Assessment of the Association Between Coronary Artery Calcification, Plaque Vulnerability, and Perivascular Inflammation via Coronary CT Angiography
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. CCTA Acquisition Protocol and Image Post-Processing Workflow
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Demographics and Clinical Characteristics of the Study Population
3.2. Coronary Plaque Distribution, Composition, and Inflammatory Characteristics According to CAC Groups
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
Abbreviations
| ACS | Acute Coronary Syndrome |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| CABG | Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting |
| CACs | Coronary Artery Calcium Score |
| CAD | Coronary Artery Disease |
| CAD-RADS | Coronary Artery Disease-Reporting and Data System |
| CaRi-Heart® | AI-powered Platform for Coronary Risk Prediction |
| CCTA | Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography |
| CVD | Cardiovascular Disease |
| DM | Diabetes Mellitus |
| DICOM | Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine |
| ESC | European Society of Cardiology |
| FAI | Fat Attenuation Index |
| HDL-Cho | High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol |
| HRP | High-Risk Plaque |
| hsCRP | High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein |
| MI | Myocardial Infarction |
| LAD | Left Anterior Descending artery |
| LAP | Low-Attenuation Plaque/Core |
| LCX | Left Circumflex Artery |
| LDL-Cho | Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol |
| LVEF | Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction |
| MACE | Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events |
| NRS | Napkin-Ring Sign |
| PCI | Percutaneous Coronary Intervention |
| PR | Positive Remodeling |
| PVAT | Perivascular Adipose Tissue |
| RCA | Right Coronary Artery |
| SC | Spotty Calcification |
| SIS | Segment Involvement Score |
| STEMI | ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction |
| TGs | Triglycerides |
| T-Cho | Total Cholesterol |
References
- Libby, P. Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Nature 2002, 420, 868–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virmani, R.; Kolodgie, F.D.; Burke, A.P.; Farb, A.; Schwartz, S.M. Lessons From Sudden Coronary Death: A Comprehensive Morphological Classification Scheme for Atherosclerotic Lesions. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2000, 20, 1262–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cury, R.C.; Abbara, S.; Achenbach, S.; Agatston, A.; Berman, D.S.; Budoff, M.J.; Dill, K.E.; Jacobs, J.E.; Maroules, C.D.; Rubin, G.D.; et al. CAD-RADSTM: Coronary Artery Disease—Reporting and Data System. