Neuroinflammatory Signaling and Immune Cell Infiltration Differ in Brains of Rats Exposed to Space Radiation and Social Isolation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Determination of Res and Vul Subgroups
2.3. Euthanasia
2.4. RNA Extraction
2.5. Nanostring Assay
2.6. Cell Isolation
2.7. Flow Cytometry
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
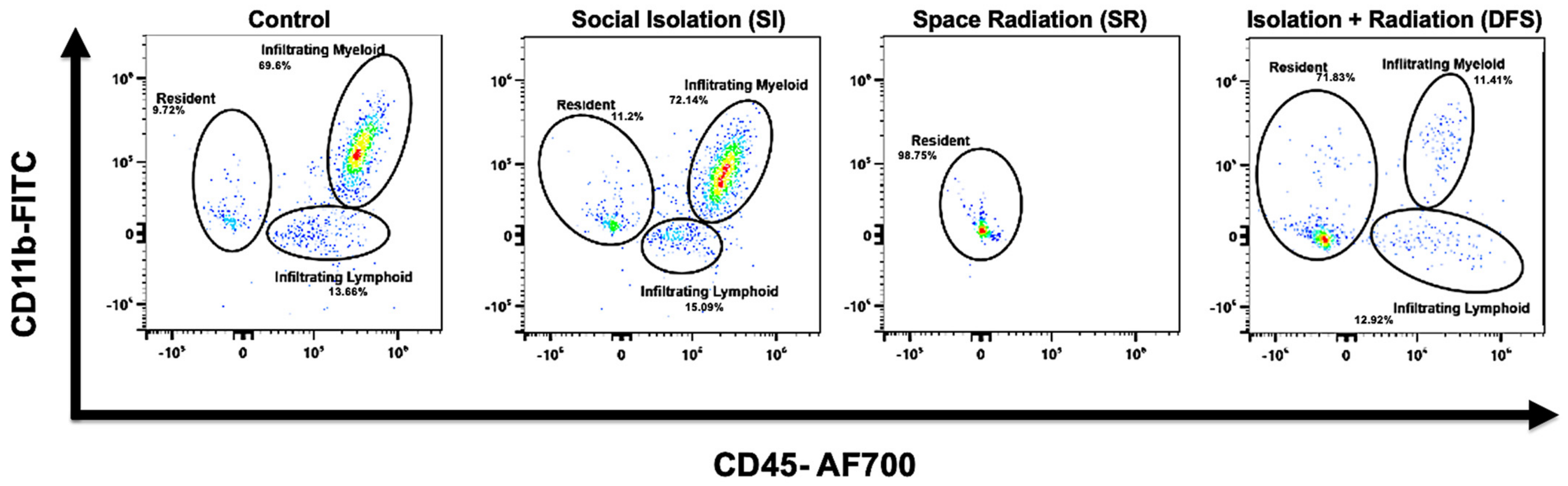
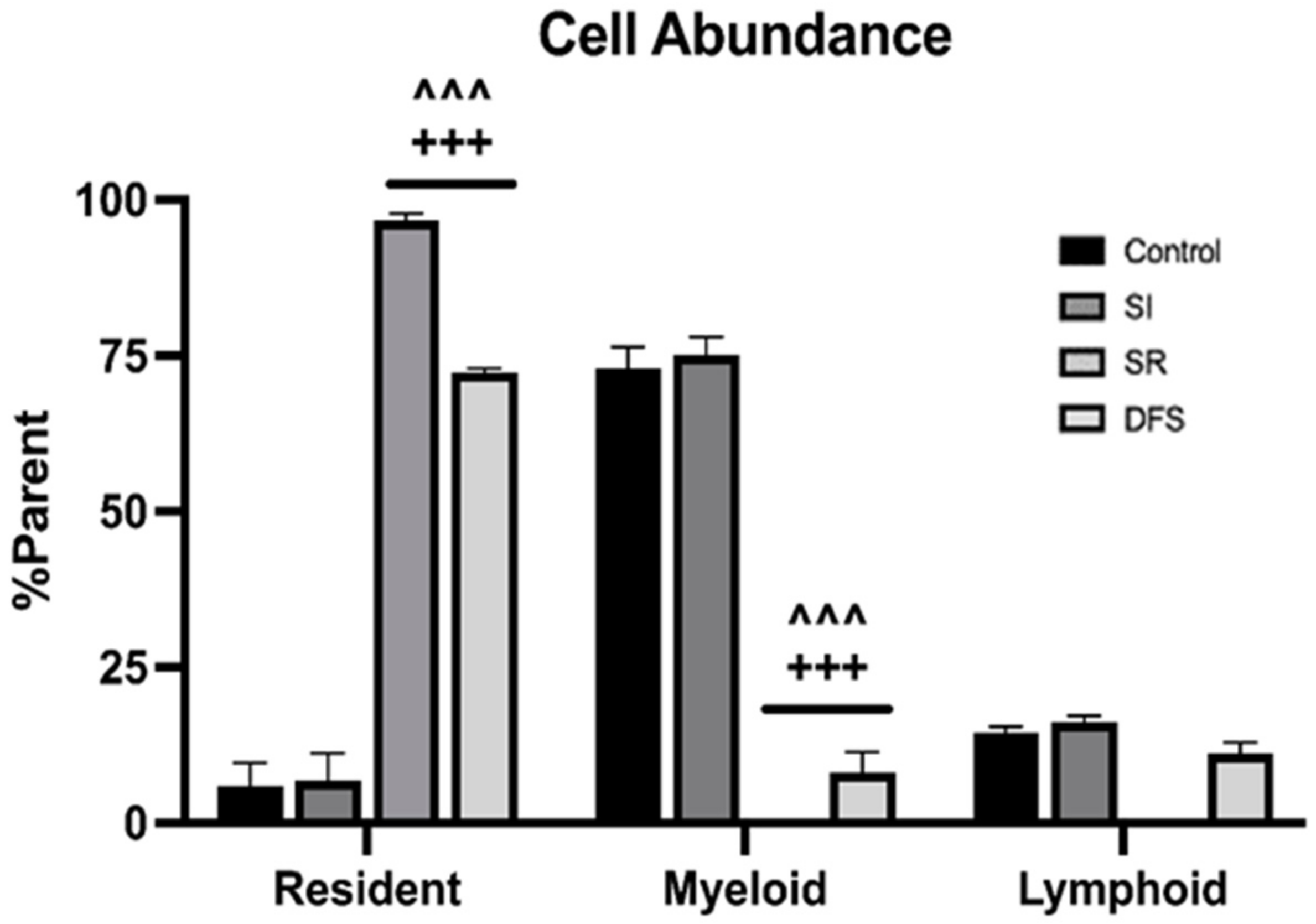
3.1. Immune Cell Infiltration
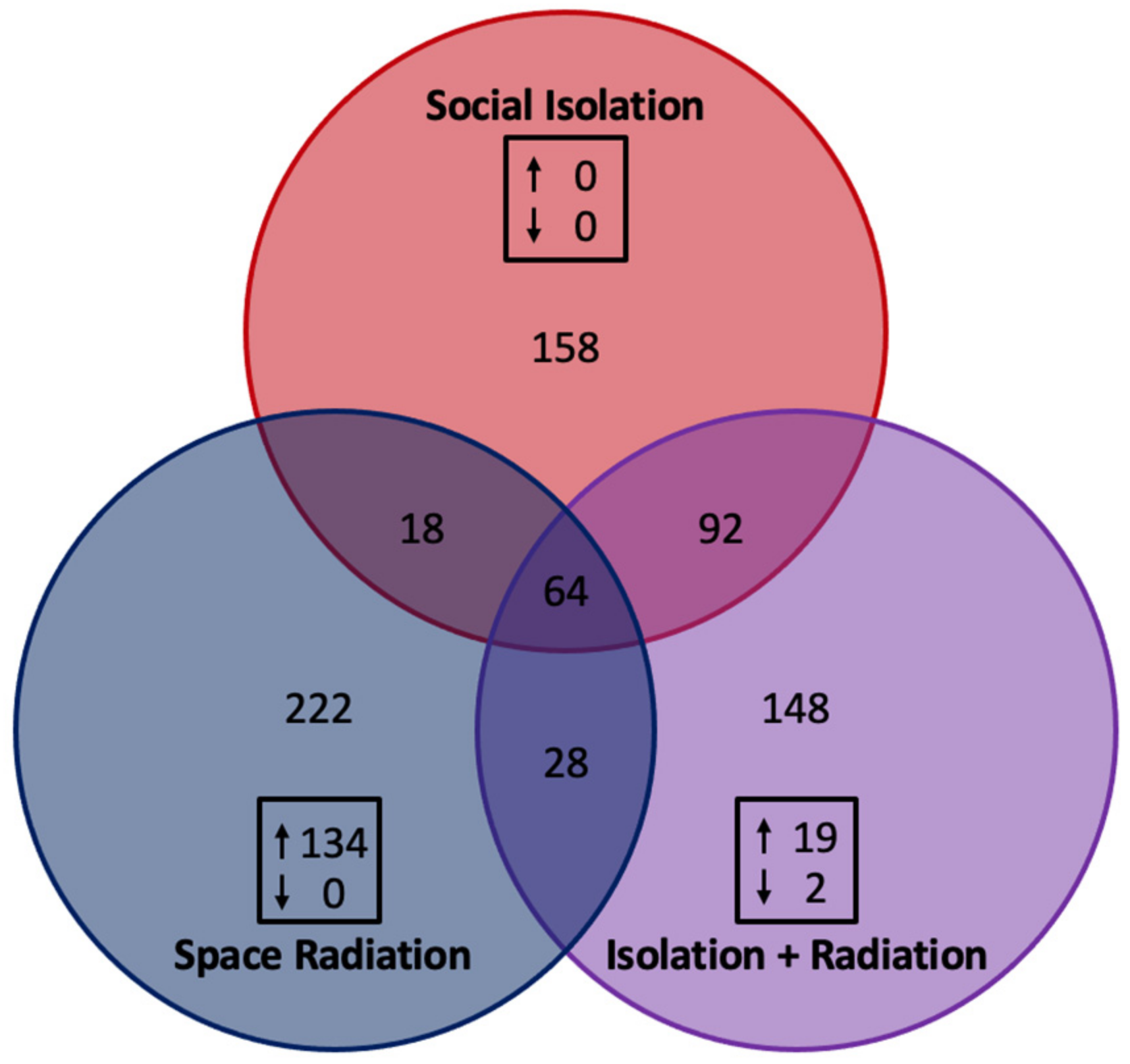
3.2. Gene Expression Related to Neuroinflammatory Signaling
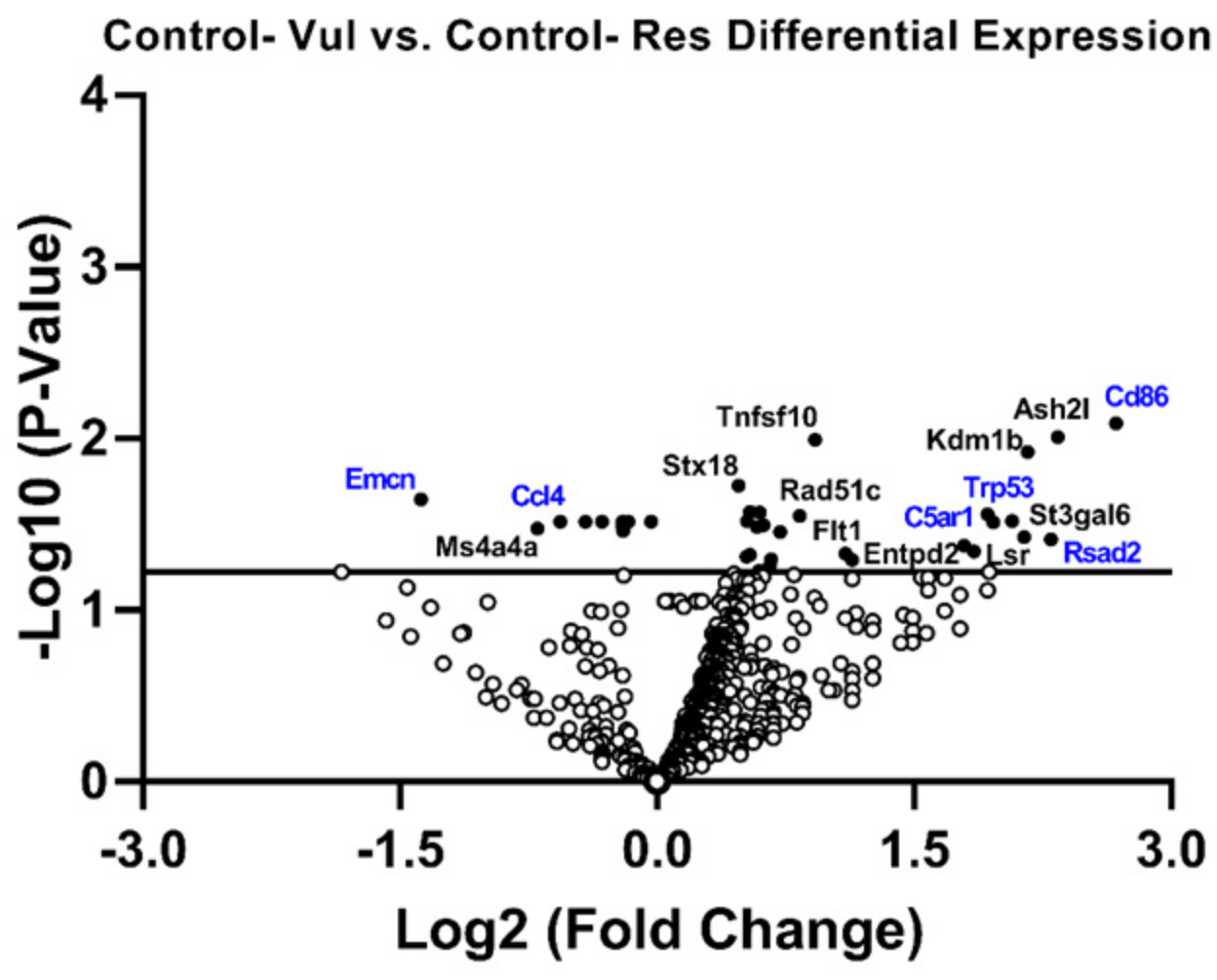
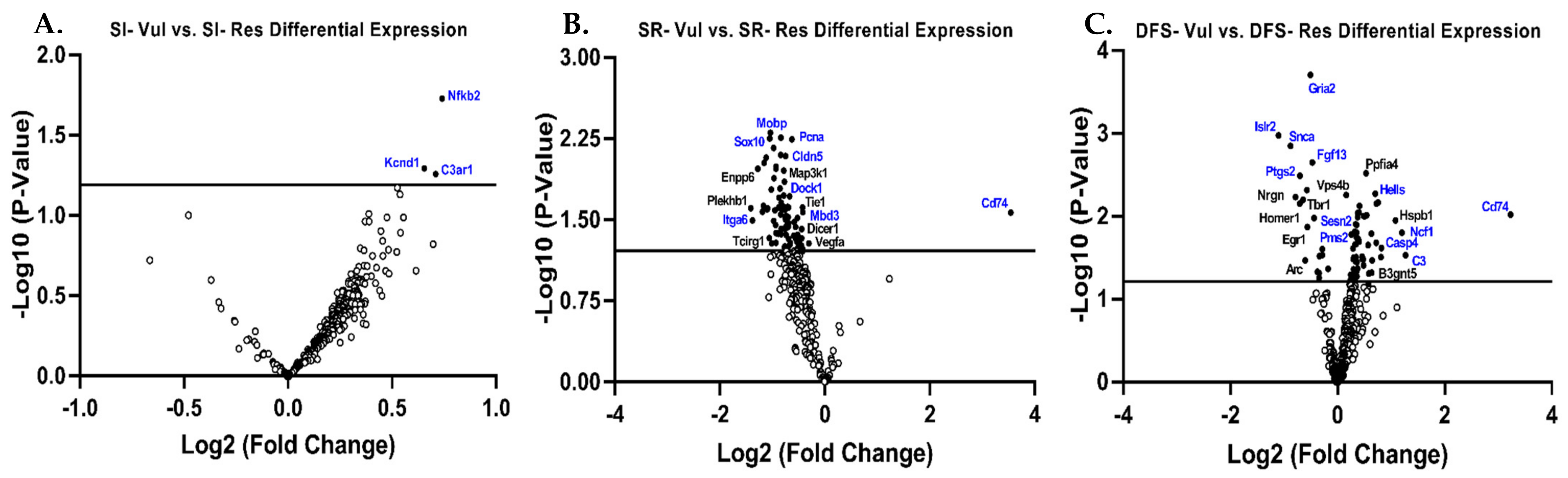
3.3. Gene Expression in Res Versus Vul Animals
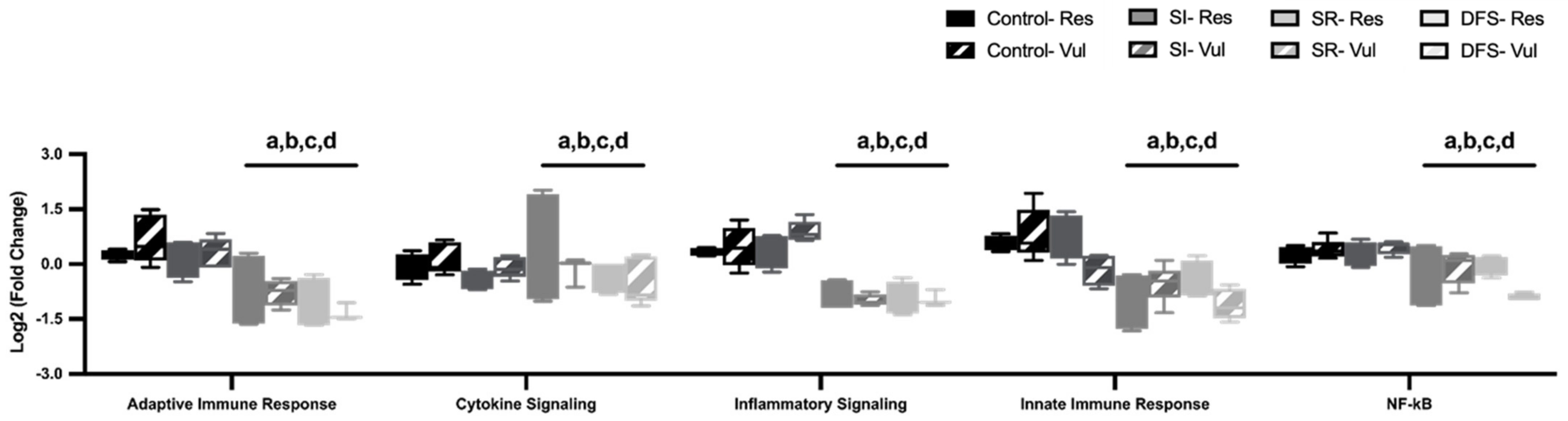
3.4. Alterations in Brain Neuroimmune Pathways
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DFS | dual flight stressors |
| HPA | Hypothalamic–Pituitary–Adrenal |
| SR | space radiation |
| SI | social isolation |
| HPC | hippocampus |
| ATSET | Attentional Set-Shifting |
| rPVT | rodent psychomotor vigilance test |
| Vul | vulnerable |
| REM | rapid eye movement sleep |
| Res | resilient |
| GCRsim | 15 cGy simplified 5-ion galactic cosmic radiation |
