Metabolic Syndrome in Older Adults: Through the Lens of Institute for Healthcare Improvement’s (IHI) 4Ms Framework and Social Determinants of Health
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Research Model
2.2. Data Collection and Search Strategy
2.3. Inclusion Criteria
- Conducted in older adult populations.
- Focused on Metabolic Syndrome.
- Discussed social determinants of health.
- Included treatments/outcomes.
- Published in the English language.
2.4. Exclusion Criteria
- They were not conducted on human subjects.
- They were not published in the English language.
3. Data Extraction and Analysis
4. Risk Factors and Related Disorders
5. Diagnostic Criteria
6. Pathogenesis of Metabolic Syndrome
7. Metabolic Syndrome in Older Adults
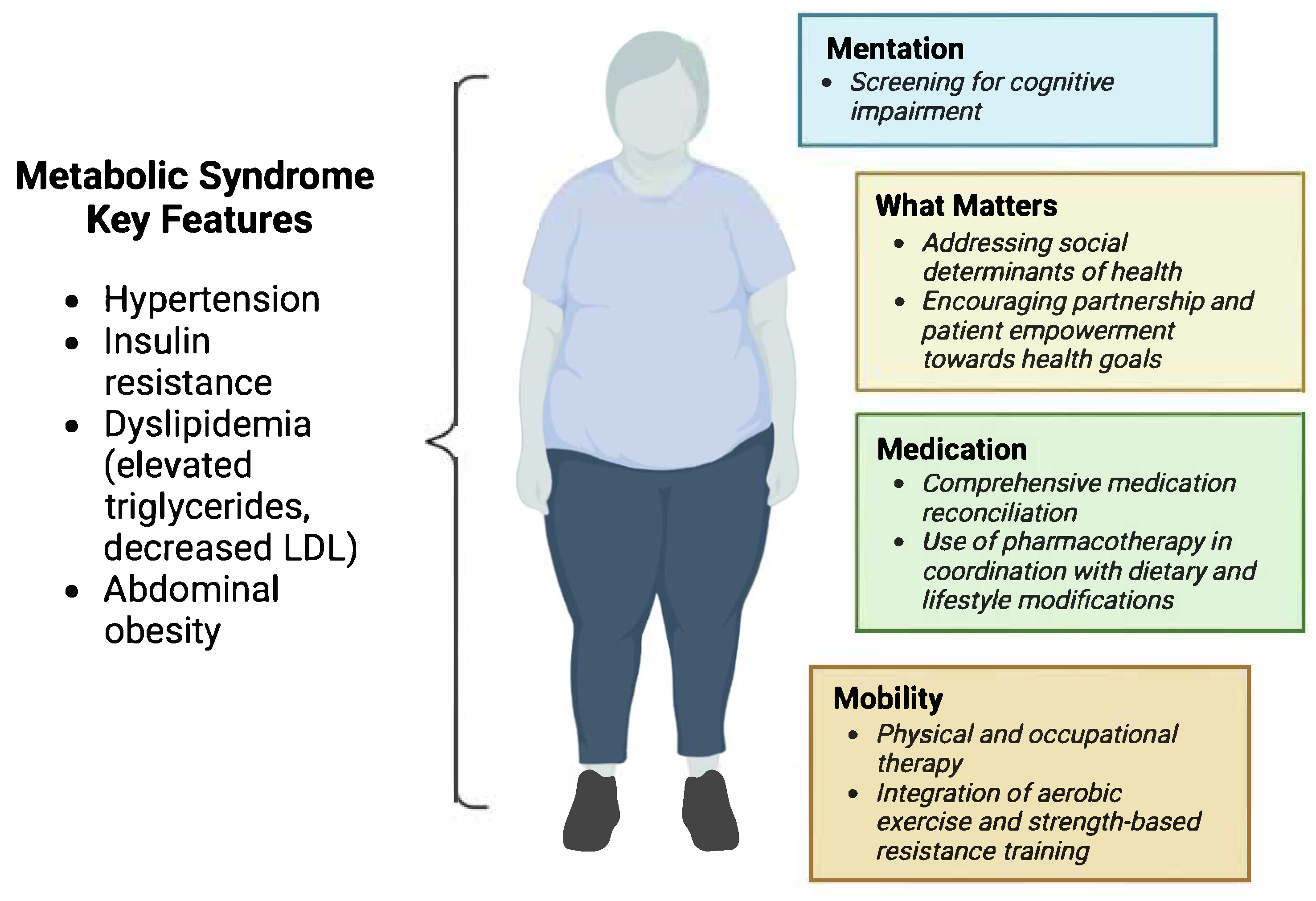
8. Adapting IHI 4Ms to Optimize Care of Geriatric Patients with Metabolic Syndrome
8.1. What Matters
8.2. Medication
8.3. Mentation
8.4. Mobility
9. Conclusions
10. Clinical Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Neeland, I.J.; Lim, S.; Tchernof, A.; Gastaldelli, A.; Rangaswami, J.; Ndumele, C.E.; Powell-Wiley, T.M.; Després, J.P. Metabolic syndrome. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2024, 10, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grundy, S.M.; Brewer, H.B., Jr.; Cleeman, J.I.; Smith, S.C., Jr.; Lenfant, C. Definition of metabolic syndrome: Report of the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute/American Heart Association conference on scientific issues related to definition. Circulation 2004, 109, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lusis, A.J.; Attie, A.D.; Reue, K. Metabolic syndrome: From epidemiology to systems biology. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2008, 9, 819–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahed, G.; Aoun, L.; Bou Zerdan, M.; Allam, S.; Bou Zerdan, M.; Bouferraa, Y.; Assi, H.I. Metabolic Syndrome: Updates on Pathophysiology and Management in 2021. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, K.G.; Eckel, R.H.; Grundy, S.M.; Zimmet, P.Z.; Cleeman, J.I.; Donato, K.A.; Fruchart, J.C.; James, W.P.; Loria, C.M.; Smith, S.C., Jr. Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: A joint interim statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation 2009, 120, 1640–1645. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, X.; Or, B.; Tsoi, M.F.; Cheung, C.L.; Cheung, B.M.Y. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome in the United States National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2011–2018. Postgrad. Med. J. 2023, 99, 985–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Jia, X.; Wang, Y.; Fan, J.; Zhao, C.; Yang, Y.; Shi, X. Trends and influence factors in the prevalence, intervention, and control of metabolic syndrome among US adults, 1999–2018. BMC Geriatr. 