Endoscopic Transsphenoidal Sellar Surgery via One Nostril: Own Experience and Systematic Review of the Literature
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Surgical Technique
2.2. Review of the Literature
2.2.1. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
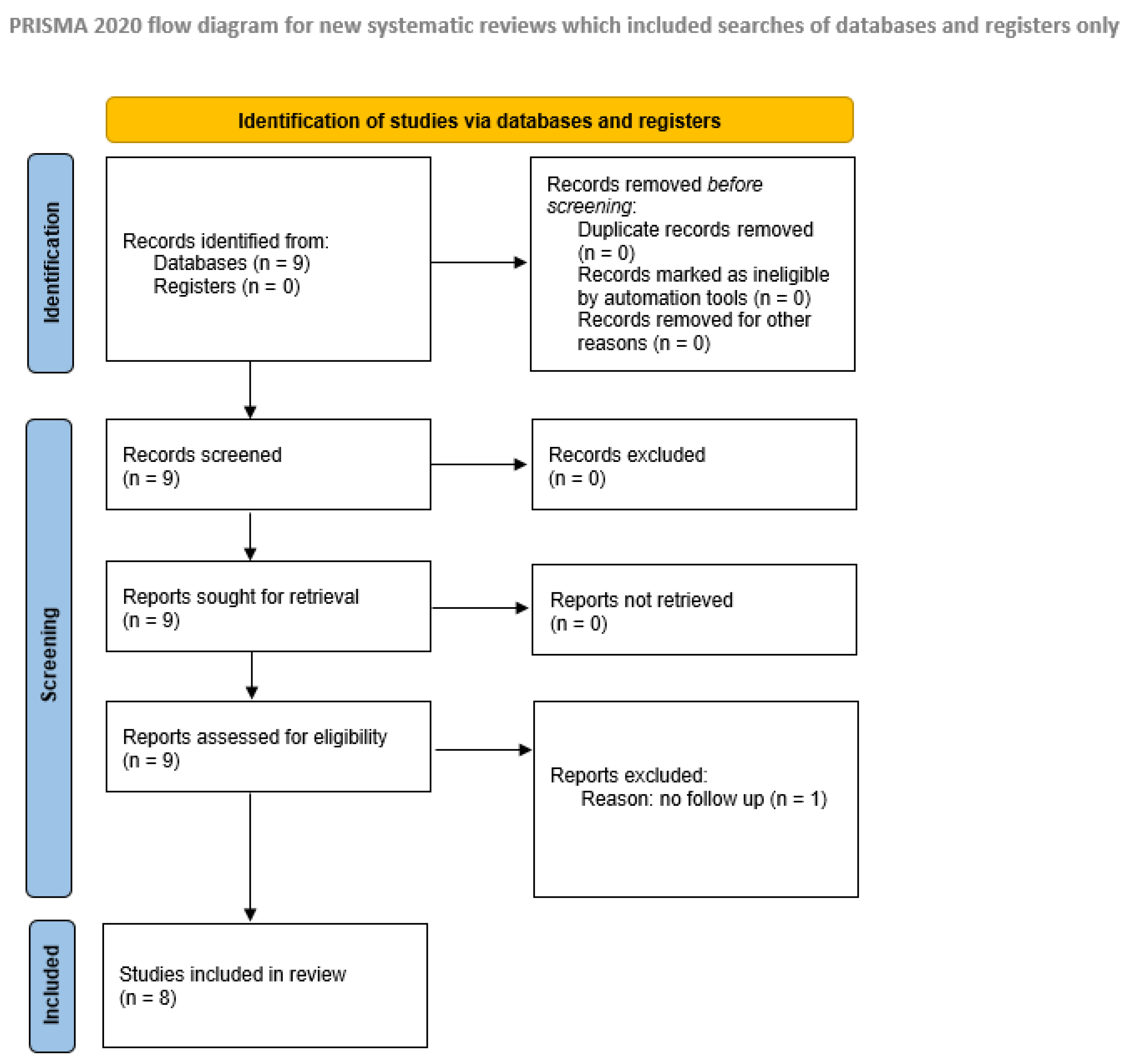
2.2.2. Study Selection, Data Extraction, and Quality Assessment
2.3. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Pathologies, Radicality, and Surgical Time
3.2. Complications
3.3. Details of the Different Mononostril Surgical Techniques
4. Discussion
Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| CT | Computer tomography |
| CSF | Cerebrospinal fluid |
| ICA | Internal carotid artery |
| ACTH | Adrenocorticotropic hormone |
| GH | Growth hormone |
| HD | High definition |
| PRIMSA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses |
References
- Kanter, A.S.; Dumont, A.S.; Asthagiri, A.R.; Oskouian, R.J.; Jane, J.A., Jr.; Laws, E.R., Jr. The transsphenoidal approach. A historical perspective. Neurosurg. Focus. 2005, 18, e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, C.B.; Burke, C.W. Current modes of treatment of pituitary tumours. Br. J. Neurosurg. 1993, 7, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciric, I.; Ragin, A.; Baumgartner, C.; Pierce, D. Complications of transsphenoidal surgery: Results of a national survey, review of the literature, and personal experience. Neurosurgery 1997, 40, 225–236; discussion 236–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahlbusch, R.; Ganslandt, O.; Buchfelder, M.; Schott, W.; Nimsky, C. Intraoperative magnetic resonance imaging during transsphenoidal surgery. J. Neurosurg. 2001, 95, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahlbusch, R.; Honegger, J.; Paulus, W.; Huk, W.; Buchfelder, M. Surgical treatment of craniopharyngiomas: Experience with 168 patients. J. Neurosurg. 1999, 90, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, J. Transphenoidal microsurgery of the normal and pathological pituitary. Clin. Neurosurg. 1969, 16, 185–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laws, E.J. Transsphenoidal approach to pituitary tumours. In Operative Neurosurgical Techniques: Indications, Methods and Results, 3rd ed.; Schmidek, H.H., Roberts, D.W., Eds.; WB Saunderes: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1995; Volume l1, pp. 283–292. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, K.; Tyagi, I.; Banerjee, D.; Chhabra, D.K.; Kaur, A.; Taneja, H.K. Rhinological complications of sublabial transseptal transsphenoidal surgery for sellar and suprasellar lesions: Prevention and management. Neurosurg. Rev. 1996, 19, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheehan, M.T.; Atkinson, J.L.; Kasperbauer, J.L.; Erickson, B.J.; Nippoldt, T.B. Preliminary comparison of the endoscopic transnasal vs the sublabial transseptal approach for clinically nonfunctioning pituitary macroadenomas. Mayo Clin. Proc. 1999, 74, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shou, X.F.; Li, S.Q.; Wang, Y.F.; Zhao, Y.; Jia, P.F.; Zhou, L.F. Treatment of pituitary adenomas with a transsphenoidal approach. Neurosurgery 2005, 56, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomale, U.W.; Stover, J.F.; Unterberg, A.W. The use of neuronavigation in transnasal transsphenoidal pituitary surgery. Zentralblatt Fur Neurochir. 2005, 66, 126–132; discussion 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, H.W.; Oertel, J.; Gaab, M.R. Endoscope-assisted microsurgical resection of epidermoid tumors of the cerebellopontine angle. J. Neurosurg. 