from pain-free controls? Clin. J. Pain 2013, 29, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usui, C.; Hatta, K.; Aratani, S.; Yagishita, N.; Nishioka, K.; Kanazawa, T.; Ito, K.; Yamano, Y.; Nakamura, H.; Nakajima, T.; et al. The Japanese version of the 2010 American College of Rheumatology Preliminary Diagnostic Criteria for Fibromyalgia and the Fibromyalgia Symptom Scale: Reliability and validity. Mod. Rheumatol. 2012, 22, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casanueva, B.; García-Fructuoso, F.; Belenguer, R.; Alegre, C.; Moreno-Muelas, J.V.; Hernández, J.L.; Pina, T.; González-Gay, M.Á. The Spanish version of the 2010 American College of Rheumatology Preliminary Diagnostic Criteria for fibromyalgia: Reliability and validity assessment. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2016, 34, 55. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, J.A.; Mailler-burch, S.; Müller, D.; Studer, M.; Känel, R.V. Rethinking the criteria for fibromyalgia in 2019: The ABC indicators. J. Pain Res. 2019, 12, 2115–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiens, J.; Shenoy, E.S. Machine learning for healthcare: On the verge of a major shift in healthcare epidemiology. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 66, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, K.; Elahi, H.; Ayub, A.; Frezza, F.; Rizzi, A. Cancer diagnosis using deep learning: A bibliographic review. Cancers 2019, 11, 1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashi, E.K.; Zaman, M.S.U.; Hasan, M.R. An expert clinical decision support system to predict disease using classification techniques. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Electrical, Computer and Communication Engineering (ECCE), Cox’s Bazar, Bangladesh, 16–18 February 2017; pp. 396–400. [Google Scholar]
- Pollettini, J.T.; Panico, S.R.; Daneluzzi, J.C.; Tinós, R.; Baranauskas, J.A.; Macedo, A.A. Using machine learning classifiers to assist healthcare-related decisions: Classification of electronic patient records. J. Med. Syst. 2012, 36, 3861–3874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stafford, I.; Kellermann, M.; Mossotto, E.; Beattie, R.; MacArthur, B.; Ennis, S. A systematic review of the applications of artificial intelligence and machine learning in autoimmune diseases. NPJ Digit. Med. 2020, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lötsch, J.; Ultsch, A. Machine learning in pain research. Pain 2018, 159, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lötsch, J.; Alfredsson, L.; Lampa, J. Machine-learning–based knowledge discovery in rheumatoid arthritis–related registry data to identify predictors of persistent pain. Pain 2020, 161, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battineni, G.; Sagaro, G.G.; Chinatalapudi, N.; Amenta, F. Applications of Machine Learning Predictive Models in the Chronic Disease Diagnosis. J. Personal. Med. 2020, 10, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Solà, M.; Woo, C.W.; Pujol, J.; Deus, J.; Harrison, B.J.; Monfort, J.; Wager, T.D. Towards a neurophysiological signature for fibromyalgia. Pain 2017, 158, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, F.; Gostine, M.; Roberts, B.; Risko, R.; Cappelleri, J.C.; Sadosky, A. Characterizing classes of fibromyalgia within the continuum of central sensitization syndrome. J. Pain Res. 2018, 11, 2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrés-Rodríguez, L.; Borràs, X.; Feliu-Soler, A.; Pérez-Aranda, A.; Rozadilla-Sacanell, A.; Arranz, B.; Montero-Marin, J.; García-Campayo, J.; Angarita-Osorio, N.; Maes, M.; et al. Machine Learning to Understand the Immune-Inflammatory Pathways in Fibromyalgia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ung, H.; Brown, J.E.; Johnson, K.A.; Younger, J.; Hush, J.; Mackey, S. Multivariate Classification of Structural MRI Data Detects Chronic Low Back Pain. Cereb. Cortex 2014, 24, 1037–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judd, M.; Zulkernine, F.; Wolfrom, B.; Barber, D.; Rajaram, A. Detecting low back pain from clinical narratives using machine learning approaches. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Database and Expert Systems Applications, Regensburg, Germany, 3–6 September 2018; pp. 126–137. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, W.; Tu, Y.; Gollub, R.L.; Ortiz, A.; Napadow, V.; Yu, S.; Wilson, G.; Park, J.; Lang, C.; Jung, M.; et al. Visual network alterations in brain functional connectivity in chronic low back pain: A resting state functional connectivity and machine learning study. NeuroImage Clin. 2019, 22, 101775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mano, H.; Kotecha, G.; Leibnitz, K.; Matsubara, T.; Sprenger, C.; Nakae, A.; Shenker, N.; Shibata, M.; Voon, V.; Yoshida, W.; et al. Classification and characterisation of brain network changes in chronic back pain: A multicenter study. Wellcome Open Res. 2018, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalev-Shwartz, S.; Ben-David, S. Understanding Machine Learning: From Theory to Algorithms; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014; pp. 6–7. [Google Scholar]
