Prognostic Significance of mTOR Expression in Recurrence Following Hepatic Metastasectomy in Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Patient Selection and Sample Collection
3. Results
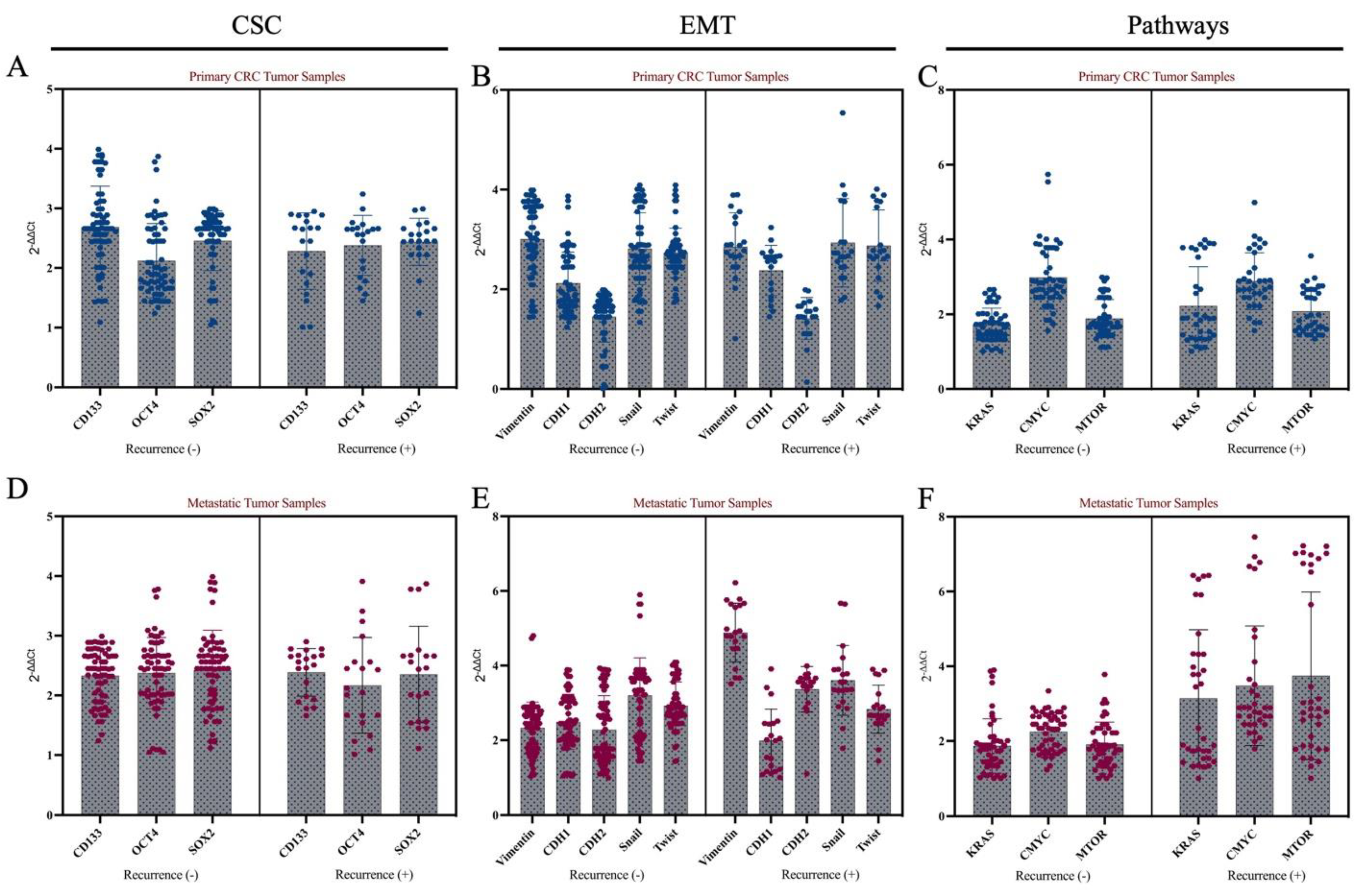
3.1. Recurrence Patterns and Clinical Correlates Following Liver Metastasectomy
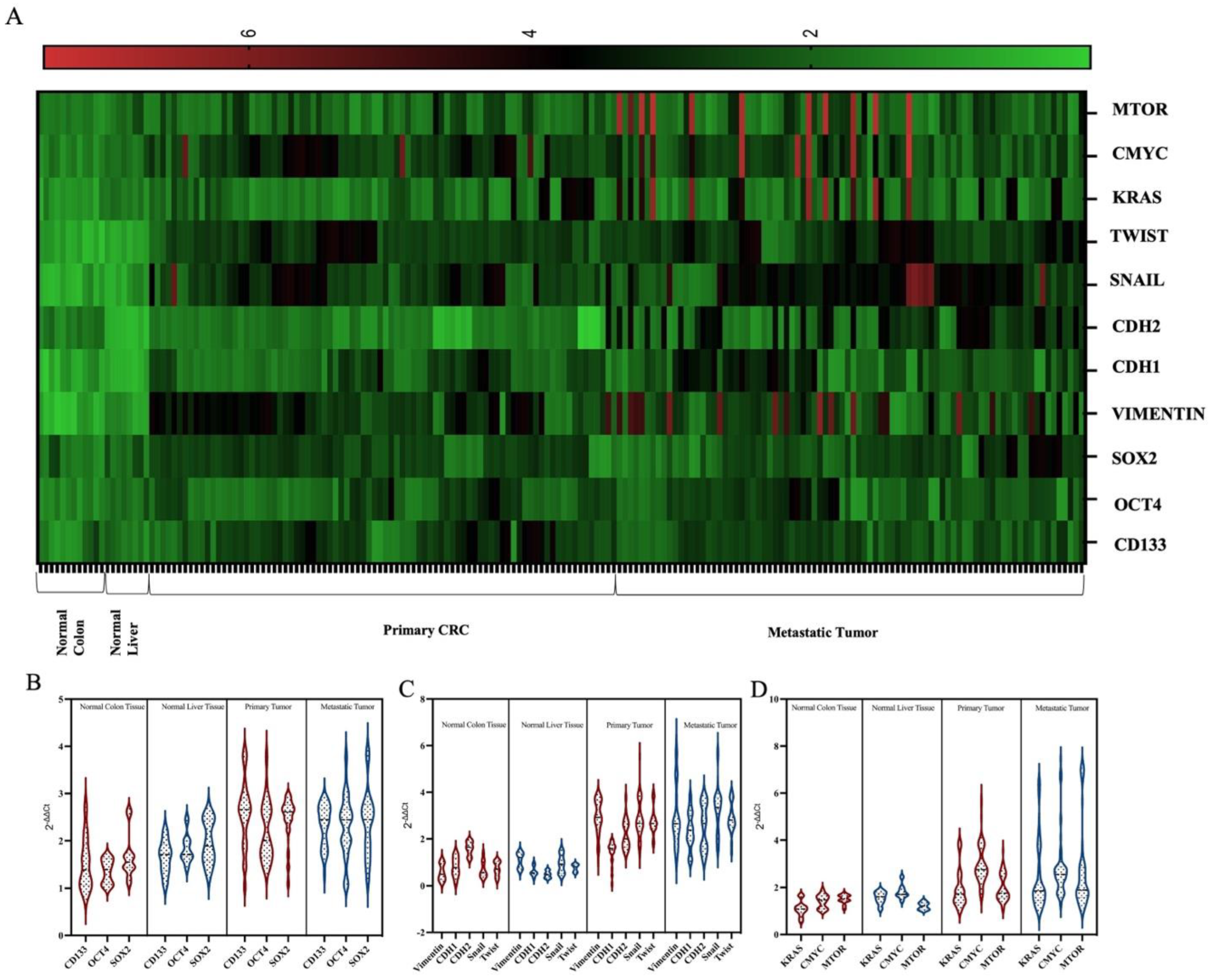
3.2. Molecular Features of Primary Tumors and Metastatic Tumors
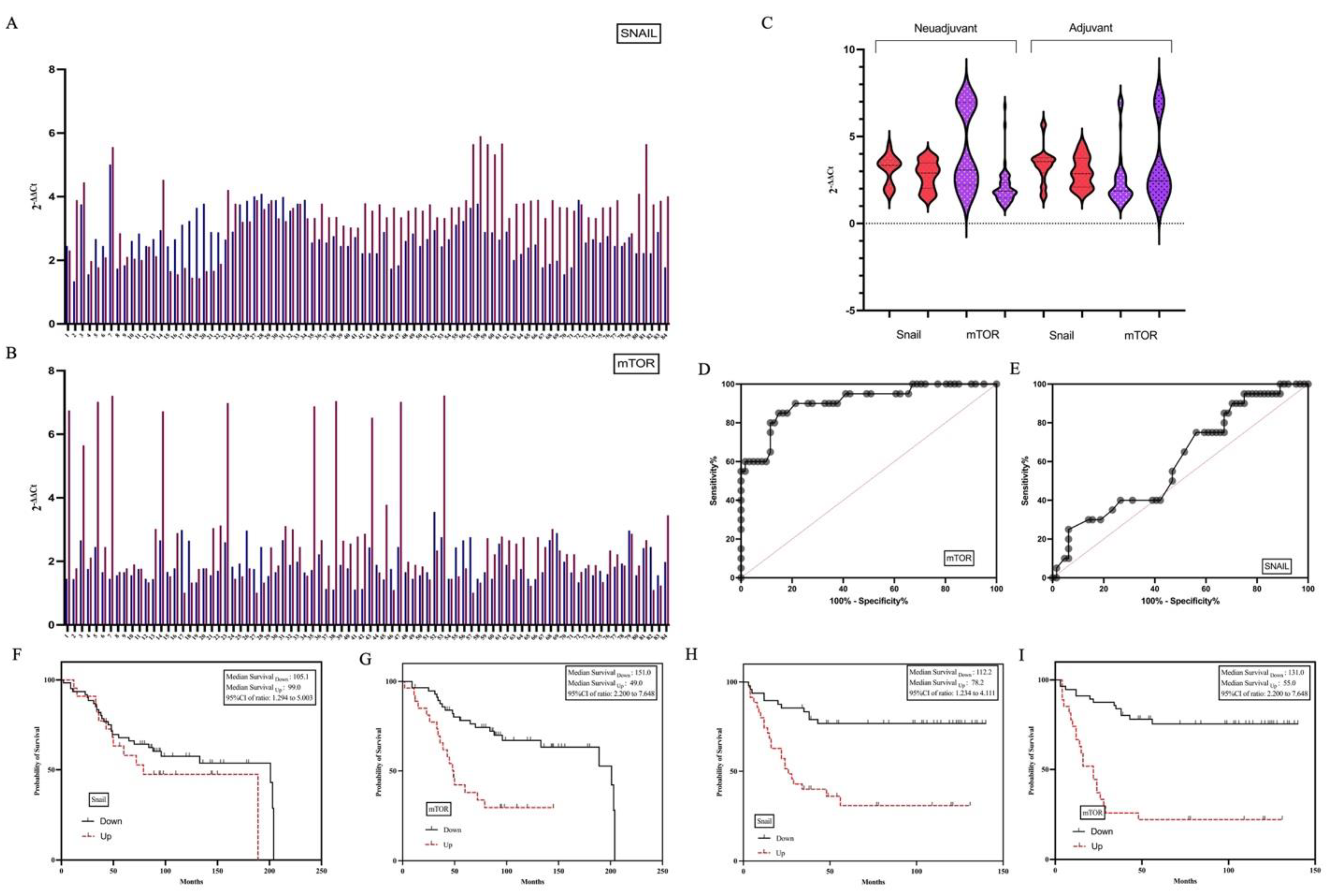
3.3. Pathological and Clinical Characteristics of Patients with High SNAIL and mTOR Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CRC | Colorectal cancer |
| OS | Overall survival |
| FFPE | Formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded |
| CSC | Cancer stem cell |
| EMT | Epithelial–mesenchymal transition |
References
- Martin, J.; Petrillo, A.; Smyth, E.C.; Shaida, N.; Khwaja, S.; Cheow, H.; Duckworth, A.; Heister, P.; Praseedom, R.; Jah, A.; et al. Colorectal liver metastases: Current management and future perspectives. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 11, 761–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Q.Y.; Wei, Y.; Chen, J.W.; Chang, W.J.; Ye, L.C.; Zhu, D.X.; Xu, J.M. Anti-EGFR and anti-VEGF agents: Important targeted therapies of colorectal liver metastases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 4263–4275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhong, X.; He, X.; Hu, Z.; Huang, H.; Chen, J.; Chen, K.; Zhao, S.; Wei, P.; Li, D. Liver metastasis from colorectal cancer: Pathogenetic development, immune landscape of the tumour microenvironment and therapeutic approaches. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. CR 2023, 42, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valderrama-Trevino, A.I.; Barrera-Mera, B.; Ceballos-Villalva, J.C.; Montalvo-Jave, E.E. Hepatic metastasis from colorectal cancer. Eur. J. Hepato-Gastroenterol. 