Effects of Curcuma longa L. and Green Propolis Extract-Loaded Microcapsules Supplementation on Inflammation in Hemodialysis Patients: Preliminary Results of a Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Inclusion and Non-Inclusion Criteria
2.2. Ethical Procedures
2.3. Composition of Propolis and Curcuma longa L.
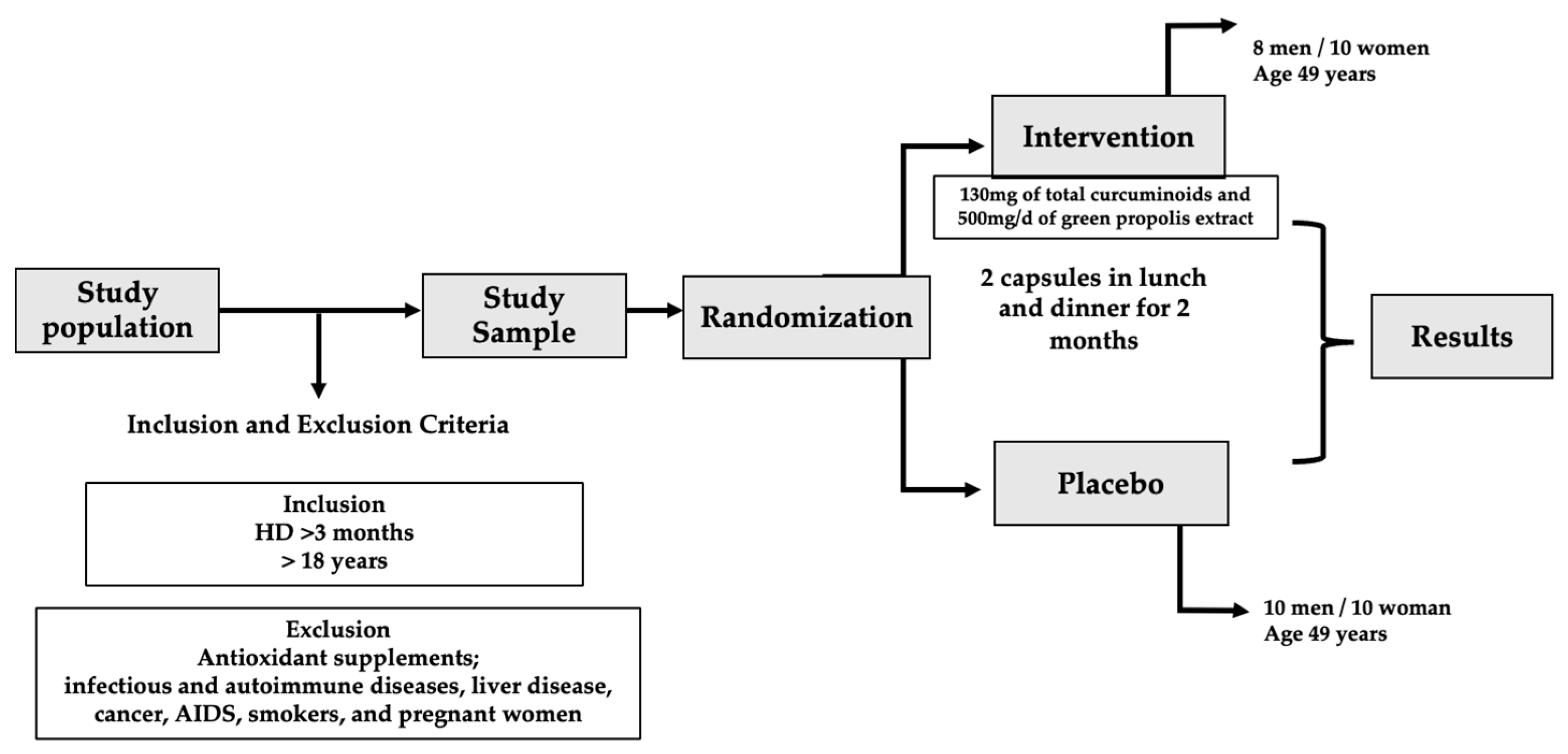
2.4. Experimental Design
2.5. Food Intake Analysis and BMI Measurement
2.6. Blood Collection
2.7. Inflammatory Cytokines
2.8. Uremic Toxins
2.9. Biochemical Parameters and Lipid Peroxidation Marker
2.10. Statistical Analysis
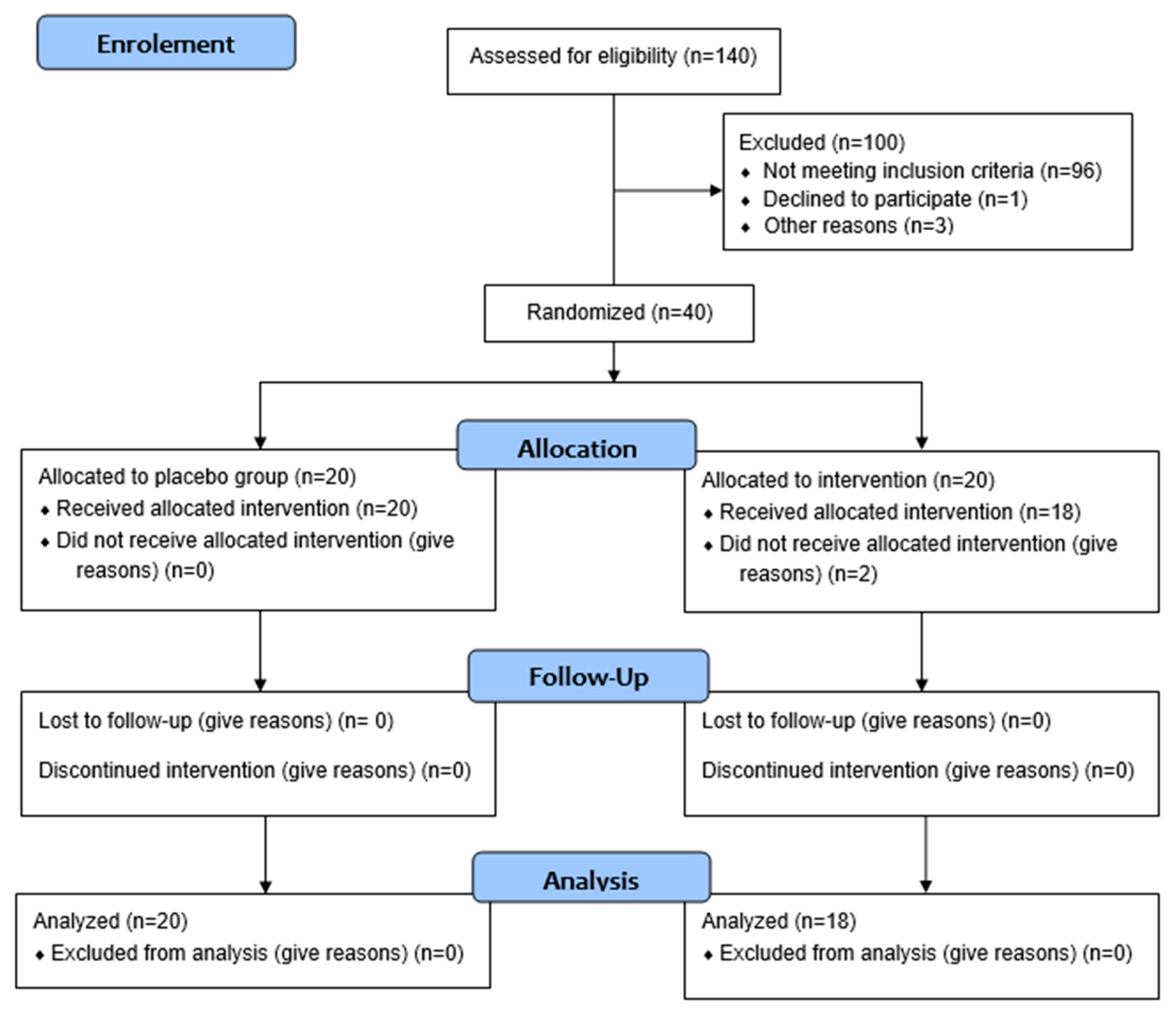
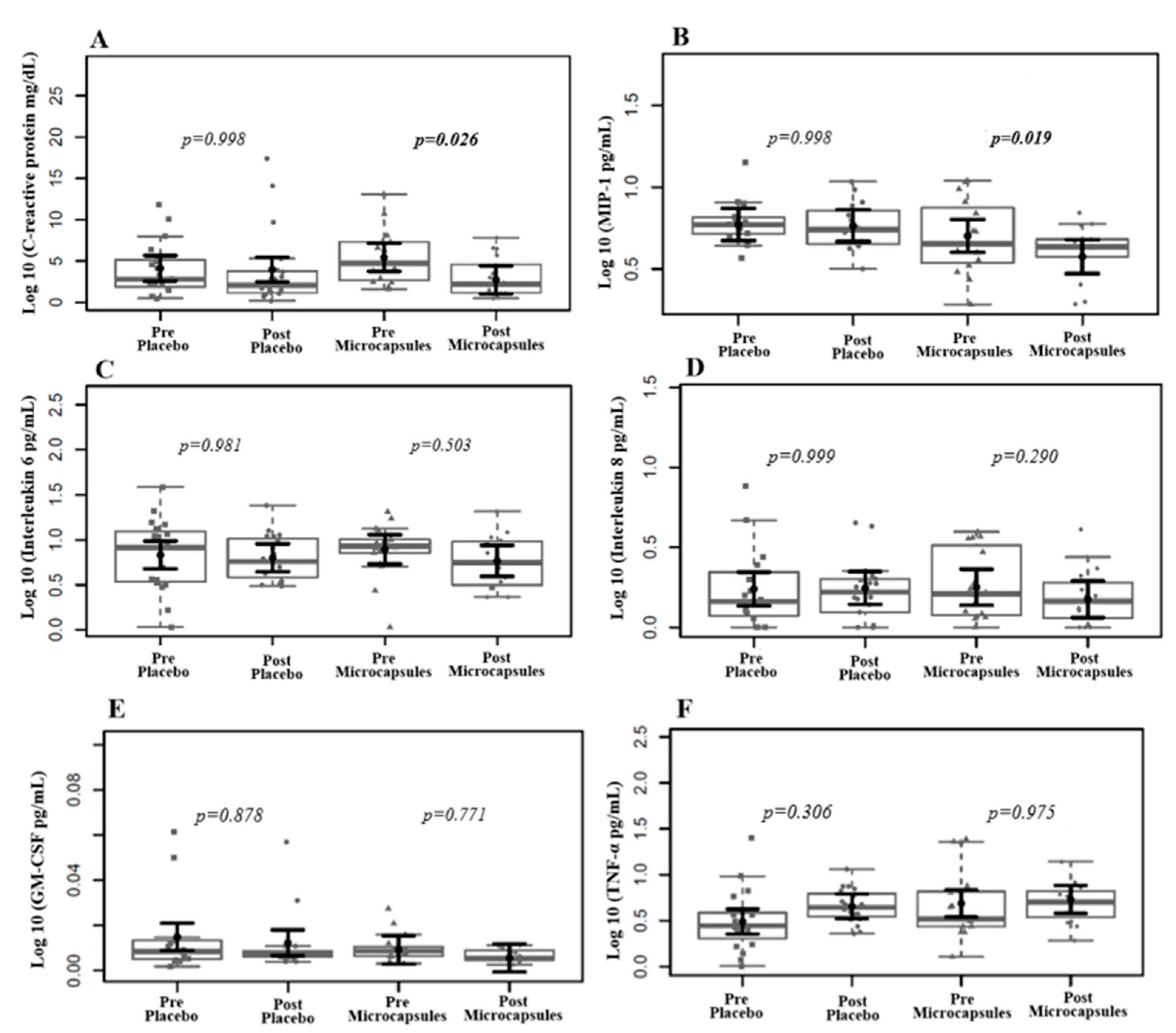
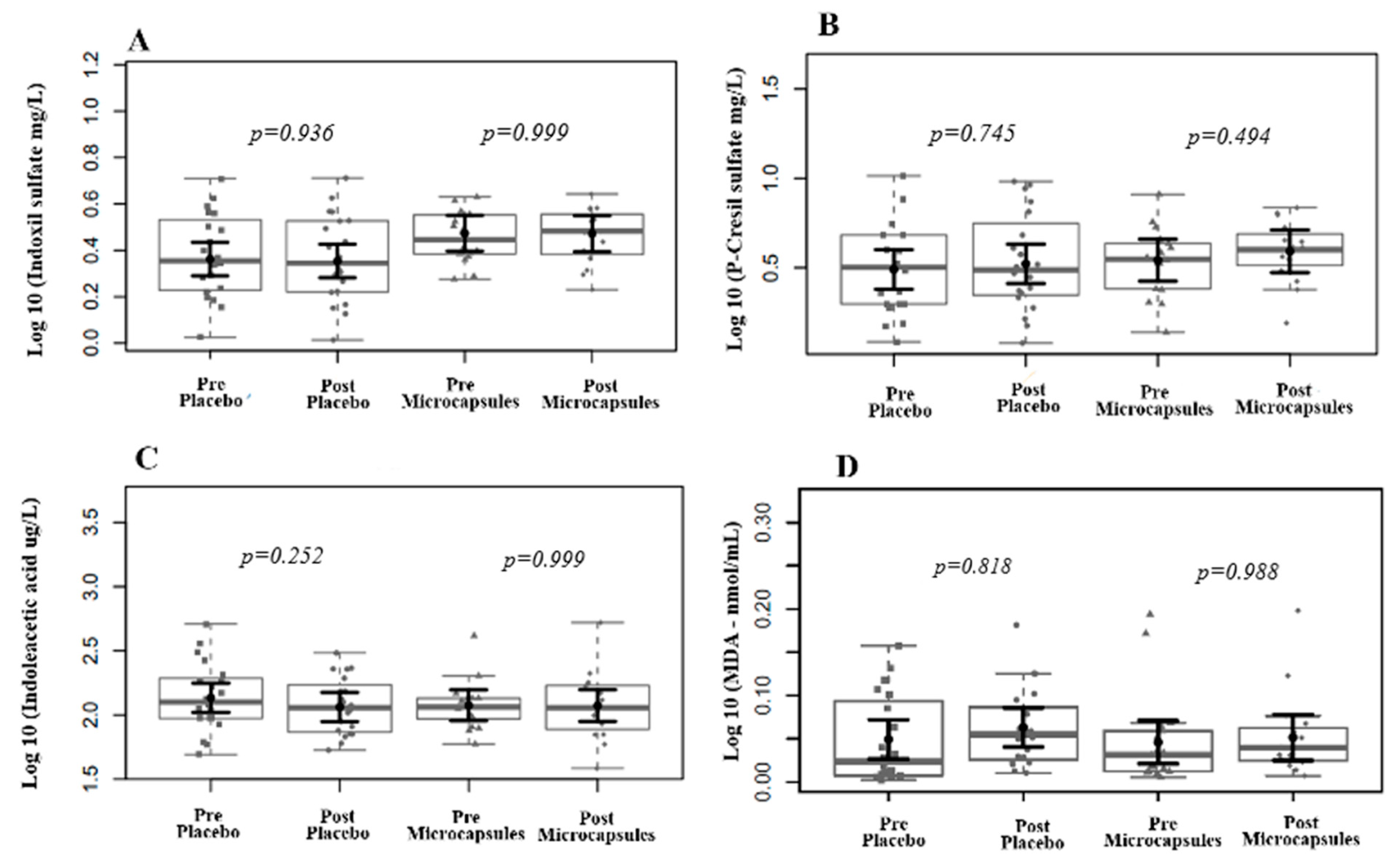
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cobo, G.; Lindholm, B.; Stenvinkel, P. Chronic Inflammation in End-Stage Renal Disease and Dialysis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2018, 33, iii35–iii40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebert, T.; Pawelzik, S.C.; Witasp, A.; Arefin, S.; Hobson, S.; Kublickiene, K.; Shiels, P.G.; Bäck, M.; Stenvinkel, P. Inflammation and Premature Ageing in Chronic Kidney Disease. Toxins 2020, 12, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.J.; Sidor, N.A.; Tonial, N.C.; Che, A.; Urquhart, B.L. Uremic Toxins in the Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease and Cardiovascular Disease: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Targets. Toxins 2021, 13, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esgalhado, M.; Stenvinkel, P.; Mafra, D. Nonpharmacologic Strategies to Modulate Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2–Related Factor 2 Pathway in Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Ren. Nutr. 2017, 27, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Jin, Y.; Chen, X.; Ye, X.; Shen, X.; Lin, M.; Zeng, C.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, J. NF-ΚB in Biology and Targeted Therapy: New Insights and Translational Implications. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Kaur, R.; Kumari, P.; Pasricha, C.; Singh, R. ICAM-1 and VCAM-1: Gatekeepers in Various Inflammatory and Cardiovascular Disorders. Clin. Chim. Acta 2023, 548, 117487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.-C.; Kuo, C.-H.; Lin, Y.-L.; Hsu, B.