Assessment of Muscle-Specific Strength in Oncology Patients: Anthropometry as a Reliable Alternative to DXA
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Anthropometric Variables
2.3. Body Composition Assessment
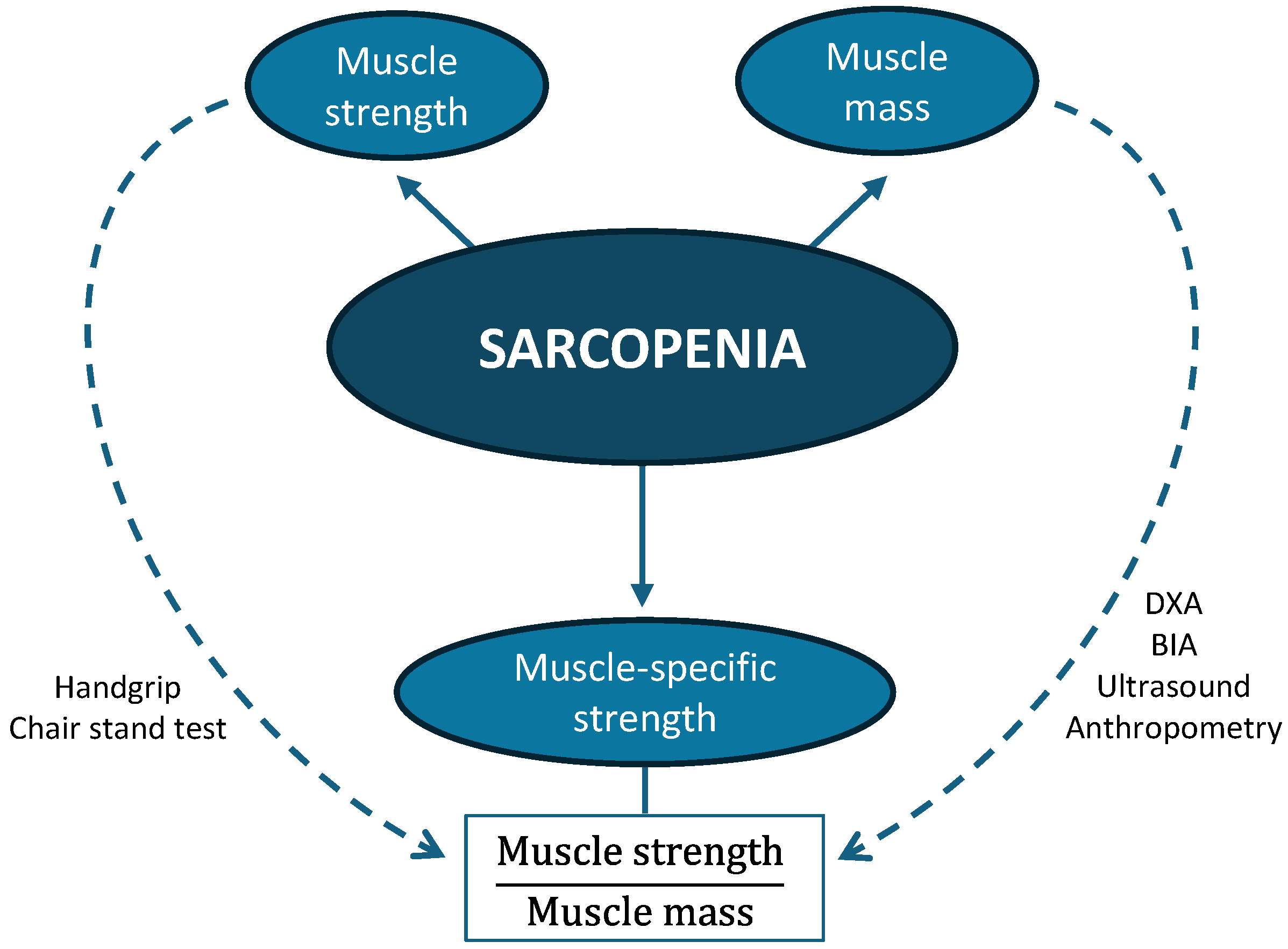
2.4. Muscle-Specific Strength
- MSS/height: handgrip strength divided by height (m);
- MSS/weight: handgrip strength divided by body weight (kg);
- MSS/BMI: handgrip strength divided by BMI;
- MSS/calf: handgrip strength divided by calf circumference (cm);
- MSS/MMA: handgrip strength divided by mid-arm muscle area (cm2);
- MSS/US: handgrip strength divided by rectus femoris area (cm2);
- MSS/BIAsf: handgrip strength divided by appendicular muscle mass from single-frequency BIA (kg);
- MSS/BIAmf: handgrip strength divided by appendicular muscle mass from multi-frequency BIA (kg);
- MSS/DXA: handgrip strength divided by appendicular lean mass measured by DXA (kg).
