Physiopathology of the Brain Renin-Angiotensin System
Abstract
1. Introduction
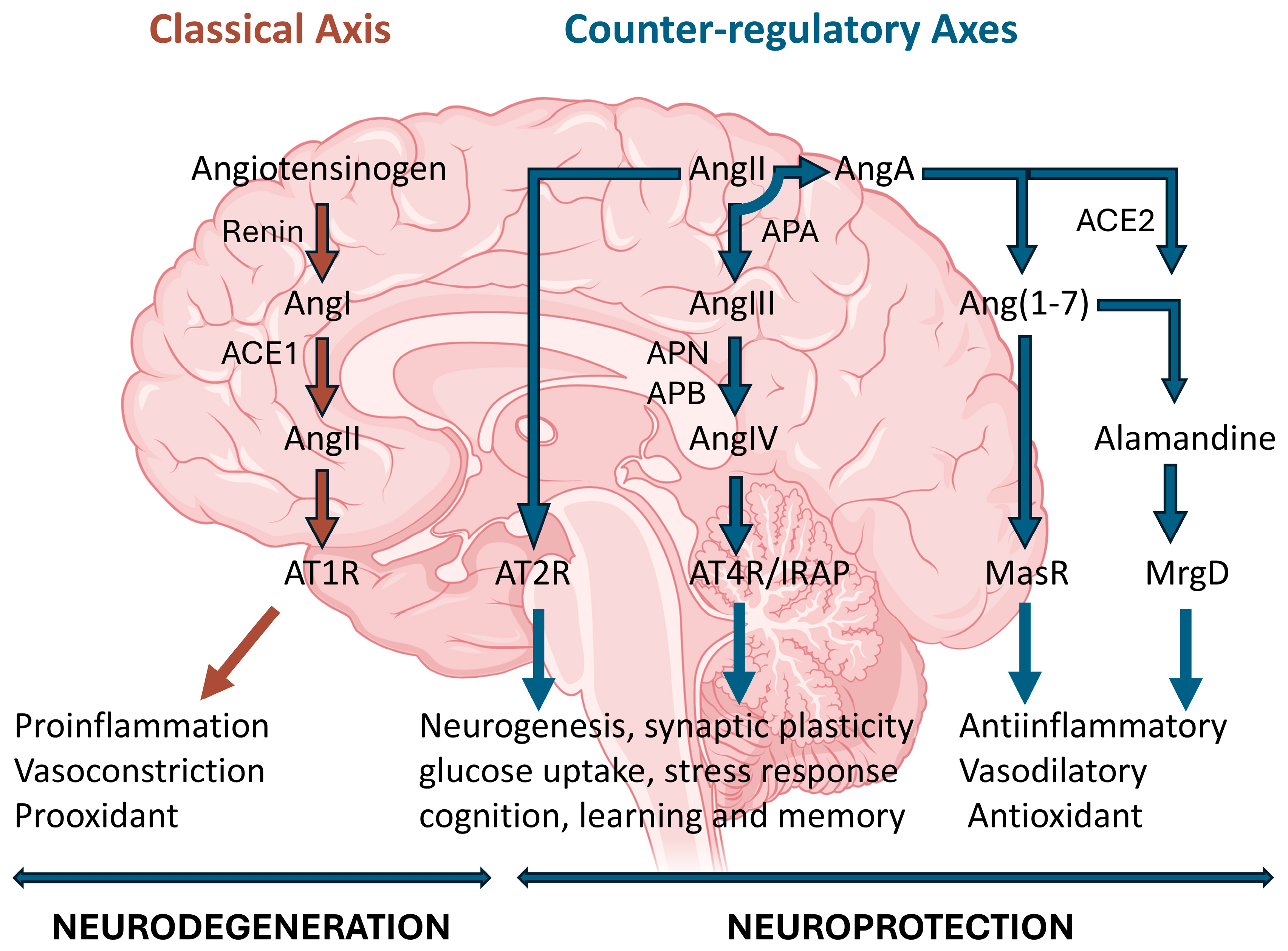
2. The Renin-Angiotensin System
2.1. Alamandine: A Novel Component of the Renin-Angiotensin System
2.2. RAS Location in Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems
2.3. Dysregulation of RAS Cascade and Pharmacological Intervention
3. Mechanisms of Action of the RAS in the Nervous System
3.1. (Pro)Renin and PRR
3.2. AT1R
3.3. AT2R
3.4. AT4R/IRAP
3.5. MasR
3.6. MrgD Receptor
4. RAS in the Aged Brain
5. RAS and Neuroinflammation: Implications in Neurodegeneration
6. RAS and Neuropsychiatric Disorders: Depression, Anxiety and Stress
7. RAS in Neuropathic Pain: Therapeutic Implications
8. RAS-Targeted Therapies in Neurological Diseases
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abiodun, O.A.; Ola, M.S. Role of brain renin angiotensin system in neurodegeneration: An update. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, S.; Khaledi, S. Brain Renin-Angiotensin System: From Physiology to Pathology in Neuronal Complications Induced by SARS-CoV-2. Anal. Cell Pathol. 2023, 2023, 8883492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labandeira-Garcia, J.L.; Labandeira, C.M.; Guerra, M.J.; Rodriguez-Perez, A.I. The role of the brain renin-angiotensin system in Parkinson s disease. Transl. Neurodegener. 2024, 13, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qahtani, Z.; Al-Kuraishy, H.M.; Al-Gareeb, A.I.; Albuhadily, A.K.; Ali, N.H.; Alexiou, A.; Papadakis, M.; Saad, H.M.; Batiha, G.E. The potential role of brain renin-angiotensin system in the neuropathology of Parkinson disease: Friend, foe or turncoat? J. Cell Mol. Med. 2024, 28, e18495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunanda, T.; Ray, B.; Mahalakshmi, A.M.; Bhat, A.; Rashan, L.; Rungratanawanich, W.; Song, B.J.; Essa, M.M.; Sakharkar, M.K.; Chidambaram, S.B. Mitochondria-Endoplasmic Reticulum Crosstalk in Parkinson’s Disease: The Role of Brain Renin Angiotensin System Components. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.H.; Al-Kuraishy, H.M.; Al-Gareeb, A.I.; Albuhadily, A.K.; Hamad, R.S.; Alexiou, A.; Papadakis, M.; Saad, H.M.; Batiha, G.E. Role of brain renin-angiotensin system in depression: A new perspective. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2024, 30, e14525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilic, A.; Ipek, B.E.; Tatonyan, S.; Kilic, K.; Demirci, H.; Atalar, F.; Ustunova, S.; Dariyerli, N. Alamandine enhanced spatial memory in rats by reducing neuroinflammation and altering BDNF levels in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 12205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genest, J.; Cantin, M.; Garcia, R.; Thibault, G.; Gutkowska, J.; Schiffrin, E.; Kuchel, O.; Hamet, P. Extrarenal angiotensin-forming enzymes. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. A 1983, 5, 1065–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, C.I. ACE inhibitors and the kidney. Nephron 1990, 55 (Suppl. 1), 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juillerat-Jeanneret, L.; Lohm, S.; Hamou, M.F.; Pinet, F. Regulation of aminopeptidase A in human brain tumor vasculature: Evidence for a role of transforming growth factor-beta. Lab. Investig. 2000, 80, 973–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Exposito, M.J.; Martinez, J.M.; Prieto, I.; Alba, F.; Ramirez, M. Comparative distribution of glutamyl and aspartyl aminopeptidase activities in mouse organs. Horm. Metab. Res. = Hormon- und Stoffwechselforschung = Horm. Et Metab. 