IgA Nephropathy in Native Kidneys: Oxford and Banff Classifications Reveal Distinct Profiles and Predict Outcomes in Pediatric and Adult Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Clinical and Laboratory Data
2.3. Treatment Protocols
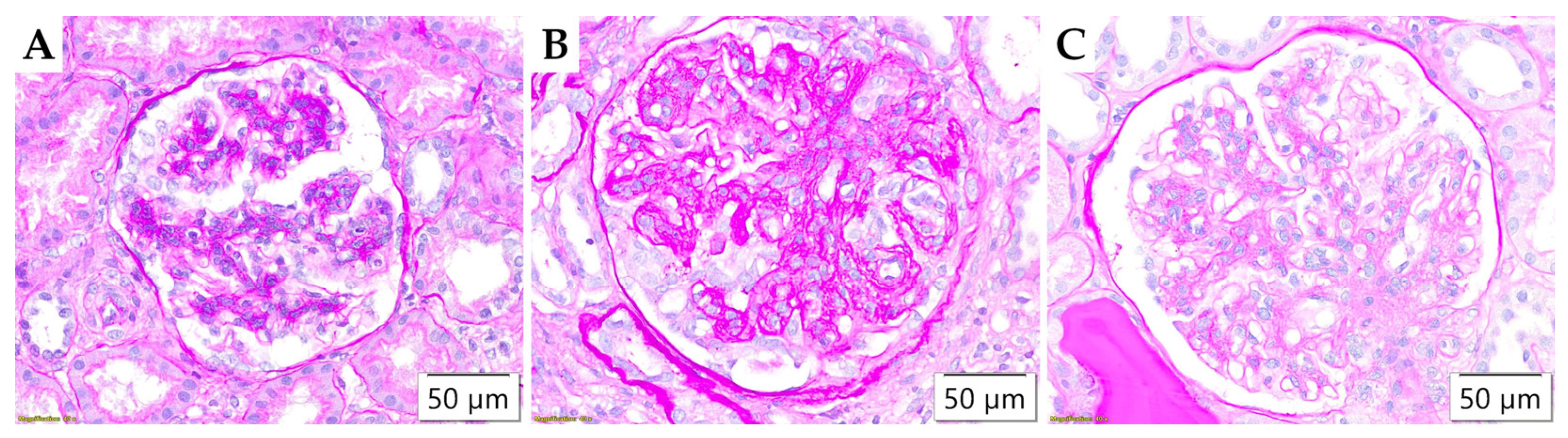
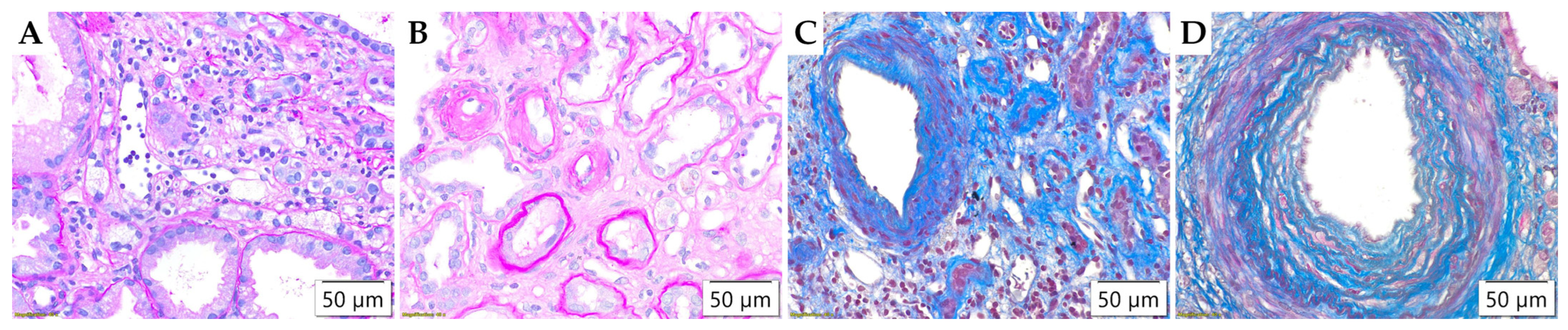
2.4. Pathohistological Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Parameters in Pediatric and Adult IgA Nephropathy
3.2. Pathohistological Parameters
3.3. Correlation of Clinical Data Collected at the Time of Biopsy with Pathohistological Parameters
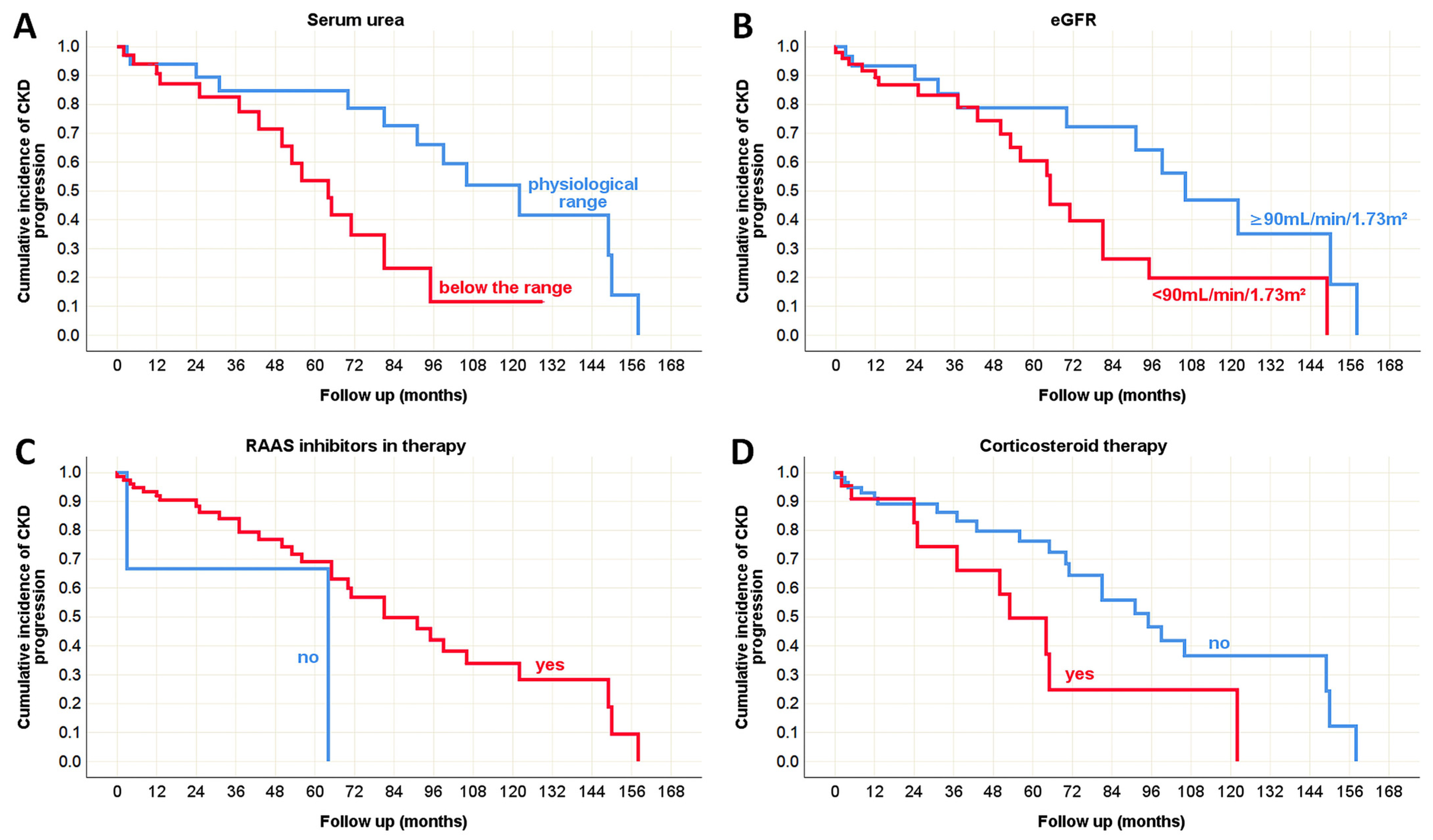
3.4. Clinical Predictors of the Outcome in Pediatric and Adult Onset IgA Nephropathy in Native Kidneys
3.5. Pathohistological Predictors of the Outcome in Pediatric and Adult Onset IgA Nephropathy in Native Kidneys
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chadban, S.J.; Atkins, R.C. Glomerulonephritis. Lancet 2005, 365, 1797–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Abbas, A.K.; Aster, J.C.; Deyrup, A.T.; Das, A. Robbins & Kumar Basic Pathology, 11th ed.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2023; pp. 462–464. [Google Scholar]
- Schena, F.P.; Nistor, I. Epidemiology of IgA Nephropathy: A Global Perspective. Semin. Nephrol. 2018, 38, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattrapornpisut, P.; Avila-Casado, C.; Reich, H.N. IgA Nephropathy: Core Curriculum 2021. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2021, 78, 429–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamei, K.; Harada, R.; Hamada, R.; Sakai, T.; Hamasaki, Y.; Hataya, H.; Ito, S.; Ishikura, K.; Honda, M. Proteinuria during Follow-Up Period and Long-Term Renal Survival of Childhood IgA Nephropathy. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadola, L.; Cabrera, M.J.; Garau, M.; Coitiño, R.; Aunchayna, M.H.; Noboa, O.; Alvarez, M.A.; Balardini, S.; Desiderio, G.; Dibello, N.; et al. Long-term follow-up of an IgA nephropathy cohort: Outcomes and risk factors. Ren. Fail. 2023, 45, 2152694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luciano, R.L.; Moeckel, G.W. Update on the Native Kidney Biopsy: Core Curriculum 2019. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2019, 73, 404–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fogo, A.B.; Lusco, M.A.; Najafian, B.; Alpers, C.E. AJKD Atlas of Renal Pathology: IgA nephropathy. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2015, 66, e33–e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Trimarchi, H.; Barratt, J.; Cattran, D.C.; Cook, H.T.; Coppo, R.; Haas, M.; Liu, Z.H.; Roberts, I.S.; Yuzawa, Y.; Zhang, H.; et al. Classification Working Group of the International IgA Nephropathy Network and the Renal Pathology Society; Conference Participants. Oxford Classification of IgA nephropathy 2016: An update from the IgA Nephropathy Classification Working Group. Kidney Int. 2017, 91, 1014–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizu, A.; Kawakami, T.; Kanno, H.; Takahashi, K.; Miyazaki, T.; Ikeda, E.; Oharaseki, T.; Ogawa, Y.; Onimaru, M.; Kurata, M.; et al. Expert perspectives on pathological findings in vasculitis. Mod. Rheumatol. 2023, 33, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parums, D.V. A Review of IgA Vasculitis (Henoch-Schonlein Purpura) Past, Present, and Future. Med. Sci. Monit. 2024, 30, e943912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Li, Y.; Wu, X. IgA vasculitis update: Epidemiology, pathogenesis, and biomarkers. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 921864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roufosse, C.; Simmonds, N.; Clahsen-van Groningen, M.; Haas, M.; Henriksen, K.J.; Horsfield, C.; Loupy, A.; Mengel, M.; Perkowska-Ptasińska, A.; Rabant, M.; et al. A 2018 Reference Guide to the Banff Classification of Renal Allograft Pathology. Transplantation 2018, 102, 1795–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plüß, M.; Hakroush, S.; Niebusch, N.; Tampe, B.; Korsten, P. Histopathological analysis of lupus nephritis incorporating Banff criteria emphasizes the importance of tubulointerstitial changes for creatinine and proteinuria at 12 months after renal biopsy. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floege, J.; Rauen, T.; Tang, S.C.W. Current treatment of IgA nephropathy. Semin. Immunopathol. 2021, 43, 717–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Glomerular Diseases Work Group. KDIGO 2021 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Glomerular Diseases. Kidney Int. 2021, 100, S1–S276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, N.; Walz, G.; Schneider, J. Effect of Cyclophosphamide and Glucocorticoid Therapy in IgA Nephropathy: A Single-Center Retrospective Analysis. Kidney360 2022, 3, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitcher, D.; Braddon, F.; Hendry, B.; Mercer, A.; Osmaston, K.; Saleem, M.A.; Steenkamp, R.; Wong, K.; Turner, A.N.; Wang, K.; et al. Long-Term Outcomes in IgA Nephropathy. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2023, 18, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Shi, S.; Zhao, J.; Wang, C.; Liu, Z.; Fu, S.; Chen, N.; Li, G.; Wang, L.; Ni, Z.; et al. Prognosis of IgA nephropathy patient with proteinuria remission by supportive therapy: Cohort from screening failed Chinese patients in TESTING study. Ren. Fail. 2024, 46, 2398826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbour, S.J.; Espino-Hernandez, G.; Reich, H.N.; Coppo, R.; Roberts, I.S.; Feehally, J.; Herzenberg, A.M.; Cattran, D.C.; Oxford Derivation, North American Validation and VALIGA Consortia; Oxford Derivation North American Validation and VALIGA Consortia. The MEST score provides earlier risk prediction in lgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2016, 89, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; You, J.; Qu, Z.; Yuan, S.; Peng, Y.; Liu, F.; Liu, H. Tubular atrophy/interstitial fibrosis scores of Oxford classification combinded with proteinuria level at biopsy provides earlier risk prediction in lgA nephropathy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeter, H.H.; Gonul, I.; Guz, G.; Helvaci, O.; Korucu, B.; Akcay, O.F.; Derici, U.; Arinsoy, T. Combining clinical features and MEST-C score in IgA nephropathy may be a better determinant of kidney survival. Rom. J. Intern. Med. 2020, 58, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhai, Z.; Zhao, C.; Tang, L. The predictive value of Oxford MEST-C classification to immunosuppressive therapy of IgA nephropathy. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2022, 54, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaihan, A.B.; Yasuda, Y.; Katsuno, T.; Kato, S.; Imaizumi, T.; Ozeki, T.; Hishida, M.; Nagata, T.; Ando, M.; Tsuboi, N.; et al. The Japanese Histologic Classification and T-score in the Oxford Classification system could predict renal outcome in Japanese IgA nephropathy patients. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2017, 21, 986–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, H.P.; Vogt, B.A. Nephrology and Urology. In Nelson Essentials of Pediatrics, 9th ed.; Marcdante, K.J., Kliegman, R.M., Schuh, A.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2023; pp. 636–637. [Google Scholar]
- Dietzen, D.J.; Willrich, M.A.V. Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins. In Tietz Textbook of Laboratory Medicine, 7th ed.; Rifai, N., Chiu, R.W.K., Young, I., Burnham, C.A.D., Wittwer, C.T., Eds.; Elsevier: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2023; pp. 349.e1–349.e42. [Google Scholar]