2022, 22, 979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeBoer, M.D.; Filipp, S.L.; Gurka, M.J. Geographical variation in the prevalence of obesity and metabolic syndrome among US adolescents. Pediatr. Obes. 2019, 14, e12483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongtang, N.; Sukmawan, R.; Llanes, E.J.B.; Lee, Z.V. Dyslipidemia management for primary prevention of cardiovascular events: Best in-clinic practices. Prev. Med. Rep. 2022, 27, 101819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foëx, P.; Sear, J. Hypertension: Pathophysiology and treatment. Contin. Educ. Anaesth. Crit. Care Pain 2004, 4, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, B.; Dey, S.; Das, T.; Sarkar, M.; Banerjee, J.; Dash, S.K. Chronic hyperglycemia mediated physiological alteration and metabolic distortion leads to organ dysfunction, infection, cancer progression and other pathophysiological consequences: An update on glucose toxicity. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 107, 306–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.Y.; Huang, W.J.; Hua, Y.; Qu, Q.; Cheng, C.; Liu, H.L.; Kong, X.Q.; Ma, Y.X.; Sun, W. Trends in general and abdominal obesity in US adults: Evidence from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2001–2018). Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 925293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patial, R.; Batta, I.; Thakur, M.; Sobti, R.C.; Agrawal, D.K. Etiology, Pathophysiology, and Treatment Strategies in the Prevention and Management of Metabolic Syndrome. Arch. Intern. Med. Res. 2024, 7, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohm, T.V.; Meier, D.T.; Olefsky, J.M.; Donath, M.Y. Inflammation in obesity, diabetes, and related disorders. Immunity 2022, 55, 31–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, A.; Sen Sarma, M. Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: A silent pandemic. World J. Hepatol. 2024, 16, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberti, K.G.; Zimmet, P.; Shaw, J. Metabolic syndrome--a new world-wide definition. A Consensus Statement from the International Diabetes Federation. Diabet. Med. 2006, 23, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grundy, S.M.; Cleeman, J.I.; Daniels, S.R.; Donato, K.A.; Eckel, R.H.; Franklin, B.A.; Gordon, D.J.; Krauss, R.M.; Savage, P.J.; Smith, S.C., Jr.; et al. Diagnosis and management of the metabolic syndrome: An American Heart Association/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Scientific Statement. Circulation 2005, 112, 2735–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boden, G.; Shulman, G.I. Free fatty acids in obesity and type 2 diabetes: Defining their role in the development of insulin resistance and beta-cell dysfunction. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 32 (Suppl. S3), 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, M.E.; Marcucci, M.J.; Cline, G.W.; Bell, K.; Barucci, N.; Lee, D.; Goodyear, L.J.; Kraegen, E.W.; White, M.F.; Shulman, G.I. Free fatty acid-induced insulin resistance is associated with activation of protein kinase C theta and alterations in the insulin signaling cascade. Diabetes 1999, 48, 1270–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, T.; Michelagnoli, S.; Longhi, R.; Gianfranceschi, G.; Pazzucconi, F.; Calabresi, L.; Sirtori, C.R.; Franceschini, G. Triglycerides are major determinants of cholesterol esterification/transfer and HDL remodeling in human plasma. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1995, 15, 1819–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisberg, S.P.; McCann, D.; Desai, M.; Rosenbaum, M.; Leibel, R.L.; Ferrante, A.W., Jr. Obesity is associated with macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1796–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassmann, S.; Stumpf, M.; Strehlow, K.; Schmid, A.; Schieffer, B.; Böhm, M.; Nickenig, G. Interleukin-6 induces oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction by overexpression of the angiotensin II type 1 receptor. Circ. Res. 2004, 94, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridker, P.M.; Hennekens, C.H.; Buring, J.E.; Rifai, N. C-reactive protein and other markers of inflammation in the prediction of cardiovascular disease in women. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 836–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotamisligil, G.S.; Murray, D.L.; Choy, L.N.; Spiegelman, B.M. Tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibits signaling from the insulin receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 4854–4858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.H.; Halbleib, M.; Ahmad, F.; Manganiello, V.C.; Greenberg, A.S. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha stimulates lipolysis in differentiated human adipocytes through activation of extracellular signal-related kinase and elevation of intracellular cAMP. Diabetes 2002, 51, 2929–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou Ziki, M.D.; Mani, A. Metabolic syndrome: Genetic insights into disease pathogenesis. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2016, 27, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunn, A.V.; Bell, J.D.; Guy, G.W. Lifestyle-induced metabolic inflexibility and accelerated ageing syndrome: Insulin resistance, friend or foe? Nutr. Metab. 2009, 6, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.X.; Chaudhary, N.; Akinyemiju, T. Metabolic Syndrome Prevalence by Race/Ethnicity and Sex in the United States, National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1988–2012. Prev. Chronic Dis. 2017, 14, E24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mate, K.; Fulmer, T.; Pelton, L.; Berman, A.; Bonner, A.; Huang, W.; Zhang, J. Evidence for the 4Ms: Interactions and Outcomes across the Care Continuum. J. Aging Health 2021, 33, 469–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, S.E.; Ruopp, M.D.; Mac, C.T.; O’Malley, K.A.; Meyerson, J.L.; Lefers, L.; Bean, J.F.; Driver, J.A.; Schwartz, A.W. Early clinical and quality impacts of the Age-Friendly Health System in a Veterans Affairs skilled nursing facility. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2024, 72, 3865–3874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brignone, E.; LeJeune, K.; Mihalko, A.E.; Shannon, A.L.; Sinoway, L.I. Self-Reported Social Determinants of Health and Area-Level Social Vulnerability. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e2412109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoveling, L.A.; Liefbroer, A.C.; Bültmann, U.; Smidt, N. Understanding socioeconomic differences in incident metabolic syndrome among adults: What is the mediating role of health behaviours? Prev. Med. 2021, 148, 106537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacchione, P.Z. Age-Friendly Health Systems: The 4Ms Framework. Clin. Nurs. Res. 2020, 29, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Improvement, I.f.H. Age-Friendly Health Systems. Available online: https://www.ihi.org/initiatives/age-friendly-health-systems (accessed on 30 October 2024).
