Sarcopenia as a Multisystem Disorder—Connections with Neural and Cardiovascular Systems—A Related PRISMA Systematic Literature Review
Abstract
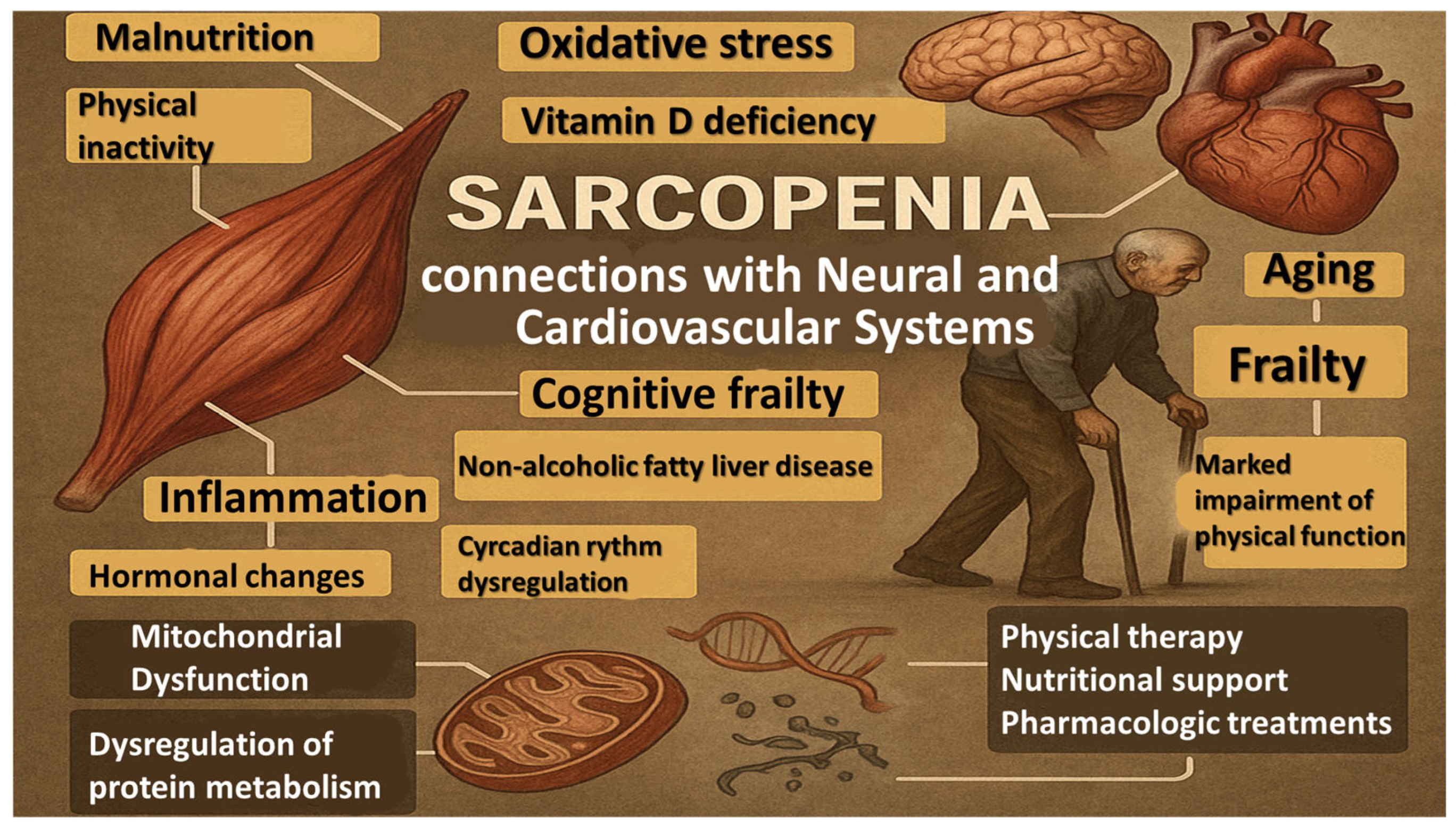
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Search Strategy
2.3. Eligibility Criteria
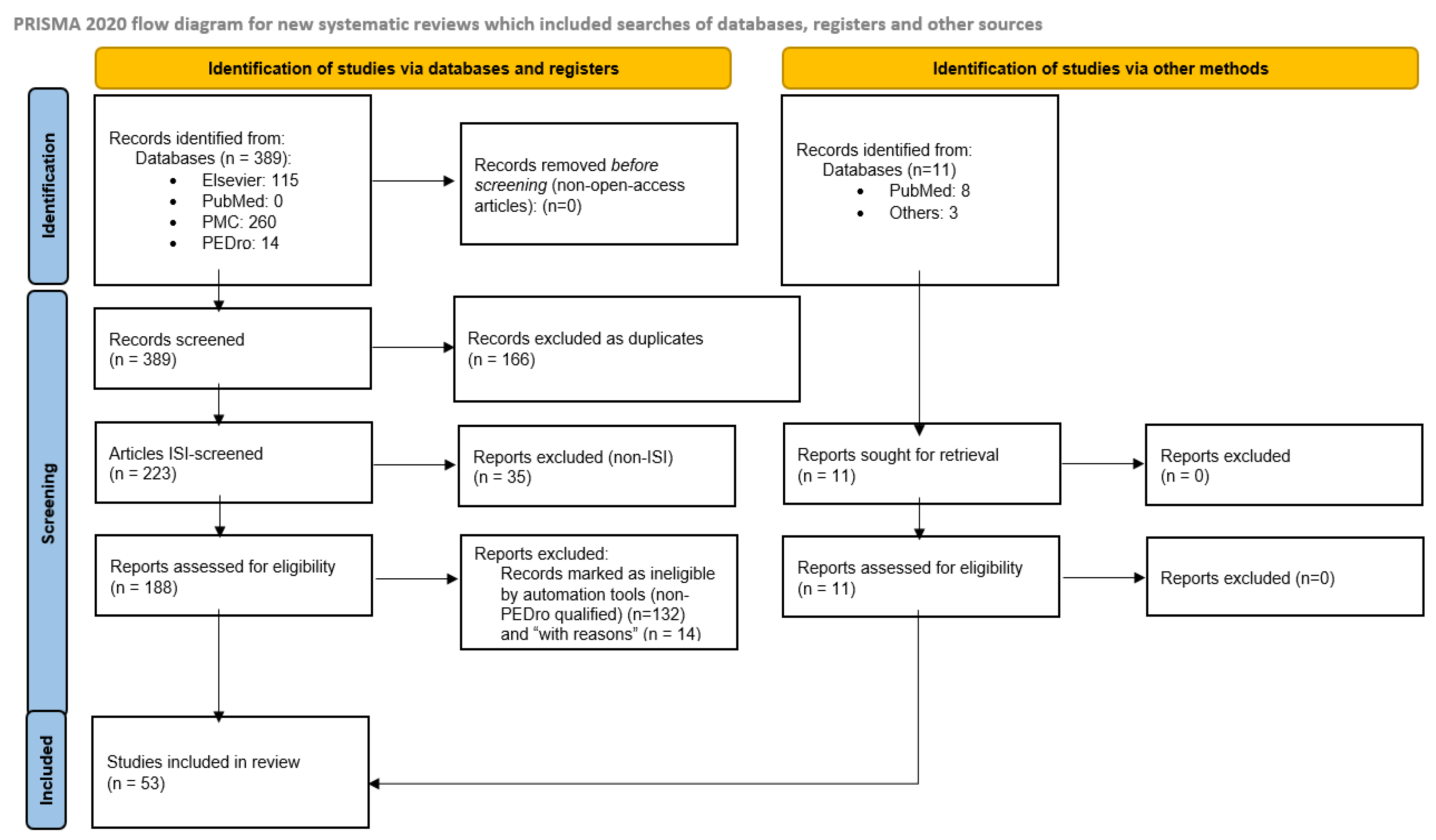
2.4. Screening and Quality Assessment
2.5. Final Selection of Studies
3. Results
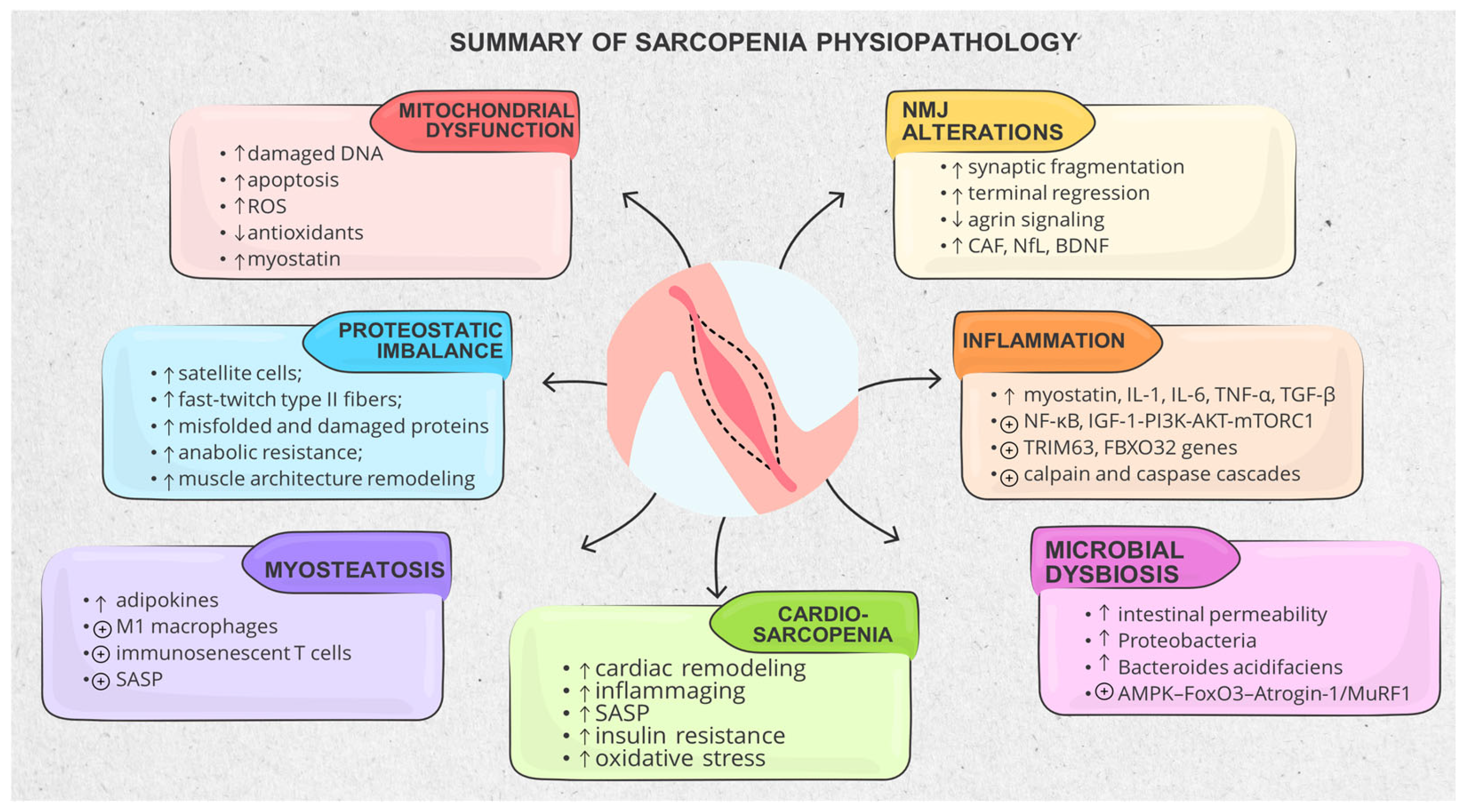
3.1. Muscle Structure and Physiopathological Mechanisms
3.1.1. Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Metabolic Stress
3.1.2. Proteostatic Imbalance, Impaired Regeneration and Anabolic Resistance
3.1.3. Muscle Architecture Remodeling and Decline in Contractile Quality
3.1.4. Inflammatory and Catabolic Signaling Dominance
3.1.5. Adipose–Muscle–Bone Crosstalk and the Metabolic Shift Toward Sarcopenic Obesity
3.1.6. Gut–Muscle–Immune Axis and Microbial Dysbiosis
3.2. Neuro-Functional Mechanisms in Sarcopenia
3.2.1. Central Nervous System (CNS) Involvement
3.2.2. Neuromuscular Junction and Motor Unit Degeneration
3.2.3. Muscle–Brain Crosstalk
3.2.4. Muscle–Nerve Regeneration Failure and Extracellular Matrix Fibrosis
3.3. Cardiovascular Intermingles with Sarcopenia (Cardio-Sarcopenia)
3.3.1. Arterial Hypertension (aHTN)
3.3.2. Heart Failure (HF)
3.3.3. Sarcopenia and Other Cardiovascular Diseases
3.3.4. Sarcopenia and Cardiovascular Surgery
3.4. Sarcopenia in Children—Is There a Connection?
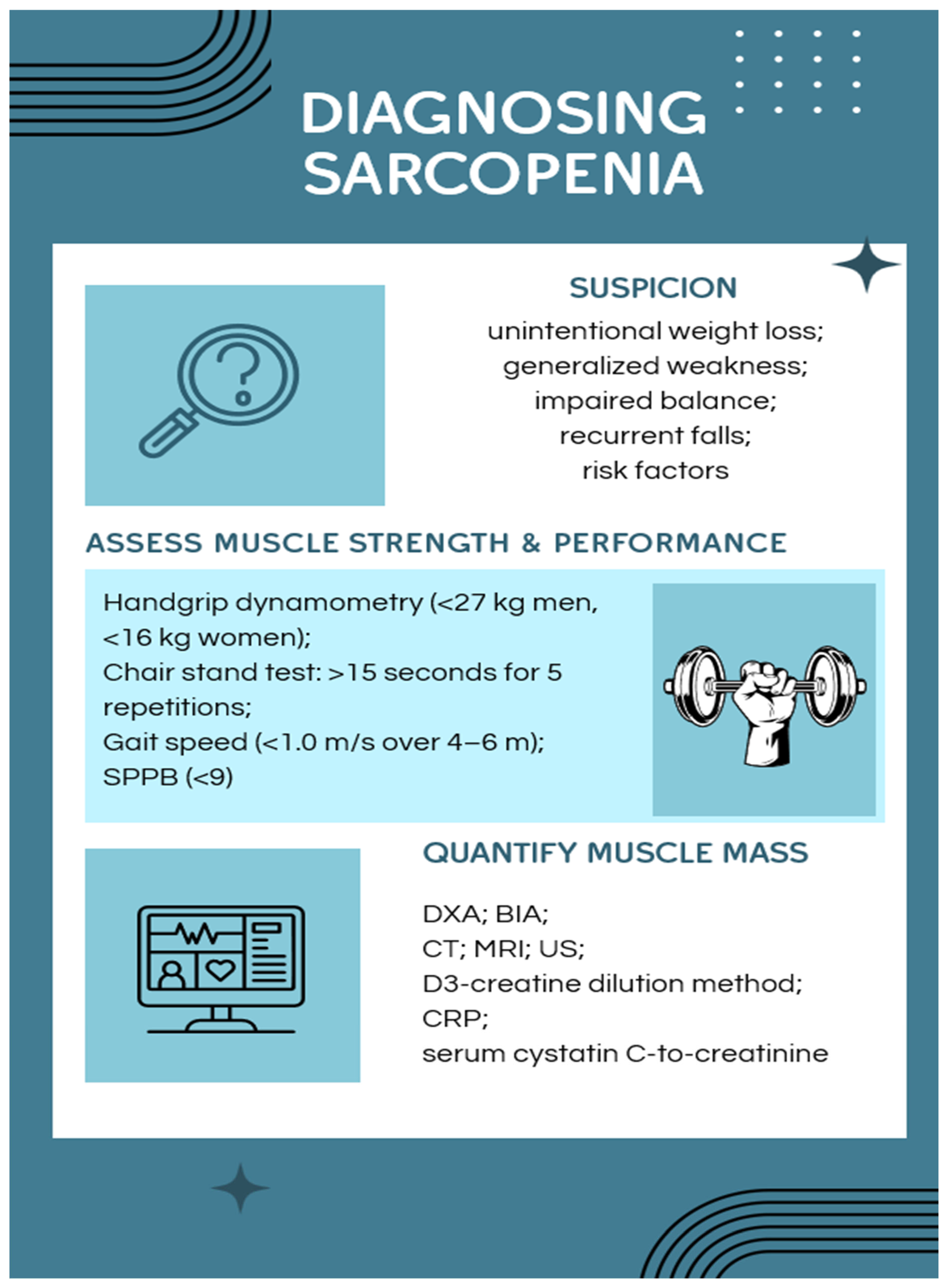
3.5. Diagnosing Sarcopenia
3.6. How Can We Interfere with the Progression of Sarcopenia?
3.6.1. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacological Modulation of Sarcopenia
Established and Repurposed Therapeutic Strategies
Experimental and Emerging Pharmacological Strategies
3.6.2. Non-Pharmacological Interventions for Sarcopenia
Nutrition and Gut Microbiota Modulation
Physical and Exercise-Based Interventions
- Mitochondrial and Molecular Mechanisms, Targeted
- 2.
- Resistance and Multimodal Training: The Therapeutic Core
- 3.
- Exerkines and Systemic Crosstalk Contribution
- 4.
- Digital Rehabilitation and Post-Pandemic Opportunities
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACE-Is | Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors |
| ACTN2/3 | α-actinins |
| ACVR2B | activin receptor type 2b |
| ADL | Activities of Daily Living |
| AGE | Advanced Glycation End Products |
| aHTN | Arterial hypertension |
| AICAR | 5-Aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleotide |
| AKT | serine/threonine kinase 1 |
| AMPK | Adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase |
| ARBs | angiotensin receptor blockers |
| ASMM | appendicular skeletal muscle mass |
| ATP | adenosine triphosphate |
| AWGS | Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia |
| BAIBA | beta-aminoisobutyric acid |
| BBB | blood–brain barrier |
| BDNF | Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor |
| BIA | bioelectrical impedance analysis |
| BMP-7 | RT enhanced Bone morphogenetic protein 7 |
| CAD | coronary artery disease |
| CAF | circulating C-terminal agrin fragment |
| COVID-19 | Coronavirus Disease 2019 |
| CNS | Central Nervous System |
| COX-2 | cyclooxygenase-2 |
| CRP | C reactive protein |
| CT | Computer Tomography |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic Acid |
| DXA | dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry |
| ECM | extracellular matrix |
| EGCG | epigallocatechin-3-gallate |
| ESPEN | European Society for Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism |
| EWGSOP2 | European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People 2 |
| FBXO32 | inducing muscle atrophy genes such as Atrogin-1 |
| FOXO | forkhead box O |
| FRAGILE-HF | Frailty and Heart Failure study |
| GDF15 | Growth Differentiation Factor 15 |
| GH | Growth hormone |
| HF | Heart Failure |
