A 15-Year One Health Approach to Antimicrobial Resistance in Kuwait from Hospitals to Environmental Contexts: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
- What has been the status of AMR in Kuwait over the past 15 years (2009–2024)?
- How do several sectors, including human health, animal health, and the environment, influence the emergence and dissemination of AMR?
- What information is available about the efficacy of One Health measures in reducing AMR in Kuwait?
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Search Strategy
2.3. Eligibility Criteria
2.4. Study Selection Process
2.5. Data Extraction
2.6. Methodological Quality Assessment
2.7. Meta-Analysis
2.8. Certainty of Evidence
3. Results
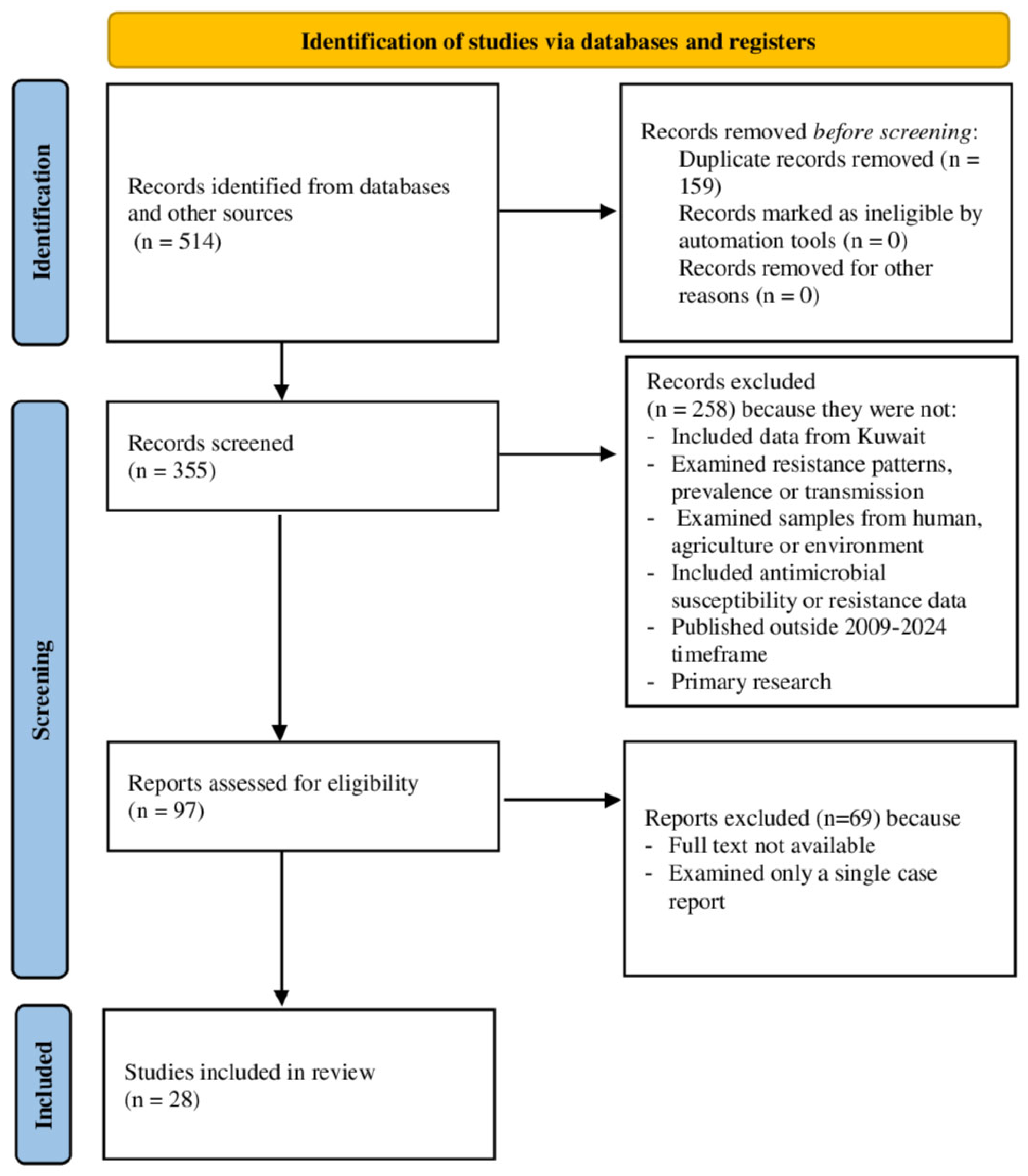
3.1. Literature Searched
3.2. General Characteristics
3.3. Resistance Patterns and Distribution
3.3.1. Clinical Resistance Patterns