2017, 7, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, R.; Delvart, V.; Pascal, G.; Valeanu, A.; Castaing, D.; Azoulay, D.; Giacchetti, S.; Paule, B.; Kunstlinger, F.; Ghémard, O.; et al. Rescue surgery for unresectable colorectal liver metastases downstaged by chemotherapy: A model to predict long-term survival. Ann. Surg. 2004, 240, 644–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanemitsu, Y.; Mizusawa, J.; Inaba, Y.; Hamaguchi, T.; Shida, D.; Ohue, M.; Komori, K.; Shiomi, A.; Shiozawa, M.; Watanabe, J.; et al. Hepatectomy Followed by mFOLFOX6 Versus Hepatectomy Alone for Liver-Only Metastatic Colorectal Cancer (JCOG0603): A Phase II or III Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 3789–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopetz, S.; Chang, G.J.; Overman, M.J.; Eng, C.; Sargent, D.J.; Larson, D.W.; Grothey, A.; Vauthey, J.-N.; Nagorney, D.M.; McWilliams, R.R. Improved Survival in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Is Associated with Adoption of Hepatic Resection and Improved Chemotherapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 3677–3683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, A.B.; Venook, A.P.; Al-Hawary, M.M.; Arain, M.A.; Chen, Y.J.; Ciombor, K.K.; Cohen, S.; Cooper, H.S.; Deming, D.; Farkas, L.; et al. Colon Cancer, Version 2.2021, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Canc. Netw. 2021, 19, 329–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 2020 Exceptional Surveillance of Colorectal Cancer (NICE Guideline NG151); Copyright © NICE 2020; National Institute for Health and Care Excellence: London, UK, 2020.
- Van Cutsem, E.; Cervantes, A.; Adam, R.; Sobrero, A.; Van Krieken, J.H.; Aderka, D.; Aranda Aguilar, E.; Bardelli, A.; Benson, A.; Bodoky, G.; et al. ESMO consensus guidelines for the management of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2016, 27, 1386–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.D.; Holzapfel, B.M.; Liu, J.; Lee, T.K.; Ma, S.; Jovanovic, L.; An, J.; Russell, P.J.; Clements, J.A.; Hutmacher, D.W.; et