| HIIT | high-intensity interval training |
| HR-QoL | health-related quality of life |
| HRS | Heart Rhythm Society |
| ICD-10 | International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision |
| ICFSR | International Clinical Practice Guidelines for Sarcopenia |
| IGF-1 | Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 |
| IL | interleukin |
| ISI | International Scientific Indexing |
| KWGS | Korean Working Group on Sarcopenia |
| LAHRS | Latin America Heart Rhythm Society |
| MD | mean difference |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| MYH | myosin heavy chain |
| MYL | myosin light chains |
| NAD | Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide |
| NAFLD | non-alcoholic fatty liver disease |
| NCBI | National Center for Biotechnology Information |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor kappa-B |
| NfL | neurofilament light chain |
| NMJ | neuromuscular junction |
| NRF | Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-Related Factor |
| PAD | peripheral artery disease |
| PEDro | Physiotherapy Evidence Database |
| PGC-1alfa | Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-Gamma |
| PI3K | phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase |
| PMC | PubMed Central |
| PPAR | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor |
| PROSPERO | International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| RT | resistance training |
| SARC-F | Strength, Assistance with walking, Rise from a chair, Climb stairs and Falls |
| SASP | senescence-associated secretory phenotype |
| SGLT2 | sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 |
| SICA-HF | Studies Investigating Comorbidities Aggravating Heart Failure |
| SIMMS | Sarcopenia Integrated Management and Measurement Systems |
| SIRT1 | Sirtuin 1 |
| SPPB | Short Physical Performance Battery |
| SRT2104 | SIRT1 activator |
| SS-31 | Szeto–Schiller peptides |
| TAME | Targeting Aging with Metformin |
| TAVR | Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement |
| TGF-alfa | Transforming Growth Factor-alpha |
| TIMP-1 | tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1 |
| TNF-alfa | tumor necrosis factor alfa |
| TUG | Timed Up and Go |
| US | Ultrasonography |
| VEGF | vascular endothelial growth factor |
| VR | Virtual reality |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
Appendix A
| Start Date: | 1 January 2023 | ||||||||
| End Date: | 31 December 2024 | ||||||||
| No of Keywords | 10 | ||||||||
| Part 1 | Part 2 | Part 3 | Part 4 | Part 5 | Part 6 | Part 7 | Part 8 | Part 9 | |
| Keywords 1 | sarcopenia | physical exercise | VR | elderly | |||||
| Keywords 2 | sarcopenia | physical exercise | virtual reality | elderly | |||||
| Keywords 3 | sarcopenia | physical exercise | VAR | elderly | |||||
| Keywords 4 | sarcopenia | physical exercise | virtual augmented reality | elderly | |||||
| Keywords 5 | sarcopenia | physical exercise | VE | elderly | |||||
| Keywords 6 | sarcopenia | physical exercise | virtual environment | elderly | |||||
| Keywords 7 | sarcopenia | physical exercise | ACEIs | elderly | |||||
| Keywords 8 | sarcopenia | physical exercise | angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitors | elderly | |||||
| Keywords 9 | sarcopenia | physical exercise | ARBs | elderly | |||||
| Keywords 10 | sarcopenia | physical exercise | angiotensin receptor blockers | elderly | |||||
| Keywords 11 | sarcopenia | physical exercise | ACVR2b | elderly | |||||
| Keywords 12 | sarcopenia | physical exercise | activin receptor type 2b | elderly | |||||
| Keywords 13 | sarcopenia | Motor end plates | desmin | titin | nebulin | myosin | actin | sarcomere | myasthenia gravis |
| Keywords 14 | sarcopenia | Motor end plates | desmin | titin | nebulin | myosin | actin | sarcomere | dystonia |
