Comparison of Effectiveness Between Ultrasound-Guided and Blind Corticosteroid Injections in Plantar Fasciitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Selection Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Methodological Quality Assessment
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
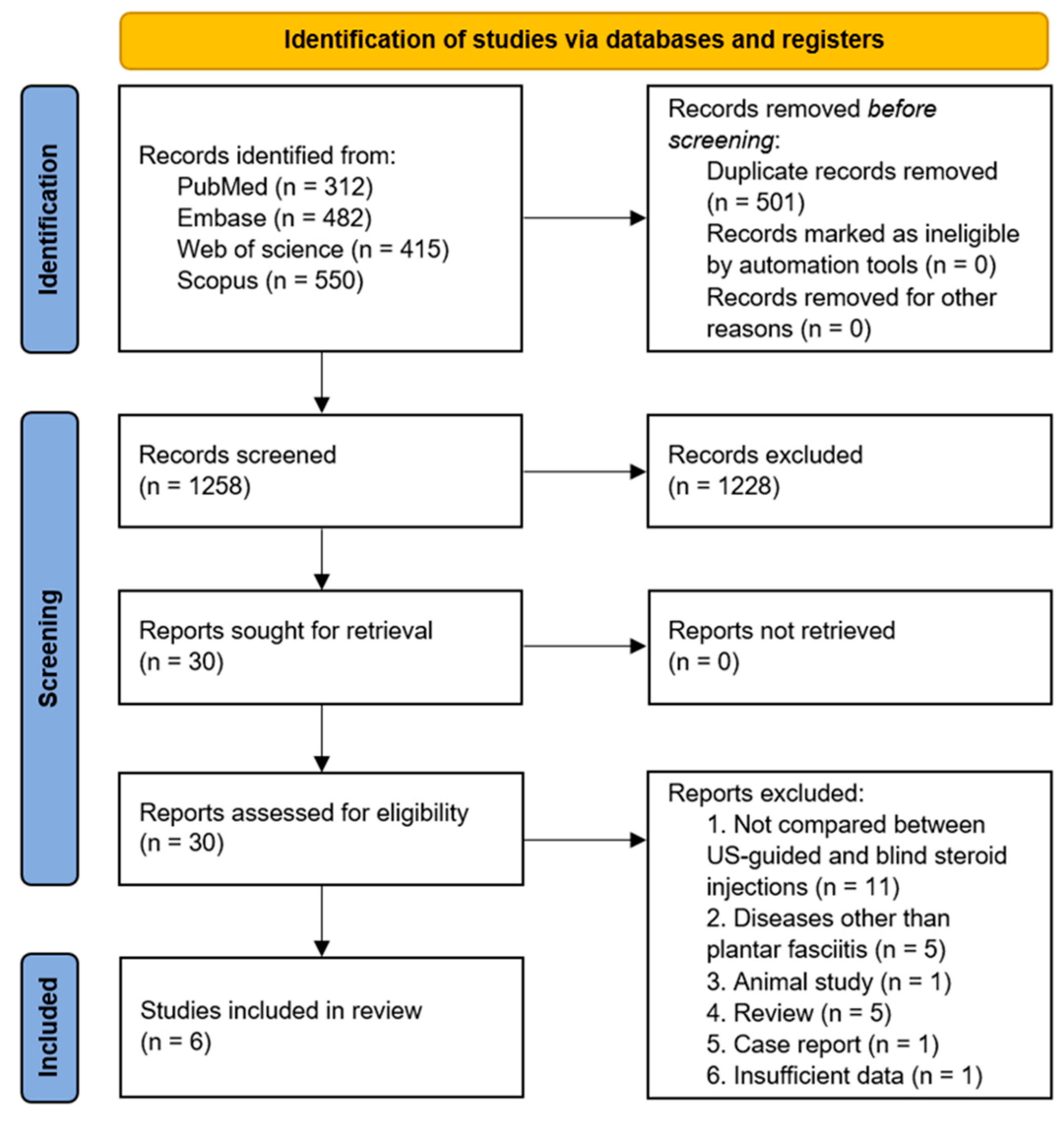
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Study Characteristics
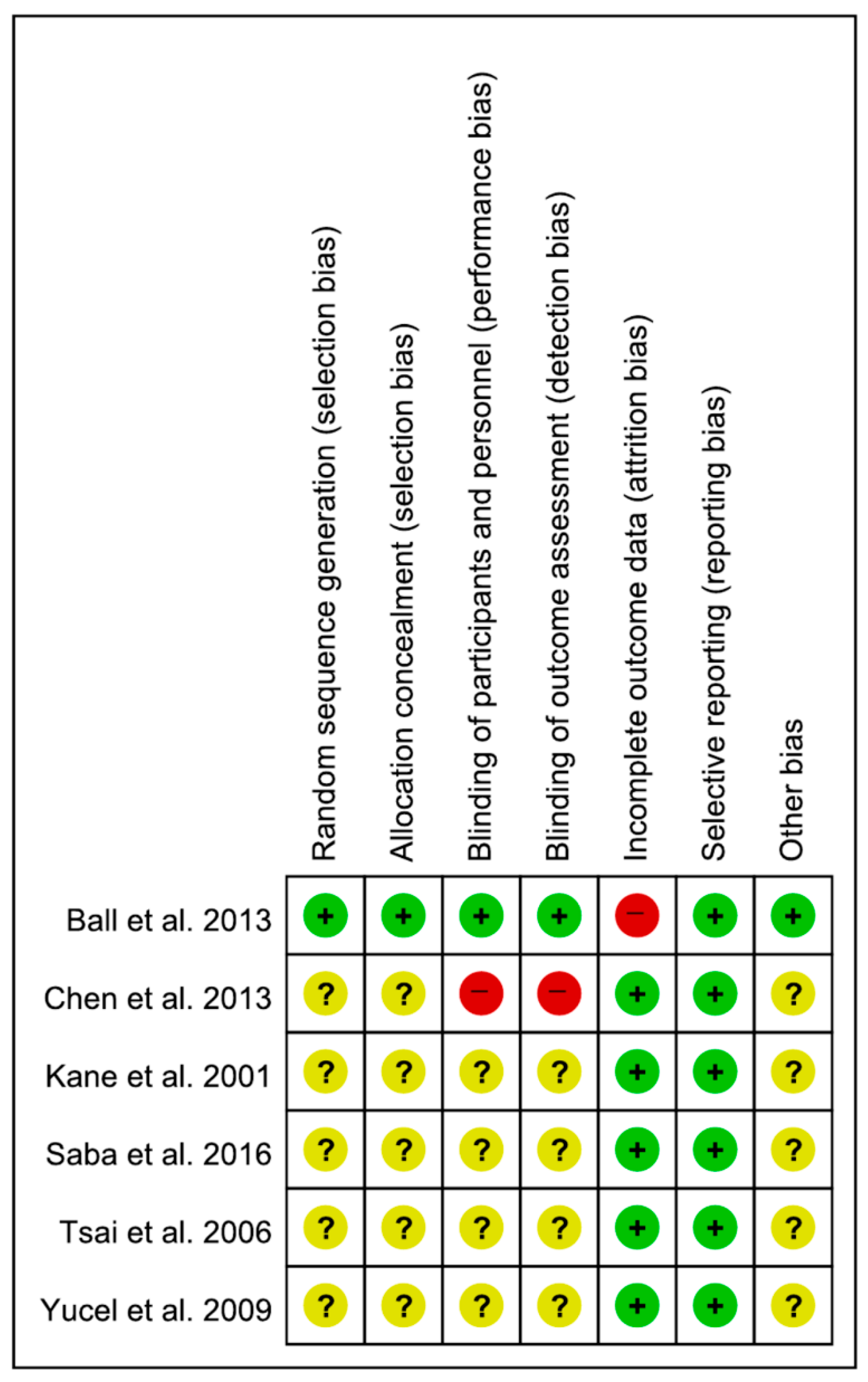
3.3. Assessment of Study Quality
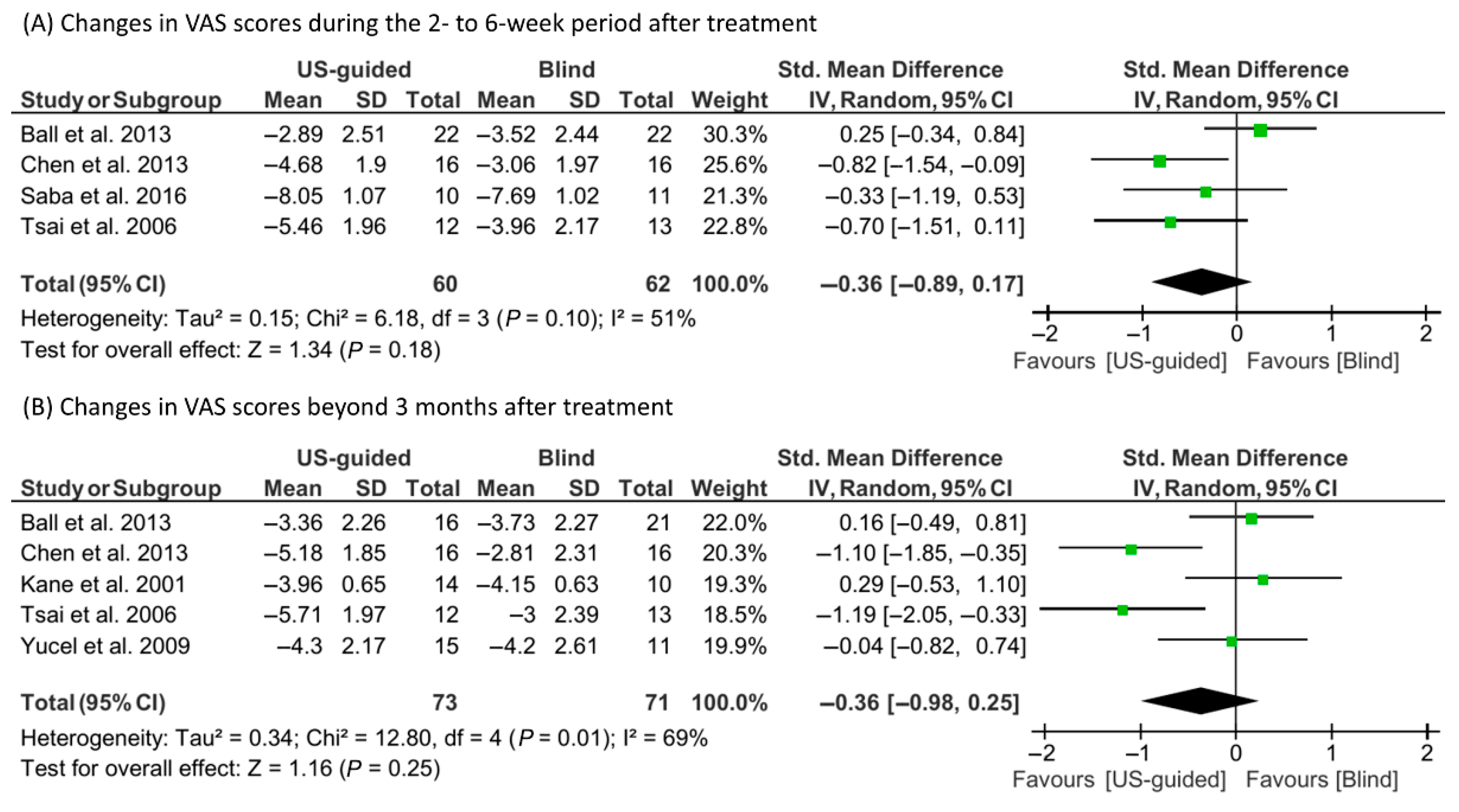
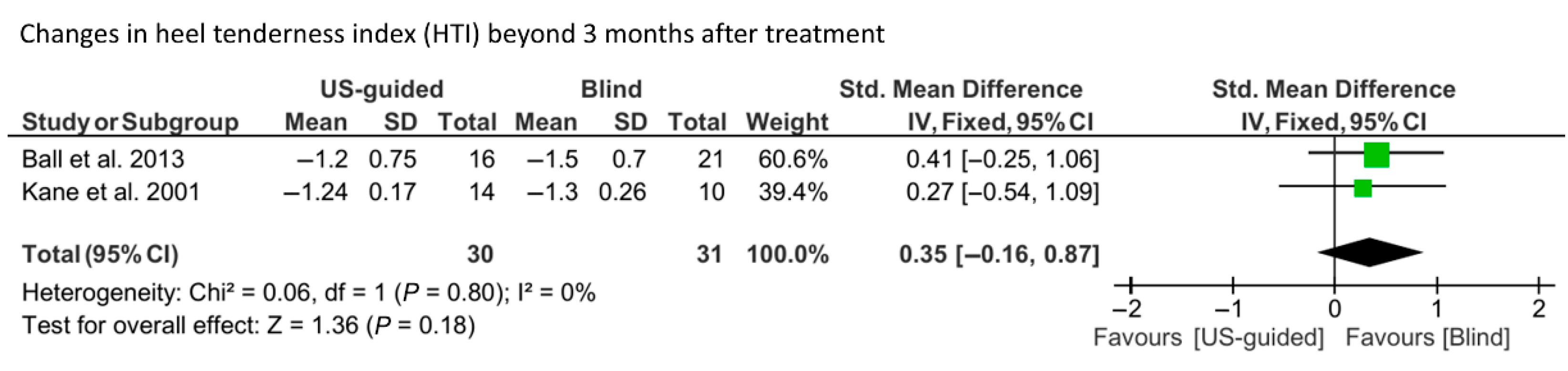
3.4. Meta-Analysis Findings
3.5. Publication Bias
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| US | Ultrasound |
| PF | Plantar fasciitis |
| VAS | Visual analog scale |
| HTI | Heel tenderness index |
| TT | Tenderness threshold |
| SMDs | Standardized mean differences |
| CIs | Confidence intervals |
| RCTs | Randomized controlled trials |
References
- Gibbon, W.W.; Long, G. Ultrasound of the plantar aponeurosis (fascia). Skelet. Radiol. 1999, 28, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchanan, B.K.; Sina, R.E.; Kushner, D. Plantar Fasciitis. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK431073/ (accessed on 4 June 2025).