al. Tie-2 regulates the stemness and metastatic properties of prostate cancer cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 2572–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshizumi, A.; Kuboki, S.; Takayashiki, T.; Takano, S.; Takayanagi, R.; Sonoda, I.; Ohtsuka, M. Tspan15-ADAM10 signalling enhances cancer stem cell-like properties and induces chemoresistance via Notch1 activation in ICC. Liver Int. 2023, 43, 2275–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, B.; Chen, X.; Xin, Y.; Li, K.; Zhang, C.; Tang, K.; Tan, Y. Cell mechanics regulate the migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via JNK signaling. Acta Biomater. 2024, 176, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Chen, K.; Hong, F.; Gao, G.; Dai, X.; Yin, H. METTL3 facilitates stemness properties and tumorigenicity of cancer stem cells in hepatocellular carcinoma through the SOCS3/JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. Cancer Gene Ther. 2024, 31, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, P.; Chi, X.; Yan, X.; Wu, F.; Liang, Z.; Yang, W.H. Alanine-Glyoxylate Aminotransferase Sustains Cancer Stemness Properties through the Upregulation of SOX2 and OCT4 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Saigusa, S.; Tanaka, K.; Toiyama, Y.; Yokoe, T.; Okugawa, Y.; Ioue, Y.; Miki, C.; Kusunoki, M. Correlation of CD133, OCT4, and SOX2 in rectal cancer and their association with distant recurrence after chemoradiotherapy. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2009, 16, 3488–3498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazouli, M.; Roubelakis, M.G.; Theodoropoulos, G.E.; Papailiou, J.; Vaiopoulou, A.; Pappa, K.I.; Nikiteas, N.; Anagnou, N.P. Anagnou OCT4 spliced variant OCT4B1 is expressed in human colorectal cancer. Mol. Carcinog. 