- Yoo, J.W.; Kang, H.-T.; Choe, I.; Kim, L.; Han, D.-H.; Shen, J.J.; Kim, Y.; Reed, P.S.; Ioanitoaia-Chaudhry, I.; Chong, M.T.; et al. Racial and Ethnic Disparity in 4Ms among Older Adults Among Telehealth Users as Primary Care. Gerontol. Geriatr. Med. 2023, 9, 23337214231189053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todd, A.; Jansen, J.; Colvin, J.; McLachlan, A.J. The deprescribing rainbow: A conceptual framework highlighting the importance of patient context when stopping medication in older people. BMC Geriatr. 2018, 18, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochon, P.A.; Petrovic, M.; Cherubini, A.; Onder, G.; O’Mahony, D.; Sternberg, S.A.; Stall, N.M.; Gurwitz, J.H. Polypharmacy, inappropriate prescribing, and deprescribing in older people: Through a sex and gender lens. Lancet Healthy Longev. 2021, 2, e290–e300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S. Role of statins in the management of dyslipidaemia. Indian Heart J. 2024, 76 (Suppl. S1), S33–S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, H.; Zeltser, R. Antihypertensive Medications. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, Q.Y.D.; Cox, A.; McNeil, S.; Sumithran, P. Obesity medications: A narrative review of current and emerging agents. Osteoarthr. Cartil. Open 2024, 6, 100472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strain, W.D.; Down, S.; Brown, P.; Puttanna, A.; Sinclair, A. Diabetes and Frailty: An Expert Consensus Statement on the Management of Older Adults with Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Ther. 2021, 12, 1227–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Li, C.; Di, D.; Zhou, L.; Qian, Y.; Qiang, C.; Ma, C.; Zhou, R.; Wang, B.; Wang, M. Evaluate the Relationship Between Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Metabolic Syndrome in Real-World Data. Nat. Sci. Sleep 2024, 16, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, R.; Sissoho, F.; Kaushik, V.P.; Raji, M.A. The Case for Early Use of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Patients with Comorbid Diabetes and Metabolic Syndrome. Life 2022, 12, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onoviran, O.F.; Li, D.; Toombs Smith, S.; Raji, M.A. Effects of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists on comorbidities in older patients with diabetes mellitus. Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2019, 10, 2040622319862691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wofford, M.R.; King, D.S.; Harrell, T.K. Drug-induced metabolic syndrome. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2006, 8, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhaegen, A.A.; Van Gaal, L.F. Drugs That Affect Body Weight, Body Fat Distribution, and Metabolism. In Endotext; Feingold, K.R., Ahmed, S.F., Anawalt, B., Blackman, M.R., Boyce, A., Chrousos, G., Corpas, E., de Herder, W.W., Dhatariya, K., Dungan, K., et al., Eds.; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Mazereel, V.; Detraux, J.; Vancampfort, D.; van Winkel, R.; De Hert, M. Impact of Psychotropic Medication Effects on Obesity and the Metabolic Syndrome in People With Serious Mental Illness. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 573479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chokka, P.; Tancer, M.; Yeragani, V.K. Metabolic syndrome: Relevance to antidepressant treatment. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2006, 31, 414. [Google Scholar]