- Lamb, E.J.; Jones, G.R.D. Kidney Function Test. In Tietz Textbook of Laboratory Medicine, 7th ed.; Rifai, N., Chiu, R.W.K., Young, I., Burnham, C.A.D., Wittwer, C.T., Eds.; Elsevier: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2023; pp. 352.e1–352.e60. [Google Scholar]
- Tesař, V. SGLT2 inhibitors in non-diabetic kidney disease. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2022, 31, 105–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heerspink, H.J.L.; Stefánsson, B.V.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Chertow, G.M.; Greene, T.; Hou, F.F.; Mann, J.F.E.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Lindberg, M.; Rossing, P.; et al. DAPA-CKD Trial Committees and Investigators. Dapagliflozin in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1436–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozzi, C.; Bolasco, P.G.; Fogazzi, G.B.; Andrulli, S.; Altieri, P.; Ponticelli, C.; Locatelli, F. Corticosteroids in IgA nephropathy: A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 1999, 353, 883–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manno, C.; Torres, D.D.; Rossini, M.; Pesce, F.; Schena, F.P. Randomized controlled clinical trial of corticosteroids plus ACE-inhibitors with long-term follow-up in proteinuric IgA nephropathy. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2009, 24, 3694–3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Li, G.; Jiang, L.; Singh, A.K.; Wang, H. Combination therapy of prednisone and ACE inhibitor versus ACE-inhibitor therapy alone in patients with IgA nephropathy: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2009, 53, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.Z.; Guo, L.; Dong, J.F.; Shi, S.F.; Liu, L.J.; Wang, J.W.; Sui, G.L.; Zhou, X.J.; Xing, Y.; Li, H.X.; et al. Persistent Hematuria and Kidney Disease Progression in IgA Nephropathy: A Cohort Study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 76, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhou, J.; Rong, L.; Feng, S.; Zhong, F.; Sun, S.; Zhang, D.; Xia, Z.; et al. Are children with IgA nephropathy different from adult patients? Pediatr. Nephrol. 2024, 39, 2403–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearney, P.M.; Whelton, M.; Reynolds, K.; Muntner, P.; Whelton, P.K.; He, J. Global burden of hypertension: Analysis of worldwide data. Lancet 2005, 365, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Xu, Y.; Pan, X.; Xu, J.; Ding, Y.; Sun, X.; Song, X.; Ren, Y.; Shan, P.F. Global, regional, and national burden and trend of diabetes in 195 countries and territories: An analysis from 1990 to 2025. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamano, C.; Shimizu, A.; Joh, K.; Hashiguchi, A.; Hisano, S.; Katafuchi, R.; Kawamura, T. Japan IgA nephropathy prospective cohort Study Group. A cross-sectional study in patients with IgA nephropathy of correlations between clinical data and pathological findings at the time of renal biopsy: A Japanese prospective cohort study. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2021, 25, 509–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, B.; Liu, W.H.; Lin, Y.; Li, Q.; Yu, D.R.; Jiang, F.; Tang, X.L.; Du, Y.Y.; Yin, J.Z.; Li, X.F.; et al. Renal Interstitial Inflammation Predicts Nephropathy Progression in IgA Nephropathy: A Two-Center Cohort Study. Am. J. Nephrol. 2022, 53, 455–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.T.; Park, T.I.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, M.S.; Park, S.H.; Lim, J.H.; Kang, Y.N.; Kim, D.; Han, M.H. Significance of intrarenal vascular lesions in Ig A nephropathy prognosis. BMC Nephrol. 2024, 25, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Xiao, T.; Yu, Z.; Huang, Y.; He, T.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Xiong, J.; Zhao, J. Arteriolar hyalinosis and renal outcomes in patients with immunoglobulin A nephropathy. Ren. Fail. 2022, 44, 994–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusco, M.A.; Najafian, B.; Alpers, C.E.; Fogo, A.B. AJKD Atlas of Renal Pathology: Arterionephrosclerosis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2016, 67, e21–e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Clinical Parameters | Population | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pediatric (n = 105) | Adult (n = 148) | |||