3.3.2. Agricultural Sources
3.3.3. Environmental Sources
3.4. Transmission Pathways
3.5. Meta-Analysis
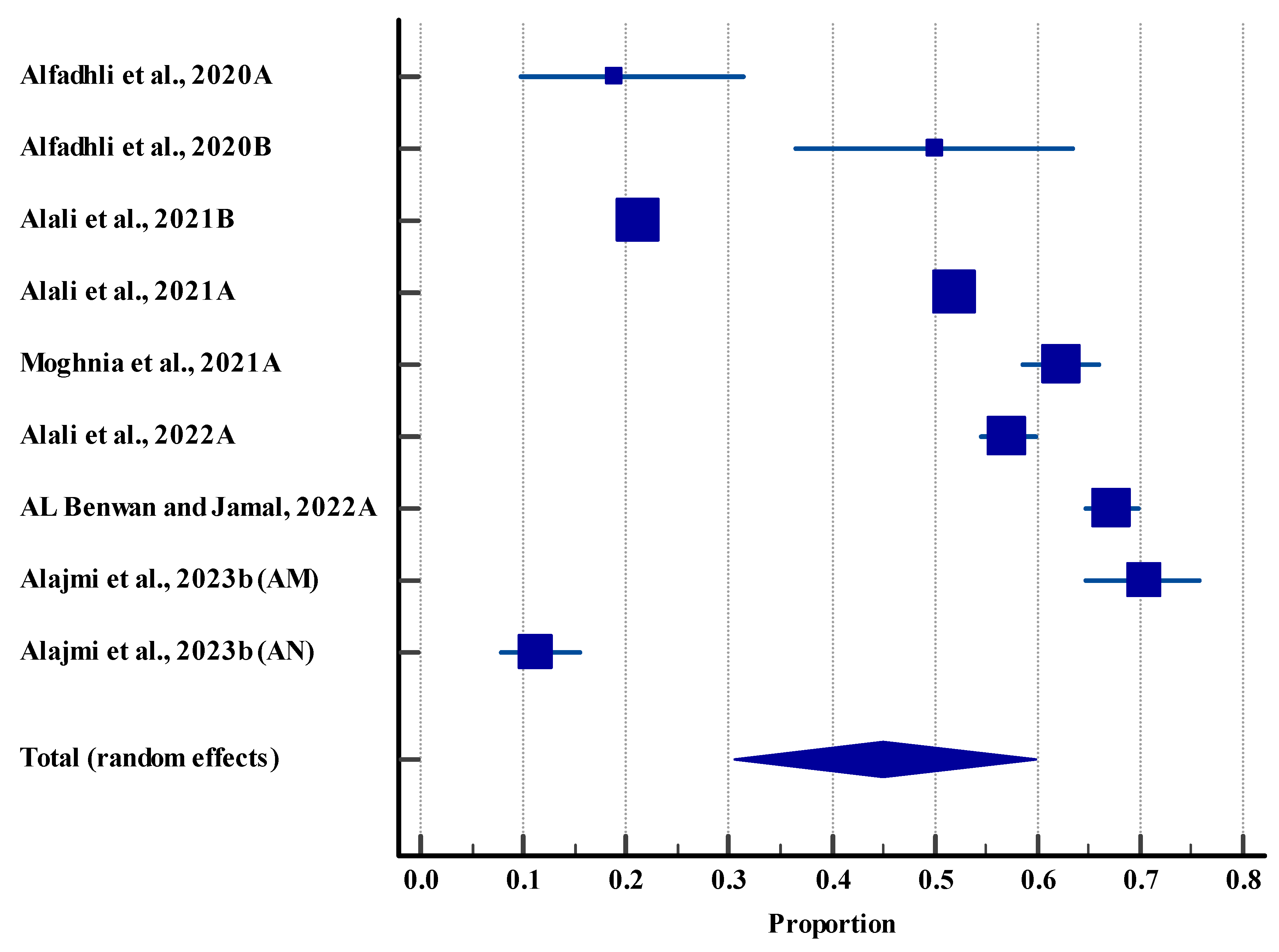
3.5.1. Prevalence of Microbes in the Clinical Settings (Human)
3.5.2. Resistance Rate (Humans)
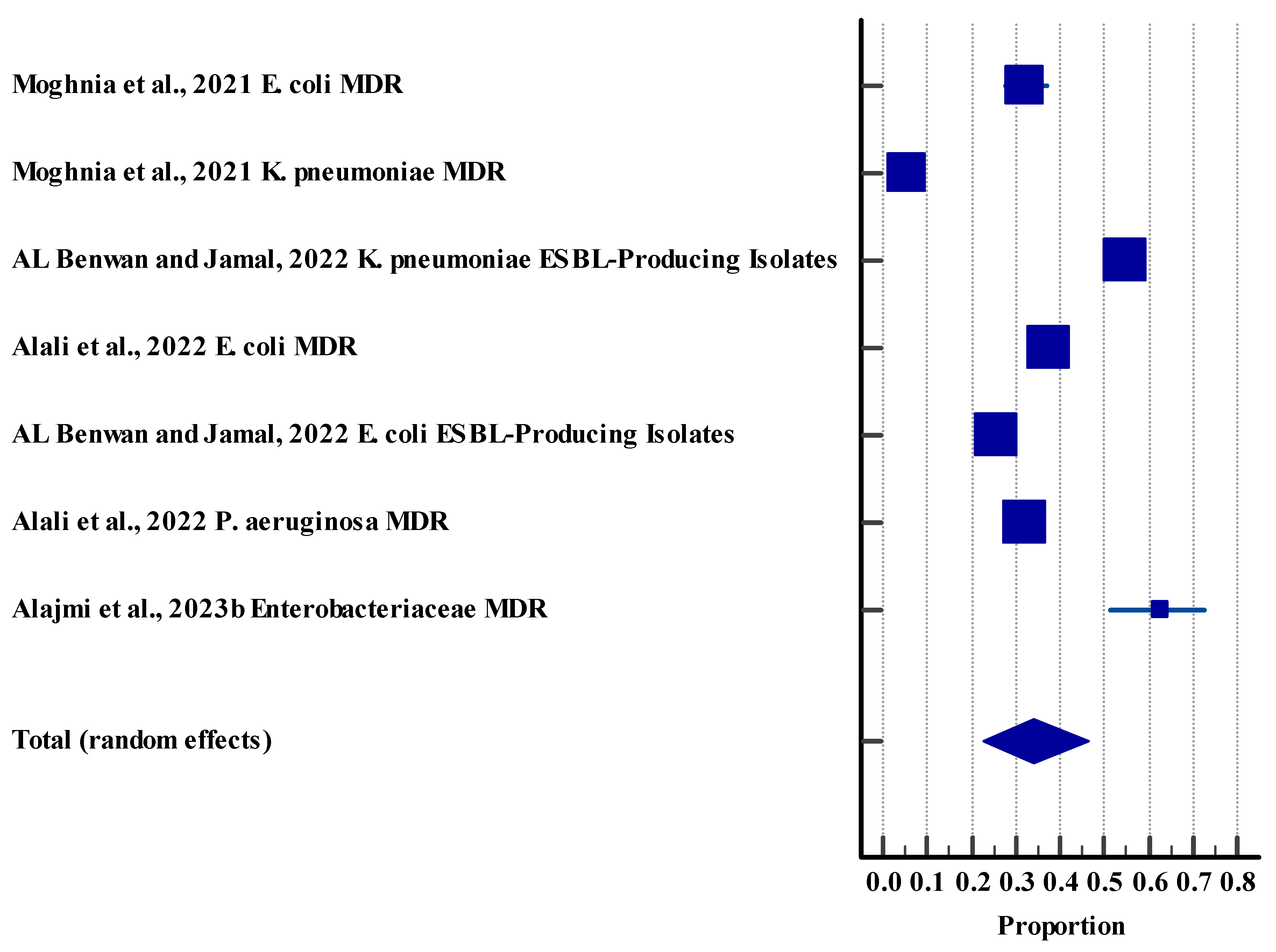
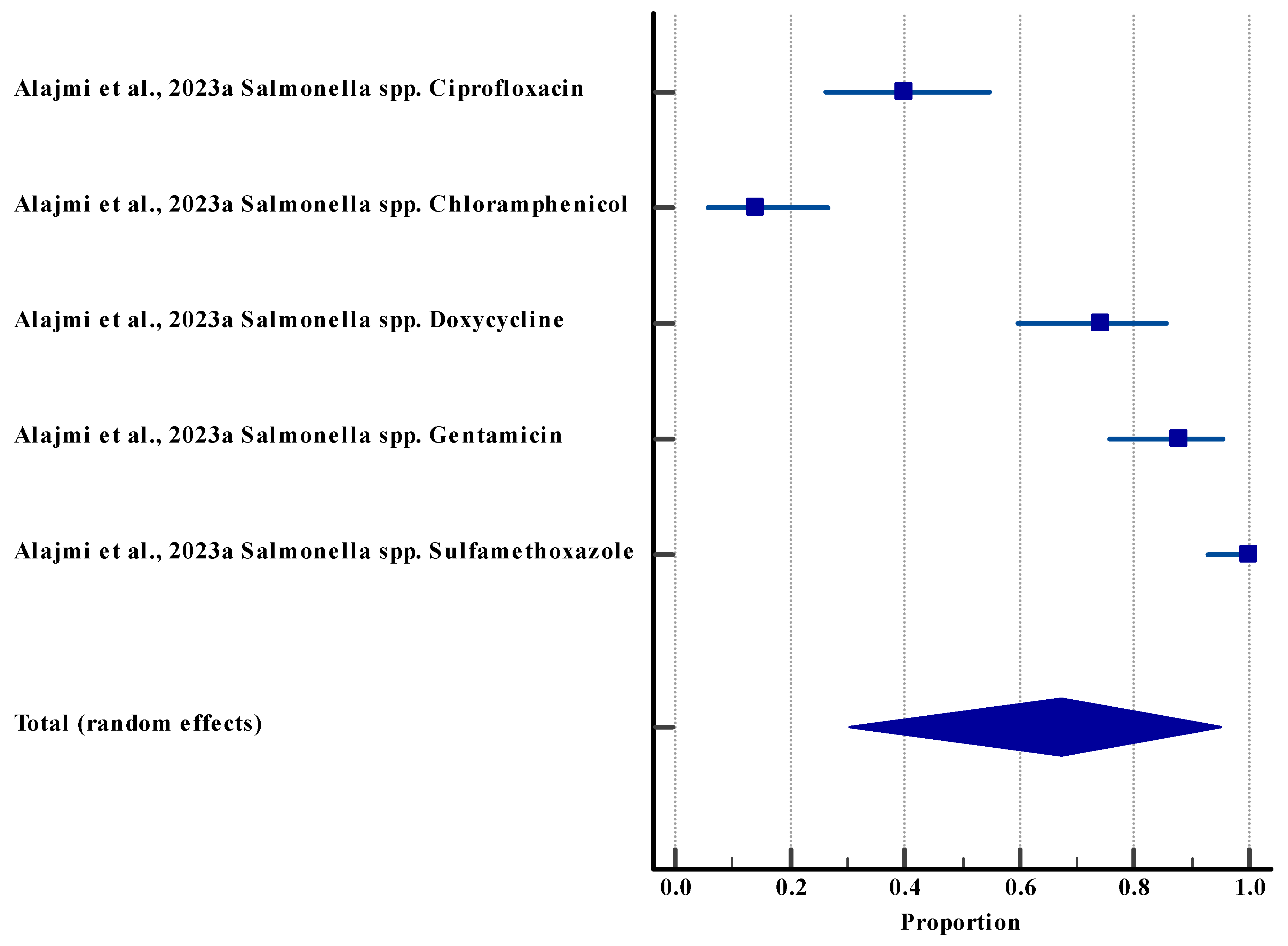
3.5.3. Resistance Rate (Agriculture (Animal))
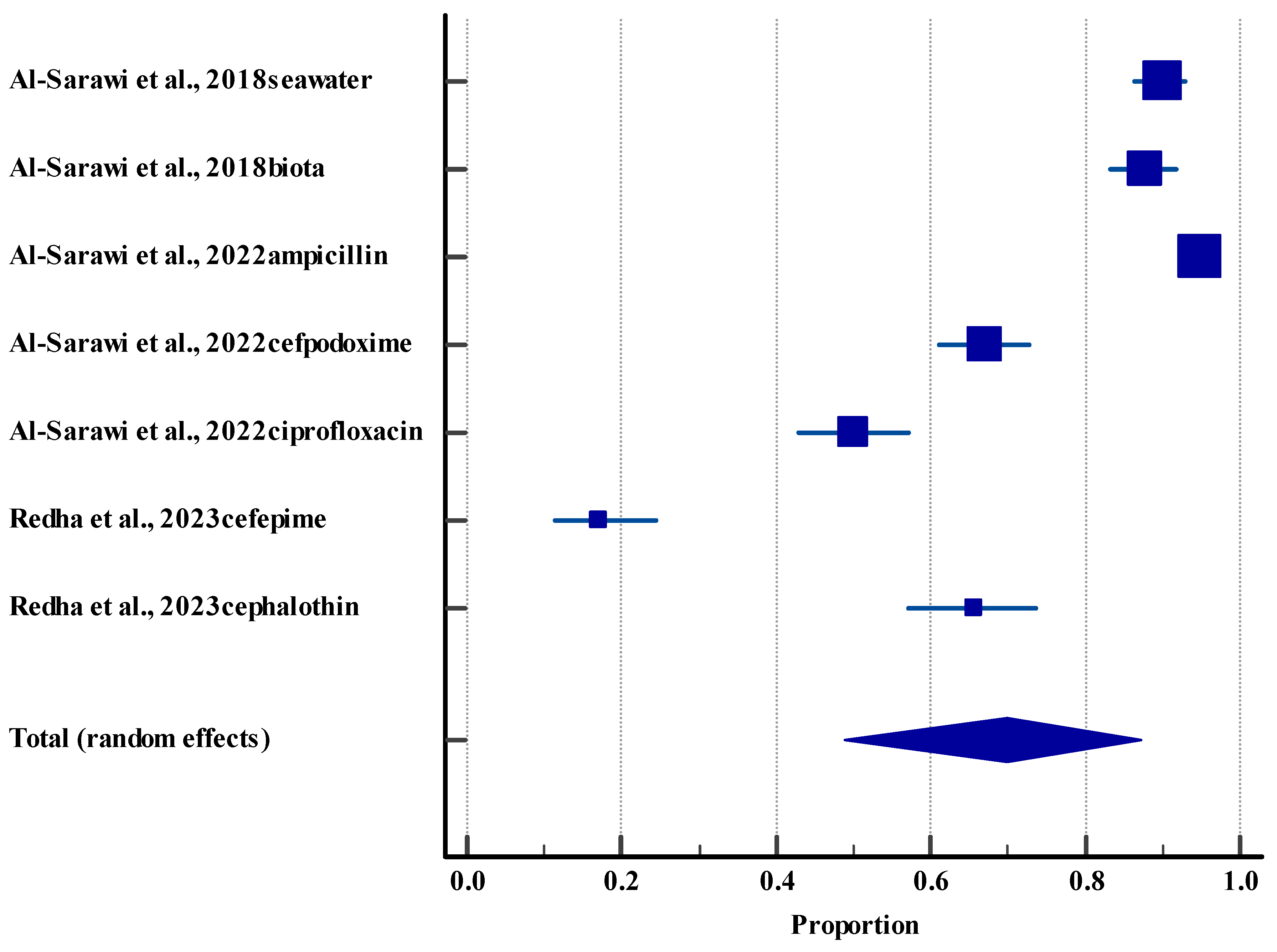
3.5.4. Resistance Rate (Environment)
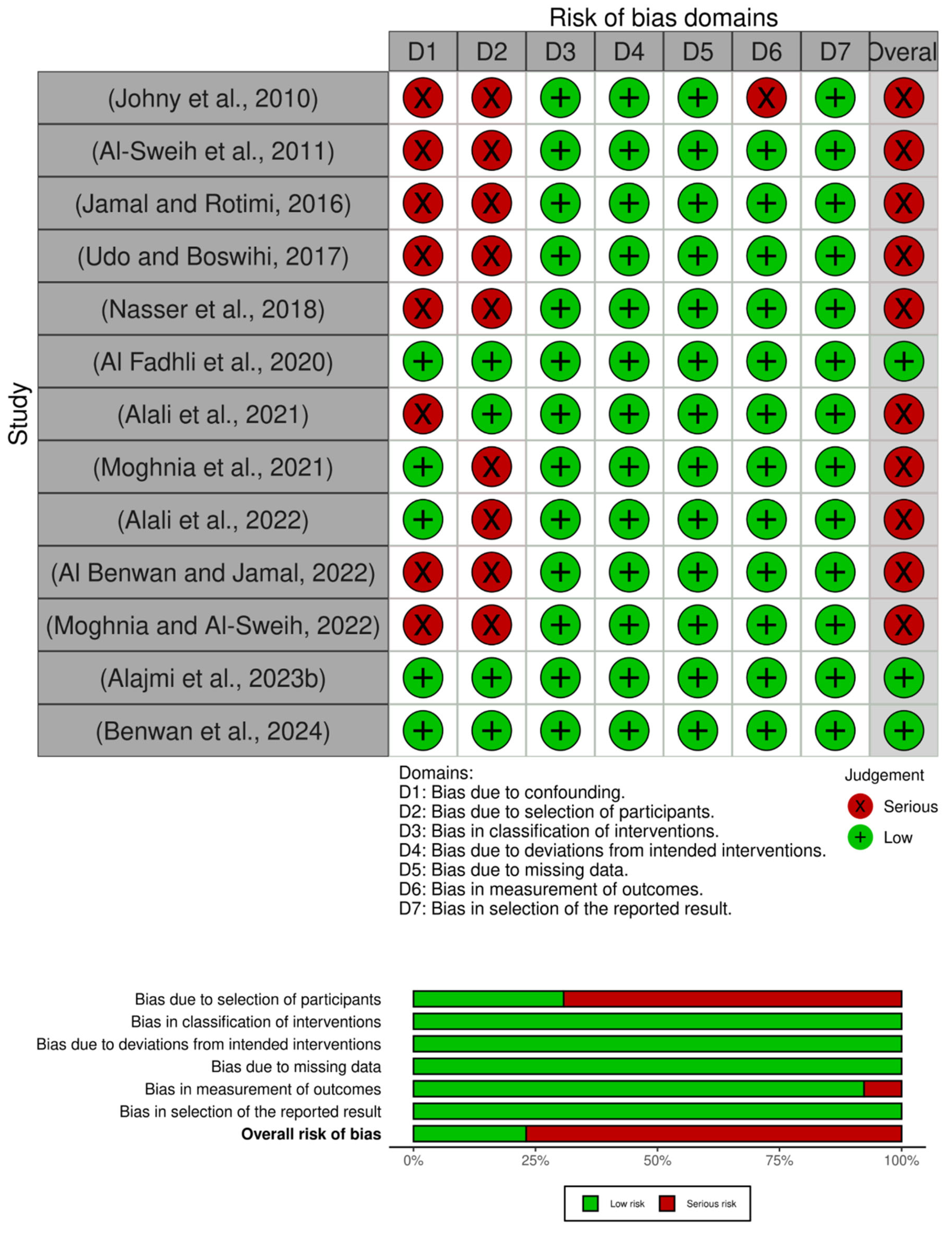
3.6. Methodological Quality Assessment
3.6.1. Clinical (Humans)
3.6.2. Agriculture (Animal) and Environmental Studies
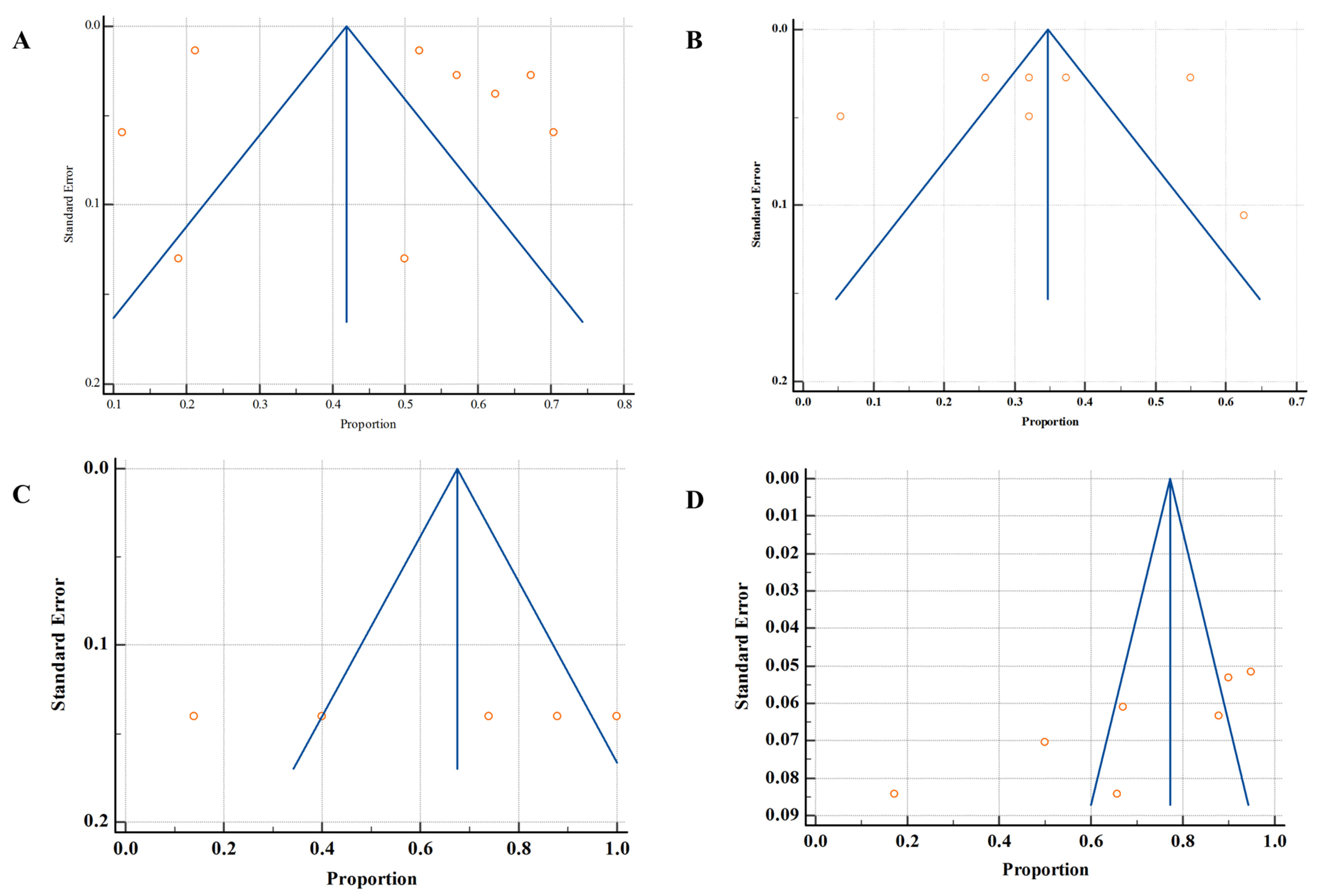
3.7. Publication Bias
3.8. Certainty of Evidence
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AMR | Antimicrobial Resistance |
| ARGs | Antibiotic Resistance Genes |
| blaCTX-M | Beta-Lactamase |
| BMC | BioMed Central |
| CA | Community-Acquired |
| CDIs | C. difficile Infections |