2000, 32, 161–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambayashi, Y.; Bardhan, S.; Takahashi, K.; Tsuzuki, S.; Inui, H.; Hamakubo, T.; Inagami, T. Molecular cloning of a novel angiotensin II receptor isoform involved in phosphotyrosine phosphatase inhibition. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 24543–24546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukoyama, M.; Nakajima, M.; Horiuchi, M.; Sasamura, H.; Pratt, R.E.; Dzau, V.J. Expression cloning of type 2 angiotensin II receptor reveals a unique class of seven-transmembrane receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 24539–24542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismael, S.; Mirzahosseini, G.; Ahmed, H.A.; Yoo, A.; Kassan, M.; Malik, K.U.; Ishrat, T. Renin-Angiotensin System Alterations in the Human Alzheimer’s Disease Brain. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2021, 84, 1473–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouveia, F.; Camins, A.; Ettcheto, M.; Bicker, J.; Falcao, A.; Cruz, M.T.; Fortuna, A. Targeting brain Renin-Angiotensin System for the prevention and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease: Past, present and future. Ageing Res. Rev. 2022, 77, 101612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazartigues, E.; Llorens-Cortes, C.; Danser, A.H.J. New Approaches Targeting the Renin-Angiotensin System: Inhibition of Brain Aminopeptidase A, ACE2 Ubiquitination, and Angiotensinogen. Can. J. Cardiol. 2023, 39, 1900–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorens-Cortes, C.; Touyz, R.M. Evolution of a New Class of Antihypertensive Drugs: Targeting the Brain Renin-Angiotensin System. Hypertension 2020, 75, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Van den Bosch, M.; Jacobs-Cacha, C.; Vergara, A.; Seron, D.; Soler, M.J. [The renin-angiotensin system and the brain]. Hipertens. Riesgo Vasc. 2021, 38, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loera-Valencia, R.; Eroli, F.; Garcia-Ptacek, S.; Maioli, S. Brain Renin-Angiotensin System as Novel and Potential Therapeutic Target for Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Lopez, E.O.; Uijl, E.; Danser, A.H.J. Fifty years of research on the brain renin-angiotensin system: What have we learned? Clin. Sci. 2021, 135, 1727–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Shao, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Cao, F.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, G.; Jiang, T.; Huang, M.; Zhang, L. Role of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in sepsis and its therapeutic targets. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2025, 162, 115192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etebar, N.; Naderpour, S.; Akbari, S.; Zali, A.; Akhlaghdoust, M.; Daghighi, S.M.; Baghani, M.; Sefat, F.; Hamidi, S.H.; Rahimzadegan, M. Impacts of SARS-CoV-2 on brain renin angiotensin system related signaling and its subsequent complications on brain: A theoretical perspective. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2024, 138, 102423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Afridi, R.; Cho, E.; Yoon, J.H.; Lim, Y.H.; Lee, H.W.; Ryu, H.; Suk, K. Soluble ANPEP Released From Human Astrocytes as a Positive Regulator of Microglial Activation and Neuroinflammation: Brain Renin-Angiotensin System in Astrocyte-Microglia Crosstalk. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2022, 21, 100424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Martos, J.M.; Canton-Habas, V.; Rich-Ruiz, M.; Reyes-Medina, M.J.; Ramirez-Exposito, M.J.; Carrera-Gonzalez, M.D.P. Sexual and Metabolic Differences in Hippocampal Evolution: Alzheimer’s Disease Implications. Life 2024, 14, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouveia, F.; Perez, M.C.; Bicker, J.; Silva, A.; Santos, A.E.; Pereira, C.F.; Camins, A.; Falcao, A.; Cruz, T.; Ettcheto, M.; et al. Protective effects of irbesartan against neurodegeneration in APP/PS1 mice: Unraveling its triple anti-apoptotic, anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant action. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2025, 188, 118167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, J.W.; Harding, J.W. Contributions by the Brain Renin-Angiotensin System to Memory, Cognition, and Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2019, 67, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosarderelioglu, C.; Nidadavolu, L.S.; George, C.J.; Oh, E.S.; Bennett, D.A.; Walston, J.D.; Abadir, P.M. Brain Renin-Angiotensin System at the Intersect of Physical and Cognitive Frailty. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 586314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanuska, A.; Ribiczey, P.; Kato, E.; Papp, Z.T.; Varga, Z.V.; Giricz, Z.; Toth, Z.E.; Konczol, K.; Zsembery, A.; Zelles, T.; et al. Potentiation of NMDA Receptors by AT1 Angiotensin Receptor Activation in Layer V Pyramidal Neurons of the Rat Prefrontal Cortex. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarpolaki, M.K.; Vafaei, A.; Fattahi, M.R.; Iranmehr, A. Mini-Review: Role of Drugs Affecting Renin-Angiotensin System (RAS) in Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI): What We Know and What We Should Know. Korean J. Neurotrauma 2023, 19, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barak, R.; Goshtasbi, G.; Fatehi, R.; Firouzabadi, N. Signaling pathways and genetics of brain Renin angiotensin system in psychiatric disorders: State of the art. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2024, 236, 173706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair-West, J.R.; Coghlan, J.P.; Denton, D.A.; Funder, J.W.; Scoggins, B.A.; Wright, R.D. The effect of the heptapeptide (2-8) and hexapeptide (3-8) fragments of angiotensin II on aldosterone secretion. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1971, 32, 575–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoghue, M.; Hsieh, F.; Baronas, E.; Godbout, K.; Gosselin, M.; Stagliano, N.; Donovan, M.; Woolf, B.; Robison, K.; Jeyaseelan, R.; et al. A novel angiotensin-converting enzyme-related carboxypeptidase (ACE2) converts angiotensin I to angiotensin 1-9. Circ. Res. 2000, 87, E1–E9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campagnole-Santos, M.J.; Peliky Fontes, M.A.; Verano-Braga, T.; Haibara, A.S.; Bader, M.; Santos, R.A.S. ACE2/Angiotensin-(1-7)/Mas and the brain. Brain Res. 2025, 1863, 149739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhang, F.; Sun, H.J.; Zhang, F.; Han, Y. Angiotensin-(1-7) enhances the effects of angiotensin II on the cardiac sympathetic afferent reflex and sympathetic activity in rostral ventrolateral medulla in renovascular hypertensive rats. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. 2015, 9, 865–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegbauer, J.; Coffman, T.M. New insights into angiotensin receptor actions: From blood pressure to aging. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2011, 20, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.Y.; Sun, X.T.; Li, Z.X.; Chen, W.Y.; Wang, X.; Liang, M.L.; Shi, H.; Yang, Z.S.; Zeng, W.T. Protective effect of angiotensin-(1-7) against hyperglycaemia-induced injury in H9c2 cardiomyoblast cells via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 1283–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, R.A.S.; Sampaio, W.O.; Alzamora, A.C.; Motta-Santos, D.; Alenina, N.; Bader, M.; Campagnole-Santos, M.J. The ACE2/Angiotensin-(1-7)/MAS Axis of the Renin-Angiotensin System: Focus on Angiotensin-(1-7). Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 505–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haron, S.; Kilmister, E.J.; Davis, P.F.; Stylli, S.S.; Mantamadiotis, T.; Kaye, A.H.; Hall, S.R.; Tan, S.T.; Wickremesekera, A.C. The renin-angiotensin system in central nervous system tumors and degenerative diseases. Front. Biosci. 2021, 26, 628–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lautner, R.Q.; Villela, D.C.; Fraga-Silva, R.A.; Silva, N.; Verano-Braga, T.; Costa-Fraga, F.; Jankowski, J.; Jankowski, V.; Sousa, F.; Alzamora, A.; et al. Discovery and characterization of alamandine: A novel component of the renin-angiotensin system. Circ. Res. 2013, 112, 1104–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida-Santos, A.F.; de Melo, L.A.; Goncalves, S.C.A.; Oliveira Amaral, L.B.; Santos, R.A.S.; Campagnole-Santos, M.J.; Kangussu, L.M. Alamandine through MrgD receptor induces antidepressant-like effect in transgenic rats with low brain angiotensinogen. Horm. Behav. 2021, 127, 104880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amado Costa, L.; Oliveira Amaral, L.B.; Mourao, F.A.G.; Bader, M.; Santos, R.A.S.; Campagnole-Santos, M.J.; Kangussu, L.M. Anxiolytic effect of alamandine in male transgenic rats with low brain angiotensinogen is dependent on activation of MrgD receptors. Horm. Behav. 2024, 163, 105551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Zhai, C.; Tang, G. Novel Antihypertensive Medications to Target the Renin-Angiotensin System: Mechanisms and Research. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2025, 26, 27963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marins, F.R.; Oliveira, A.C.; Qadri, F.; Motta-Santos, D.; Alenina, N.; Bader, M.; Fontes, M.A.P.; Santos, R.A.S. Alamandine but not angiotensin-(1-7) produces cardiovascular effects at the rostral insular cortex. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2021, 321, R513–R521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, Z.; Hekmat, A.S.; Abbasi, A.; Javanmardi, K. Alamandine injection in the periaqueductal gray and rostral ventromedial medulla attenuates allodynia induced by sciatic nerve ligation in rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2024, 818, 137568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hami, J.; von Bohlen Und Halbach, V.; Tetzner, A.; Walther, T.; von Bohlen Und Halbach, O. Localization and expression of the Mas-related G-protein coupled receptor member D (MrgD) in the mouse brain. Heliyon 2021, 7, e08440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, S.C.A.; Bassi, B.L.T.; Kangussu, L.M.; Alves, D.T.; Ramos, L.K.S.; Fernandes, L.F.; Alves, M.T.R.; Sinisterra, R.; Bruch, G.E.; Santos, R.A.S.; et al. Alamandine Induces Neuroprotection in Ischemic Stroke Models. Curr. Med. Chem. 2022, 29, 3483–3498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villapol, S.; Janatpour, Z.C.; Affram, K.O.; Symes, A.J. The