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BIA | Bioelectrical impedance analysis |
| BIAsf | Single-frequency bioelectrical impedance analysis |
| BIAmf | Multi-frequency bioelectrical impedance analysis |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| CT | Computed tomography |
| DXA | Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry |
| EWGSOP | European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People |
| GLIS | Global Leadership Initiative on Sarcopenia |
| GLP-1 | Glucagon-like peptide-1 |
| MAC | Mid-arm circumference |
| MMA | Mid-arm muscle area |
| MSS | Muscle-specific strength |
| US | Ultrasound |
| TS | Triceps skinfold |
References
- Alabadi, B.; Civera, M.; De La Rosa, A.; Martinez-Hervas, S.; Gomez-Cabrera, M.C.; Real, J.T. Low Muscle Mass Is Associated with Poorer Glycemic Control and Higher Oxidative Stress in Older Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudart, C.; Demonceau, C.; Reginster, J.Y.; Locquet, M.; Cesari, M.; Cruz Jentoft, A.J.; Bruyère, O. Sarcopenia and health-related quality of life: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2023, 14, 1228–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, L.; Nguo, K.; Furness, K.; Porter, J.; Huggins, C.E. Association between skeletal muscle mass and quality of life in adults with cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2022, 13, 839–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shachar, S.S.; Williams, G.R.; Muss, H.B.; Nishijima, T.F. Prognostic value of sarcopenia in adults with solid tumours: A meta-analysis and systematic review. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 57, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Sayer, A.A. Sarcopenia. Lancet 2019, 393, 2636–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyère, O.; Cederholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A.; et al. Sarcopenia: Revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Kirk, B.; Cawthon, P.M.; Arai, H.; A Ávila-Funes, J.; Barazzoni, R.; Bhasin, S.; Binder, E.F.; Bruyere, O.; Cederholm, T.; Chen, L.-K.; et al. The Conceptual Definition of Sarcopenia: Delphi Consensus from the Global Leadership Initiative in Sarcopenia (GLIS). Age Ageing 2024, 53, afae052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cawthon, P.M.; Visser, M.; Arai, H.; Ávila-Funes, J.A.; Barazzoni, R.; Bhasin, S.; Binder, E.; Bruyère, O.; Cederholm, T.; Chen, L.