- Latt, L.D.; Jaffe, D.E.; Tang, Y.; Taljanovic, M.S. Evaluation and treatment of chronic plantar fasciitis. Foot Ankle Orthop. 2020, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemont, H.; Ammirati, K.M.; Usen, N. Plantar fasciitis: A degenerative process (fasciosis) without inflammation. J. Am. Podiatr. Med. Assoc. 2003, 93, 234–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautham, P.; Nuhmani, S.; Kachanathu, S.J. Plantar fasciitis: A review of literature. Saudi J. Sports Med. 2014, 14, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchbinder, R. Plantar fasciitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 2159–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, J.A.; Sankarapandian, V.; Christopher, P.R.; Chatterjee, A.; Macaden, A.S. Injected corticosteroids for treating plantar heel pain in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 6, CD009348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, T.W. The effectiveness of corticosteroid injection in the treatment of plantar fasciitis. Singapore Med. J. 2015, 56, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellman, J.R. Plantar fascia rupture associated with corticosteroid injection. Foot Ankle Int. 1994, 15, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahstrom, J.R. Spontaneous rupture of the plantar fascia. Am. J. Sports Med. 1988, 16, 306–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdemir, H.; Özdemir, A.; Söyüncü, Y.; Ürgüden, M. The role of bone scintigraphy in determining the etiology of heel pain. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2002, 16, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, A.S.; Sahoo, R.K. Ultrasound-guided injection for plantar fasciitis: A brief review. Saudi J. Anaesth. 2016, 10, 440–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kane, D.; Greaney, T.; Bresnihan, B.; Gibney, R.; FitzGerald, O. Ultrasound guided injection of recalcitrant plantar fasciitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1998, 57, 383–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, W.; Hsu, C.; Chen, C.P.; Chen, M.J.; Yu, T.; Chen, Y. Plantar fasciitis treated with local steroid injection: Comparison between sonographic and palpation guidance. J. Clin. Ultrasound 2006, 34, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.M.; Chen, J.S.; Tsai, W.C.; Hsu, H.C.; Chen, K.H.; Lin, C.H. Effectiveness of device-assisted ultrasound-guided steroid injection for treating plantar fasciitis. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2013, 92, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, E.K.; El-Sherif, S.M. Ultrasound-guided versus palpation-guided local corticosteroid injection therapy for treatment of plantar fasciitis. Egypt. Rheumatol. 2016, 38, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kane, D.; Greaney, T.; Shanahan, M.; Duffy, G.; Bresnihan, B.; Gibney, R.; FitzGerald, O. The role of ultrasonography in the diagnosis and management of idiopathic plantar fasciitis. Rheumatology 2001, 40, 1002–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liggins, C.A. The measurement of pain—A brief review. S. Afr. J. Physiother. 