2004, 101, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, H.W.; Oertel, J.; Gaab, M.R. Incidence of complications in neuroendoscopic surgery. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2004, 20, 878–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappabianca, P.; Decq, P.; Schroeder, H.W. Future of endoscopy in neurosurgery. Surg. Neurol. 2007, 67, 496–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappabianca, P.; de Divitiis, E. Endoscopy and transsphenoidal surgery. Neurosurgery 2004, 54, 1043–1048; discussion 1048–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappabianca, P.; Cavallo, L.M.; Colao, A.; Del Basso De Caro, M.; Esposito, F.; Cirillo, S.; Lombardi, G.; de Divitiis, E. Endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal approach: Outcome analysis of 100 consecutive procedures. Minim. Invasive Neurosurg. 2002, 45, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappabianca, P.; Cavallo, L.M.; de Divitiis, E. Endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal surgery. Neurosurgery 2004, 55, 933–940; discussion 940–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jho, H.D.; Alfieri, A. Endoscopic endonasal pituitary surgery: Evolution of surgical technique and equipment in 150 operations. Minim. Invasive Neurosurg. 2001, 44, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linsler, S.; Gaab, M.R.; Oertel, J. Endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal approach to sellar lesions: A detailed account of our mononostril technique. J. Neurol. Surg. B Skull Base 2013, 74, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linsler, S.; Hero-Gross, R.; Friesenhahn-Ochs, B.; Sharif, S.; Lammert, F.; Oertel, J. Preservation of hormonal function by identifying pituitary gland at endoscopic surgery. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2017, 43, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linsler, S.; Senger, S.; Hero-Gross, R.; Steudel, W.I.; Oertel, J. The endoscopic surgical resection of intrasellar lesions conserves the hormonal function: A negative correlation to the microsurgical technique. J. Neurosurg. Sci. 2018, 64, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oertel, J.; Linsler, S. Perspective Statement: “Hyponatremia after pituitary surgery”. World Neurosurg. 2016, 90, 648–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassam, A.B.; Gardner, P.; Snyderman, C.; Mintz, A.; Carrau, R. Expanded endonasal approach: Fully endoscopic, completely transnasal approach to the middle third of the clivus, petrous bone, middle cranial fossa, and infratemporal fossa. Neurosurg. Focus. 2005, 19, E6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linsler, S.; Oertel, J. Endoscopic Endonasal Transclival Resection of a Brainstem Cavernoma: A Detailed Account of Our Technique and Comparison with the Literature. World Neurosurg. 2015, 84, 2064–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, J.; Ayyad, A.; Wuster, C.; Omran, W.; Weber, M.M.; Konerding, M.A.; Muller-Forell, W.; Giese, A.; Oertel, J. Binostril versus mononostril approaches in endoscopic transsphenoidal pituitary surgery: Clinical evaluation and cadaver study. J. Neurosurg. 2016, 125, 334–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallapiazza, R.F.; Grober, Y.; Starke, R.M.; Laws, E.R., Jr.; Jane, J.A., Jr. Long-term results of endonasal endoscopic transsphenoidal resection of nonfunctioning pituitary macroadenomas. Neurosurgery 2015, 76, 42–52; discussion 52–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linsler, S.; Breuskin, D.; Tschernig, T.; Oertel, J. Reaching the sellar region endonasally—One or both nostrils? A pilot study in body donors. Ann. Anat. Anat. Anz. Off. Organ. Anat. Ges. 2018, 217, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linsler, S.; Fischer, G.; Skliarenko, V.; Stadie, A.; Oertel, J. Endoscopic Assisted Supraorbital Keyhole Approach or Endoscopic Endonasal Approach in Case of Tuberculum Sellae Meningioma: Which Surgical Route Should be Favoured? World Neurosurg. 