| Keywords 15 | sarcopenia | Motor end plates | desmin | titin | nebulin | myosin | actin | sarcomere | Parkinson’s Disease |
| Keywords 16 | sarcopenia | Motor end plates | desmin | titin | nebulin | myosin | actin | sarcomere | Alzheimer’s Disease |
| Keywords 17 | sarcopenia | Motor end plates | desmin | titin | nebulin | myosin | actin | sarcomere | stroke |
| Keywords 18 | sarcopenia | Motor end plates | desmin | titin | nebulin | myosin | actin | sarcomere | spinal muscular atrophy |
| Keywords 19 | sarcopenia | Motor end plates | desmin | titin | nebulin | myosin | actin | sarcomere | diabetic polyneuropathy |
| Keywords 20 | sarcopenia | Motor end plates | desmin | titin | nebulin | myosin | actin | sarcomere | amyotrophic lateral sclerosis |
| Keywords 21 | sarcopenia | Motor end plates | desmin | titin | nebulin | myosin | actin | sarcomere | multiple sclerosis |
| Keywords 22 | sarcopenia | Motor end plates | desmin | titin | nebulin | myosin | actin | sarcomere | spinal cord injury |
Appendix B
| Title | Year of Publication | Number of Citations | Citations Per Year | PEDro Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Role of diet and exercise in aging, Alzheimer’s disease, and other chronic diseases | 2023 | 62 | 20.6666667 | 10 |
| Falls caused by balance disorders in the elderly with multiple systems involved: Pathogenic mechanisms and treatment strategies | 2023 | 113 | 37.6666667 | 10 |
| Perspectives on Aging and Quality of Life | 2023 | 61 | 20.3333333 | 10 |
| The molecular athlete: exercise physiology from mechanisms to medals | 2023 | 182 | 60.6666667 | 10 |
| Mitochondrial dysfunction: roles in skeletal muscle atrophy | 2023 | 192 | 64 | 10 |
| A Role for Advanced Glycation End Products in Molecular Ageing | 2023 | 92 | 30.6666667 | 10 |
| C-Reactive Protein: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, False Test Results and a Novel Diagnostic Algorithm for Clinicians | 2023 | 97 | 32.3333333 | 10 |
| EHRA expert consensus document on the management of arrhythmias in frailty syndrome, endorsed by the Heart Rhythm Society (HRS), Asia Pacific Heart Rhythm Society (APHRS), Latin America Heart Rhythm Society (LAHRS), and Cardiac Arrhythmia Society of Southern Africa (CASSA) | 2023 | 98 | 32.6666667 | 10 |
| Sarcopenia and Cardiovascular Diseases | 2023 | 392 | 130.666667 | 10 |
| Insights into Pathogenesis, Nutritional and Drug Approach in Sarcopenia: A Systematic Review | 2023 | 62 | 20.6666667 | 10 |
| Sarcopenia and Cognitive Decline in Older Adults: Targeting the Muscle–Brain Axis | 2023 | 86 | 28.6666667 | 10 |
| Challenges in developing Geroscience trials | 2023 | 61 | 20.3333333 | 10 |
| Sex Differences in Inflammation and Muscle Wasting in Aging and Disease | 2023 | 71 | 23.6666667 | 10 |
| Systemic aging fuels heart failure: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic avenues | 2024 | 22 | 22 | 10 |
| Fiber-Type Shifting in Sarcopenia of Old Age: Proteomic Profiling of the Contractile Apparatus of Skeletal Muscles | 2023 | 55 | 18.3333333 | 10 |
| Multidisciplinary Care in Heart Failure Services | 2023 | 48 | 16 | 10 |
| Frailty in patients on dialysis | 2024 | 33 | 16.5 | 10 |
| Frailty, Sarcopenia, Cachexia, and Malnutrition in Heart Failure | 2024 | 25 | 12.5 | 7 |
| Mini-encyclopedia of mitochondria-relevant nutraceuticals protecting health in primary and secondary care—clinically relevant 3PM innovation | 2024 | 22 | 11 | 7 |
| A Phase 1 study for safety and pharmacokinetics of BIO101 (20-hydroxyecdysone) in healthy young and older adults | 2023 | 34 | 11.3333333 | 7 |
| Diagnosis and Management of Malnutrition in Patients with Heart Failure | 2023 | 33 | 11 | 7 |
| Microgravity and Musculoskeletal Health: What Strategies Should Be Used for a Great Challenge? | 2023 | 34 | 11.3333333 | 7 |
| Aging Skeletal Muscles: What Are the Mechanisms of Age-Related Loss of Strength and Muscle Mass, and Can We Impede Its Development and Progression? | 2024 | 20 | 10 | 6 |