1982, 38, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, D.A.; Lambert, B.S.; Boutris, N.; Boutris, N.; McCulloch, P.C.; Robbins, A.B.; Moreno, M.R.; Harris, J.D. Validation of digital visual analog scale pain scoring with a traditional paper-based visual analog scale in adults. JAAOS Glob. Res. Rev. 2018, 2, e088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, E.M.; McKeeman, H.M.; Patterson, C.; Burns, J.; Yau, W.H.; Moore, O.A.; Benson, C.; Foo, J.; Wright, G.D.; Taggart, A.J. Steroid injection for inferior heel pain: A randomised controlled trial. Ann. Rheu Dis. 2013, 72, 996–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, A.A. Pressure algometry over normal muscles. Standard values, validity and reproducibility of pressure threshold. Pain 1987, 30, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinal, E.; Chhem, R.K.; Beauregard, C.G.; Aubin, B.; Pelletier, M. Plantar fasciitis: Sonographic evaluation. Radiology 1996, 201, 257–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yucel, I.; Yazici, B.; Degirmenci, E.; Erdogmus, B.; Dogan, S. Comparison of ultrasound-, palpation-, and scintigraphy-guided steroid injections in the treatment of plantar fasciitis. Arch. Orthop. Trauma. Surg. 2009, 129, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiech, K.; Tracey, I. The influence of negative emotions on pain: Behavioral