| COVID-19 | Coronavirus disease |
| CRE | Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae |
| DDDs | Defined Daily Doses |
| ESBL | Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase |
| FAO | Food and Agriculture Organization |
| GCC | Gulf Cooperation Council |
| GRADE | Grading, Reporting, Assessment, Development, and Evaluation |
| HA | Healthcare-Associated |
| intI1 | Integron Integrase |
| mdf A | Multidrug Efflux |
| MDR | Multiple Drug Resistance |
| MENA | Middle East and North Africa |
| MRSA | Meticillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus |
| NAPs | National Action Plans |
| Non-RCTs | Non-Randomized Controlled Trials |
| OIE | World Organization for Animal Health |
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses |
| Qnr | Quinolone Resistance |
| ROBINS-I | Risk of Bias In Non-Randomized Studies—Interventions |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| WWTPs | Wastewater Treatment Plants |
| XDR | Extensively Drug Resistance |
| YLDs | Years Lived with Disability |
References
- Gupta, R.; Sharma, S. Antimicrobial Use in Humans. In Handbook on Antimicrobial Resistance: Current Status, Trends in Detection and Mitigation Measures; Mothadaka, M.P., Vaiyapuri, M., Rao Badireddy, M., Nagarajrao Ravishankar, C., Bhatia, R., Jena, J., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2023; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Pokharel, S.; Shrestha, P.; Adhikari, B. Antimicrobial use in food animals and human health: Time to implement ‘One Health’ approach. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2020, 9, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Antimicrobial Resistance. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/antimicrobial-resistance (accessed on 29 June 2025).