-G. Gut-Derived Uremic Toxins and Cardiovascular Health in Chronic Kidney Disease. Tzu Chi Med. J. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumanli, Z.; Vural, I.M.; Alp Avci, G. Chronic Kidney Disease, Uremic Toxins and Microbiota. Microbiota Host 2025, 3, e240012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, R.d.C.S.O.; Theodoro, J.M.V.; da Silva, B.P.; Queiroz, V.A.V.; de Castro Moreira, M.E.; Mantovani, H.C.; Hermsdorff, H.H.; Martino, H.S.D. Synbiotic Meal Decreases Uremic Toxins in Hemodialysis Individuals: A Placebo-Controlled Trial. Food Res. Int. 2019, 116, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Gelder, M.K.; Middel, I.R.; Vernooij, R.W.M.; Bots, M.L.; Verhaar, M.C.; Masereeuw, R.; Grooteman, M.P.; Nubé, M.J.; van den Dorpel, M.A.; Blankestijn, P.J.; et al. Protein-Bound Uremic Toxins in Hemodialysis Patients Relate to Residual Kidney Function, Are Not Influenced by Convective Transport, and Do Not Relate to Outcome. Toxins 2020, 12, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teodoro, A.J. Bioactive Compounds of Food: Their Role in the Prevention and Treatment of Diseases. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2019, 2019, 3765986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Qin, C.; Wen, M.; Zhang, L.; Wang, W. The Effects of Food Nutrients and Bioactive Compounds on the Gut Microbiota: A Comprehensive Review. Foods 2024, 13, 1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pivari, F.; Mingione, A.; Piazzini, G.; Ceccarani, C.; Ottaviano, E.; Brasacchio, C.; Dei Cas, M.; Vischi, M.; Cozzolino, M.G.; Fogagnolo, P.; et al. Curcumin Supplementation (Meriva® ) Modulates Inflammation, Lipid Peroxidation and Gut Microbiota Composition in Chronic Kidney Disease. Nutrients 2022, 14, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Josa, E.; Barril, G.; Ruperto, M. Potential Effects of Bioactive Compounds of Plant-Based Foods and Medicinal Plants in Chronic Kidney Disease and Dialysis: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2024, 16, 4321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’andurain, J.; López, V.; Arazo-Rusindo, M.; Tiscornia, C.; Aicardi, V.; Simón, L.; Mariotti-Celis, M.S. Effect of Curcumin Consumption on Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Patients on Hemodialysis: A