effects and neural mechanisms. Neuroimage 2009, 47, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, H.; Cho, Y.; Cho, S. Does past/current pain change pain experience? Comparing self-reports and pupillary responses. Front. Psychol. 2023, 14, 1094903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayan, M.C. Culture’s effects on pain assessment and management. Am. J. Nurs. 2010, 110, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogger, R.; Bello, C.; Romero, C.S.; Urman, R.D.; Luedi, M.M.; Filipovic, M.G. Cultural framing and the impact on acute pain and pain services. Curr. Pain. Headache Rep. 2023, 27, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fan, H. Self-efficacy and chronic pain outcomes: A meta-analytic review. J. Pain 2014, 15, 800–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wearing, S.C.; Smeathers, J.E.; Sullivan, P.M.; Yates, B.; Urry, S.R.; Dubois, P. Plantar fasciitis: Are pain and fascial thickness associated with arch shape and loading? Phys. Ther. 2007, 87, 1002–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahowald, S.; Legge, B.S.; Grady, J.F. The correlation between plantar fascia thickness and symptoms of plantar fasciitis. J. Am. Podiatr. Med. Assoc. 2011, 101, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, P.; Jirankali, V.; Garg, S.K. Evaluation of plantar fascia using high-resolution ultrasonography in clinically diagnosed cases of plantar fasciitis. Pol. J. Radiol. 