2011, 51, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Tang, J.; Gao, W.; Sun, J.; Liu, G.; Zhou, J. PPP2R1B abolishes colorectal cancer liver metastasis and sensitizes Oxaliplatin by inhibiting MAPK/ERK signaling pathway. Cancer Cell Int. 2024, 24, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Niu, W.; Liu, Q.; Huo, X.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, X. TL1A promotes metastasis and EMT process of colorectal cancer. Heliyon 2024, 10, e24392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Aksoy, S.A.; Tunca, B.; Erçelik, M.; Tezcan, G.; Ozturk, E.; Cecener, G.; Ugras, N.; Yilmazlar, T.; Yerci, O. Early-stage colon cancer with high MALAT1 expression is associated with the 5-Fluorouracil resistance and future metastasis. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 11243–11253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Craene, B.; Berx, G. Regulatory networks defining EMT during cancer initiation and progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hata, N.; Shigeyasu, K.; Umeda, Y.; Yano, S.; Takeda, S.; Yoshida, K.; Fuji, T.; Yoshida, R.; Yasui, K.; Umeda, H.; et al. ADAR1 is a promising risk stratification biomarker of remnant liver recurrence after hepatic metastasectomy for colorectal cancer. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Xin, Z.C.; Wang, K. Impact of Molecular Status on Metastasectomy of Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastases. Clin. Colon Rectal Surg. 2023, 36, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sun, M.; Jiang, Z.; Gu, P.; Guo, B.; Li, J.; Cheng, S.; Ba, Q.; Wang, H. Cadmium promotes colorectal cancer metastasis through EGFR/Akt/mTOR signaling cascade and dynamics. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 899, 165699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Tian, T.T.; Wang, F.Q.; Pan, C.S.; Sun, K.; Wang, X.Y.; Yang, B.; Yang, Z.; Tang, D.X.; Han, J.Y. Chanling Gao suppresses colorectal cancer via PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway modulation and enhances quality of survival. Environ. Toxicol. 2024, 39, 1107–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Features | Non-Recurrent | Recurrent | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| n = 50 (59.5%) | n = 34 (40.5%) | ||