- Prestinaci, F.; Pezzotti, P.; Pantosti, A. Antimicrobial resistance: A global multifaceted phenomenon. Pathog. Glob. Health 2015, 109, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, C.J.L.; Ikuta, K.S.; Sharara, F.; Swetschinski, L.; Robles Aguilar, G.; Gray, A.; Han, C.; Bisignano, C.; Rao, P.; Wool, E.; et al. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: A systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariuki, S. Global burden of antimicrobial resistance and forecasts to 2050. Lancet 2024, 404, 1172–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alomari, R.; Abdel-Razeq, A.; Shamiah, H. Comprehensive assessment of the global burden of antimicrobial resistance: Trends and insights from 2000 to 2023. Am. J. BioMed. 2024, 12, 151–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghavi, M.; Vollset, S.E.; Ikuta, K.S.; Swetschinski, L.R.; Gray, A.P.; Wool, E.E.; Aguilar, G.R.; Mestrovic, T.; Smith, G.; Han, C. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance 1990–2021: A systematic analysis with forecasts to 2050. Lancet 2024, 404, 1199–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousham, E.K.; Unicomb, L.; Islam, M.A. Human, animal and environmental contributors to antibiotic resistance in low-resource settings: Integrating behavioural, epidemiological and One Health approaches. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 285, 20180332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, H.K.; Donato, J.; Wang, H.H.; Cloud-Hansen, K.A.; Davies, J.; Handelsman, J. Call of the wild: Antibiotic resistance genes in natural environments. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Li, M.; Jing, Y.; Liu, K.; Wu, Y.; Peng, Z. What Are the Drivers Triggering Antimicrobial Resistance Emergence and Spread? Outlook from a One Health Perspective. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samreen; Ahmad, I.; Malak, H.A.; Abulreesh, H.H. Environmental antimicrobial resistance and its drivers: A potential threat to public health. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2021, 27, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taneja, N.; Sharma, M. Antimicrobial resistance in the environment: The Indian scenario. Indian J. Med. Res. 2019, 149, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, D.G.J.; Gaze, W.H.; Laxminarayan, R.; Topp, E. AMR, One Health and the environment. Nat. Microbiol. 2023, 8, 754–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Yang, S.; Zhu, Q.; Zhu, X. Effects of different oxygen conditions on pollutants removal and the abundances of tetracycline resistance genes in activated sludge systems. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 132681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarean, M.; Dave, S.H.; Brar, S.K.; Kwong, R.W.M. Environmental drivers of antibiotic resistance: Synergistic effects of climate change, co-pollutants, and microplastics. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2025, 19, 100768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Lu, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Guo, H.; Ma, Q.; Zhou, J.; Li, H.; Wang, T. Water temperature disturbance alters the conjugate transfer of antibiotic resistance genes via affecting ROS content and intercellular aggregation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 479, 135762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacFadden, D.R.; McGough, S.F.; Fisman, D.; Santillana, M.; Brownstein, J.S. Antibiotic resistance increases with local temperature. Nat. Clim. Change 2018, 8, 510–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaba, H.E.J.; Kuhlmann, E.; Scheithauer, S. Thinking outside the box: Association of antimicrobial resistance with climate warming in Europe—A 30 country observational study. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2020, 223, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robas, M.; Probanza, A.; González, D.; Jiménez, P.A. Mercury and Antibiotic Resistance Co-Selection in Bacillus sp. Isolates from the Almadén Mining District. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, C.; Chen, Z.; Sun, H.; Wang, L. Bacterial Community under the Influence of Microplastics in Indoor Environment and the Health Hazards Associated with Antibiotic Resistance Genes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Global Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241509763 (accessed on 28 June 2025).
- Aly, M.; Balkhy, H.H. The prevalence of antimicrobial resistance in clinical isolates from Gulf Corporation Council countries. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2012, 1, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Light, E.; Baker-Austin, C.; Card, R.M.; Ryder, D.; Alves, M.T.; Al-Sarawi, H.A.; Abdulla, K.H.; Stahl, H.; Al-Ghabshi, A.; Alghoribi, M.F.; et al. Establishing a marine monitoring programme to assess antibiotic resistance: A case study from the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) region. Environ. Adv. 2022, 9, 100268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzouk, E.; Abalkhail, A.; Alqahtani, J.; Alsowat, K.; Alanazi, M.; Alzaben, F.; Alnasser, A.; Alasmari, A.; Rawway, M.; Draz, A.; et al. Proteome analysis, genetic characterization, and antibiotic resistance patterns of Klebsiella pneumoniae clinical isolates. AMB Express 2024, 14, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkuraythi, D.M.; Alkhulaifi, M.M. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus prevalence in food-producing animals and food products in Saudi Arabia: A review. Vet. World 2024, 17, 1753–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hays, J.P.; Safain, K.S.; Almogbel, M.S.; Habib, I.; Khan, M.A. Extended Spectrum- and Carbapenemase-Based β-Lactam Resistance in the Arabian Peninsula—A Descriptive Review of Recent Years. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idrees, E.K.; Aldriwesh, M.G.; Alkhulaifi, M.M.; Alghoribi, M.F. Systematic review of multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in the Arabian Peninsula: Molecular epidemiology and resistance patterns. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1489317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushahidur Rahman, A.; Ahmed, S.E.; Osman, S.A.; Al-Haddad, R.A.; Almiski, A.; Kamar, R.; Abdelrahman, H.; Kassem, I.I.; Dogliero, A.; Eltai, N.O. A Snapshot of Antimicrobial Resistance in Semi-Wild Oryx: Baseline Data from Qatar. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdalla, T.; Al-Rumaithi, H.; Osaili, T.M.; Hasan, F.; Obaid, R.S.; Abushelaibi, A.; Ayyash, M.M. Prevalence, Antibiotic-Resistance, and Growth Profile of Vibrio spp. Isolated from Fish and Shellfish in Subtropical-Arid Area. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 861547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Myshkevych, Y.; Wang, T.; Monjed, M.K.; Hong, P.-Y. Wastewater surveillance unveils the impact of mass gatherings on antimicrobial resistance after the COVID-19 pandemic in Saudi Arabia. Nat. Water 2025, 3, 693–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Eggleston, K.; Rotimi, V.; Zeckhauser, R.J. Antibiotic resistance as a global threat: Evidence from China, Kuwait and the United States. Glob. Health 2006, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghnieh, R.; Al-Motawaa, A. Kuwait National Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance 2022; Infection Control Directorate MOH-WHO NFP AMR: Kuwait City, Kuwait, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterne, J.A.; Hernán, M.A.; Reeves, B.C.; Savović, J.; Berkman, N.D.; Viswanathan, M.; Henry, D.; Altman, D.G.; Ansari, M.T.; Boutron, I.; et al. ROBINS-I: A tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomised studies of interventions. BMJ 2016, 355, i4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuinness, L.A.; Higgins, J.P. Risk-of-bias VISualization (robvis): An R package and Shiny web app for visualizing risk-of-bias assessments. Res. Synth. Methods 2021, 12, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooijmans, C.R.; Rovers, M.M.; de Vries, R.B.; Leenaars, M.; Ritskes-Hoitinga, M.; Langendam, M.W. SYRCLE’s risk of bias tool for animal studies. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2014, 14, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilotta, G.S.; Milner, A.M.; Boyd, I.L. Quality assessment tools for evidence from environmental science. Environ. Evid. 2014, 3, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barendregt, J.J.; Doi, S.A.; Lee, Y.Y.; Norman, R.E.; Vos, T. Meta-analysis of prevalence. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2013, 67, 974–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Benwan, K.; Jamal, W. Etiology and Antibiotic Susceptibility Patterns of Urinary Tract Infections in Children in a General Hospital in Kuwait: A 5-Year Retrospective Study. Med. Princ. Pract. 2022, 31, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Fadhli, A.H.; Jamal, W.Y.; Rotimi, V.O. Prevalence of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae and emergence of high rectal colonization rates of blaOXA-181-positive isolates in patients admitted to two major hospital intensive care units in Kuwait. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0241971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alali, W.Q.; Abdo, N.M.; AlFouzan, W.; Dhar, R. Antimicrobial resistance pattern in clinical Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates obtained from a secondary-care hospital prior to and during the COVID-19 pandemic in Kuwait. Germs 2022, 12, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alali, W.Q.; AlFouzan, W.; Dhar, R. Prevalence of antimicrobial resistance in Gram-negative clinical isolates from a major secondary hospital in Kuwait: A retrospective descriptive study. Germs 2021, 11, 498–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sweih, N.A.; Al-Hubail, M.A.; Rotimi, V.O. Emergence of tigecycline and colistin resistance in Acinetobacter species isolated from patients in Kuwait hospitals. J. Chemother. 2011, 23, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benwan, K.A.; Jamal, W.; Shahin, M. Third Kuwaiti Multicenter Survey of Antibiotic Susceptibility of Anaerobic Bacteria: A Comparative Analysis of 20-Year Data. Microb. Drug Resist. 2024, 30, 372–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johny, M.; Babelly, M.; Al-Obaid, I.; Al-Benwan, K.; Udo, E.E. Antimicrobial resistance in clinical isolates of Streptococcus pneumoniae in a tertiary hospital in Kuwait, 1997–2007: Implications for empiric therapy. J. Infect. Public Health 2010, 3, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghnia, O.H.; Al-Sweih, N.A. Whole Genome Sequence Analysis of Multidrug Resistant Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae Strains in Kuwait. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udo, E.E.; Boswihi, S.S. Antibiotic Resistance Trends in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Isolated in Kuwait Hospitals: 2011–2015. Med. Princ. Pract. 2017, 26, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alajmi, R.Z.; Alfouzan, W.A.; Mustafa, A.S. The Prevalence of Multidrug-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae among Neonates in Kuwait. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasser, K.; Mustafa, A.S.; Khan, M.W.; Purohit, P.; Al-Obaid, I.; Dhar, R.; Al-Fouzan, W. Draft Genome Sequences of Six Multidrug-Resistant Clinical Strains of Acinetobacter baumannii, Isolated at Two Major Hospitals in Kuwait. Genome Announc. 2018, 6, e00264-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Otaibi, D.; Akbar, A.; Drobiova, H.; Obuekwe, C.; Al-Saleh, E. Dissemination of potentially pathogenic bacteria into the environment. WIT Trans. Biomed. Health 2009, 14, 151–159. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Al-Sarawi, H.A.; Habibi, N.; Uddin, S.; Jha, A.N.; Al-Sarawi, M.A.; Lyons, B.P. Antibiotic Resistance Mediated by Escherichia coli in Kuwait Marine Environment as Revealed through Genomic Analysis. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sarawi, H.A.; Jha, A.N.; Baker-Austin, C.; Al-Sarawi, M.A.; Lyons, B.P. Baseline screening for the presence of antimicrobial resistance in E. coli isolated from Kuwait’s marine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 129, 893–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sarawi, H.A.; Najem, A.B.; Lyons, B.P.; Uddin, S.; Al-Sarawi, M.A. Antimicrobial Resistance in Escherichia coli Isolated from Marine Sediment Samples from Kuwait Bay. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, N.; Uddin, S.; Al-Sarawi, H.; Aldhameer, A.; Shajan, A.; Zakir, F.; Abdul Razzack, N.; Alam, F. Metagenomes from Coastal Sediments of Kuwait: Insights into the Microbiome, Metabolic Functions and Resistome. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, N.; Uddin, S.; Behbehani, M.; Al-Sarawi, H.A.; Kishk, M.; Al-Zakri, W.; AbdulRazzack, N.; Shajan, A.; Zakir, F. A Comparative Assessment of High-Throughput Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction versus Shotgun Metagenomic Sequencing in Sediment Resistome Profiling. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 11229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, N.; Uddin, S.; Behbehani, M.; Kishk, M.; Abdul Razzack, N.; Zakir, F.; Shajan, A. Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Aerosols: Baseline from Kuwait. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habibi, N.; Uddin, S.; Lyons, B.; Al-Sarawi, H.A.; Behbehani, M.; Shajan, A.; Razzack, N.A.; Zakir, F.; Alam, F. Antibiotic Resistance Genes Associated with Marine Surface Sediments: A Baseline from the Shores of Kuwait. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redha, M.A.; Al Sweih, N.; Albert, M.J. Multidrug-Resistant and Extensively Drug-Resistant Escherichia coli in Sewage in Kuwait: Their Implications. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uddin, S.; Habibi, N.; Saeed, T.; Al-Sarawi, H.A.; Behbehani, M.; Faizuddin, M. Antibiotic Resistance Genes and Faecal Sterols in Marine Sediments: An Evidence of Their Presence away from Point Sources–Kuwait’s Example. Sustainability 2024, 16, 4320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmeh, R.; Akbar, A.; Almutairi, B.; Kishk, M.; Jordamovic, N.B.; Al-Ateeqi, A.; Shajan, A.; Al-Sherif, H.; Esposito, A.; Al-Momin, S.; et al. Camel Milk Resistome in Kuwait: Genotypic and Phenotypic Characterization. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alajmi, A.D.; Sheet, O.H.; Al-Mahmood, O.; Saadeldin, I.; Alsanjary, R.A. Isolation and identification of Salmonella from chickens prepared for slaughter in the State of Kuwait. J. Appl. Vet. Sci. 2023, 8, 22–29. [Google Scholar]