-K.; et al. Defining terms commonly used in sarcopenia research: A glossary proposed by the Global Leadership in Sarcopenia (GLIS) Steering Committee. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2022, 13, 1239–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, F.T.; Cai, Y.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Goodpaster, B.H.; Prado, C.M.; Haqq, A.M. Poor muscle quality: A hidden and detrimental health condition in obesity. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa Pereira, J.P.d.; Prado, C.M.; Gonzalez, M.C.; da Silva Diniz, A.; Miranda, A.L.; de Medeiros, G.O.C.; Souza, N.C.; Mauricio, S.F.; Costa, E.C.; Fayh, A.P.T. Strength-to-muscle radiodensity: A potential new index for muscle quality. Clin. Nutr. 2024, 43, 1667–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, W.B.; Li, Z.Z.; He, C.H.; Xi, W.T.; Wu, G.F.; Ke, H.W.; Zhu, Y.-C.; Yan, X.-L.; Shen, X.; Huang, D.-D. Muscle-specific strength predicts postoperative complications and survival in patients undergoing curative colectomy for colorectal cancer. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2025, 51, 110020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fayh, A.P.T.; de Sousa, I.M.; Gonzalez, M.C. New insights on how and where to measure muscle mass. Curr. Opin. Support. Palliat. Care 2020, 14, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferri Burgel, C.; Freitas, I.M.; de Carvalho, B.Z.O.; Costa-Pereira, J.P.; Fayh, A.P.T.; Moraes Silva, F. A new anthropometry-based muscle quality index predicts adverse outcomes in hospitalized patients. Clin. Nutr. 2025, 50, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa Pereira, J.P.; Prado, C.M.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Cabral, P.C.; de Oliveira Guedes, F.F.; da Silva Diniz, A.; Fayh, A.P.T. Prognostic significance of novel muscle quality index utilization in hospitalized adults with cancer: A secondary analysis. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2025, 49, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González Arnáiz, E.; López Gómez, J.J.; Ariadel Cobo, D.; Estébanez, B.; García Duque, M.; Dameto Pons, C.; Galindo, D.B.; Sastre, D.G.; Fondo, A.U.; Cuevas, M.J.; et al. Valores de dinamometría absolutos y ajustados en pacientes con obesidad. Endocrinol. Diabetes Nutr. 2025, 72, 501560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisancho, A.R. New norms of upper limb fat and muscle areas for assessment of nutritional status. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1981, 34, 2540–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyle, U.G.; Bosaeus, I.; De Lorenzo, A.D.; Deurenberg, P.; Elia, M.; Manuel Gómez, J.; Heitmann, B.L.; Kent-Smith, L.; Melchior, J.-C.; Pirlich, M.; et al. Bioelectrical impedance analysis-part II: Utilization in clinical practice. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 23, 1430–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergi, G.; De Rui, M.; Veronese, N.; Bolzetta, F.; Berton, L.; Carraro, S.; Bano, G.; Coin, A.; Manzato, E.; Perissinotto, E. Assessing appendicular skeletal muscle mass with bioelectrical impedance analysis in free-living Caucasian older adults. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 34, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreoli, A.; Scalzo, G.; Masala, S.; Tarantino, U.; Guglielmi, G. Body composition assessment by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA). La Radiol. Medica 2009, 114, 286–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkisas, S.; Baudry, S.; Bauer, J.; Beckwée, D.; De Cock, A.M.; Hobbelen, H.; Jager-Wittenaar, H.; Kasiukiewicz, A.; Landi, F.; Marco, E.; et al. Application of ultrasound for muscle assessment in sarcopenia: Towards standardized measurements. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2018, 9, 739–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkisas, S.; Bastijns, S.; Baudry, S.; Bauer, J.; Beaudart, C.; Beckwée, D.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.; Gasowski, J.; Hobbelen, H.; Jager-Wittenaar, H.; et al. Application of ultrasound for muscle assessment in sarcopenia: 2020 SARCUS update. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2021, 12, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, H.C.; Denison, H.J.; Martin, H.J.; Patel, H.P.; Syddall, H.; Cooper, C.; Sayer, A.A. A review of the measurement of grip strength in clinical and epidemiological studies: Towards a standardised approach. Age Ageing 2011, 40, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukaka, M.M. Statistics corner: A guide to appropriate use of correlation coefficient in medical research. Malawi Med. J. 2012, 24, 69–71. [Google Scholar]