2017, 104, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linsler, S.; Quack, F.; Schwerdtfeger, K.; Oertel, J. Prognosis of pituitary adenomas in the early 1970s and today-Is there a benefit of modern surgical techniques and treatment modalities? Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2017, 156, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappabianca, P.; Alfieri, A.; Colao, A.; Cavallo, L.M.; Fusco, M.; Peca, C.; Lombardi, G.; de Divitiis, E. Endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal surgery in recurrent and residual pituitary adenomas: Technical note. Minim. Invasive Neurosurg. 2000, 43, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappabianca, P.; Alfieri, A.; Thermes, S.; Buonamassa, S.; de Divitiis, E. Instruments for endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal surgery. Neurosurgery 1999, 45, 392–395; discussion 395–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jho, H.D. Endoscopic pituitary surgery. Pituitary 1999, 2, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jho, H.D. Endoscopic transsphenoidal surgery. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2001, 54, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallo, L.M.; de Divitiis, O.; Aydin, S.; Messina, A.; Esposito, F.; Iaconetta, G.; Talat, K.; Cappabianca, P.; Tschabitscher, M. Extended endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal approach to the suprasellar area: Anatomic considerations—Part 1. Neurosurgery 2007, 61, 24–33; discussion 33–34. [Google Scholar]
- de Divitiis, E.; Cavallo, L.M.; Esposito, F.; Stella, L.; Messina, A. Extended endoscopic transsphenoidal approach for tuberculum sellae meningiomas. Neurosurgery 2007, 61, 229–237; discussion 237–238. [Google Scholar]
- Kassam, A.B.; Prevedello, D.M.; Carrau, R.L.; Snyderman, C.H.; Thomas, A.; Gardner, P.; Zanation, A.; Duz, B.; Stefko, S.T.; Byers, K.; et al. Endoscopic endonasal skull base surgery: Analysis of complications in the authors’ initial 800 patients. J. Neurosurg. 2011, 114, 1544–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paluzzi, A.; Fernandez-Miranda, J.C.; Tonya Stefko, S.; Challinor, S.; Snyderman, C.H.; Gardner, P.A. Endoscopic endonasal approach for pituitary adenomas: A series of 555 patients. Pituitary 2014, 17, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eseonu, C.I.; ReFaey, K.; Pamias-Portalatin, E.; Asensio, J.; Garcia, O.; Boahene, K.D.; Quinones-Hinojosa, A. Three-Hand Endoscopic Endonasal Transsphenoidal Surgery: Experience with an Anatomy-Preserving Mononostril Approach Technique. Oper. Neurosurg. 2018, 14, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Ding, X.; Tie, X.; Liu, Y.; Xia, J.; Yan, A.; Wu, A. Endoscopic endonasal trans-sphenoidal approach for pituitary adenomas: Is one nostril enough? Acta Neurochir. 2013, 155, 1601–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oertel, J.; Gaab, M.R.; Tschan, C.A.; Linsler, S. Mononostril endoscopic transsphenoidal approach to sellar and peri-sellar lesions: Personal experience and literature review. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2015, 29, 532–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peeters, S.; Levinson, S.; Wahjoepramono, E.J.; July, J. A case series and review of the mononostril endoscopic transnasal transsphenoidal approach: Safe and effective in a low resource setting. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2021, 202, 106499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oertel, J.; Senger, S.; Linsler, S. The extended endoscopic approach to perisellar and skull base lesions: Is one nostril enough? Neurosurg. Rev. 2020, 43, 1519–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, H.; El-Hadi, U.; Haddad, G.; Najjar, M. Management of Pituitary Adenomas: Mononostril Endoscopic Transsphenoidal Surgery. Basic. Clin. Neurosci. 2018, 9, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontes, J.P.M.; Udoma-Udofa, O.C.; de Oliveira, J.S.; Larcipretti, A.L.L.; Dagostin, C.S.; Gomes, F.C.; Nager, G.B.; de Andrade Bannach, M. Efficacy and safety of cavernous sinus medial wall resection in pituitary adenoma surgery: A systematic review and a single-arm meta-analysis. Pituitary 2023, 26, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Miranda, J.C.; Gardner, P.A.; Prevedello, D.M.; Kassam, A.B. Expanded endonasal approach for olfactory groove meningioma. Acta Neurochir. 2009, 151, 287–288; author reply 289–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oertel, J.; Gaab, M.R.; Linsler, S. The endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal approach to sellar lesions allows a high radicality: The benefit of angled optics. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2016, 146, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenzie, J.E.; Hetrick, S.E.; Page, M.J. Updated reporting guidance for systematic reviews: Introducing PRISMA 2020 to readers of the Journal of Affective Disorders. J. Affect. Disord. 2021, 292, 56–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baussart, B.; Declerck, A.; Gaillard, S. Mononostril endoscopic endonasal approach for pituitary surgery. Acta Neurochir. 2021, 163, 655–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linsler, S.; Prokein, B.; Hendrix, P.; Oertel, J. Sinonasal outcome after endoscopic mononostril transsphenoidal surgery: A single center cohort study. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2018, 53, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotenberg, B.; Tam, S.; Ryu, W.H.; Duggal, N. Microscopic versus endoscopic pituitary surgery: A systematic review. Laryngoscope 2010, 120, 1292–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emengen, A.; Yilmaz, E.; Gokbel, A.; Uzuner, A.; Balci, S.; Tavukcu Ozkan, S.; Ergen, A.; Caklili, M.; Cabuk, B.; Anik, I.; et al. Refining Endoscopic and Combined Surgical Strategies for Giant Pituitary Adenomas: A Tertiary-Center Evaluation of 49 Cases over the Past Year. Cancers 2025, 17, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asemota, A.O.; Ishii, M.; Brem, H.; Gallia, G.L. Comparison of Complications, Trends, and Costs in Endoscopic vs Microscopic Pituitary Surgery: Analysis from a US Health Claims Database. Neurosurgery 2017, 81, 458–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallapiazza, R.; Bond, A.E.; Grober, Y.; Louis, R.G.; Payne, S.C.; Oldfield, E.H.; Jane, J.A., Jr. Retrospective analysis of a concurrent series of microscopic versus endoscopic transsphenoidal surgeries for Knosp Grades 0–2 nonfunctioning pituitary macroadenomas at a single institution. J. Neurosurg. 2014, 121, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Divitiis, E.; Cappabianca, P. Microscopic and endoscopic transsphenoidal surgery. Neurosurgery 2002, 51, 1527–1529; author reply 1529–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, H.A.; Awad, A.W.; Bohl, M.A.; Chapple, K.; Knecht, L.; Jahnke, H.; White, W.L.; Little, A.S. Comparison of outcomes between a less experienced surgeon using a fully endoscopic technique and a very experienced surgeon using a microscopic transsphenoidal technique for pituitary adenoma. J. Neurosurg. 