| Inflammaging and Brain Aging | 2024 | 20 | 10 | 6 |
| Skeletal Muscle Injury in Chronic Kidney Disease—From Histologic Changes to Molecular Mechanisms and to Novel Therapies | 2024 | 20 | 10 | 6 |
| Frailty and the Interactions between Skeletal Muscle, Bone, and Adipose Tissue-Impact on Cardiovascular Disease and Possible Therapeutic Measures | 2023 | 32 | 10.6666667 | 6 |
| The complex pathophysiology of cardiac cachexia: A review of current pathophysiology and implications for clinical practice | 2023 | 24 | 8 | 5 |
| Gut microbiota and myocardial fibrosis | 2023 | 24 | 8 | 5 |
| Effects of a 2-year exercise training on neuromuscular system health in older individuals with low muscle function | 2023 | 25 | 8.33333333 | 5 |
| Mechanism-Driven Strategies for Reducing Fall Risk in the Elderly: A Multidisciplinary Review of Exercise Interventions | 2024 | 16 | 8 | 5 |
| Exercise Interventions Delivered Through Telehealth to Improve Physical Functioning for Older Adults with Frailty, Cognitive, or Mobility Disability: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis | 2024 | 18 | 9 | 5 |
| The efficacy of different interventions in the treatment of sarcopenia in middle-aged and elderly people: a network meta-analysis | 2023 | 24 | 8 | 5 |
| Exercise, Neuroprotective Exerkines, and Parkinson’s Disease: A Narrative Review | 2024 | 15 | 7.5 | 4 |
| Elderly patients’ reactions to gamification-based digital therapeutics (DTx): The relevance of socialization tendency seeking | 2024 | 12 | 6 | 4 |
| Adipose tissue in older individuals: a contributing factor to sarcopenia | 2024 | 14 | 7 | 4 |
| Home-Based Exergame Program to Improve Physical Function, Fall Efficacy, Depression and Quality of Life in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial | 2023 | 19 | 6.33333333 | 4 |
| Osteosarcopenia in NAFLD/MAFLD: An Underappreciated Clinical Problem in Chronic Liver Disease | 2023 | 19 | 6.33333333 | 4 |
| Cell non-autonomous regulation of cerebrovascular aging processes by the somatotropic axis | 2023 | 22 | 7.33333333 | 4 |
| Impaired age-associated mitochondrial translation is mitigated by exercise and PGC-1α | 2023 | 19 | 6.33333333 | 4 |
| Pathogenesis of Sarcopenia in Chronic Kidney Disease—The Role of Inflammation, Metabolic Dysregulation, Gut Dysbiosis, and microRNA | 2024 | 12 | 6 | 4 |
| Prevention and Rehabilitation After Heart Transplantation: A Clinical Consensus Statement of the European Association of Preventive Cardiology, Heart Failure Association of the ESC, and the European Cardio Thoracic Transplant Association, a Section of ESOT | 2024 | 13 | 6.5 | 4 |
| Sarcopenia as the Mobility Phenotype of Aging: Clinical Implications | 2024 | 13 | 6.5 | 4 |
References
- Dawson, R.; Oliveira, J.S.; Kwok, W.S.; Bratland, M.; Rajendran, I.M.; Srinivasan, A.; Chu, C.Y.; Pinheiro, M.B.; Hassett, L.; Sherrington, C. Exercise Interventions Delivered Through Telehealth to Improve Physical Functioning for Older Adults with Frailty, Cognitive, or Mobility Disability: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Telemed. e-Health 2024, 30, 940–950. Available online: https://home.liebertpub.com/tmj (accessed on 2 December 2025). [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Jung, H.-W.; Baek, J.Y.; Jang, I.-Y.; Lee, E. Sarcopenia as the Mobility Phenotype of Aging: Clinical Implications. J. Bone Metab. 