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2016, 13, 1458–1466.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cury, R.C.; Leipsic, J.; Abbara, S.; Achenbach, S.; Berman, D.; Bittencourt, M.; Budoff, M.; Chinnaiyan, K.; Choi, A.D.; Ghoshhajra, B.; et al. CAD-RADSTM 2.0-2022 Coronary Artery Disease-Reporting and Data System. J. Cardiovasc. Comput. Tomogr. 2022, 16, 536–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budoff, M.J.; Shaw, L.J.; Liu, S.T.; Weinstein, S.R.; Tseng, P.H.; Flores, F.R.; Callister, T.Q.; Raggi, P.; Berman, D.S.; Mosler, T.P. Long-Term Prognosis Associated With Coronary Calcification. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2007, 49, 1860–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenland, P.; Blaha, M.J.; Budoff, M.J.; Erbel, R.; Watson, K.E. Coronary Calcium Score and Cardiovascular Risk. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 72, 434–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motoyama, S.; Sarai, M.; Harigaya, H.; Anno, H.; Inoue, K.; Hara, T.; Naruse, H.; Ishii, J.; Hishida, H.; Wong, N.D.; et al. Computed Tomographic Angiography Characteristics of Atherosclerotic Plaques Subsequently Resulting in Acute Coronary Syndrome. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 54, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Shao, M.; Li, M.; Li, T.; Zheng, Y.; Sun, W.; Ni, C.; Li, L. Sphingolipid metabolites involved in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis: Perspectives on sphingolipids in atherosclerosis. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2025, 30, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Chen, Y.; Lin, X.; Deng, S.; Sun, B.; Zheng, J.; Zeng, F.; Xue, Y. Relationship between fetal-type posterior cerebral artery and basilar artery atherosclerosis. Front. Neurol. 2025, 16, 1533281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, C.; Luo, J.; Lei, L.; Chen, M.; Zhang, Y.; Sheng, R.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Jiang, X.; et al. A novel small-molecule PCSK9 inhibitor E28362 ameliorates hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2024, 45, 2119–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonopoulos, A.S.; Sanna, F.; Sabharwal, N.; Thomas, S.; Oikonomou, E.K.; Herdman, L.; Margaritis, M.; Shirodaria, C.; Kampoli, A.-M.; Akoumianakis, I.; et al. Detecting human coronary inflammation by imaging perivascular fat. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaal2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oikonomou, E.K.; Marwan, M.; Desai, M.Y.; Mancio, J.; Alashi, A.; Hutt Centeno, E.; Thomas, S.; Herdman, L.; Kotanidis, C.P.; Thomas, K.E.; et al. Non-invasive detection of coronary inflammation using computed tomography and prediction of residual cardiovascular risk (the CRISP CT study): A post-hoc analysis of prospective outcome data. Lancet 2018, 392, 929–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, D.; Shou, B.L.; Matheson, M.B.; Ostovaneh, M.R.; Rochitte, C.; Chen, M.Y.; Dewey, M.; Ortman, J.; Cox, C.; Lima, J.A.C.; et al. Perivascular fat attenuation for predicting adverse cardiac events in stable patients undergoing invasive coronary angiography. J. Cardiovasc. Comput. Tomogr. 2022, 16, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikonomou, E.K.; Antonopoulos, A.S.; Schottlander, D.; Marwan, M.; Mathers, C.; Tomlins, P.; Siddique, M.; Klüner, L.V.; Shirodaria, C.; Mavrogiannis, M.C.; et al. Standardized measurement of coronary inflammation using cardiovascular computed tomography: Integration in clinical care as a prognostic medical device. Cardiovasc. Res. 2021, 117, 2677–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Cao, Z.; Xu, J.; Guan, X.; He, H.; Duan, L.; Ji, L.; Liu, G.; Guo, Q.; You, Y.; et al. Peri-coronary fat attenuation index combined with high-risk plaque characteristics quantified from coronary computed tomography angiography for risk stratification in new-onset chest pain individuals without acute myocardial infarction WR, ed. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0304137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiecinski, J.; Dey, D.; Cadet, S.; Lee, S.-E.; Otaki, Y.; Huynh, P.T.; Doris, M.K.; Eisenberg, E.; Yun, M.; Jansen, M.A.; et al. Peri-Coronary Adipose Tissue Density Is Associated With 18F-Sodium Fluoride Coronary Uptake in Stable Patients With High-Risk Plaques. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2019, 12, 2000–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Rosendael, S.E.; Kamperidis, V.; Maaniitty, T.; De Graaf, M.A.; Saraste, A.; McKay-Goodall, G.E.; Jukema, J.W.; Knuuti, J.; Bax, J.J. Pericoronary adipose tissue for predicting long-term outcomes. Eur. Heart J.-Cardiovasc. Imaging 2024, 25, 1351–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.C.; Kwiecinski, J.; Doris, M.; McElhinney, P.; D’Souza, M.S.; Cadet, S.; Adamson, P.D.; Moss, A.J.; Alam, S.; Hunter, A.; et al. Low-Attenuation Noncalcified Plaque on Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography Predicts Myocardial Infarction: Results From the Multicenter SCOT-HEART Trial (Scottish Computed Tomography of the HEART). Circulation 2020, 141, 1452–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Günay, B.; Tepe, M.S.; Öztürk, H.H.; Küskün, A.; Gençbay, M. Pericoronary fat attenuation in stenotic and vulnerable coronary artery