Literature Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salami, F.; Mohebbati, R.; Hosseinian, S.; Shahraki, S.; Hossienzadeh, H.; Rad, A.K. Propolis and Its Therapeutic Effects on Renal Diseases, a Review. Iran. J. Basic. Med. Sci. 2024, 27, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, R.; Quispe, C.; Khan, R.A.; Saikat, A.S.M.; Ray, P.; Ongalbek, D.; Yeskaliyeva, B.; Jain, D.; Smeriglio, A.; Trombetta, D.; et al. Propolis: An Update on Its Chemistry and Pharmacological Applications. Chin. Med. 2022, 17, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavda, V.P.; Chaudhari, A.Z.; Teli, D.; Balar, P.; Vora, L. Propolis and Their Active Constituents for Chronic Diseases. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Ao, M.; Dong, B.; Jiang, Y.; Yu, L.; Chen, Z.; Hu, C.; Xu, R. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Curcumin in the Inflammatory Diseases: Status, Limitations and Countermeasures. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 2021, 15, 4503–4525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beserra, F.P.; Gushiken, L.F.S.; Hussni, M.F.; Ribeiro, V.P.; Bonamin, F.; Jackson, C.J.; Pellizzon, C.H.; Bastos, J.K. Artepillin C as an Outstanding Phenolic Compound of Brazilian Green Propolis for Disease Treatment: A Review on Pharmacological Aspects. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 2274–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Duan, X.; Ke, L.; Pan, X.; Liu, J.; Song, X.; Ma, W.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Fan, Y. Extraction, Purification, Structural Character and Biological Properties of Propolis Flavonoids: A Review. Fitoterapia 2022, 157, 105106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.S.; Acharya, A.; Ray, R.S.; Agrawal, R.; Raghuwanshi, R.; Jain, P. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Curcumin in Prevention and Treatment of Disease. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 887–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pakfetrat, M.; Akmali, M.; Malekmakan, L.; Dabaghimanesh, M.; Khorsand, M. Role of Turmeric in Oxidative Modulation in End-Stage Renal Disease Patients. Hemodial. Int. 2015, 19, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyisan, B.; Landfester, K. Modular Approach for the Design of Smart Polymeric Nanocapsules. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2019, 40, e1800577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, J.; Ralaivao, M.; Estevinho, B.N.; Rocha, F. A New Approach for the Microencapsulation of Curcumin by a Spray Drying Method, in Order to Value Food Products. Powder Technol. 2020, 362, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano-Higuita, D.M.; Vélez, H.A.V.; Telis, V.R.N. Microencapsulation of Turmeric Oleoresin Microencapsulation of TurMeric Oleoresin in Binary and Ternary Blends of GuM Arabic, Maltodextrin and Modified Starch Microencapsulação de Oleoresina de Cúrcuma Em Misturas Binárias e Ternárias de Goma Arábica, Maltodextrina e Amido Modificado. Cienc. Agrotecnologia 2015, 39, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arpagaus, C.; Collenberg, A.; Rütti, D.; Assadpour, E.; Jafari, S.M. Nano Spray Drying for Encapsulation of Pharmaceuticals. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 546, 194–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assadpour, E.; Mahdi Jafari, S. Advances in Spray-Drying Encapsulation of Food Bioactive Ingredients: From Microcapsules to Nanocapsules. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 10, 103–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eun, J.B.; Maruf, A.; Das, P.R.; Nam, S.H. A Review of Encapsulation of Carotenoids Using Spray Drying and Freeze Drying. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 3547–3572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Zhong, S.; Wang, J.; Gao, Y.; Cui, X. Advances in Chitosan-Based Microcapsules and Their Applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 300, 120265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashwan, A.K.; Karim, N.; Xu, Y.; Xie, J.; Cui, H.; Mozafari, M.R.; Chen, W. Potential Micro-/Nano-Encapsulation Systems for Improving Stability and Bioavailability of Anthocyanins: An Updated Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 63, 3362–3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Xia, J.; Zhao, Q.; Niu, Y.; Zhao, D. Maltodextrin as Wall Material for Microcapsules: A Review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 298, 120113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarenga, L.; Salarolli, R.; Cardozo, L.F.M.F.; Santos, R.S.; de Brito, J.S.; Kemp, J.A.; Reis, D.; de Paiva, B.R.; Stenvinkel, P.; Lindholm, B.; et al. Impact of Curcumin Supplementation on Expression of Inflammatory Transcription Factors in Hemodialysis Patients: A Pilot Randomized, Double-Blind, Controlled Study. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 3594–3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquiafável, F.; Nascimento, A.; Barud, H.; Marquele-Oliveira, F.; de-Freitas, L.; Berretta, A. Development and Characterization of a Novel Standardized Propolis Dry Extract Obtained by Factorial Design with High Artepillin C Content. J. Pharm. Technol. Drug Res. 2015, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berretta, A.A.; De Lima, J.A.; Falcão, S.I.; Calhelha, R.; Amorim, N.A.; Gonçalves, I.S.; Zamarrenho, L.G.; Barud, H.d.S.; Bastos, J.K.; De Jong, D.; et al. Development and Characterization of High-Absorption Microencapsulated Organic Propolis EPP-AF® Extract (i-CAPs). Molecules 2023, 28, 7128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berretta, A.A.; Nascimento, A.P.; Bueno, P.C.P.; Vaz, M.M.d.O.L.L.; Marchetti, J.M. Propolis Standardized Extract (EPP-AF ®), an Innovative Chemically and Biologically Reproducible Pharmaceutical Compound for Treating Wounds. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2012, 8, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaprakasha, G.K.; Rao, L.J.M.; Sakariah, K.K. Improved HPLC Method for the Determination of Curcumin, Demethoxycurcumin, and Bisdemethoxycurcumin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 3668–3672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chermut, T.R.; Fonseca, L.; Figueiredo, N.; de Oliveira Leal, V.; Borges, N.A.; Cardozo, L.F.M.F.; Correa Leite, P.E.; Alvarenga, L.; Regis, B.; Delgado, A.; et al. Effects of Propolis on Inflammation Markers in Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis: A Randomized, Double-Blind Controlled Clinical Trial. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 2023, 51, 101732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazilian Health Regulatory Agency (ANVISA). Traditional Herbal Products Eligible for Notification According to the Formulations Published in the 2nd Edition of the Brazilian Pharmacopoeia Herbal Formulary. ANVISA. 2021. Available online: https://www.gov.br/anvisa/pt-br/setorregulado/regularizacao/medicamentos/notificados/PTFpassveisdenotificao.pdf (accessed on 23 April 2025).