| ISS | international space station |
References
- Stahn, A.C.; Bucher, D.; Eulenburg, P.Z.; Denise, P.; Smith, N.; Pagnini, F.; White, O. Paving the way to better understand the effects of prolonged spaceflight on operational performance and its neural bases. NPJ Microgravity 2023, 9, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncharova, L.B.; Tarakanov, A.O. Why chemokines are cytokines while their receptors are not cytokine ones? Curr. Med. Chem. 2008, 15, 1297–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Bueno, B.; Caso, J.R.; Leza, J.C. Stress as a neuroinflammatory condition in brain: Damaging and protective mechanisms. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2008, 32, 1136–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiecolt-Glaser, J.K.; McGuire, L.; Robles, T.F.; Glaser, R. Emotions, morbidity, and mortality: New perspectives from psychoneuroimmunology. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2002, 53, 83–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakata, A. psychosocial job stress and immunity: A systematic review. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 934, 39–75. [Google Scholar]
- Garate, I.; Garcia-Bueno, B.; Madrigal, J.L.M.; Bravo, L.; Caso, J.R.; Alou, L.; Gomez-Lus, M.L.; Micó, J.A.; Leza, J.C. Stress-induced neuroinflammation: Role of the Toll-like receptor-4 pathway. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 73, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelidou, A.; Asadi, S.; Alysandratos, K.-D.; Karagkouni, A.; Kourembanas, S.; Theoharides, T.C. Perinatal stress, brain inflammation and risk of autism-review and proposal. BMC Pediatr. 2012, 12, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frischer, J.M.; Bramow, S.; Dal-Bianco, A.; Lucchinetti, C.F.; Rauschka, H.; Schmidbauer, M.; Laursen, H.; Sorensen, P.S.; Lassmann, H. The relation between inflammation and neurodegeneration in multiple sclerosis brains. Brain J. Neurol. 2009, 132 Pt 5, 1175–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagkouni, A.; Alevizos, M.; Theoharides, T.C. Effect of stress on brain inflammation and multiple sclerosis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2013, 12, 947–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagberg, H.; Gressens, P.; Mallard, C. Inflammation during fetal and neonatal life: Implications for neurologic and neuropsychiatric disease in children and adults. Ann. Neurol. 