- Bredella, M.A. Sex Differences in Body Composition. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 1043, 9–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, M.; Hashimoto, Y.; Mochizuki, Y.; Inoguchi, T.; Kouzuma, A.; Deguchi, M.; Saito, M.; Homma, H.; Kikuchi, N.; Okamoto, T. Effects of free weight and body massbased resistance training on thigh muscle size, strength and intramuscular fat in healthy young and middleaged individuals. Exp. Physiol. 2023, 108, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodete, C.S.; Thuraka, B.; Pasupuleti, V.; Malisetty, S. Hormonal Influences on Skeletal Muscle Function in Women across Life Stages: A Systematic Review. Muscles 2024, 3, 271–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshiko, A.; Hioki, M.; Kanehira, N.; Shimaoka, K.; Koike, T.; Sakakibara, H.; Oshida, Y.; Akima, H. Three-dimensional comparison of intramuscular fat content between young and old adults. BMC Med. Imaging 2017, 17, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.F.; He, C.H.; Xi, W.T.; Zhai, W.B.; Li, Z.Z.; Zhu, Y.C.; Tang, X.-B.; Yan, X.-L.; Lynch, G.S.; Shen, X.; et al. Sarcopenia defined by the global leadership initiative in sarcopenia (GLIS) consensus predicts adverse postoperative outcomes in patients undergoing radical gastrectomy for gastric cancer: Analysis from a prospective cohort study. BMC Cancer 2025, 25, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arends, J.; Baracos, V.; Bertz, H.; Bozzetti, F.; Calder, P.C.; Deutz, N.E.P.; Erickson, N.; Laviano, A.; Lisanti, M.P.; Lobo, D.N.; et al. ESPEN expert group recommendations for action against cancer-related malnutrition. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 1187–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.N.; Kim, S.O.; Jung, C.H.; Lee, W.J.; Kim, M.J.; Cho, Y.K. Preserved Muscle Strength Despite Muscle Mass Loss After Bariatric Metabolic Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Obes. Surg. 2023, 33, 