| Sex [n (%)] | Male | 71 (42%) | 97 (58%) | 0.730 (χ2 test) |
| Female | 34 (40%) | 51 (60%) | ||
| IgA vasculitis signs and symptoms [n (%)] | Absent | 53 (29%) | 127 (71%) | <0.001 * (χ2 test) |
| Present | 52 (71%) | 21 (29%) | ||
| Hematuria [n (%)] | Absent | 14 (28%) | 37 (72%) | <0.001 * (χ2 test) |
| Microscopic | 40 (41%) | 90 (69%) | ||
| Macroscopic | 48 (72%) | 19 (28%) | ||
| Proteinuria [n (%)] | Absent | 15 (52%) | 14 (48%) | 0.383 (χ2 test) |
| Subnephrotic | 54 (38%) | 87 (62%) | ||
| Nephrotic | 34 (43%) | 45 (57%) | ||
| Serum total protein (g/L) | 65 ± 9.8 69.5 (39–74) | 65 ± 9.5 66 (33–84) | 0.901 (t-test) | |
| Serum albumin (g/L) | 37 ± 10.1 40 (7–48) | 38 ± 8.1 40 (10–51) | 0.921 (MW) | |
| Serum urea (mmol/L) | 6.6 ± 3.86 5.4 (2.4–17.1) | 8.8 ± 4.89 7.8 (2.0–31.5) | 0.017 * (MW) | |
| Serum creatinine (μmol/L) | 91 ± 78.5 65 (29–455) | 145 ± 99.6 115 (41–771) | <0.001 * (MW) | |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73m2) | 117 ± 44.3 134 (17–182) | 71 ± 37.2 62 (8–192) | <0.001 * (t-test) | |
| Chronic kidney disease stage [n (%)] | G1 | 25 (35%) | 47 (65%) | 0.012 * (χ2 test) |
| G2 | 6 (27%) | 16 (73%) | ||
| G3a | 2 (7%) | 26 (93%) | ||
| G3b | 2 (12%) | 14 (88%) | ||
| G4 | 1 (7%) | 14 (93%) | ||
| G5 | 0 (0%) | 5 (100%) | ||
| Hypertension [n (%)] | Absent | 99 (60%) | 65 (40%) | <0.001 * (χ2 test) |
| Present | 6 (7%) | 83 (93%) | ||
| Diabetes mellitus [n (%)] | Absent | 105 (43%) | 140 (57%) | 0.022 * (Fisher) |
| Present | 0 (0%) | 8 (100%) | ||
| SGLT2 inhibitors in therapy [n (%)] | No | 61 (58%) | 45 (42%) | <0.001 * (χ2 test) |
| Yes | 1 (2%) | 49 (98%) | ||
| RAAS inhibitors in therapy [n (%)] | No | 21 (72%) | 8 (28%) | <0.001 * (χ2 test) |
| Yes | 41 (32%) | 86 (68%) | ||
| Corticosteroids in therapy [n (%)] | No | 41 (38%) | 67 (62%) | 0.495 (χ2 test) |
| Yes | 21 (44%) | 27 (56%) | ||
| Oxford Classification Parameters | Population | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pediatric | Adult | |||
| Mesangial hypercellularity [n (%)] | M0 | 1 (100%) | 0 (0%) | 0.433 (Fisher) |
| M1 | 83 (43%) | 110 (57%) | ||
| Endocapillary hypercellularity [n (%)] | E0 | 50 (44%) | 65 (56%) | 0.952 (χ2 test) |
| E1 | 34 (43%) | 45 (57%) | ||
| Segmental glomerulosclerosis/adhesion [n (%)] | S0 | 45 (53%) | 40 (47%) | 0.017 * (χ2 test) |
| S1 | 39 (36%) | 70 (64%) | ||
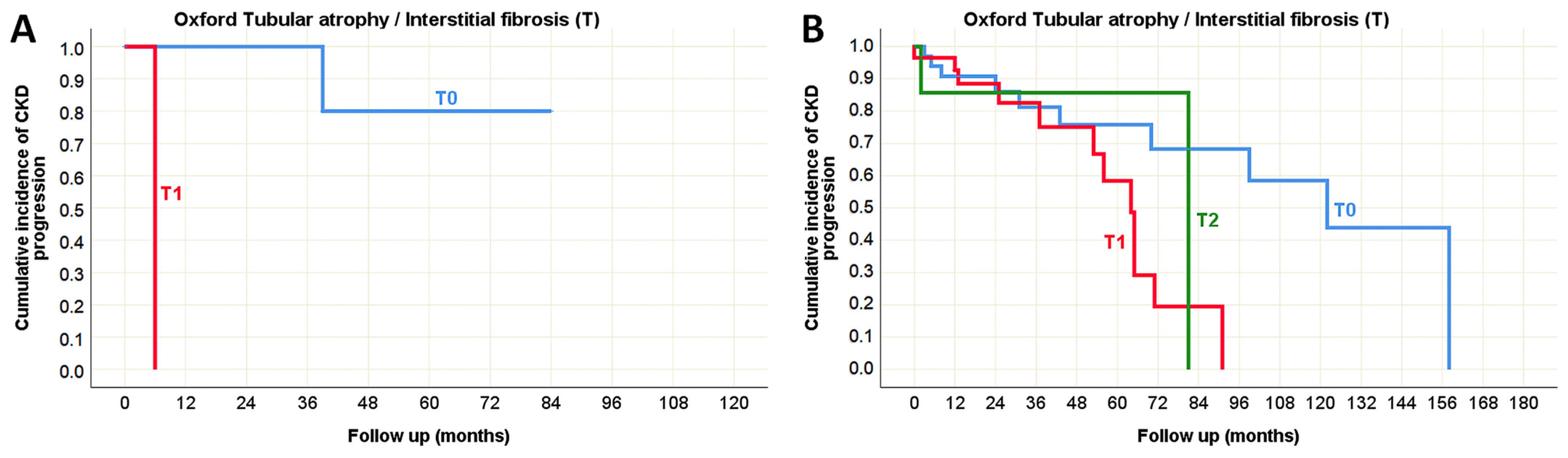
| Tubular atrophy/interstitial fibrosis [n (%)] | T0 | 81 (56%) | 63 (44%) | <0.001 * (χ2 test) |
| T1 | 3 (8%) | 37 (92%) | ||
| T2 | 0 (0%) | 10 (100%) | ||
| Cellular/fibrocellular crescents [n (%)] | C0 | 47 (39%) | 73 (61%) | 0.057 (χ2 test) |
| C1 | 31 (56%) | 24 (44%) | ||
| C2 | 6 (32%) | 13 (68%) | ||
| Banff Classification Parameters | Population | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pediatric | Adult | |||
| Glomerulitis (g) [n (%)] | g0 | 49 (39%) | 77 (61%) | 0.552 (χ2 test) |
| g1 | 26 (48%) | 28 (52%) | ||
| g2 | 11 (39%) | 17 (61%) | ||
| g3 | 0 (0%) | 1 (100%) | ||
| GBM double contours (cg) [n (%)] | cg0 | 27 (38%) | 45 (62%) | 0.047 * (χ2 test) |
| cg1 | 57 (47%) | 65 (53%) | ||
| cg2 | 2 (14%) | 12 (86%) | ||
| cg3 | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | ||
| Mesangial matrix expansion (mm) [n (%)] | mm0 | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0.897 (χ2 test) |