Renin Angiotensin System as a Therapeutic Target in Traumatic Brain Injury. Neurotherapeutics 2023, 20, 1565–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, K.; Aggarwal, S.; Kandpal, A.; Kaur, R.; Jaggi, A.S.; Yadav, H.N.; Singh, D.; Chopra, D.; Singh, N. Unraveling the role of brain renin angiotensin system in vascular dementia: Mechanisms and therapeutic perspectives. Exp. Brain Res. 2025, 243, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFall, A.; Nicklin, S.A.; Work, L.M. The counter regulatory axis of the renin angiotensin system in the brain and ischaemic stroke: Insight from preclinical stroke studies and therapeutic potential. Cell Signal 2020, 76, 109809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urmila, A.; Rashmi, P.; Nilam, G.; Subhash, B. Recent Advances in the Endogenous Brain Renin-Angiotensin System and Drugs Acting on It. J. Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2021, 2021, 9293553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, L.C.; Kimbark, K.D.; Vernail, V.L.; Silberman, Y.; Arnold, A.C. Angiotensin-(1-7) protective effects in neurocognitive disorders: Molecular mechanisms to therapeutic implications. Front. Physiol. 2025, 16, 1565270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, L.; Eldahshan, W.; Fagan, S.C.; Ergul, A. Within the Brain: The Renin Angiotensin System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Kloet, A.D.; Pitra, S.; Wang, L.; Hiller, H.; Pioquinto, D.J.; Smith, J.A.; Sumners, C.; Stern, J.E.; Krause, E.G. Angiotensin Type-2 Receptors Influence the Activity of Vasopressin Neurons in the Paraventricular Nucleus of the Hypothalamus in Male Mice. Endocrinology 2016, 157, 3167–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J.W.; Harding, J.W. The brain renin-angiotensin system: A diversity of functions and implications for CNS diseases. Pflugers Arch. 2013, 465, 133–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsi, A.A.; Mersal, E.A.; Abdel All, M.O.; Abdelmenem, A.M.; Dawood, A.F.; Alanazi, A.; Mahdi, N.; Salim, M.S. ADAM17/ACE2 interaction mediates cadmium-induced brain damage and neuroinflammation in Wistar rats. Cytokine 2025, 190, 156936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennion, D.M.; Steckelings, U.M.; Sumners, C. Neuroprotection via AT(2) receptor agonists in ischemic stroke. Clin. Sci. 2018, 132, 1055–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzahosseini, G.; Ismael, S.; Ahmed, H.A.; Ishrat, T. Manifestation of renin angiotensin system modulation in traumatic brain injury. Metab. Brain Dis. 2021, 36, 1079–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyesiji Abiodun, A.; AlDosari, D.I.; Alghamdi, A.; Aziz Al-Amri, A.; Ahmad, S.; Ola, M.S. Diabetes-induced stimulation of the renin-angiotensin system in the rat brain cortex. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2023, 30, 103779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freund, M.; Walther, T.; von Bohlen und Halbach, O. Immunohistochemical localization of the angiotensin-(1-7) receptor Mas in the murine forebrain. Cell Tissue Res. 2012, 348, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keum, M.; Byun, M.S.; Yi, D.; Ahn, H.; Jung, G.; Jung, J.H.; Kong, N.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, Y.K.; Lee, Y.S.; et al. The Use of Antihypertensive Medication and In Vivo Alzheimer’s Disease Pathology. Ann. Neurol. 