3422–3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilding, J.P.H.; Batterham, R.L.; Calanna, S.; Davies, M.; Van Gaal, L.F.; Lingvay, I.; McGowan, B.M.; Rosenstock, J.; Tran, M.T.; Wadden, T.A.; et al. Once-Weekly Semaglutide in Adults with Overweight or Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 989–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jastreboff, A.M.; Aronne, L.J.; Ahmad, N.N.; Wharton, S.; Connery, L.; Alves, B.; Kiyosue, A.; Zhang, S.; Liu, B.; Bunck, M.C.; et al. Tirzepatide Once Weekly for the Treatment of Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, Y.; Fujino, Y.; Miura, K.; Toida, A.; Matsuda, T.; Makita, S. Intra- and inter-rater reliability of rectus femoris muscle thickness measured using ultrasonography in healthy individuals. Ultrasound J. 2021, 15, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Total (n = 205) | Men (n = 133) | Women (n = 72) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 62.0 ± 11.8 | 62.5 ± 11.8 | 61.1 ± 11.8 |
| Weight (kg) | 71.9 ± 15.4 | 75.9 ± 14.8 | 64.5 ± 13.7 * |
| Height (m) | 1.67 ± 0.10 | 1.72 ± 0.08 | 1.59 ± 0.06 * |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 25.5 ± 4.6 | 25.5 ± 4.2 | 25.4 ± 5.2 |
| Calf circumference (cm) | 35.3 ± 4.0 | 25.7 ± 4.0 | 34.5 ± 3.8 * |
| Mid-upper-arm circumference (cm) | 29.8 ± 4.1 | 30.3 ± 4.1 | 29.0 ± 4.0 * |
| Triceps skinfold (mm) | 16.3 ± 8.4 | 13.7 ± 7.9 | 21.6 ± 6.7 * |
| Mid-arm muscle area (cm2) | 48.7 ± 14.1 | 54.3 ± 13.5 | 37.3 ± 6.5 * |
| Rectus femoris area (cm2) | 4.48 ± 1.60 | 4.88 ± 1.66 | 3.72 ± 1.16 * |
| Appendicular muscle mass by BIAsf (kg) | 19.6 ± 4.5 | 21.8 ± 3.7 | 15.6 ± 2.6 * |
| Appendicular muscle mass by BIAmf (kg) | 20.7 ± 5.1 | 23.4 ± 4.1 | 16.0 ± 2.7 * |
| Appendicular lean mass by DXA (kg) | 18.2 ± 4.4 | 20.4 ± 3.6 | 14.2 ± 2.4 * |
| Maximum muscle strength (kg) | 35.3 ± 11.0 | 40.5 ± 9.4 | 25.3 ± 5.6 * |
| Total (n = 205) | Standard Error of Estimate | Men (n = 133) | Women (n = 72) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSS/height | 20.8 ± 5.8 | 0.41 | 23.5 ± 5.0 | 15.8 ± 3.3 * |
| MSS/weight | 0.49 ± 0.14 | 0.01 | 0.54 ± 0.13 | 0.40 ± 0.10 * |
| MSS/BMI | 1.41 ± 0.47 | 0.03 | 1.62 ± 0.42 | 1.02 ± 0.27 * |
| MSS/calf | 1.00 ± 0.28 | 0.02 | 1.13 ± 0.23 | 0.74 ± 0.16 * |
| MSS/MMA | 0.74 ± 0.19 | 0.01 | 0.77 ± 0.19 | 0.68 ± 0.17 * |
