A Prokaryotic Twist on Argonaute Function
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Structural Organization of Argonaute
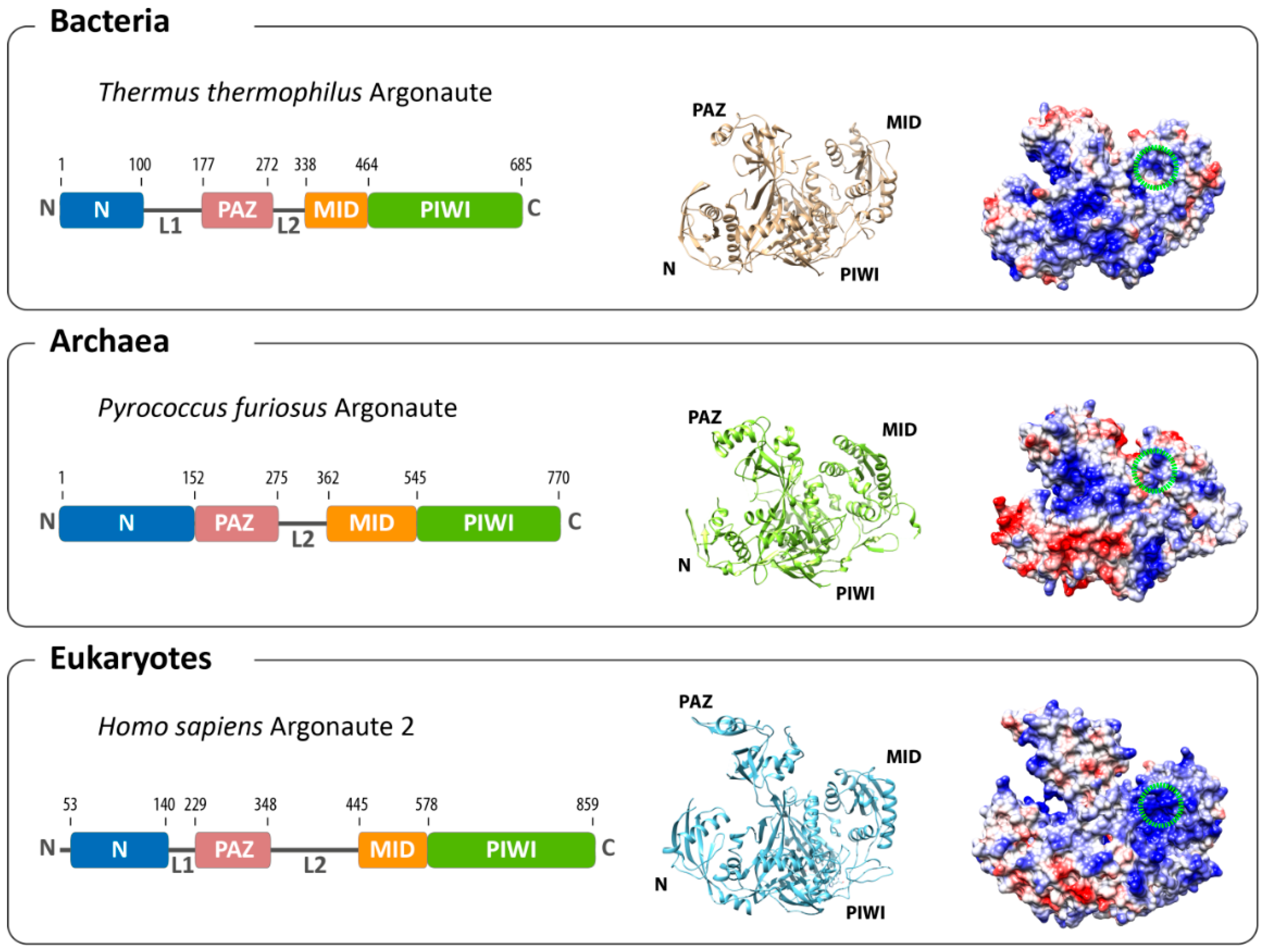
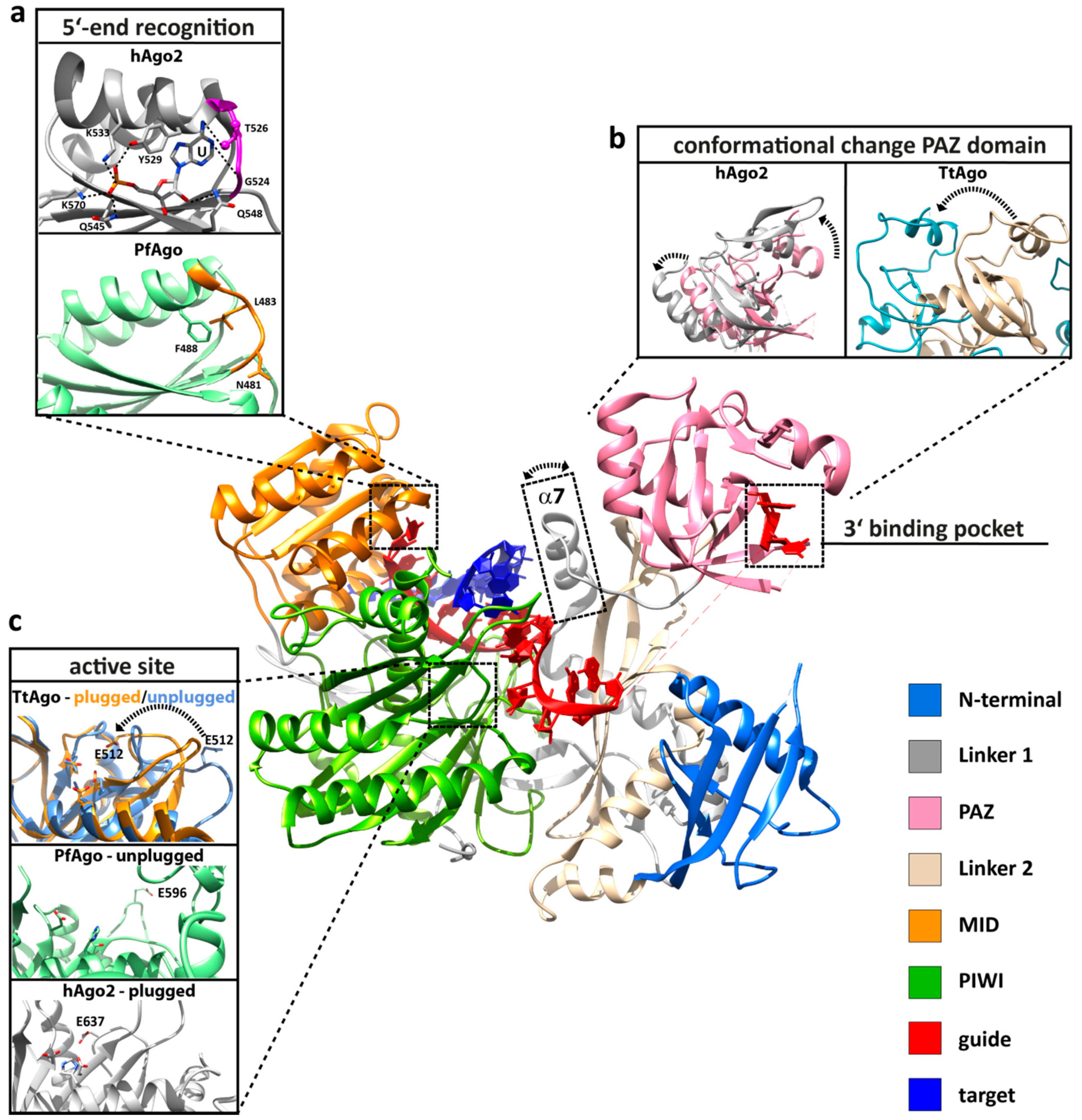
3. Conformational Flexibility Facilitates Argonaute Function
4. Molecular Mechanism of the Silencing Process
4.1. RNA Interference Mediated by Human Argonaute 2
4.2. Prokaryotic Argonaute Acts in DNA-Silencing Pathways

4.2. Diversity in Recognition and Selection of Guide and Target Strands
| Argonaute Variant | Guide Strand Bound | Preference/Enrichment For 1st Guide Nucleotide | Target Strands Bound | Target Strands Cleaved | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Archaea | |||||
| M. jannaschii Ago | DNA #, (RNA) # | {G} # | DNA #, RNA # | DNA # | [10] |
| A. fulgidus Ago | DNA #, (RNA) # | n.d. | DNA #, RNA # | n.d. | [19] |
| Bacteria | |||||
| A. aeolicus Ago | DNA *, (RNA) * | n.d. | RNA #, DNA # | n.d. | [69] |
| R. sphaeroides Ago | RNA *, DNA * | U * | RNA *, plasmid DNA# | inactive | [8] |
| T. thermophilus Ago | DNA *,#, (RNA) # | C * | DNA *,#, RNA #, plasmid DNA *,# | DNA #, RNA #, plasmid DNA *,# | [9,14] |
5. An Archaeal Perspective
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bohmert, K.; Camus, I.; Bellini, C.; Bouchez, D.; Caboche, M.; Benning, C. Ago1 defines a novel locus of arabidopsis controlling leaf development. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Spradling, A.C. A novel group of pumilio mutations affects the asymmetric division of germline stem cells in the drosophila ovary. Development 1997, 124, 2463–2476. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Burroughs, A.M.; Ando, Y.; Aravind, L. New perspectives on the diversification of the RNA interference system: Insights from comparative genomics and small RNA sequencing. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2014, 5, 141–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerutti, L.; Mian, N.; Bateman, A. Domains in gene silencing and cell differentiation proteins: The novel PAZ domain and redefinition of the piwi domain. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2000, 25, 481–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makarova, K.S.; Wolf, Y.I.; van der Oost, J.; Koonin, E.V. Prokaryotic homologs of Argonaute proteins are predicted to function as key components of a novel system of defense against mobile genetic elements. Biol. Direct 2009, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swarts, D.C.; Makarova, K.; Wang, Y.; Nakanishi, K.; Ketting, R.F.; Koonin, E.V.; Patel, D.J.; van der Oost, J. The evolutionary journey of Argonaute proteins. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2014, 21, 743–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burroughs, A.M.; Iyer, L.M.; Aravind, L. Two novel piwi families: Roles in inter-genomic conflicts in bacteria and mediator-dependent modulation of transcription in eukaryotes. Biol. Direct 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olovnikov, I.; Chan, K.; Sachidanandam, R.; Newman, D.K.; Aravin, A.A. Bacterial Argonaute samples the transcriptome to identify foreign DNA. Mol. Cell 2013, 51, 594–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swarts, D.C.; Jore, M.M.; Westra, E.R.; Zhu, Y.; Janssen, J.H.; Snijders, A.P.; Wang, Y.; Patel, D.J.; Berenguer, J.; Brouns, S.J.; et al. DNA-guided DNA interference by a prokaryotic Argonaute. Nature 2014, 507, 258–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zander, A.; Holzmeister, P.; Klose, D.; Tinnefeld, P.; Grohmann, D. Single-molecule fret supports the two-state model of Argonaute action. RNA Biol. 2014, 11, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, U.J.; Paterok, D.; Koglin, A.; Gohlke, H.; Piehler, J.; Chen, J.C. Structure of aquifex aeolicus Argonaute highlights conformational flexibility of the PAZ domain as a potential regulator of RNA-induced silencing complex function. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 13824–13832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.J.; Smith, S.K.; Hannon, G.J.; Joshua-Tor, L. Crystal structure of Argonaute and its implications for risc slicer activity. Science 2004, 305, 1434–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Juranek, S.; Li, H.; Sheng, G.; Tuschl, T.; Patel, D.J. Structure of an Argonaute silencing complex with a seed-containing guide DNA and target RNA duplex. Nature 2008, 456, 921–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Juranek, S.; Li, H.; Sheng, G.; Wardle, G.S.; Tuschl, T.; Patel, D.J. Nucleation, propagation and cleavage of target RNAs in ago silencing complexes. Nature 2009, 461, 754–761. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Sheng, G.; Juranek, S.; Tuschl, T.; Patel, D.J. Structure of the guide-strand-containing Argonaute silencing complex. Nature 2008, 456, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakanishi, K.; Weinberg, D.E.; Bartel, D.P.; Patel, D.J. Structure of yeast Argonaute with guide RNA. Nature 2012, 486, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schirle, N.T.; MacRae, I.J. The crystal structure of human Argonaute2. Science 2012, 336, 1037–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schirle, N.T.; Sheu-Gruttadauria, J.; MacRae, I.J. Gene regulation. Structural basis for microRNA targeting. Science 2014, 346, 608–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.B.; Yuan, Y.R.; Meister, G.; Pei, Y.; Tuschl, T.; Patel, D.J. Structural basis for 5'-end-specific recognition of guide RNA by the A. fulgidus piwi protein. Nature 2005, 434, 666–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elkayam, E.; Kuhn, C.D.; Tocilj, A.; Haase, A.D.; Greene, E.M.; Hannon, G.J.; Joshua-Tor, L. The structure of human Argonaute-2 in complex with mir-20a. Cell 2012, 150, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, F.; Sonenberg, N.; Nagar, B. Structural basis for 5'-nucleotide base-specific recognition of guide RNA by human Ago2. Nature 2010, 465, 818–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, J.S.; Roe, S.M.; Barford, D. Crystal structure of a piwi protein suggests mechanisms for siRNA recognition and slicer activity. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 4727–4737. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sheng, G.; Zhao, H.; Wang, J.; Rao, Y.; Tian, W.; Swarts, D.C.; van der Oost, J.; Patel, D.J.; Wang, Y. Structure-based cleavage mechanism of thermus thermophilus Argonaute DNA guide strand-mediated DNA target cleavage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, J.S.; Parizotto, E.A.; Wang, M.; Roe, S.M.; Barford, D. Enhancement of the seed-target recognition step in RNA silencing by a piwi/mid domain protein. Mol. Cell 2009, 33, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brennecke, J.; Stark, A.; Russell, R.B.; Cohen, S.M. Principles of microRNA-target recognition. PLoS Biol. 2005, 3, e85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lewis, B.P.; Burge, C.B.; Bartel, D.P. Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell 2005, 120, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faehnle, C.R.; Elkayam, E.; Haase, A.D.; Hannon, G.J.; Joshua-Tor, L. The making of a slicer: Activation of human Argonaute-1. Cell Rep. 2013, 3, 1901–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.B.; Ye, K.; Patel, D.J. Structural basis for overhang-specific small interfering RNA recognition by the PAZ domain. Nature 2004, 429, 318–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lingel, A.; Simon, B.; Izaurralde, E.; Sattler, M. Structure and nucleic-acid binding of the drosophila Argonaute 2 PAZ domain. Nature 2003, 426, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deerberg, A.; Willkomm, S.; Restle, T. Minimal mechanistic model of siRNA-dependent target RNA slicing by recombinant human Argonaute 2 protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 17850–17855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leuschner, P.J.; Ameres, S.L.; Kueng, S.; Martinez, J. Cleavage of the siRNA passenger strand during risc assembly in human cells. EMBO Rep. 2006, 7, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schurmann, N.; Trabuco, L.G.; Bender, C.; Russell, R.B.; Grimm, D. Molecular dissection of human Argonaute proteins by DNA shuffling. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2013, 20, 818–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauptmann, J.; Dueck, A.; Harlander, S.; Pfaff, J.; Merkl, R.; Meister, G. Turning catalytically inactive human Argonaute proteins into active slicer enzymes. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2013, 20, 814–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauptmann, J.; Kater, L.; Loffler, P.; Merkl, R.; Meister, G. Generation of catalytic human Ago4 identifies structural elements important for RNA cleavage. RNA 2014, 20, 1532–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakanishi, K.; Ascano, M.; Gogakos, T.; Ishibe-Murakami, S.; Serganov, A.A.; Briskin, D.; Morozov, P.; Tuschl, T.; Patel, D.J. Eukaryote-specific insertion elements control human Argonaute slicer activity. Cell Rep. 2013, 3, 1893–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meister, G. Argonaute proteins: Functional insights and emerging roles. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2013, 14, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, S.R.; Kim, E.; Hwang, W.; Shin, S.; Song, J.J.; Hohng, S. Dynamic anchoring of the 3'-end of the guide strand controls the target dissociation of Argonaute-guide complex. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 16865–16871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomari, Y.; Zamore, P.D. Perspective: Machines for RNAi. Genes Dev. 2005, 19, 517–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutvagner, G.; Simard, M.J. Argonaute proteins: Key players in RNA silencing. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacRae, I.J.; Ma, E.; Zhou, M.; Robinson, C.V.; Doudna, J.A. In vitro reconstitution of the human risc-loading complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sontheimer, E.J. Assembly and function of RNA silencing complexes. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matranga, C.; Tomari, Y.; Shin, C.; Bartel, D.P.; Zamore, P.D. Passenger-strand cleavage facilitates assembly of siRNA into Ago2-containing RNAi enzyme complexes. Cell 2005, 123, 607–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haley, B.; Zamore, P.D. Kinetic analysis of the RNAi enzyme complex. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2004, 11, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutvagner, G.; Zamore, P.D. A microRNA in a multiple-turnover RNAi enzyme complex. Science 2002, 297, 2056–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filipowicz, W.; Bhattacharyya, S.N.; Sonenberg, N. Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by microRNAs: Are the answers in sight? Nat. Rev. Genet. 2008, 9, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukaya, T.; Iwakawa, H.O.; Tomari, Y. MicroRNAs block assembly of eIF4F translation initiation complex in drosophila. Mol. Cell 2014, 56, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukao, A.; Mishima, Y.; Takizawa, N.; Oka, S.; Imataka, H.; Pelletier, J.; Sonenberg, N.; Thoma, C.; Fujiwara, T. MicroRNAs trigger dissociation of eIF4AI and eIF4AII from target mRNAs in humans. Mol. Cell 2014, 56, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallory, A.; Vaucheret, H. Form, function, and regulation of Argonaute proteins. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 3879–3889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, V.; Li, L.C. Demystifying the nuclear function of Argonaute proteins. RNA Biol. 2014, 11, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.C. Chromatin remodeling by the small RNA machinery in mammalian cells. Epigenetics 2014, 9, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cernilogar, F.M.; Onorati, M.C.; Kothe, G.O.; Burroughs, A.M.; Parsi, K.M.; Breiling, A.; Lo Sardo, F.; Saxena, A.; Miyoshi, K.; Siomi, H.; et al. Chromatin-associated RNA interference components contribute to transcriptional regulation in drosophila. Nature 2011, 480, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, V.; Zheng, J.; Qi, Z.; Wang, J.; Place, R.F.; Yu, J.; Li, H.; Li, L.C. Ago1 interacts with RNA polymerase ii and binds to the promoters of actively transcribed genes in human cancer cells. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allo, M.; Buggiano, V.; Fededa, J.P.; Petrillo, E.; Schor, I.; de la Mata, M.; Agirre, E.; Plass, M.; Eyras, E.; Elela, S.A.; et al. Control of alternative splicing through siRNA-mediated transcriptional gene silencing. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2009, 16, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ameyar-Zazoua, M.; Rachez, C.; Souidi, M.; Robin, P.; Fritsch, L.; Young, R.; Morozova, N.; Fenouil, R.; Descostes, N.; Andrau, J.C.; et al. Argonaute proteins couple chromatin silencing to alternative splicing. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2012, 19, 998–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Hu, J.; Corey, D.R. Expanding the action of duplex RNAs into the nucleus: Redirecting alternative splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 1240–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Wei, W.; Li, M.M.; Wu, Y.S.; Ba, Z.; Jin, K.X.; Liao, Y.Q.; Adhikari, S.; Chong, Z.; Zhang, T.; et al. Ago2 facilitates Rad51 recruitment and DNA double-strand break repair by homologous recombination. Cell Res. 2014, 24, 532–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, L.; Meister, G. Argonaute proteins: Mediators of RNA silencing. Mol. Cell 2007, 26, 611–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yigit, E.; Batista, P.J.; Bei, Y.; Pang, K.M.; Chen, C.C.; Tolia, N.H.; Joshua-Tor, L.; Mitani, S.; Simard, M.J.; Mello, C.C. Analysis of the C. elegans Argonaute family reveals that distinct Argonautes act sequentially during RNAi. Cell 2006, 127, 747–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meister, G.; Landthaler, M.; Patkaniowska, A.; Dorsett, Y.; Teng, G.; Tuschl, T. Human Argonaute2 mediates RNA cleavage targeted by miRNAs and siRNAs. Mol. Cell 2004, 15, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Carmell, M.A.; Rivas, F.V.; Marsden, C.G.; Thomson, J.M.; Song, J.J.; Hammond, S.M.; Joshua-Tor, L.; Hannon, G.J. Argonaute2 is the catalytic engine of mammalian RNAi. Science 2004, 305, 1437–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, W.F.; Wu, H.; Nichols, J.G.; Sun, H.; Murray, H.M.; Crooke, S.T. Binding and cleavage specificities of human Argonaute2. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 26017–26028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbashir, S.M.; Harborth, J.; Lendeckel, W.; Yalcin, A.; Weber, K.; Tuschl, T. Duplexes of 21-nucleotide RNAs mediate RNA interference in cultured mammalian cells. Nature 2001, 411, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivas, F.V.; Tolia, N.H.; Song, J.J.; Aragon, J.P.; Liu, J.; Hannon, G.J.; Joshua-Tor, L. Purified Argonaute2 and an siRNA form recombinant human risc. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2005, 12, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, M.; Kim, V.N. Regulation of microRNA biogenesis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 509–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, E.; Caudy, A.A.; Hammond, S.M.; Hannon, G.J. Role for a bidentate ribonuclease in the initiation step of RNA interference. Nature 2001, 409, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macrae, I.J.; Zhou, K.; Li, F.; Repic, A.; Brooks, A.N.; Cande, W.Z.; Adams, P.D.; Doudna, J.A. Structural basis for double-stranded RNA processing by dicer. Science 2006, 311, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.E.; Heo, I.; Tian, Y.; Simanshu, D.K.; Chang, H.; Jee, D.; Patel, D.J.; Kim, V.N. Dicer recognizes the 5' end of RNA for efficient and accurate processing. Nature 2011, 475, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Simanshu, D.K.; Ma, J.B.; Park, J.E.; Heo, I.; Kim, V.N.; Patel, D.J. A phosphate-binding pocket within the platform-PAZ-connector helix cassette of human dicer. Mol. Cell 2014, 53, 606–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.R.; Pei, Y.; Ma, J.B.; Kuryavyi, V.; Zhadina, M.; Meister, G.; Chen, H.Y.; Dauter, Z.; Tuschl, T.; Patel, D.J. Crystal structure of A. aeolicus Argonaute, a site-specific DNA-guided endoribonuclease, provides insights into RISC-mediated mRNA cleavage. Mol. Cell 2005, 19, 405–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.Y.; Yan, Z.; Xu, Y.; Hu, H.; Menzel, C.; Zhou, Y.H.; Chen, W.; Khaitovich, P. Sequence features associated with microRNA strand selection in humans and flies. BMC Genomics 2009, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamata, T.; Seitz, H.; Tomari, Y. Structural determinants of miRNAs for RISC loading and slicer-independent unwinding. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2009, 16, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, S.; Cai, T.; Hu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Hodges, E.; Ni, F.; Wu, L.; Li, S.; Zhou, H.; Long, C.; et al. Sorting of small RNAs into arabidopsis Argonaute complexes is directed by the 5' terminal nucleotide. Cell 2008, 133, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boland, A.; Tritschler, F.; Heimstadt, S.; Izaurralde, E.; Weichenrieder, O. Crystal structure and ligand binding of the mid domain of a eukaryotic Argonaute protein. EMBO Rep. 2010, 11, 522–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, F.; Hauver, J.; Sonenberg, N.; Nagar, B. Arabidopsis Argonaute mid domains use their nucleotide specificity loop to sort small RNAs. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 3588–3595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Willkomm, S.; Zander, A.; Gust, A.; Grohmann, D. A Prokaryotic Twist on Argonaute Function. Life 2015, 5, 538-553. https://doi.org/10.3390/life5010538
Willkomm S, Zander A, Gust A, Grohmann D. A Prokaryotic Twist on Argonaute Function. Life. 2015; 5(1):538-553. https://doi.org/10.3390/life5010538
Chicago/Turabian StyleWillkomm, Sarah, Adrian Zander, Alexander Gust, and Dina Grohmann. 2015. "A Prokaryotic Twist on Argonaute Function" Life 5, no. 1: 538-553. https://doi.org/10.3390/life5010538
APA StyleWillkomm, S., Zander, A., Gust, A., & Grohmann, D. (2015). A Prokaryotic Twist on Argonaute Function. Life, 5(1), 538-553. https://doi.org/10.3390/life5010538