2012, 71, 444–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theoharides, T.C.; Conti, P.; Economu, M. Brain inflammation, neuropsychiatric disorders, and immunoendocrine effects of luteolin. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2014, 34, 187–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, M.G.; Weber, M.D.; Watkins, L.R.; Maier, S.F. Stress-induced neuroinflammatory priming: A liability factor in the etiology of psychiatric disorders. Neurobiol. Stress 2016, 4, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Culley, D.J.; Snayd, M.; Baxter, M.G.; Xie, Z.; Lee, I.H.; Rudolph, J.; Inouye, S.K.; Marcantonio, E.R.; Crosby, G. Systemic inflammation impairs attention and cognitive flexibility but not associative learning in aged rats: Possible implications for delirium. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2014, 6, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parihar, V.K.; Allen, B.; Tran, K.K.; Macaraeg, T.G.; Chu, E.M.; Kwok, S.F.; Chmielewski, N.N.; Craver, B.M.; Baulch, J.E.; Acharya, M.M.; et al. What happens to your brain on the way to mars. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1400256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obenaus, A.; Huang, L.; Smith, A.; Favre, C.J.; Nelson, G.; Kendall, E. Magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy of the rat hippocampus 1 month after exposure to 56Fe-particle radiation. Radiat. Res. 2008, 169, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulose, S.M.; Bielinski, D.F.; Carrihill-Knoll, K.L.; Rabin, B.M.; Shukitt-Hale, B. Exposure to 16O-particle radiation causes aging-like decrements in rats through increased oxidative stress, inflammation and loss of autophagy. Radiat. Res. 2011, 176, 761–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krukowski, K.; Grue, K.; Frias, E.S.; Pietrykowski, J.; Jones, T.; Nelson, G.; Rosi, S. Female mice are protected from space radiation-induced maladaptive responses. Brain Behav. Immun. 2018, 74, 106–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parihar, V.K.; Angulo, M.C.; Allen, B.D.; Syage, A.; Usmani, M.T.; de la Chapelle, E.P.; Amin, A.N.; Flores, L.; Lin, X.; Giedzinski, E.; et al. Sex-Specific Cognitive Deficits Following Space Radiation Exposure. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 535885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Omran, A.J.; Shao, A.S.; Watanabe, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Xue, C.; Watanabe, J.; Davies, D.L.; Shao, X.M.; Liang, J. Social isolation induces neuroinflammation and microglia overactivation, while dihydromyricetin prevents and improves them. J. Neuroinflamm. 2022, 19, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorovic, N.; Filipovic, D. The antidepressant- and anxiolytic-like effects of fluoxetine and clozapine in chronically isolated rats involve inhibition of hippocampal TNF-α. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2017, 163, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipovic, D.; Stanisavljevic, A.; Jasnic, N.; Bernardi, R.E.; Inta, D.; Peric, I.; Gass, P. Chronic Treatment with Fluoxetine or Clozapine of Socially Isolated Rats Prevents Subsector-Specific Reduction of Parvalbumin Immunoreactive Cells in the Hippocampus. Neuroscience 2018, 371, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, J.A. Moving Stress Research Forward. Director’s Message. 2018. Available online: https://www.nimh.nih.gov/about/director/messages (accessed on 26 October 2018).