plaques: Implications for coronary artery disease and associated conditions. Acta Radiol. Open 2025, 14, 20584601251342312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniades, C.; Tousoulis, D.; Vavlukis, M.; Fleming, I.; Duncker, D.J.; Eringa, E.; Manfrini, O.; Antonopoulos, A.S.; Oikonomou, E.; Padró, T.; et al. Perivascular adipose tissue as a source of therapeutic targets and clinical biomarkers. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 3827–3844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrints, C.; Andreotti, F.; Koskinas, K.C.; Rossello, X.; Adamo, M.; Ainslie, J.; Banning, A.P.; Budaj, A.; Buechel, R.R.; Chiariello, G.A.; et al. 2024 ESC Guidelines for the management of chronic coronary syndromes. Eur. Heart J. 2024, 45, 3415–3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.; Wahome, E.; Tsiachristas, A.; Antonopoulos, A.S.; Patel, P.; Lyasheva, M.; Kingham, L.; West, H.; Oikonomou, E.K.; Volpe, L.; et al. Inflammatory risk and cardiovascular events in patients without obstructive coronary artery disease: The ORFAN multicentre, longitudinal cohort study. Lancet 2024, 403, 2606–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mátyás, B.-B.; Gerculy, R.; Rat, N.; Blîndu, E.; Stănescu, A.G.; Roșca, A.; Buicu, C.-F.; Benedek, I.; Benedek, T. Highly Inflamed Non-Calcified Coronary Plaques Sealed with Stents in Patients with Zero Calcium Score—A Case Series and Review of the Literature. J. Cardiovasc. Emergencies 2024, 10, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mátyás, B.-B.; Blîndu, E.; Rat, N.; Kovács, I.; Buicu, C.-F.; Benedek, T. A Race Against Time: Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography Discovers a Highly Inflamed Plaque in 49-Year-Old Right Before STEMI. J. Cardiovasc. Emergencies 2024, 10, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaha, M.J.; Cainzos-Achirica, M.; Greenland, P.; McEvoy, J.W.; Blankstein, R.; Budoff, M.J.; Dardari, Z.; Sibley, C.T.; Burke, G.L.; Kronmal, R.A.; et al. Role of Coronary Artery Calcium Score of Zero and Other Negative Risk Markers for Cardiovascular Disease: The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA). Circulation 2016, 133, 849–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, K.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Blaha, M.J.; Blankstein, R.; Agatson, A.S.; Rivera, J.J.; Miedema, M.D.; Sibley, C.T.; Shaw, L.J.; Blumenthal, R.S.; et al. Implications of Coronary Artery Calcium Testing Among Statin Candidates According to American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Cholesterol Management Guidelines. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 66, 1657–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virmani, R.; Burke, A.P.; Farb, A.; Kolodgie, F.D. Pathology of the Vulnerable Plaque. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006, 47, C13–C18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neves, P.O.; Andrade, J.; Monção, H. Coronary artery calcium score: Current status. Radiol. Bras. 2017, 50, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikonomou, E.K.; Desai, M.Y.; Marwan, M.; Kotanidis, C.P.; Antonopoulos, A.S.; Schottlander, D.; Channon, K.M.; Neubauer, S.; Achenbach, S.; Antoniades, C. Perivascular Fat Attenuation Index Stratifies Cardiac Risk Associated With High-Risk Plaques in the CRISP-CT Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 755–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klüner, L.V.; Oikonomou, E.K.; Antoniades, C. Assessing Cardiovascular Risk by Using the Fat Attenuation Index in Coronary CT Angiography. Radiol. Cardiothorac. Imaging 2021, 3, e200563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saydam, C.D. Subclinical cardiovascular disease and utility of coronary artery calcium score. IJC Heart Vasc. 2021, 37, 100909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goeller, M.; Tamarappoo, B.K.; Kwan, A.C.; Cadet, S.; Commandeur, F.; Razipour, A.; Slomka, P.J.; Gransar, H.; Chen, X.; Otaki, Y.; et al. Relationship between changes in pericoronary adipose tissue attenuation and coronary plaque burden quantified from coronary computed tomography angiography. Eur. Heart J.-Cardiovasc. Imaging 2019, 20, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goeller, M.; Achenbach, S.; Cadet, S.; Kwan, A.C.; Commandeur, F.; Slomka, P.J.; Gransar, H.; Albrecht, M.H.; Tamarappoo, B.K.; Berman, D.S.; et al. Pericoronary Adipose Tissue Computed Tomography Attenuation and High-Risk Plaque Characteristics in Acute Coronary Syndrome Compared With Stable Coronary Artery Disease. JAMA Cardiol. 2018, 3, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simantiris, S.; Pappa, A.; Papastamos, C.; Korkonikitas, P.; Antoniades, C.; Tsioufis, C.; Tousoulis, D. Perivascular Fat: A Novel Risk Factor for Coronary Artery Disease. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotecha, T.; Knight, D.S.; Razvi, Y.; Kumar, K.; Vimalesvaran, K.; Thornton, G.; Patel, R.; Chacko, L.; Brown, J.T.; Coyle, C.; et al. Patterns of myocardial injury in recovered troponin-positive COVID-19 patients assessed by cardiovascular magnetic resonance. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 1866–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshavarz, P.; Yazdanpanah, F.; Emad, M.; Hajati, A.; Nejati, S.F.; Ebrahimian Sadabad, F.; Azrumelashvili, T.; Mizandari, M.; Raman, S.S. Myocarditis Following COVID-19 Vaccination: Cardiac Imaging Findings in 118 Studies. Tomography 2022, 8, 1959–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blîndu, E.; Benedek, I.; Rodean, I.