2015, 124, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappabianca, P.; Cavallo, L.M.; Colao, A.; de Divitiis, E. Surgical complications associated with the endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal approach for pituitary adenomas. J. Neurosurg. 2002, 97, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardner, P.A.; Prevedello, D.M.; Kassam, A.B.; Snyderman, C.H.; Carrau, R.L.; Mintz, A.H. The evolution of the endonasal approach for craniopharyngiomas. J. Neurosurg. 2008, 108, 1043–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyderman, C.H.; Gardner, P.A. “How much is enough?” endonasal surgery for olfactory neuroblastoma. Skull Base 2010, 20, 309–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, G.; Tang, C.; Zhong, C.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Li, L.; Yang, Y.; Ma, C. Mononostril versus Binostril Endoscopic Transsphenoidal Approach for Pituitary Adenomas: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Jho n = 50 | Cappabianca n = 146 | Linsler n = 218 | Han n = 200 | Eseonu n = 275 | Darwish n = 64 | Oertel n = 55 | Peeters n = 512 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean age | 38 years (14–88 yrs) | 46.06 years (16–74 yrs) | 58 years (23–83 yrs) | 43.8 years (19–71 yrs) | 50.4 years (18–85) | 40 yrs | 55.3 yrs | 48.1 yrs |
| Mean follow-up evaluation period | 6 months | 6 months | 4.61 yrs | 4–42 months | 6 months | 4–72 months | 6.2 yrs | 1–10 yrs |
| Pathologies: Non-functioning adenomas | 38% | 55% | 68% | 60.5% | 63.5% | 39% | 58% | 62.6% |
| GH-secreting adenomas | 0 | 25% | 13% | 16.5% | 17.2% | 18% | 0 | 16.4% |
| Prolactinomas | 34% | 9.5% | 4% | 12.5% | 2.8% | 17% | 0 | 8% |
| ACTH-secreting adenomas | 16% | 9.5% | 2.5% | 8.5% | 15.3% | 26% | 0 | 12.5% |
| TSH-secreting adenomas | 0 | 1% | 0 | 1% | 0.75% | 0 | 0 | 0.5% |
| Craniopharyngioma | 2% | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 9% | 0 |
| Clivus chordoma | 2% | 0 | 1.5% | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7% | 0 |
| Rathke’s cleft cyst | 2% | 0 | 5% | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6% | 0 |
| Meningiomas | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 11% | 0 |
| Others | 6% | 0 | 6% | 0 | 0 | 0 | 9% | 0 |
| Radicality | Jho n = 50 | Cappabianca n = 146 | Linsler n = 218 | Han n = 200 | Eseonu n = 275 | Darwish n = 64 | Oertel n = 55 | Peeters n = 512 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All non-functioning adenomas | 84% | 56% | 88% | - | 85.1% | 74% | 93% | - |
| Non-invasive adenomas | 100% | - | 91% | 94% | - | 78% | - | 87% |
| Invasive and giant adenomas | 0/3 | - | 0% | 0% | - | 13% | - | 75% |
| Prolactinomas | 77% | 89% | 87.5% | 85% | n.a. | - | ||
| ACTH adenoma | 75% | 77% | 84% | 81% | 87.9% | 82% | - | 81% |
| GH adenoma | - | 64% | 85% | 72% | 87.9% | 54% | - | 58% |
| Rathke’s cleft cyst | 100% | - | 83% | - | - | - | 100% | - |
| Meningiomas | - | - | - | - | - | - | 83% | - |
| Craniopharyngiomas | - | - | - | - | - | - | 100% | - |
| Others | - | - | - | - | - | - | 100% | - |
| Recurrence rate | n.a. | n.a. | 2.2% | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | 4% | 8.2% |
| Jho n = 50 | Cappabianca n = 146 | Linsler n = 218 | Han n = 200 | Eseonu n = 275 | Darwish n = 64 | Oertel n = 55 | Peeters n = 512 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sellar hematoma | 0 | 1% | 0.5% | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | 4% | 0 |
| CSF fistula | 4% | 2% | 3.2% | 3.5% | 3.6% | 1.4% | 2% | 4.1% |