- Davis, C.M.; DeCicco-Skinner, K.L.; Roma, P.G.; Hienz, R.D. Individual differences in attentional deficits and dopaminergic protein levels following exposure to proton radiation. Radiat. Res. 2014, 181, 258–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonart, G.; Parris, B.; Johnson, A.M.; Miles, S.; Sanford, L.D.; Singletary, S.J.; Britten, R.A. Executive function in rats is impaired by low (20 cGy) doses of 1 GeV/u 56Fe particles. Radiat. Res. 2012, 178, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyrobek, A.J.; Britten, R.A. Individual variations in dose response for spatial memory learning among outbred wistar rats exposed from 5 to 20 cGy of 56Fe particles. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2016, 57, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, L.; Luo, S.S.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Luo, D.; Yang, H.; Li, W.; He, J.; Zhong, X.L.; Liu, Z.H.; et al. The critical role of the hippocampal NLRP3 inflammasome in social isolation-induced cognitive impairment in male mice. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2020, 175, 107301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, S.; Al Omran, A.; Shao, A.S.; Xue, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Davies, D.L.; Shao, X.M.; Watanabe, J.; Liang, J. Dihydromyricetin improves social isolation-induced cognitive impairments and astrocytic changes in mice. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellman, L.L.; Fitzpatrick, M.E.; Hallum, O.Y.; Sutton, A.M.; Williams, B.L.; Sanford, L.D. Individual Differences in Animal Stress Models: Considering Resilience, Vulnerability, and the Amygdala in Mediating the Effects of Stress and Conditioned Fear on Sleep. Sleep 2016, 39, 1293–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellman, L.L.; Fitzpatrick, M.E.; Hallum, O.Y.; Sutton, A.M.; Williams, B.L.; Sanford, L.D. The basolateral amygdala can mediate the effects of fear memory on sleep independently of fear behavior and the peripheral stress response. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2017, 137, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellman, L.L.; Fitzpatrick, M.E.; Sutton, A.M.; Williams, B.L.; Machida, M.; Sanford, L.D. Antagonism of corticotropin releasing factor in the basolateral amygdala of resilient and vulnerable rats: Effects on fear-conditioned sleep, temperature and freezing. Horm. Behav. 2018, 100, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adkins, A.M.; Colby, E.M.; Boden, A.F.; Gotthold, J.D.; Harris, R.D.; Britten, R.A.; Wellman, L.L.; Sanford, L.D. Differential Impact of Social Isolation and Space Radiation on Behavior and Motor Learning in Rats. Life 2023, 13, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adkins, A.M.; Colby, E.M.; Boden, A.F.; Gotthold, J.D.; Harris, R.D.; Britten, R.A.; Wellman, L.L.; Sanford, L.D. Effects of social isolation and galactic cosmic radiation on fine motor skills and behavioral performance. Life Sci. Space Res. 2024, 41, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adkins, A.M.; Luyo, Z.N.M.; Gibbs, A.J.; Boden, A.F.; Heerbrandt, R.S.; Gotthold, J.D.; Britten, R.A.; Wellman, L.L.; Sanford, L.D. Alterations in Blood Brain Barrier Integrity and Lateral Ventricle Differ in Rats Exposed to Space Radiation and Social Isolation. Life 2024, 14, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akiyama, T.; Horie, K.; Hinoi, E.; Hiraiwa, M.; Kato, A.; Maekawa, Y.; Takahashi, A.; Furukawa, S. How does spaceflight affect the acquired immune system? NPJ Microgravity 2020, 6, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bigley, A.B.; Agha, N.H.; Baker, F.L.; Spielmann, G.; Kunz, H.E.; Mylabathula, P.L.; Rooney, B.V.; Laughlin, M.S.; Mehta, S.K.; Pierson, D.L.; et al. NK cell function is impaired during long-duration spaceflight. J. Appl. Physiol. 2019, 126, 842–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kernagis, D.N.; Balcer-Kubiczek, E.; Bazyar, S.; Orschell, C.M.; Jackson, I.L. Medical countermeasures for the hematopoietic-subsyndrome of acute radiation syndrome in space. Life Sci. Space Res. 2022, 35, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peanlikhit, T.; Honikel, L.; Liu, J.; Zimmerman, T.; Rithidech, K. Countermeasure efficacy of apigenin for silicon-ion-induced early damage in blood and bone marrow of exposed C57BL/6J mice. Life Sci. Space Res. 2022, 35, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dainiak, N. Hematologic consequences of exposure to ionizing radiation. Exp. Hematol. 