- Sallam, K.I.; Saad, F.S.S.; Abdelkhalek, A. Health risk assessment of antimicrobial residues in sheep carcasses marketed in Kuwait. Food Chem. 2022, 383, 132401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alenezi, M.S.; Tartor, Y.H.; El-Sherbini, M.; Pet, E.; Ahmadi, M.; Abdelkhalek, A. Antibiotic Residues in Milk and Milk-Based Products Served in Kuwait Hospitals: Multi-Hazard Risk Assessment. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, W.Y.; Rotimi, V.O. Surveillance of Antibiotic Resistance among Hospital- and Community-Acquired Toxigenic Clostridium difficile Isolates over 5-Year Period in Kuwait. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghnia, O.H.; Rotimi, V.O.; Al-Sweih, N.A. Monitoring antibiotic resistance profiles of faecal isolates of Enterobacteriaceae and the prevalence of carbapenem-resistant isolates among food handlers in Kuwait. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2021, 25, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tello, A.; Austin, B.; Telfer, T.C. Selective pressure of antibiotic pollution on bacteria of importance to public health. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 1100–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, E.Y.; Impalli, I.; Poleon, S.; Denoel, P.; Cipriano, M.; Van Boeckel, T.P.; Pecetta, S.; Bloom, D.E.; Nandi, A. Global trends in antibiotic consumption during 2016–2023 and future projections through 2030. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2411919121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aly, N.Y.; Omar, A.A.; Badawy, D.A.; Al-Mousa, H.H.; Sadek, A.A. Audit of Physicians’ Adherence to the Antibiotic Policy Guidelines in Kuwait. Med. Princ. Pract. 2012, 21, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyad, S.; Al-Owaisheer, A.; Al-Banwan, F.; Al-Mejalli, A.; Shukkur, M.; Thalib, L. Evidence-Based Practice in the Use of Antibiotics for Respiratory Tract Infections in Primary Health Centers in Kuwait. Med. Princ. Pract. 2010, 19, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, A.I.; Aboud, E.A. Knowledge, attitude and practice towards antibiotic use among the public in Kuwait. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta, A.; Tirkaso, W.; Nicolli, F.; Van Boeckel, T.P.; Cinardi, G.; Song, J. The future of antibiotic use in livestock. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwu, C.D.; Korsten, L.; Okoh, A.I. The incidence of antibiotic resistance within and beyond the agricultural ecosystem: A concern for public health. Microbiologyopen 2020, 9, e1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Ning, J.; Ahmed, S.; Huang, J.; Ullah, R.; An, B.; Hao, H.; Dai, M.; Huang, L.; Wang, X.; et al. Selection and dissemination of antimicrobial resistance in Agri-food production. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2019, 8, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.B.; Arnipalli, S.R.; Ziouzenkova, O. Antibiotics in Food Chain: The Consequences for Antibiotic Resistance. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bombaywala, S.; Mandpe, A.; Paliya, S.; Kumar, S. Antibiotic resistance in the environment: A critical insight on its occurrence, fate, and eco-toxicity. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 24889–24916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Kaur, R.; Verma, S.; Singh, S. Antimicrobials and Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Water Bodies: Pollution, Risk, and Control. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 830861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevao, B.; Uddin, S.; Dupont, S. Baseline concentrations of pharmaceuticals in Kuwait’s coastal marine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 173, 113040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshemmari, H.; Talebi, L. Heavy metal concentrations in the surface sediments of the northwestern Arabian Gulf, Kuwait. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleisa, E.; Aljuwaisseri, A.; Alshayji, K.; Al-Mutiri, A. Environmental Impacts of Reverse Osmosis in Wastewater Treatment Versus Desalination to Mend the Water Cycle: A Life Cycle Assessment. Waste Manag. Environ. Impact 2022, 257, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevao, B.; Uddin, S.; Krishnan, D.; Rajagopalan, S.; Habibi, N. Antibiotics in Wastewater: Baseline of the Influent and Effluent Streams in Kuwait. Toxics 2022, 10, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Enezi, G.; Hamoda, M.F.; Fawzi, N. Heavy metals content of municipal wastewater and sludges in Kuwait. J. Environ. Sci. Health A Tox. Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 2004, 39, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Criteria Category | Inclusion Criteria | Exclusion Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Geographic Focus | Studies included data specifically from Kuwait | Studies did not include data from Kuwait |
| Study Topic | Studies examined antibiotic resistance patterns, prevalence, or transmission | Studies that do not examine antibiotic resistance patterns, prevalence, or transmission |
| Study Design | Primary research studies (randomized, observational, experimental, surveillance) | Studies that are not primary research |
| Study Setting | Studies examined samples from at least one of the following: human populations, agricultural practices/livestock, or the environment | Studies that do not examine samples from human populations, agricultural practices/livestock, or environmental sources |
| Data Type | Studies included antimicrobial susceptibility or resistance data | Studies that do not include antimicrobial susceptibility or resistance data |
| Study Scope | Studies examined more than a single case report | Studies that examine only a single case report |
| Timeline | Studies published between 2009 and 2024 | Studies published outside the 2009–2024 timeframe |
| Language | In English | Not in English |
| Study | Study Setting | Primary Focus | Study Design | Sample Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [51] | Environmental (marine) | Pathogenic bacteria in seawater | Environmental sampling | 230 bacteria |
| [46] | Clinical (hospital) | Streptococcus pneumoniae | Retrospective | 1353 strains |
| [44] | Clinical (hospital) | Tigecycline/colistin resistance in Acinetobacter | Cross-sectional Surveillance | 250 isolates |
| [65] | Clinical (hospital/community) | Clostridioides difficile resistance | Surveillance | 146 isolates |
| [48] | Clinical (hospital) | MRSA resistance trends | Surveillance | 6922 isolates |
| [53] | Environmental (marine) | Resistance in Escherichia coli from seawater/biota | Environmental sampling, surveillance | 598 isolates |
| [50] | Clinical (hospital) | Genomics of MDR Acinetobacter baumannii | Not clearly stated | 6 isolates |
| [41] | Clinical (hospital) | Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae | Retrospective | 590 sample |
| [43] | Clinical (hospital) | Antimicrobial resistance prevalence in Gram-negative bacteria | Retrospective descriptive, surveillance | 5290 isolates |
| [66] | Clinical (hospital/community) | Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae | Prospective | 681 isolates |
| [42] | Clinical (hospital) | Resistance in E. coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa pre/during COVID-19 | Observational (retrospective) | 1303 isolates |
| [40] | Clinical (hospital) | Resistance in gram-negative bacteria | Retrospective | 9742 urine samples |
| [54] | Environmental (marine sediment) | Resistance in E. coli from sediment | Environmental sampling | 395 isolates |
| [47] | Clinical (hospital) | MDR E. coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae | Retrospective | 2 samples |
| [58] | Environmental (marine sediment) | ARGs in marine sediments | Environmental sampling, cross-sectional | 12 samples |
| [24] | Environmental (marine) | AMR monitoring in GCC marine environment | Surveillance, environmental sampling | 560 isolates |
| [63] | Agricultural (sheep meat) | AMR residues in sheep carcasses | Observational (retrospective), surveillance | 450 samples |
| [59] | Environmental (sewage) | MDR/XDR E. coli in sewage | Environmental sampling, observational (retrospective) | 140 isolates |
| [52] | Environmental (marine) | Genomic AMR in E. coli | Surveillance, environmental sampling | 395 isolates |
| [62] | Agricultural (poultry) | Salmonella in broiler chickens | Observational (retrospective) | 4128 samples |
