Deep Learning Algorithm to Determine the Presence of Rectal Cancer from Transrectal Ultrasound Images
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
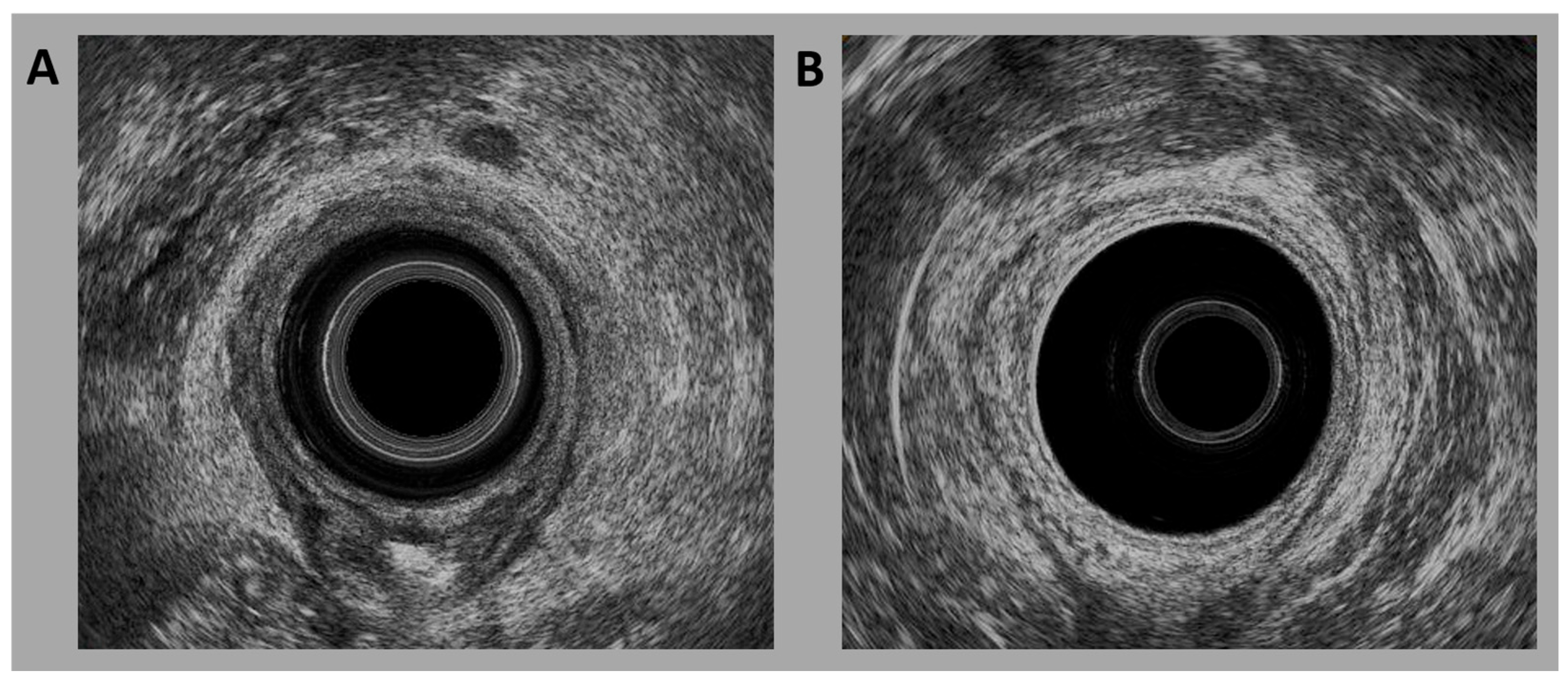
2.1. TRUS Image Collection
2.2. TRUS
2.3. DL Algorithms
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TRUS | Transrectal ultrasound |
| CNNs | convolutional neural networks |
| T | Tumor |
| LN | Lymph node |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| US | Ultrasonography |
| ML | Machine learning |
| DL | Deep learning |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristic |
| AUC | Area under the curve |
References
- Hajri, A.; Fatine, A.; Eddaoudi, Y.; Rifki El Jay, S.; Boufettal, R.; Erreguibi, D.; Chehab, F. Epidemiology, incidence and treatment of rectal cancer in young women case serie about 11 cases (case series). Ann. Med. Surg. 2022, 82, 104693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, M.; Moreira, D.N.; Ghidini, M. Colon and rectal cancer: An emergent public health problem. World J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 30, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vabi, B.W.; Gibbs, J.F.; Parker, G.S. Implications of the growing incidence of global colorectal cancer. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2021, 12 (Suppl. S2), S387–S398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eng, C.; Jácome, A.A.; Agarwal, R.; Hayat, M.H.; Byndloss, M.X.; Holowatyj, A.N.; Bailey, C.; Lieu, C.H. A comprehensive framework for early-onset colorectal cancer research. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, e116–e128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Surabhi, V.R.; Kassam, Z.; Chang, K.J.; Kaur, H. Imaging of colon and rectal cancer. Curr. Probl. Cancer 2023, 47, 100970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, J.B.; Maggard, M.A.; Livingston, E.H.; Yo, C.K. Colorectal cancer in the young. Am. J. Surg. 2004, 187, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, J.B.; Maggard, M.A.; Liu, J.H.; Etzioni, D.A.; Livingston, E.H.; Ko, C.Y. Rates of colon and rectal cancers are increasing in young adults. Am. Surg. 2003, 69, 866–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kekelidze, M.; D’Errico, L.; Pansini, M.; Tyndall, A.; Hohmann, J. Colorectal cancer: Current imaging methods and future perspectives for the diagnosis, staging and therapeutic response evaluation. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 8502–8514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barabouti, D.G.; Wong, W.D. Clinical Staging of Rectal Cancer. Semin. Colon Rectal Surg. 2005, 16, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milanzi, E.; Pelly, R.M.; Hayes, I.P.; Gibbs, P.; Faragher, I.; Reece, J.C. Accuracy of Baseline Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Staging Rectal Cancer Patients Proceeding Directly to Surgery. J. Surg. Oncol. 