2024, 31, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, D.; Fujimoto, Y.; Nakade, T.; Abe, T.; Ishihara, S.; Jujo, K.; Matsue, Y. Frailty, Sarcopenia, Cachexia, and Malnutrition in Heart Failure. Korean Circ. J. 2024, 54, 363–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Zhou, D.; Hong, Z. Adipose tissue in older individuals: A contributing factor to sarcopenia. Metabolism 2024, 160, 155998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khemka, S.; Reddy, A.; Garcia, R.I.; Jacobs, M.; Reddy, R.P.; Roghani, A.K.; Pattoor, V.; Basu, T.; Sehar, U.; Reddy, P.H. Role of diet and exercise in aging, Alzheimer’s disease, and other chronic diseases. Ageing Res. Rev. 2023, 91, 102091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zgutka, K.; Tkacz, M.; Tomasiak, P.; Tarnowski, M. A Role for Advanced Glycation End Products in Molecular Ageing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damluji, A.A.; Alfaraidhy, M.; AlHajri, N.; Rohant, N.N.; Kumar, M.; Al Malouf, C.; Bahrainy, S.; Kwak, M.J.; Batchelor, W.B.; Forman, D.E.; et al. Sarcopenia and Cardiovascular Diseases. Circulation 2023, 147, 1534–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafsson, T.; Ulfhake, B. Aging Skeletal Muscles: What Are the Mechanisms of Age-Related Loss of Strength and Muscle Mass, and Can We Impede Its Development and Progression? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanapholsart, J.; Khan, E.; Ismail, T.F.; Lee, G.A. The complex pathophysiology of cardiac cachexia: A review of current path-ophysiology and implications for clinical practice. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2022, 365, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretti, A.; Tomaino, F.; Paoletta, M.; Liguori, S.; Migliaccio, S.; Rondanelli, M.; Di Iorio, A.; Pellegrino, R.; Donnarumma, D.; Di Nunzio, D.; et al. Physical exercise for primary sarcopenia: An expert opinion. Front. Rehabil. Sci. 2025, 6, 1538336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban-Fernández, A.; Villar-Taibo, R.; Alejo, M.; Arroyo, D.; Palomas, J.L.B.; Cachero, M.; Joaquin, C.; Bailón, M.M.; Pérez-Rivera, J.Á.; Romero-Vigara, J.C.; et al. Diagnosis and Management of Malnutrition in Patients with Heart Failure. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arosio, B.; Calvani, R.; Ferri, E.; Coelho-Junior, H.J.; Carandina, A.; Campanelli, F.; Ghiglieri, V.; Marzetti, E.; Picca, A. Sarcopenia and Cognitive Decline in Older Adults: Targeting the Muscle–Brain Axis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deniza Ciubean, A.; Popa, T.; Mihaela Ciortea, V.; Dogaru, G.; Irsay, L. Disrupted Circadian Rhythms as a Novel Driver of Sar-copenia: Mechanisms, Evidence, and Future Directions. Balneo PRM Res. J. 2025, 16, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ji, Y.; Liu, R.; Zhu, X.; Wang, K.; Yang, X.; Liu, B.; Gao, Z.; Huang, Y.; Shen, Y.; et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction: Roles in skeletal muscle atrophy. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heitman, K.; Alexander, M.S.; Faul, C. Skeletal Muscle Injury in Chronic Kidney Disease—From Histologic Changes to Molecular Mechanisms and to Novel Therapies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savelieva, I.; Fumagalli, S.; Kenny, R.A.; Anker, S.; Benetos, A.; Boriani, G.; Bunch, J.; Dagres, N.; Dubner, S.; Fauchier, L.; et al. EHRA expert consensus document on the management of arrhythmias in frailty syndrome, endorsed by the Heart Rhythm Society (HRS), Asia Pacific Heart Rhythm Society (APHRS), Latin America Heart Rhythm Society (LAHRS), and Cardiac Arrhythmia Society of Southern Africa (CASSA). EP Eur. 2023, 25, 1249–1276. [Google Scholar]
- Soto, M.E.; Pérez-Torres, I.; Rubio-Ruiz, M.E.; Cano-Martínez, A.; Manzano-Pech, L.; Guarner-Lans, V. Frailty and the Interactions between Skeletal Muscle, Bone, and Adipose Tissue-Impact on Cardiovascular Disease and Possible Therapeutic Measures. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K. Home-Based Exergame Program to Improve Physical Function, Fall Efficacy, Depression and Quality of Life in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Healthcare 2023, 11, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Q.; Zhai, H.; Wang, L.; Wei, H.; Hou, S. The efficacy of different interventions in the treatment of sarcopenia in middle-aged and elderly people: A network meta-analysis. Medicine 2023, 102, e34254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dioh, W.; Tourette, C.; Del Signore, S.; Daudigny, L.; Dupont, P.; Balducci, C.; Dilda, P.J.; Lafont, R.; Veillet, S. A Phase 1 study for safety and pharmacokinetics of BIO101 (20-hydroxyecdysone) in healthy young and older adults. J. Cachex-Sarcopenia Muscle 2023, 14, 1259–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noto, S. Perspectives on Aging and Quality of Life. Healthcare 2023, 11, 2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellen, R.H.; Girotto, O.S.; Marques, E.B.; Laurindo, L.F.; Grippa, P.C.; Mendes, C.G.; Garcia, L.N.H.; Bechara, M.D.; Barbalho, S.M.; Sinatora, R.V.; et al. Insights into Pathogenesis, Nutritional and Drug Approach in Sarcopenia: A Systematic Review. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Della Peruta, C.; Lozanoska-Ochser, B.; Renzini, A.; Moresi, V.; Riera, C.S.; Bouché, M.; Coletti, D. Sex Differences in Inflammation and Muscle Wasting in Aging and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aurelian, J.; Zamfirescu, A.; Aurelian, S.M.; Mihalache, R.; Gîdei, M.S.; Gîță, C.D.; Prada, A.G.; Constantin, T.; Nedelescu, M.; Oancea, C. Impact of Physical Performance on Hemodynamic and Cognitive Status in Romanian Older Adults. Romanian J. Mil. Med. 2025, 128, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Smalen, L.M.; Börsch, A.; Leuchtmann, A.B.; Gill, J.F.; Ritz, D.; Zavolan, M.; Handschin, C. Impaired age-associated mitochondrial translation is mitigated by exercise and PGC-1α. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2302360120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakinowska, E.; Olejnik-Wojciechowska, J.; Kiełbowski, K.; Skoryk, A.; Pawlik, A. Pathogenesis of Sarcopenia in Chronic Kidney Disease—The Role of Inflammation, Metabolic Dysregulation, Gut Dysbiosis, and microRNA. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monti, E.; Tagliaferri, S.; Zampieri, S.; Sarto, F.; Sirago, G.; Franchi, M.V.; Ticinesi, A.; Longobucco, Y.; Adorni, E.; Lauretani, F.; et al. Effects of a 2-year exercise training on neuromuscular system health in older individuals with low muscle function. J. Cachex-Sarcopenia Muscle 2023, 14, 794–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sestino, A.; D’ANgelo, A. Elderly patients’ reactions to gamification-based digital therapeutics (DTx): The relevance of social-ization tendency seeking. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2024, 205, 123526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orimo, H.; Ito, H.; Suzuki, T.; Araki, A.; Hosoi, T.; Sawabe, M. Reviewing the definition of “elderly”. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2006, 6, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; Moher, D.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. PRISMA 2020 explanation and elaboration: Updated guidance and exemplars for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n160. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ (accessed on 21 August 2025).
- PMC Home. Available online: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ (accessed on 21 August 2025).
- Elsevier|A Global Leader for Advanced Information and Decision Support in Science and Healthcare. Available online: http://www.elsevier.com (accessed on 21 August 2025).
- Pedro Engine. Available online: http://search.pedro.org.au/search (accessed on 21 August 2025).
- Web of Science. Available online: https://mjl.clarivate.com/home (accessed on 21 August 2025).
- PEDro Scale—PEDro. Available online: https://pedro.org.au/english/resources/pedro-scale/ (accessed on 21 August 2025).
- PEDro Score—Strokengine. Available online: https://www.strokengine.ca/glossary/pedro--score/ (accessed on 21 August 2025).