| MSS/US | 8.37 ± 2.75 | 0.19 | 8.95 ± 2.81 | 7.30 ± 2.28 * |
| MSS/BIAsf | 1.79 ± 0.38 | 0.03 | 1.88 ± 0.36 | 1.63 ± 0.36 * |
| MSS/BIAmf | 1.71 ± 0.35 | 0.02 | 1.77 ± 0.33 | 1.60 ± 0.35 * |
| MSS/DXA | 1.94 ± 0.39 | 0.03 | 2.01 ± 0.36 | 1.80 ± 0.40 * |
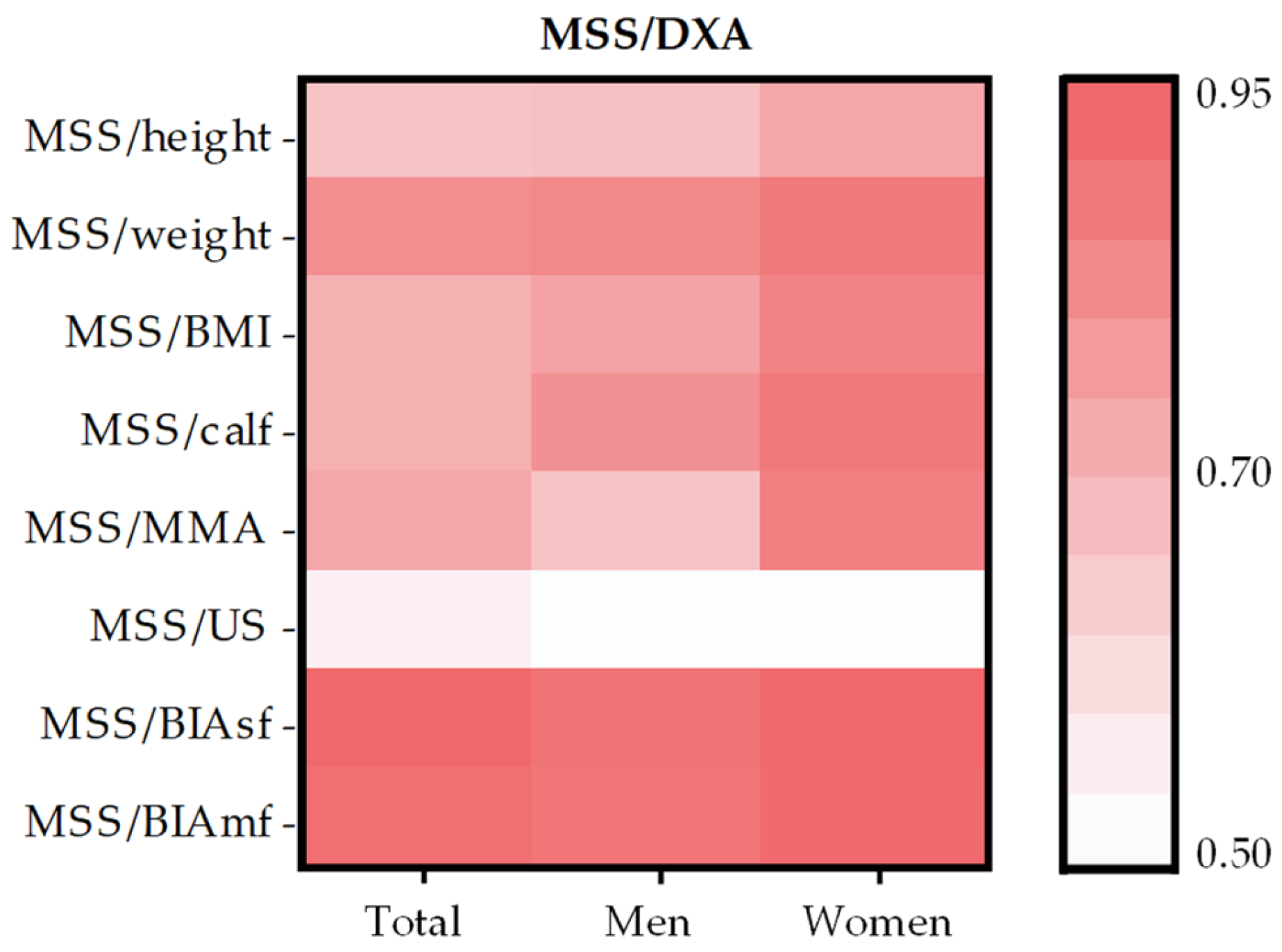
| Total (n = 205) | Men (n = 133) | Women (n = 72) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| MSS/DXA | |||
| MSS/height | 0.68 * | 0.69 * | 0.77 * |
| MSS/weight | 0.84 * | 0.86 * | 0.90 * |
| MSS/BMI | 0.74 * | 0.78 * | 0.87 * |
| MSS/calf | 0.74 * | 0.83 * | 0.90 * |
| MSS/MMA | 0.77 * | 0.68 * | 0.88 * |
| MSS/US | 0.55 * | 0.51 * | 0.51 * |
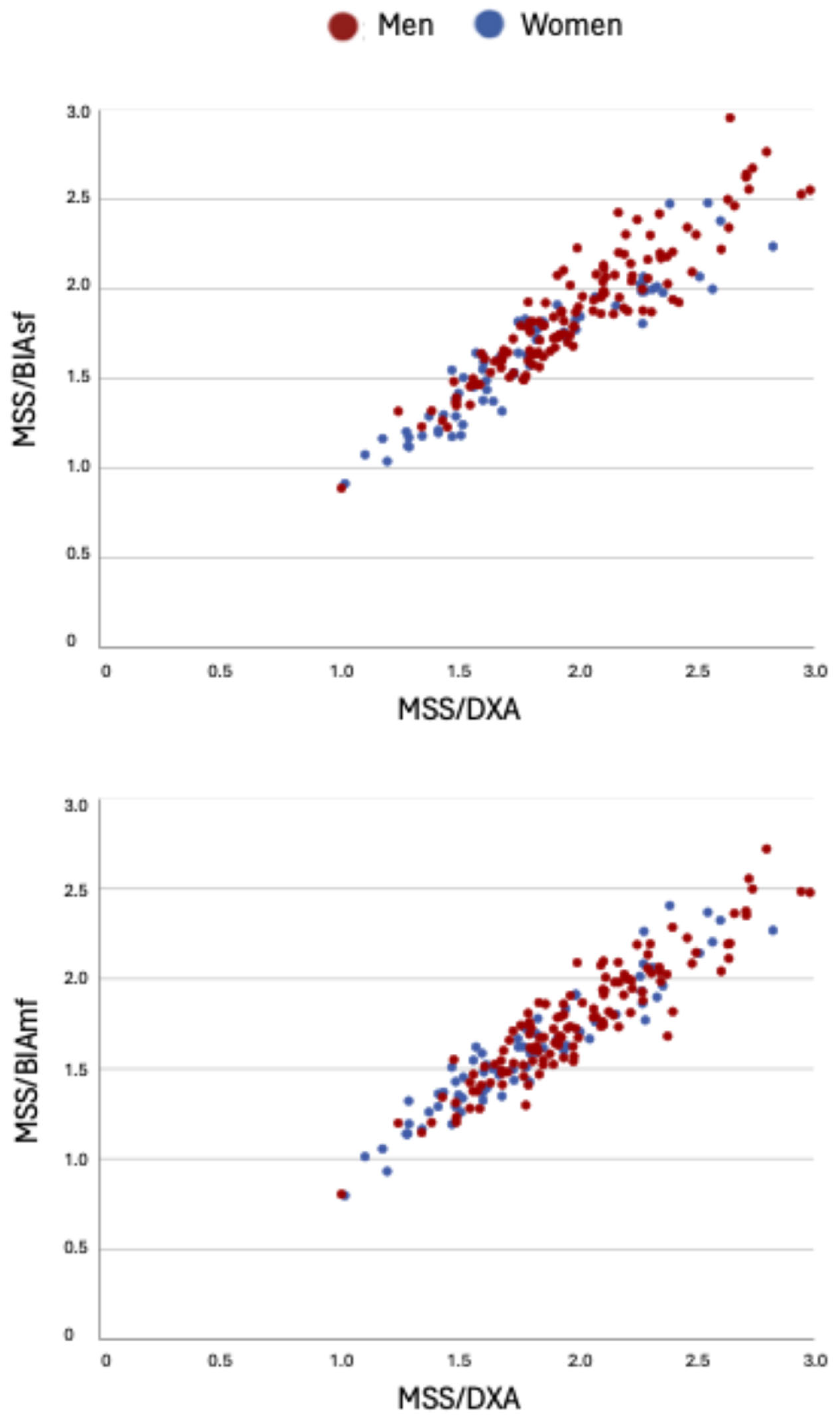
| MSS/BIAsf | 0.95 * | 0.92 * | 0.95 * |
| MSS/BIAmf | 0.93 * | 0.91 * | 0.94 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alabadi, B.; Amores, S.; Moriana, M.; Wu Xiong, N.Y.; García-Malpartida, K.; Pedrón, J.A.; Monrós, C.; Martínez-Hervás, S.; Real, J.T.; Civera, M. Assessment of Muscle-Specific Strength in Oncology Patients: Anthropometry as a Reliable Alternative to DXA. Life 2025, 15, 1300. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081300
Alabadi B, Amores S, Moriana M, Wu Xiong NY, García-Malpartida K, Pedrón JA, Monrós C, Martínez-Hervás S, Real JT, Civera M. Assessment of Muscle-Specific Strength in Oncology Patients: Anthropometry as a Reliable Alternative to DXA. Life. 2025; 15(8):1300. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081300
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlabadi, Blanca, Sandra Amores, Miriam Moriana, Ning Yun Wu Xiong, Katherine García-Malpartida, José Antonio Pedrón, Clàudia Monrós, Sergio Martínez-Hervás, José T. Real, and Miguel Civera. 2025. "Assessment of Muscle-Specific Strength in Oncology Patients: Anthropometry as a Reliable Alternative to DXA" Life 15, no. 8: 1300. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081300
APA StyleAlabadi, B., Amores, S., Moriana, M., Wu Xiong, N. Y., García-Malpartida, K., Pedrón, J. A., Monrós, C., Martínez-Hervás, S., Real, J. T., & Civera, M. (2025). Assessment of Muscle-Specific Strength in Oncology Patients: Anthropometry as a Reliable Alternative to DXA. Life, 15(8), 1300. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081300