2024, 130, 1674–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Zang, Y.; Zhou, D.; Chen, Z.; Xin, C.; Zang, W.; Tu, X. The importance of preoperative T3 stage substaging by 3D endorectal ultrasonography for the prognosis of middle and low rectal cancer. J. Clin. Ultrasound 2024, 52, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serracant, A.; Consola, B.; Ballesteros, E.; Sola, M.; Novell, F.; Montes, N.; Serra-Aracil, X. How to Study the Location and Size of Rectal Tumors That Are Candidates for Local Surgery: Rigid Rectoscopy, Magnetic Resonance, Endorectal Ultrasound or Colonoscopy? An Interobservational Study. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J. Transrectal ultrasonography of anorectal diseases: Advantages and disadvantages. Ultrasonography 2015, 34, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Ye, J.; Wang, Y.; Xiong, W.; Xu, J.; He, Y.; Cai, S.; Tan, M.; Yuan, Y. The Optimal Application of Transrectal Ultrasound in Staging of Rectal Cancer Following Neoadjuvant Therapy: A Pragmatic Study for Accuracy Investigation. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 784–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhu, F.; Li, P.; Zhu, J. Artificial intelligence-assisted endoscopic ultrasound in the diagnosis of gastrointestinal stromal tumors: A meta-analysis. Surg. Endosc. 2023, 37, 1649–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, Y.J.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, J.H.; Chang, M.C.; Park, D. Machine learning analysis to predict the need for ankle foot orthosis in patients with stroke. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.K.; Choo, Y.J.; Chang, M.C. Prediction of Motor Function in Stroke Patients Using Machine Learning Algorithm: Development of Practical Models. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2021, 30, 105856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.K.; Lv, Z.; Park, D.; Chang, M.C. Practical Machine Learning Model to Predict the Recovery of Motor Function in Patients with Stroke. Eur. Neurol. 2022, 85, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzubaidi, L.; Zhang, J.; Humaidi, A.J.; Al-Dujaili, A.; Duan, Y.; Al-Shamma, O.; Santamaría, J.; Fadhel, M.A.; Al-Amidie, M.; Farhan, L. Review of deep learning: Concepts, CNN architectures, challenges, applications, future directions. J. Big Data 2021, 8, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, R.Y.; Coyner, A.S.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J.; Chiang, M.F.; Campbell, J.P. Introduction to Machine Learning, Neural Networks, and Deep Learning. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2020, 9, 14. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sarker, I.H. Deep Learning: A Comprehensive Overview on Techniques, Taxonomy, Applications and Research Directions. SN Comput. Sci. 2021, 2, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, J.W.; Olgin, J.E.; Avram, R.; Abreau, S.A.; Sittler, T.; Radia, K.; Hsia, H.; Walters, T.; Lee, B.; Gonzalez, J.E.; et al. Performance of a Convolutional Neural Network and Explainability Technique for 12-Lead Electrocardiogram Interpretation. JAMA Cardiol. 2021, 6, 1285–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, R.; Nishio, M.; Do, R.K.G.; Togashi, K. Convolutional neural networks: An overview and application in radiology. Insights Imaging 2018, 9, 611–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLong, E.R.; DeLong, D.M.; Clarke-Pearson, D.L. Comparing the areas under two or more correlated receiver operating characteristic curves: A nonparametric approach. Biometrics 1988, 44, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.K.; Choo, Y.J.; Shin, H.; Choi, G.S.; Chang, M.C. Prediction of ambulatory outcome in patients with corona radiata infarction using deep learning. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandrekar, J.N. Receiver operating characteristic curve in diagnostic test assessment. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2010, 5, 1315–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Yang, Z.; Qin, W.; Li, X.; Su, S.; Huang, J. Construction of machine learning models based on transrectal ultrasound combined with contrast-enhanced ultrasound to predict preoperative regional lymph node metastasis of rectal cancer. Heliyon 2024, 10, e26433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Fei, B. 3D Prostate Segmentation of Ultrasound Images Combining Longitudinal Image Registration and Machine Learning. In Proceedings of SPIE—The International Society for Optical Engineering; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2012; Volume 8316, p. 83162O. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlando, N.; Gillies, D.J.; Gyacskov, I.; Romagnoli, C.; D’Souza, D.; Fenster, A. Automatic prostate segmentation using deep learning on clinically diverse 3D transrectal ultrasound images. Med. Phys. 2020, 47, 2413–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arafa, M.A.; Omar, I.; Farhat, K.H.; Elshinawy, M.; Khan, F.; Alkhathami, F.A.; Mokhtar, A.; Althunayan, A.; Rabah, D.M.; Badawy, A.A. A Comparison of Systematic, Targeted, and Combined Biopsy Using Machine Learning for Prediction of Prostate Cancer Risk: A Multi-Center Study. Med. Princ. Pract. 2024, 33, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, J.; Wildman-Tobriner, B.; Buda, M.; Yang, J.; Ho, L.M.; Allen, B.C.; Ehieli, W.L.; Miller, C.M.; Zhang, J.; Mazurowski, M.A. Deep learning for classification of thyroid nodules on ultrasound: Validation on an independent dataset. Clin. Imaging 2023, 99, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Kong, D.; Xu, X.; Hu, S.; Li, Z.; Tian, J. Deep learning-based classification of breast lesions using dynamic ultrasound video. Eur. J. Radiol. 