- Vlădulescu-Trandafir, A.-I.; Bojincă, V.-C.; Munteanu, C.; Anghelescu, A.; Popescu, C.; Stoica, S.-I.; Aurelian, S.; Bălănescu, A.; Băetu, C.; Ciobanu, V.; et al. Rheumatoid Arthritis and COVID-19 at the Intersection of Immunology and Infectious Diseases: A Related PRISMA Systematic Literature Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowling, P.; Gargan, S.; Swandulla, D.; Ohlendieck, K. Fiber-Type Shifting in Sarcopenia of Old Age: Proteomic Profiling of the Contractile Apparatus of Skeletal Muscles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, G.C.K.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Ng, J.K.C.; Tian, N.; Burns, A.; Chow, K.M.; Szeto, C.-C.; Li, P.K.-T. Frailty in patients on dialysis. Kidney Int. 2024, 106, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golubnitschaja, O.; Kapinova, A.; Sargheini, N.; Bojkova, B.; Kapalla, M.; Heinrich, L.; Gkika, E.; Kubatka, P. Mini-encyclopedia of mitochon-dria-relevant nutraceuticals protecting health in primary and secondary care—Clinically relevant 3PM innovation. EPMA J. 2024, 15, 163–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Bao, Y.; Wang, B.; Shi, M.; Wei, Y.; Huang, X.; Dai, Y.; Shi, H.; Gai, X.; Luo, Q.; et al. Falls caused by balance disorders in the elderly with multiple systems involved: Pathogenic mechanisms and treatment strategies. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1128092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonanni, R.; Cariati, I.; Marini, M.; Tarantino, U.; Tancredi, V. Microgravity and Musculoskeletal Health: What Strategies Should Be Used for a Great Challenge? Life 2023, 13, 1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Raza, U.; Song, J.; Lu, J.; Yao, S.; Liu, X.; Zhang, W.; Li, S. Systemic aging fuels heart failure: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic avenues. ESC Hear. Fail. 2025, 12, 1059–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolland, Y.; Sierra, F.; Ferrucci, L.; Barzilai, N.; De Cabo, R.; Mannick, J.; Oliva, A.; Evans, W.; Angioni, D.; Barreto, P.D.S.; et al. Challenges in developing Geroscience trials. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musio, A.; Perazza, F.; Leoni, L.; Stefanini, B.; Dajti, E.; Menozzi, R.; Petroni, M.L.; Colecchia, A.; Ravaioli, F. Osteosarcopenia in NAFLD/MAFLD: An Underappreciated Clinical Problem in Chronic Liver Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurcau, M.C.; Jurcau, A.; Cristian, A.; Hogea, V.O.; Diaconu, R.G.; Nunkoo, V.S. Inflammaging and Brain Aging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z. Analysis of Health and Longevity in Oldest-Old Population: A Health Capital Approach. In Healthy Longevity in China; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Bickel, M.A.; Csik, B.; Gulej, R.; Ungvari, A.; Nyul-Toth, A.; Conley, S.M. Cell non-autonomous regulation of cerebrovascular aging processes by the somatotropic axis. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1087053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kara, M.; Kara, Ö.; Ceran, Y.; Kaymak, B.; Kaya, T.C.; Çıtır, B.N.; Durmuş, M.E.; Durmuşoğlu, E.; Razaq, S.; Doğan, Y.; et al. SARcopenia Assessment in Hypertension: The SARAH Study. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2023, 102, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokos, G.; Kido, K.; Panjrath, G.; Benton, E.; Page, R.; Patel, J.; Smith, P.J.; Korous, S.; Guglin, M. Multidisciplinary Care in Heart Failure Services. J. Card. Fail. 2023, 29, 943–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ma, F.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Huang, J. Occurrence of sarcopenia in elderly patients with coronary heart disease and its association with short-term prognosis. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2025, 25, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonenko, M.; Hansen, D.; Niebauer, J.; Volterrani, M.; Adamopoulos, S.; Amarelli, C.; Ambrosetti, M.; Anker, S.D.; Bayes-Genis, A.; Gal, T.B.; et al. Prevention and Rehabilitation after Heart Transplantation: A Clinical Consensus Statement of the European Association of Preventive Cardiology, Heart Failure Association of the ESC, and the European Cardio Thoracic Transplant Association, a Section of ESOT. Transpl. Int. 2024, 37, 13191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, P.H.; Thompson-Hodgetts, S.; Pritchard-Wiart, L.; Gilmour, S.M.; Mager, D.R. Pediatric Sarcopenia: A Paradigm in the Overall Definition of Malnutrition in Children? J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2020, 44, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, T.; Wakabayashi, H.; Kawase, F.; Kokura, Y.; Takamasu, T.; Fujiwara, D.; Maeda, K. Diagnostic criteria, prevalence, and clinical outcomes of pediatric sarcopenia: A scoping review. Clin. Nutr. 2024, 43, 1825–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiosis, G.; Ioannou, D.; Skourtsidis, K.; Fouskas, V.; Stergiou, K.; Kavvadas, D.; Papamitsou, T.; Karachrysafi, S.; Kourti, M. Newer Insights on the Occurrence of Sarco-penia in Pediatric Patients with Cancer: A Systematic Review of the Past 5 Years of Literature. Cancers 2025, 17, 3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, W.J.; Hellerstein, M.; Orwoll, E.; Cummings, S.; Cawthon, P.M. D3-Creatine dilution and the importance of accuracy in the assessment of skeletal muscle mass. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2019, 10, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouliou, D.S. C-Reactive Protein: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, False Test Results and a Novel Diagnostic Algorithm for Clinicians. Diseases 2023, 11, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aurelian, J.; Zamfirescu, A.; Nedelescu, M.; Stoleru, S.; Monica Gîdei, S.; Daniela Gîță, C.; Prada, A.; Oancea, C.; Vladulescu-Trandafir, A.-I.; Prada, S.M.A.; et al. Vitamin D impact on stress and cognitive decline in older romanian adults. Farmacia 2024, 72, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Yang, F.; Bao, Z. Gut microbiota and myocardial fibrosis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 940, 175355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furrer, R.; Hawley, J.A.; Handschin, C. The molecular athlete: Exercise physiology from mechanisms to medals. Physiol. Rev. 2023, 103, 1693–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etayo-Urtasun, P.; de Asteasu, M.L.S.; Izquierdo, M. Effects of Exercise on DNA Methylation: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. Sports Med. 2024, 54, 2059–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedelcu, A.-D.; Stanciu, L.-E.; Mitroi, A.-F.; Petcu, L.-C.; Oprea, C.; Aschie, M.; Cozaru, G.-C.; Iliescu, M.-G. The Impact of Polymorphisms on Complex Medical Rehabilitation Treatment in Patients with Sarcopenia and Sarcopenic Obesity (SARCOGEN). Balneo PRM Res. J. 2025, 16, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, A.K.; Bliss, R.R.; Church, F.C. Exercise, Neuroprotective Exerkines, and Parkinson’s Disease: A Narrative Review. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.-J.; Meng, Q.; Su, C.