-P.; Halațiu, V.-B.; Raț, N.; Țolescu, C.; Mihăilă, T.; Roșca, A.; Mátyás, B.-B.; Szabó, E.; et al. Regional Differences in the Level of Inflammation Between the Right and Left Coronary Arteries—A Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography Study of Epicardial Fat Attenuation Index in Four Scenarios of Cardiovascular Emergencies. J. Cardiovasc. Emergencies 2023, 9, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Bijl, P.; Kuneman, J.H.; Bax, J.J. Pericoronary adipose tissue attenuation: Diagnostic and prognostic implications. Eur. Heart J.-Cardiovasc. Imaging 2022, 23, e537–e538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwiecinski, J.; Lassen, M.L.; Slomka, P.J. Advances in Quantitative Analysis of18 F-Sodium Fluoride Coronary Imaging. Mol. Imaging 2021, 2021, 8849429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coerkamp, C.F.; Verpalen, V.A.; Kuipers, R.S.; Driessen-Waaijer, A.; Van Der Hulst, V.P.M.; Planken, N.R.; Henriques, J.P.S.; Riezebos, R.K. Perivascular fat attenuation index (FAI) on computed tomography coronary angiography reclassifies individual cardiovascular risk estimation. Int. J. Cardiol. Cardiovasc. Risk Prev. 2025, 24, 200360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dweck, M.R.; Fayad, Z.A. Perivascular fat—An unheralded informant of coronary inflammation. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2017, 14, 573–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matyas, B.; Benedek, I.; Rat, N.; Blindu, E.; Gerculy, R.; Rosca, A.; Benedek, T. Redefining cardiovascular risk evaluation: Employing the CaRi-Heart validated FAI-score in patients screened with SCORE2 and CAD-RADS 2.0 techniques. Eur. Heart J. 2024, 45 (Suppl. 1), ehae666.171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
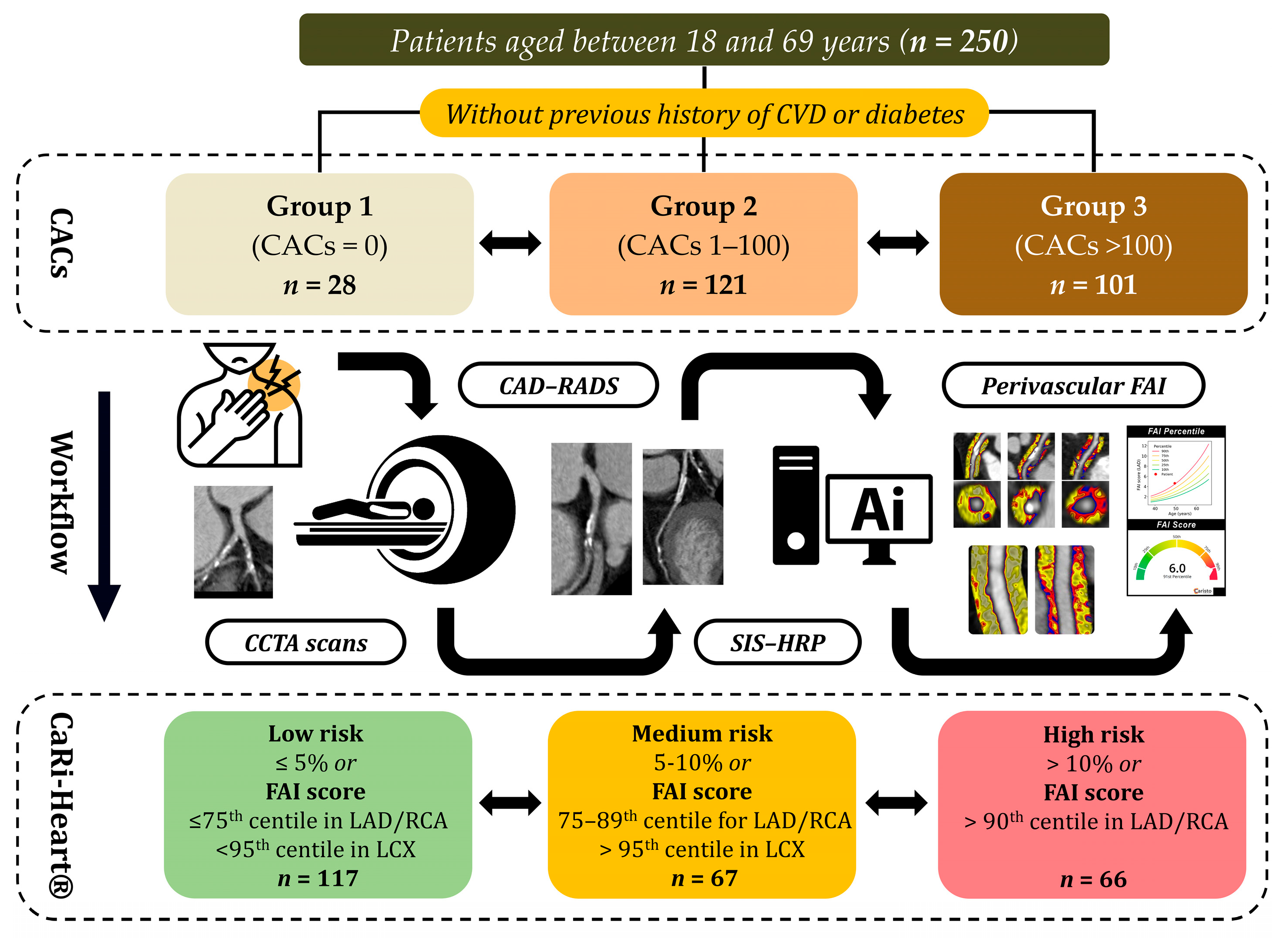
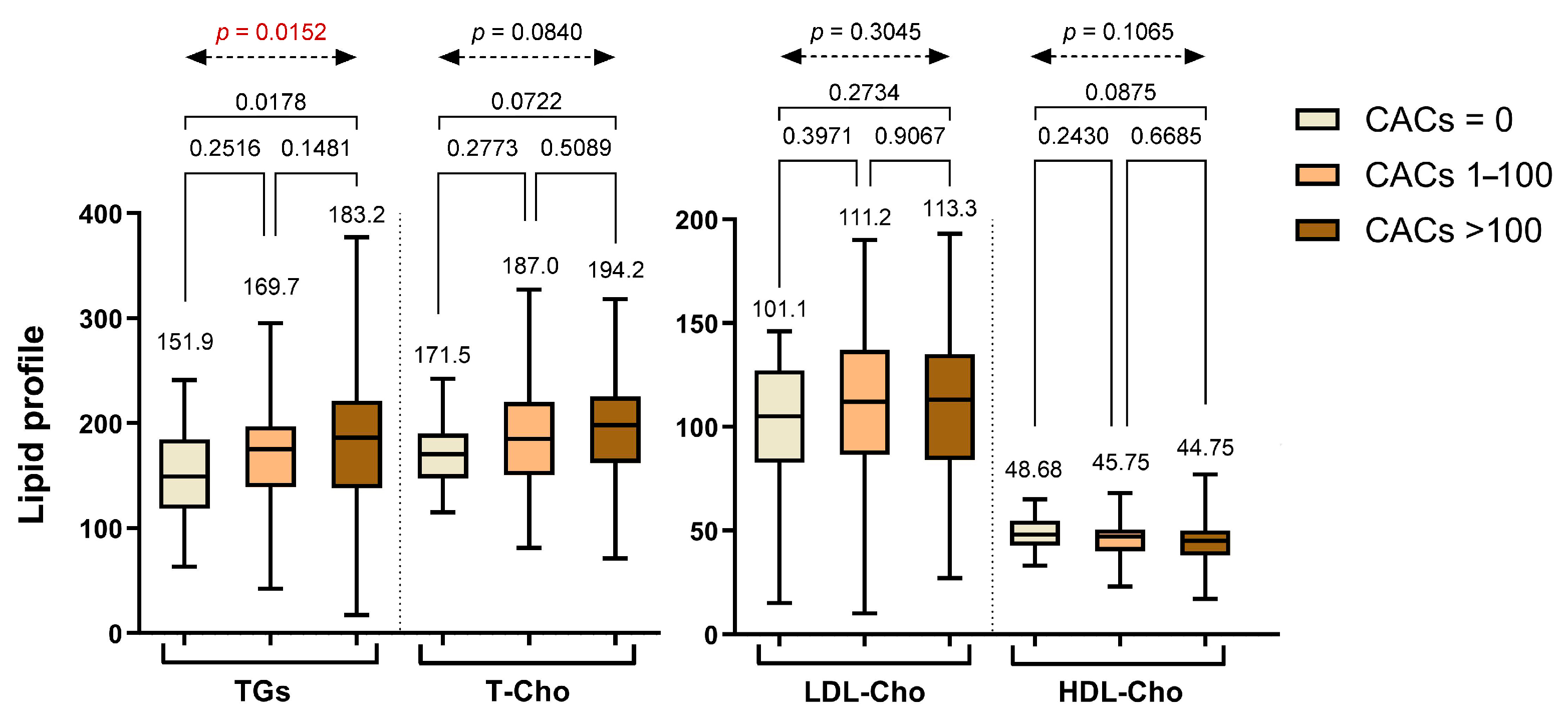

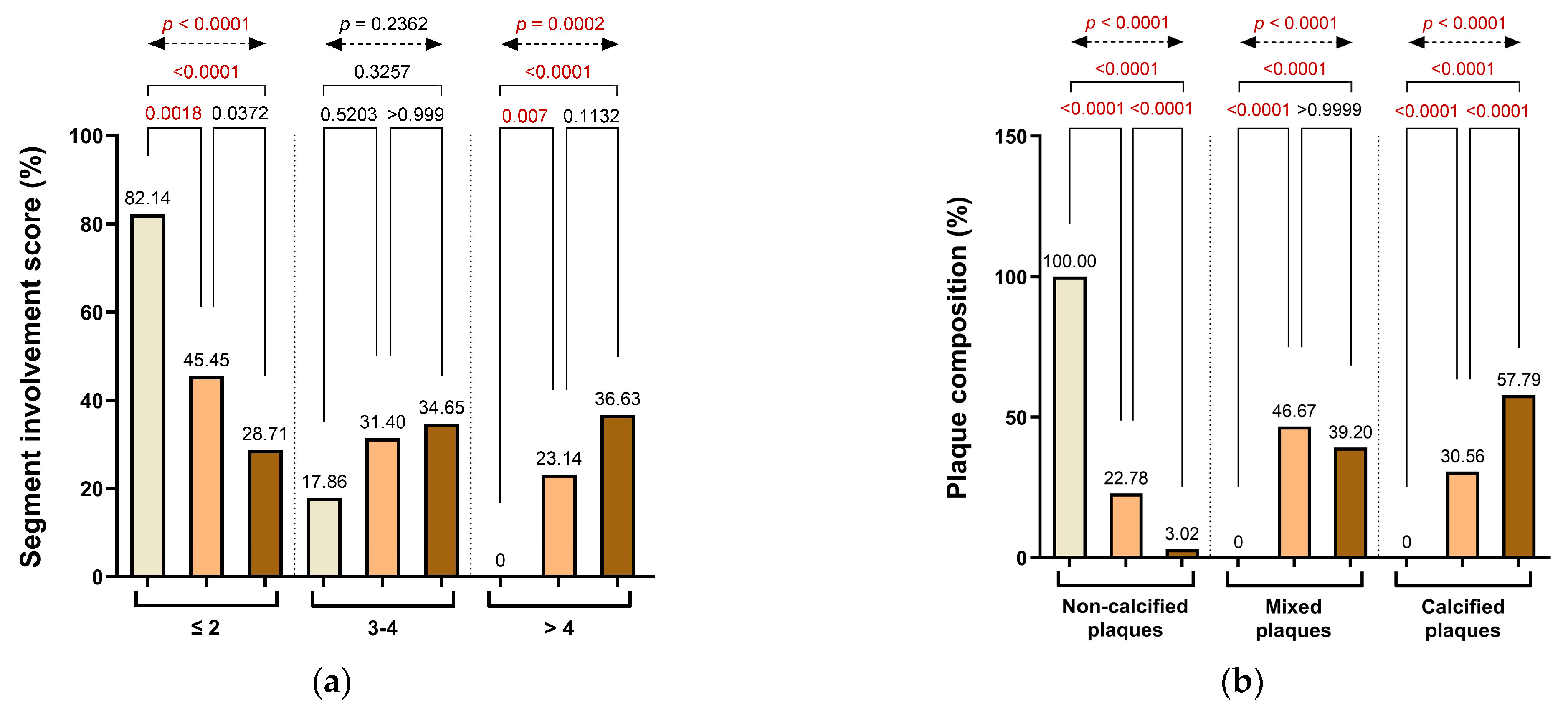
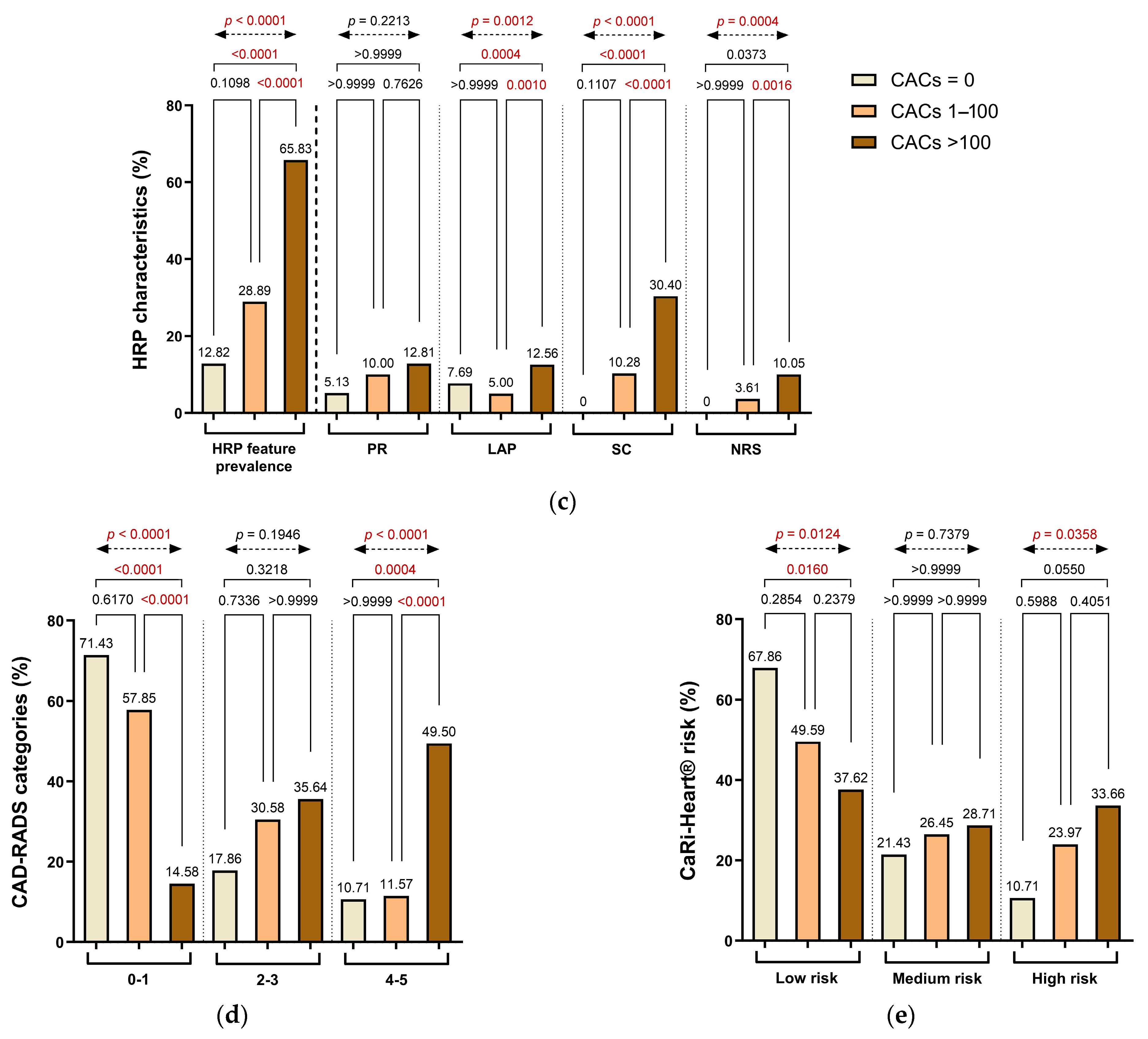

| Parameters | Whole Study Sample (n = 250) | Group 1 (CACs = 0) (n = 28) | Group 2 (CACs 1–100) (n = 121) | Group 3 (CACs > 100) (n = 101) | p Value 1 | p Value 2 | p Value 3 | p Value 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, (years), mean ± SD | 61.1 ± 6.3 | 55.9 ± 7.1 | 60.4 ± 6.4 | 63.4 ± 4.8 | 0.0011 | 0.0004 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Male gender, n (%) | 185 (74.00%) | 17 (60.71%) | 88 (72.73%) | 80 (79.21%) | 0.7540 | 0.8284 | 0.1561 | 0.1290 |
| BMI 5, (kg/m2), mean ± SD | 27.67 ± 3.8 | 25.05 ± 3.5 | 27.93 ± 3.9 | 28.07 ± 3.4 | 0.0008 | 0.9589 | 0.0005 | 0.0005 |