| Sex | 0.017 | ||
| Male | 31 (62.0%) | 25 (85.3%) | |
| Female | 19 (38.0%) | 5 (14.7%) | |
| Age (median, IQR) | 60.0 (55.0–68.5) | 59.0 (53.0–65.0) | 0.226 |
| Primary Tumor Site | 0.513 | ||
| Sigmoid | 16 (32.0%) | 11 (32.4%) | |
| Left colon | 6 (12.0%) | 2 (5.9%) | |
| Right colon | 6 (12.0%) | 4 (11.8%) | |
| Transvers colon | 2 (4.0%) | 1 (2.9%) | |
| Rectum | 20 (40.0%) | 16 (47.1%) | |
| Primary Tumor (T) | 0.507 | ||
| 1 | 1 (2.0%) | 1 (2.9%) | |
| 2 | 4 (8.0%) | 6 (17.6%) | |
| 3 | 39 (78.0%) | 22 (67.7%) | |
| 4 | 6 (12.0%) | 5 (14.7%) | |
| Regional Lymph Node (N) | 0.711 | ||
| 0 | 17 (34.0%) | 12 (35.3%) | |
| 1 | 15 (30.0%) | 7 (20.6%) | |
| 2 | 18 (36.0%) | 15 (44.1%) | |
| Lymphatic Invasion | 0.502 | ||
| Absence | 35 (70.%) | 23 (67.6%) | |
| Presence | 15 (30.0%) | 11 (32.4%) | |
| Perineural Invasion | 0.302 | ||
| Absence | 39 (78.0%) | 24 (70.6%) | |
| Presence | 11 (22.0%) | 10 (29.4%) | |
| Vascular Invasion | 0.375 | ||
| Absence | 40 (80.0%) | 29 (85.3%) | |
| Presence | 10 (20.0%) | 5 (14.7%) | |
| Type of Liver Metastasis | 0.173 | ||
| Metachronous | 43 (86.0%) | 24 (70.6%) | |
| Synchronous | 7 (14.0%) | 10 (29.4%) | |
| Adjuvant Therapy | 0.032 | ||
| Absence | 10 (20.0%) | 14 (41.2%) | |
| Presence | 40 (80.0%) | 20 (58.8%) | |
| Neoadjuvant Therapy | 0.363 | ||
| Absence | 41 (82.0%) | 26 (76.5%) | |
| Presence | 9 (18.0%) | 8 (23.5%) |
| Localization | Neoadjuvant | Adjuvant | Recurrence After Metastasectomy | Snail | mTOR | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (−) | (+) | (−) | (+) | (−) | (+) | Down | Up | Down | Up | |