-H. Mechanism-Driven Strategies for Reducing Fall Risk in the Elderly: A Multidisciplinary Review of Exercise Interventions. Healthcare 2024, 12, 2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maria Aurelian, S.; Aurelian, J.; Isabelle Stoica, S.; Iulia Vlădulescu-Trandafir, A.; Zamfirescu, A.; Onose, G. How do physicians estimate cardiovascular risk in the elderly using E-health-a pilot study. Balneo PRM Res. J. 2024, 15, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.; Ali, N.M.; Salim, M.H.M.; Rezaldi, M.Y. A Literature Review of Virtual Reality Exergames for Older Adults: Enhancing Physical, Cognitive, and Social Health. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuan, S.-H.; Chang, L.-H.; Sun, S.-F.; Li, C.-H.; Chen, G.-B.; Tsai, Y.-J. Assessing the Clinical Effectiveness of an Exergame-Based Exercise Training Program Using Ring Fit Adventure to Prevent and Postpone Frailty and Sarcopenia Among Older Adults in Rural Long-Term Care Facilities: Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Med. Internet Res. 2024, 26, e59468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ge, Y.; Zhao, W.; Shu, X.; Kang, L.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Y. A 4-Week Mobile App–Based Telerehabilitation Program vs Conventional In-Person Rehabilitation in Older Adults with Sarcopenia: Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Med. Internet Res. 2024, 27, e67846. Available online: https://www.jmir.org/2025/1/e67846 (accessed on 1 December 2025). [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Meng, D.; Wei, M.; Guo, H.; Yang, G.; Wang, Z. Proposal and validation of a new approach in tele-rehabilitation with 3D human posture estimation: A randomized controlled trial in older individuals with sarcopenia. BMC Geriatr. 2024, 24, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlădulescu-Trandafir, A.-I.; Popescu, C.; Mirea, A.; Petcu, I.-R.; Bojincă, V.-C.; Bălănescu, A.-R.; Badiu, D.-C.; Suciu, A.-V.; Mandu, M.; Grădinaru, E.; et al. Rheumatology Meets Rehabilitation: Post-Acute COVID-19 Sequelae Clinical Phenotypes and Targeted Care in Patients with Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Rheumatic Diseases. Balneo PRM Res. J. 2025, 16, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, M.; Glusman, G.; Brogaard, K.; Price, N.D.; Hood, L. P4 medicine: How systems medicine will transform the healthcare sector and society. Pers. Med. 2013, 10, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trache, D.; Mandu, M.; Serbanoiu, L.; Busnatu, N.; Lacraru, A.; Pana, M.; Gherasie, F.; Iancu, A.; Chioncel, V.; Onose, G.; et al. An integrated digital platform for continuity of care in post-myocardial infarction patients: A comprehensive approach to secondary prevention and rehabilitation. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2025, 32, zwaf236-341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandu, M.; Onose, G.; Andrei, C.L.; Lacraru, A.E.; Andone, I.; Spinu, A.; Popescu, C.; Trache, D.-A.; Ion, A.; Nastasa, I.; et al. The preparation and inception of a National Electronic Register for Cardiovascular Rehabilitation (NERCVR) with initial results, as part of a National Electronic Register for Car-diovascular Diseases (NERCVD). J. Med. Life 2025, 18, 656–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Mechanistic Domain | Clinical Relevance | Commonly Used Diagnostic Tools | Broad Intervention Domains |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mitochondrial dysfunction and metabolic stress | Reduced muscle endurance, early fatigability, impaired physical performance; contribution to multisystem vulnerability | Functional performance tests (e.g., handgrip strength, gait speed, chair stand test); imaging-based assessment of muscle quality | Resistance and aerobic exercise; nutritional optimization; correction of vitamin D deficiency; pharmacological agents targeting metabolic pathways (under investigation) |
| Proteostatic imbalance and anabolic resistance | Progressive loss of muscle mass and strength; reduced responsiveness to anabolic stimuli | DXA or BIA; functional performance tests | Progressive RT; individualized nutrition; hormonal or anabolic agents explored in selected contexts; multimodal rehabilitation |
| Inflammatory and catabolic signaling | Association with frailty, reduced physiological reserve, and comorbidity burden | Inflammatory markers (e.g., CRP) as contextual information; functional performance tests | Exercise-based rehabilitation; comorbidity management; lifestyle interventions; supportive anti-inflammatory or immunomodulatory approaches |
| Neuromuscular junction and motor unit degeneration | Impaired motor control, reduced coordination, increased fall risk | Gait speed, balance tests; neuro-functional performance tests | Task-oriented and balance training; neuromuscular activation exercises; experimental pharmacological modulation of neuromuscular signaling |
| Central nervous system involvement and muscle–brain crosstalk | Cognitive–motor interference, impaired adaptability to physical stressors | Cognitive screening tools; dual-task performance | Combined motor–cognitive training; multidisciplinary rehabilitation; centrally acting agents influencing neuroplasticity (context-dependent) |
| Cardio-sarcopenia (muscle–cardiovascular interactions) | Reduced exercise tolerance, poorer prognosis in cardiovascular disease, postoperative vulnerability | Functional capacity testing; body composition assessment; cardiovascular evaluation | Integrated cardiopulmonary and RT; cardiovascular rehabilitation; cardiometabolic drugs with potential muscle-related effects |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Popescu, C.; Aurelian, S.-M.; Mirea, A.; Munteanu, C.; Vlădulescu-Trandafir, A.-I.; Anghelescu, A.; Oancea, C.; Andone, I.; Spînu, A.; Suciu, A.-V.; et al. Sarcopenia as a Multisystem Disorder—Connections with Neural and Cardiovascular Systems—A Related PRISMA Systematic Literature Review. Life 2026, 16, 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/life16010068
Popescu C, Aurelian S-M, Mirea A, Munteanu C, Vlădulescu-Trandafir A-I, Anghelescu A, Oancea C, Andone I, Spînu A, Suciu A-V, et al. Sarcopenia as a Multisystem Disorder—Connections with Neural and Cardiovascular Systems—A Related PRISMA Systematic Literature Review. Life. 2026; 16(1):68. https://doi.org/10.3390/life16010068
Chicago/Turabian StylePopescu, Cristina, Sorina-Maria Aurelian, Andrada Mirea, Constantin Munteanu, Andreea-Iulia Vlădulescu-Trandafir, Aurelian Anghelescu, Corina Oancea, Ioana Andone, Aura Spînu, Andreea-Valentina Suciu, and et al. 2026. "Sarcopenia as a Multisystem Disorder—Connections with Neural and Cardiovascular Systems—A Related PRISMA Systematic Literature Review" Life 16, no. 1: 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/life16010068
APA StylePopescu, C., Aurelian, S.-M., Mirea, A., Munteanu, C., Vlădulescu-Trandafir, A.-I., Anghelescu, A., Oancea, C., Andone, I., Spînu, A., Suciu, A.-V., Stoica, S.-I., Gîdei, S.-M., Alecu, V.-M., Gîță, C.-D., Pop, N.-L., Ciobanu, V., & Onose, G. (2026). Sarcopenia as a Multisystem Disorder—Connections with Neural and Cardiovascular Systems—A Related PRISMA Systematic Literature Review. Life, 16(1), 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/life16010068