- Burdack, J.; Horst, F.; Giesselbach, S.; Hassan, I.; Daffner, S.; Schöllhorn, W.I. Systematic Comparison of the Influence of Different Data Preprocessing Methods on the Performance of Gait Classifications Using Machine Learning. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.; Markey, M.K. A machine learning perspective on the development of clinical decision support systems utilizing mass spectra of blood samples. J. Biomed. Inform. 2006, 39, 227–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggensperger, K.; Lindauer, M.; Hoos, H.H.; Hutter, F.; Leyton-Brown, K. Efficient benchmarking of algorithm configurators via model-based surrogates. Mach. Learn. 2018, 107, 15–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rijn, J.N.; Hutter, F. Hyperparameter importance across datasets. In Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data, Mining, London, UK, 19–23 August 2018; pp. 2367–2376. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, A.T.; Steer, R.A.; Brown, G.K. Manual for the Beck Depression Inventory-II; Psychological Corporation: San Antonio, TX, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Spielberger, C.D.; Gorsuch, R.L.; Lushene, R.; Vagg, P.R.; Jacobs, G.A. Manual for the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory; Consulting Psychologists Press: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Breivik, H.; Collett, B.; Ventafridda, V.; Cohen, R.; Gallacher, D. Survey of chronic pain in Europe: Prevalence, impact on daily life, and treatment. Eur. J. Pain 2006, 10, 287–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Heer, E.W.; ten Have, M.; van Marwijk, H.W.; Dekker, J.; de Graaf, R.; Beekman, A.T.; van der Feltz-Cornelis, C.M. Pain as a risk factor for common mental disorders. Results from the Netherlands Mental Health Survey and Incidence Study-2: A longitudinal, population-based study. Pain 2018, 159, 712–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dersh, J.; Polatin, P.B.; Gatchel, R.J. Chronic pain and psychopathology: Research findings and theoretical considerations. Psychosom. Med. 2002, 64, 773–786. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rapti, E.; Damigos, D.; Apostolara, P.; Roka, V.; Tzavara, C.; Lionis, C. Patients with chronic pain: Evaluating depression and their quality of life in a single center study in Greece. BMC Psychol. 2019, 7, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villafaina, S.; Sitges, C.; Collado-Mateo, D.; Fuentes-García, J.P.; Gusi, N. Influence of depressive feelings in the brain processing of women with fibromyalgia: An EEG study. Medicine 2019, 98, e15564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, I.R.; Royston, P.; Wood, A.M. Multiple imputation using chained equations: Issues and guidance for practice. Stat. Med. 2011, 30, 377–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.f.; Huang, F.l.; Lin, C.J. Dual coordinate descent methods for logistic regression and maximum entropy models. Mach. Learn. 2011, 85, 41–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altman, N.S. An introduction to kernel and nearest-neighbor nonparametric regression. Am. Stat. 1992, 46, 175–185. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L.; Friedman, J.H.; Olshen, R.A.; Stone, C.J. Classification and regression trees. Int. Group 1984, 432, 151–166. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. Xgboost: A scalable tree boosting system. In Proceedings of the 22nd Acm Sigkdd International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- Bergstra, J.; Bengio, Y. Random search for hyper-parameter optimization. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2012, 13, 281–305. [Google Scholar]
- Fawcett, T. An introduction to ROC analysis. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2006, 27, 861–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, C.M. Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; p. 209. [Google Scholar]
- Nijeweme-d’Hollosy, W.O.; van Velsen, L.; Poel, M.; Groothuis-Oudshoorn, C.G.; Soer, R.; Hermens, H. Evaluation of three machine learning models for self-referral decision support on low back pain in primary care. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2018, 110, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouthillier, X.; Varoquaux, G. Survey of Machine-Learning Experimental Methods at NeurIPS2019 and ICLR2020; Research Report; Inria Saclay Ile de France: Pairs, France, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, K.D.; Gelbart, T.; Whisenant, T.C.; Waalen, J.; Mondala, T.S.; Iklé, D.N.; Salomon, D.R.; Bennett, R.M.; Kurian, S.M. Genome-wide expression profiling in the peripheral blood of patients with fibromyalgia. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2016, 34, 89. [Google Scholar]
- Schmukler, J.; Jamal, S.; Castrejon, I.; Block, J.A.; Pincus, T. Fibromyalgia Assessment Screening Tools (FAST) based on only Multidimensional Health Assessment Questionnaire (MDHAQ) scores as clues to fibromyalgia. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2019, 1, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, K.A.; Castrejon, I.; Descallar, J.; Pincus, T. Fibromyalgia Assessment Screening Tool (FAST): Clues to fibromyalgia on a multidimensional health assessment questionnaire (MDHAQ) for routine care. J. Rheumatol. 2019, 47, 761–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerrits, M.M.; van Marwijk, H.W.; van Oppen, P.; van der Horst, H.; Penninx, B.W. Longitudinal association between pain, and depression and anxiety over four years. J. Psychosom. Res. 2015, 78, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, S.E.; Nicolson, K.P.; Smith, B.H. Chronic pain: A review of its epidemiology and associated factors in population-based studies. Br. J. Anaesth. 