| mm1 | 1 (50%) | 1 (50%) | ||
| mm2 | 2 (33%) | 4 (67%) | ||
| mm3 | 83 (41%) | 118 (59%) | ||
| Banff Classification Parameters | Population | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pediatric | Adult | |||
| Tubulitis (t) [n (%)] | t0 | 85 (47%) | 96 (53%) | <0.001 * (χ2 test) |
| t1 | 0 (0%) | 18 (100%) | ||
| t2 | 1 (11%) | 8 (89%) | ||
| t3 | 0 (0%) | 2 (100%) | ||
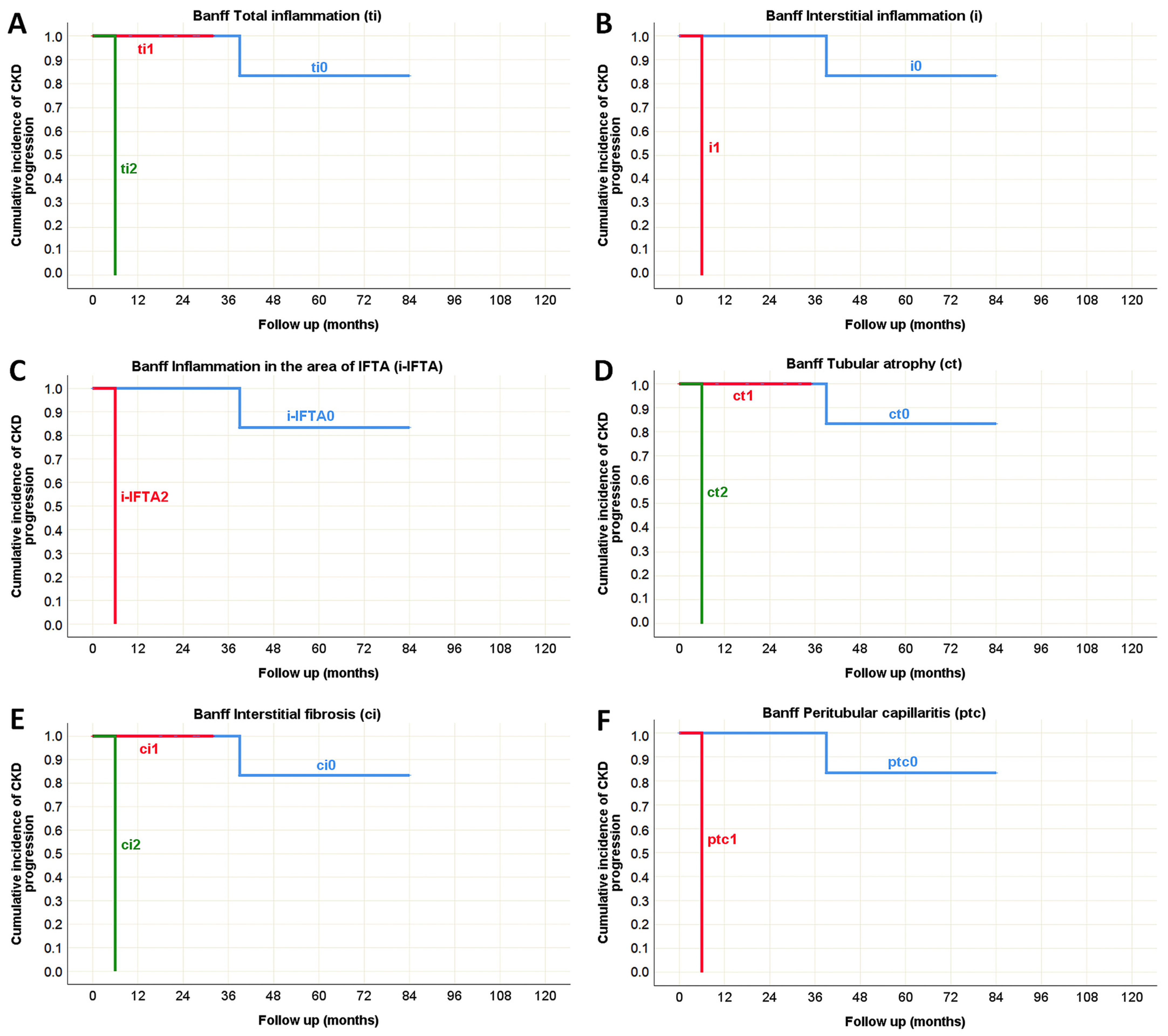
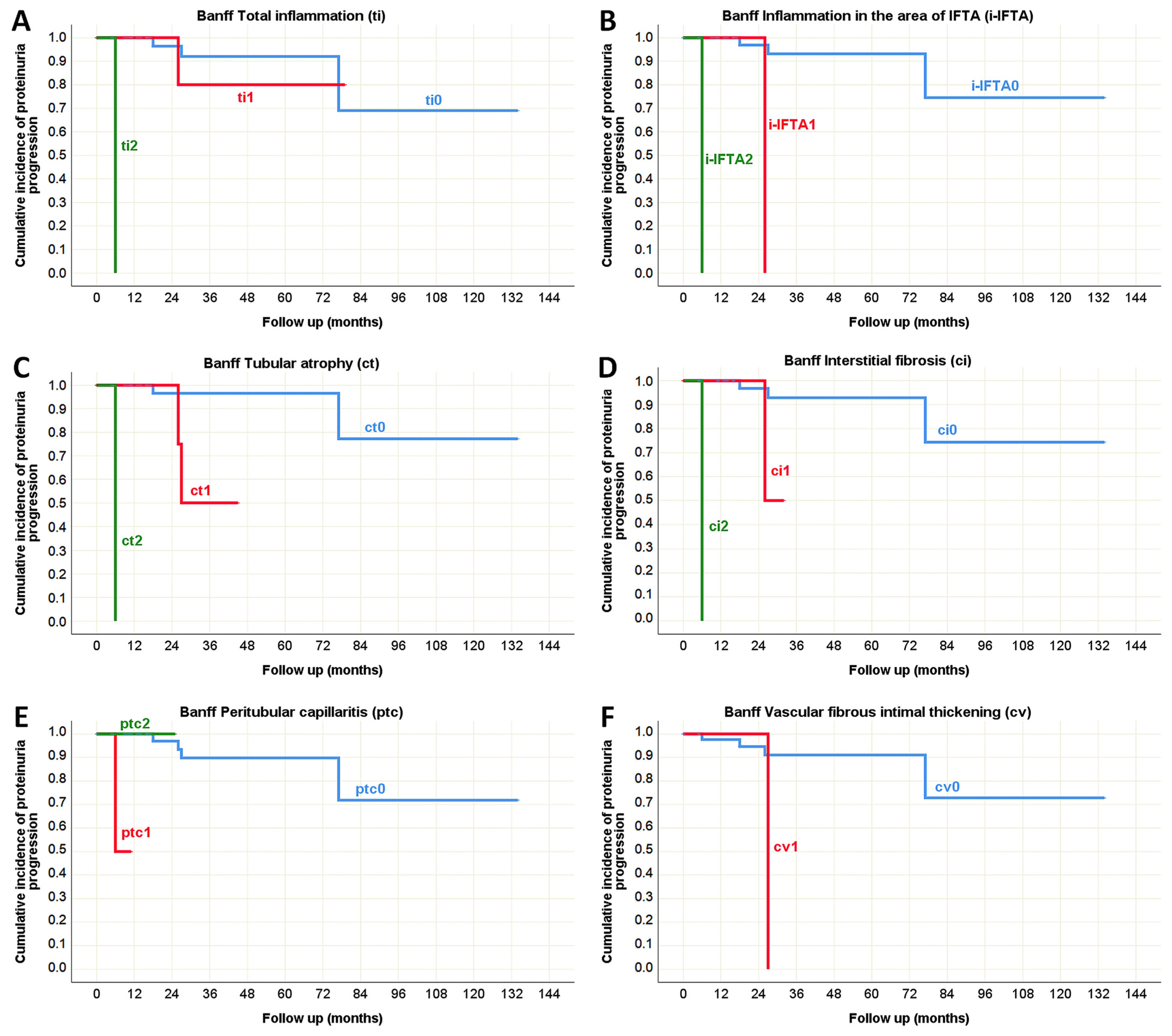
| Total inflammation (ti) [n (%)] | ti0 | 61 (63%) | 36 (37%) | <0.001 * (χ2 test) |
| ti1 | 23 (35%) | 42 (65%) | ||
| ti2 | 2 (6%) | 34 (94%) | ||
| ti3 | 0 (0%) | 12 (100%) | ||
| Interstitial inflammation (i) [n (%)] | i0 | 67 (54%) | 57 (46%) | <0.001 * (χ2 test) |
| i1 | 19 (25%) | 58 (75%) | ||
| i2 | 0 (0%) | 8 (100%) | ||
| i3 | 0 (0%) | 1 (100%) | ||
| Inflammation in the area of IFTA (i-IFTA) [n (%)] | i-IFTA0 | 78 (55%) | 64 (45%) | <0.001 * (χ2 test) |
| i-IFTA1 | 7 (14%) | 45 (86%) | ||
| i-IFTA2 | 1 (7%) | 14 (93%) | ||
| i-IFTA3 | 0 (0%) | 1 (100%) | ||
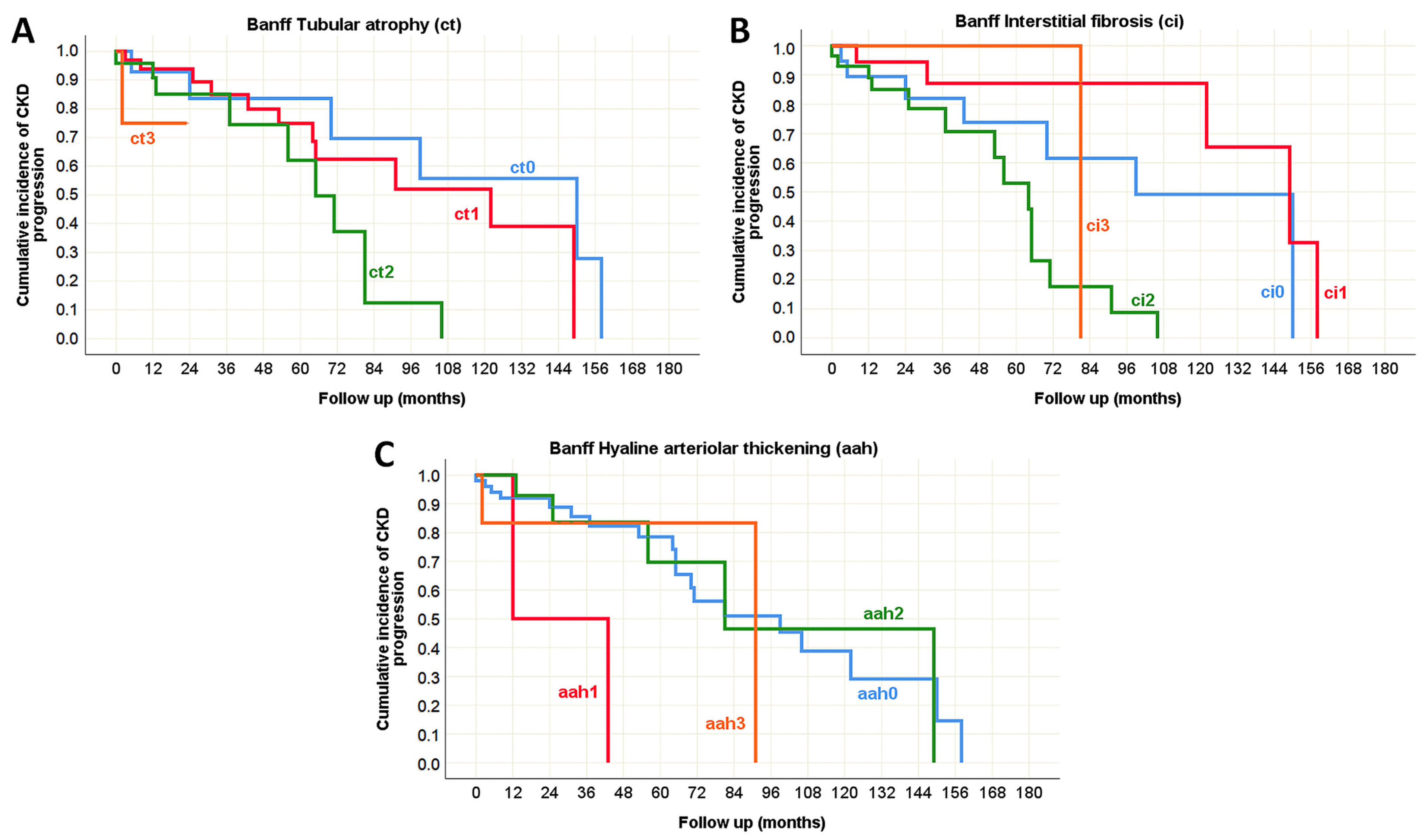
| Tubular atrophy (ct) [n (%)] | ct0 | 67 (72%) | 26 (28%) | <0.001 * (χ2 test) |
| ct1 | 17 (22%) | 60 (78%) | ||
| ct2 | 2 (6%) | 34 (94%) | ||
| ct3 | 0 (0%) | 4 (100%) | ||
| Interstitial fibrosis (ci) [n (%)] | ci0 | 70 (64%) | 39 (36%) | <0.001 * (χ2 test) |
| ci1 | 14 (30%) | 32 (70%) | ||
| ci2 | 2 (5%) | 38 (95%) | ||
| ci3 | 0 (0%) | 15 (100%) | ||
| Banff Classification Parameter | Population | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pediatric | Adult | |||
| Peritubular capillaritis (ptc) [n (%)] | ptc0 | 82 (45%) | 100 (55%) | 0.022 * (χ2 test) |
| ptc1 | 2 (13%) | 13 (87%) | ||
| ptc2 | 2 (17%) | 10 (83%) | ||
| ptc3 | 0 (0%) | 1 (100%) | ||
| Vascular fibrous intimal thickening (cv) [n (%)] | cv0 | 83 (46%) | 99 (54%) | 0.004 * (χ2 test) |
| cv1 | 2 (25%) | 6 (75%) | ||
| cv2 | 0 (0%) | 9 (100%) | ||
| cv3 | 1 (9%) | 10 (91%) | ||
| Arteriolar hyalinosis (ah) [n (%)] | ah0 | 84 (51%) | 82 (49%) | <0.001 * (χ2 test) |
| ah1 | 1 (6%) | 17 (94%) | ||
| ah2 | 1 (8%) | 11 (92%) | ||
| ah3 | 0 (0%) | 14 (100%) | ||
| Hyaline arteriolar thickening (aah) [n (%)] | aah0 | 84 (51%) | 82 (49%) | <0.001 * (χ2 test) |
| aah1 | 1 (33%) | 2 (67%) | ||
| aah2 | 0 (0%) | 27 (100%) | ||
| aah3 | 1 (7%) | 13 (93%) | ||
| Hematuria | Proteinuria | s Total Protein | s Albumin | s Urea | eGFR | CKD Stage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mesangial hypercellularity (M) | rs = 0.178 p = 0.110 | rs = 0.178 p = 0.108 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Endocapillary hypercellularity (E) | rs = 0.049 p = 0.664 | rs = 0.079 p = 0.478 | rs = −0.525 p = 0.119 | rs = −0.437 p = 0.156 | rs = 0.157 p = 0.546 | rs = −0.068 p = 0.737 | rs = 0.249 p = 0.210 |
| Segmental glomerulosclerosis (S) | rs = 0.063 p = 0.575 | rs = 0.280 p = 0.010 * | rs = −0.263 p = 0.463 | rs = −0.077 p = 0.812 | rs = 0.343 p = 0.178 | rs = −0.148 p = 0.463 | rs = 0.125 p = 0.533 |
| Tubular atrophy/Interstitial fibrosis (T) | rs = 0.081 p = 0.468 | rs = 0.042 p = 0.709 | N/A | N/A | rs = 0.408 p = 0.104 | rs = −0.418 p = 0.030 * | rs = 0.500 p = 0.008 * |
| Cellular and fibrocellular crescents (C) | rs = −0.074 p = 0.510 | rs = 0.202 p = 0.067 | rs = −0.775 p = 0.008 * | rs = −0.701 p = 0.011 * | rs = 0.548 p = 0.023 * | rs = −0.221 p = 0.267 | rs = 0.116 p = 0.565 |
| Glomerulitis (g) | rs = 0.042 p = 0.707 | rs = 0.100 p = 0.364 | rs = −0.531 p = 0.114 | rs = −0.109 p = 0.722 | rs = 0.156 p = 0.563 | rs = 0.074 p = 0.713 | rs = 0.169 p = 0.398 |
| GBM double contours (cg) | rs = −0.042 p = 0.706 | rs = 0.105 p = 0.339 | rs = −0.263 p = 0.463 | rs = −0.220 p = 0.470 | rs = −0.084 p = 0.757 | rs = 0.251 p = 0.207 | rs = −0.220 p = 0.270 |
