Accurate Chemogenetics Determines Electroacupuncture Analgesia Through Increased CB1 to Suppress the TRPV1 Pathway in a Mouse Model of Fibromyalgia
Abstract
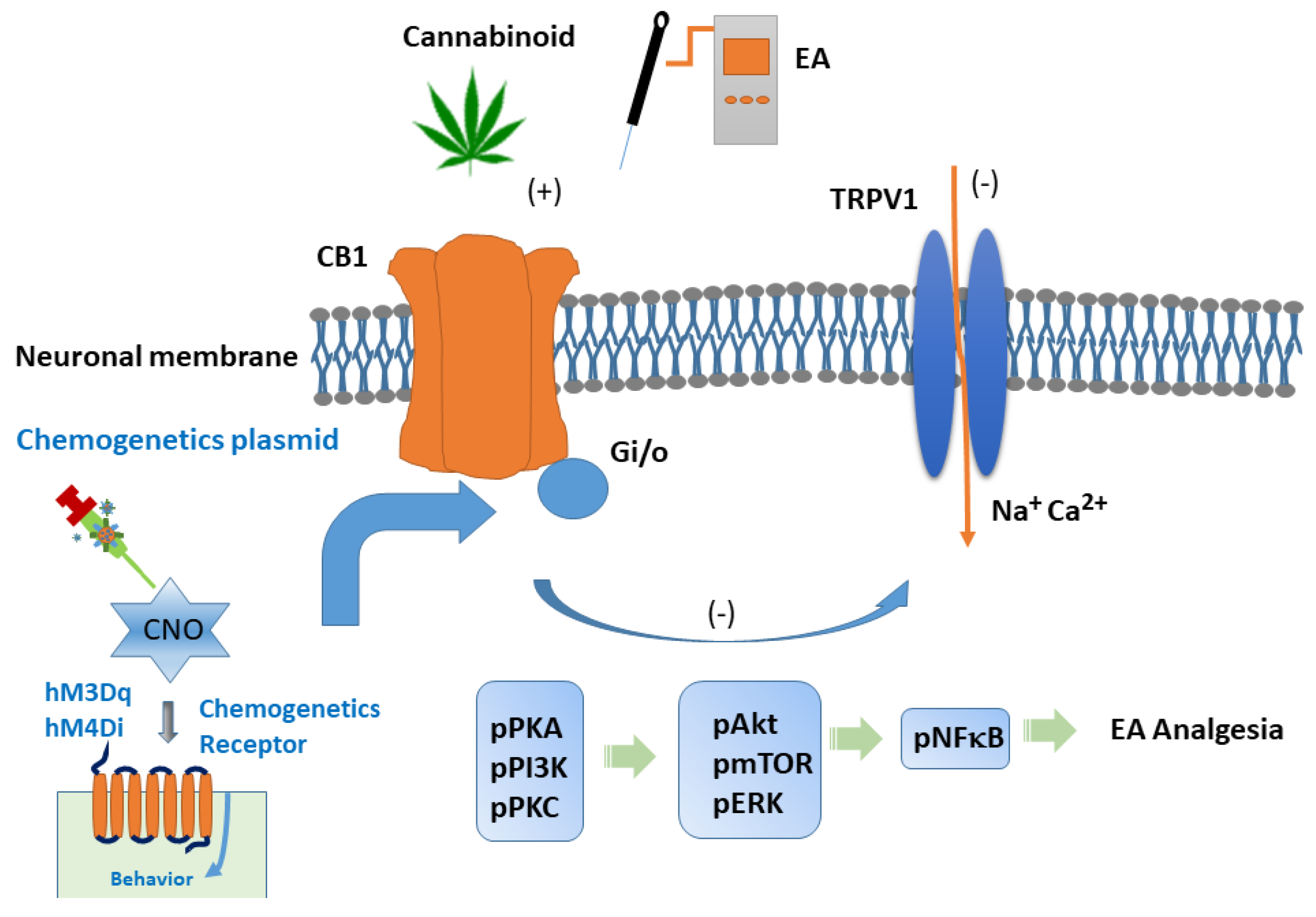
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Mouse Fibromyalgia Pain Induction
2.3. Electroacupuncture
2.4. Pain Behavior Test
2.5. Western Blot Analysis
2.6. Immunofluorescence
2.7. CB1 Receptor Agonist and Antagonist Administration
2.8. Chemogenetic Operation
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
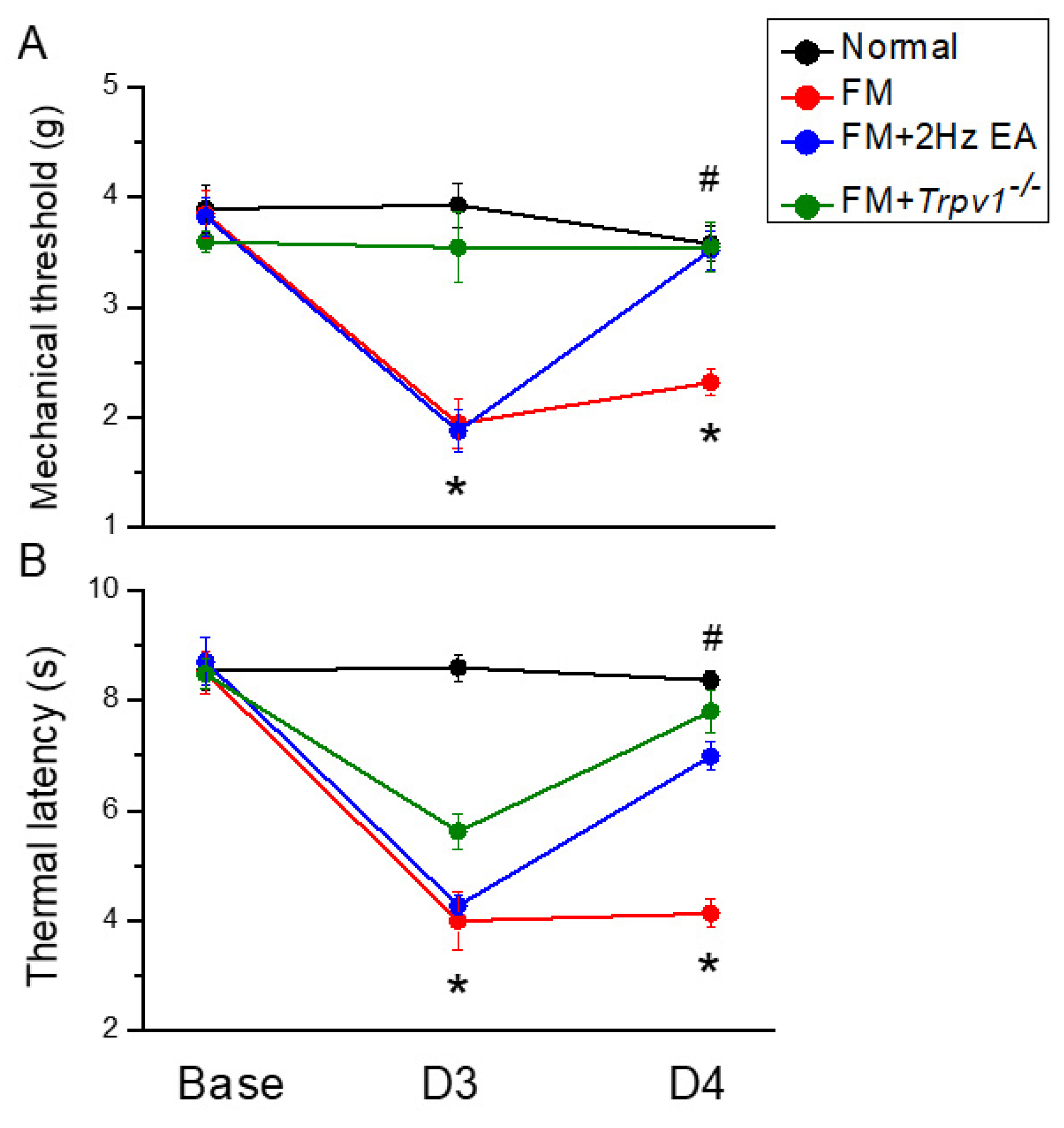
3.1. Intermittent Cold Stress-Induced Fibromyalgia Pain in Mice Reversed by Electroacupuncture
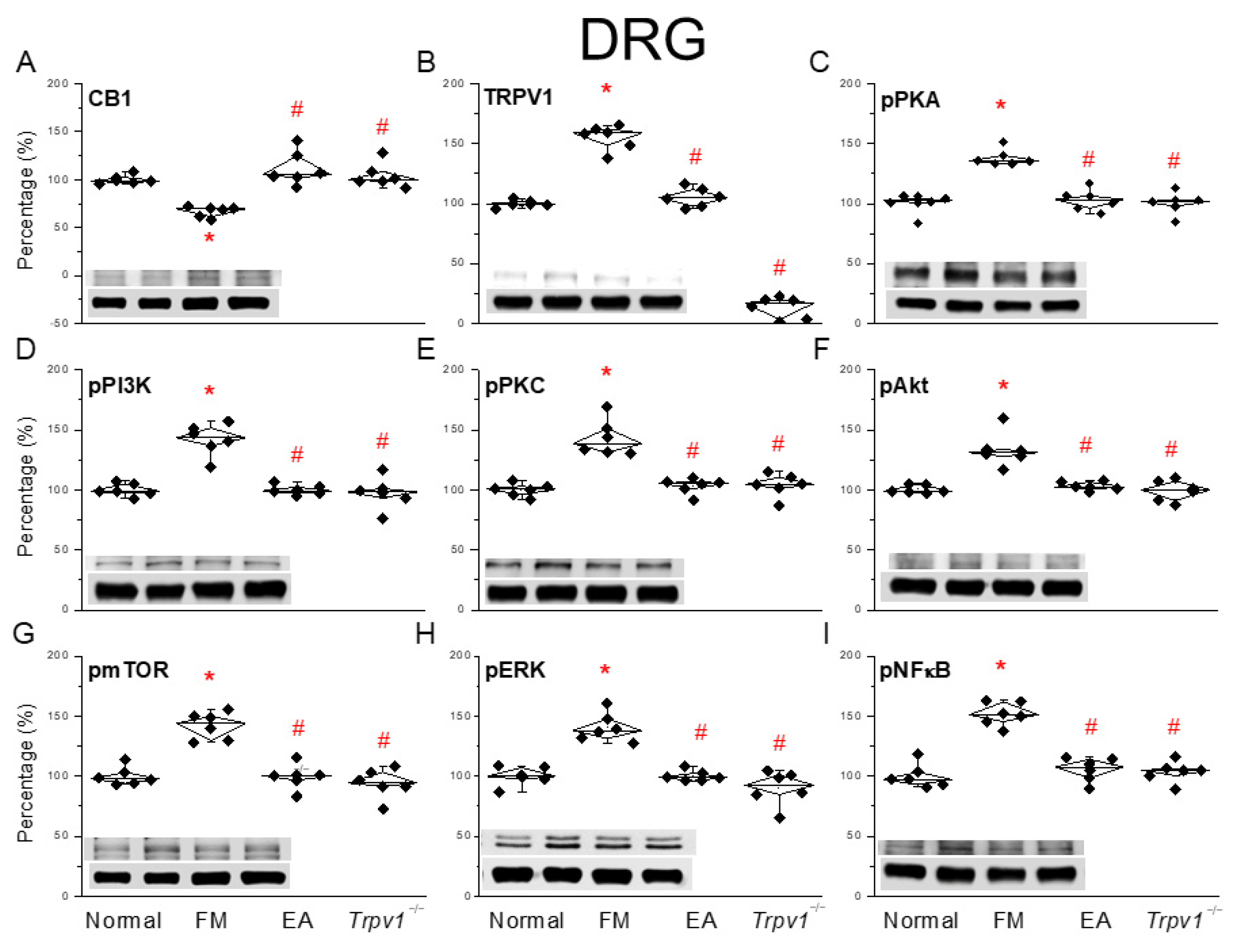
3.2. EA Regulated CB1 on TRPV1 Signaling Pathway of Fibromyalgia Pain in the Mouse Peripheral DRG
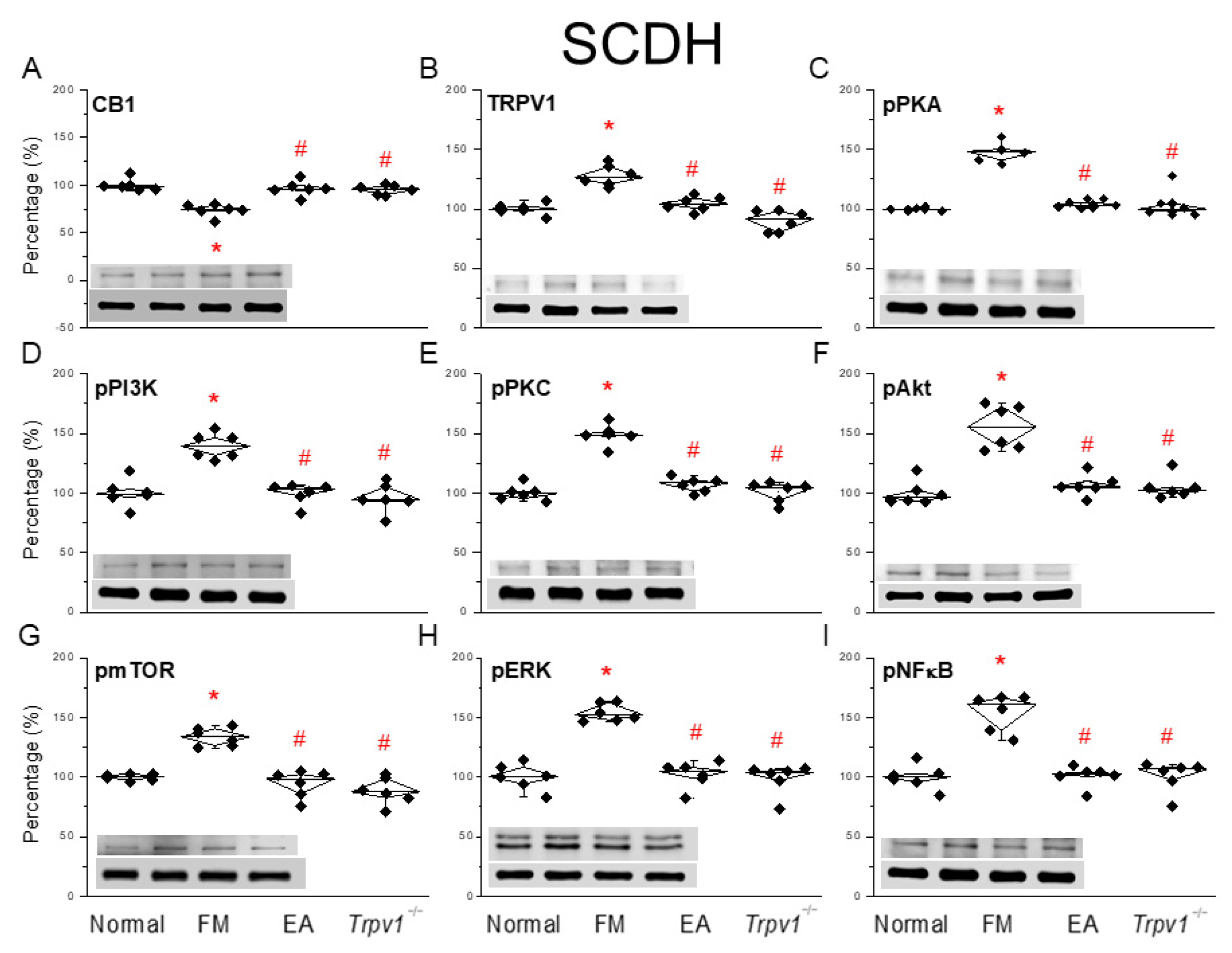
3.3. EA at the ST36 Acupoint Decreased Cold Stress-Induced Fibromyalgia Pain Through CB1-TRPV1 in the SCDH
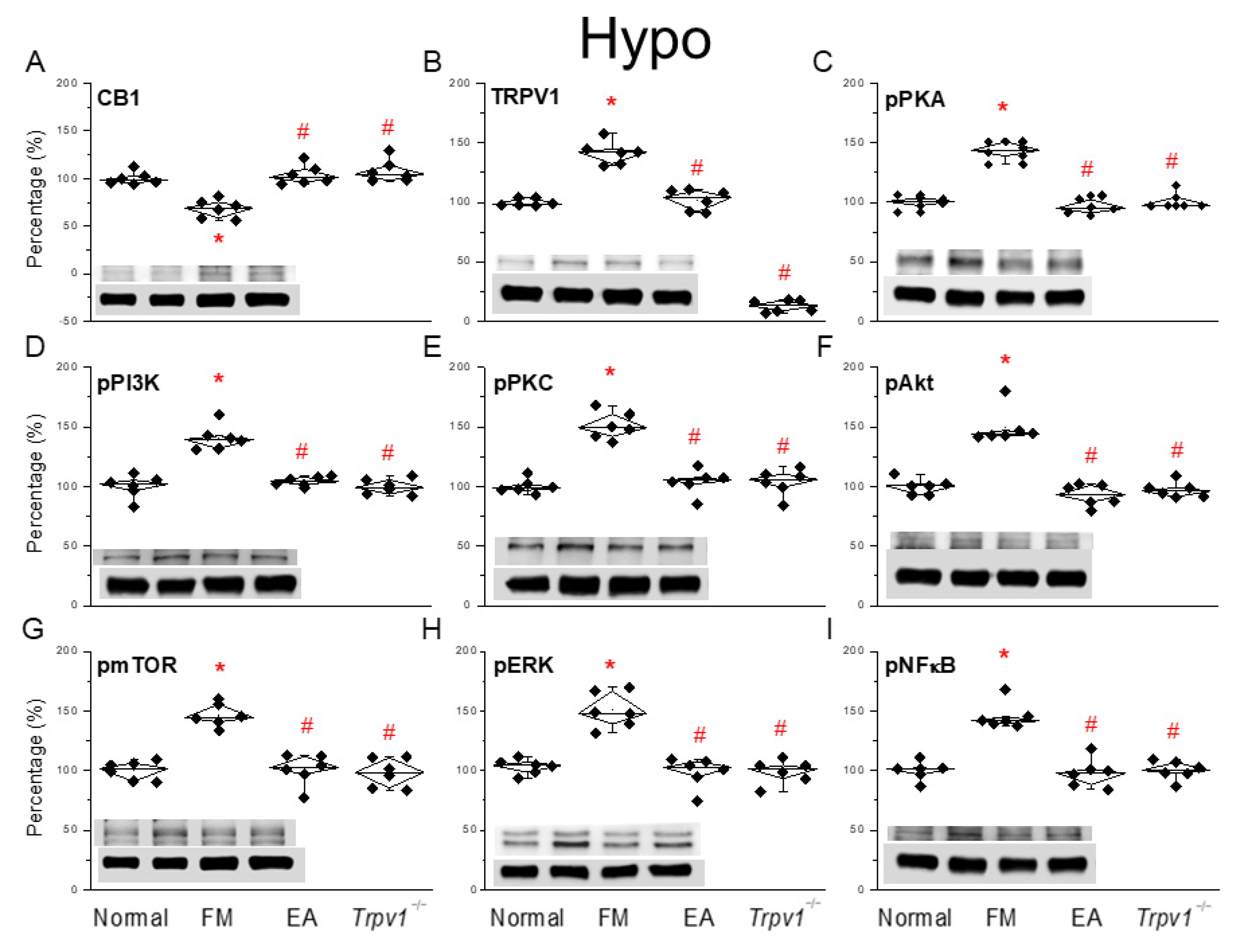
3.4. EA at the ST36 Acupoint Decreased Cold Stress-Induced Fibromyalgia Pain and Regulated CB1-TRPV1 Signaling Pathway in the Hypothalamus
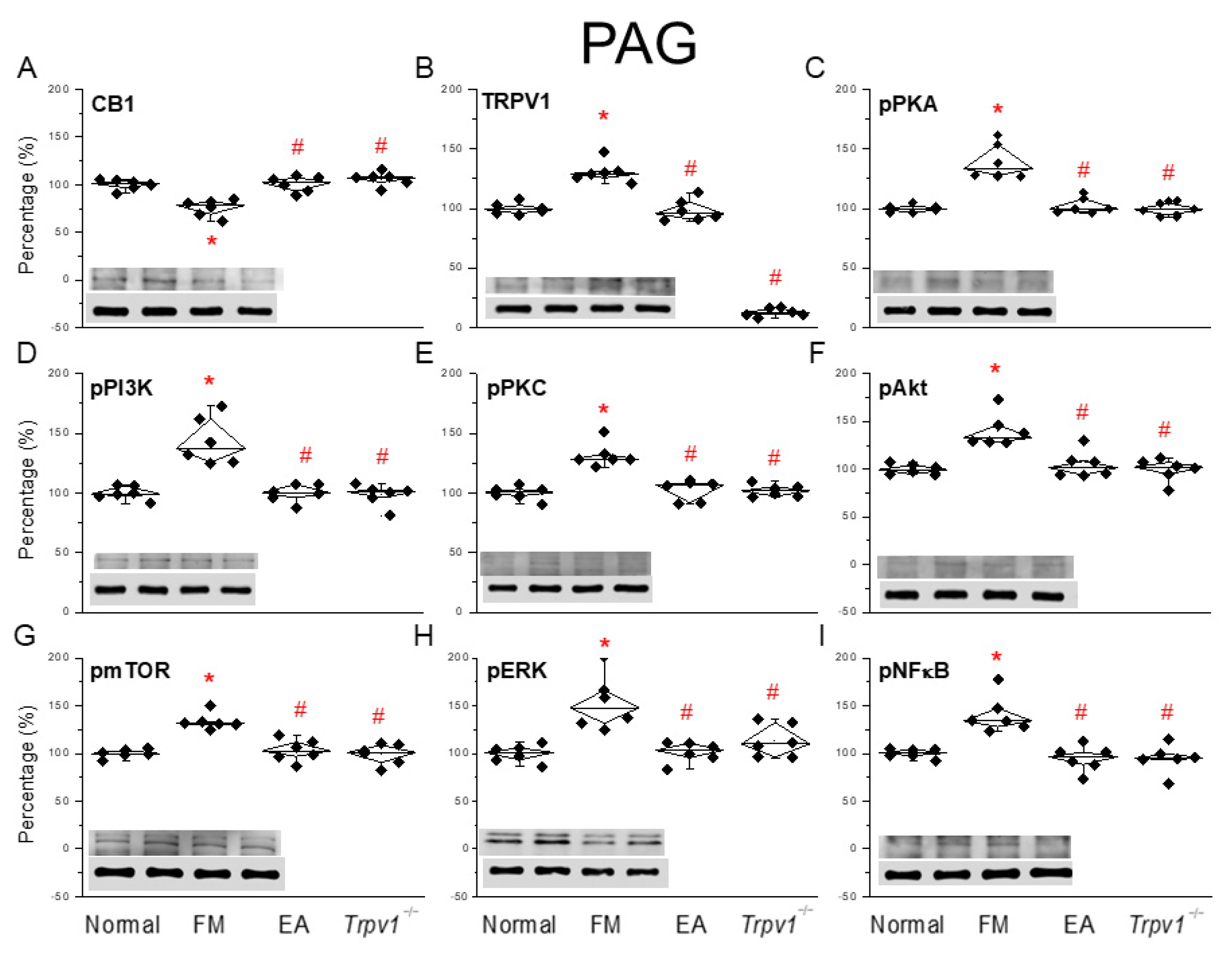
3.5. CB1-TRPV1 and Related Factors Were Inhibited in the PAG, an Effect Reversed by EA and Trpv1 Gene Deletion
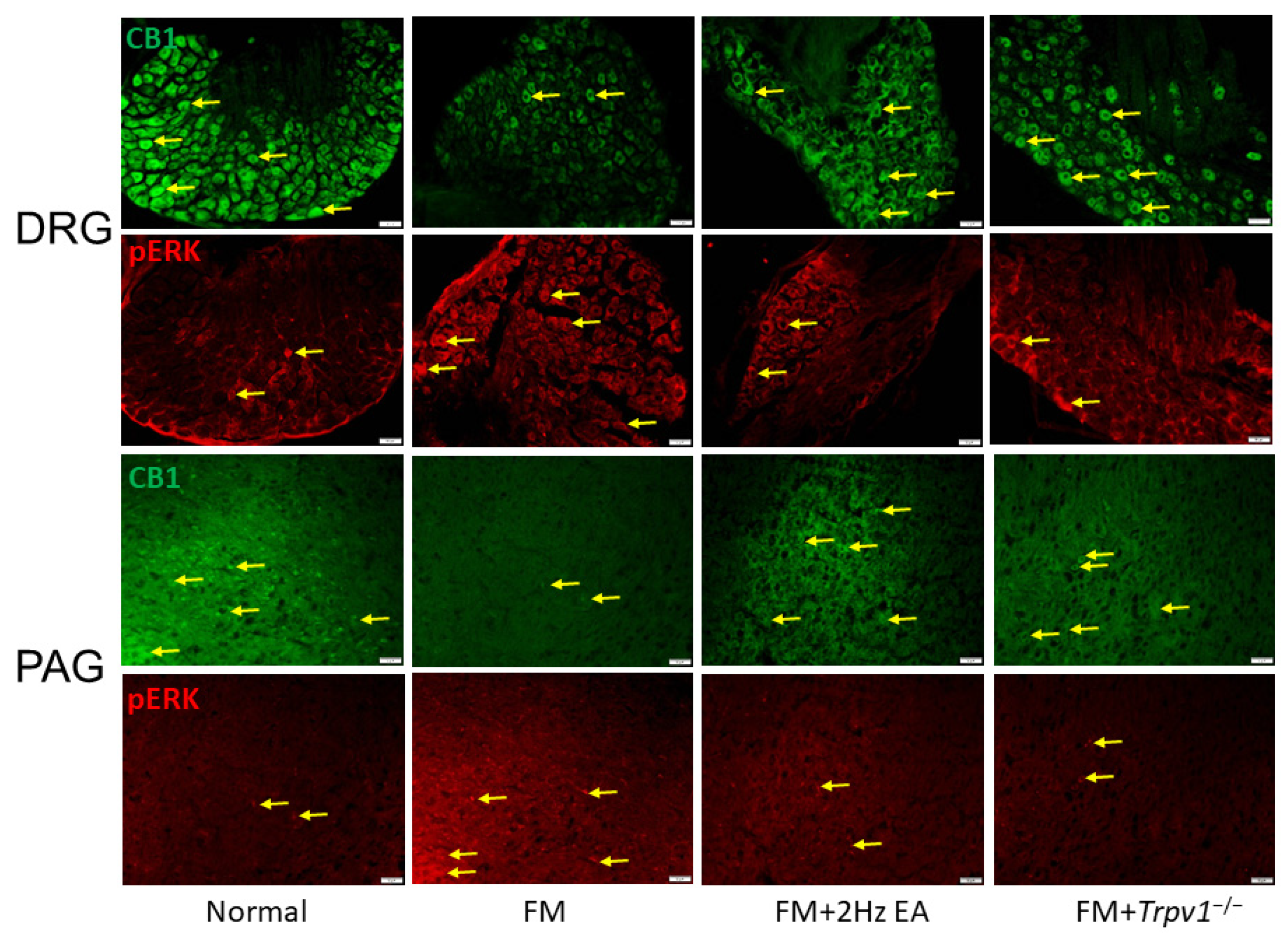
3.6. CB1 and pERK Expression in Peripheral DRG and Central PAG Regions Can Be Modulated by EA or Trpv1 Gene Deletion
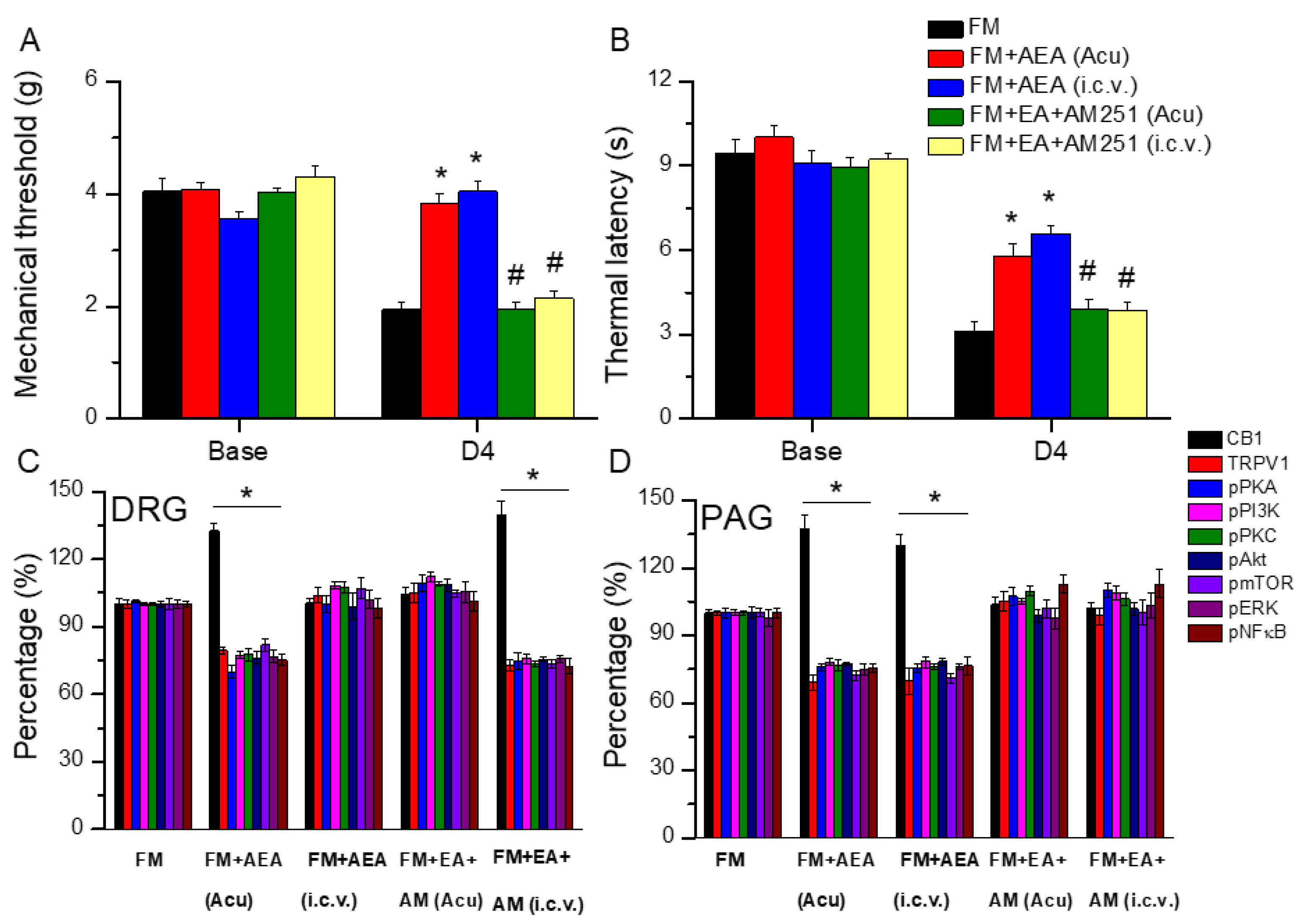
3.7. EA Diminished Fibromyalgia Directly Targets the CB1 Receptor in the Mice Acupoint or Brain
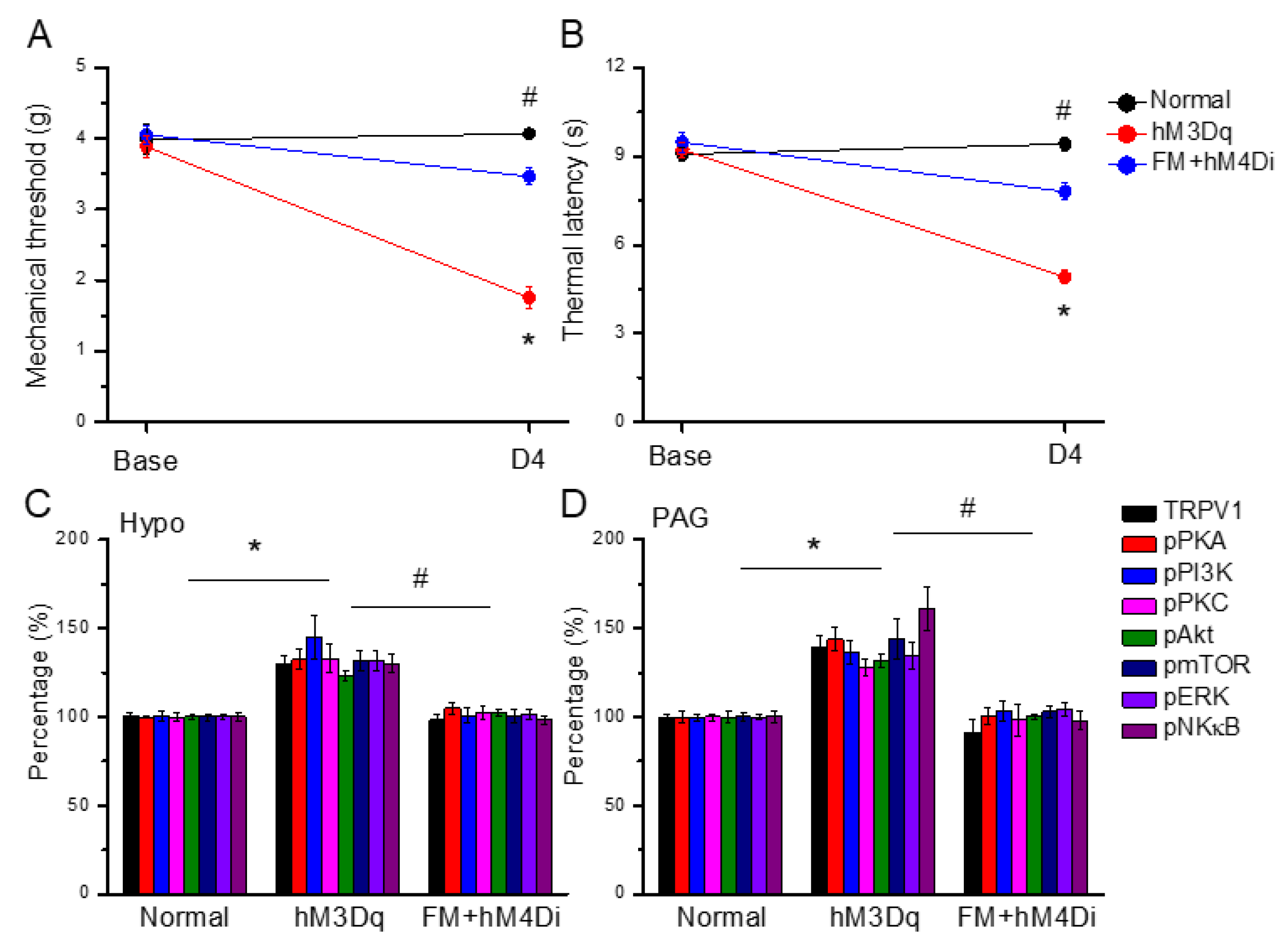
3.8. Chemogenetic Activation of the Paraventricular Nucleus Initiated Fibromyalgia Pain, and ICS-Induced Fibromyalgia Pain Can Be Further Attenuated by Chemogenetic Inhibition
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TRPV1 | Transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 |
| Trpv1−/− | Trpv1 gene knockout |
| EA | Electroacupuncture |
| CB1 | Cannabinoid receptor 1 |