2019, 123, e273–e283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giesecke, T.; Gracely, R.H.; Grant, M.A.; Nachemson, A.; Petzke, F.; Williams, D.A.; Clauw, D.J. Evidence of Augmented Central Pain Processing in Idiopathic Chronic Low Back Pain. Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 50, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, S.; Manniche, C.; Graven-Nielsen, T.; Arendt-Nielsen, L. Generalized deep-tissue hyperalgesia in patients with chronic low-back pain. Eur. J. Pain 2007, 11, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, F.; Smythe, H.A.; Yunus, M.B.; Bennett, R.M.; Bombardier, C.; Goldenberg, D.O.N.L.; Tugwell, P.; Campbell, S.M.; Abeles, M.; Clark, P.; et al. The american college of rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of fibromyalgia report of the Multicenter Criteria Committee. Arthritis Rheum. 1990, 33, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgopoulos, V.; Akin-Akinyosoye, K.; Zhang, W.; McWilliams, D.F.; Hendrick, P.; Walsh, D.A. Quantitative sensory testing and predicting outcomes for musculoskeletal pain, disability, and negative affect: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pain 2019, 160, 1920–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vierck, C.J.; Wong, F.; King, C.D.; Mauderli, A.P.; Schmidt, S.; Riley, J.L., III. Characteristics of sensitization associated with chronic pain conditions. Clin. J. Pain 2014, 30, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slade, G.D.; Sanders, A.E.; Ohrbach, R.; Fillingim, R.B.; Dubner, R.; Gracely, R.H.; Bair, E.; Maixner, W.; Greenspan, J.D. Pressure pain thresholds fluctuate with, but do not usefully predict, the clinical course of painful temporomandibular disorder. Pain 2014, 155, 2134–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meeus, M. Are pain beliefs, cognitions, and behaviors influenced by race, ethnicity, and culture in patients with chronic musculoskeletal pain: A systematic review. Pain Phys. 2018, 21, 541–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahavard, B.B.; Candido, K.D.; Knezevic, N.N. Different pain responses to chronic and acute pain in various ethnic/racial groups. Pain Manag. 2017, 7, 427–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botvinik-Nezer, R.; Holzmeister, F.; Camerer, C.F.; Dreber, A.; Huber, J.; Johannesson, M.; Kirchler, M.; Iwanir, R.; Mumford, J.A.; Adcock, R.A.; et al. Variability in the analysis of a single neuroimaging dataset by many teams. Nature 2020, 582, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Classifier | Set of Hyper-Parameters | Number of Combinations Evaluated |
|---|---|---|
| Dummy Classifier | strategy = [’constant’, ’uniform’, ’stratified’, ’prior’, ’most_frequent’]; constant = [0, 1]; | 10 |
| Logistic Regression | solver = [’liblinear’]; penalty = [’l1’, ’l2’]; C = []; dual = [True, False]; | 22 |
| SVC | kernel = [’rbf’, ’poly’]; tol = []; C = []; | 110 |
| K Neighbors Classifier | n_neighbors = range(1, 101, 1); weights = [’uniform’, ’distance’]; p = [1, 2]; | 2000 |
| Decision Tree Classifier | criterion = [’gini’, ’entropy’]; max_depth = range(1, 19, 1); min_samples_split = range(2, 21, 1); min_samples_leaf = range(1, 21, 1); | 1000 |
| Random Forest Classifier | n_estimators = [3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 100]; criterion = [’gini’, ’entropy’]; max_features = range(); min_samples_split = range(2, 21, 1); min_samples_leaf = range(1, 21, 1); bootstrap = [True, False]; | 1000 |
| Extra Trees Classifier | n_estimators = range(100, 500, 50); criterion = [’gini’, ’entropy’]; max_features = range(); min_samples_split = range(2, 21, 1); min_samples_leaf = range(1, 21, 1); bootstrap = [True, False]; | 1000 |
| MPL | hidden_layer_sizes = range(5, 100, 5); solver = [’lbfgs’, ’adam’, ’sgd’]; learning_rate = [’adaptive’, ’invscaling’, ’constant’]; learning_rate_init = [] | 684 |
| XGB Classifier | n_estimators = range(100, 500, 50); max_depth = range(1, 11, 1); learning_rate = []; subsample = range(); min_child_weight = range(1, 21, 1); nthread = [1]; | 1000 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santana, A.N.; de Santana, C.N.; Montoya, P. Chronic Pain Diagnosis Using Machine Learning, Questionnaires, and QST: A Sensitivity Experiment. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 958. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10110958
Santana AN, de Santana CN, Montoya P. Chronic Pain Diagnosis Using Machine Learning, Questionnaires, and QST: A Sensitivity Experiment. Diagnostics. 2020; 10(11):958. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10110958
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantana, Alex Novaes, Charles Novaes de Santana, and Pedro Montoya. 2020. "Chronic Pain Diagnosis Using Machine Learning, Questionnaires, and QST: A Sensitivity Experiment" Diagnostics 10, no. 11: 958. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10110958
APA StyleSantana, A. N., de Santana, C. N., & Montoya, P. (2020). Chronic Pain Diagnosis Using Machine Learning, Questionnaires, and QST: A Sensitivity Experiment. Diagnostics, 10(11), 958. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10110958