| LVEF 6 (%), mean ± SD | 54.43 ± 4.55 | 54.46 ± 4.53 | 54.17 ± 4.07 | 54.73 ± 5.09 | 0.9504 | 0.6349 | 0.9590 | 0.6613 |
| Cardiovascular risk factors: | ||||||||
| Hypertension, n (%) | 150 (60.00%) | 9 (32.14%) | 71 (58.68%) | 70 (69.31%) | 0.0376 | 0.3710 | 0.0023 | 0.0017 |
| Hypercholesterolemia, n (%) | 142 (56.80%) | 7 (25.00%) | 69 (57.02%) | 66 (65.35%) | 0.0089 | 0.6513 | 0.0006 | 0.0007 |
| Smoking, n (%) | 71 (28.40%) | 5 (17.86%) | 38 (31.40%) | 28 (27.72%) | 0.5203 | >0.9999 | >0.9999 | 0.3515 |
| Obesity, n (%) | 51 (20.40%) | 3 (10.71%) | 28 (23.14%) | 20 (19.80%) | 0.5941 | >0.9999 | >0.9999 | 0.3329 |
| Familial history of CAD 7, n (%) | 44 (17.60%) | 2 (7.14%) | 22 (18.18%) | 22 (21.78%) | 0.7551 | >0.9999 | 0.3033 | 0.2084 |
| SCORE2 8 risk assessment: | ||||||||
| Low–moderate risk, n (%) | 103 (41.20%) | 16 (57.14%) | 47 (38.84%) | 40 (39.60%) | 0.2754 | >0.9999 | 0.3939 | 0.1901 |
| High risk, n (%) | 87 (34.80%) | 8 (28.57%) | 45 (37.19%) | 34 (33.66%) | >0.9999 | >0.9999 | >0.9999 | 0.6567 |
| Very high risk, n (%) | 60 (24.00%) | 4 (14.29%) | 29 (23.97%) | 27 (26.73%) | 0.9654 | >0.9999 | 0.6498 | 0.3941 |
| Parameters | Whole Study Sample (n = 250) | Group 1 (CACs = 0) (n = 28) | Group 2 (CACs 1–100) (n = 121) | Group 3 (CACs > 100) (n = 101) | p Value 1 | p Value 2 | p Value 3 | p Value 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Segments/Subject, Mean ± SD, (Range), {Sum} | 3.18 ± 1.93 (0–8), {797} | 1.39 ± 1.10 (0–4), {39} | 2.97 ± 1.57 (1–6), {360} | 3.94 ± 2.10 (1–8), {398} | <0.0001 | 0.0002 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Segment involvement score: | ||||||||
| ≤2, n (%) | 107 (42.80%) | 23 (82.14%) | 55 (45.45%) | 29 (28.71%) | 0.0018 | 0.0372 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| 3–4, n (%) | 78 (31.20%) | 5 (17.86%) | 38 (31.40%) | 35 (34.65%) | 0.5203 | >0.9999 | 0.3257 | 0.2362 |
| >4, n (%) | 65 (26.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | 28 (23.14%) | 37 (36.63%) | 0.0070 | 0.1132 | <0.0001 | 0.0002 |
| Plaque composition: | ||||||||
| Non-calcified plaques, n (%) | 133 (16.69%) | 39 (100.00%) | 82 (22.78%) | 12 (3.02%) | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Mixed plaques, n (%) | 324 (40.65%) | 0 (0.00%) | 168 (46.67%) | 156 (39.20%) | <0.0001 | >0.9999 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Calcified plaques, n (%) | 340 (42.66%) | 0 (0.00%) | 110 (30.56%) | 230 (57.79%) | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| HRP 5 characteristics: | ||||||||
| HRP feature prevalence, n (%) | 371 (46.55%) | 5 (12.82%) | 104 (28.89%) | 262 (65.83%) | 0.1098 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| PR 6, n (%) | 89 (11.17%) | 2 (5.13%) | 36 (10.00%) | 51 (12.81%) | >0.9999 | 0.7626 | >0.9999 | 0.2213 |