| pPKA | Phosphorylated protein kinase A |
| pPI3K | Phosphorylated phosphoinositide 3-kinase |
| pPKC | Phosphorylated protein kinase C |
| pAkt | Phosphorylated Akt |
| pmTOR | Phosphorylated mammalian target of rapamycin |
| pERK | Phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| pNF-kB | Phosphorylated nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells |
| ICS | Intermittent cold stress |
| PVN | Paraventricular nucleus |
| DRG | Dorsal root ganglion |
| SCDH | Spinal cord dorsal horn |
| Hypo | Hypothalamus |
| PAG | Periaqueductal gray |
References
- Gyorfi, M.; Rupp, A.; Abd-Elsayed, A. Fibromyalgia Pathophysiology. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocyigit, B.F.; Akyol, A. Fibromyalgia syndrome: Epidemiology, diagnosis and treatment. Reumatologia 2022, 60, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masood, R.; Mandalia, K.; Moverman, M.A.; Puzzitiello, R.N.; Pagani, N.R.; Menendez, M.E.; Salzler, M.J. Patients with Functional Somatic Syndromes-Fibromyalgia, Irritable Bowel Syndrome, Chronic Headaches, and Chronic Low Back Pain-Have Lower Outcomes and Higher Opioid Usage and Cost After Shoulder and Elbow Surgery. Arthroscopy 2023, 39, 1529–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galvez-Sanchez, C.M.; Reyes Del Paso, G.A. Diagnostic Criteria for Fibromyalgia: Critical Review and Future Perspectives. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Onghia, M.; Ciaffi, J.; Ruscitti, P.; Cipriani, P.; Giacomelli, R.; Ablin, J.N.; Ursini, F. The economic burden of fibromyalgia: A systematic literature review. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2022, 56, 152060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giorgi, V.; Sirotti, S.; Romano, M.E.; Marotto, D.; Ablin, J.N.; Salaffi, F.; Sarzi-Puttini, P. Fibromyalgia: One year in review 2022. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2022, 40, 1065–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; Su, Y.; Qi, L.; Yang, W.; Fu, M.; Jing, X.