| Meningitis | 0 | 1% | 1.4% | 0.5% | 1% | 1.4% | 2% | n.a. |
| Worsening of visual deficit | 0 | 1% | 0.5% | 0 | 5.6% | 0 | 2% | 2% |
| Brain infarction | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.7% | 0 | 0% | 0 |
| ICA injury | 0 | 1% | 0 | 0.5% | 0.4% | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| CN VI palsy | 0 | 1% | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Sinusitis | 0 | 2% | 0 | 6% | 0.4% | n.a. | 0 | n.a. |
| Epistaxis | n.a. | 1.4% | 0 | 6% | 0.4% | 1.4% | 0 | n.a. |
| Cacosmia | n.a. | 1.4% | 1.2% | 6% | 0.4% | 0 | 0 | 2.1% |
| Diabetes insipidus | n.a. | n.a. | 0.4% | 5% | 0.7% | 1.4% | 3% | 3.7% |
| Hormonal dysfunction | n.a | n.a. | n.a. | 3% | 4.8% | 9.3% | 4% | n.a. |
| Death | n.a. | 0.7% | 0 | 0.5% | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Jho n = 50 | Cappabianca n = 146 | Linsler n = 218 | Han n = 200 | Eseonu n = 275 | Darwish n = 64 | Oertel n = 55 | Peeters n = 512 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Speculum | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | No/yes |
| Endoscope holding device | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| 2-hand technique | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| 3-/4-hand technique | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | No |
| Neuronavigation | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Lateral fluoroscopy | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | Yes |
| Mean surgical time | n.a. | n.a. | 87 min | 115 min | 161.6 min | 168 min | 90.1 min | 118 min |
| n = 250 | Binostril n = 50 | Mononostril n = 200 | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| (A) | |||
| Gross total resection rate | 84% | 87% | n.s. |
| Hormonal remission | 79% | 81% | n.s. |
| Visual improvement after surgery | 87.5% | 91% | n.s. |
| CSF leak | 4% | 3.5% | n.s. |
| Diabetes insipidus | 2% | 4.5% | n.s. |
| Pituitary insufficiency | 2% | 2.5% | n.s. |
| Surgical time (min) | 156 ± 17.3 | 115 ± 15.2 | s. |
| Blood loss | 150 ± 18.3 | 94 ± 20.5 | s. |
| Recurrence rate | None | None | |
| Progression | None | None | |
| (B) | |||
| surgical time (min) | 123 ± 40 | 93 ± 28 | n.s. |
| CSF fistula intraoperatively | 6 | 4 | n.s. |
| Restricting by nasal speculum | 0 | 5 | n.s. |
| Nasal packing required | 0 | 4 | n.s. |
| Resolution of preoperative pituitary insufficiency | 1/10 | 1/9 | n.s. |
| New postoperative pituitary insufficiency | 3 | 1 | n.s. |
| ACTH deficiency | 3 | 1 | n.s. |
| Resolution of visual field deficits | 7/8 | 5/6 | n.s. |
| Residual tumor | 4 | 2 | n.s. |
| Diabetes insipidus | 1 | 0 | n.s. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Linsler, S.; Reyes Medina, B.; Saffour, S. Endoscopic Transsphenoidal Sellar Surgery via One Nostril: Own Experience and Systematic Review of the Literature. Life 2025, 15, 1233. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081233
Linsler S, Reyes Medina B, Saffour S. Endoscopic Transsphenoidal Sellar Surgery via One Nostril: Own Experience and Systematic Review of the Literature. Life. 2025; 15(8):1233. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081233
Chicago/Turabian StyleLinsler, Stefan, Bernardo Reyes Medina, and Safwan Saffour. 2025. "Endoscopic Transsphenoidal Sellar Surgery via One Nostril: Own Experience and Systematic Review of the Literature" Life 15, no. 8: 1233. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081233
APA StyleLinsler, S., Reyes Medina, B., & Saffour, S. (2025). Endoscopic Transsphenoidal Sellar Surgery via One Nostril: Own Experience and Systematic Review of the Literature. Life, 15(8), 1233. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081233