| [49] | Clinical (hospital, neonates) | MDR Enterobacteriaceae in neonates/mothers | Cross-sectional | 484 samples |
| [55] | Environmental (coastal sediment) | Microbiome, metabolic function, resistome | Environmental sampling | 12 samples |
| [56] | Environmental (sediment) | HT-qPCR vs. metagenomics for resistome | Surveillance, environmental sampling | Not stated |
| [57] | Environmental (aerosols) | ARGs in aerosols | Environmental sampling | Not stated |
| [61] | Agricultural (camel milk) | Resistome in camel milk | Environmental sampling | 8 samples |
| [64] | Agricultural (milk and milk-based products) | Antibiotic resistance | Not clearly stated | 200 samples |
| [60] | Environmental (marine sediment) | Antibiotic resistant genes and fecal sterols | Not clearly stated | 20 samples |
| [45] | Clinical (hospital) | Anaerobes | Prospective | 2317 isolates |
| Category | Subcategory/Detail | Number of Studies/Details | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Study Setting | Clinical | 11 | Some studies overlap categories |
| Environmental | 11 | ||
| Agricultural (animal) | 4 | ||
| Mixed settings (Clinical/Community) | 2 | ||
| Regional (multi-country) | 1 | ||
| Single country | 27 | ||
| Primary Focus | Antimicrobial resistance prevalence/trends (including specific organisms) | 23 | e.g., E. coli, MRSA, Salmonella spp. |
| Resistome or antimicrobial resistance genes | 5 | ||
| Study Design | Surveillance design (including environmental surveillance and sampling) | 11 | Some overlap with environmental sampling |
| Retrospective/observational | 9 | ||
| Cross-sectional | 3 | ||
| Prospective | 2 | ||
| Not clearly stated | 3 | No clear design in study/abstract; however, we consider these studies non-randomized | |
| Sample Size | Sample size reported | 26 | Ranged from 2 to 6922 (isolates/samples/individuals) |
| Sample size not reported | 2 | Not clearly mentioned in study/abstract | |
| One Health approach | None | 0 | None of the studies used the One Health approach or integrated surveillance program for AMR in humans, agriculture (animals), and environment |
| Bacterial Species | Resistance Pattern | Prevalence | Domain of Detection | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E. coli | Multidrug resistance, extended-spectrum beta-lactamase, carbapenem, and ampicillin resistance | Multidrug resistance: 38.7–91.4%; extended-spectrum beta-lactamase: up to 62.4%; carbapenem: up to 10% | Clinical, sewage, marine (seawater and biota), sediment | [42,49,59,66] |
| K. pneumoniae | Multidrug resistance, extended-spectrum beta-lactamase, carbapenem resistance | Multidrug resistance: up to 36.2%; extended-spectrum beta-lactamase: up to 91%; carbapenem: up to 38% | Clinical, environmental | [40,42,49,53] |
| P. aeruginosa | Multidrug resistance, carbapenem resistance | Multidrug resistance: up to 32.1%; carbapenem: variable | Clinical | [42,49] |
| Acinetobacter baumannii | Multidrug resistance, carbapenem, and colistin resistance | Multidrug resistance: up to 88.4%; carbapenem: up to 25.2%; colistin: up to 12%. | Clinical | [43,44] |
| Methicillin-resistant S. aureus | Multi-antibiotic resistance | 32–60.7% methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus; resistance to multiple agents | Clinical | [48] |
| Salmonella | Multi-antibiotic resistance | High resistance to multiple antibiotics | Agriculture (animal [poultry]) | [62] |
| Antimicrobial resistance genes (environmental) | Beta-lactams, fluoroquinolones, aminoglycosides, etc | 402 antimicrobial resistance genes in sediment; 98% of E. coli in sediment are resistant | Marine, sediment, aerosols | [24,56,57,58] |
| Resistance Type | Human Health Impact | Agricultural Link | Environmental Presence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (e.g., CTX-M-15) | Limits treatment options for infections; associated with outbreaks | Detected in poultry, camel milk | Found in sewage, marine, and sediment |
| Carbapenemases (e.g., OXA-48, NDM-1) | Associated with multidrug-resistant/extensively drug-resistant infections, high mortality | Detected in the food animal regionally | Detected in environmental samples |
| Colistin resistance (e.g., mcr genes) Fluoroquinolone resistance (e.g., qnr genes) | Last-resort antibiotic compromised Reduces efficacy of key antibiotics | Detected in the food chain regionally Detected in poultry, camel milk | Detected in environmental samples found in marine and sediment |
| Integrons (e.g., intI1) | Facilitates horizontal gene transfer | Detected in food/environment | Found in marine, sediment |
| Study ID | Selection Bias | Performance Bias | Detection Bias | Attrition Bias | Reporting Bias | Other Bias |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Animal studies | ||||||
| [63] | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [62] | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [61] | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [64] | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| Environmental studies | ||||||
| [51] | High | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [53] | High | High | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [54] | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [58] | Some concerns | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [24] | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [59] | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [52] | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [57] | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [56] | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [55] | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [60] | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| Outcomes | Studies | Risk of Bias | Inconsistency | Indirectness | Imprecision | Publication Bias | Effect Size | Certainty of Evidence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prevalence of microbes in humans | 9 | High | Serious (I2 = 99.62%) | Not serious | Not serious | No | 44.95%, 95% CI (30.58 to 59.76), | Low θθ |
| Resistance rate (humans) | 7 | High | Serious (I2 = 98.94%) | Not serious | Not serious | No | 34.05%, 95% CI (22.81 to 46.27) | Low θθ |
| Resistance rate (animal) | 5 | Low | Not serious (I2 = 97.40%) | Not serious | Not serious | Yes | 67.42%, 95% CI (30.30 to 94.93) | Low θθ |
| Resistance rate (environment) | 4 | Low | Serious (I2 = 98.78%) | Not serious | Not serious | Yes | 69.86%, 95% CI (48.80 to 87.26) | Low θθ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Dhumair, A.; Al-Hasan, M.; Al-Khalaifah, H.; Al-Mutawa, Q. A 15-Year One Health Approach to Antimicrobial Resistance in Kuwait from Hospitals to Environmental Contexts: A Systematic Review. Life 2025, 15, 1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15091344
Al-Dhumair A, Al-Hasan M, Al-Khalaifah H, Al-Mutawa Q. A 15-Year One Health Approach to Antimicrobial Resistance in Kuwait from Hospitals to Environmental Contexts: A Systematic Review. Life. 2025; 15(9):1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15091344
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Dhumair, Ahmad, Mohammad Al-Hasan, Hanan Al-Khalaifah, and Qadriya Al-Mutawa. 2025. "A 15-Year One Health Approach to Antimicrobial Resistance in Kuwait from Hospitals to Environmental Contexts: A Systematic Review" Life 15, no. 9: 1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15091344
APA StyleAl-Dhumair, A., Al-Hasan, M., Al-Khalaifah, H., & Al-Mutawa, Q. (2025). A 15-Year One Health Approach to Antimicrobial Resistance in Kuwait from Hospitals to Environmental Contexts: A Systematic Review. Life, 15(9), 1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15091344