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Q. A neuroanatomical basis for electroacupuncture to drive the vagal-adrenal axis. Nature 2021, 598, 641–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Rosas, R.; Yehia, G.; Pena, G.; Mishra, P.; del Rocio Thompson-Bonilla, M.; Moreno-Eutimio, M.A.; Arriaga-Pizano, L.A.; Isibasi, A.; Ulloa, L. Dopamine mediates vagal modulation of the immune system by electroacupuncture. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, I.H.; Liao, H.Y.; Cheng, C.M.; Yen, C.M.; Lin, Y.W. Paper-Based Detection Device for Microenvironment Examination: Measuring Neurotransmitters and Cytokines in the Mice Acupoint. Cells 2022, 11, 2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, X.; Wang, S.; Shao, F.; Fang, J.; Xu, Y.; Wang, W.; Sun, H.; Liu, X.; Du, J.; Fang, J. Electroacupuncture Stimulation Alleviates CFA-Induced Inflammatory Pain Via Suppressing P2X3 Expression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Chen, H.; Wang, T.; Su, H.; Li, J.; He, Y.; Su, S. Electroacupuncture promotes synaptic plasticity in rats with chronic inflammatory pain-related depression by upregulating BDNF/TrkB/CREB signaling pathway. Brain Behav. 2023, 13, e3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yin, C.; Li, X.; Liu, B.; Wang, J.; Zheng, X.; Shao, X.; Liang, Y.; Du, J.; Fang, J.; et al. Electroacupuncture Alleviates Paclitaxel-Induced Peripheral Neuropathic Pain in Rats via Suppressing TLR4 Signaling and TRPV1 Upregulation in Sensory Neurons. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Yue, J.; Lin, L.; Yu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Ying, X.; Chen, X.; Tu, W.; Lou, X.; Yang, G.; et al. Electroacupuncture may alleviate neuropathic pain via suppressing P2X7R expression. Mol. Pain 2021, 17, 1744806921997654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, C.; Kui, W.; Huang, A.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Gu, Z.; Xie, L.; Kong, S.; Yu, J.; Ruan, H.; et al. Electroacupuncture suppresses neuronal ferroptosis to relieve chronic neuropathic pain. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2024, 28, e18240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moro, M.Z.; de Oliveira Vidal, E.I.; Pinheiro Modolo, N.S.; Bono Fukushima, F.; Moreira de Barros, G.A. Dry needling, trigger point electroacupuncture and motor point electroacupuncture for the treatment of myofascial pain syndrome involving the trapezius: A randomised clinical trial. Acupunct. Med. 2024, 42, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, A.E.; Buchtel, H.; Mawla, I.; Ichesco, E.; Larkin, T.; Harte, S.E.; Zhan, E.; Napadow, V.; Harris, R.E. Temporal Summation but Not Expectations of Pain Relief Predict Response to Acupuncture Treatment in Fibromyalgia. J. Pain 2024, 25, 104622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.W.; Chou, A.I.W.; Su, H.; Su, K.P. Transient receptor potential V1 (TRPV1) modulates the therapeutic effects for comorbidity of pain and depression: The common molecular implication for electroacupuncture and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 89, 604–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, D.A.; Yudowski, G.A. Cannabinoid Receptors in the Central Nervous System: Their Signaling and Roles in Disease. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, S.; Kumar, U. Cannabinoid Receptors and the Endocannabinoid System: Signaling and Function in the Central Nervous System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deventer, M.H.; Van Uytfanghe, K.; Vinckier, I.M.J.; Reniero, F.; Guillou, C.; Stove, C.P. Cannabinoid receptor activation potential of the next generation, generic ban evading OXIZID synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonists. Drug Test. Anal. 2022, 14, 1565–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaca, S.; Busardo, F.P.; Nittari, G.; Sirignano, A.; Ricci, G. Fourth Generation of Synthetic Cannabinoid Receptor Agonists: A Review on the Latest Insights. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2022, 28, 2603–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazdarica, M.; Noda, J.; Durydivka, O.; Novosadova, V.; Mackie, K.; Pin, J.P.; Prezeau, L.; Blahos, J. SGIP1 modulates kinetics and interactions of the cannabinoid receptor 1 and G protein-coupled receptor kinase 3 signalosome. J. Neurochem. 2022, 160, 625–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bujak, J.K.; Kosmala, D.; Szopa, I.M.; Majchrzak, K.; Bednarczyk, P. Inflammation, Cancer and Immunity-Implication of TRPV1 Channel. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iftinca, M.; Defaye, M.; Altier, C. TRPV1-Targeted Drugs in Development for Human Pain Conditions. Drugs 2021, 81, 7–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benitez-Angeles, M.; Morales-Lazaro, S.L.; Juarez-Gonzalez, E.; Rosenbaum, T. TRPV1: Structure, Endogenous Agonists, and Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, K.W.; Hsieh, C.L.; Yang, J.; Lin, Y.W. Effects of electroacupuncture in a mouse model of fibromyalgia: Role of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors and related mechanisms. Acupunct. Med. 2017, 35, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Hsieh, C.L.; Lin, Y.W. Role of Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 1 in Electroacupuncture Analgesia on Chronic Inflammatory Pain in Mice. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 5068347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghowsi, M.; Qalekhani, F.; Farzaei, M.H.; Mahmudii, F.; Yousofvand, N.; Joshi, T. Inflammation, oxidative stress, insulin resistance, and hypertension as mediators for adverse effects of obesity on the brain: A review. Biomedicine 2021, 11, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.Y.; Liao, H.Y.; Lin, Y.W. Effects and Mechanisms of Electroacupuncture on Chronic Inflammatory Pain and Depression Comorbidity in Mice. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2020, 2020, 4951591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.Y.; Hsieh, C.L.; Huang, C.P.; Lin, Y.W. Electroacupuncture Attenuates CFA-induced Inflammatory Pain by suppressing Nav1.8 through S100B, TRPV1, Opioid, and Adenosine Pathways in Mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.W.; Hsieh, C.L. Auricular electroacupuncture reduced inflammation-related epilepsy accompanied by altered TRPA1, pPKCα, pPKCε, and pERk1/2 signaling pathways in kainic acid-treated rats. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 493480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Gregorio, D.; McLaughlin, R.J.; Posa, L.; Ochoa-Sanchez, R.; Enns, J.; Lopez-Canul, M.; Aboud, M.; Maione, S.; Comai, S.; Gobbi, G. Cannabidiol modulates serotonergic transmission and reverses both allodynia and anxiety-like behavior in a model of neuropathic pain. Pain 2019, 160, 136–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binzen, U.; Greffrath, W.; Hennessy, S.; Bausen, M.; Saaler-Reinhardt, S.; Treede, R.D. Co-expression of the voltage-gated potassium channel Kv1.4 with transient receptor potential channels (TRPV1 and TRPV2) and the cannabinoid receptor CB1 in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. Neuroscience 2006, 142, 527–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.Q.; Qiu, F.; Qiu, C.Y.; Cai, Q.; Zou, P.; Wu, H.; Hu, W.P. Cannabinoids inhibit acid-sensing ion channel currents in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Hooker, B.A.; Garrison, T.R.; El-Kouhen, O.F.; Idler, K.B.; Holley-Shanks, R.R.; Meyer, M.D.; Yao, B.B. Pharmacological and molecular characterization of a dorsal root ganglion cell line expressing cannabinoid CB1 and CB2 receptors. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 659, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eeswara, A.; Pacheco-Spiewak, A.; Jergova, S.; Sagen, J. Combined non-psychoactive Cannabis components cannabidiol and β-caryophyllene reduce chronic pain via CB1 interaction in a rat spinal cord injury model. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0282920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Bai, Z.; Yi, W.; Hu, Z.; Hao, J. Overexpression of miR-338-5p in exosomes derived from mesenchymal stromal cells provides neuroprotective effects by the Cnr1/Rap1/Akt pathway after spinal cord injury in rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2021, 761, 136124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nerandzic, V.; Mrozkova, P.; Adamek, P.; Spicarova, D.; Nagy, I.; Palecek, J. Peripheral inflammation affects modulation of nociceptive synaptic transmission in the spinal cord induced by N-arachidonoylphosphatidylethanolamine. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 2322–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Fang, Z.; Deng, J.; Zhang, X.; Shen, B.; Wu, Z.; Yang, Q.; Xiong, L. Combined-Acupoint Electroacupuncture Induces Better Analgesia via Activating the Endocannabinoid System in the Spinal Cord. Neural Plast. 2022, 2022, 7670629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Kopruszinski, C.M.; Moutal, A.; Ikegami, D.; Khanna, R.; Chen, Y.; Ross, S.; Mackenzie, K.; Stratton, J.; Dodick, D.W.; et al. Dysregulation of serum prolactin links the hypothalamus with female nociceptors to promote migraine. Brain 2022, 145, 2894–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomholt, S.F.; Harbuz, M.S.; Blackburn-Munro, G.; Blackburn-Munro, R.E. Involvement and role of the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) stress axis in animal models of chronic pain and inflammation. Stress 2004, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slamberova, R.; Rimanoczy, A.; Riley, M.A.; Vathy, I. Hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis-regulated stress response and negative feedback sensitivity is altered by prenatal morphine exposure in adult female rats. Neuroendocrinology 2004, 80, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Lu, J.; Guo, J.; Chen, J.; Xiong, F.; Wang, X.; Chen, L.; Yu, C. Ventrolateral Periaqueductal Gray Astrocytes Regulate Nociceptive Sensation and Emotional Motivation in Diabetic Neuropathic Pain. J. Neurosci. 