2002, 30, 513–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dainiak, N.; Gent, R.N.; Carr, Z.; Schneider, R.; Bader, J.; Buglova, E.; Chao, N.; Coleman, C.N.; Ganser, A.; Gorin, C.; et al. First global consensus for evidence-based management of the hematopoietic syndrome resulting from exposure to ionizing radiation. Disaster Med. Public Health Prep. 2011, 5, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achanta, P.; Fuss, M.; Martinez, J.L., Jr. Ionizing radiation impairs the formation of trace fear memories and reduces hippocampal neurogenesis. Behav. Neurosci. 2009, 123, 1036–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menard, C.; Pfau, M.L.; Hodes, G.E.; Russo, S.J. Immune and Neuroendocrine Mechanisms of Stress Vulnerability and Resilience. Neuropsychopharmacology 2017, 42, 62–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pressman, S.D.; Cohen, S.; Miller, G.E.; Barkin, A.; Rabin, B.S.; Treanor, J.J. Loneliness, social network size, and immune response to influenza vaccination in college freshmen. Health Psychol. 2005, 24, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S.; Doyle, W.J.; Skoner, D.P.; Rabin, B.S.; Gwaltney, J.M., Jr. Social ties and susceptibility to the common cold. JAMA 1997, 277, 1940–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, E.M.; Hayney, M.S.; Love, G.D.; Urry, H.L.; Rosenkranz, M.A.; Davidson, R.J.; Singer, B.H.; Ryff, C.D. Social relationships, sleep quality, and interleukin-6 in aging women. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 18757–18762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, E.M. Sleep quality, social well-being, gender, and inflammation: An integrative analysis in a national sample. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1231, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacioppo, J.T.; Ernst, J.M.; Burleson, M.H.; McClintock, M.K.; Malarkey, W.B.; Hawkley, L.C.; Kowalewski, R.B.; Paulsen, A.; Hobson, J.A.; Hugdahl, K.; et al. Lonely traits and concomitant physiological processes: The MacArthur social neuroscience studies. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2000, 35, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boden-Albala, B.; Litwak, E.; Elkind, M.S.V.; Rundek, T.; Sacco, R.L. Social isolation and outcomes post stroke. Neurology 2005, 64, 1888–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt-Lunstad, J.; Smith, T.B.; Baker, M.; Harris, T.; Stephenson, D. Loneliness and social isolation as risk factors for mortality: A meta-analytic review. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 2015, 10, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilvis, R.S.; Laitala, V.; Routasalo, P.E.; Pitkala, K.H. Suffering from loneliness indicates significant mortality risk of older people. J. Aging Res. 2011, 2011, 534781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Psychological Association. Resilience. 2018. Available online: https://www.apa.org/topics/resilience (accessed on 10 September 2024).
- Cohen, S. Social relationships and health. Am. Psychol. 2004, 59, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segerstrom, S.C.; Miller, G.E. Psychological stress and the human immune system: A meta-analytic study of 30 years of inquiry. Psychol. Bull. 2004, 130, 601–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanford, L.D.; Wellman, L.L.; Adkins, A.M.; Guo, M.-L.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, R.; Yang, L.; Tang, X. Modeling integrated fear, stress, sleep and neuroimmune responses: Relevance for understanding trauma and stress-related disorders. Neurobiol. Stress 2023, 23, 100517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Adkins, A.M.; Luyo, Z.N.M.; Boden, A.F.; Heerbrandt, R.S.; Britten, R.A.; Wellman, L.L.; Sanford, L.D. Neuroinflammatory Signaling and Immune Cell Infiltration Differ in Brains of Rats Exposed to Space Radiation and Social Isolation. Life 2025, 15, 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15050747
Adkins AM, Luyo ZNM, Boden AF, Heerbrandt RS, Britten RA, Wellman LL, Sanford LD. Neuroinflammatory Signaling and Immune Cell Infiltration Differ in Brains of Rats Exposed to Space Radiation and Social Isolation. Life. 2025; 15(5):747. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15050747
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdkins, Austin M., Zachary N. M. Luyo, Alea F. Boden, Riley S. Heerbrandt, Richard A. Britten, Laurie L. Wellman, and Larry D. Sanford. 2025. "Neuroinflammatory Signaling and Immune Cell Infiltration Differ in Brains of Rats Exposed to Space Radiation and Social Isolation" Life 15, no. 5: 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15050747
APA StyleAdkins, A. M., Luyo, Z. N. M., Boden, A. F., Heerbrandt, R. S., Britten, R. A., Wellman, L. L., & Sanford, L. D. (2025). Neuroinflammatory Signaling and Immune Cell Infiltration Differ in Brains of Rats Exposed to Space Radiation and Social Isolation. Life, 15(5), 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15050747