| Rectum | 25 (69.4) | 11 (%30.6) | 11 (30.6) | 25 (69.4) | 20 (55.6) | 16 (44.4) | 15 (41.7) | 21 (58.3) | 21 (58.3) | 15 (41.7) |
| Sigmoid | 23 (85.2) | 4 (14.8) | 10 (37) | 17 (63) | 16 (59.3) | 11 (40.7) | 9 (33.3) | 18 (66.7) | 20 (74.1) | 7 (25.9) |
| Left Colon | 8 (100) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 8 (100) | 6 (75) | 2 (25) | 2 (25) | 6 (75) | 7 (87.5) | 1 (12.5) |
| Right Colon | 9 (90%) | 1 (10) | 3 (30) | 7 (70) | 6 (60) | 4 (40) | 3 (30) | 7 (70) | 7 (70) | 3 (30) |
| Transvers Colon | 2 (66.7) | 1 (33.3) | 0 (0) | 3 (100) | 2 (66.7) | 1 (33.3) | 2 (66.7) | 1 (33.3) | 2 (66.7) | 1 (33.3) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aksoy, F.; Ak-Aksoy, S.; Karamustafaoglu, A.; Tekin, C.; Ercelik, M.; Tunca, B.; Duman, B.O.; Isik, O.; Ugras, N.; Kaya, E. Prognostic Significance of mTOR Expression in Recurrence Following Hepatic Metastasectomy in Colorectal Cancer. Life 2025, 15, 877. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15060877
Aksoy F, Ak-Aksoy S, Karamustafaoglu A, Tekin C, Ercelik M, Tunca B, Duman BO, Isik O, Ugras N, Kaya E. Prognostic Significance of mTOR Expression in Recurrence Following Hepatic Metastasectomy in Colorectal Cancer. Life. 2025; 15(6):877. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15060877
Chicago/Turabian StyleAksoy, Fuat, Secil Ak-Aksoy, Ahmet Karamustafaoglu, Cagla Tekin, Melis Ercelik, Berrin Tunca, Busra Oncel Duman, Ozgen Isik, Nesrin Ugras, and Ekrem Kaya. 2025. "Prognostic Significance of mTOR Expression in Recurrence Following Hepatic Metastasectomy in Colorectal Cancer" Life 15, no. 6: 877. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15060877
APA StyleAksoy, F., Ak-Aksoy, S., Karamustafaoglu, A., Tekin, C., Ercelik, M., Tunca, B., Duman, B. O., Isik, O., Ugras, N., & Kaya, E. (2025). Prognostic Significance of mTOR Expression in Recurrence Following Hepatic Metastasectomy in Colorectal Cancer. Life, 15(6), 877. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15060877