2022, 42, 8184–8199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, C.Y.; Yang, Y.B.; Chou, D.; Xu, J.H. The Ventrolateral Periaqueductal Gray Contributes to Depressive-Like Behaviors in Recovery of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Rat Model. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.B.; Liang, S.H.; Li, F.; Zhao, W.J.; Bai, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wu, Z.Y.; Ding, T.; Sun, Y.; Liu, H.X.; et al. dmPFC-vlPAG projection neurons contribute to pain threshold maintenance and antianxiety behaviors. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 6555–6570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, H.-C.; Park, H.-J.; Liao, H.-Y.; Chuang, K.-T.; Lin, Y.-W. Accurate Chemogenetics Determines Electroacupuncture Analgesia Through Increased CB1 to Suppress the TRPV1 Pathway in a Mouse Model of Fibromyalgia. Life 2025, 15, 819. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15050819
Lin H-C, Park H-J, Liao H-Y, Chuang K-T, Lin Y-W. Accurate Chemogenetics Determines Electroacupuncture Analgesia Through Increased CB1 to Suppress the TRPV1 Pathway in a Mouse Model of Fibromyalgia. Life. 2025; 15(5):819. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15050819
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Huan-Chin, Hi-Joon Park, Hsien-Yin Liao, Kai-Ting Chuang, and Yi-Wen Lin. 2025. "Accurate Chemogenetics Determines Electroacupuncture Analgesia Through Increased CB1 to Suppress the TRPV1 Pathway in a Mouse Model of Fibromyalgia" Life 15, no. 5: 819. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15050819
APA StyleLin, H.-C., Park, H.-J., Liao, H.-Y., Chuang, K.-T., & Lin, Y.-W. (2025). Accurate Chemogenetics Determines Electroacupuncture Analgesia Through Increased CB1 to Suppress the TRPV1 Pathway in a Mouse Model of Fibromyalgia. Life, 15(5), 819. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15050819