2023, 165, 110885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jesus-Rodriguez, H.J.; Morgan, M.A.; Sagreiya, H. Deep Learning in Kidney Ultrasound: Overview, Frontiers, and Challenges. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2021, 28, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Layer (Type) | Output Shape | Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| StochasticDepth | 7 × 7 × 256 | 0 |
| MBConv | 7 × 7 × 256 | 0 |
| Conv2d | 7 × 7 × 1280 | 327,680 |
| BatchNorm2d | 7 × 7 × 1280 | 2560 |
| SiLU | 7 × 7 × 1280 | 0 |
| AdaptiveAvgPool2d | 1 × 1 × 1280 | 0 |
| Linear | 2 | 2562 |
| Total parameters | 20,180,050 | |
| Trainable parameters | 20,180,050 | |
| Non-trainable parameters | 0 |
| Sample size (patients) | 544, 79.88% for training, 137, 20.12% for validation, total 681 | ||||
| Sample ratio (patients) | Rectal cancer: 533, 78.27%; normal rectum: 148, 21.73%; | ||||
| Rectal cancer: 426, 78.31%; normal rectum: 118, 21.69% for training | |||||
| Rectal cancer: 107, 78.10%; normal rectum: 30, 21.90% for validation | |||||
| Model details | EfficientNetV2-S CNN model with full learning (unfreeze all layers) | ||||
| Adam optimizer, SiLU activation | |||||
| Learning rate 1 × 10−3, batch size 32, Epoch 25 | |||||
| Batch normalization and dropout for regularization | |||||
| Image resized to 224 (H) × 224 (W) | |||||
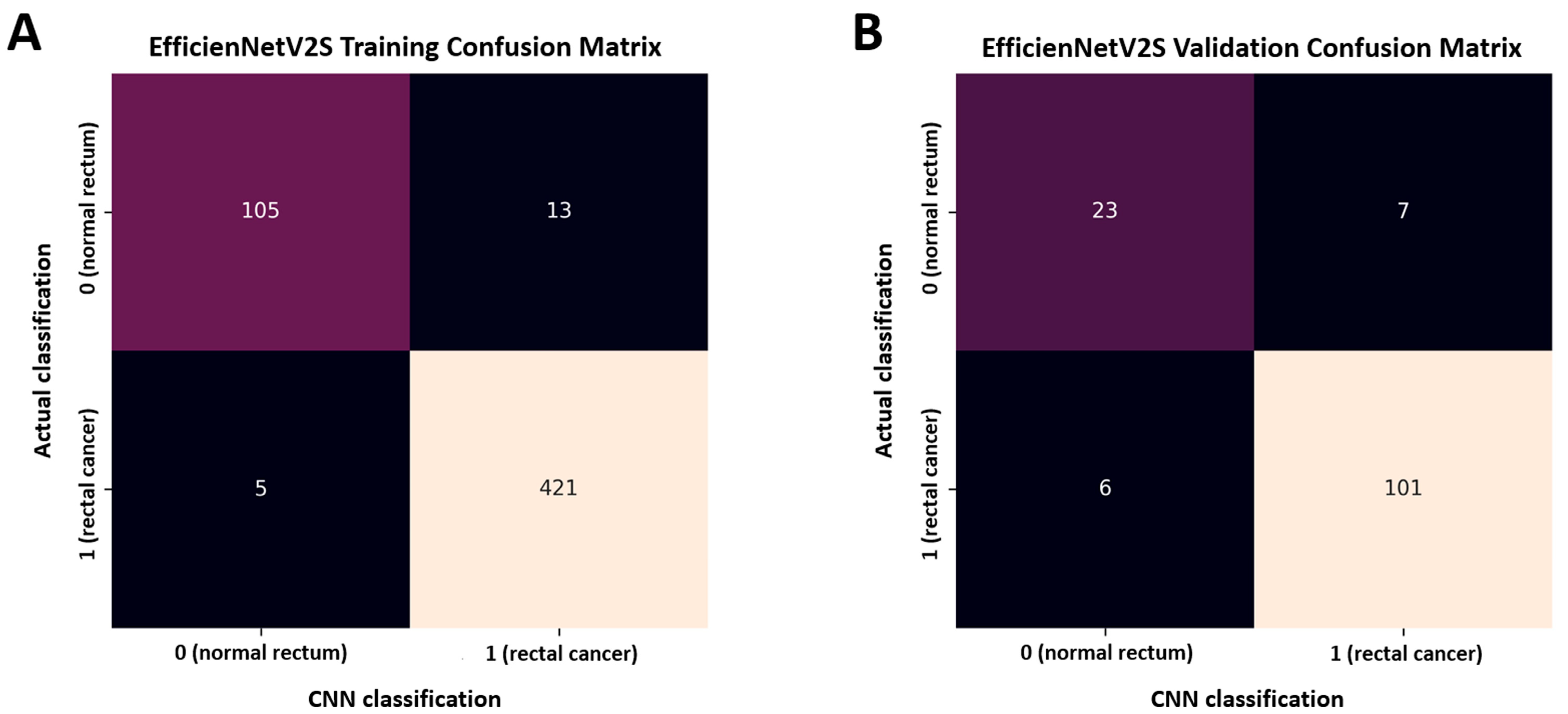
| Training accuracy: 96.7%, AUC 0.996 with 95% CI [0.990–1.000] | |||||
| Validation accuracy: 90.5%, AUC 0.945 with 95% CI [0.907–0.983] | |||||
| Class | Precision | Recall | F1-score | Support | |
| Model performance (validation data) | Rectal cancer (1) | 0.935 | 0.944 | 0.940 | 107 |
| Normal rectum (0) | 0.793 | 0.767 | 0.780 | 30 | |
| Macro average | 0.864 | 0.855 | 0.860 | 137 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, M.C.; Kang, S.I.; Kim, S. Deep Learning Algorithm to Determine the Presence of Rectal Cancer from Transrectal Ultrasound Images. Life 2025, 15, 1358. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15091358
Chang MC, Kang SI, Kim S. Deep Learning Algorithm to Determine the Presence of Rectal Cancer from Transrectal Ultrasound Images. Life. 2025; 15(9):1358. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15091358
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Min Cheol, Sung Il Kang, and Sohyun Kim. 2025. "Deep Learning Algorithm to Determine the Presence of Rectal Cancer from Transrectal Ultrasound Images" Life 15, no. 9: 1358. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15091358
APA StyleChang, M. C., Kang, S. I., & Kim, S. (2025). Deep Learning Algorithm to Determine the Presence of Rectal Cancer from Transrectal Ultrasound Images. Life, 15(9), 1358. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15091358