| LAP 7, n (%) | 71 (8.91%) | 3 (7.69%) | 18 (5.00%) | 50 (12.56%) | >0.9999 | 0.0010 | 0.0004 | 0.0012 |
| SC 8, n (%) | 158 (19.82%) | 0 (0.00%) | 37 (10.28%) | 121 (30.40%) | 0.1107 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| NRS 9, n (%) | 53 (6.65%) | 0 (0.00%) | 13 (3.61%) | 40 (10.05%) | >0.9999 | 0.0016 | 0.0373 | 0.0004 |
| CAD-RADS 10 categories: | ||||||||
| 0–1, n (%) | 105 (42.00%) | 20 (71.43%) | 70 (57.85%) | 15 (14.58%) | 0.6170 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| 2–3, n (%) | 78 (31.20%) | 5 (17.86%) | 37 (30.58%) | 36 (35.64%) | 0.7336 | >0.9999 | 0.3218 | 0.1946 |
| 4–5, n (%) | 67 (26.80%) | 3 (10.71%) | 14 (11.57%) | 50 (49.50%) | >0.9999 | <0.0001 | 0.0004 | <0.0001 |
| CaRi-Heart® risk assessment: | ||||||||
| Low risk, n (%) | 117 (46.80%) | 19 (67.86%) | 60 (49.59%) | 38 (37.62%) | 0.2854 | 0.2379 | 0.0160 | 0.0124 |
| Medium risk, n (%) | 67 (26.80%) | 6 (21.43%) | 32 (26.45%) | 29 (28.71%) | >0.9999 | >0.9999 | >0.9999 | 0.7379 |
| High risk, n (%) | 66 (26.40%) | 3 (10.71%) | 29 (23.97%) | 34 (33.66%) | 0.5988 | 0.4051 | 0.0550 | 0.0358 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mátyás, B.B.; Benedek, I.; Rat, N.; Blîndu, E.; Rodean, I.P.; Haja, I.; Păcurar, D.; Mihăilă, T.; Benedek, T. Assessment of the Association Between Coronary Artery Calcification, Plaque Vulnerability, and Perivascular Inflammation via Coronary CT Angiography. Life 2025, 15, 1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081288
Mátyás BB, Benedek I, Rat N, Blîndu E, Rodean IP, Haja I, Păcurar D, Mihăilă T, Benedek T. Assessment of the Association Between Coronary Artery Calcification, Plaque Vulnerability, and Perivascular Inflammation via Coronary CT Angiography. Life. 2025; 15(8):1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081288
Chicago/Turabian StyleMátyás, Botond Barna, Imre Benedek, Nóra Rat, Emanuel Blîndu, Ioana Patricia Rodean, Ioana Haja, Delia Păcurar, Theofana Mihăilă, and Theodora Benedek. 2025. "Assessment of the Association Between Coronary Artery Calcification, Plaque Vulnerability, and Perivascular Inflammation via Coronary CT Angiography" Life 15, no. 8: 1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081288
APA StyleMátyás, B. B., Benedek, I., Rat, N., Blîndu, E., Rodean, I. P., Haja, I., Păcurar, D., Mihăilă, T., & Benedek, T. (2025). Assessment of the Association Between Coronary Artery Calcification, Plaque Vulnerability, and Perivascular Inflammation via Coronary CT Angiography. Life, 15(8), 1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081288