| Mesangial matrix expansion (mm) | rs = 0.178 p = 0.104 | rs = 0.046 p = 0.675 | rs = −0.175 p = 0.628 | rs = −0.387 p = 0.192 | rs = 0.196 p = 0.467 | rs = −0.189 p = 0.345 | rs = 0.136 p = 0.500 |
| Tubulitis (t) | rs = −0.067 p = 0.546 | rs = −0.037 p = 0.738 | N/A | N/A | N/A | rs = −0.277 p = 0.162 | rs = 0.347 p = 0.077 |
| Total inflammation (ti) | rs = 0.104 p = 0.345 | rs = 0.041 p = 0.708 | N/A | rs = −0.464 p = 0.110 | rs = 0.575 p = 0.020 * | rs = −0.691 p < 0.001 * | rs = 0.738 p < 0.001 * |
| Interstitial inflammation (i) | rs = 0.140 p = 0.204 | rs = −0.089 p = 0.416 | N/A | N/A | rs = 0.420 p = 0.105 | rs = −0.551 p = 0.003 * | rs = 0.564 p = 0.002 * |
| Inflammation in the area of IFTA (i-IFTA) | rs = 0.125 p = 0.259 | rs = 0.040 p = 0.718 | N/A | N/A | rs = 0.420 p = 0.105 | rs = −0.418 p = 0.030 * | rs = 0.500 p = 0.008 * |
| Tubular atrophy (ct) | rs = 0.196 p = 0.074 | rs = −0.053 p = 0.628 | rs < 0.001 p = 1.000 | rs = −0.147 p = 0.632 | rs = 0.678 p = 0.004 * | rs = −0.333 p = 0.090 | rs = 0.357 p = 0.068 |
| Interstitial fibrosis (ci) | rs = −0.074 p = 0.505 | rs = 0.019 p = 0.862 | N/A | rs = −0.464 p = 0.110 | rs = 0.575 p = 0.020 * | rs = −0.390 p = 0.044 * | rs = 0.541 p = 0.004 * |
| Peritubular capillaritis (ptc) | rs = 0.126 p = 0.252 | rs = 0.101 p = 0.359 | N/A | N/A | rs = 0.420 p = 0.105 | rs = −0.417 p = 0.031 * | rs = 0.500 p = 0.008 * |
| Vascular fibrous intimal thickening (cv) | rs = 0.019 p = 0.862 | rs = −0.148 p = 0.176 | N/A | rs = 0.193 p = 0.527 | N/A | rs = −0.025 p = 0.901 | rs = −0.136 p = 0.500 |
| Arteriolar hyalinosis (ah) | rs = −0.246 p = 0.024 * | rs = −0.153 p = 0.162 | N/A | N/A | rs = −0.420 p = 0.105 | rs = 0.327 p = 0.096 | rs = −0.136 p = 0.500 |
| Hyaline arteriolar thickening (aah) | rs = −0.246 p = 0.024 * | rs = −0.153 p = 0.162 | N/A | N/A | rs = −0.420 p = 0.105 | rs = 0.327 p = 0.096 | rs = −0.136 p = 0.500 |
| Hematuria | Proteinuria | s Total Protein | s Albumin | s Urea | eGFR | CKD Stage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mesangial hypercellularity (M) | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Endocapillary hypercellularity (E) | rs = 0.142 p = 0.140 | rs = 0.191 p = 0.045 * | rs = −0.210 p = 0.065 | rs = −0.188 p = 0.095 | rs = 0.101 p = 0.347 | rs = −0.271 p = 0.006 * | rs = 0.245 p = 0.013 * |
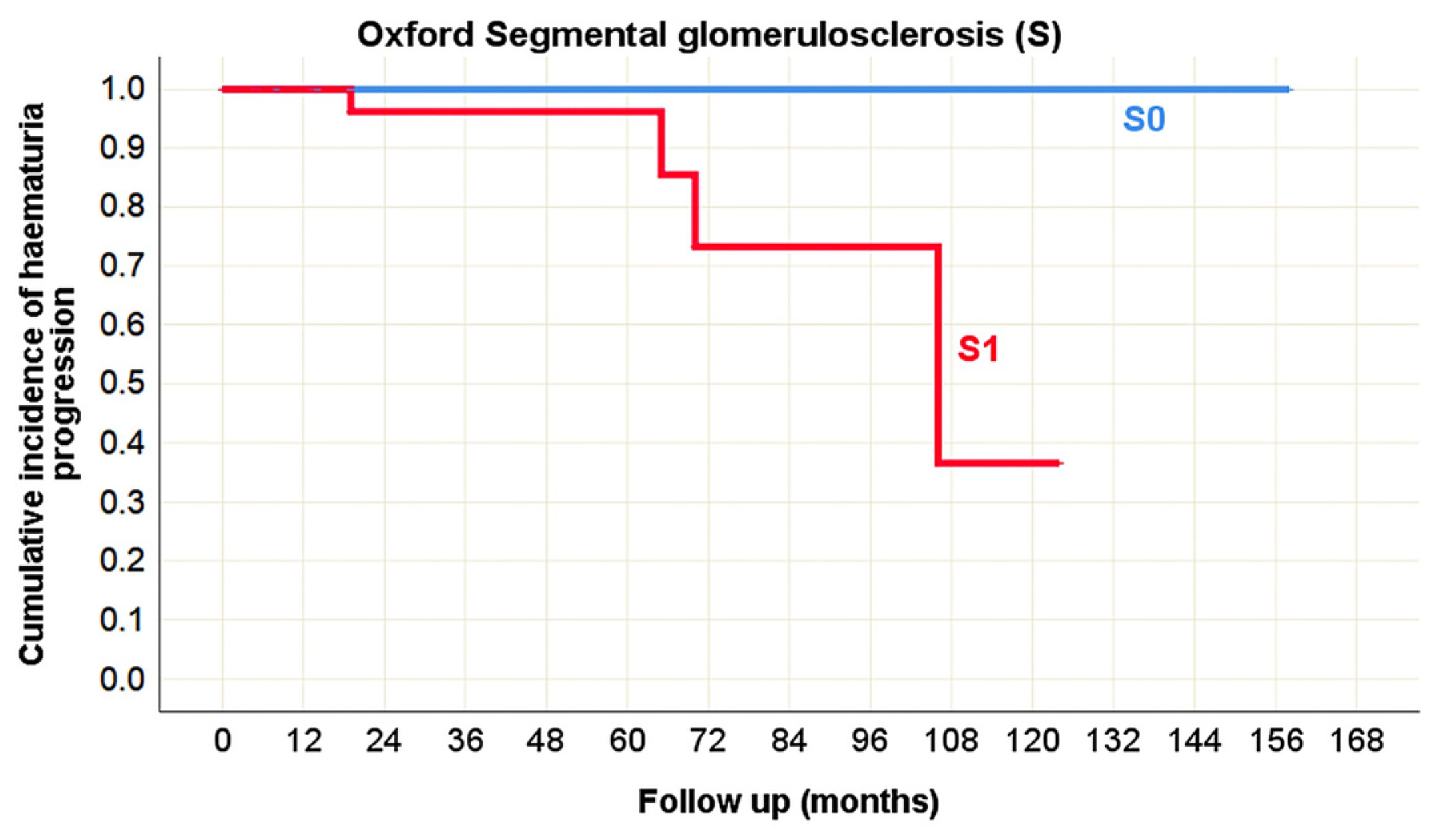
| Segmental glomerulosclerosis (S) | rs = −0.011 p = 0.906 | rs = 0.056 p = 0.562 | rs = −0.005 p = 0.968 | rs = 0.025 p = 0.826 | rs = 0.055 p = 0.612 | rs = −0.234 p = 0.019 * | rs = 0.174 p = 0.080 |
| Tubular atrophy/interstitial fibrosis (T) | rs = −0.032 p = 0.740 | rs = 0.163 p = 0.088 | rs = −0.134 p = 0.241 | rs = −0.222 p = 0.047 * | rs = 0.559 p < 0.001 * | rs = −0.636 p < 0.001 * | rs = 0.667 p < 0.001 * |
| Cellular and fibrocellular crescents (C) | rs = 0.182 p = 0.058 | rs = 0.194 p = 0.042 * | rs = −0.166 p = 0.146 | rs = −0.222 p = 0.048 * | rs = 0.125 p = 0.247 | rs = −0.327 p = 0.001 * | rs = 0.309 p = 0.002 * |
| Glomerulitis (g) | rs = 0.120 p = 0.185 | rs = 0.192 p = 0.033 * | rs = −0.181 p = 0.091 | rs = −0.286 p = 0.007 * | rs = 0.161 p = 0.113 | rs = −0.318 p = 0.001 * | rs = 0.311 p = 0.001 * |
| GBM double contours (cg) | rs = 0.006 p = 0.949 | rs = −0.131 p = 0.151 | rs = −0.021 p = 0.845 | rs = 0.035 p = 0.751 | rs = −0.162 p = 0.110 | rs = 0.065 p = 0.496 | rs = −0.035 p = 0.716 |
| Mesangial matrix expansion (mm) | rs = 0.033 p = 0.718 | rs = 0.160 p = 0.078 | rs = −0.065 p = 0.547 | rs = 0.119 p = 0.270 | rs = 0.068 p = 0.501 | rs = −0.106 p = 0.262 | rs = 0.111 p = 0.238 |
| Tubulitis (t) | rs = −0.025 p = 0.781 | rs = 0.042 p = 0.645 | rs = −0.039 p = 0.719 | rs = −0.105 p = 0.332 | rs = 0.331 p = 0.001 * | rs = −0.418 p < 0.001 * | rs = 0.456 p < 0.001 * |
| Total inflammation (ti) | rs = −0.056 p = 0.540 | rs = 0.066 p = 0.464 | rs = 0.021 p = 0.847 | rs = −0.104 p = 0.335 | rs = 0.554 p < 0.001 * | rs = −0.639 p < 0.001 * | rs = 0.659 p < 0.001 * |