- Universidade Estadual de Campinas. Núcleo de Estudos e Pesquisas em Alimentação–NEPA. Tabela Brasileira de Composição de Alimentos–TACO, 4th ed.; NEPA-UNICAMP: Campinas, Brazil, 2011. Available online: https://www.gov.br/agricultura/pt-br/assuntos/inspecao/produtos-vegetal/legislacao-de-produtos-origem-vegetal/biblioteca-de-normas-vinhos-e-bebidas/tabela-brasileira-de-composicao-de-alimentos_taco_2011.pdf (accessed on 23 April 2025).
- World Health Organization. Obesity: Preventing and Managing the Global Epidemic. Rep. WHO Consult. 2000, 894, i-253. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ohkawa, H.; Ohishi, N.; Yagi, K. Assay for Lipid Peroxides in Animal Tissues by Thiobarbituric Acid Reaction. Anal. Biochem. 1979, 95, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samadian, F.; Dalili, N.; Poor -reza Gholi, F.; Fattah, M.; Malih, N.; Nafar, M.; Firoozan, A.; Ahmadpoor, P.; Samavat, S.; Ziaie, S. Evaluation of Curcumin’s Effect on Inflammation in Hemodialysis Patients. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2017, 22, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmi, Y.; Yagmayee, P.; Khadem-Ansari, M.-H.; Makhdomii, K.; Rasooli, J. The Effects of Nano-Curcumin Supplementation on Serum Level of Hs-CRP, Adhesion Molecules, and Lipid Profiles in Hemodialysis Patients, A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Iran. J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 14, 52–61. [Google Scholar]
- Duarte Silveira, M.A.; Malta-Santos, H.; Rebouças-Silva, J.; Teles, F.; Batista Dos Santos Galvão, E.; Pinto De Souza, S.; Dantas Dutra, F.R.; Dantas Gomes, M.M.; Teixeira, M.B.; Miranda Rebelo Da Conceição, L.F.; et al. Effects of Standardized Brazilian Green Propolis Extract (EPP-AF®) on Inflammation in Haemodialysis Patients: A Clinical Trial. Int. J. Nephrol. 2022, 2022, 1035475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, S.; Buttari, B.; Panieri, E.; Profumo, E.; Saso, L. An Overview of Nrf2 Signaling Pathway and Its Role in Inflammation. Molecules 2020, 25, 5474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sproston, N.R.; Ashworth, J.J. Role of C-Reactive Protein at Sites of Inflammation and Infection. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graterol Torres, F.; Molina, M.; Soler-Majoral, J.; Romero-González, G.; Rodríguez Chitiva, N.; Troya-Saborido, M.; Socias Rullan, G.; Burgos, E.; Paúl Martínez, J.; Urrutia Jou, M.; et al. Evolving Concepts on Inflammatory Biomarkers and Malnutrition in Chronic Kidney Disease. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huen, S.C.; Cantley, L.G. Macrophages in Renal Injury and Repair. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2017, 79, 449–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridker, P.M.; Rane, M. Interleukin-6 Signaling and Anti-Interleukin-6 Therapeutics in Cardiovascular Disease. Circ. Res. 2021, 128, 1728–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciechanowska, A.; Popiolek-Barczyk, K.; Pawlik, K.; Ciapała, K.; Oggioni, M.; Mercurio, D.; De Simoni, M.G.; Mika, J. Changes in Macrophage Inflammatory Protein-1 (MIP-1) Family Members Expression Induced by Traumatic Brain Injury in Mice. Immunobiology 2020, 225, 151911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.T.; Li, S.Y.; Lin, L.Y.; Chen, C.; Chen, J.W. Macrophage Inflammatory Protein-1β as a Novel Therapeutic Target for Renal Protection in Diabetic Kidney Disease. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 161, 114450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germolec, D.R.; Shipkowski, K.A.; Frawley, R.P.; Evans, E. Markers of Inflammation. In Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press Inc.: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2018; Volume 1803, pp. 57–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, H.C.N.; Martins, T.F.P.; Santana, N.C.F.e.S.; Braga, C.C.; Silva, M.A.C.; Cunha, L.C.d.; Sugizaki, C.S.d.A.; Freitas, A.T.V.d.S.; Costa, N.A.; Peixoto, M.d.R.G. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Response to Curcumin Supplementation in Hemodialysis Patients: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2021, 44, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salarolli, R.T.; Alvarenga, L.; Cardozo, L.F.M.F.; Teixeira, K.T.R.; de S. G. Moreira, L.; Lima, J.D.; Rodrigues, S.D.; Nakao, L.S.; Fouque, D.; Mafra, D. Can Curcumin Supplementation Reduce Plasma Levels of Gut-Derived Uremic Toxins in Hemodialysis Patients? A Pilot Randomized, Double-Blind, Controlled Study. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2021, 53, 1231–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, B.H.; Karaca, T.; Al Suleimani, Y.; Za’abi, M.; Kalbani, J.; Ashique, M.; Nemmar, A. The Effect of Swimming Exercise on Adenine-Induced Kidney Disease in Rats, and the Inffuence of Curcumin or Lisinopril Thereon. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca, L.; Ribeiro, M.; Schultz, J.; Borges, N.A.; Cardozo, L.; Leal, V.O.; Ribeiro-Alves, M.; Paiva, B.R.; Leite, P.E.C.; Sanz, C.L.; et al. Effects of Propolis Supplementation on Gut Microbiota and Uremic Toxin Profiles of Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis. Toxins 2024, 16, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palliyage, G.H.; Hussein, N.; Mimlitz, M.; Weeder, C.; Alnasser, M.H.A.; Singh, S.; Ekpenyong, A.; Tiwari, A.K.; Chauhan, H. Novel Curcumin-Resveratrol Solid Nanoparticles Synergistically Inhibit Proliferation of Melanoma Cells. Pharm. Res. 2021, 38, 851–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdolahi, M.; Tafakhori, A.; Togha, M.; Okhovat, A.A.; Siassi, F.; Eshraghian, M.R.; Sedighiyan, M.; Djalali, M.; Mohammadzadeh Honarvar, N.; Djalali, M. The Synergistic Effects of ω-3 Fatty Acids and Nano-Curcumin Supplementation on Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF)-α Gene Expression and Serum Level in Migraine Patients. Immunogenetics 2017, 69, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarenga, L.; Cardozo, L.F.M.F.; Ribeiro-Alves, M.; Damasceno, N.R.T.; Berretta, A.A.; Lima, J.A.; Khosla, P.; Fouque, D.; Mafra, D. Effects of Turmeric Extract Supplementation on the Lipid and Lipoprotein Subfraction Profile in Hemodialysis Patients: A Randomised, Double-Blind, Crossover and Controlled Trial. Phytother. Res. 2023, 37, 3424–3437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarenga, L.d.A.; Leal, V.d.O.; Borges, N.A.; de Aguiar, A.S.; Faxén-Irving, G.; Stenvinkel, P.; Lindholm, B.; Mafra, D. Curcumin—A Promising Nutritional Strategy for Chronic Kidney Disease Patients. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 40, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, A.; Dinarvand, N.; Hariri, M. Propolis Supplementation Can Reduce Serum Level of Interleukin-6, C-Reactive Protein, and Tumor Necrosis Factor-α: An Updated Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis on Randomized Clinical Trials. J. Health Popul. Nutr. 2024, 43, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Component | Fractions | (mg/Day) |
|---|---|---|
| Propolis | Total Flavonoids (Quercetin) | 25.0 |
| Total phenolics (Gallic acid) | 32.75 | |
| Artepellin C | 32.37 | |
| Turmeric | Curcumin | 103.2 |
| Demethoxycurcumin | 25.2 | |
| Bisdemethoxycurcumin | 5.76 |
| Parameters | Overall (N = 38) | Placebo (N = 20) | Microcapsules (N = 18) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (F/M) | 20 (52.6%)/18 (47.4%) | 10 (50%)/10 (50%) | 10 (55.6%)/8 (44.4%) | 0.986 |
| Age (Years) | 49 (17.7) | 49 (18.7) | 49 (16.2) | 0.907 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.03 (4.1) | 24.34 (3.4) | 21.6 (5.2) | 0.034 |
| Time on HD (Months) | 35.0 (33) | 31.5 (24.7) | 37.5 (41.7) | 0.527 |
| Kt/V | 1.5 (0.5) | 1.4 (0.5) | 1.6 (0.4) | 0.096 |
| HAS | 27 (71.1%) | 17 (85%) | 10 (55.6%) | 0.101 |
| DM | 6 (15.8%) | 4 (20%) | 2 (11.1) | 0.761 |
| Biochemical Parameters | Overall (N = 38) | Placebo (N = 20) | Microcapsules (N = 18) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 143.5 (35.2) | 138.0 (36.0) | 145.5 (32.7) | 0.682 |
| High-density lipoprotein (mg/dL) | 39.5 (14.7) | 37 (11.5) | 44 (12.3) | 0.160 |
| Low-density lipoprotein (mg/dL) | 70.1 (24.4) | 68.8 (24.1) | 72.8 (18.6) | 0.806 |
| Albumin (mg/dL) | 3.1 (0.4) | 3.2 (0.4) | 3.1 (0.3) | 0.536 |
| Phosphorus (mg/dL) | 5.2 (2.3) | 5.6 (2.3) | 4.8 (2.2) | 0.388 |