2025, 97, 1051–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danigo, A.; Rovini, A.; Bessaguet, F.; Bouchenaki, H.; Bernard, A.; Sturtz, F.; Bourthoumieu, S.; Desmouliere, A.; Magy, L.; Demiot, C. The Angiotensin II Type 2 Receptor, a Target for Protection and Regeneration of the Peripheral Nervous System? Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Worker, C.J.; Feng Earley, Y. The hypothalamus as a key regulator of glucose homeostasis: Emerging roles of the brain renin-angiotensin system. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2023, 325, C141–C154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.B.; Du, H.B.; Zhai, J.Y.; Sun, S.; Cui, J.L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Z.A.; Wu, J.L.; Johnson, A.K.; Xue, B.; et al. Controlled Hemorrhage Sensitizes Angiotensin II-Elicited Hypertension through Activation of the Brain Renin-Angiotensin System Independently of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2022, 2022, 6371048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.S.; Lin, C.L.; Lee, C.W.; Lin, H.C.; Wu, Y.T.; Shih, Y.H. Exercise Normalized the Hippocampal Renin-Angiotensin System and Restored Spatial Memory Function, Neurogenesis, and Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability in the 2K1C-Hypertensive Mouse. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzidic-Krivic, A.; Fajkic, A.; Farhat, E.K.; Lekic, L.; Ejubovic, A.; Vukas, S.K.; Ejubovic, M.; Lepara, O.; Sher, E.K. Linking Metabolic Syndrome to Neurodegeneration Mechanisms and Potential Treatments. Mol. Neurobiol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, C.A.; Oliveira, B.D.S.; Fernandes, H.B.; de Carvalho, R.T.; Pozzolin, E.T.; Kangussu, L.M.; Carvalho, B.C.; Teixeira, A.L.; de Miranda, A.S. Striatal damage may underlie motor learning impairment following experimental mild traumatic brain injury in mice. Mol. Cell Neurosci. 2025, 133, 104013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Barros, J.; Cardoso, M.G.; Machado, C.A.; Vieira, E.L.M.; Faleiro, R.M.; Pedroso, V.S.P.; Simoes, E.S.A.C.; de Souza, L.C.; Teixeira, A.L.; de Miranda, A.S.; et al. The potential role of renin-angiotensin system in mild traumatic brain injury. Neurol. Sci. 2022, 43, 3353–3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janatpour, Z.C.; Symes, A.J. The extended renin-angiotensin system: A promising target for traumatic brain injury therapeutics. Neural Regen. Res. 2020, 15, 1025–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, C.A.; Oliveira, B.D.S.; de Barros, J.; Fernandes, H.B.; de Brito Toscano, E.C.; Kangussu, L.M.; Guimaraes, P.P.G.; Simoes, E.S.A.C.; Teixeira, A.L.; de Miranda, A.S. Involvement of Renin-Angiotensin system (RAS) components in mild traumatic brain injury. Brain Res. 2025, 1846, 149266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, H.; Capuano, A.W.; Mehta, R.I.; Sood, A.; Bennett, D.A.; Ahima, R.S.; Arnold, S.E.; Arvanitakis, Z. Associations of renin-angiotensin system inhibitor use with brain insulin signaling and neuropathology. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2024, 11, 2112–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Pallares, J.; Garcia-Crivaro, L.A.; Parga, J.A.; Labandeira-Garcia, J.L. Renin-angiotensin system as an emerging target to modulate adult neurogenesis in health and disease. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2025, 16, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespo, R.; Angulo, S.; Nigro, L.; Bartolozzi, R.; Herenu, C. Trophic factors and essential oils as potential neuromodulators of Renin-Angiotensin system. Brain Res. 2025, 1863, 149777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glodzik, L.; Santisteban, M.M. Blood-Brain Barrier Crossing Renin-Angiotensin System Drugs: Considerations for Dementia and Cognitive Decline. Hypertension 2021, 78, 644–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida-Santos, A.F.; Kangussu, L.M.; Campagnole-Santos, M.J. The Renin-Angiotensin System and the Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Brief Review. Protein Pept. Lett. 2017, 24, 841–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, K.B.; de Melo, I.S.; da Silva, B.R.M.; Oliveira, K.; Sabino-Silva, R.; Anhezini, L.; Katayama, P.L.; Santos, V.R.; Shetty, A.K.; de Castro, O.W. SARS-CoV-2 and Hypertension: Evidence Supporting Invasion into the Brain Via Baroreflex Circuitry and the Role of Imbalanced Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone-System. Neurosci. Insights 2023, 18, 26331055231151926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Perez, A.I.; Serrano-Heras, G.; Labandeira, C.M.; Camacho-Meno, L.; Castro-Robles, B.; Suarez-Quintanilla, J.A.; Munoz-Lopez, M.; Piqueras-Landete, P.; Guerra, M.J.; Segura, T.; et al. Serum angiotensin type-1 receptor autoantibodies and neurofilament light chain as markers of neuroaxonal damage in post-COVID patients. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1571027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyadomari, W.Y.; Santiago, T.C.; Basso, L.; Oliveira, V.; Cruz, F.C.; Nani, J.V.; Hayashi, M.A.F. Long-term treatment with haloperidol modulates angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) activity in transgenic animal model with construct validity for schizophrenia studies. Brain Res. 2025, 1859, 149640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Sanchez, M.; Ramirez-Exposito, M.J.; Martinez-Martos, J.M. Pathophysiology, Clinical Heterogeneity, and Therapeutic Advances in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A Comprehensive Review of Molecular Mechanisms, Diagnostic Challenges, and Multidisciplinary Management Strategies. Life 2025, 15, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutra-Tavares, A.C.; Maia, J.G.; de Souza, T.P.; Filgueiras, C.C.; Ribeiro-Carvalho, A.; Manhaes, A.C.; Abreu-Villaca, Y. Telmisartan mitigates behavioral and cytokine level alterations but impairs spatial working memory in a phencyclidine-induced mouse model of schizophrenia. Psychopharmacology 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cueto-Ureña, C.; Ramírez-Expósito, M.J.; Carrera-González, M.P.; Martínez-Martos, J.M. Physiopathology of the Brain Renin-Angiotensin System. Life 2025, 15, 1333. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081333
Cueto-Ureña C, Ramírez-Expósito MJ, Carrera-González MP, Martínez-Martos JM. Physiopathology of the Brain Renin-Angiotensin System. Life. 2025; 15(8):1333. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081333
Chicago/Turabian StyleCueto-Ureña, Cristina, María Jesús Ramírez-Expósito, María Pilar Carrera-González, and José Manuel Martínez-Martos. 2025. "Physiopathology of the Brain Renin-Angiotensin System" Life 15, no. 8: 1333. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081333
APA StyleCueto-Ureña, C., Ramírez-Expósito, M. J., Carrera-González, M. P., & Martínez-Martos, J. M. (2025). Physiopathology of the Brain Renin-Angiotensin System. Life, 15(8), 1333. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081333