2020, 85, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillan, A.M.; Landorf, K.B.; Gilheany, M.F.; Bird, A.R.; Morrow, A.D.; Menz, H.B. Ultrasound guided corticosteroid injection for plantar fasciitis: Randomised controlled trial. BMJ 2012, 344, e3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, J.L.; Purdam, C.R. Is tendon pathology a continuum? A pathology model to explain the clinical presentation of load-induced tendinopathy. Br. J. Sports Med. 2009, 43, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
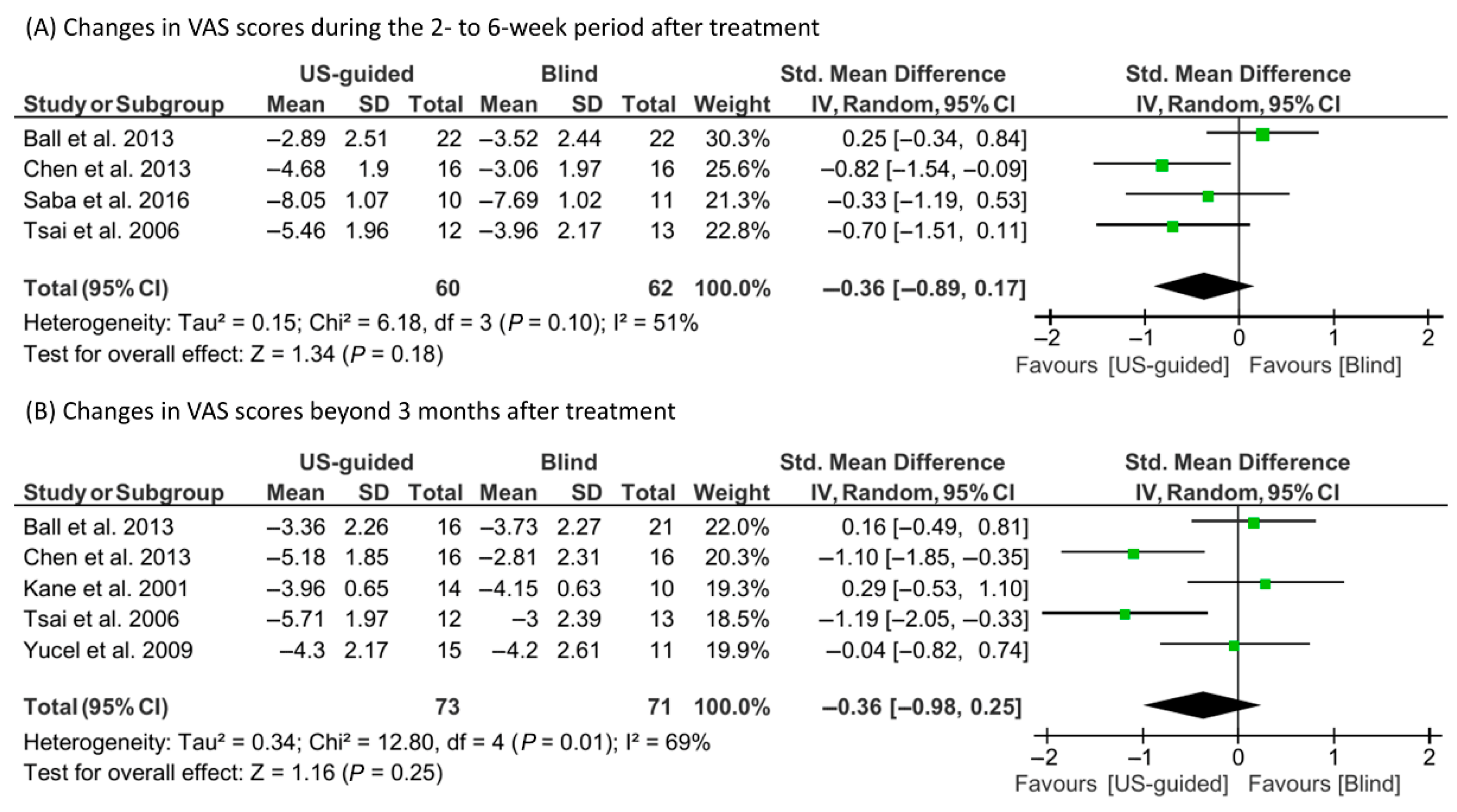
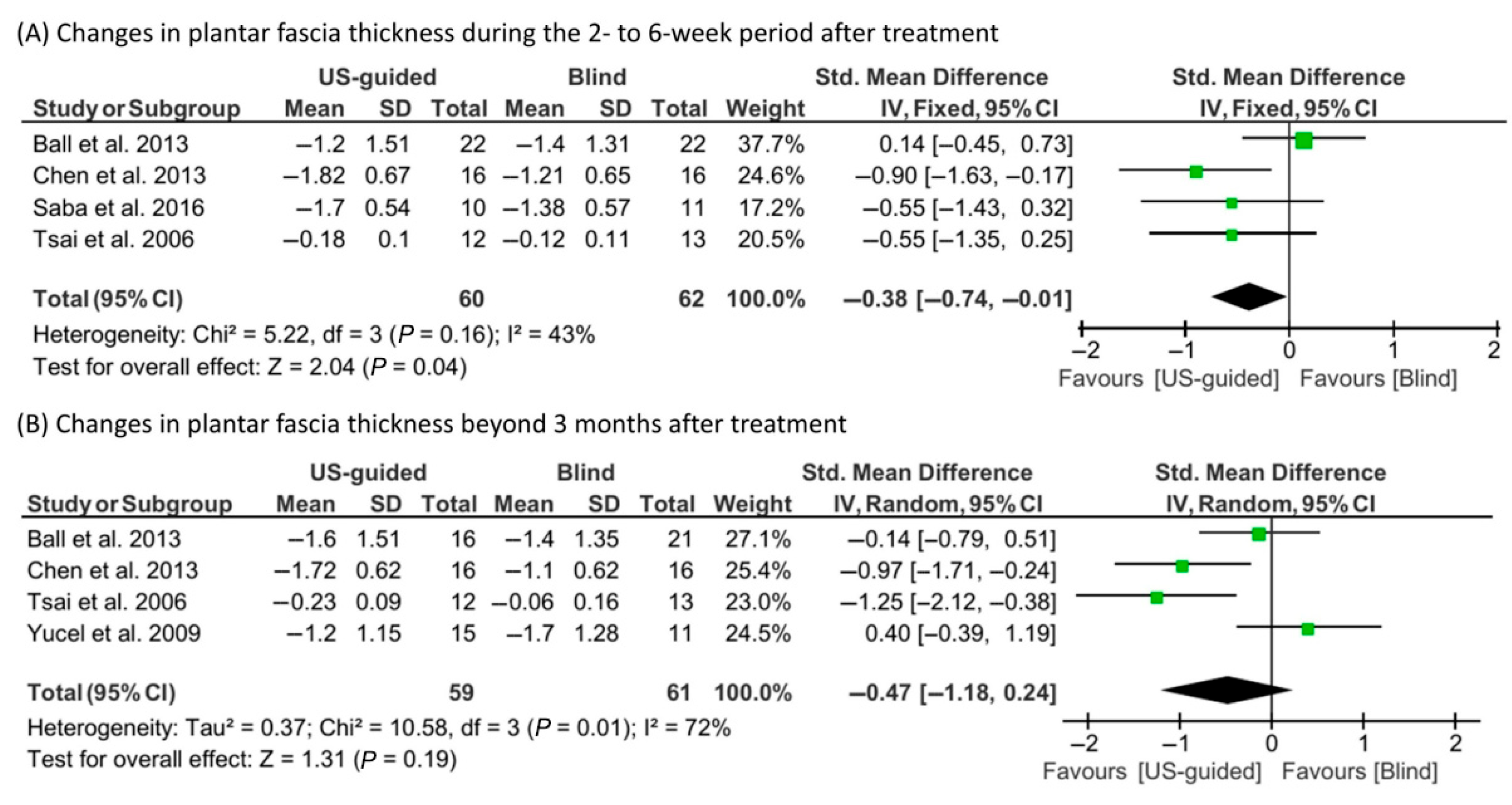

| Study | Study Design | Number of Treated Feet (US-Guided/Blind) | Post-Treatment Follow-Up | Outcome Measures |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ball et al. [20] 2013 | RCT | 22/22 | 6 and 12 weeks | VAS, HTI, plantar fascia thickness |
| Chen et al. [15] 2013 | RCT | 16/16 | 3 weeks and 3 months | VAS, TT, plantar fascia thickness, heel pad thickness, incidence of hypoechogenic fascia |
| Kane et al. [17] 2001 | RCT | 14/10 | Mean 13.4 weeks (range 6–48 weeks) | VAS, HTI |
| Saba et al. [16] 2016 | RCT | 10/11 | 2 and 4 weeks | VAS, plantar fasciitis pain/disability scale, plantar fascia thickness, plantar fascia echogenicity, clinical remission, ultrasonographic remission, clinical and ultrasonographic remission |
| Tsai et al. [14] 2006 | RCT | 12/13 | 2 weeks, 2 months, and 1 year | VAS, TT, plantar fascia thickness, hypoechogenicity |
| Yucel et al. [23] 2009 | RCT | 15/11 | Mean 25.3 months (range 22.2–27.2 months) | VAS, plantar fascia thickness, fat pad thickness, fascial hypoechogenicity |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Doan, H.N.; Choo, Y.J.; Chang, M.C. Comparison of Effectiveness Between Ultrasound-Guided and Blind Corticosteroid Injections in Plantar Fasciitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Life 2025, 15, 1107. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15071107
Doan HN, Choo YJ, Chang MC. Comparison of Effectiveness Between Ultrasound-Guided and Blind Corticosteroid Injections in Plantar Fasciitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Life. 2025; 15(7):1107. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15071107
Chicago/Turabian StyleDoan, Hoa Ngan, Yoo Jin Choo, and Min Cheol Chang. 2025. "Comparison of Effectiveness Between Ultrasound-Guided and Blind Corticosteroid Injections in Plantar Fasciitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Life 15, no. 7: 1107. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15071107
APA StyleDoan, H. N., Choo, Y. J., & Chang, M. C. (2025). Comparison of Effectiveness Between Ultrasound-Guided and Blind Corticosteroid Injections in Plantar Fasciitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Life, 15(7), 1107. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15071107