| Calcium (mg/dL) | 9.6 (1.2) | 9.8 (1.2) | 9.4 (1.0) | 0.320 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 105.5 (83.2) | 105.5 (96.0) | 105.5 (64.2) | 0.770 |
| Urea (mg/dL) | 107.5 (41.7) | 102.5 (42.7) | 109.5 (37.5) | 0.292 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 9.4 (3.6) | 9.4 (3.5) | 9.4 (3.6) | 0.630 |
| C-reactive protein (mg/dL) | 4.1 (4.3) | 2.8 (3.2) | 4.7 (4.5) | 0.105 |
| Food Intake | Overall (N = 38) | Placebo (N = 20) | Microcapsules (N = 18) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energy (Kcal/d) | 1352.4 (653.6) | 1353 (500.9) | 1350 (711.8) | 0.988 |
| Energy (Kcal/kg/d) | 21 (12.1) | 19.4 (8.3) | 23.6 (14.5) | 0.239 |
| Proteins (g/d) | 68.6 (42.8) | 68.6 (36.3) | 69.3 (44.6) | 0.897 |
| Proteins (g/kg/d) | 1.1 (0.8) | 1.0 (0.5) | 1.1 (0.8) | 0.421 |
| Carbohydrates (g/d) | 176.1 (79.7) | 171.1 (54.7) | 177.6 (98.6) | 0.762 |
| Lipids (g/d) | 37.2 (27.2) | 36.2 (31.2) | 40.3 (25.7) | 0.726 |
| Monounsaturated (g/d) | 12.6 (8.2) | 12.1 (9.1) | 13.3 (7.5) | 0.988 |
| Polyunsaturated (g/d) | 6.2 (3.4) | 6.5 (3.5) | 5.2 (3.0) | 0.520 |
| Saturated (g/d) | 14.7 (13.2) | 14.1 (15.4) | 16 (10.0) | 1.000 |
| Cholesterol (g/d) | 275.3 (187.4) | 277.8 (181.3) | 275.3 (197.3) | 0.828 |
| Calcium (mg/d) | 241.4 (225.8) | 258.6 (194.3) | 235.4 (287.9) | 0.443 |
| Iron (mg/d) | 6.87 (4.9) | 7.3 (2.4) | 6.7 (3.0) | 0.225 |
| Fiber (g/d) | 19.9 (8.2) | 20.7 (11.3) | 18.98 (7.2) | 0.165 |
| Sodium (mg/d) | 1231.5 (924.5) | 1240.7 (762.0) | 1225 (1032.7) | 0.919 |
| Parameters | Overall (N = 38) | Placebo (N = 20) | Microcapsules (N = 18) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cytokines | ||||
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | 74.9 (79.1) | 76.9 (101.0) | 74.9 (30) | 0.988 |
| IL-8 (pg/mL) | 5.3 (13.2) | 4.5 (9.0) | 6.1 (19.1) | 0.678 |
| MIP-1β (pg/mL) | 42.8 (31.4) | 46.5 (19.9) | 32.9 (39.7) | 0.678 |
| GM-CSF (pg/mL) | 0.2 (0.17) | 0.2 (0.19) | 0.2 (0.08) | 0.865 |
| TNF-α (pg/mL) | 21.4 (37.7) | 17.8 (15.4) | 28.7 (44.7) | 0.061 |
| Uremic Toxins | ||||
| IS (mg/L) | 15.0 (15) | 12.6 (15.9) | 17.9 (10.8) | 0.141 |
| pCS (mg/L) | 24.2 (24.0) | 21.8 (28.3) | 25.2 (16.2) | 0.438 |
| IAA (ug/L) | 1181.3 (670.1) | 1254.8 (934.5) | 1144.6 (406.9) | 0.409 |
| Lipid Peroxidation Marker | ||||
| MDA (mmol/L) | 0.67 (1.3) | 0.56 (2.1) | 0.75 (1.1) | 0.659 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Britto, I.; Couto, H.; de Paiva, B.R.; de Brito, J.S.; Alvarenga, L.; Cardozo, L.F.M.F.; Leite, P.E.C.; Berretta, A.A.; Ribeiro-Alves, M.; Delgado, V.P.; et al. Effects of Curcuma longa L. and Green Propolis Extract-Loaded Microcapsules Supplementation on Inflammation in Hemodialysis Patients: Preliminary Results of a Randomized Clinical Trial. Life 2025, 15, 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15060891
Britto I, Couto H, de Paiva BR, de Brito JS, Alvarenga L, Cardozo LFMF, Leite PEC, Berretta AA, Ribeiro-Alves M, Delgado VP, et al. Effects of Curcuma longa L. and Green Propolis Extract-Loaded Microcapsules Supplementation on Inflammation in Hemodialysis Patients: Preliminary Results of a Randomized Clinical Trial. Life. 2025; 15(6):891. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15060891
Chicago/Turabian StyleBritto, Isadora, Heloiza Couto, Bruna Regis de Paiva, Jessyca S. de Brito, Livia Alvarenga, Ludmila F. M. F. Cardozo, Paulo Emilio Correa Leite, Andresa A. Berretta, Marcelo Ribeiro-Alves, Virgílio Pimentel Delgado, and et al. 2025. "Effects of Curcuma longa L. and Green Propolis Extract-Loaded Microcapsules Supplementation on Inflammation in Hemodialysis Patients: Preliminary Results of a Randomized Clinical Trial" Life 15, no. 6: 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15060891
APA StyleBritto, I., Couto, H., de Paiva, B. R., de Brito, J. S., Alvarenga, L., Cardozo, L. F. M. F., Leite, P. E. C., Berretta, A. A., Ribeiro-Alves, M., Delgado, V. P., Cunha, D. F. d., Sanz, C. L., Nakao, L. S., & Mafra, D. (2025). Effects of Curcuma longa L. and Green Propolis Extract-Loaded Microcapsules Supplementation on Inflammation in Hemodialysis Patients: Preliminary Results of a Randomized Clinical Trial. Life, 15(6), 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15060891