| Interstitial inflammation (i) | rs = 0.042 p = 0.646 | rs = 0.127 p = 0.159 | rs = −0.043 p = 0.691 | rs = −0.113 p = 0.296 | rs = 0.405 p < 0.001 * | rs = −0.538 p < 0.001 * | rs = 0.547 p < 0.001 * |
| Inflammation in the area of IFTA (i-IFTA) | rs = −0.044 p = 0.626 | rs = 0.051 p = 0.570 | rs = −0.013 p = 0.904 | rs = −0.132 p = 0.221 | rs = 0.578 p < 0.001 * | rs = −0.667 p < 0.001 * | rs = 0.655 p < 0.001 * |
| Tubular atrophy (ct) | rs = 0.038 p = 0.678 | rs = 0.057 p = 0.530 | rs = −0.038 p = 0.724 | rs = −0.122 p = 0.258 | rs = 0.431 p < 0.001 * | rs = −0.600 p < 0.001 * | rs = 0.610 p < 0.001 * |
| Interstitial fibrosis (ci) | rs = −0.021 p = 0.820 | rs = 0.069 p = 0.444 | rs = −0.055 p = 0.610 | rs = −0.141 p = 0.191 | rs = 0.569 p < 0.001 * | rs = −0.640 p < 0.001 * | rs = 0.659 p < 0.001 * |
| Peritubular capillaritis (ptc) | rs = −0.092 p = 0.309 | rs = 0.055 p = 0.541 | rs = −0.050 p = 0.642 | rs = −0.141 p = 0.191 | rs = 0.283 p = 0.005 * | rs = −0.401 p < 0.001 * | rs = 0.384 p < 0.001 * |
| Vascular fibrous intimal thickening (cv) | rs = 0.040 p = 0.657 | rs = 0.115 p = 0.202 | rs = −0.102 p = 0.344 | rs = −0.177 p = 0.100 | rs = 0.200 p = 0.047 * | rs = −0.355 p < 0.001 * | rs = 0.362 p < 0.001 * |
| Arteriolar hyalinosis (ah) | rs = −0.143 p = 0.112 | rs = 0.200 p = 0.026 * | rs = −0.094 p = 0.386 | rs = −0.188 p = 0.079 | rs = 0.351 p < 0.001 * | rs = −0.294 p = 0.002 * | rs = 0.259 p = 0.005 * |
| Hyaline arteriolar thickening (aah) | rs = −0.164 p = 0.069 | rs = 0.189 p = 0.036 * | rs = −0.077 p = 0.475 | rs = −0.170 p = 0.113 | rs = 0.331 p = 0.001 * | rs = −0.285 p = 0.002 * | rs = 0.250 p = 0.007 * |
| Population | p | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pediatric | Adult | |||
| CKD progression [n (%)] | progression | 2 (6%) | 32 (94%) | 0.036 * (χ2 test) |
| without change | 13 (29%) | 32 (71%) | ||
| regression | 4 (19%) | 17 (81%) | ||
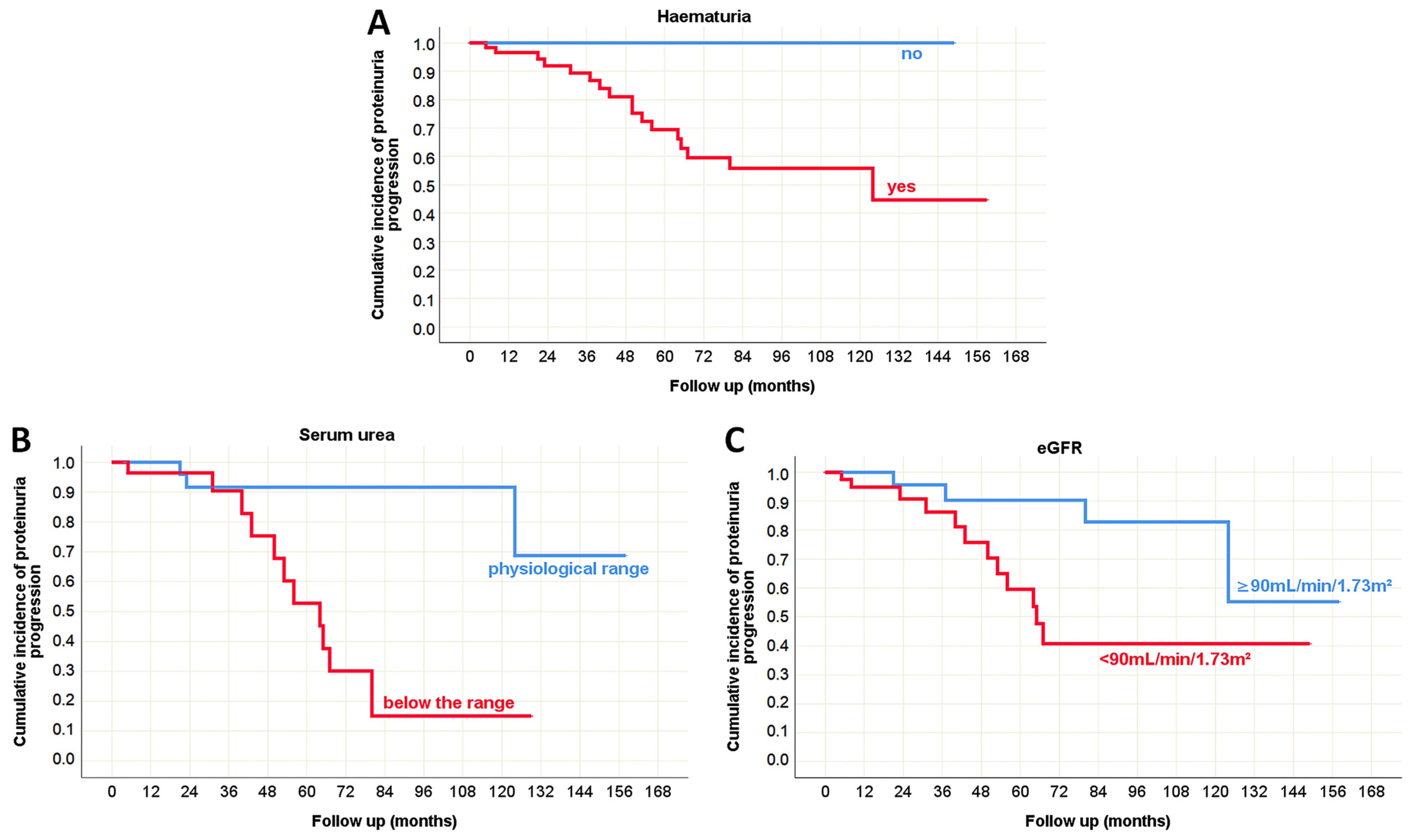
| Proteinuria progression [n (%)] | progression | 5 (23%) | 17 (77%) | 0.196 (χ2 test) |
| without change | 11 (48%) | 12 (52%) | ||
| regression | 35 (40%) | 52 (60%) | ||
| Hematuria progression [n (%)] | progression | 1 (14%) | 6 (86%) | 0.155 (χ2 test) |
| without change | 18 (32%) | 38 (68%) | ||
| regression | 34 (44%) | 43 (56%) | ||
| Pediatric Population | Adult Population | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CKD Progression | Proteinuria Progression | Hematuria Progression | CKD Progression | Proteinuria Progression | Hematuria Progression | |
| Sex | p = 0.599 | p = 0.144 | p = 0.237 | p = 0.313 | p = 0.430 | p = 0.435 |
| IgA vasculitis signs and symptoms | p = 0.397 | p = 0.253 | p = 0.480 | p = 0.792 | p = 0.195 | p = 0.464 |
| Hematuria | p = 0.558 | p = 0.368 | N/A | p = 0.116 | p = 0.040 * | N/A |
| Proteinuria | p = 0.500 | N/A | p = 0.564 | p = 0.244 | N/A | p = 0.418 |
| Serum total protein | N/A | N/A | N/A | p = 0.735 | p = 0.293 | p = 0.317 |
| Serum albumin | N/A | p = 0.527 | N/A | p = 0.273 | p = 0.603 | p = 0.617 |
| Serum urea | p = 0.127 | p = 0.090 | N/A | p = 0.008 * | p < 0.001 * | p = 0.429 |
| eGFR | p = 0.219 | p = 0.965 | N/A | p = 0.041 * | p = 0.019 * | p = 0.237 |
| Hypertension | p = 0.808 | p = 0.710 | N/A | p = 0.348 | p = 0.590 | p = 0.546 |
| Diabetes mellitus | N/A | N/A | N/A | p = 0.836 | p = 0.776 | p = 0.272 |
| SGLT2 inhibitors | N/A | N/A | N/A | p = 0.332 | p = 0.730 | p = 0.538 |
| RAAS inhibitors | p = 0.431 | p = 0.878 | p = 0.480 | p = 0.038 * | p = 0.976 | p = 0.582 |
| Corticosteroids | p = 0.327 | p = 0.631 | p = 0.655 | p = 0.033 * | p = 0.439 | p = 0.077 |
| Pediatric Population | Adult Population | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CKD Progression | proteinuria Progression | Hematuria Progression | CKD Progression | Proteinuria Progression | Hematuria Progression | |