- Scheen, A.J. Metabolic disorders induced by psychotropic drugs. Ann. Endocrinol. 2023, 84, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavan, A.H.; Gallagher, P. Predicting risk of adverse drug reactions in older adults. Ther. Adv. Drug Saf. 2016, 7, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, W.W.; Passos, L.C.; Gama, R.S.; Souza, R.M.; Oliveira, M.G. Factors associated with older patients’ misunderstandings of medication dosage regimen instructions after consultation in primary care in Brazil. J. Eval. Clin. Pract. 2021, 27, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuhec, M.; Gorenc, K.; Zelko, E. Evaluation of a collaborative care approach between general practitioners and clinical pharmacists in primary care community settings in elderly patients on polypharmacy in Slovenia: A cohort retrospective study reveals positive evidence for implementation. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2019, 19, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, E.W.; Rung, A.L.; Leon, K.A.; Firestein, C.; Krousel-Wood, M.A. Medication Adherence in Older Adults: A Qualitative Study. Educ. Gerontol. 2014, 40, 198–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvat, M.; Eržen, I.; Vrbnjak, D. Barriers and Facilitators to Medication Adherence among the Vulnerable Elderly: A Focus Group Study. Healthcare 2024, 12, 1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrowolski, P.; Prejbisz, A.; Kuryłowicz, A.; Baska, A.; Burchardt, P.; Chlebus, K.; Dzida, G.; Jankowski, P.; Jaroszewicz, J.; Jaworski, P.; et al. Metabolic syndrome—A new definition and management guidelines. A joint position paper by the Polish Society of Hypertension, Polish Society for the Treatment of Obesity, Polish Lipid Association, Polish Association for Study of Liver, Polish Society of Family Medicine, Polish Society of Lifestyle Medicine, Division of Prevention and Epidemiology Polish Cardiac Society, “Club 30” Polish Cardiac Society, and Division of Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery Society of Polish Surgeons. Arch. Med. Sci. 2022, 18, 1133–1156. [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi, D.; Topiwala, A.; Al Abid, S.U.; Allen, N.E.; Kuźma, E.; Littlejohns, T.J. Association of Metabolic Syndrome With Neuroimaging and Cognitive Outcomes in the UK Biobank. Diabetes Care 2024, 47, 1415–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atti, A.R.; Valente, S.; Iodice, A.; Caramella, I.; Ferrari, B.; Albert, U.; Mandelli, L.; De Ronchi, D. Metabolic Syndrome, Mild Cognitive Impairment, and Dementia: A Meta-Analysis of Longitudinal Studies. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2019, 27, 625–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diz-Chaves, Y.; Mastoor, Z.; Spuch, C.; González-Matías, L.C.; Mallo, F. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of GLP-1 Receptor Activation in the Brain in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuansangeam, M.; Phadungsaksawasdi, P.; Park, H.J.; Yang, Y.H. Exploring the link between GLP-1 receptor agonists and dementia: A comprehensive review. J. Alzheimers Dis. Rep. 2025, 9, 25424823251342182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penninx, B.; Lange, S.M.M. Metabolic syndrome in psychiatric patients: Overview, mechanisms, and implications. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2018, 20, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vancampfort, D.; Stubbs, B.; Mitchell, A.J.; De Hert, M.; Wampers, M.; Ward, P.B.; Rosenbaum, S.; Correll, C.U. Risk of metabolic syndrome and its components in people with schizophrenia and related psychotic disorders, bipolar disorder and major depressive disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World Psychiatry 2015, 14, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Hua, Y.Y.; Ma, Q.H.; Xu, Y.; Chen, X.; Pan, C.W. Depressive symptoms and 5-year incident metabolic syndrome among older adults. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull, F.C.; Al-Ansari, S.S.; Biddle, S.; Borodulin, K.; Buman, M.P.; Cardon, G.; Carty, C.; Chaput, J.P.; Chastin, S.; Chou, R.; et al. World Health Organization 2020 guidelines on physical activity and sedentary behaviour. Br. J. Sports Med. 2020, 54, 1451–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chomiuk, T.; Niezgoda, N.; Mamcarz, A.; Śliż, D. Physical activity in metabolic syndrome. Front. Physiol. 2024, 15, 1365761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppert, J.M.; Bellicha, A.; Ciangura, C. Physical activity in management of persons with obesity. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2021, 93, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Component | Criterion |
|---|---|
| Abdominal Obesity | Waist circumference ≥ 102 cm (40 in) in men Waist circumference ≥ 88 cm (35 in) in women |
| Triglycerides | ≥150 mg/dL (1.7 mmol/L) or on drug treatment for elevated triglycerides |
| HDL Cholesterol | <40 mg/dL (1 mmol/L) in men <50 mg/dL (1.3 mmol/L) in women or on drug treatment for low HDL |
| Blood Pressure | ≥130/85 mmHg or on antihypertensive medication |
| Fasting Plasma Glucose | ≥100 mg/dL (5.6 mmol/L) or on drug treatment for elevated glucose |
| Diagnosis requires at least 3 out of 5 criteria. | |
| Component | Criterion |
|---|---|
| Waist Circumference | Increased waist circumference with ethnic-specific cut-off values
|
| Triglycerides | ≥150 mg/dL (1.7 mmol/L) or on drug treatment for elevated triglycerides |
| HDL Cholesterol | <40 mg/dL (1 mmol/L) in men <50 mg/dL (1.3 mmol/L) in women or on drug treatment for low HDL |
| Blood Pressure | ≥130/85 mmHg or on antihypertensive medication Or treatment for hypertension |
| Fasting Plasma Glucose | ≥100 mg/dL (5.6 mmol/L) or previously diagnosed type 2 diabetes |
| Diagnosis requires at least 3 out of 5 criteria. | |
| Metabolic Syndrome | Indication | Medications |
|---|---|---|
| Insulin Resistance | Diabetes Prediabetes | Metformin GLP1RA SGLT2i + Others |
| Obesity | BMI > 27 kg/m2 | GLP1RA Naltrexone/Bupropion Orlistat Metabolic Surgery |
| Hypertension | ≥140/90 mmHg (In-office measurement) ≥135/85 mmHg (ambulatory measurements) | ACEi/ARB +CCB +TD +Aldosterone antagonist β-blocker |
| Dyslipidemia | LDL-C ≥ 70/55 mg/dL (in high risk groups) TG > 200 mg/dL | Statin (maximal tolerated dose) Ezetimibe +Fenofibrate |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Goddard, G.; Rajagopal, S.; Wahbah Makhoul, G.; Raji, M.A. Metabolic Syndrome in Older Adults: Through the Lens of Institute for Healthcare Improvement’s (IHI) 4Ms Framework and Social Determinants of Health. Life 2025, 15, 1370. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15091370
Goddard G, Rajagopal S, Wahbah Makhoul G, Raji MA. Metabolic Syndrome in Older Adults: Through the Lens of Institute for Healthcare Improvement’s (IHI) 4Ms Framework and Social Determinants of Health. Life. 2025; 15(9):1370. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15091370
Chicago/Turabian StyleGoddard, Gabrielle, Shilpa Rajagopal, Gennifer Wahbah Makhoul, and Mukaila A. Raji. 2025. "Metabolic Syndrome in Older Adults: Through the Lens of Institute for Healthcare Improvement’s (IHI) 4Ms Framework and Social Determinants of Health" Life 15, no. 9: 1370. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15091370
APA StyleGoddard, G., Rajagopal, S., Wahbah Makhoul, G., & Raji, M. A. (2025). Metabolic Syndrome in Older Adults: Through the Lens of Institute for Healthcare Improvement’s (IHI) 4Ms Framework and Social Determinants of Health. Life, 15(9), 1370. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15091370