| Oxford classification parameters | ||||||
| Mesangial hypercellularity (M) | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Endocapillary hypercellularity (E) | p = 0.323 | p = 0.313 | p = 0.513 | p = 0.194 | p = 0.260 | p = 0.417 |
| Segmental glomerulosclerosis (S) | p = 0.093 | p = 0.275 | p = 0.414 | p = 0.145 | p = 0.328 | p = 0.025 * |
| Tubular atrophy/Interstitial fibrosis (T) | p < 0.001 * | p = 0.001 * | N/A | p = 0.042 * | p = 0.207 | p = 0.305 |
| Cellular and fibrocellular crescents (C) | p = 0.886 | p = 0.710 | p = 0.472 | p = 0.984 | p = 0.867 | p = 0.837 |
| Banff classification parameters | ||||||
| Glomerulitis (g) | p = 0.506 | p = 0.385 | p = 0.700 | p = 0.378 | p = 0.386 | p = 0.882 |
| GBM double contours (cg) | p = 0.531 | p = 0.969 | N/A | p = 0.777 | p = 0.006 * | p = 0.834 |
| Mesangial matrix expansion (mm) | N/A | p = 0.879 | p = 0.763 | p = 0.713 | p = 0.783 | p = 0.589 |
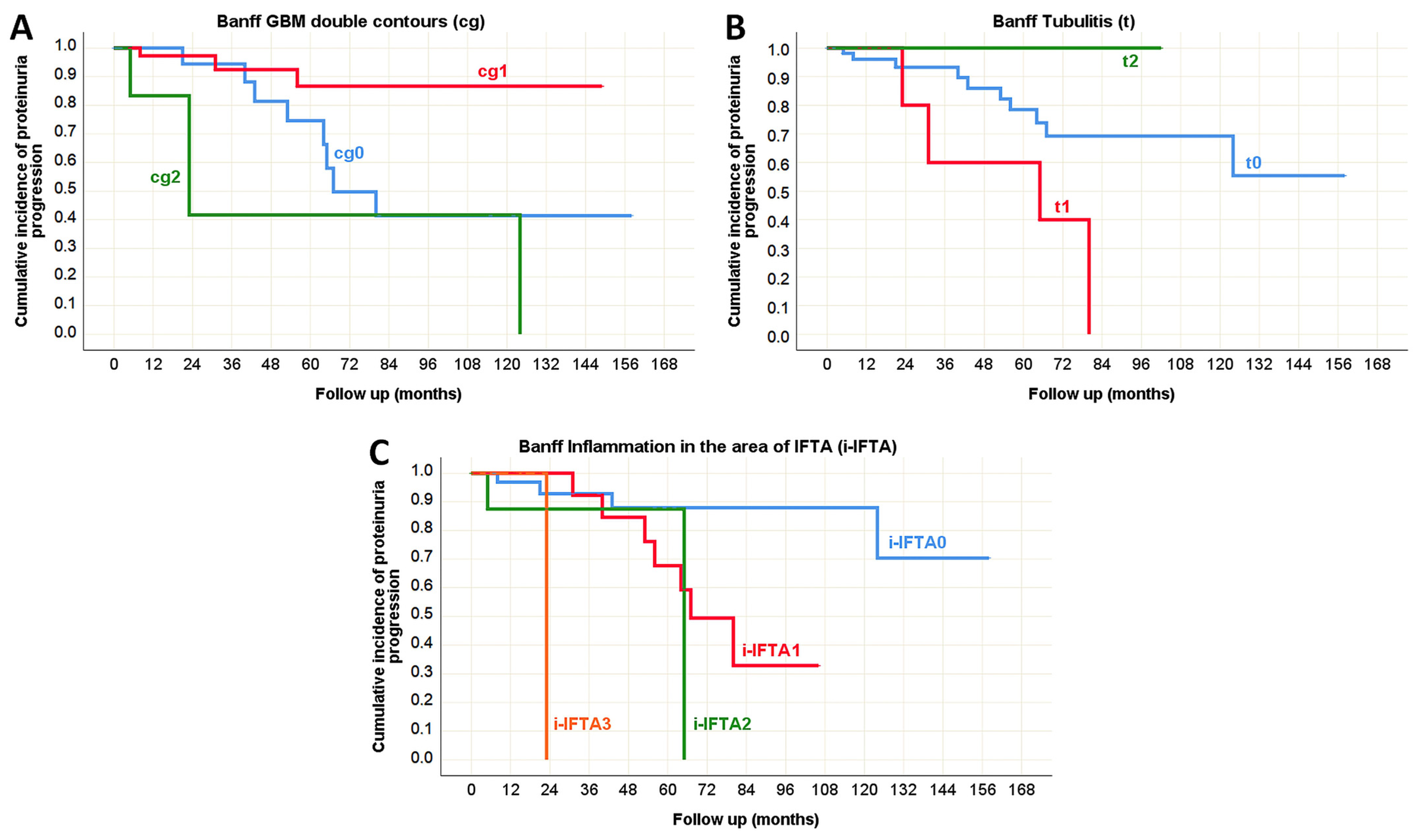
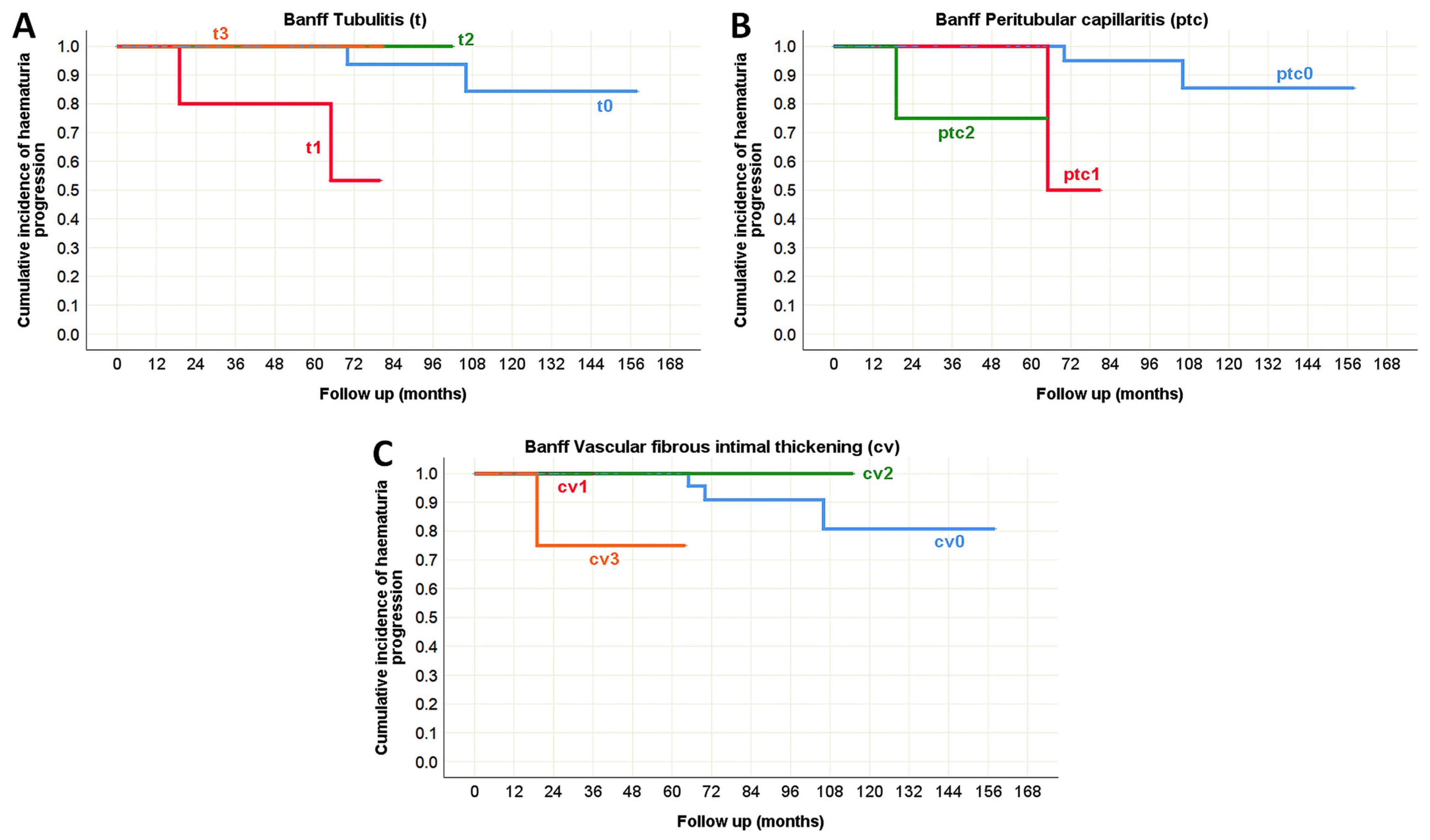
| Tubulitis (t) | N/A | N/A | N/A | p = 0.893 | p = 0.038 * | p = 0.006 * |
| Total inflammation (ti) | p = 0.001 * | p < 0.001 * | p = 0.882 | p = 0.052 | p = 0.070 | p = 0.867 |
| Interstitial inflammation (i) | p < 0.001 * | p = 0.090 | p = 0.655 | p = 0.127 | p = 0.448 | p = 0.876 |
| Inflammation in the area of IFTA (i-IFTA) | p < 0.001 * | p < 0.001 * | N/A | p = 0.067 | p < 0.001 * | p = 0.979 |
| Tubular atrophy (ct) | p = 0.001 * | p < 0.001 * | N/A | p = 0.047 * | p = 0.232 | p = 0.753 |
| Interstitial fibrosis (ci) | p = 0.001 * | p < 0.001 * | N/A | p = 0.002 * | p = 0.099 | p = 0.442 |
| Peritubular capillaritis (ptc) | p < 0.001 * | p < 0.001 * | N/A | p = 0.356 | p = 0.776 | p = 0.005 * |
| Vascular fibrous intimal thickening (cv) | p = 0.789 | p = 0.025 * | N/A | p = 0.305 | p = 0.787 | p = 0.007 * |
| Arteriolar hyalinosis (ah) | p = 0.789 | p = 0.716 | N/A | p = 0.523 | p = 0.488 | p = 0.615 |
| Hyaline arteriolar thickening (aah) | p = 0.789 | p = 0.716 | N/A | p = 0.021 * | p = 0.284 | p = 0.934 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Milivojević, D.; Nikolić, G.; Tampe, B.; Pecić, M.; Babac, S.; Paripović, D.; Miloševski Lomić, G.; Brković, V.; Baralić, M.; Janković, A.; et al. IgA Nephropathy in Native Kidneys: Oxford and Banff Classifications Reveal Distinct Profiles and Predict Outcomes in Pediatric and Adult Patients. Life 2025, 15, 1231. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081231
Milivojević D, Nikolić G, Tampe B, Pecić M, Babac S, Paripović D, Miloševski Lomić G, Brković V, Baralić M, Janković A, et al. IgA Nephropathy in Native Kidneys: Oxford and Banff Classifications Reveal Distinct Profiles and Predict Outcomes in Pediatric and Adult Patients. Life. 2025; 15(8):1231. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081231
Chicago/Turabian StyleMilivojević, Danijel, Gorana Nikolić, Björn Tampe, Maja Pecić, Snežana Babac, Dušan Paripović, Gordana Miloševski Lomić, Voin Brković, Marko Baralić, Aleksandar Janković, and et al. 2025. "IgA Nephropathy in Native Kidneys: Oxford and Banff Classifications Reveal Distinct Profiles and Predict Outcomes in Pediatric and Adult Patients" Life 15, no. 8: 1231. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081231
APA StyleMilivojević, D., Nikolić, G., Tampe, B., Pecić, M., Babac, S., Paripović, D., Miloševski Lomić, G., Brković, V., Baralić, M., Janković, A., Đurić, P., Stajić, N., Putnik, J., Radojević Škodrić, S., & Životić, M. (2025). IgA Nephropathy in Native Kidneys: Oxford and Banff Classifications Reveal Distinct Profiles and Predict Outcomes in Pediatric and Adult Patients. Life, 15(8), 1231. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081231







